Analysis of Ex-Vessel Steam Explosion under RPV Side Break Cases
-
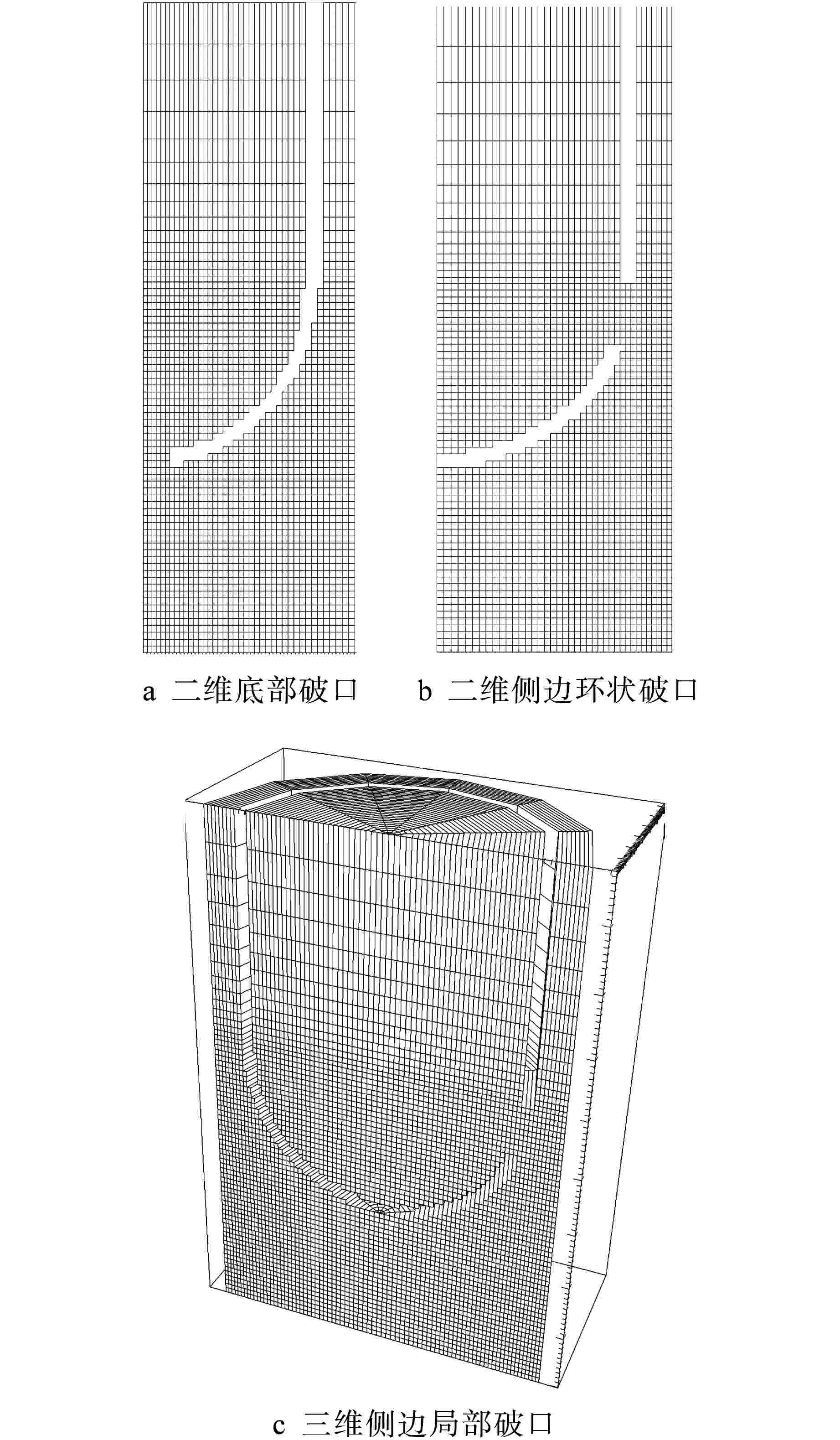
摘要: 针对实际过程中更有可能发生的压力容器(RPV)侧边破口条件开展蒸汽爆炸计算分析。根据经济合作与发展组织(OECD)发布的现象识别与重要度排序表(PIRT),选取堆外蒸汽爆炸敏感性分析参数,使用MC3D软件建立三维局部破口和二维环状破口几何模型,对影响计算结果的重要参数(破口尺寸、堆坑水位、破口位置、触发条件、液柱碎化和液滴碎化模型)开展RPV侧边破口条件下敏感性分析,获得最恶劣计算工况条件。敏感性分析结果表明,在大破口失水事故(LBLOCA)工况下,当堆坑处于满水位、RPV发生二维侧边环状破口、接触堆坑侧壁面时触发蒸汽爆炸、采用CONST模型和Classical模型时,堆坑侧壁面的压力载荷计算结果最为保守,对堆坑和安全壳完整性威胁最大。Abstract: The calculation and analysis of steam explosion were carried out for the pressure vessel (RPV) side breach conditions that are more likely to occur in the actual process. According to the Phenomena Identification and Ranking Table (PIRT) issued by Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), the sensitivity analysis parameters for ex-vessel steam explosion are selected. By establishing 3D local break and 2D circular break geometric models with MC3D, the sensitivity analysis under RPV side break conditions is carried out for the important parameters affecting the calculation results (break size, pit water level, break position, trigger conditions, liquid column fragmentation and droplet fragmentation model), and the worst calculation conditions are obtained. The sensitivity analysis results show that under the condition of large break loss of coolant accident (LBLOCA), when the reactor pit is at full water level, 2D side circular break occurs in RPV, steam explosion is triggered when contacting the reactor pit side wall, and CONST model and Classical model are adopted, the calculation results of pressure load on the reactor pit side wall are the most conservative and pose the greatest threat to the integrity of the reactor pit and containment.
-
Key words:
- Ex-vessel steam explosion /
- RPV side break /
- MC3D
-
表 1 堆外蒸汽爆炸工况参数PIRT
Table 1. PIRT for Condition Parameters of Ex-vessel Steam Explosion
工况参数 重要程度排序 认知状态 熔融物过热度 高 充分 冷却剂(水)温度 高 充分 安全壳压力 中 中等 熔融物液柱流速 高 中等 熔融物液柱直径 高 不足 堆坑水位 高 中等 破口位置 高 不足 冷却剂杂质 中 中等 熔融物物性 介于中~高 中等 表 2 堆外蒸汽爆炸现象参数PIRT
Table 2. PIRT for Phenomenon Parameters of Ex-vessel Steam Explosion
现象参数 重要程度排序 认知状态 液柱在气空间碎化 低 充分 液柱在水中碎化 高 中等 预混阶段熔融液滴特性 高 中等 熔融物凝固 高 中等 预混过程空泡 高 中等 增压机理 高 中等 换热 高 充分 分层蒸汽爆炸 高 不足 熔融物氧化 高 不足 触发条件 高 中等 爆炸过程细粒碎化 高 中等 表 3 蒸汽爆炸敏感性分析计算算例
Table 3. Calculation Examples for Sensitivity Analysis of Steam Explosion
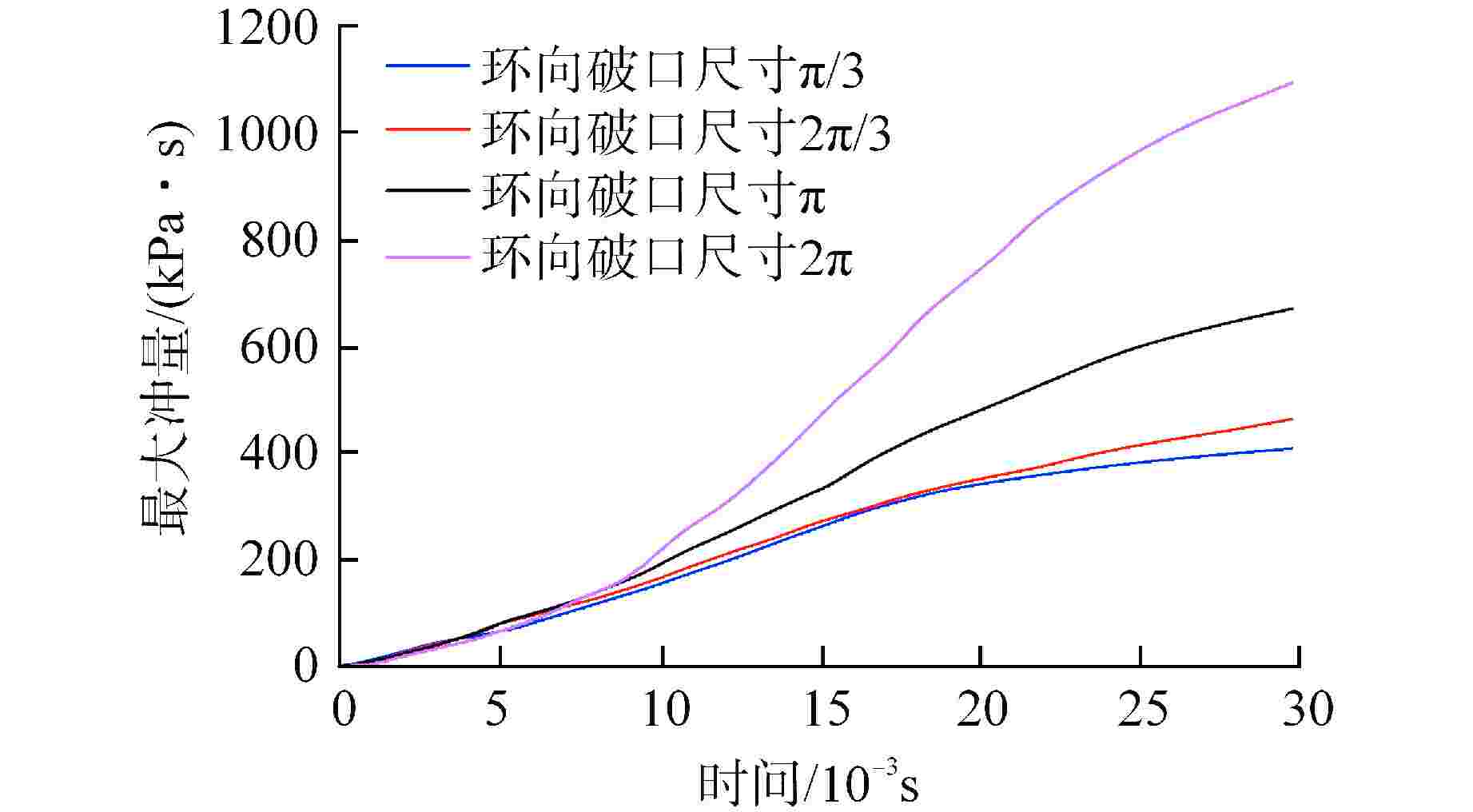
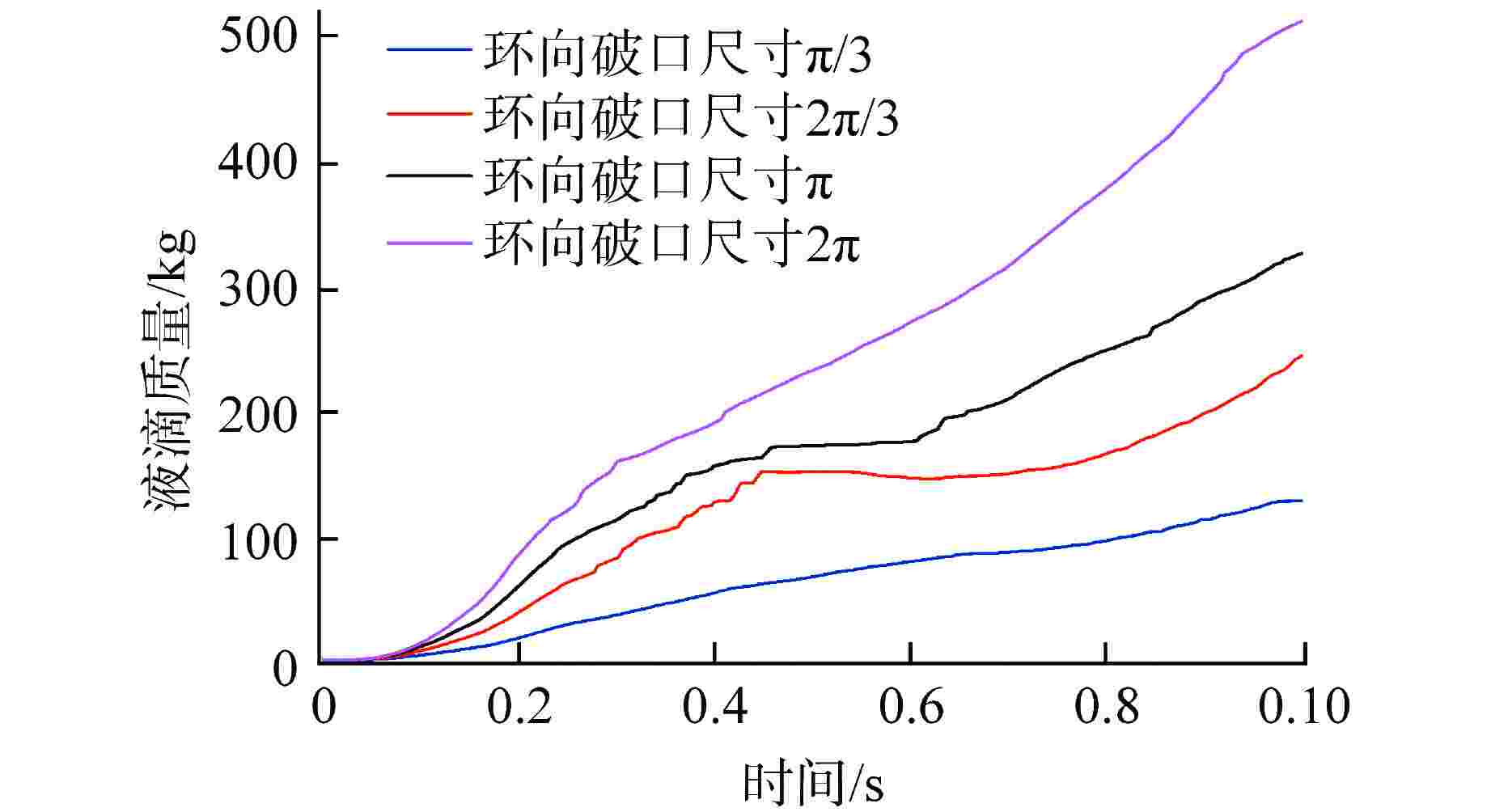
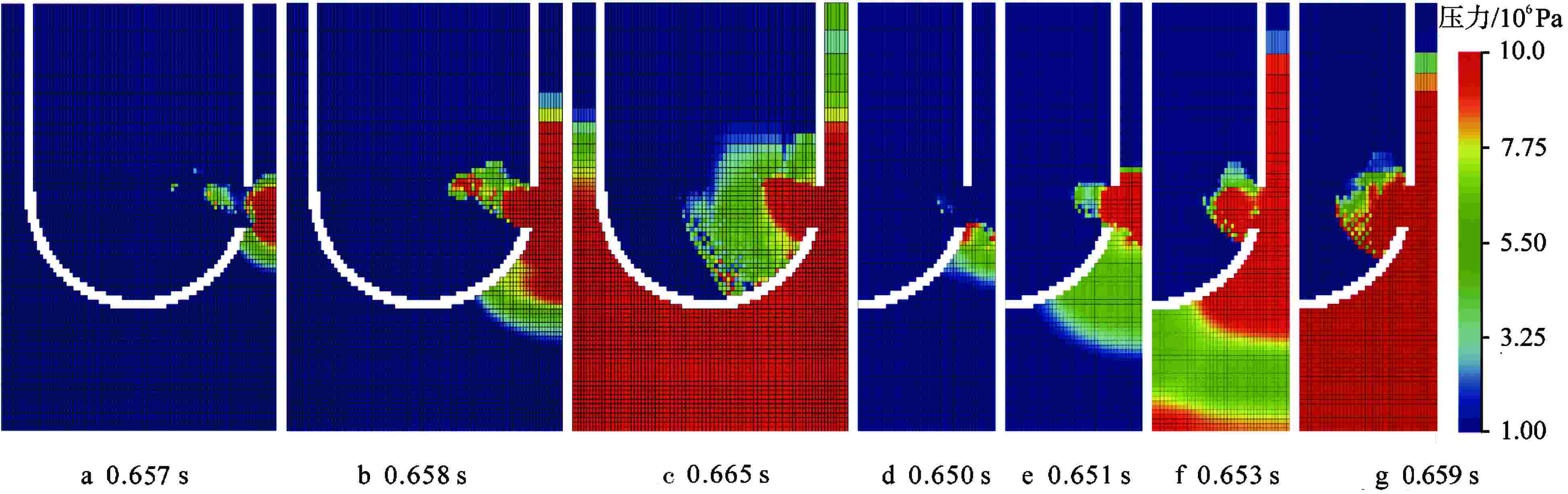
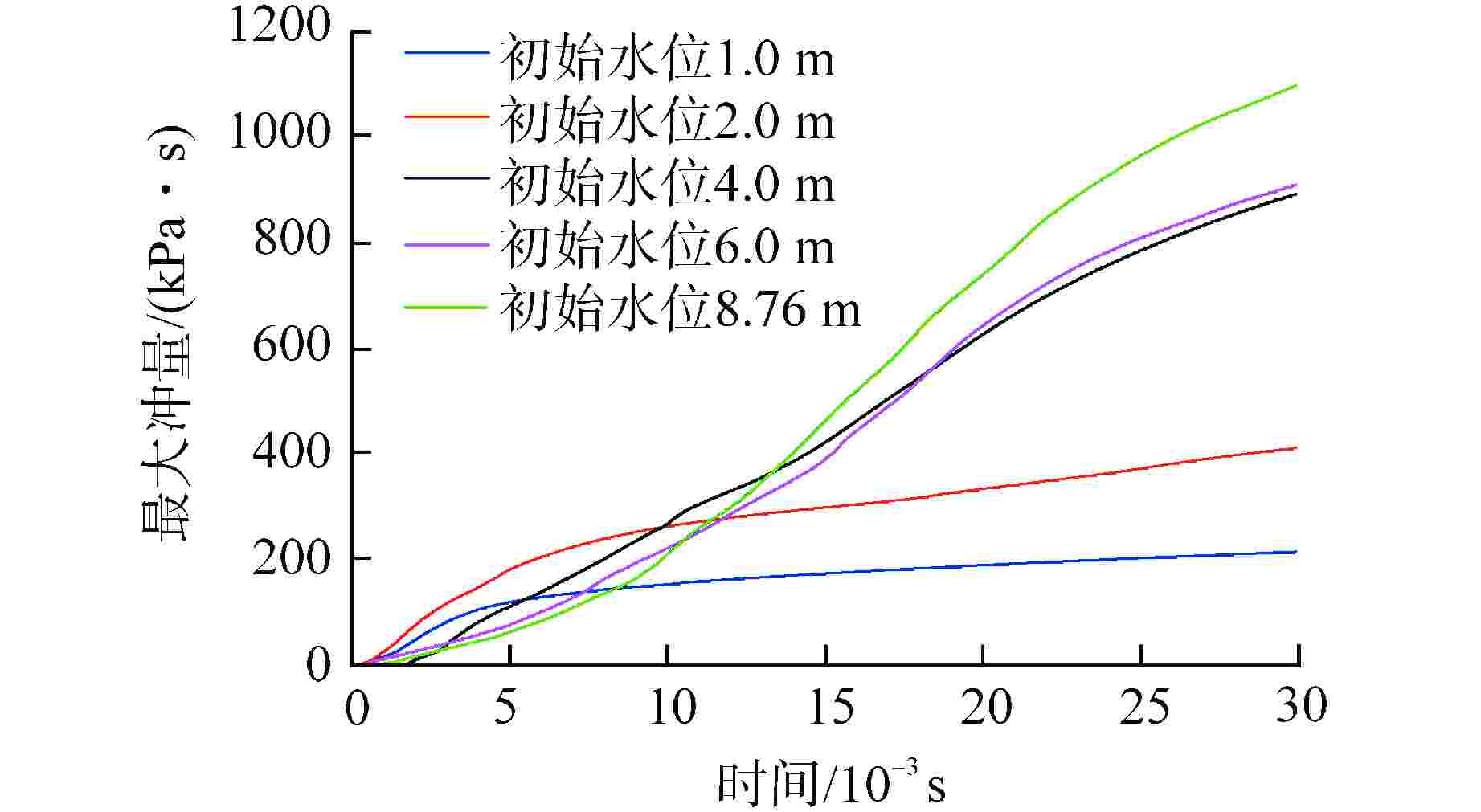
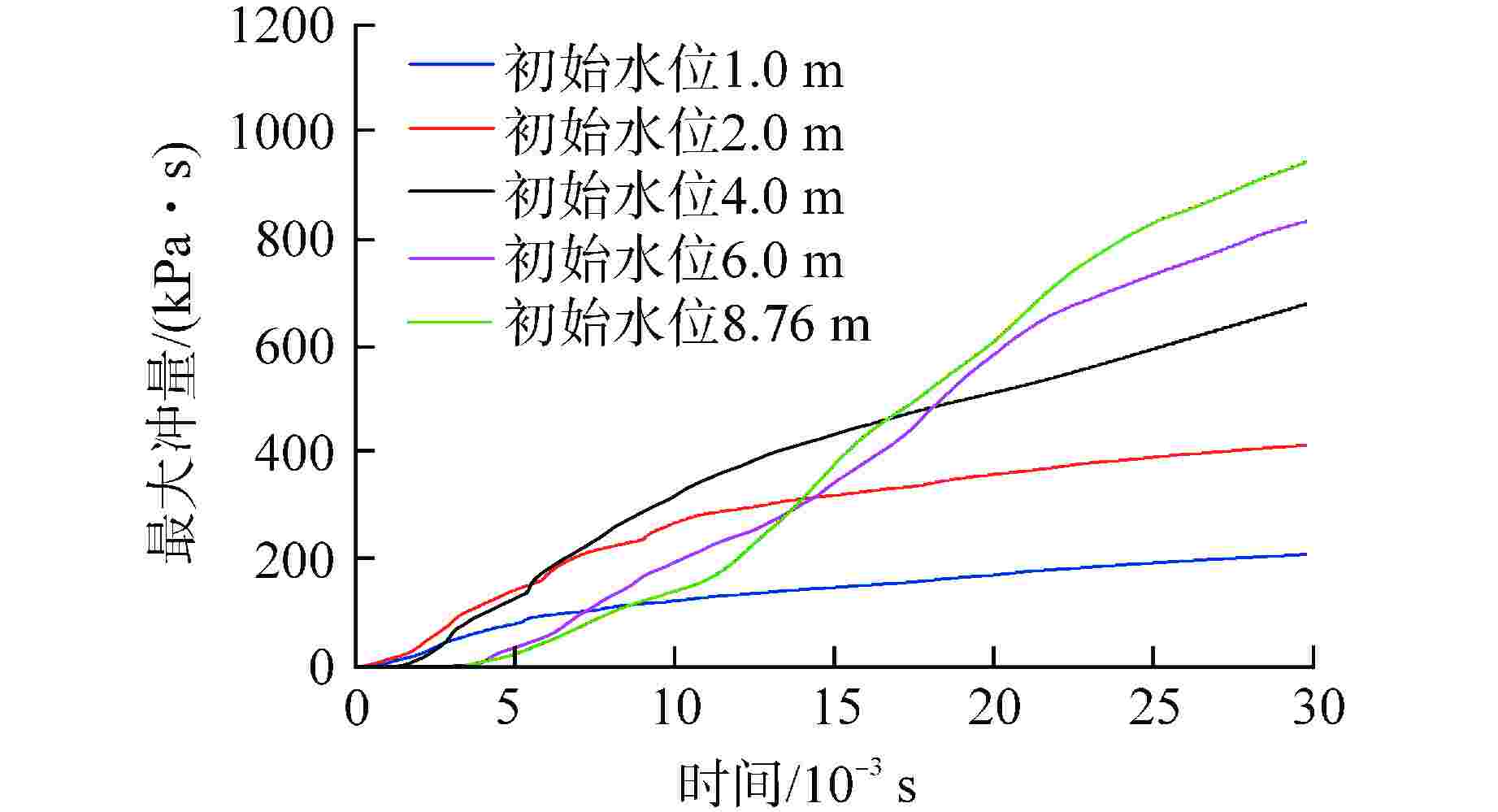
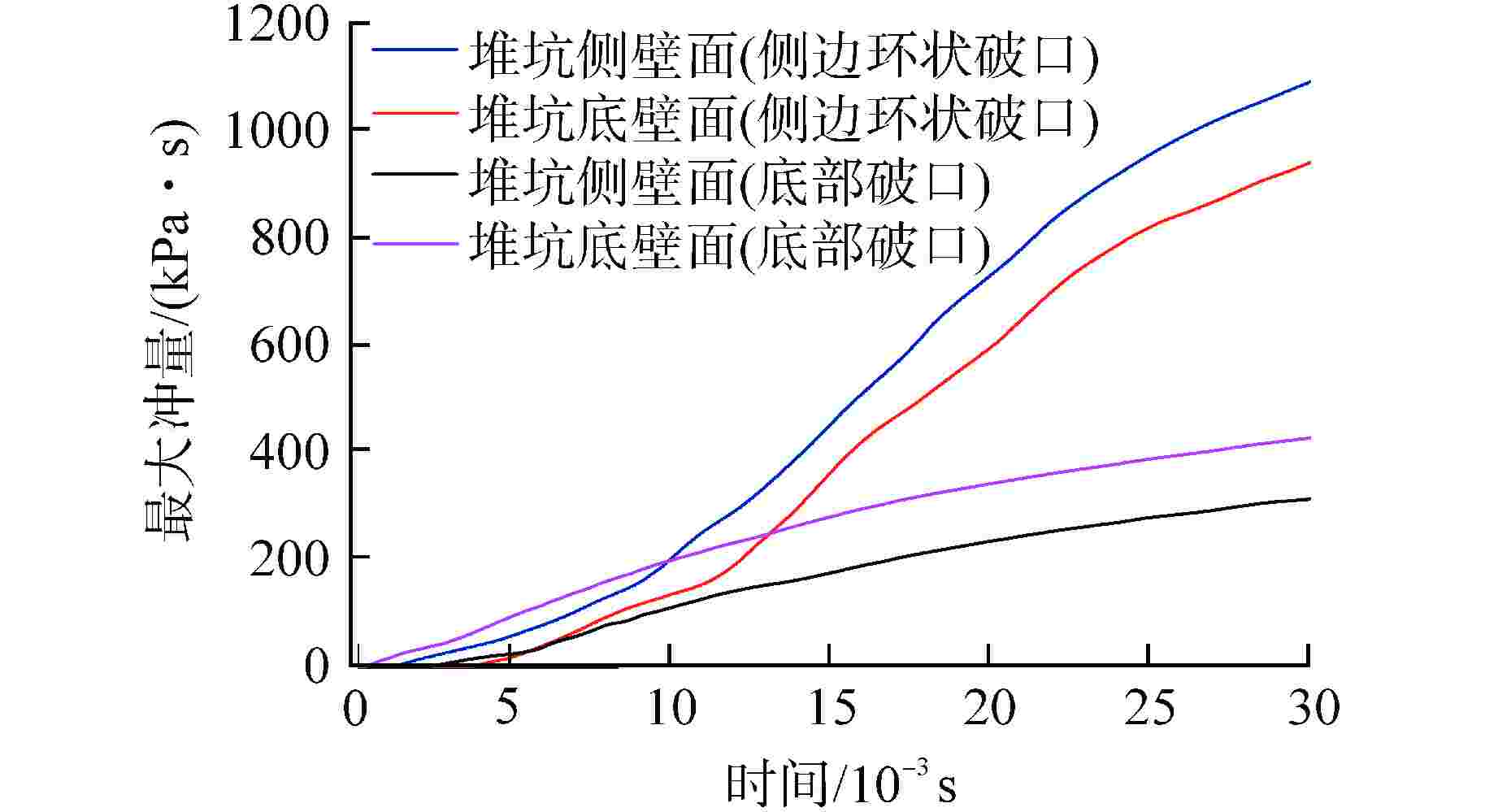
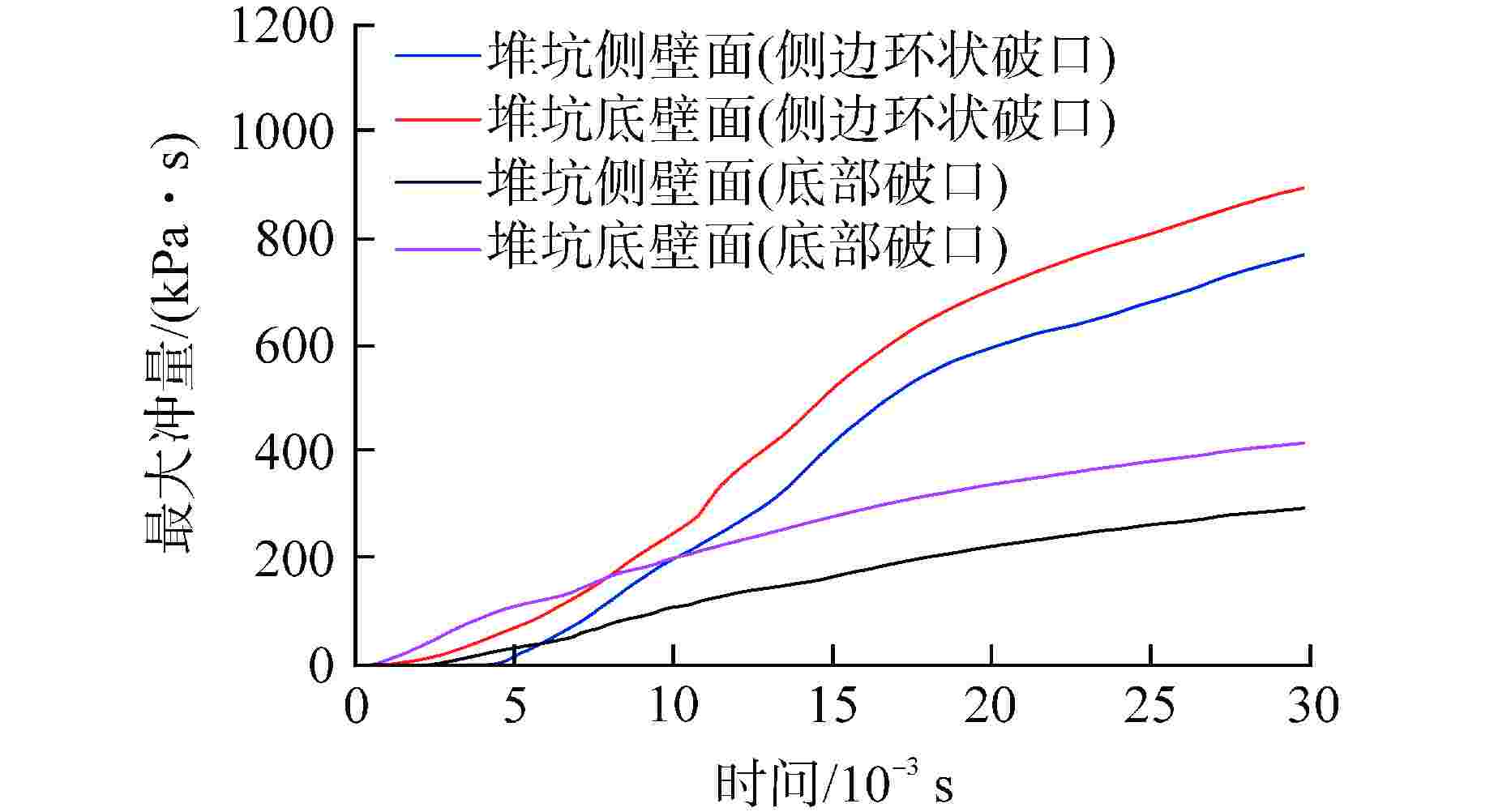
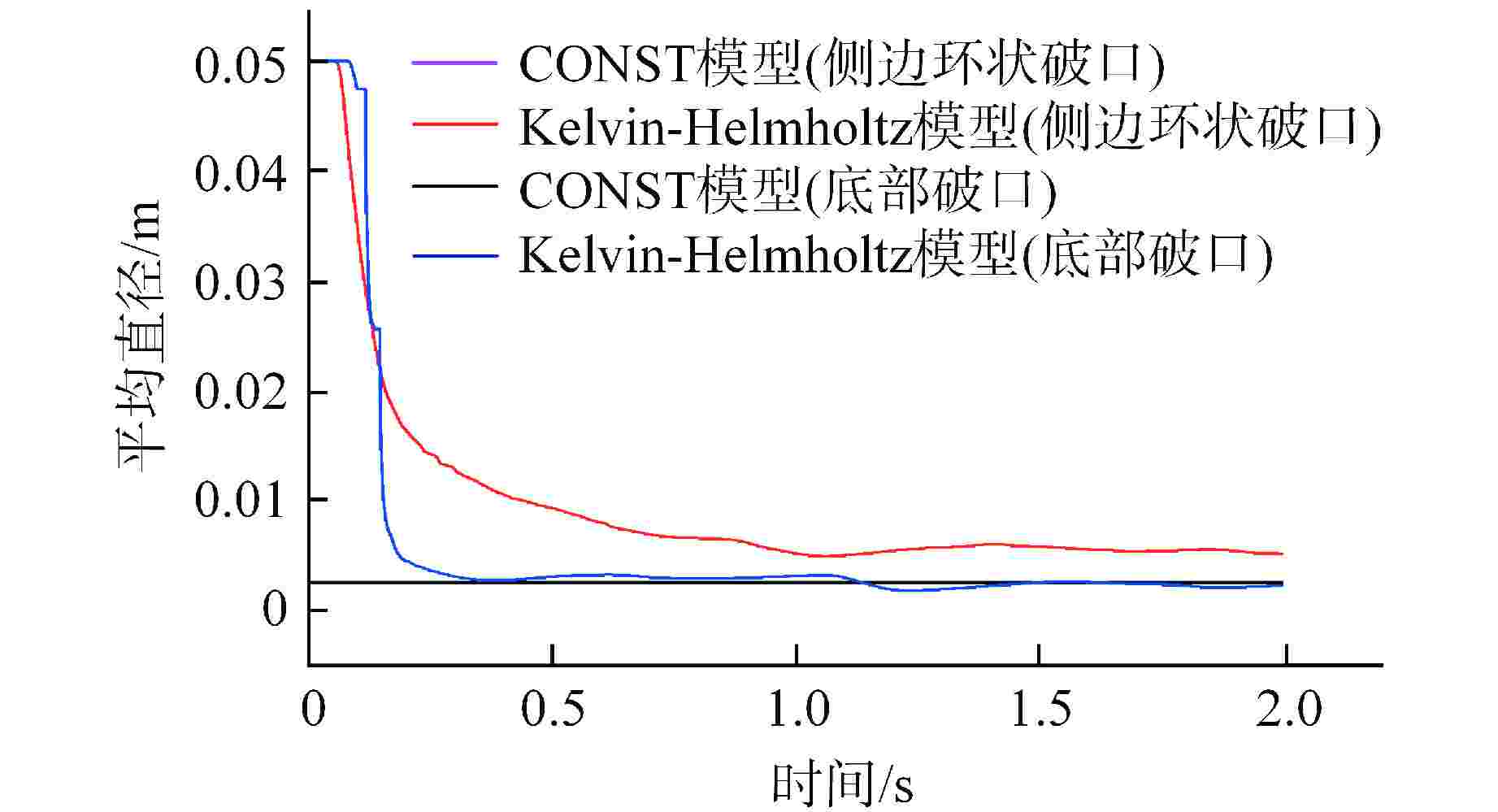
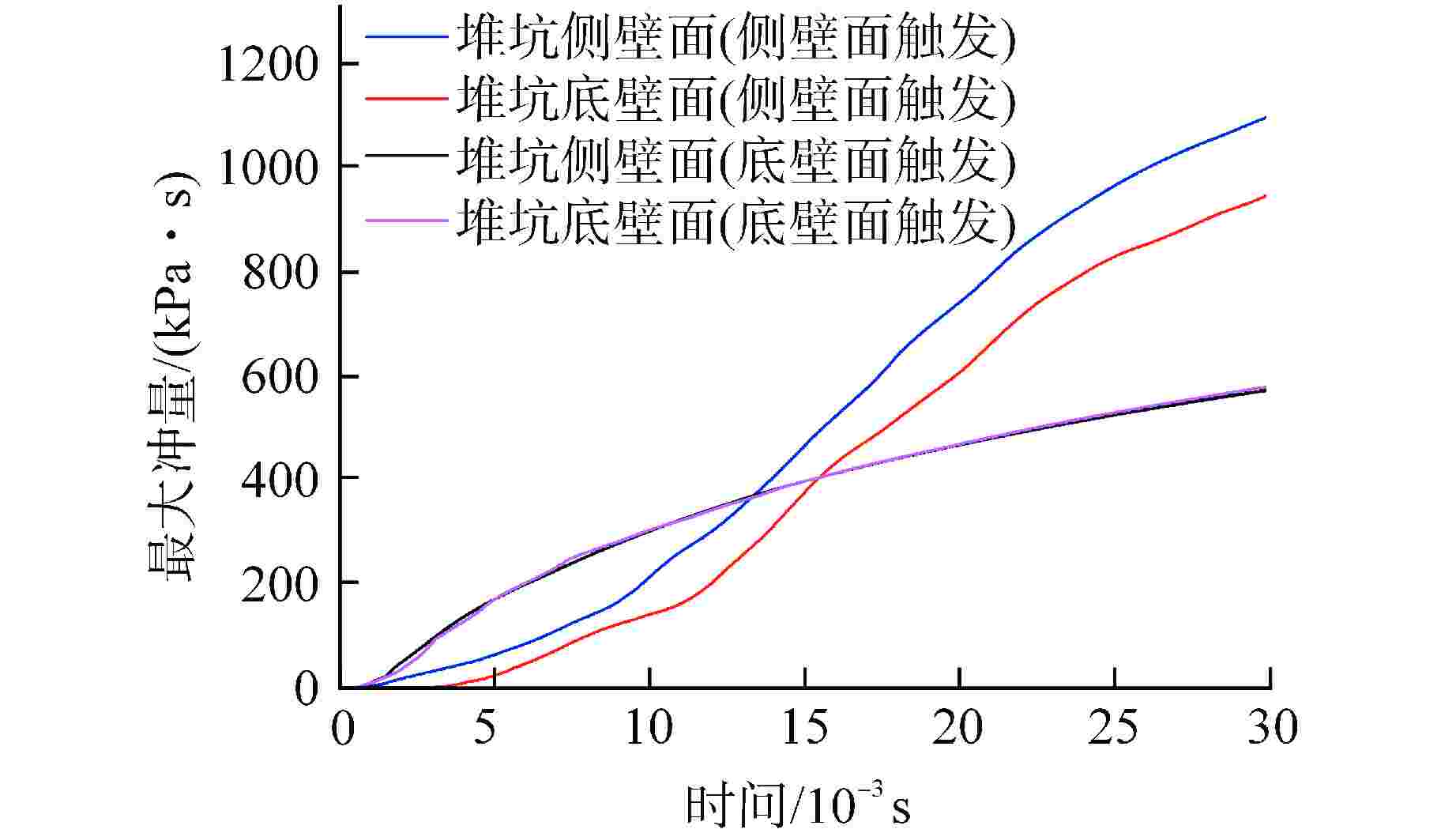
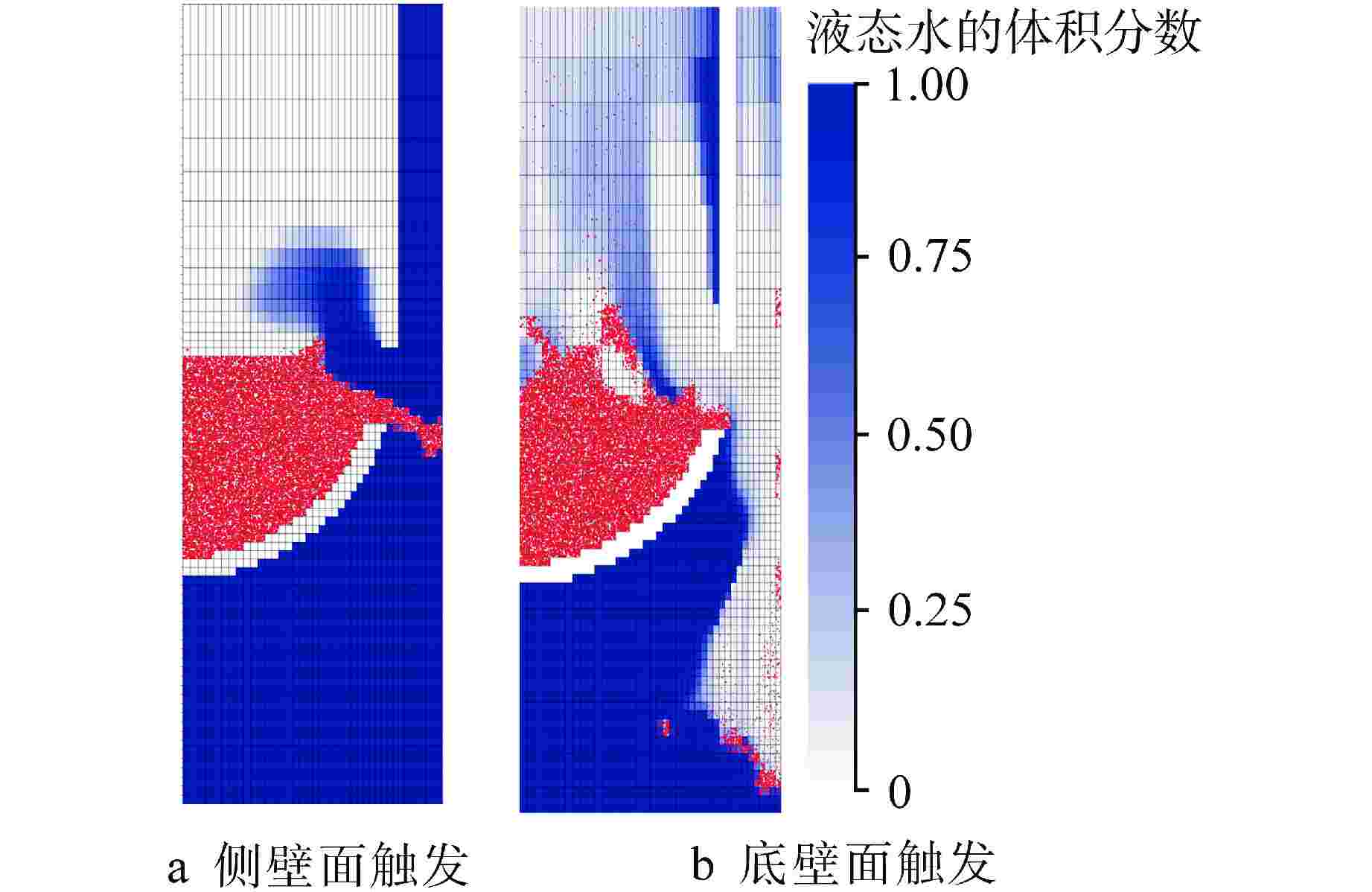
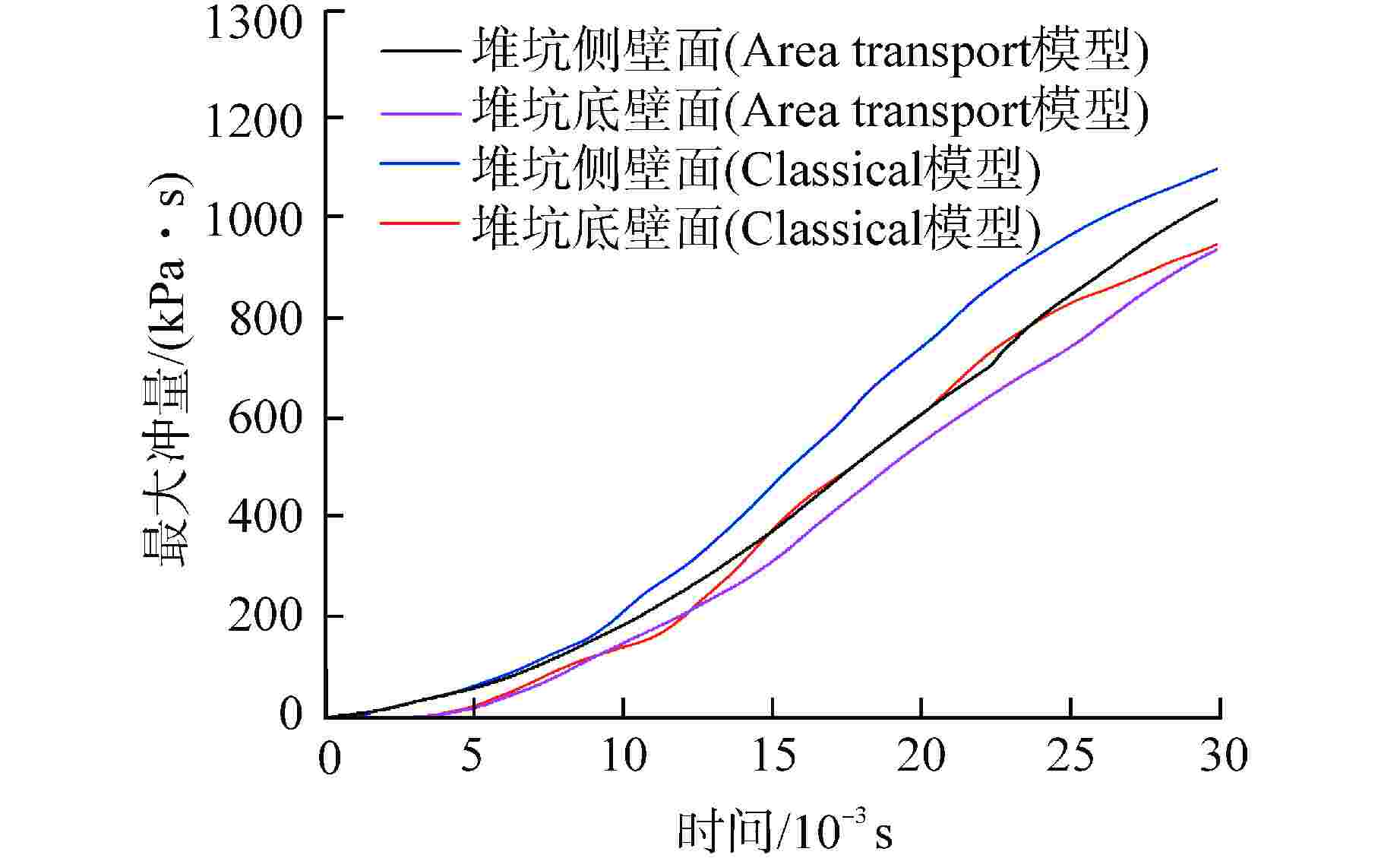
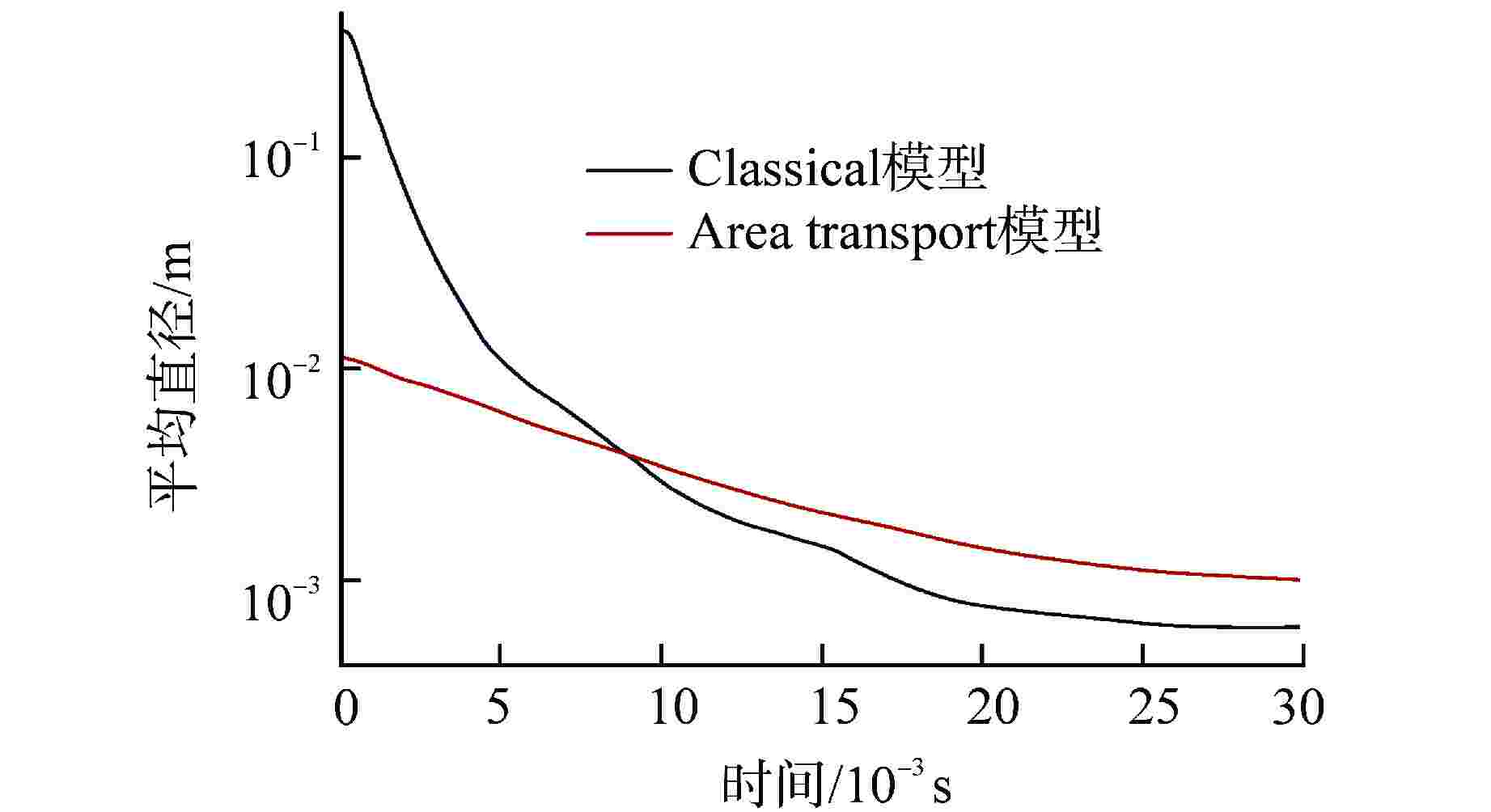
算例 破口位置 破口尺寸 堆坑初始水位/m 液柱碎化模型 触发条件 爆炸细粒碎化模型 Case 1 侧边局部破口 环向π/3 8.76 CONST模型 堆坑侧壁面触发 Classical Case 2 侧边局部破口 环向2π/3 8.76 CONST模型 堆坑侧壁面触发 Classical Case 3 侧边局部破口 环向π 8.76 CONST模型 堆坑侧壁面触发 Classical Case 4 侧边环状破口 环向2π 8.76 CONST模型 堆坑侧壁面触发 Classical Case 5 侧边环状破口 环向2π 1.0 CONST模型 堆坑底壁面触发 Classical Case 6 侧边环状破口 环向2π 2.0 CONST模型 堆坑底壁面触发 Classical Case 7 侧边环状破口 环向2π 4.0 CONST模型 堆坑底壁面触发 Classical Case 8 侧边环状破口 环向2π 6.0 CONST模型 堆坑侧壁面触发 Classical Case 9 底部破口 半径0.33 m 8.76 CONST模型 堆坑底壁面触发 Classical Case 10 底部破口 半径0.33 m 8.76 Kelvin-Helmholtz模型 堆坑底壁面触发 Classical Case 11 侧边环状破口 环向2π 8.76 Kelvin-Helmholtz模型 堆坑侧壁面触发 Classical Case 12 侧边环状破口 环向2π 8.76 CONST模型 堆坑底壁面触发 Classical Case 13 侧边环状破口 环向2π 8.76 CONST模型 堆坑侧壁面触发 Area transport -
[1] MA W M, YUAN Y D, SEHGAL B R. In-vessel melt retention of pressurized water reactors: historical review and future research needs[J]. Engineering, 2016, 2(1): 103-111. doi: 10.1016/J.ENG.2016.01.019 [2] 李春,杨志义,丁超,等. 基于MC3D软件对核电厂压力容器蒸汽爆炸的重要参数计算及研究[J]. 核安全,2018, 17(2): 58-65. [3] 陈巧艳,王辉,石雪垚. 熔融物液柱碎化模型对先进压水堆堆外蒸汽爆炸计算的影响分析[J]. 原子能科学技术,2016, 50(5): 812-818. [4] 黄伟峰. 运用MC3D程序计算分析堆坑内堆芯熔融物与冷却剂反应[J]. 原子能科学技术,2011, 45(8): 960-965. [5] 雷蕾,林萌,周源,等. 蒸汽爆炸中熔融物液滴直径敏感性分析[J]. 核技术,2013, 36(3): 69-74. [6] 黄熙,杨燕华,王溪. 堆外蒸汽爆炸堆腔压力冲量分布计算分析[J]. 核动力工程,2011, 32(3): 15-21. [7] THAKRE S, MA W. Simulations of ex-vessel fuel coolant interactions in a Nordic BWR using MC3D code: NKS-DECOSE Report-3/2012 [R]. Sweden :Royal Institute of Technology, KTH,, 2013. [8] LESKOVAR M, URŠIČ M. Ex-Vessel steam explosion analysis for pressurized water reactor and boiling water reactor[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 2016, 48(1): 72-86. doi: 10.1016/j.net.2015.08.012 [9] WANG X, LI T S, HUANG X, et al. Analysis of fuel coolant interaction in PWR with experiment and computer code[C]//18th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering. Xi’an, China: ASME, 2010. [10] GIACOSA A, URŠIČ M, LESKOVAR M. Analysis and sensitivity study of BWR Ex-Vessel steam explosion with MC3D Code[C]//20th International Conference Nuclear Energy for New Europe. Bovec, Slovenia, 2011. [11] LESKOVAR M. PWR Ex-Vessel steam explosion analysis with MC3D code[C]//21th International Conference Nuclear Energy for New Europe. Sloveni, 2012. [12] SKOBE T, LESKOVAR M. Influence of metal corium oxidation on ex-vessel steam explosion[J]. 26th International Conference Nuclear Energy for New Europe. Slovenia,2017 [13] OECD/NEA. Status report on ex-vessel steam explosion: NEA/CSNI/R(2017)15[R]. OECD NEA, 2017. [14] MORIYAMA K, PARK H S. Parameter dependence of steam explosion loads and proposal of a simple evaluation method[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 2015, 47(7): 907-914. doi: 10.1016/j.net.2015.07.004 [15] ZHONG M J, LI Z G, LIN M, et al. Numerical analysis of pressure load in a PWR cavity in an ex-vessel steam explosion[J]. Nuclear Science and Techniques, 2014, 25(3): 65-75. [16] LESKOVAR M, URŠIČ M. Estimation of ex-vessel steam explosion pressure loads[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2009, 239(11): 2444-2458. doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2009.07.023 [17] 黄熙, 王溪. CPR1000堆内注水蒸汽爆炸最终分析模型及详细风险评估[Z]. 堆腔注水有效性及负面风险研究报告. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2009. [18] 钟明君,林萌,张政铭,等. 基于1000 MW级压水堆核电厂压力容器外蒸汽爆炸的模拟研究[J]. 核动力工程,2014, 35(4): 43-47. [19] LESKOVAR M, URŠIČ M. Analysis of PWR ex-vessel steam explosion for axial and side melt release[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2015, 283: 40-50. doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2014.03.014 [20] IRSN. Description of the physical models of the EXPLOSION application:PSN-RES/SAG/2017-00074 [R]. Saint Paul Lez Durance Cedex: Institut de Radioprotection et de Sûreté Nucléaire, 2017. -





 下载:
下载: