Research on Optimization of Post-72h Procedures for Passive Nuclear Power Plant
-
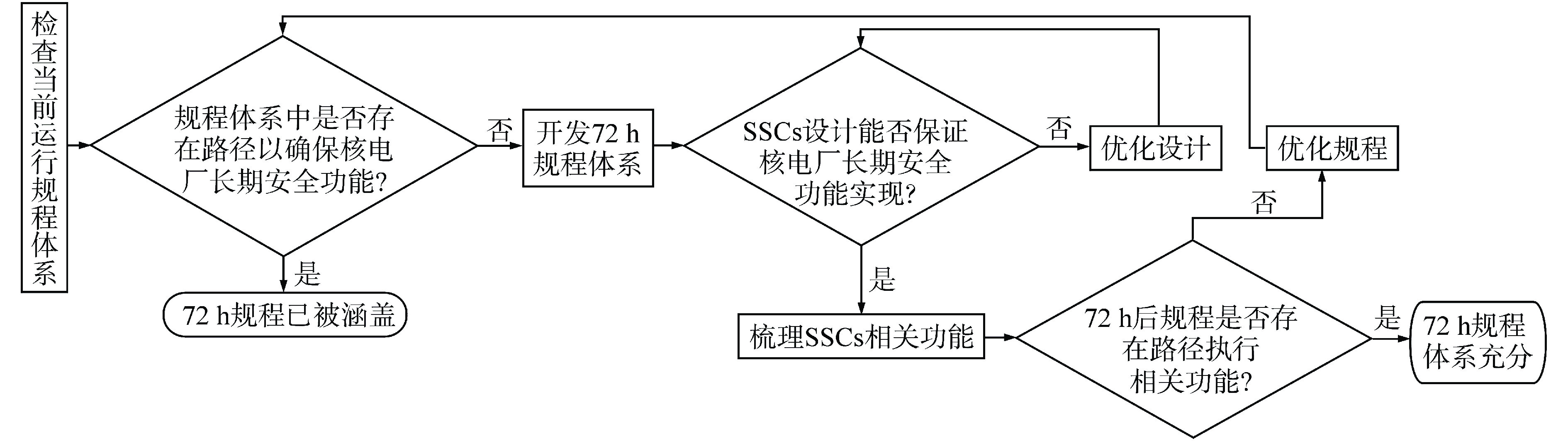
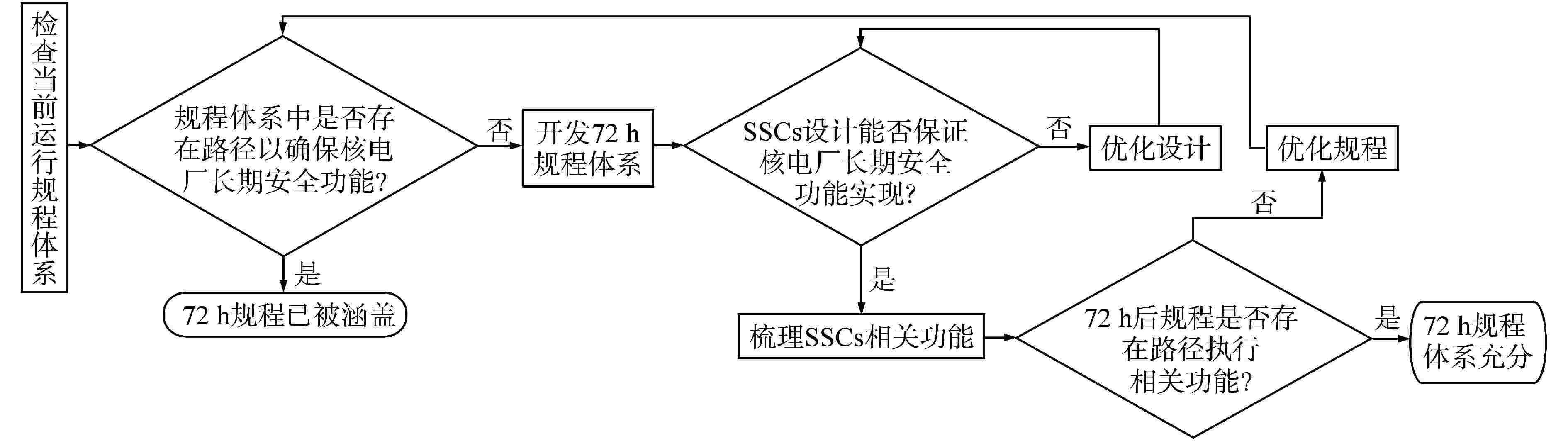
摘要: 事故72 h后规程是非能动核电厂特有的一类规程。为了评价非能动核电厂事故72 h后规程的必要性和充分性,并对其薄弱环节进行优化改进,本研究对示范项目非能动核电厂设计基准和运行规程体系的总体逻辑进行了分析,并基于事故72 h后规程的内容和结构,提出了评价事故72 h后规程必要性和充分性的通用方法,运用规程执行逻辑框图识别了规程执行过程中可能存在的风险项,并针对示范项目的规程提出了优化建议。分析结果表明,事故72 h后规程对于非能动核电厂的安全运行是充分必要的;其表达方式与规程体系结构相关;明确规程操作路径优先级、减少规程跳转能够提高规程执行效率。相关优化建议可为非能动核电厂事故后长期安全运行提供技术参考。Abstract: Post-72h procedures are special procedures for passive nuclear power plants. In order to evaluate the necessity and sufficiency of post-72 h procedures for passive nuclear power plants, and optimize and improve their weak links, this study analyzes the overall logic of the design basis and operating procedure system for passive nuclear power plants in demonstration projects. Based on the content and structure of the post-72 h procedures, this study proposes a general method for evaluating the necessity and sufficiency of the post-72 h procedures, the possible risk items in the process of procedure implementation are identified by using the logical block diagram of procedure implementation, and some optimization suggestions are put forward according to the rules of the demonstration project. The analysis results show that the post-72 h procedures are sufficient and necessary for the safe operation of passive nuclear power plants; their expressions are related to the procedure architecture; Clarifying the priority of procedure operation path and reducing procedure jump can improve the efficiency of procedure implementation. The relevant optimization suggestions can provide technical reference for the long-term safe operation of passive nuclear power plants after accidents.
-
Key words:
- Passive nuclear power plant /
- Operations /
- Post-72 h procedures
-
表 1 事故 72 h 后规程架构
Table 1. Framework of Post-72h Procedures
序号 规程简码 规程名称 规程内容 对应功能项目 1 ECS-720 辅助柴油
发电机运行附件1(1号辅助柴油发电机启动)附件2(2号辅助柴油发电机启动)
附件3(1号辅助柴油发电机停机)附件4(2号辅助柴油发电机停机)长期电源 2 VBS-720 主控室可居留 附件1(投运辅助风机)
附件2(停运辅助风机)主控室长期可居留 3 PCS-720 非能动安全壳
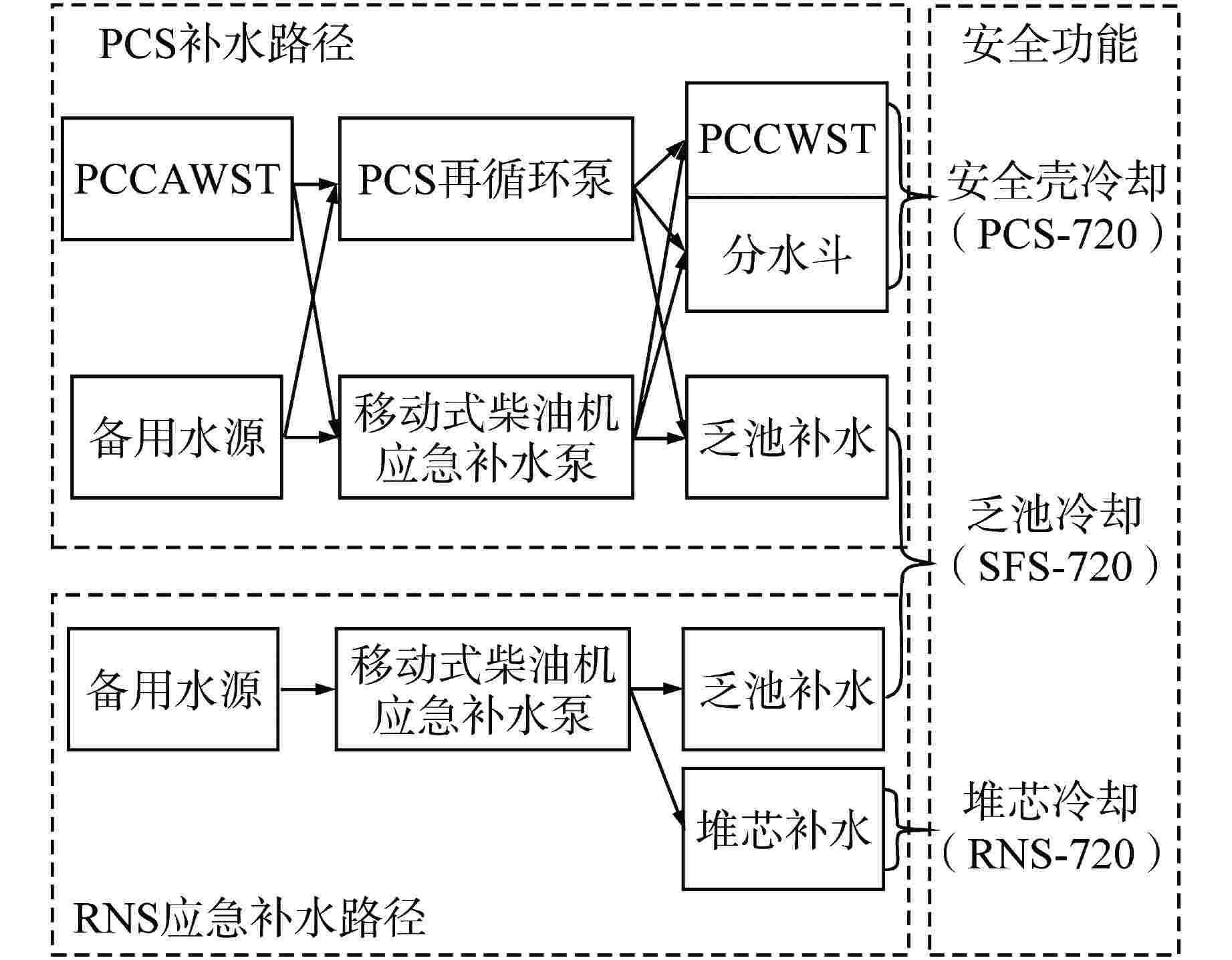
冷却附件1(通过再循环泵从PCCAWST取水向PCCWST、乏池和分水斗补水)附件2(通过再循环泵从备用水源取水向PCCWST、乏池和分水斗补水)附件3(通过移动泵从PCCAWST取水向PCCWST、乏池和分水斗补水)附件4(通过移动泵从备用水源取水向PCCWST、乏池和分水斗补水)附件5 [ 应急补水措施(PCS失效)]附件6 [ 应急补水措施(PCS未失效)] 安全壳长期冷却 4 RNS-720 向安全壳补水 附件1(从临时水源向安全壳内补水) 堆芯长期冷却 5 SFS-720 乏池冷却 附件1(从PCCWST通过重力向乏池补水)
附件2(从PCCAWST或备用水源向乏池补水)附件3(应急补水措施)乏燃料长期冷却 ECS——主交流电源系统;VBS——核岛非放射性通风系统;PCCWST——非能动安全壳冷却水箱;PCCAWST——非能动安全壳冷却辅助水箱;PCS——非能动安全壳冷却系统;RNS——正常余热排出系统;SFS——乏燃料池冷却系统 表 2 安全设计基准
Table 2. Design Basis for Safe Operation
项目 操纵员72 h不干预的安全设计基准 72 h后SSCs运行策略 事故72 h
后规程厂内电源 发生DBA(包括失去全部交流电)时,IDS系统的4个独立1E 级220 V 直流蓄电池系统可带预期载荷,保证72 h内实现并维持安全停堆 运行辅助柴油发电机、移动电源(低压移动式柴油发电机、中压移动式柴油发电机) ECS-720 主控室可居留 失去VBS 系统后72 h内,VES 系统为主控制室、仪表间和直流设备间提供非能动热阱(由房间顶板和墙体混凝土蓄热体构成)以限制温升,应急压缩空气储存罐为主控室人员提供呼吸级空气 运行辅助风机引入室外新风 VBS-720 安全壳冷却 发生DBA后的72 h内,PCS系统利用非能动方式排出安全壳内热量(PCCWST重力补水、安全壳地坑再循环) 利用移动泵/再循环泵从PCCAWST/备用水源取水向PCCWST/分水斗补水 PCS-720 堆芯冷却 PXS系统在没有操作员干预和没有任何厂内厂外电源的情况下,能够在事故后维持72 h的安全停堆工况 利用移动泵从备用水源取水向DVI补水 RNS-720 乏燃料冷却 乏池水量和其他安全有关补水(清洗池、装料池、PCCWST)能以非能动方式维持72 h的冷却 连接厂内或厂外水源至乏池 SFS-720 IDS——1E 级直流和UPS 系统;VES——主控制室应急可居留系统;PXS——非能动堆芯冷却系统; DVI——堆芯直接注射管线 表 3 规程执行检查表示例
Table 3. Example of Procedure Implementation Checklist
可用水源 可用补水泵 可用补
水路径规程操作 PCCAWST □ PCS再循环泵 □ PCCWST □ 执行PCS-720附件1第4.3节 分水斗 □ 执行PCS-720附件1第4.4节 移动式柴油机应急补水泵 □ PCCWST □ 执行PCS-720附件3第4.4节 分水斗 □ 执行PCS-720附件3第4.5节 备用水源 □ PCS再循环泵 □ PCCWST □ 执行PCS-720附件2第4.4节 分水斗 □ 执行PCS-720附件2第4.5节 移动式柴油机应急补水泵 □ PCCWST □ 执行PCS-720附件4第4.4节 分水斗 □ 执行PCS-720附件4第4.5节 □——操纵员检查确认框,确认该SSCs可用时打钩 -
[1] 国家核安全局. 核动力厂运行安全规定: HAF 103—2004[S]. 北京: 国家核安全局, 2004: 1-25. [2] 叶道权. 三门核电AP1000运行规程特点及管理浅析[C]//中国核学会. 中国核科学技术进展报告(第四卷)——中国核学会2015年学术年会论文集第3册(核能动力分卷(下)). 北京: 中囯原子能出版社, 2015: 135-139. [3] 国家核安全局. 核动力厂设计安全规定: HAF 102—2016[S]. 北京: 国家核安全局, 2016: 1-62. [4] 施锦. 核电厂运行规程整定值研究[J]. 核动力工程,2017, 38(2): 134-139. [5] 阎昌琪, 曹夏昕. 核反应堆安全传热[M]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学出版社, 2010: 79. [6] Institute of Nuclear Power Operations. Human performance tools for workers: INPO 06-002[R]. Atlanta: INPO, 2006. -





 下载:
下载: