Research on Intelligent Optimization Method for Core Flow Zoning of Lead-bismuth Reactor
-
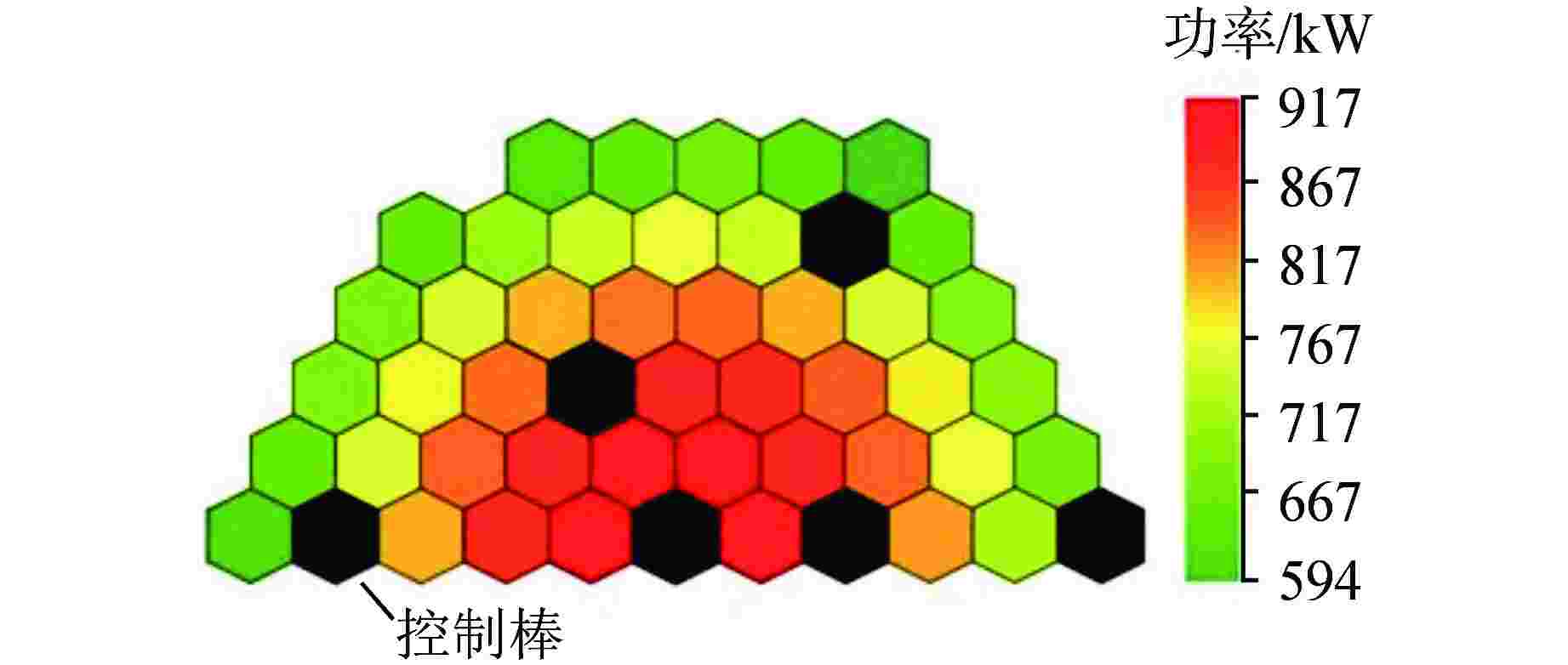
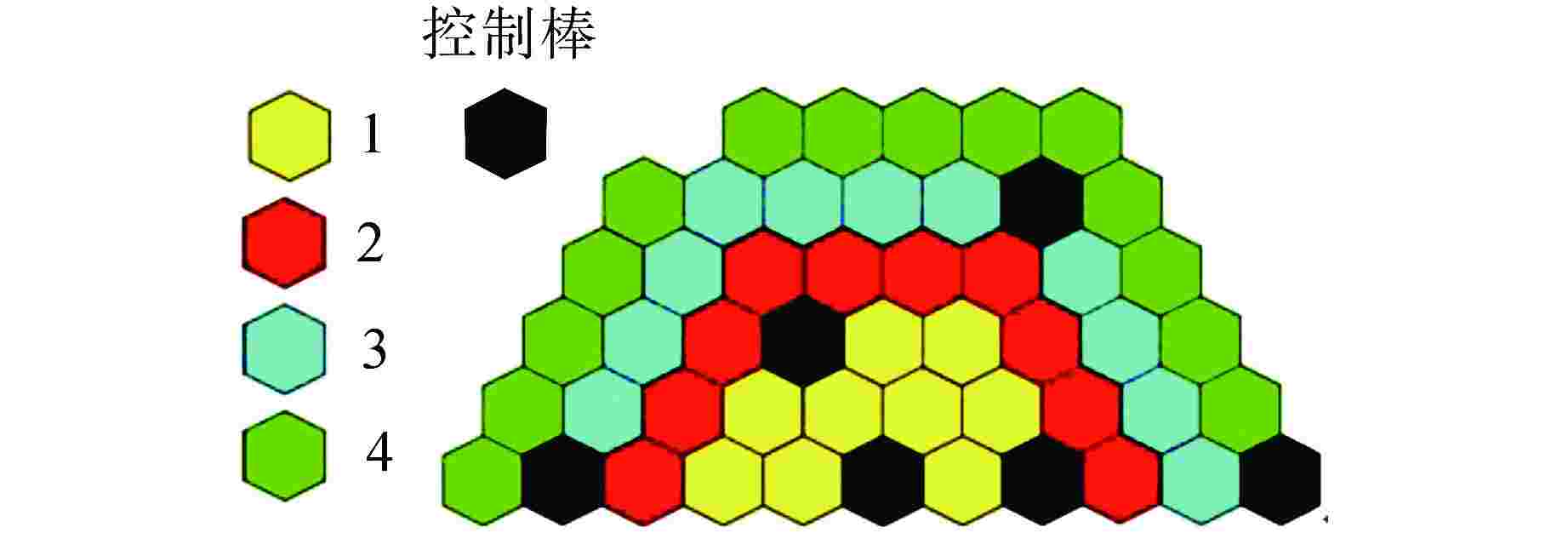
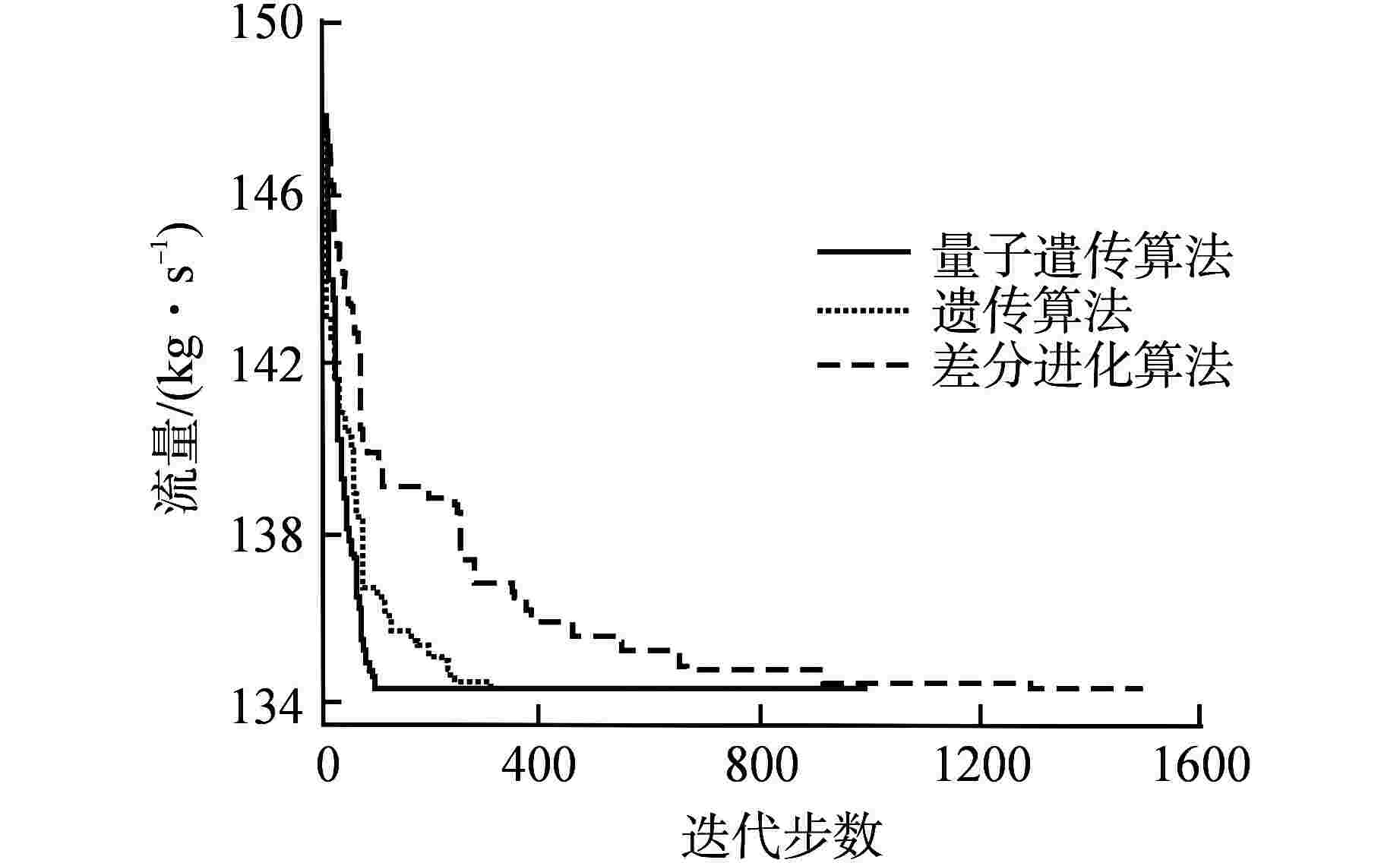
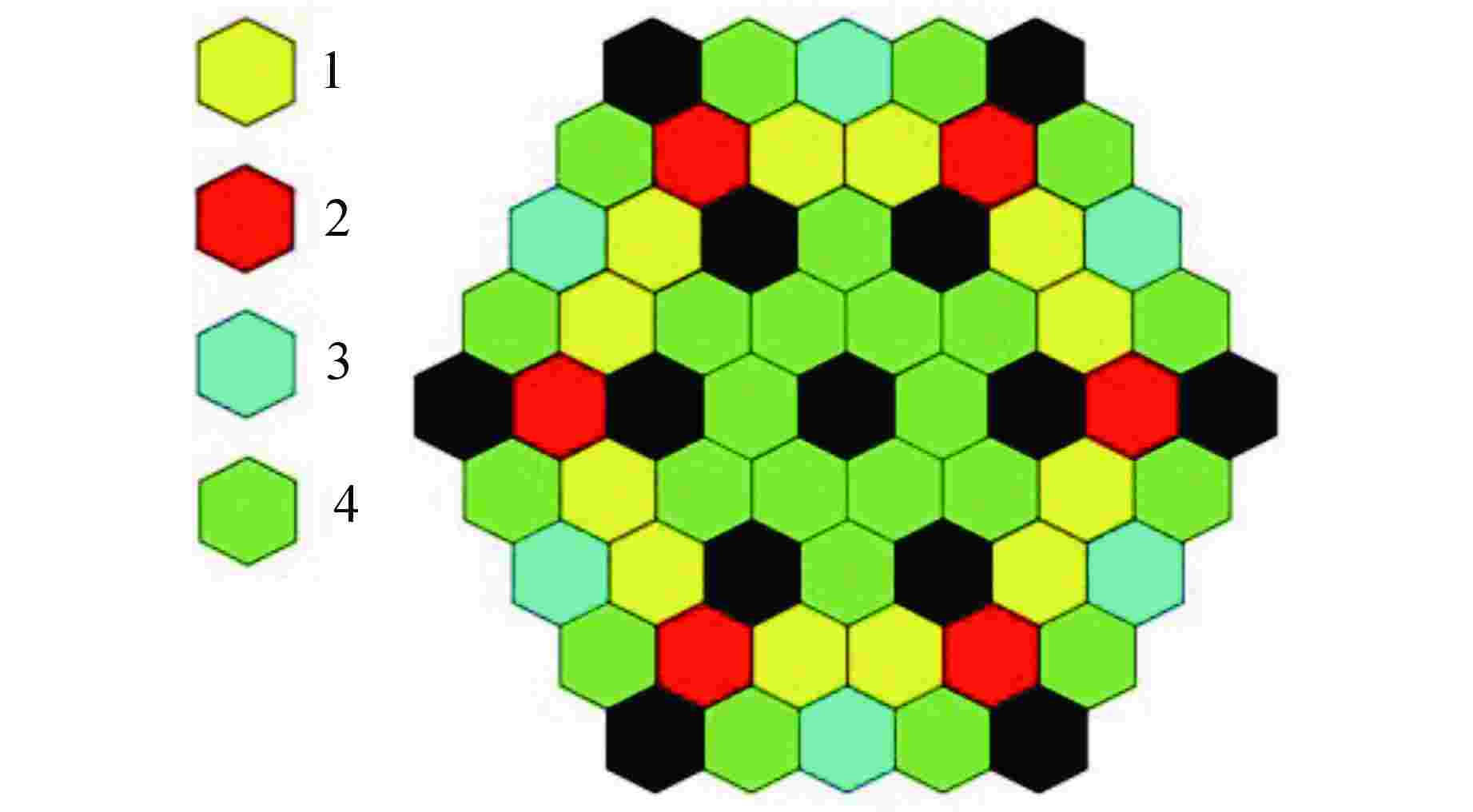
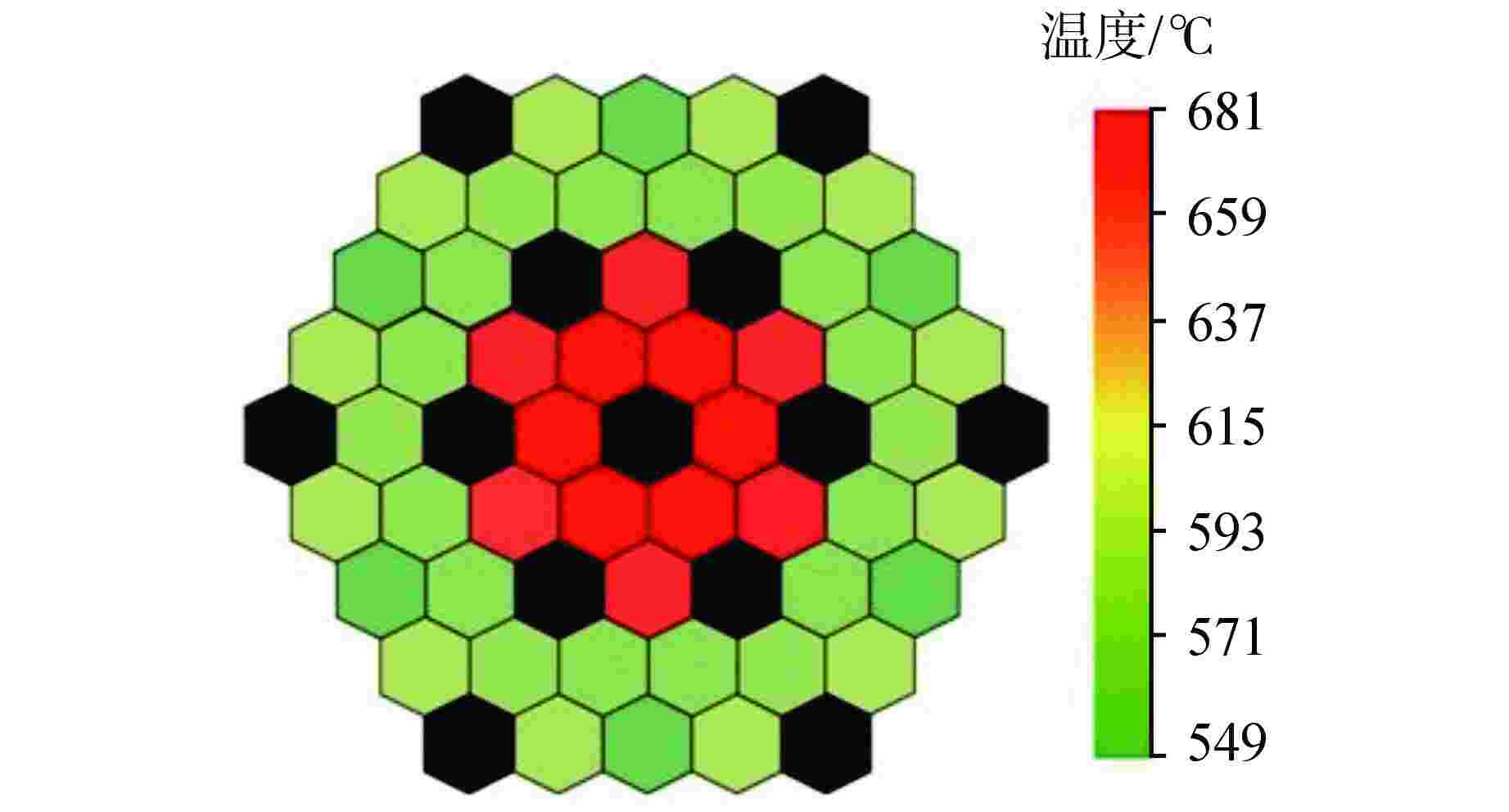
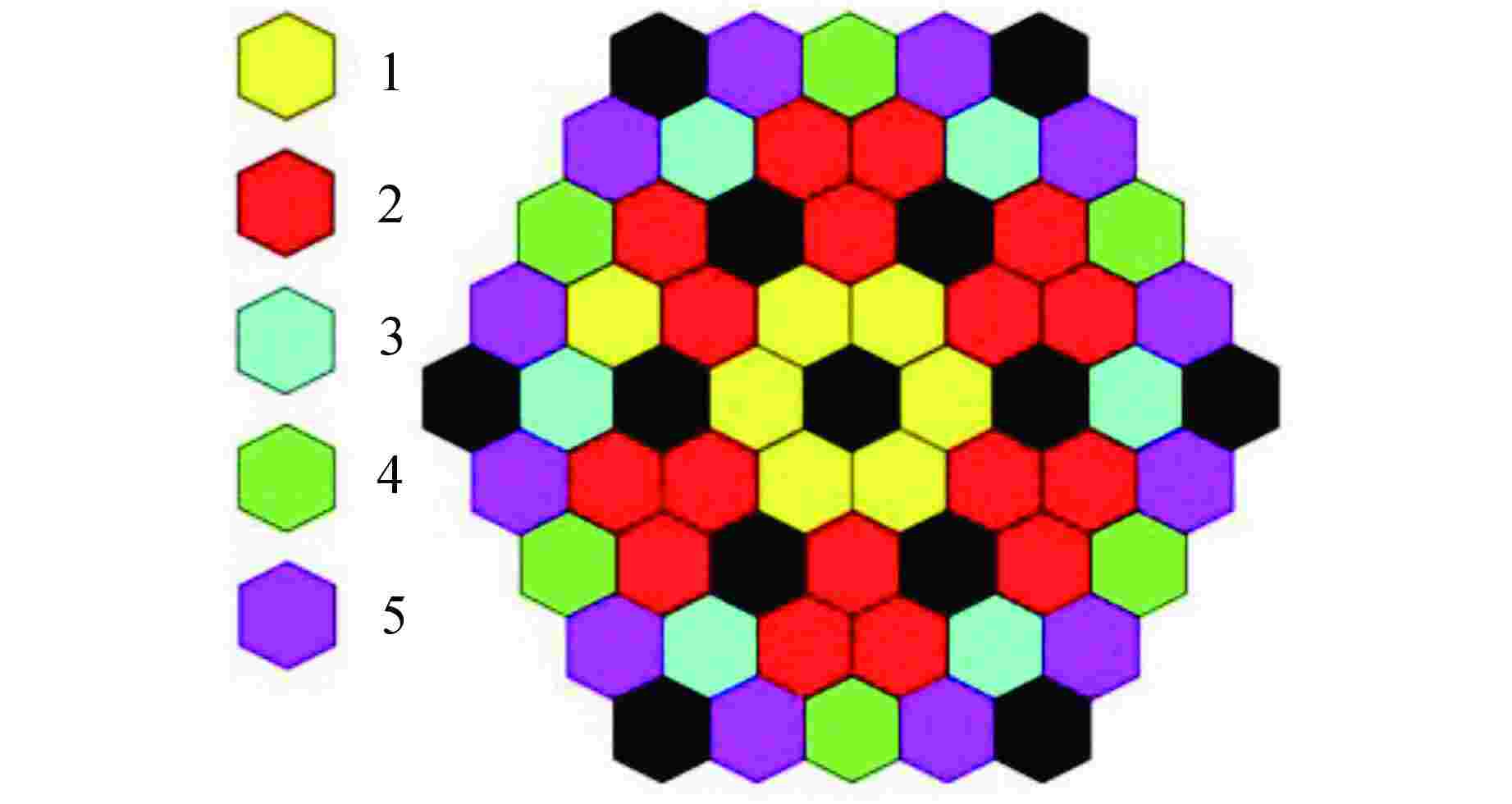
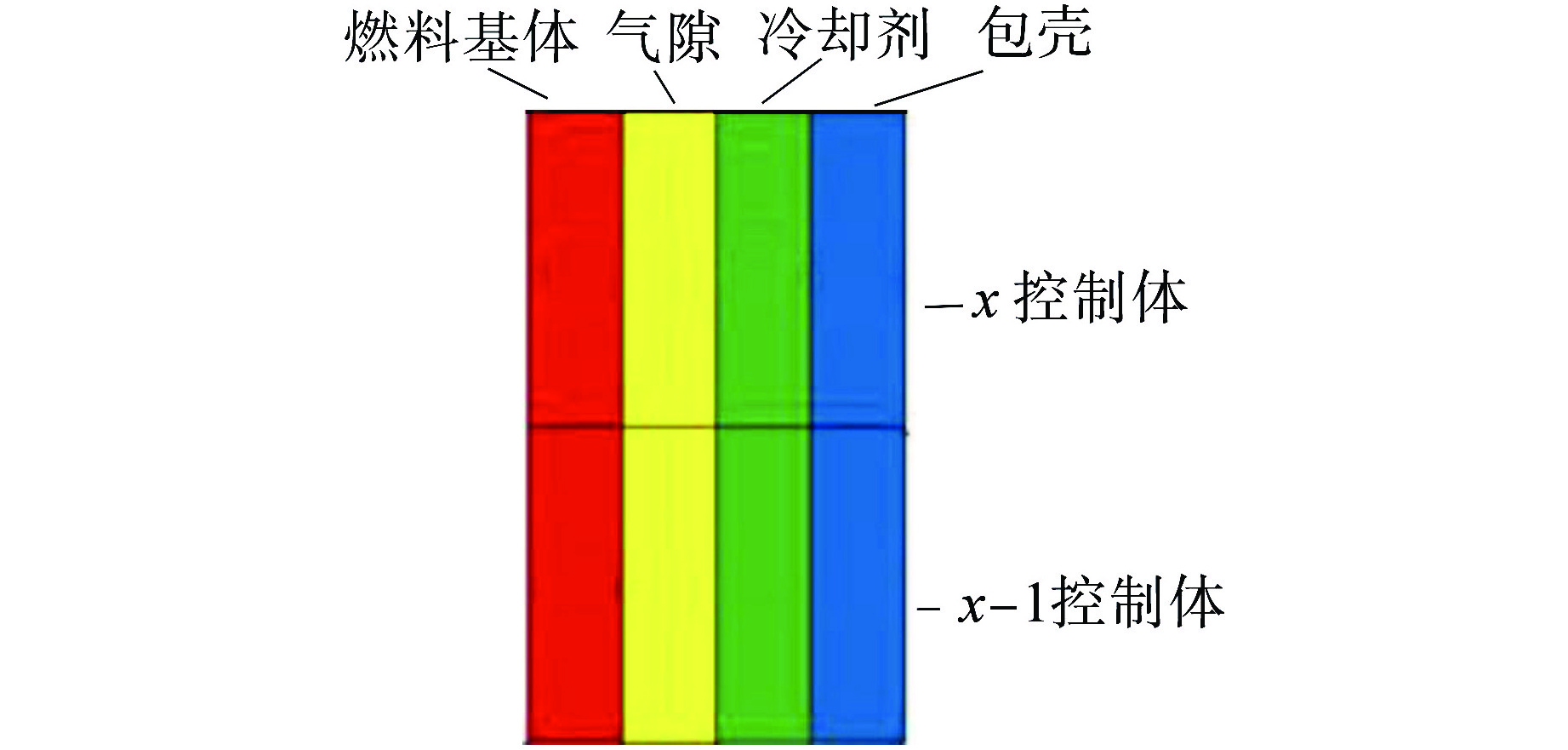
摘要: 堆芯流量分区是实现堆芯出口温度展平的重要手段,合理地分区可以提高反应堆的安全性和经济性。本文将人工智能优化算法与单通道模型进行耦合,构建了反应堆堆芯流量分区计算模型,分别开展遗传算法、差分进化算法、量子遗传算法在反应堆流量分区问题上的收敛性分析。根据所得最优算法,分别以寿期初功率分布、各燃料组件在整个寿期内最大功率为样本数据,基于小型长寿命自然循环铅铋快堆SPALLER -100开展两种不同流量分区方案对比分析。研究结果表明,在3种智能优化算法中,量子遗传算法在反应堆流量分区问题上收敛性最佳,能较快地搜索到最优分区结果;基于寿期初功率分布样本数据所得燃料组件最大出口温度超出反应堆热工安全限值,而基于各燃料组件在整个寿期内最大功率所得燃料组件最大出口温度降低了140 K,且始终保持在热工安全限值之下;SPALLER-100反应堆最佳分区数为5,再增加分区数对提高反应堆热工安全性能影响较小。Abstract: Core flow zoning is an important means to achieve core outlet temperature flattening. Reasonable zoning can improve the reactor safety and economy. In this paper, the artificial intelligence optimization algorithm is coupled with the single channel model, and the calculation model of reactor core flow zoning is constructed. The convergence analysis of genetic algorithm, differential evolution algorithm and quantum genetic algorithm in reactor flow zoning is carried out respectively. According to the obtained optimal algorithm, taking the power distribution at the beginning of life cycle as the sample data and the maximum power of each fuel assembly throughout the life cycle as the sample data, the comparative analysis of two different flow zoning schemes is carried out based on the small long-life natural circulation lead-bismuth fast reactor SPALLER -100. The results show that among the three intelligent optimization algorithms, the quantum genetic algorithm has the best convergence on the reactor flow zoning problem, and can quickly search the optimal zoning results; The maximum outlet temperature of the fuel assembly based on the power distribution at the beginning of the life cycle exceeds the thermal safety limit of the reactor, while the maximum outlet temperature of the fuel assembly based on the maximum power of each fuel assembly during the entire life by 140 K and remains below the thermal safety limit; The optimal number of zones for SPALLER-100 reactor is 5, and increasing the number of zones has little effect on improving the thermal safety performance of the reactor.
-
表 1 SPALLER热工水力设计限值
Table 1. Thermal Hydraulic Design Limits of SPALLER
参数名 参数限值 燃料最高温度/℃ 2300 包壳最高温度/℃ 550(正常工况)、650(事故工况) 冷却剂最高流速/ (m·s−1) 2 冷却剂最低温度/℃ 200 -
[1] NAGY K, KLOOSTERMAN J L, LATHOUWERS D, et al. The effects of core zoning on the graphite lifespan and breeding gain of a moderated molten salt reactor[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2012, 43: 19-25. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2011.12.025 [2] 周志伟,杨红义,李淞,等. CFR600堆芯热工水力设计程序初步研发[J]. 原子能科学技术,2018, 52(1): 56-63. [3] 李淞, 周志伟, 冯预恒, 等. 快堆堆芯内冷却剂流量分区方法: 中国, 109615110A[P]. 2019-04-12. [4] 王晓坤,王端,齐少璞,等. 基于遗传算法的钠冷快堆堆芯流量分区优化设计方法[J]. 原子能科学技术,2020, 54(9): 1660-1665. doi: 10.7538/yzk.2020.youxian.0093 [5] 张顶学. 遗传算法与粒子群算法的改进及应用[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学: 2007. [6] 张庆科. 粒子群优化算法及差分进行算法研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2017. [7] 杨若黎,顾基发. 一种高效的模拟退火全局优化算法[J]. 系统工程理论与实践,1997, 17(5): 30-36. [8] 盖佳妮. 量子遗传算法的改进与研究[D]. 锦州: 渤海大学, 2017. [9] 马莹,王怀晓,刘贺,等. 一种新的自适应量子遗传算法研究[J]. 计算机工程与应用,2018, 54(20): 99-103. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1803-0156 [10] 刘紫静,赵鹏程,张斌,等. 超长寿命小型自然循环铅铋快堆 堆芯概念设计研究[J]. 原子能科学技术,2020, 54(7): 1254-1265. doi: 10.7538/yzk.2019.youxian.0720 -






 下载:
下载: