Preliminary Analysis of Unprotected Reactivity Introduction Accident of Liquid Molten Salt Reactor with Graphite Channel based on TREND Program
-
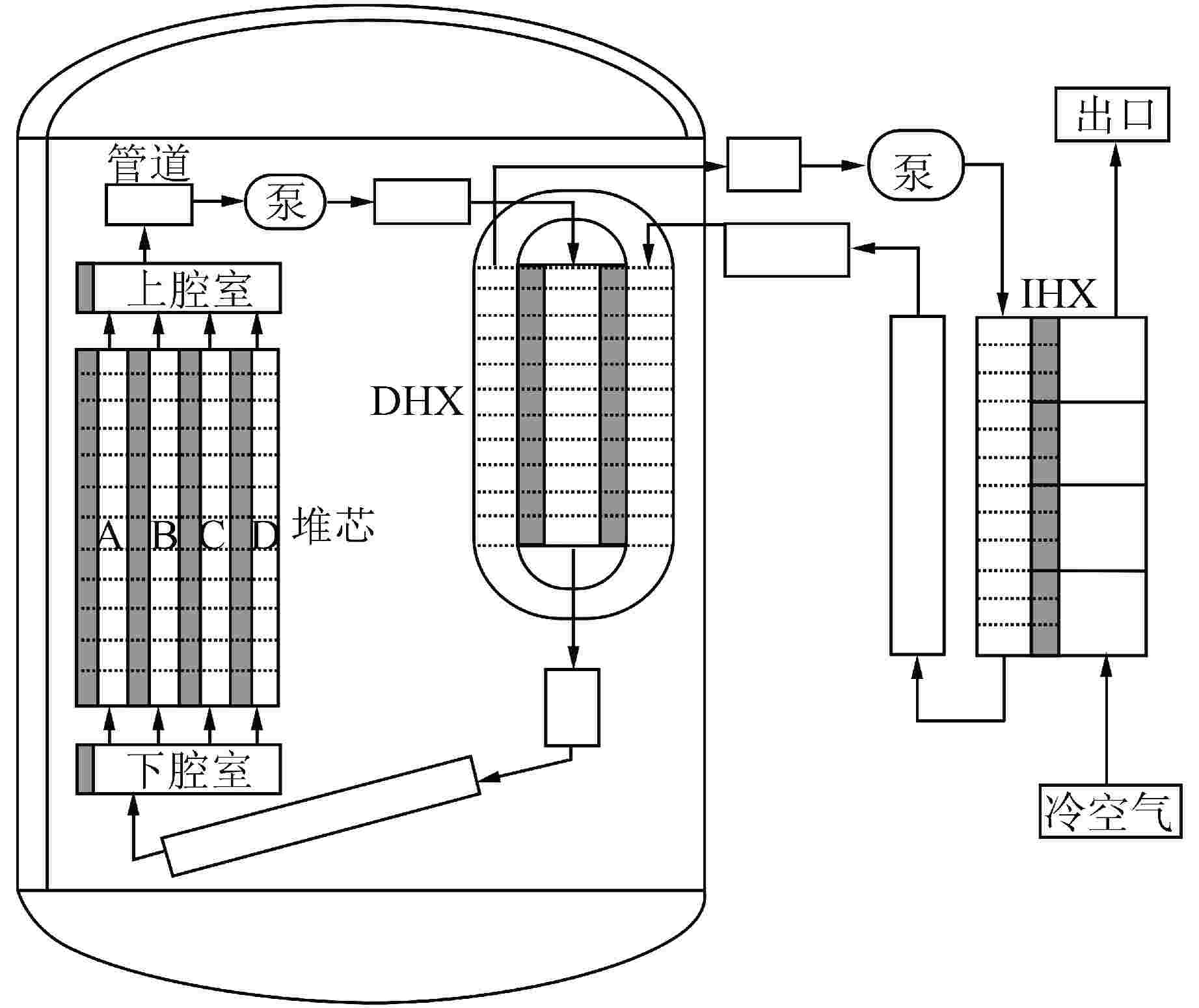
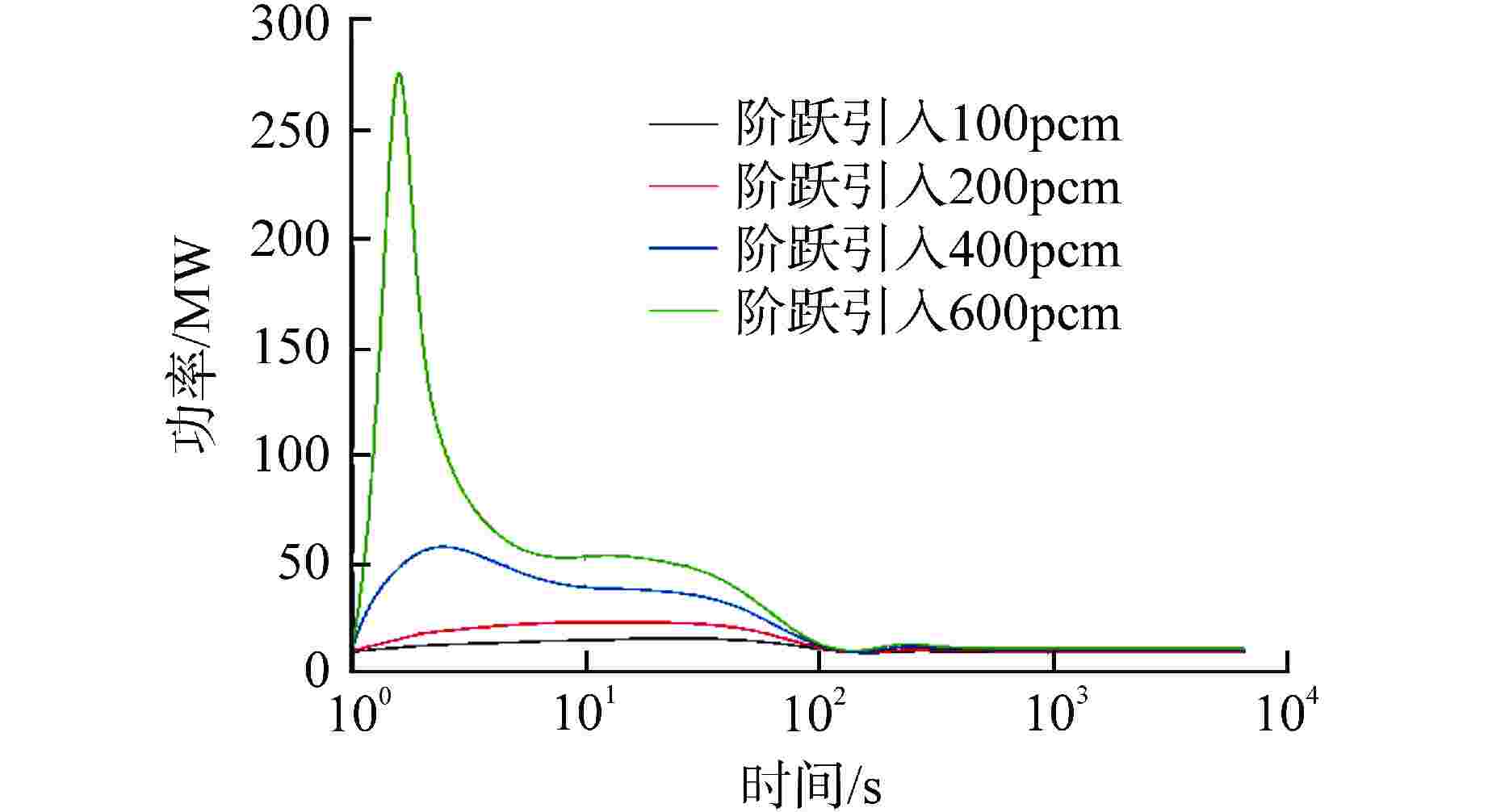
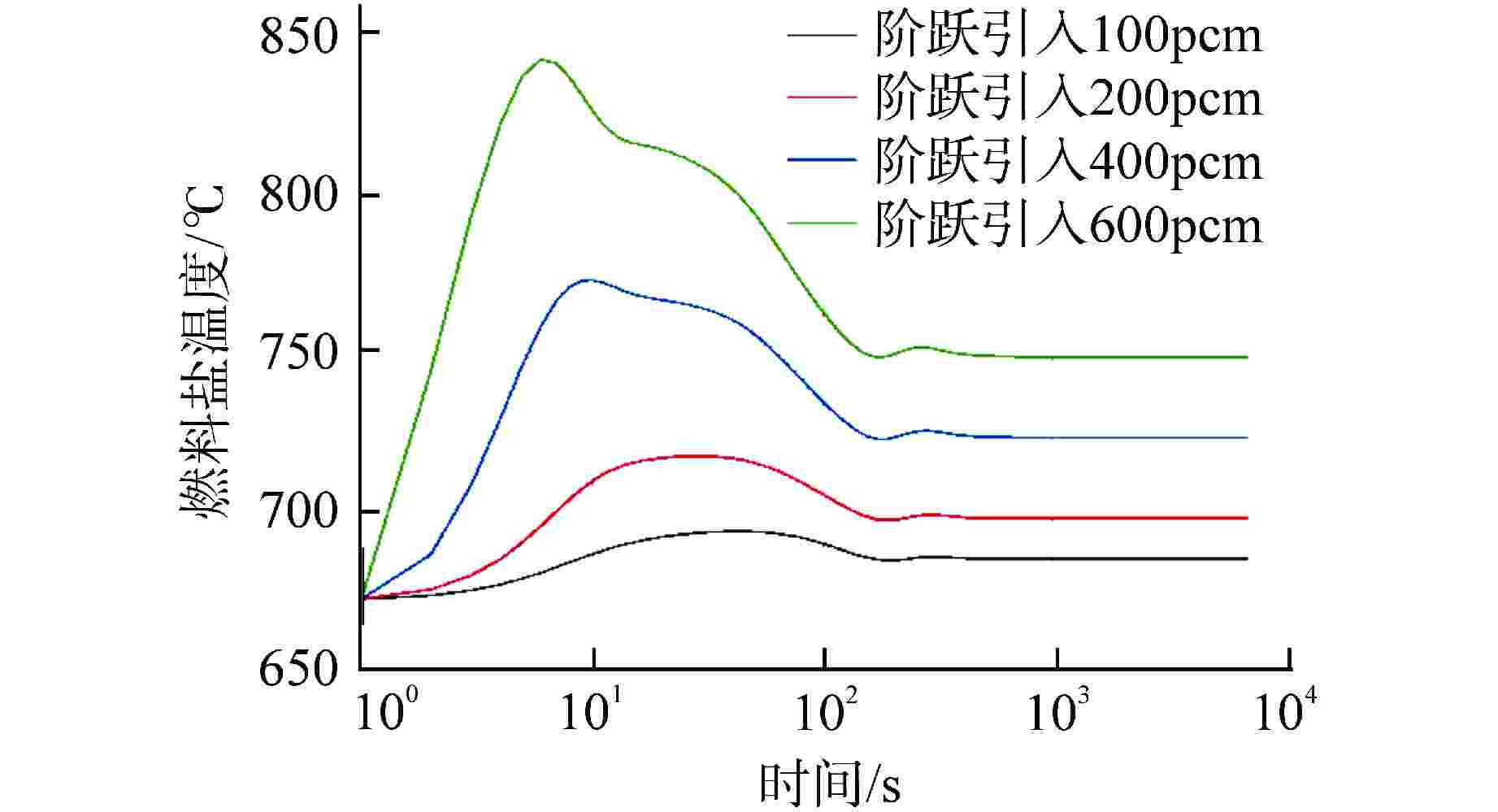
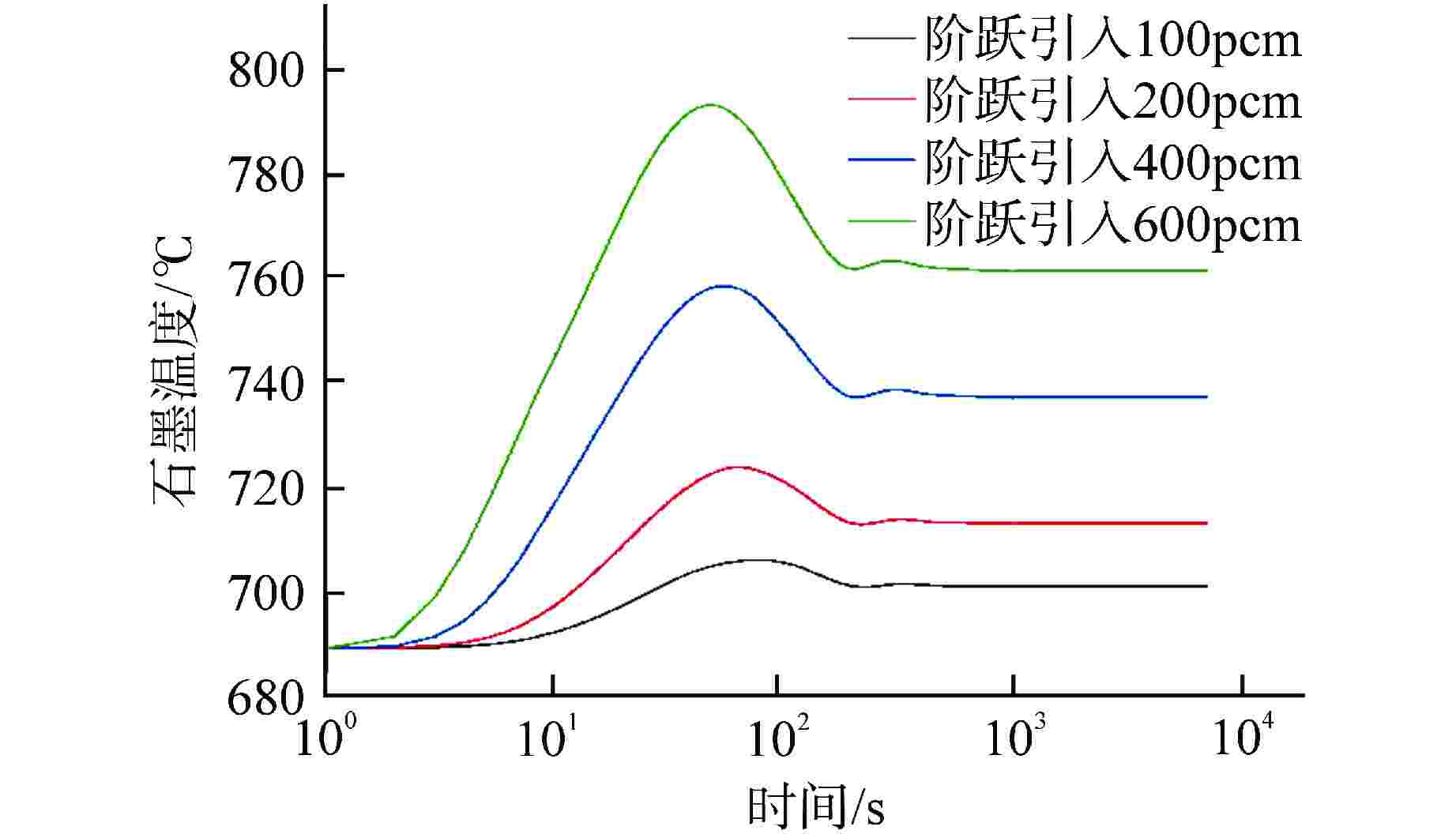
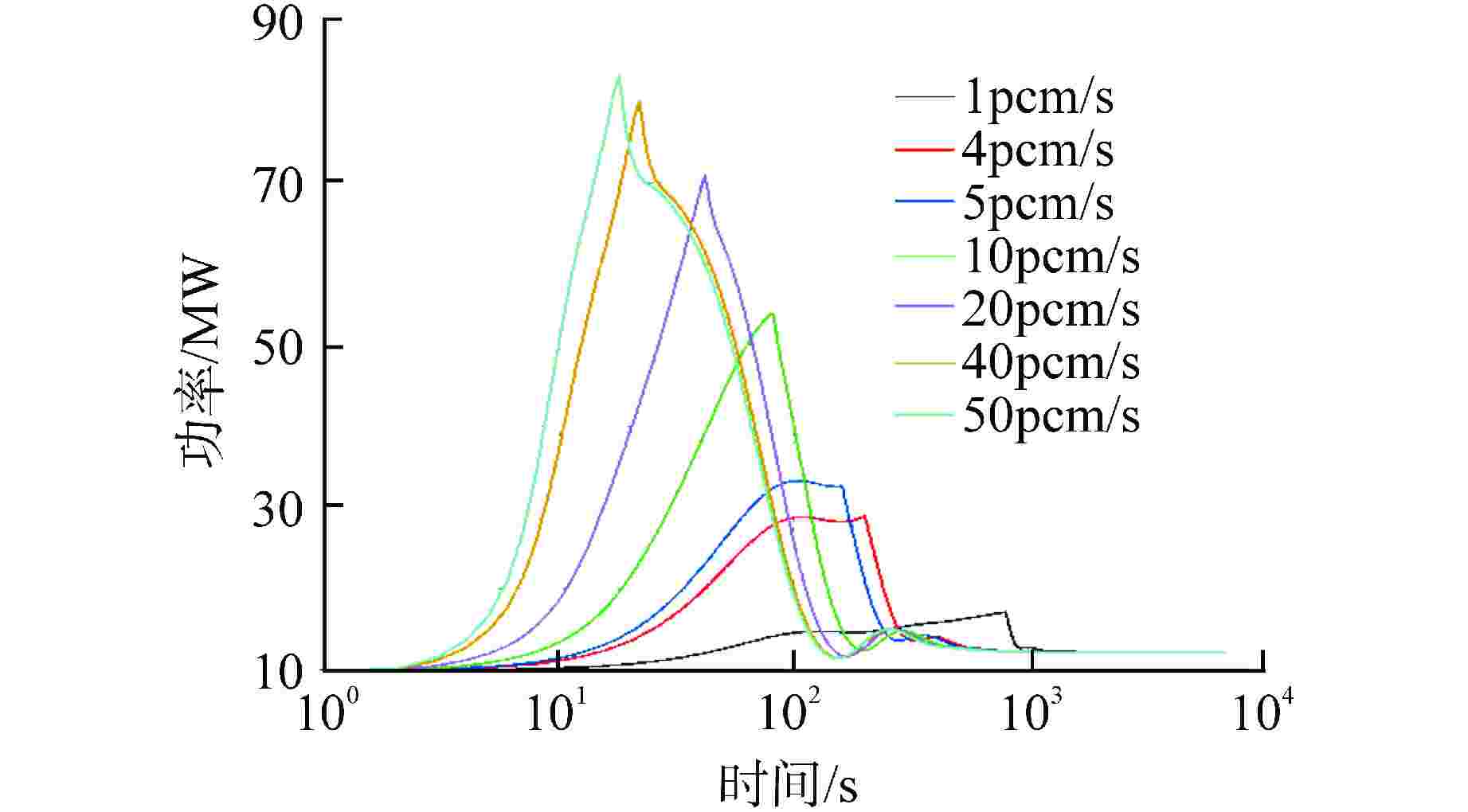
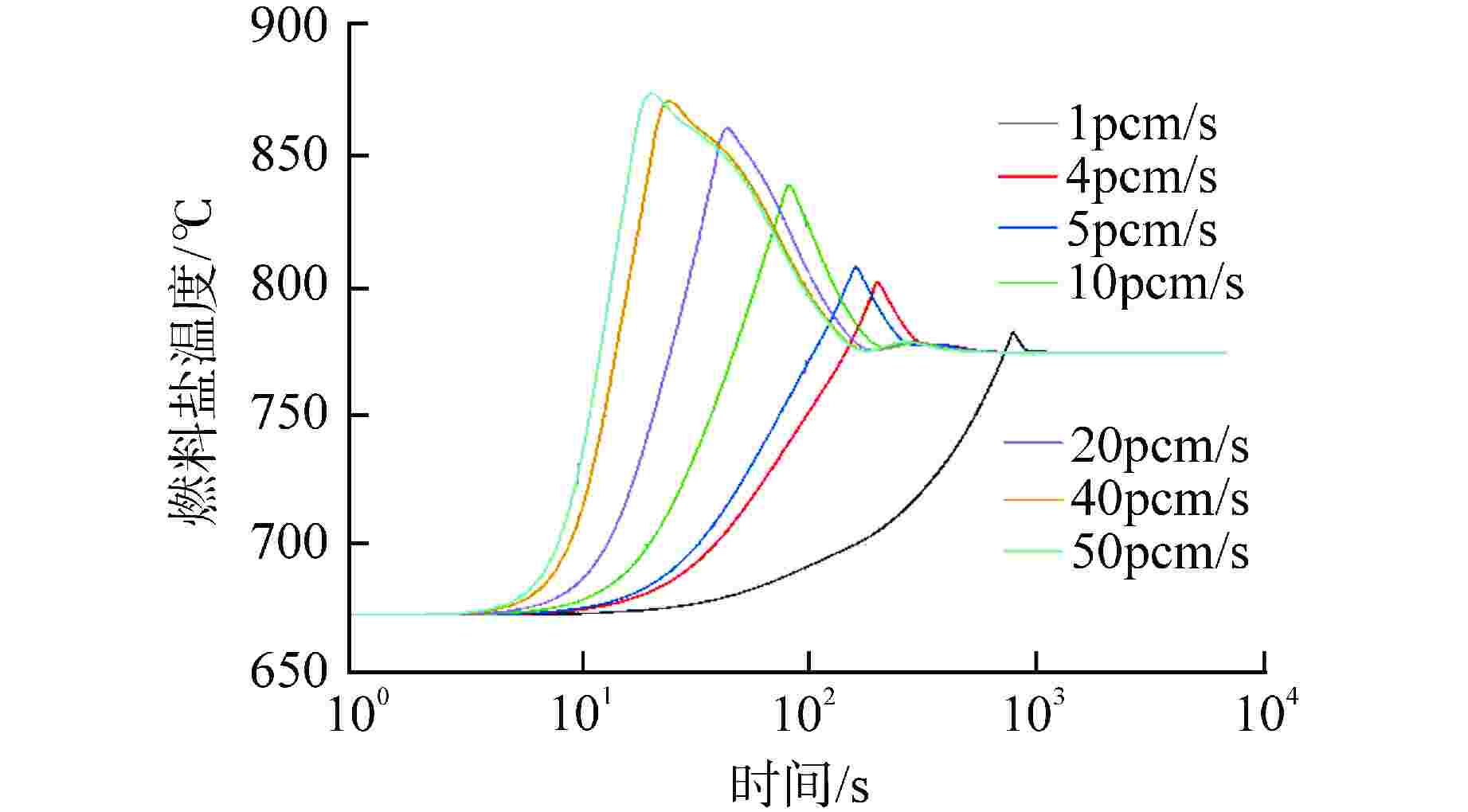
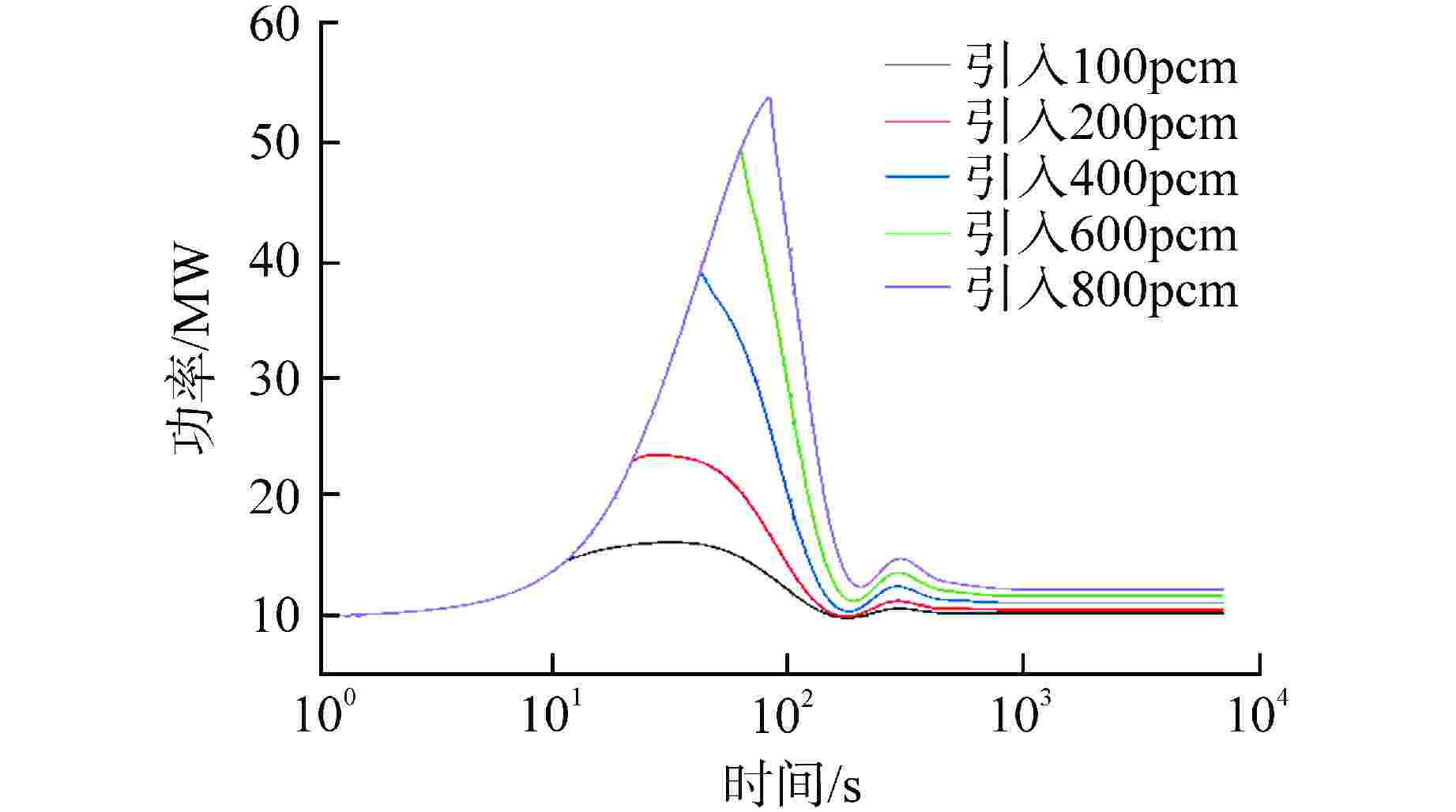
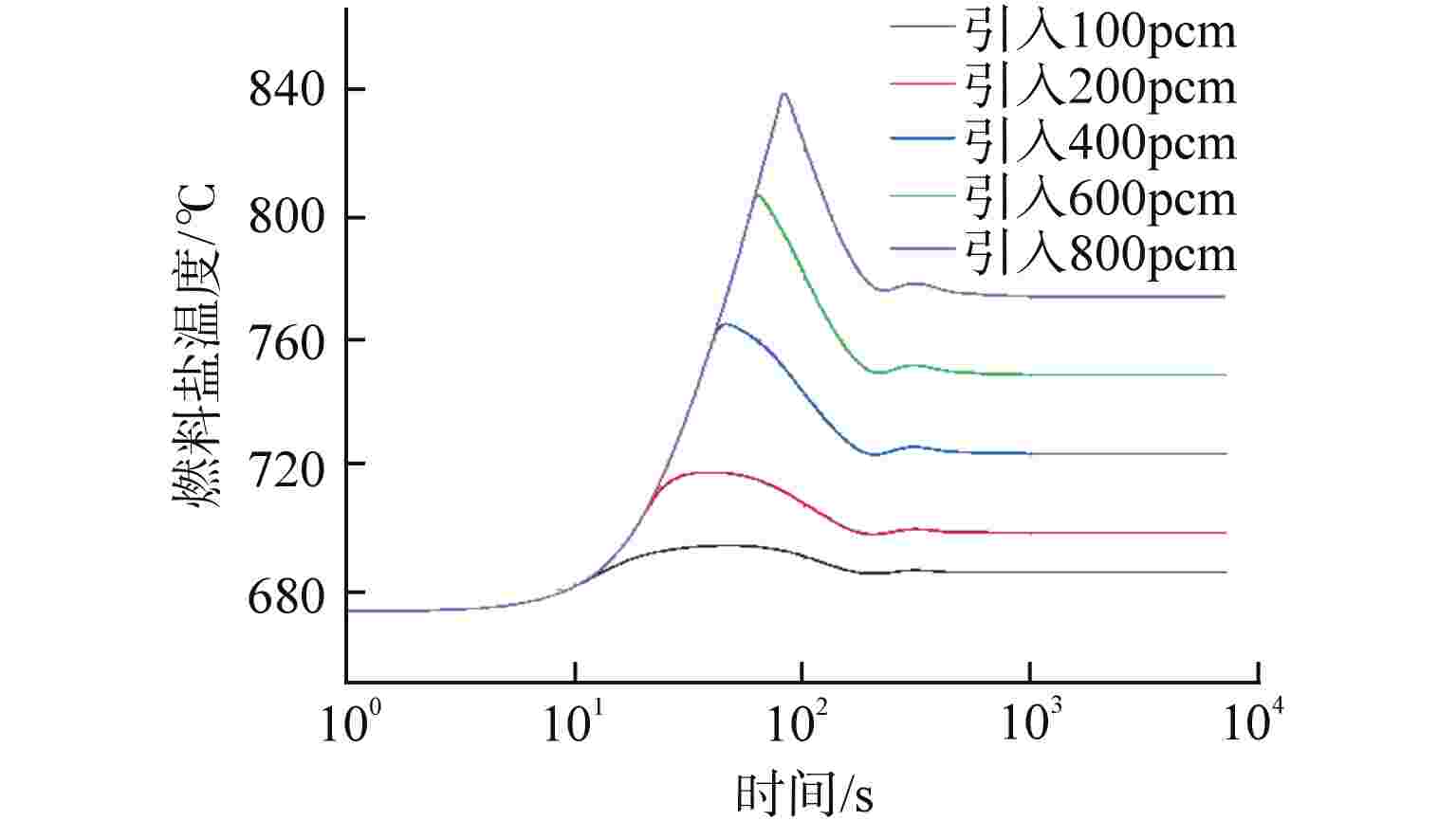
摘要: 采用自编系统分析程序TREND,基于液态点堆动力学模型,针对10 MW石墨通道液态熔盐堆的设计,研究分析不同反应性在阶跃引入和线性引入情况下10 MW石墨通道液态熔盐堆堆芯功率、石墨温度和堆芯出口熔盐温度的瞬态变化。结果表明,阶跃引入低于570pcm(1pcm=10−5)反应性,堆系统能在无保护的情况下安全运行;当单根控制棒失提引入约800pcm时,反应性引入速率不超过8pcm/s,反应堆能够利用自身的温度、功率负反馈特性有效地控制功率峰值和降低堆芯出口温度,保证反应堆在无保护情况下安全运行。因此,液态熔盐堆具有良好的固有安全性。Abstract: Using the self-developed system analysis code TREND and based on the liquid point reactor dynamics model, aiming at the design of 10 MW liquid molten salt reactor with graphite channel, the transient changes of core power, graphite temperature and molten salt temperature at the core outlet of 10 MW liquid molten salt reactor with graphite channel with different reactivity under step introduction and linear introduction are studied and analyzed. The results show that the reactor system can operate safely without protection when the reactivity step introduction is lower than 570pcm (1pcm=10−5). When about 800pcm is introduced due to loss of lift of single control rod, the reactivity introduction rate does not exceed 8pcm/s, and the reactor can effectively control the peak power and reduce the core outlet temperature by making use of its own negative feedback characteristics of temperature and power, so as to ensure the safe operation of the reactor without protection. Therefore, liquid molten salt reactor has good inherent safety.
-
Key words:
- Molten salt reactor /
- System code /
- Transient analysis
-
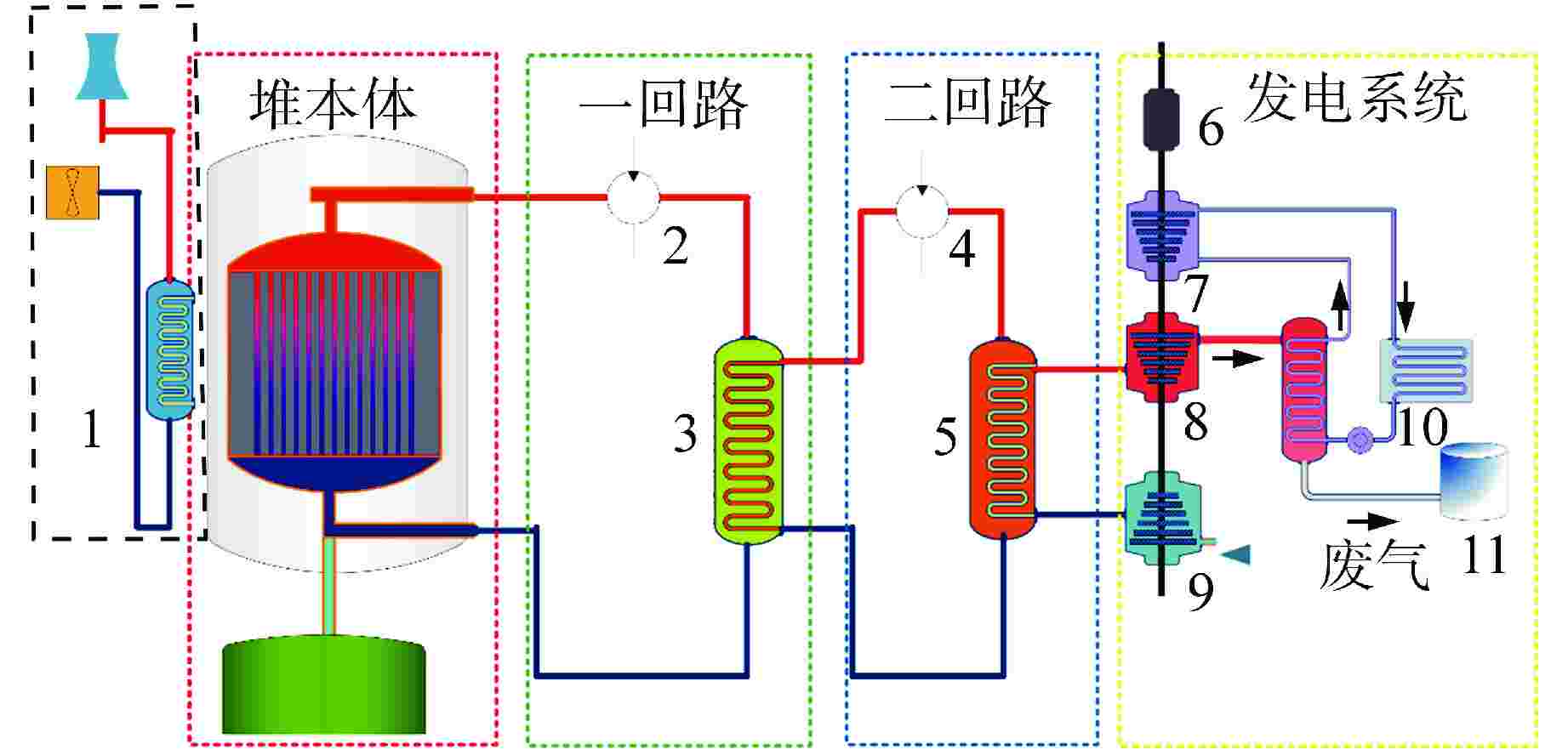
表 1 10 MW石墨通道液态熔盐堆设计参数
Table 1. Design Parameters of 10 MW Liquid Molten Salt Reactor with Graphite Channel
参数名 参数值 参数名 参数值 堆芯功率/ MW 10 石墨温度反应性系数/(pcm·℃−1) −4.0 燃料盐 LiF-BeF2−ZrF4−UF4−ThF4 燃料盐温度反应性系数/(pcm·℃−1) −5.1 冷却盐 LiF-BeF2 二回路流量/(kg·s−1) 200 反射层 石墨 二回路主换热器进出口温度/℃ 562/583 一回路堆芯进出口温度/℃ 638/673 空气流量/(kg·s−1) 50.3 一回路流量/(kg·s−1) 145 空气进出口温度/℃ 40/235 1pcm=10−5 表 2 燃料盐和冷却盐物性参数
Table 2. Physical Parameter of Fuel Salt and Coolant Salt
物性参数 冷却盐 燃料盐 密度/(kg·m−3) −0.4884 (T−273.15)+ 2413 2665-0.3833(T+273.15) 比热容/[J·(kg·K)−1] 2386 2000 粘度/(Pa·s) 0.000116exp[3755/(T+273.15)] 3.8×10−6exp[6982.06/(T+273.15)] 导热系数/[W·(m·K)−1] 0.6297+0.0005(T+273.15) 1.4 表 3 10 MW石墨通道液态熔盐堆参数设计值计算值对比
Table 3. Comparison of Parameter Design Value/Calculated Value of 10 MW Liquid Molten Salt Reactor with Graphite Channel
参数名 设计值 计算值 误差/
%堆芯功率/MW 10 9.997 0.03 堆芯进口温度/℃ 638.5 638.7 0.03 堆芯出口温度/℃ 673 673.3 0.04 一回路流量/
(kg·s−1)145 146.0 0.69 ABCD通道流量比 1∶0.69∶0.76∶1.18 1∶0.69∶0.76∶1.17 — 二回路换热器进
口温度/℃562 562.5 0.09 二回路换热器出
口温度/℃582 582.9 0.15 “—”表示无此项 -
[1] USDOE. A technology roadmap for generation IV nuclear energy systems[J]. Philosophical Review, 2002, 66(2): 239-241. [2] 徐洪杰,戴志敏,蔡翔舟,等. 钍基熔盐堆和核能综合利用[J]. 现代物理知识,2018, 30(4): 25-34. [3] HARGRAVES R, MOIR R. Liquid fluoride thorium reactors: an old idea in nuclear power gets reexamined[J]. American Scientist, 2010, 98(4): 304-313. doi: 10.1511/2010.85.304. [4] MATHIEU L, HEUER D, BRISSOT R, et al. The thorium molten salt reactor: moving on from the MSBR[J]. Progress in Nuclear Energy, 2006, 48(7): 664-679. doi: 10.1016/j.pnucene.2006.07.005 [5] 江绵恒,徐洪杰,戴志敏. 未来先进核裂变能−TMSR核能系统[J]. 中国科学院院刊,2012, 27(3): 366-374. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3045.2012.03.016 [6] ROBERTSON R C. Conceptual design study of a single-fluid molten-salt breeder reactor: ORNL-4541[R]. Oak Ridge: ORNL, 1971. [7] 魏泉,梅龙伟,战志超,等. 液态熔盐堆运行安全特性初步研究[J]. 原子能科学技术,2014, 48(12): 2280-2286. doi: 10.7538/yzk.2014.48.12.2280 [8] NESTOR JR C W. Murgatroyd – an IBM 7090 program for the analysis of the kinetics of the MSRE: ORNL-TM-203[R]. USA: Atomic Energy Commission, 1962 [9] KŘEPEL J, GRUNDMANN U, ROHDE U, et al. DYN1D-MSR dynamics code for molten salt reactors[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2005, 32(17): 1799-1824. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2005.07.007 [10] SHI C B, CHENG M S, LIU G M. Development and application of a system analysis code for liquid fueled molten salt reactors based on RELAP5 code[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2016, 305: 378-388. doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2016.05.034 [11] 阮见. 熔盐堆系统瞬态分析程序开发[D]. 上海: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院上海应用物理研究所), 2018. [12] YU W, RUAN J, HE L, et al. Development of TREND dynamics code for molten salt reactors[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 2021, 53(2): 455-465. doi: 10.1016/j.net.2020.07.030 [13] SIEDER E N, TATE G E. Heat transfer and pressure drop of liquids in tubes[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry, 1936, 28(12): 1429-1435. [14] GNIELINSKI V. New equations for heat and mass transfer in turbulent pipe and channel flow[J]. International Chemical Engineering, 1976, 16(2): 359-368. [15] 茹卡乌斯卡斯. 换热器内的对流传热[M]. 马昌文, 译. 北京: 科学出版社, 1986: 337-370. [16] Haynes International, Inc. HASTELLOY® N alloy: H-2052B[R]. USA: Haynes International, Inc, 2002 -





 下载:
下载: