Thermal-Hydraulic Performance Analysis of Horizontal Spiral Tube Steam Generator for European Lead-Cooled Fast Reactor
-
摘要: 以欧洲铅冷堆(ELSY)水平螺旋管式蒸汽发生器(HST-SG)为研究对象,结合其结构参数和运行参数,选取了合适的传热阻力模型开发了一维稳态热工水力计算程序,采用该程序首先对ELSY HST-SG进行校核计算,以验证程序计算的准确性,再结合计算结果,对ELSY HST-SG热工水力性能进行详细分析,并针对不同运行参数开展对比分析研究。分析结果表明,ELSY HST-SG各项参数选择合理,热工水力性能优良,结构紧凑。因此,该程序可用于ELSY HST-SG的设计开发和性能分析。Abstract: Taking the horizontal spiral tube steam generator (HST-SG) of European lead-cooled system (ELSY) as the research object, combined with its structural and operating parameters, this paper selects an appropriate heat transfer resistance model and develops a one-dimensional steady-state thermal hydraulic calculation program. Firstly, the program is used to check and calculate ELSY HST-SG to verify the accuracy of the program calculation. Then, combined with the calculation results, the thermal and hydraulic performance of ELSY HST-SG is analyzed in detail, and the comparative analysis and research is carried out for different operation parameters. The analysis results show that the selection of various parameters of ELSY HST-SG is reasonable, the thermal and hydraulic performance is excellent, and the purpose of compact structure is achieved. Therefore, this program can be used for design development and performance analysis of ELSY HST-SG.
-
Key words:
- Horizontal spiral tube /
- Steam generator /
- Lead-cooled fast reactor /
- Thermal hydraulics
-
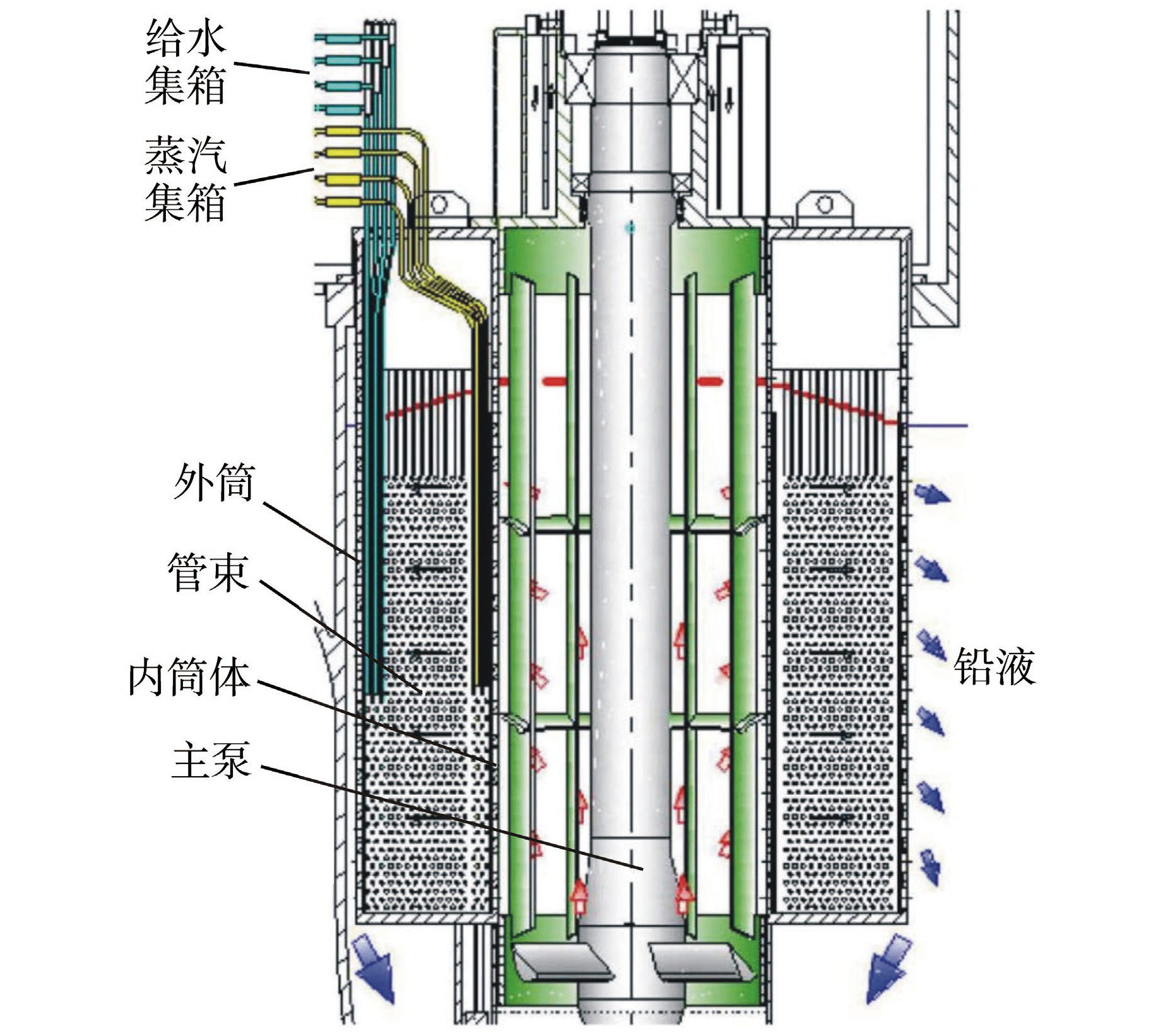
图 1 SG-PP一体化设计示意图[8]
Figure 1. Schematic Diagram of Integrated Design of Main Pump and SG
表 1 ELSY 堆主热传输系统参数[8]
Table 1. Main Parameters of ELSY Heat Transfer System[8]
参数 参数值 参数 参数值 反应堆
电功率/ MW600 SG模块数量 8 单台SG
热功率/MW175 蒸汽压力/MPa 18 铅进口温度/℃ 480.0 给水温度/℃ 335 铅出口温度/℃ 400.0 蒸汽出口温度/℃ 450 表 2 SG主要结构参数[8]
Table 2. Main Structural Parameterrs of SG
参数 参数值 参数 参数值 SG内筒外径/mm 1240 传热管长度/m 55 SG外筒内径/mm 2420 每层的传热管
数量2 螺旋管束区高度/mm 2620 传热管外径、壁厚/mm 22.22、2.5 传热管数量 219 轴向、径向间距/mm 24、24 表 3 传热经验关系式汇总
Table 3. Summary of Heat Transfer Relationship
表 4 程序校核计算结果
Table 4. Program Check and Calculation Results
参数 功率/
MW铅进口
温度/℃铅出口
温度/℃给水温
度/℃蒸汽出口
温度/℃管长/m 设计
参数175.00 480.0 400.00 335.0 450.0 55.0 校核
计算179.68 480.0 397.88 335.0 462.5 55.0 误差 2.67% — −0.53% — 2.78% — “—”表示无误差 表 5 不同压力下额定功率设计参数对比
Table 5. Comparison of Design Parameters of Rated Power under Different Pressures
压力/MPa 14 16 18 20 给水温度/℃ 335 335 335 335 蒸汽出口温度/℃ 463.3 461.5 459.8 459.1 功率/ MW 186.9 183.0 179.1 174.7 蒸汽流速/(m·s−1) 45.57 38.66 33.12 28.79 管内阻力/ kPa 1392.1 1169.6 965.5 768.2 表 6 不同给水温度情况下参数变化
Table 6. Parameter Changes under Different Feed Water Temperatures
给水温度/℃ 330 335 345 355 蒸汽压力/ MPa 18 18 18 18 蒸汽出口温度/℃ 458.3 459.8 463.0 466.4 两相区长度/m 20.42 20.49 20.44 20.34 沿程压降/kPa 951.5 965.5 1000.0 1040.5 功率/MW 182.28 179.15 172.38 164.08 -
[1] ALEMBERTI A, LFROGHERI M. Lead-cooled Fast Reactor (LFR) risk and safety assessmentwhite paper[C]//GEN Ⅳ International Forum, 2014: 16-17 [2] INGERSOLL D T, CARELLI M D. Handbook of small modular nuclear reactors[M]. 2nd ed. Duxford: Woodhead Publishing, 2020: 33-34, 40-41. [3] CACUCI D G. Handbook of nuclear engineering[M]. New York: Springer, 2010: 2400-2406. [4] GRABEZHNAYA V A, MIKHEEV A S, KALYAKIN S G, et al. Testing the steam generator model with helical coiled lead-heated tubes[J]. Thermal Engineering, 2014, 61(11): 777-784. doi: 10.1134/S0040601514110019 [5] CINOTTI L, SMITH C F, SEKIMOTO H, et al. Lead-cooled system design and challenges in the frame of generation IV International Forum[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2011, 415(3): 245-253. doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2011.04.042 [6] 刘法钰,张小英,陈佳跃,等. 螺旋管直流蒸汽发生器一、二次侧耦合传热特性分析[J]. 核动力工程,2020, 41(5): 24-29. [7] NARCISI V, GIANNETTI F, MARTELLI E, et al. Steam generator mock-up preliminary design suitable for Pb-Li technology demonstration and code assessment[J]. Fusion Engineering and Design, 2019, 146: 1126-1130. doi: 10.1016/j.fusengdes.2019.02.022 [8] ALEMBERTI A, CARLSSON J, MALAMBU E, et al. European lead fast reactor—ELSY[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2011, 241(9): 3470-3480. doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2011.03.029 [9] CHERNYSH A, IARMONOV M, MAKHOV K, et al. Experimental study of the characteristics of heat transfer in an HLMC cross-flow around tubes[J]. Journal of Nuclear Engineering and Radiation Science, 2015, 1(4): 041015. doi: 10.1115/1.4030365 [10] MORI Y, NAKAYAMA W. Study of forced convective heat transfer in curved pipes (2nd report, turbulent region)[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 1967, 10(1): 37-59. doi: 10.1016/0017-9310(67)90182-2 [11] CHEN J C. Correlation for boiling heat transfer to saturated fluids in convective flow[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Process Design and Development, 1966, 5(3): 322-329. [12] MANABE F, KOSUGI T, TSUCHIYA T, et al. Experimental studies of heat transfer performance with the No.2 50 MW steam generator in Japan: PNC-TN941 82-27[R]. Ibaraki-ken, Japan: Power Reactor and Nuclear Fuel Development Corporation, 1982. [13] RIVAS E, MUÑOZ-ANTÓN J. Dryout study of a helical coil once-through steam generator integrated in a thermal storage prototype[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2020, 170: 115013. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2020.115013 [14] ITŌ H. Friction factors for turbulent flow in curved pipes[J]. Journal of Basic Engineering, 1959, 81(2): 123-132. doi: 10.1115/1.4008390 [15] LOCKHART R W, MARTINELLI R C. Proposed correlation of data for isothermal two-phase, two-component flow in pipes[J]. Chemical Engineering Progress, 1949, 45(1): 39-48. [16] FAZIO C, SOBOLEV V P, AERTS A, et al. Handbook on lead-bismuth eutectic alloy and lead properties, materials compatibility, thermal-hydraulics and technologies: 2015 edition[R]. Issy-les-Moulineaux, France: Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development, 2015. [17] 毕勤成,陈听宽,田永生,等. HTGR蒸汽发生器螺旋管内壁温分布和传热恶化规律的研究[J]. 核动力工程,1998, 19(5): 408-412. [18] XIAO Y, HU Z X, CHEN S, et al. Experimental investigation and prediction of post-dryout heat transfer for steam-water flow in helical coils[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2018, 127: 515-525. [19] HEJZLAR P, BUONGIORNO J, MACDONALD P E, et al. Design strategy and constraints for medium-power lead-alloy–cooled actinide burners[J]. Nuclear Technology, 2004, 147(3): 321-343. doi: 10.13182/NT147-321 -






 下载:
下载: