Prediction of Vertical-Downward Two-Phase Flow Pattern based on PCA-GA-SVM
-
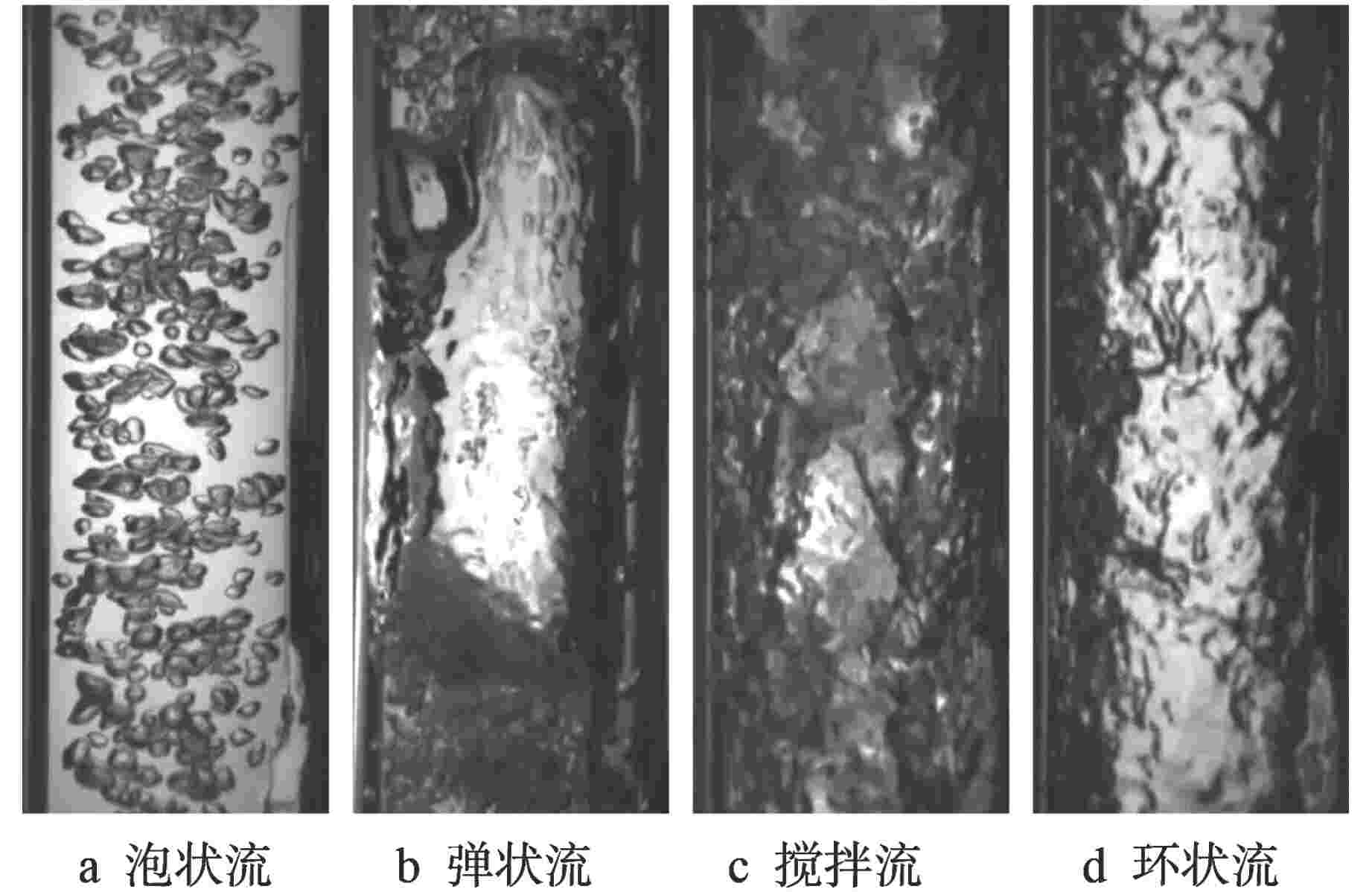
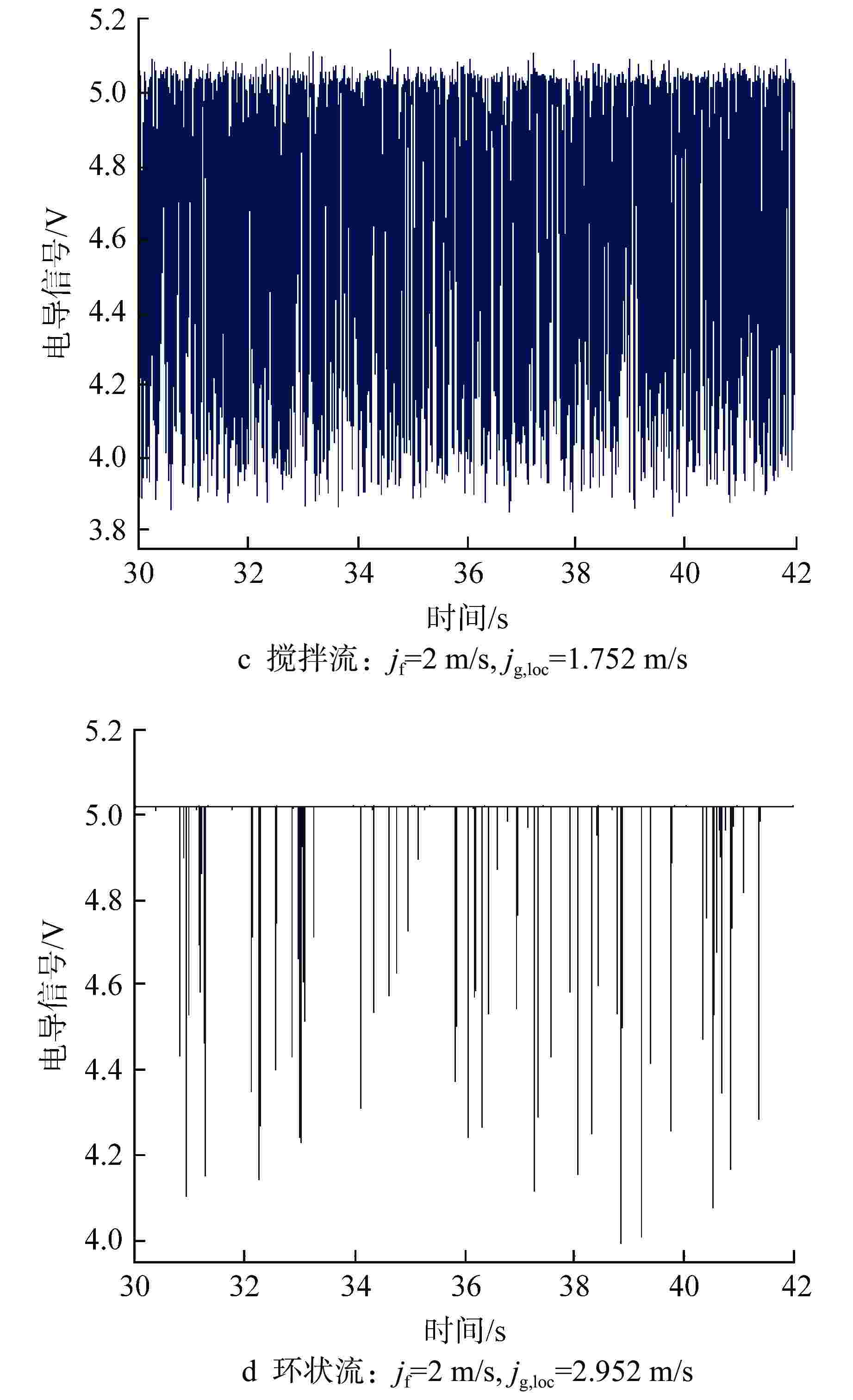
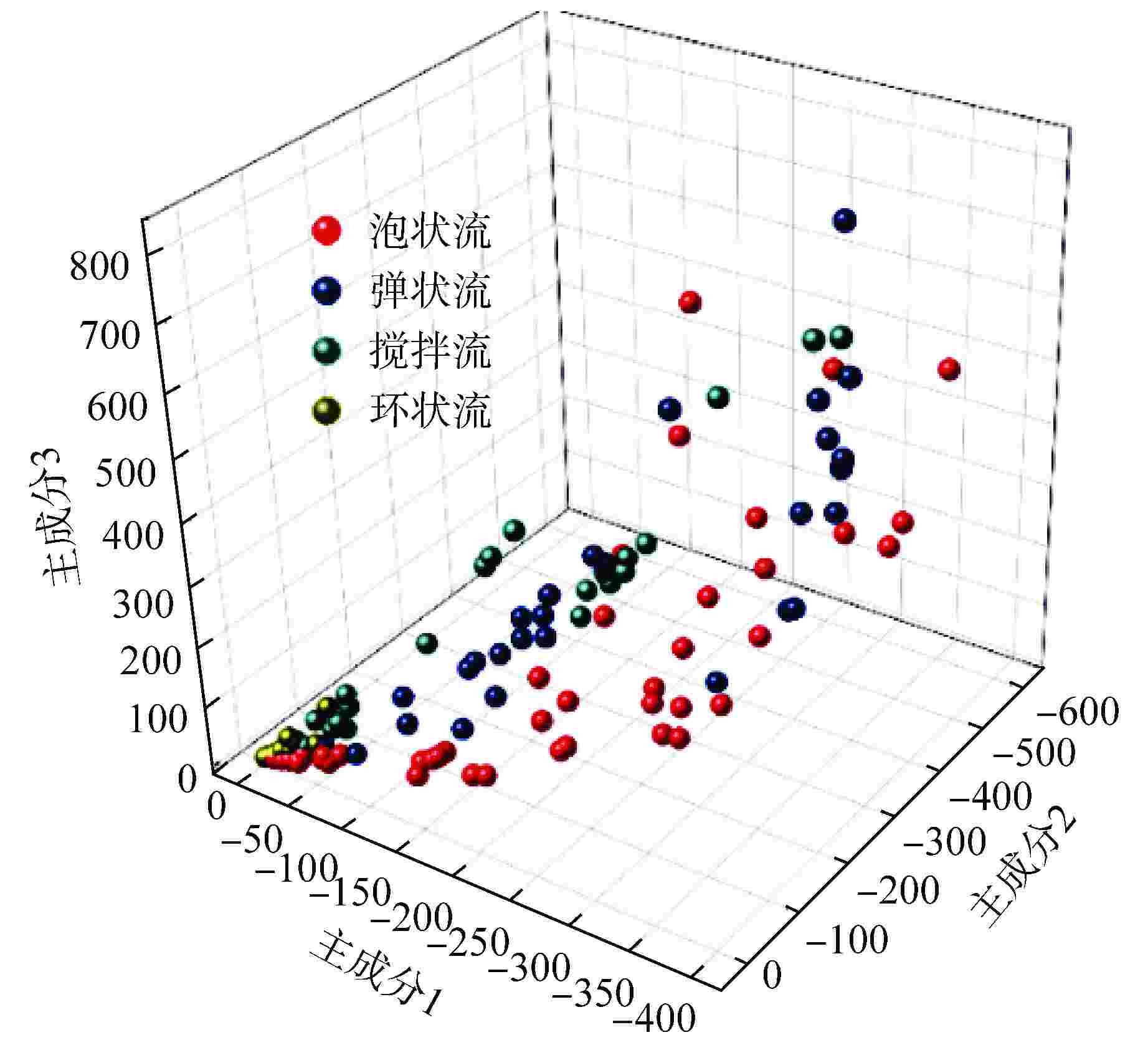
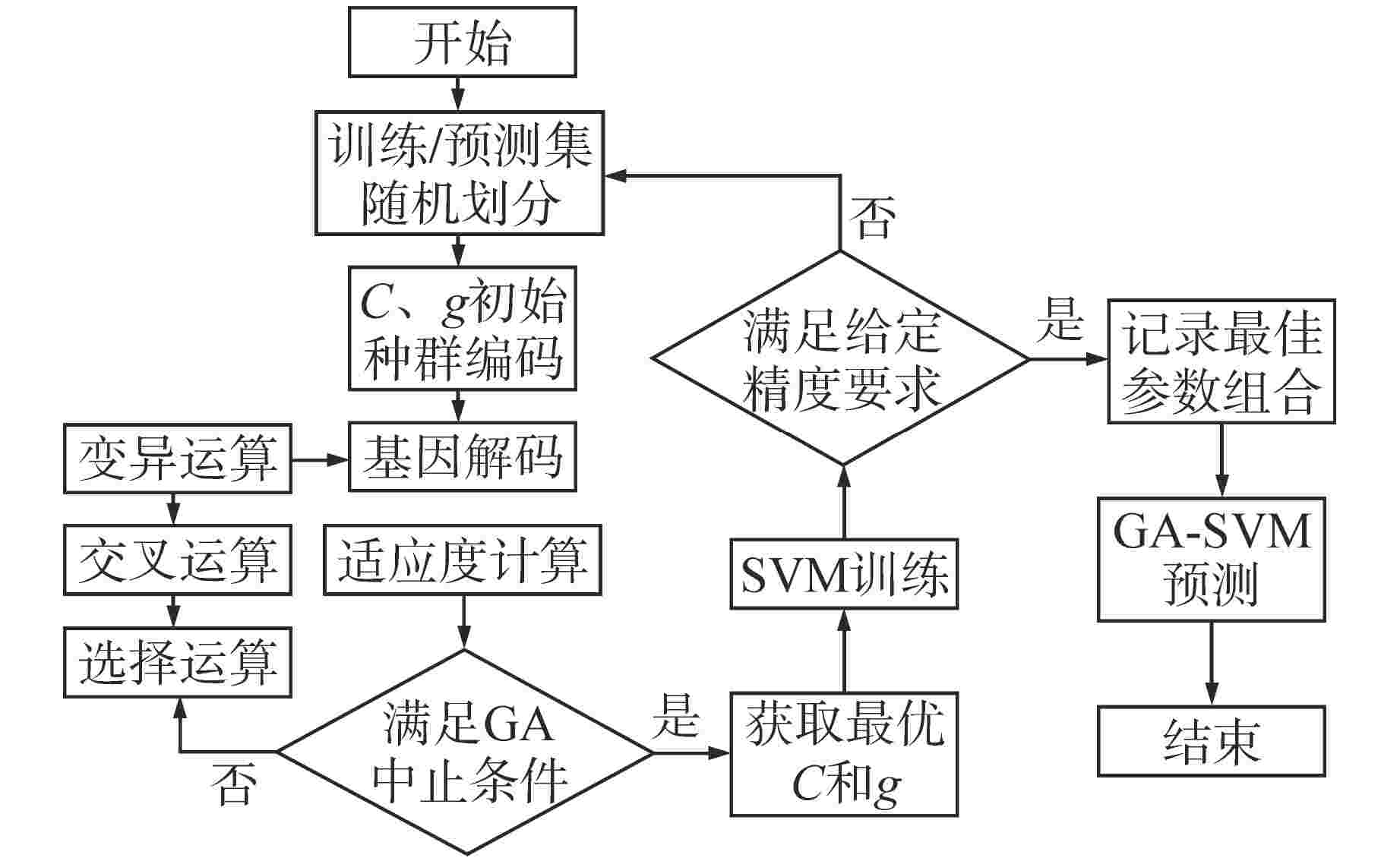
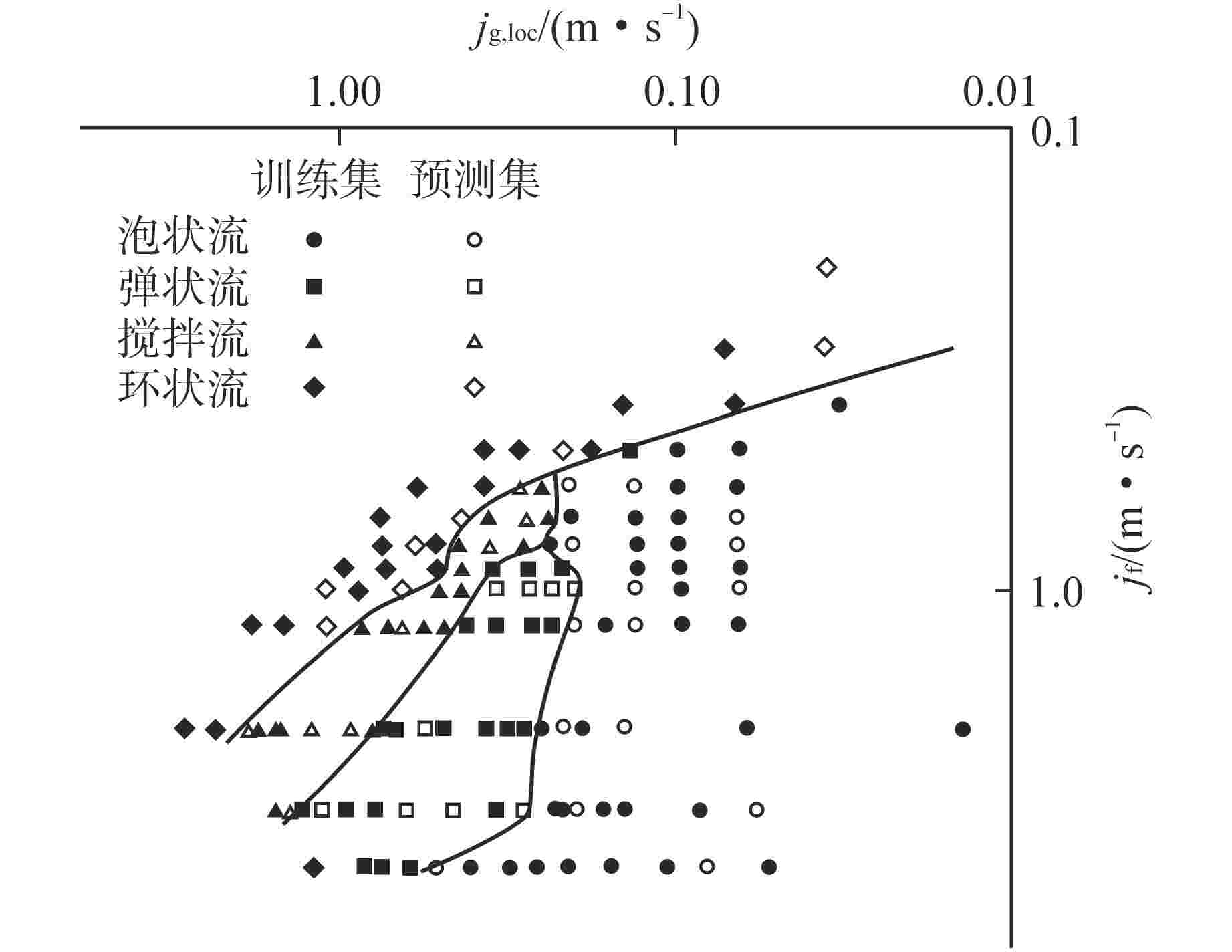
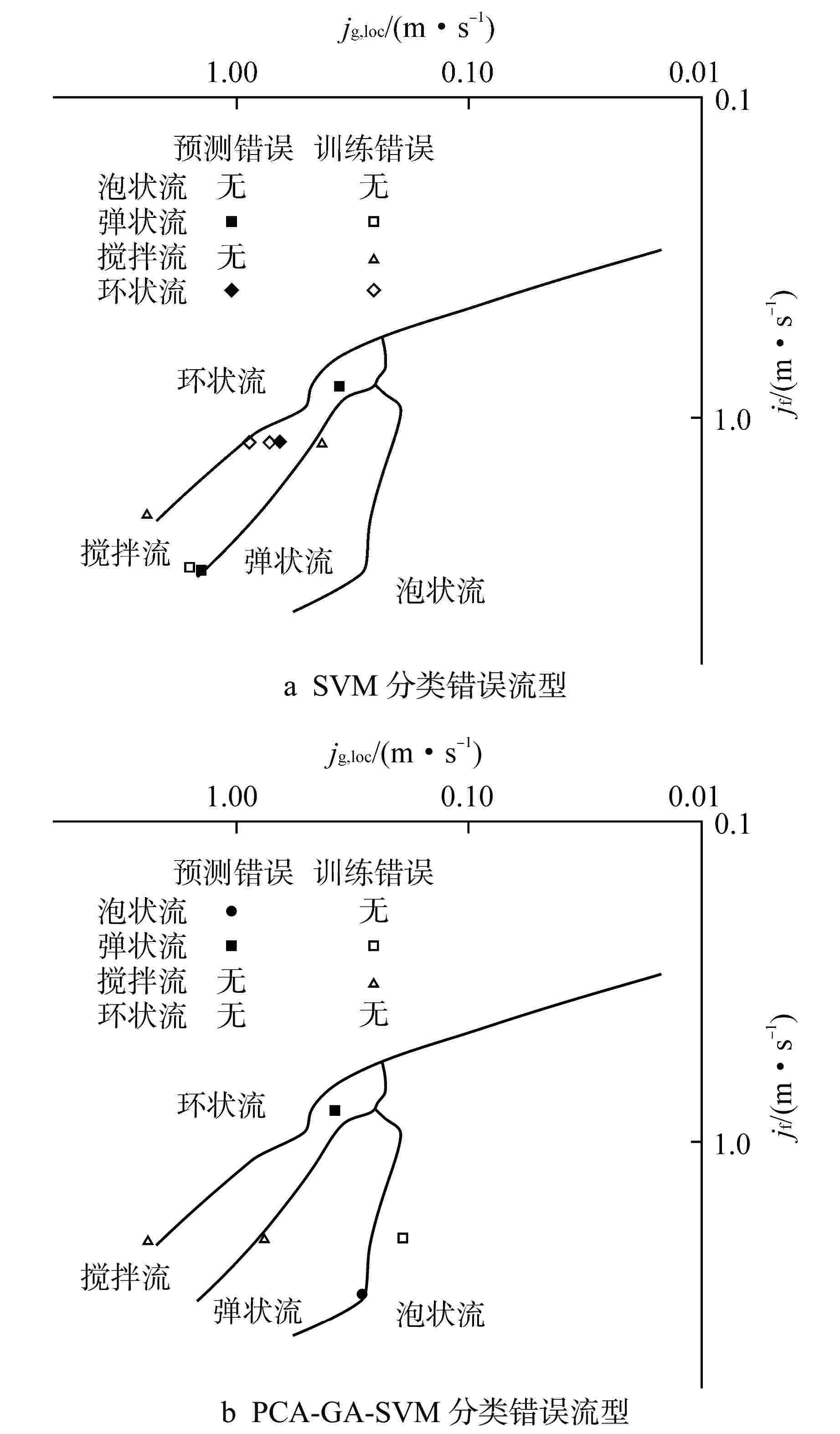
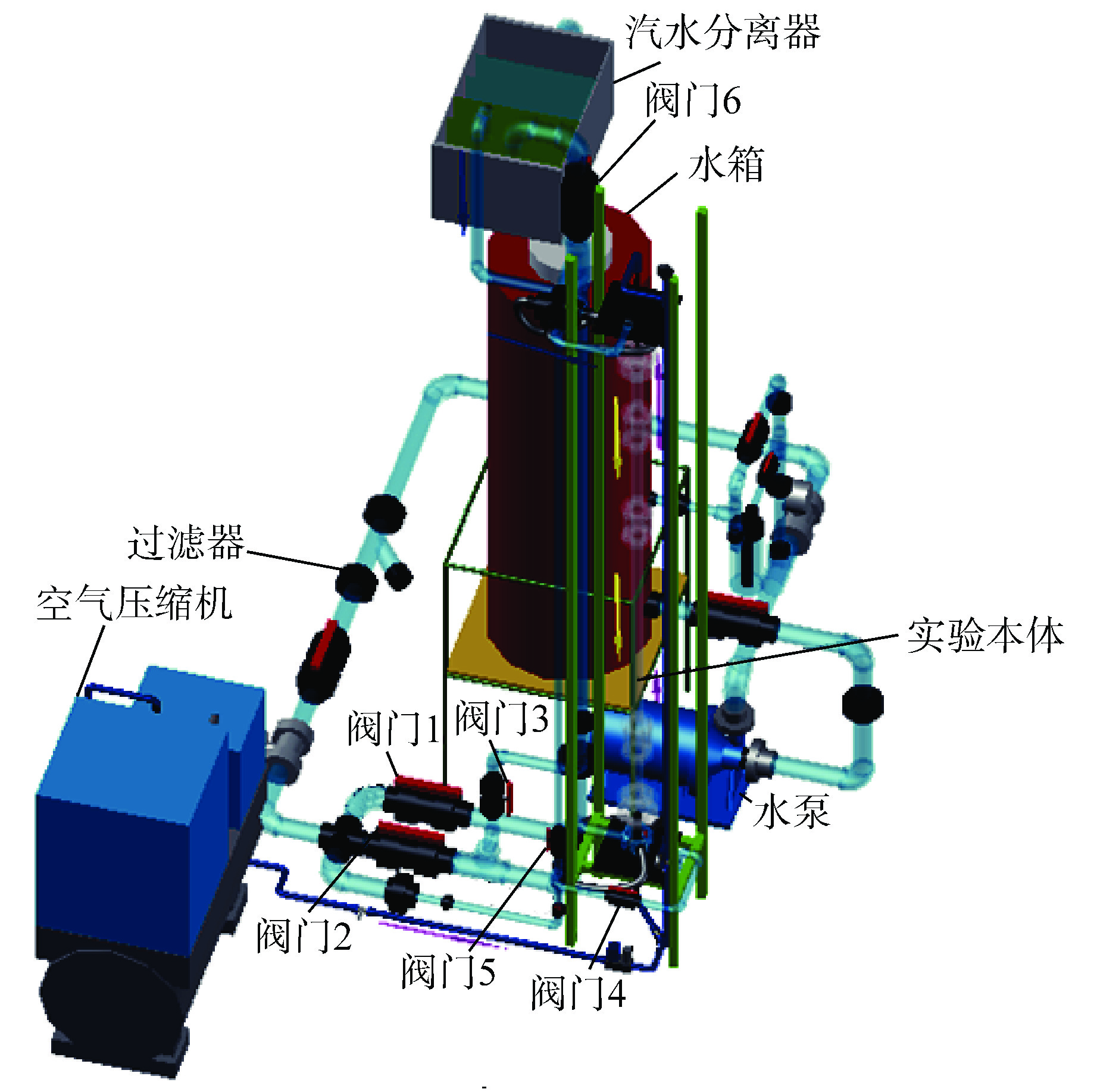
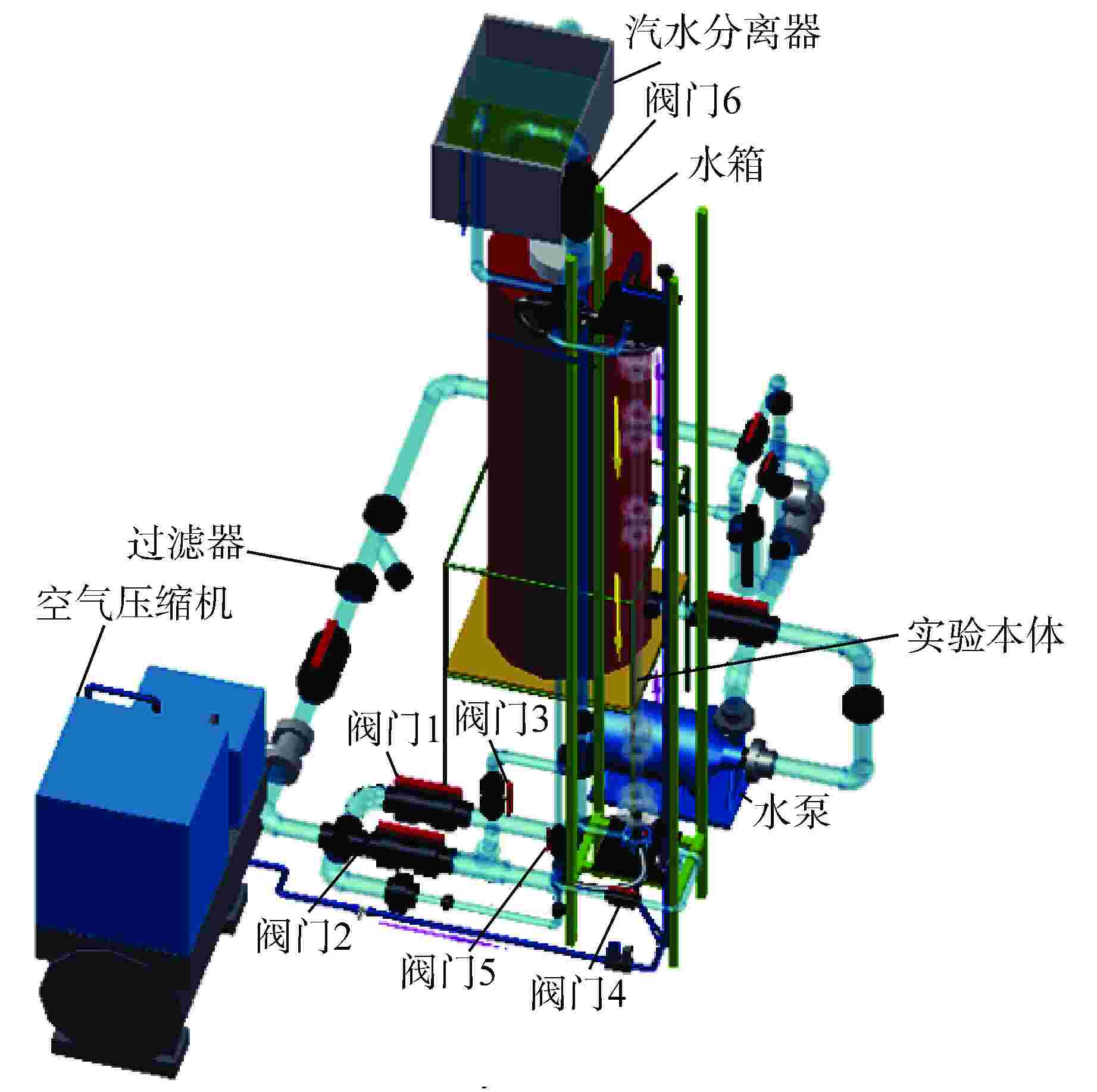
摘要: 为提高小样本条件下的流型识别精度和时效性,提出了一种融合小波包分解(WPD)、主元分析(PCA)、遗传算法(GA)和支持向量机(SVM)的优化识别模型,并成功应用在竖直下降两相流流型辨识工作中。利用WPD对非平稳电导波动信号进行分解、重构,提取小波包能量构造特征向量;通过PCA对特征向量进行降维,降低特征输入的复杂性;同时采取GA全局迭代寻优的方式确定SVM的关键参数惩罚因子(C)和核函数参数(g)。对PCA-GA-SVM识别效果进行验证后与SVM、PCA-SVM、GA-SVM网络进行对比。结果表明,经过PCA和GA优化后的SVM网络在流型识别精度和时效性方面均提升显著,对泡状流、弹状流、搅拌流和环状流的总体预测精度达到了94.87%,耗时仅3.95 s,可满足在线识别需求。Abstract: In order to improve the accuracy and timeliness of flow pattern identification under the condition of small samples, an optimized identification model integrating wavelet packet decomposition (WPD), principal component analysis (PCA), genetic algorithm (GA) and support vector machine (SVM) is proposed and successfully applied to the flow pattern recognition of vertical-downward two-phase flow. WPD is used to decompose and reconstruct the non-stationary conductivity fluctuation signal, extract the wavelet packet energy and construct the feature vector; The dimension of feature vector is reduced by PCA to reduce the complexity of feature input; At the same time, the key parameters penalty factor (C) and kernel function parameter (g) of SVM are determined by GA global iterative optimization. After verifying the identification effect of PCA-GA-SVM, it is compared with SVM, PCA-SVM and GA-SVM networks. The results show that the SVM network optimized by PCA and GA is significantly improved in terms of flow pattern identification accuracy and timeliness. The overall prediction accuracy of bubble flow, slug flow, stirred flow and annular flow reaches 94.87%, and the time consumed is only 3.95 s, which can meet the needs of on-line identification.
-
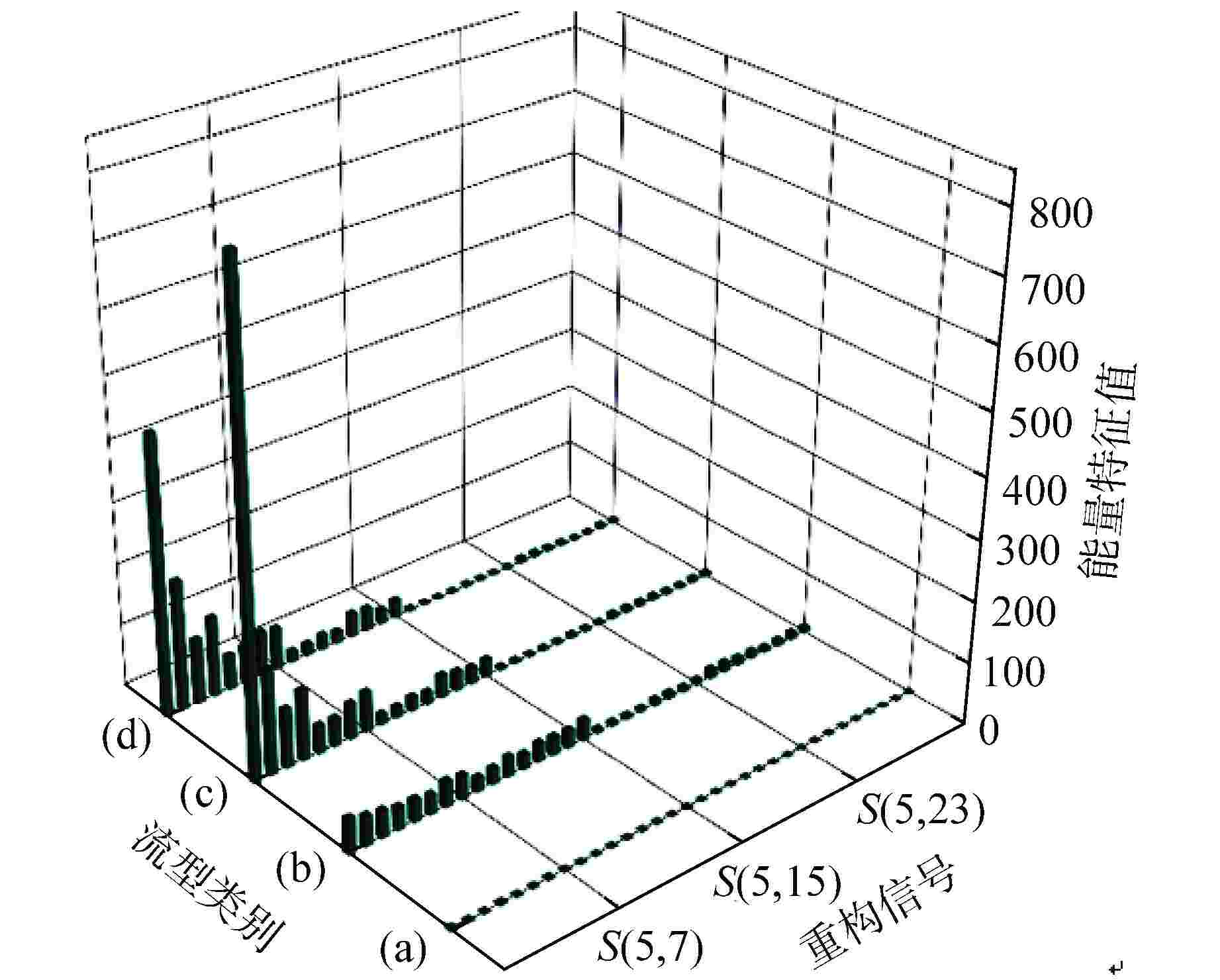
表 1 最底层各节点重构信号所处频率范围
Table 1. The Frequency Range of Reconstructed Signals of Each Node at the Lowest Layer
信号 频率范围/Hz S(5,0) 0~15.625 S(5,1) 15.625~31.25 S(5,2) 31.25~46.875 S(5,3) 46.875~62.5 S(5,4) 62.5~78.125 S(5,5) 78.125~93.75 S(5,6) 93.75~109.375 S(5,7) 109.375~125 S(5,8) 125~140.625 $\cdots $ $\cdots $ S(5, 31) 484.375~500 表 2 4类模型流型分类效果对比
Table 2. Comparison of Flow Pattern Classification Results Using Four Types of Models
分类模型 训练精度/% 预测精度/% 耗时/s SVM 94.62 92.30 33.15 GA-SVM 95.69 92.30 5.42 PCA-SVM 96.77 94.87 13.96 PCA-GA-SVM 96.77 94.87 3.95 -
[1] 周立加,杨瑞昌,张彬,等. 垂直上升管内气液两相流流型鉴别研究[J]. 工程热物理学报,2000, 21(3): 358-362. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-231X.2000.03.024 [2] ARCHIBONG-ESO A, BABA Y, NSEFIK-EYO E, et al. A study of two-phase air-water flow in horizontal and inclined pipelines[J]. International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, 2016, 7(12): 296-303. [3] BHAGWAT S M, GHAJAR A J. Similarities and differences in the flow patterns and void fraction in vertical upward and downward two phase flow[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2012, 39: 213-227. doi: 10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2012.01.026 [4] MILAN M, BORHANI N, THOME J R. Adiabatic vertical downward air–water flow pattern map: Influence of inlet device, flow development length and hysteresis effects[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2013, 56: 126-137. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmultiphaseflow.2013.06.003 [5] QIAO S X, MENA D, KIM S. Inlet effects on vertical-downward air–water two-phase flow[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2017, 312: 375-388. doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2016.04.033 [6] LI Z X, WANG G Y, YOUSAF M, et al. Flow structure and flow regime transitions of downward two-phase flow in large diameter pipes[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2018, 118: 812-822. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2017.11.037 [7] 薛玉卿,李会雄,姚超,等. 垂直向下管内两相流泡状-弹状流型转换研究[J]. 应用力学学报,2017, 34(4): 603-609. [8] TRAFALIS T B, OLADUNNI O, PAPAVASSILIOU D V. Two-phase flow regime identification with a multiclassification support vector machine (SVM) model[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2005, 44(12): 4414-4426. [9] 孙斌,周云龙. 基于支持向量机和小波包能量特征的气液两相流流型识别方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2005, 25(17): 93-99. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-8013.2005.17.019 [10] 孙斌,周云龙,赵鹏,等. 基于奇异值分解和最小二乘支持向量机的气-液两相流流型识别方法[J]. 核动力工程,2007, 28(6): 62-66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0926.2007.06.015 [11] ZHANG Y C, AZMAN A N, XU K W, et al. Two-phase flow regime identification based on the liquid-phase velocity information and machine learning[J]. Experiments in Fluids, 2020, 61(10): 212. doi: 10.1007/s00348-020-03046-x [12] KIM S, FU X Y, WANG X, et al. Development of the miniaturized four-sensor conductivity probe and the signal processing scheme[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2000, 43(22): 4101-4118. doi: 10.1016/S0017-9310(00)00046-6 [13] 乔守旭,钟文义,谭思超,等. 竖直下降两相流相界面结构输运特性[J]. 原子能科学技术,2021, 55(2): 229-236. doi: 10.7538/yzk.2020.youxian.0166 [14] 唐川林,汪志能,胡东,等. 基于小波包与Elman神经网络的气力提升装置流型识别技术研究[J]. 振动与冲击,2016, 35(15): 149-153. [15] 王奉涛,马孝江,邹岩崑,等. 基于小波包分解的频带局部能量特征提取方法[J]. 农业机械学报,2004, 35(5): 177-180. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1298.2004.05.044 [16] JOLLIFFE I T, CADIMA J. Principal component analysis: a review and recent developments[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A:Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2016, 374(2016): 20150202. [17] 丁世飞,齐丙娟,谭红艳. 支持向量机理论与算法研究综述[J]. 电子科技大学学报,2011, 40(1): 2-10. [18] HSU C W, LIN C J. A comparison of methods for multiclass support vector machines[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2002, 13(2): 415-425. doi: 10.1109/72.991427 [19] 韩华,谷波,康嘉. 基于遗传算法和支持矢量机参数优化的制冷机组故障检测与诊断研究[J]. 机械工程学报,2011, 47(16): 120-126. -





 下载:
下载: