Analysis of Influencing Factors of Control Rod Downward Motion Characteristics
-
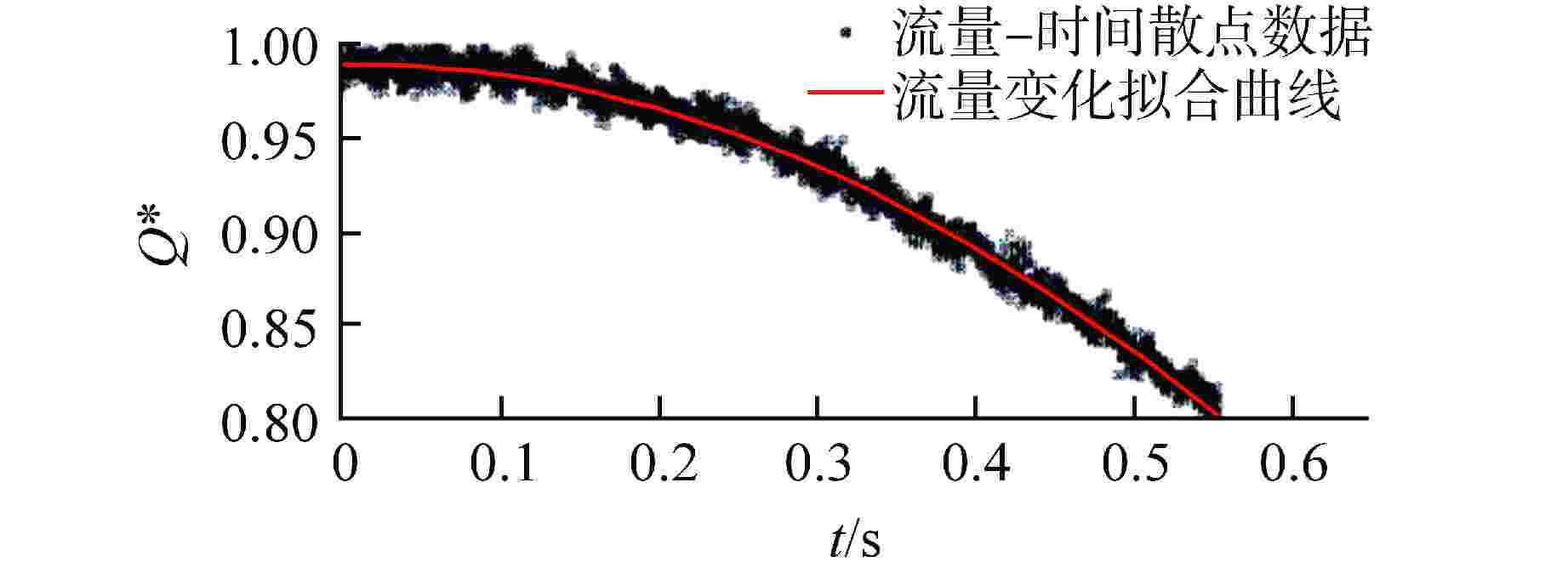
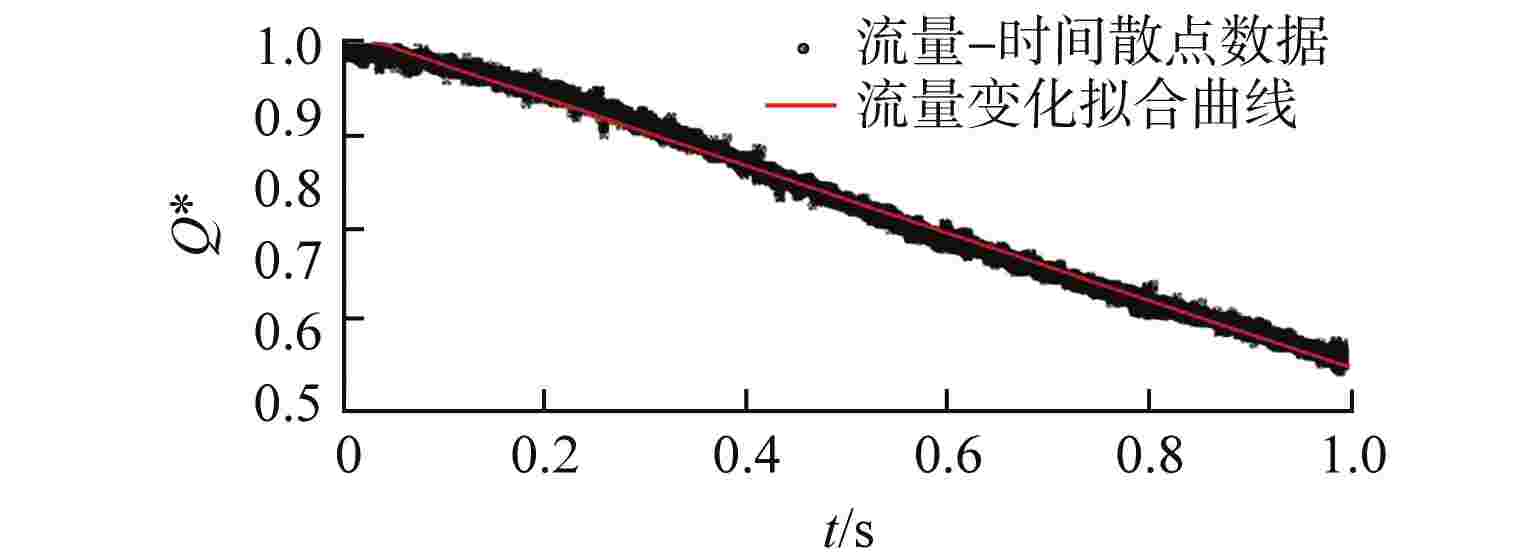
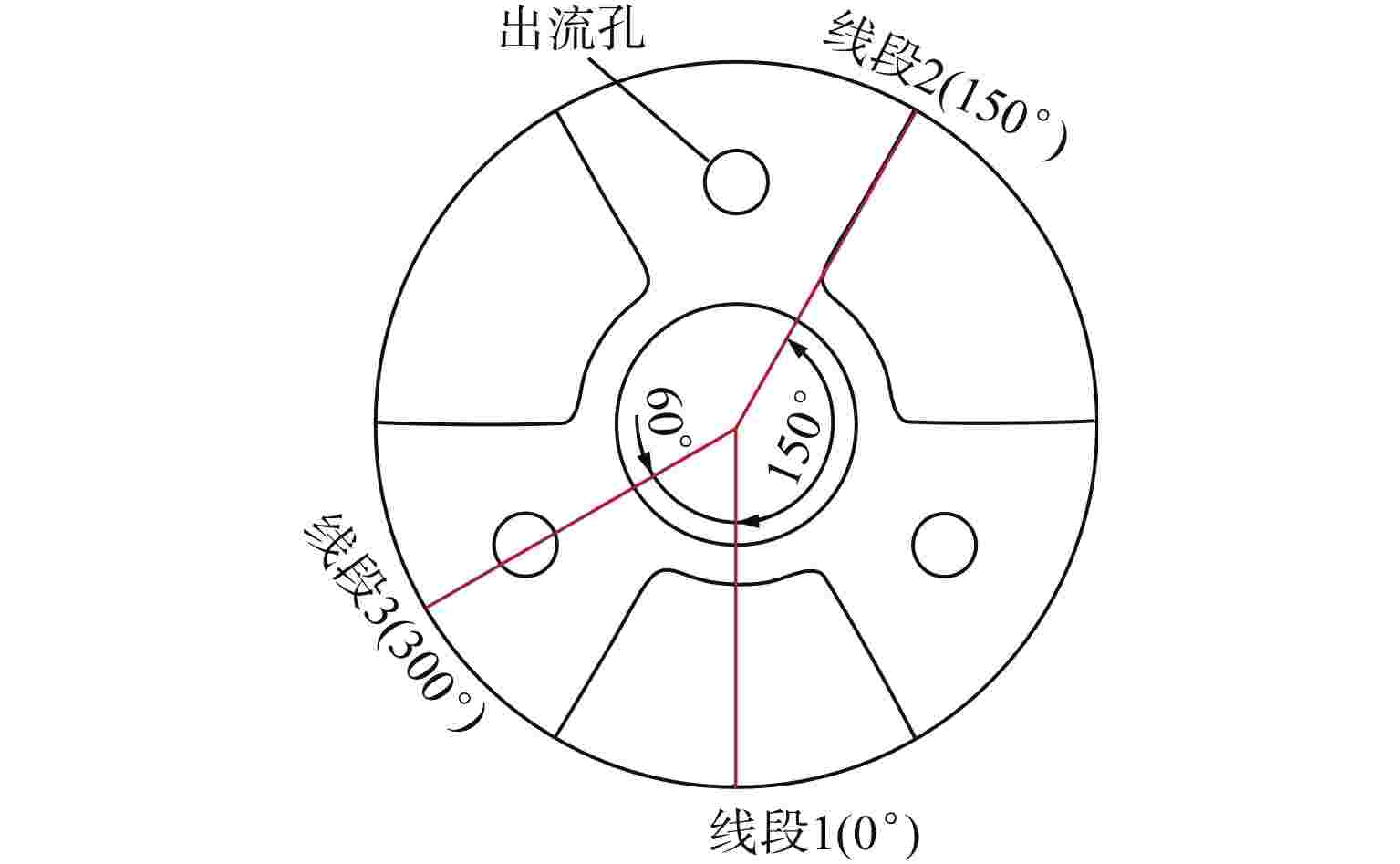
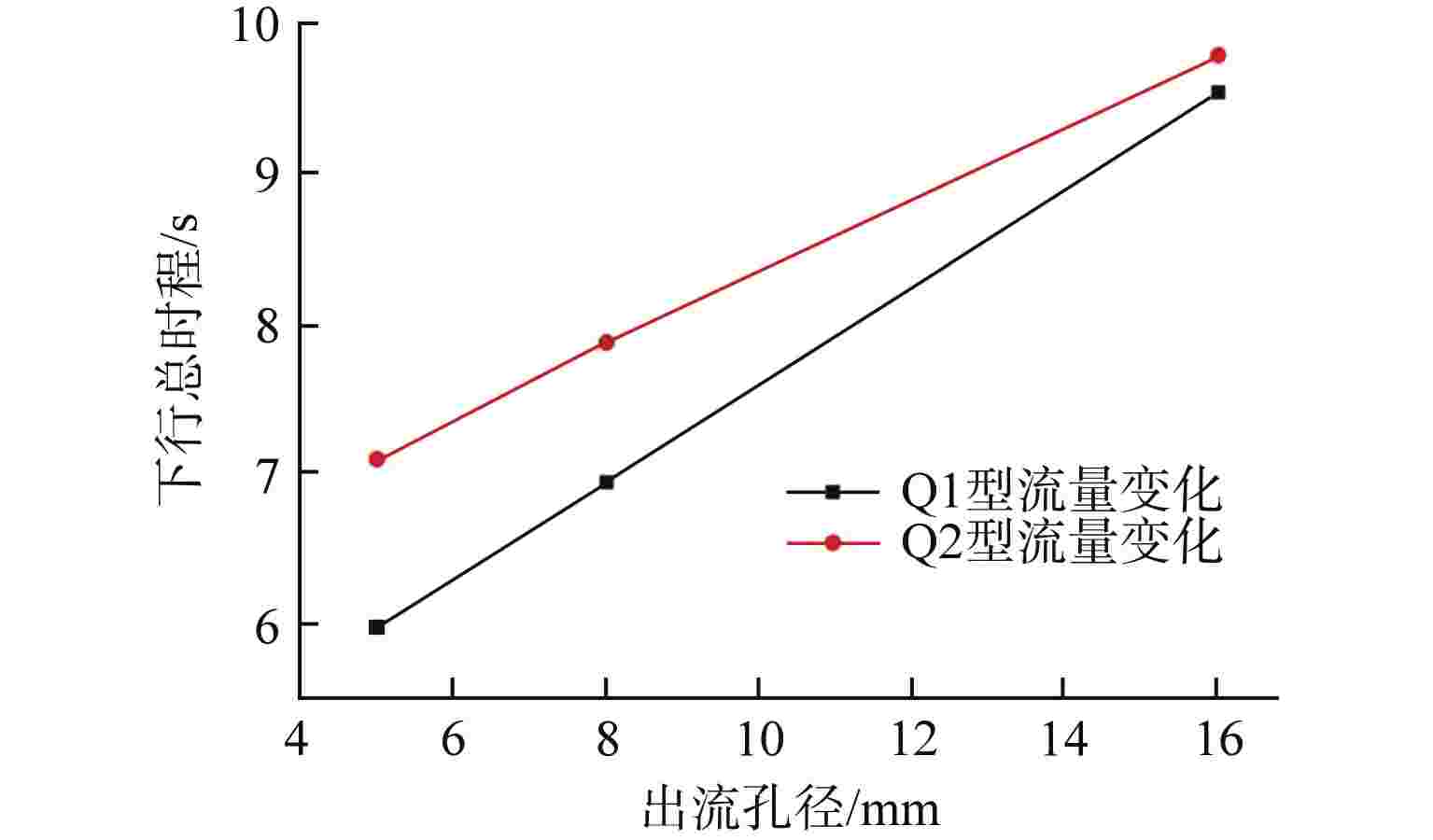
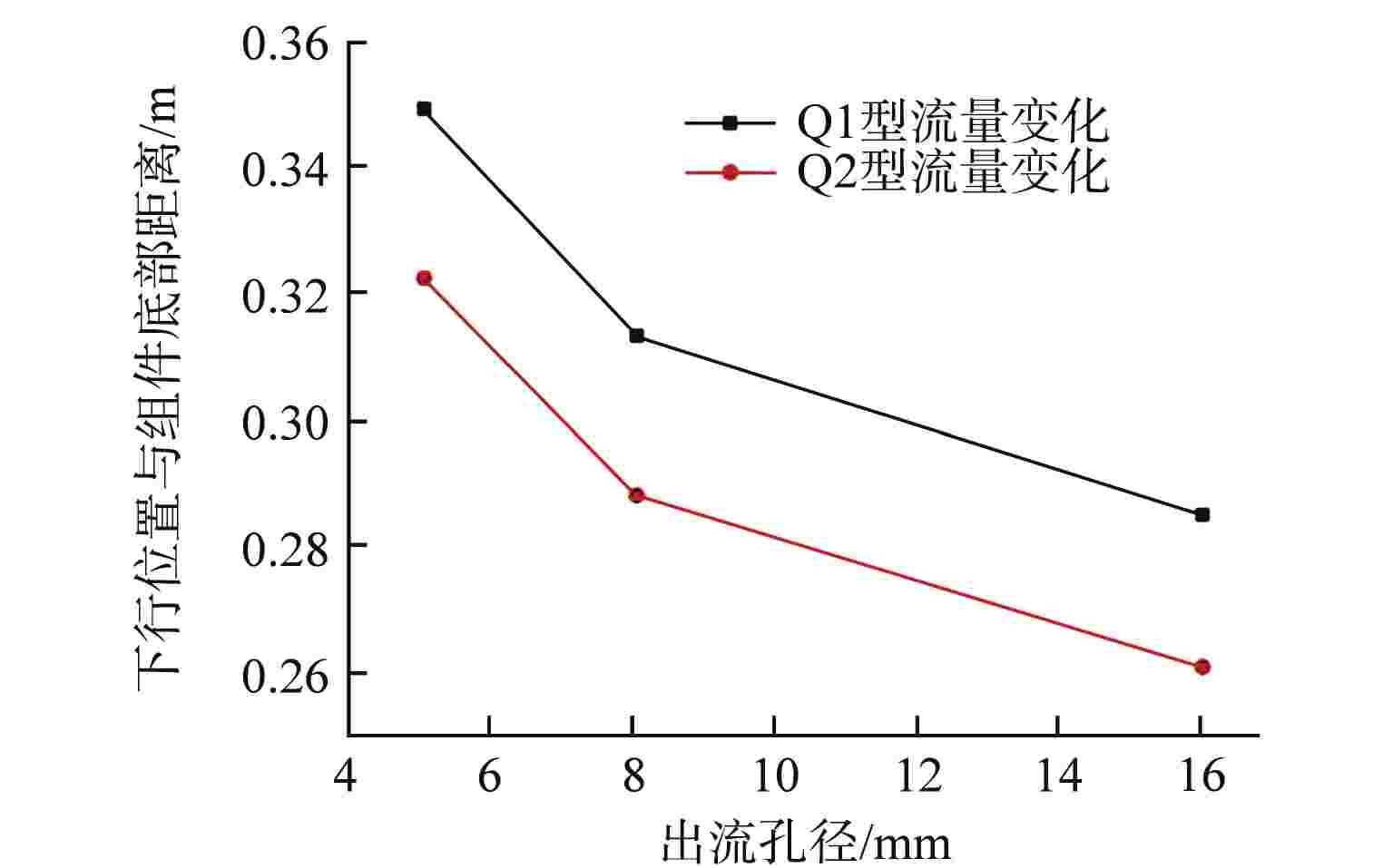
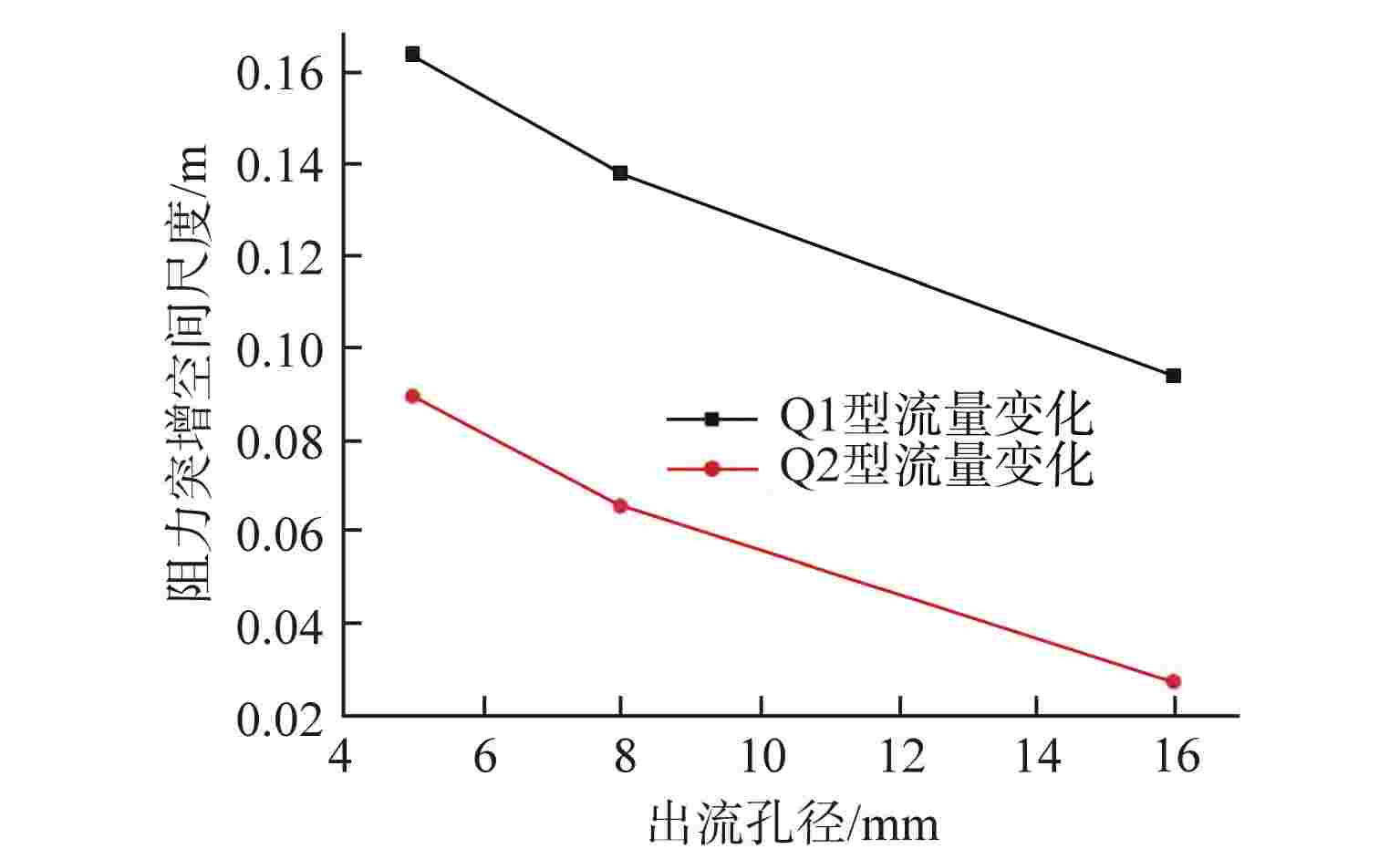
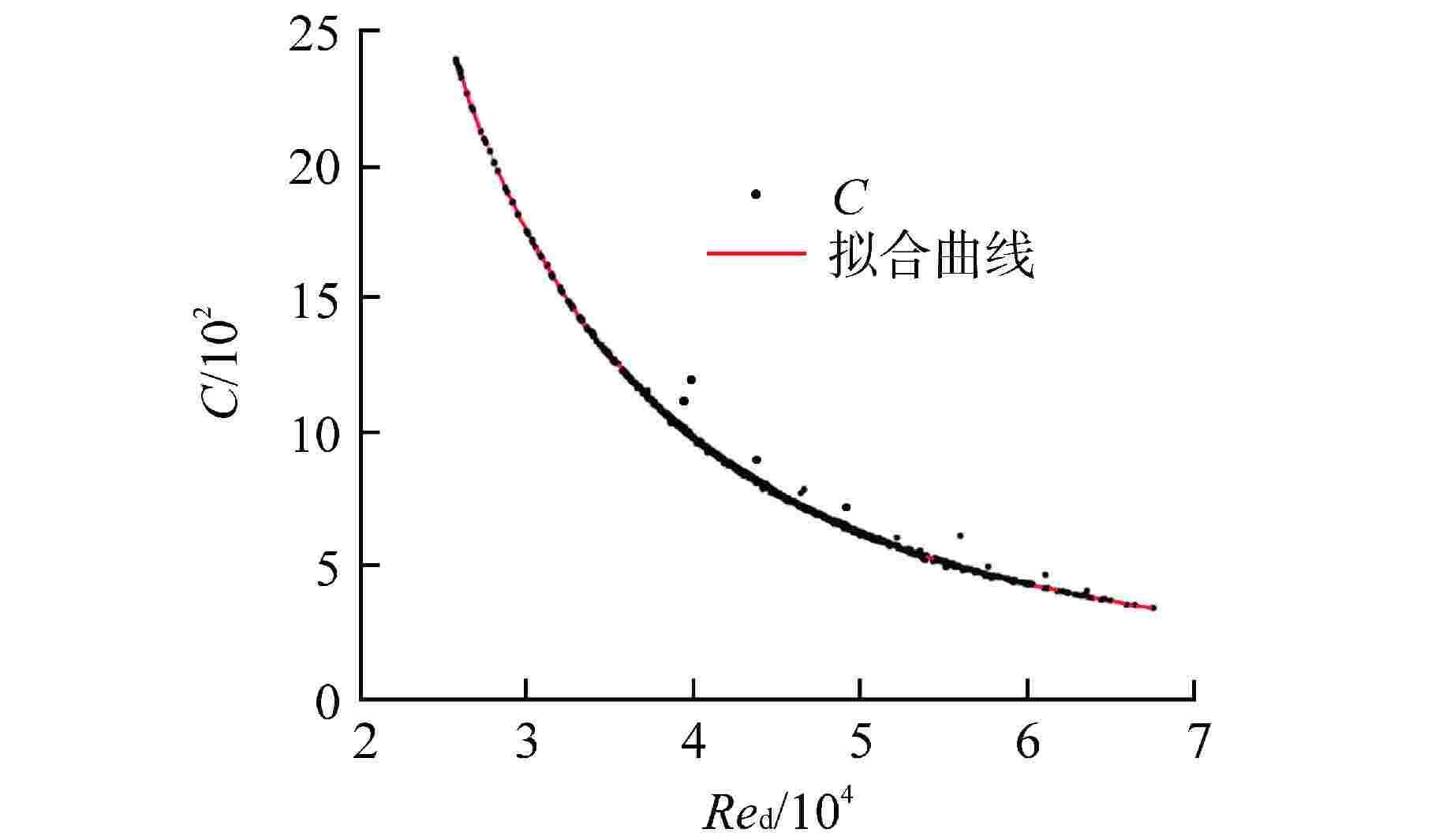
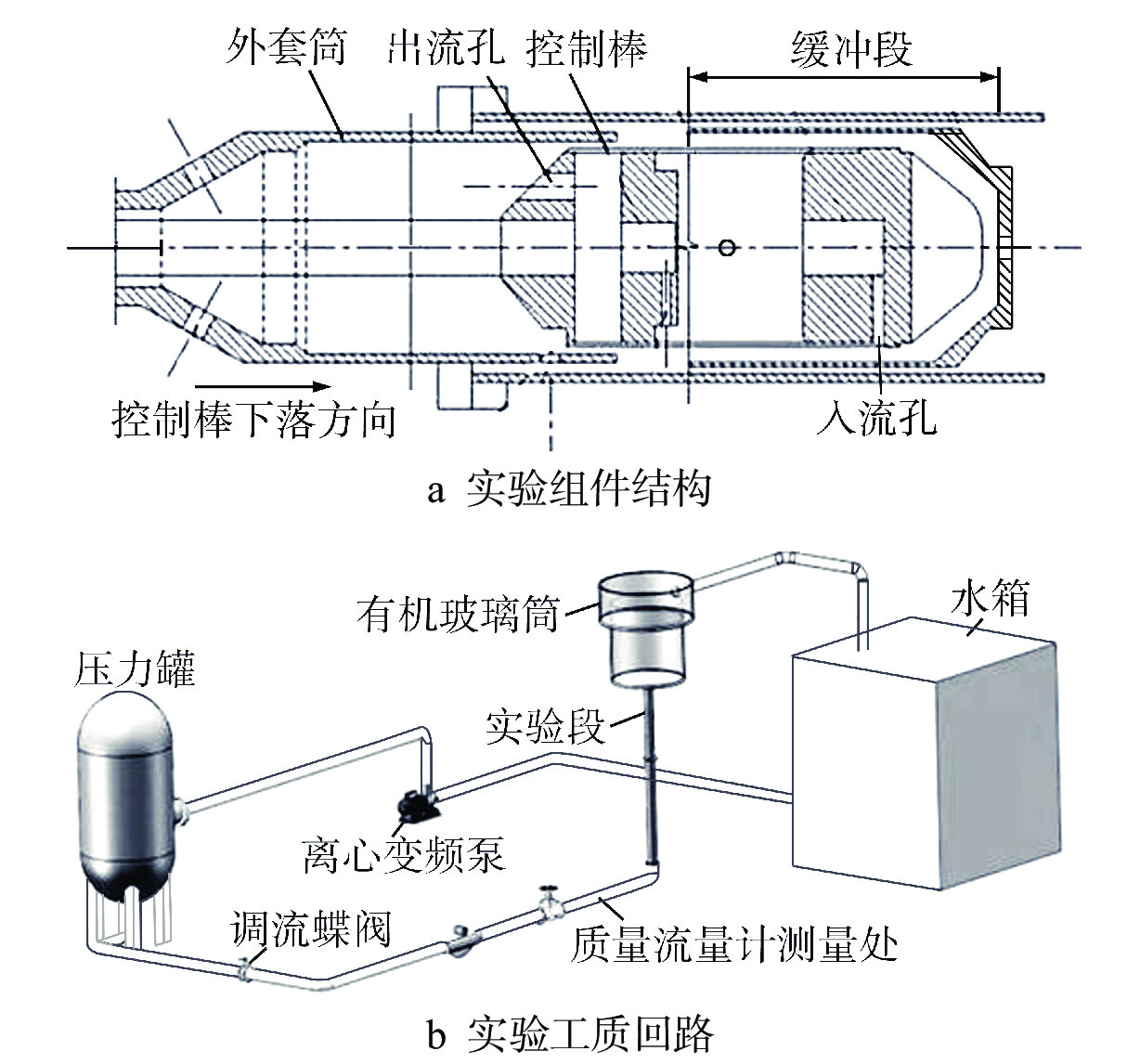
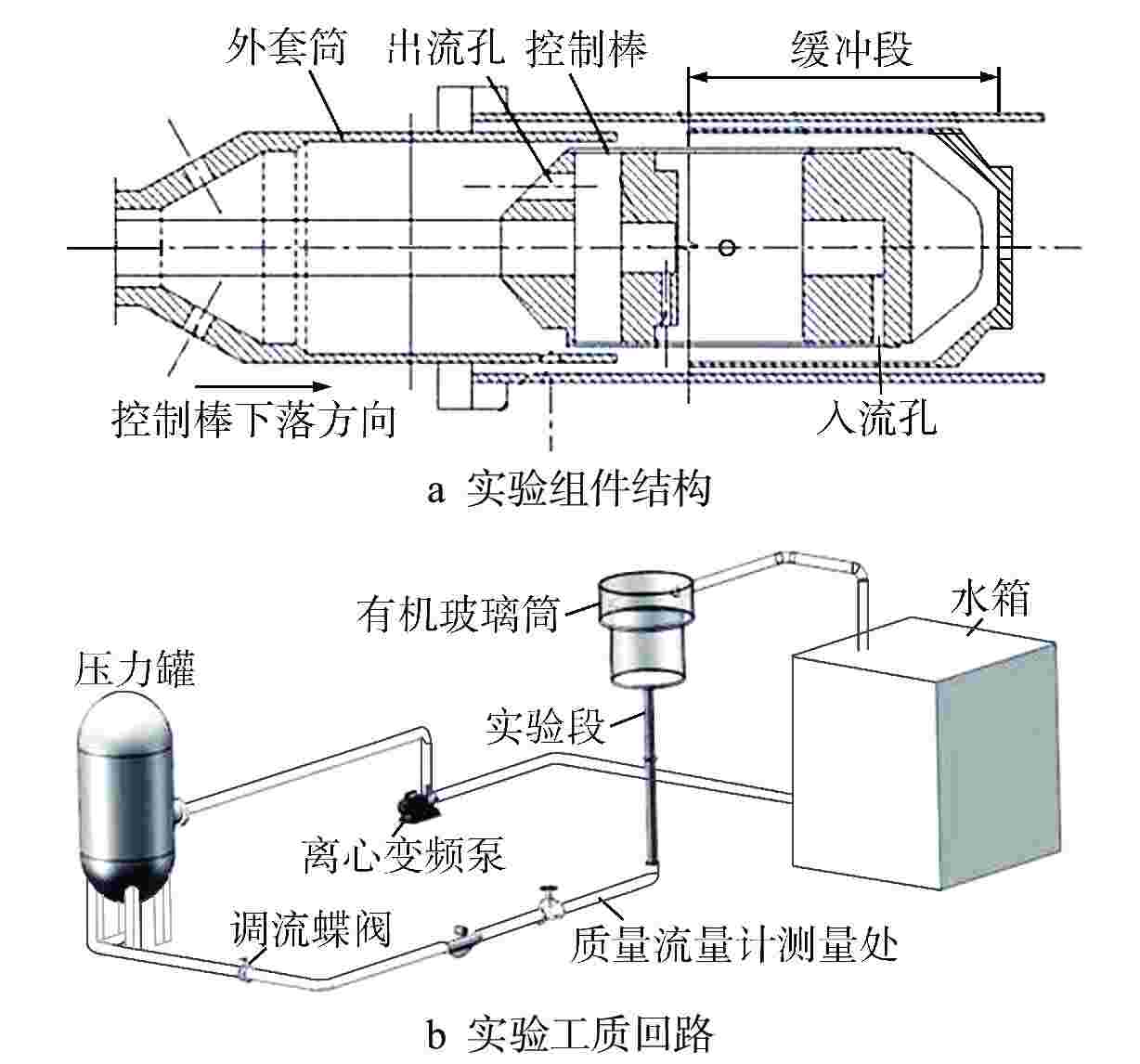
摘要: 液体悬浮式非能动停堆技术是近年来核反应安全领域的研究热点之一,研究控制棒下行的运动特性对核电厂的安全运行有着重要意义。本文选取2种典型非保护瞬态失流事故(ULOF)为依据设计多种工况进行模型实验,结合实验数据对控制棒下行运动进行受力分析得出其阻力的时程变化。通过控制变量法对比分析了控制棒尾部出流孔径和初始周向位置对控制棒下行运动时程及缓冲效果的影响,并得出了下行时的阻力系数与雷诺数之间的函数关系。本研究可为优化控制棒组件结构提供依据,给控制棒下行运动受力研究中阻力系数的选取提供参考。Abstract: Liquid suspension passive shutdown technology is one of the research hotspots in the field of nuclear reaction safety in recent years. It is important to study the downward motion characteristics of control rods for the safe operation of nuclear power plants. Two typical unprotected transient loss of flow accidents (ULOF) were selected as the basis to design various working conditions for model experiments. Combined with the experimental data, the force analysis of the downward motion of the control rod was carried out to obtain the time-history change of its resistance. The influence of outlet aperture and initial circumferential position on the time history and buffering effect of the control rod was analyzed by the control variable method, and the function relationship between resistance coefficient and Reynolds number was obtained. It can provide the basis for optimizing the structure of control rod assembly and the selection of resistance coefficient in the study of the downward motion force of control rod.
-
Key words:
- Control rod assembly /
- Rod dropping process /
- Fluid resistance /
- Sensitivity analysis
-
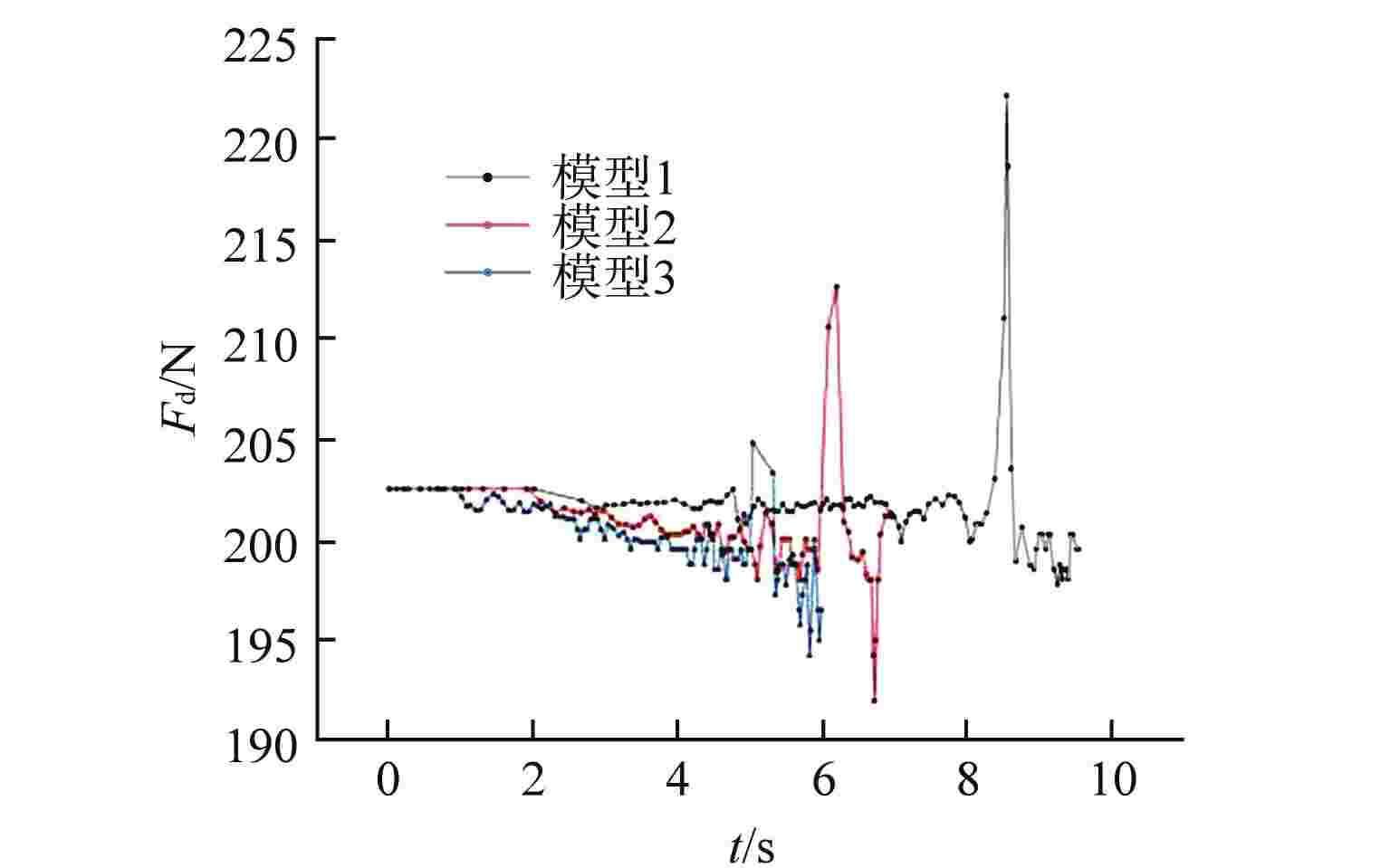
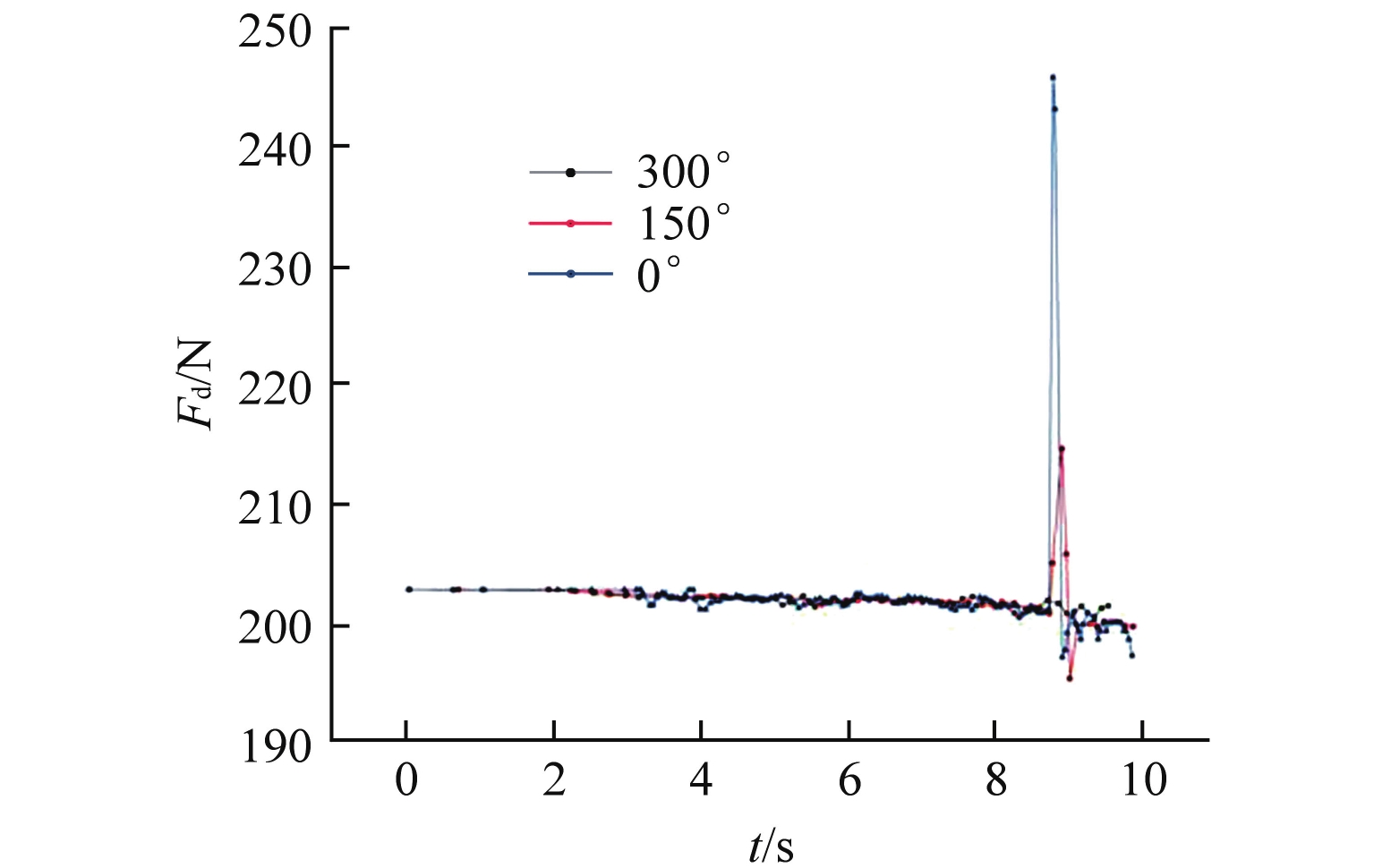
表 1 不同模型各初始周向角时下行阻力突增峰值
Table 1. Peak Value of the Sudden Increase of the Downward Resistance at Each Initial Circumferential Angle of Different Models
模型 出流孔
径/mm各初始周向角突增阻力峰值/N 突增阻力
变化/N0° 150° 300° 1 16 245.615 214.346 无突增 31.269 2 8 223.213 234.631 无突增 11.418 3 5 220.455 222.383 无突增 1.928 -
[1] 苏著亭, 叶长源, 阎凤文, 等. 钠冷快增殖堆[M]. 北京: 中国原子能出版社, 1991. [2] DONIS J M, GOLLER H. A mathematical model of a control rod drop[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 1972, 23(1): 107-120. doi: 10.1016/0029-5493(72)90193-8 [3] SHARMA D D, RAM K S. Fault tree analysis of CANDU shut-down system[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 1980, 61(2): 265-276. doi: 10.1016/0029-5493(80)90054-0 [4] BO H L, ZHENG Y H, ZHENG W X, et al. Study on step-up characteristic of hydraulic control rod driving system[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2002, 216(1-2): 69-75. [5] BO H L, ZHENG WX, DONG D, et al. Studies on the performance of the hydraulic control rod drive for the NHR-200[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2000, 195(1): 117-121. doi: 10.1016/S0029-5493(99)00200-9 [6] 胡文军,任丽霞,李政昕,等. 池式钠冷快堆非能动停堆技术方案研究[J]. 核科学与工程,2014, 34(1): 23-27. [7] 于建华,魏泳涛,孙磊,等. 控制棒组件在流体环境中下落时所受阻力的计算[J]. 核动力工程,2001, 22(3): 236-241. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0926.2001.03.010 [8] 孙磊,于建华,魏永涛,等. 控制棒组件落棒时间与历程计算[J]. 核动力工程,2003, 24(1): 59-62,76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0926.2003.01.015 [9] 彭冠男,匡波,王欣,等. 快堆悬浮式非能动停堆组件移动体落棒性能分析[J]. 应用科技,2019, 46(2): 116-121. [10] RAJAN BABU V, THANIGAIYARASU G, CHELLAPANDI P. Mathematical modelling of performance of safety rod and its drive mechanism in sodium cooled fast reactor during scram action[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2014, 278: 601-617. doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2014.08.015 [11] 黎闫,任丽霞. 钠冷快堆中安全棒落棒过程的水力计算[J]. 核科学与工程,2019, 39(1): 67-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0918.2019.01.011 [12] 肖忠,马超,郭晓明. 燃料组件结构参数对于控制棒组件落棒缓冲效果的敏感性分析[J]. 核动力工程,2016, 37(5): 111-114. [13] 郭晓明,马超,陈平,等. CF系列燃料组件落棒性能综合评价[J]. 核动力工程,2017, 38(6): 167-169. [14] 李磊实,秦本科,薄涵亮. 控制棒水压驱动系统落棒减速部件三维流场分析[J]. 原子能科学技术,2017, 51(10): 1791-1799. doi: 10.7538/yzk.2017.51.10.1791 [15] 袁浩然,匡波,刘鹏飞,等. 液体悬浮式非能动停堆组件落棒分析程序的试验验证[J]. 应用科技,2019, 46(6): 79-84. [16] 归柯庭, 汪军, 王秋颖. 工程流体力学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013: 157-161. [17] 张小峰, 刘兴年, 吴保生. 河流动力学[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2016: 28-36. -





 下载:
下载: