Experimental Study on Two-phase Natural Circulation Characteristics under Low-voltage and Low-power Conditions
-
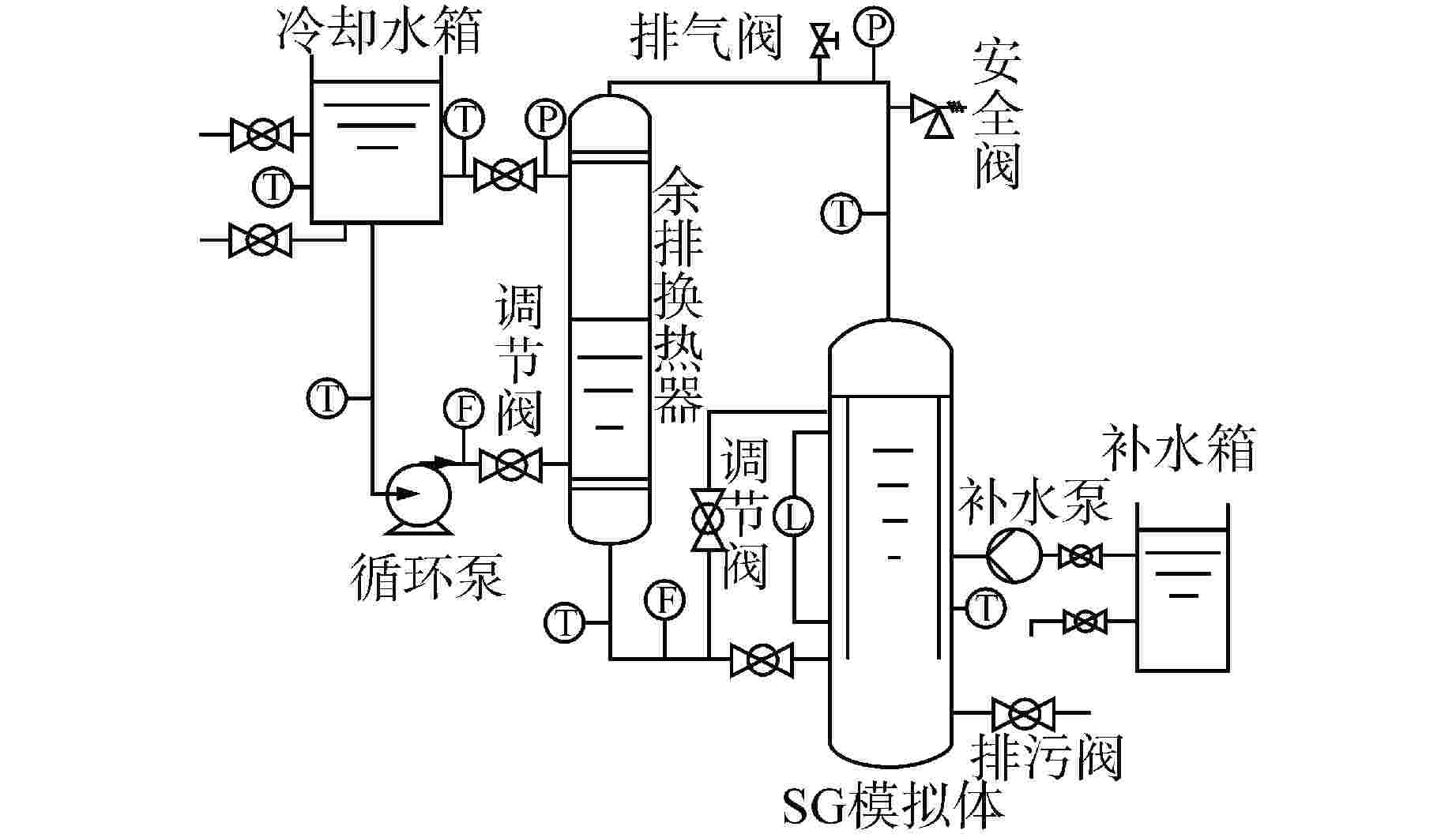
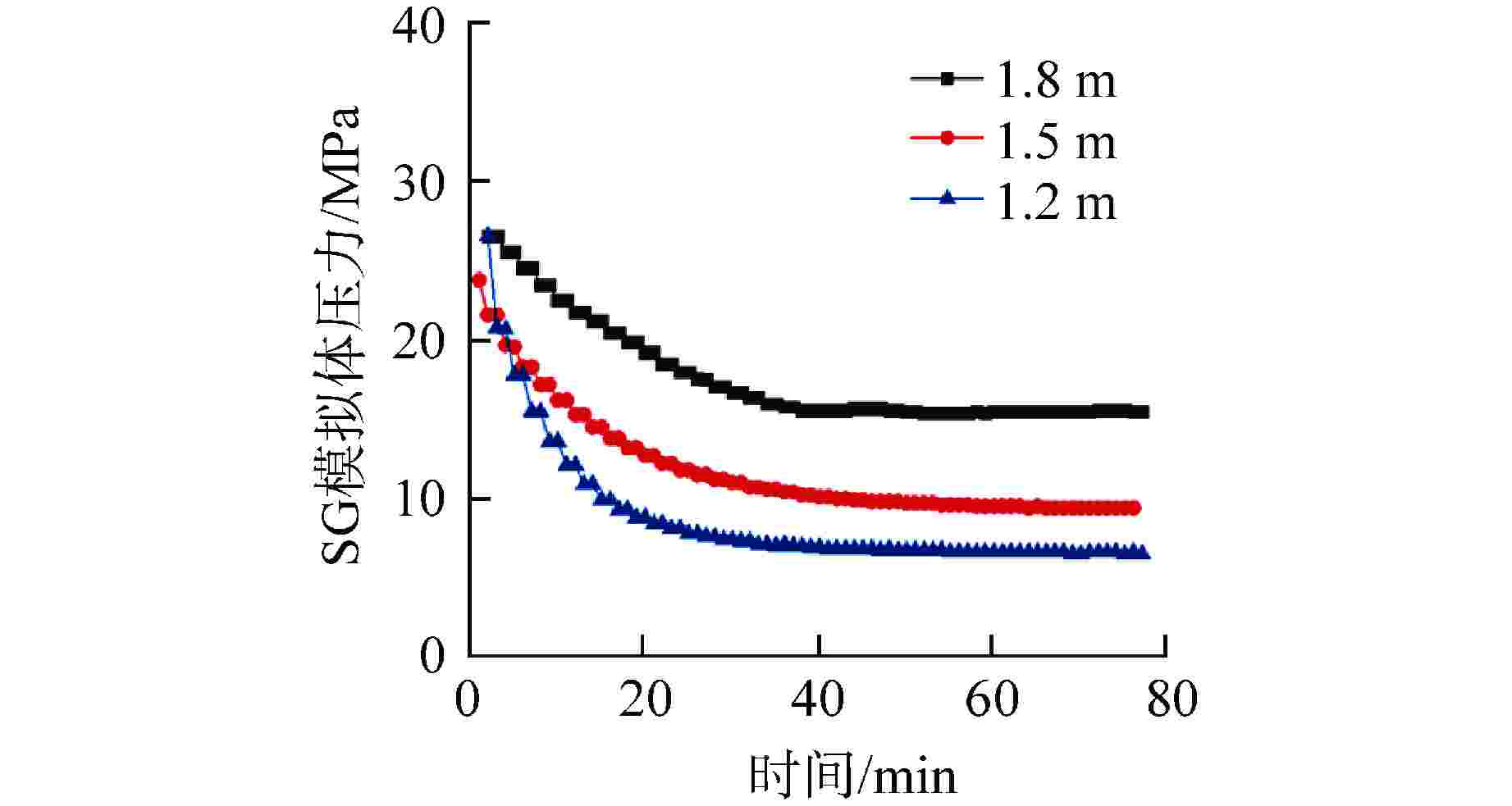
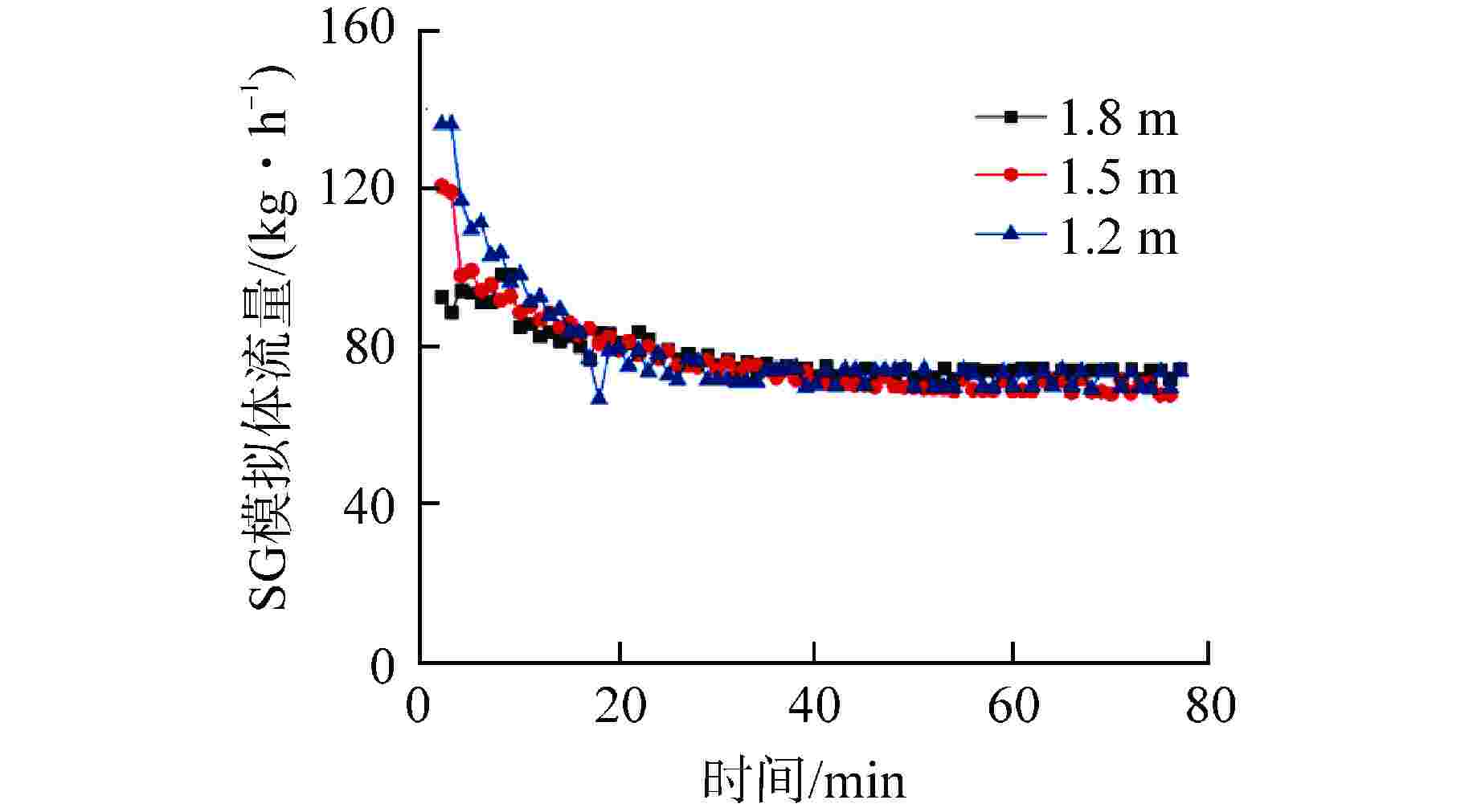
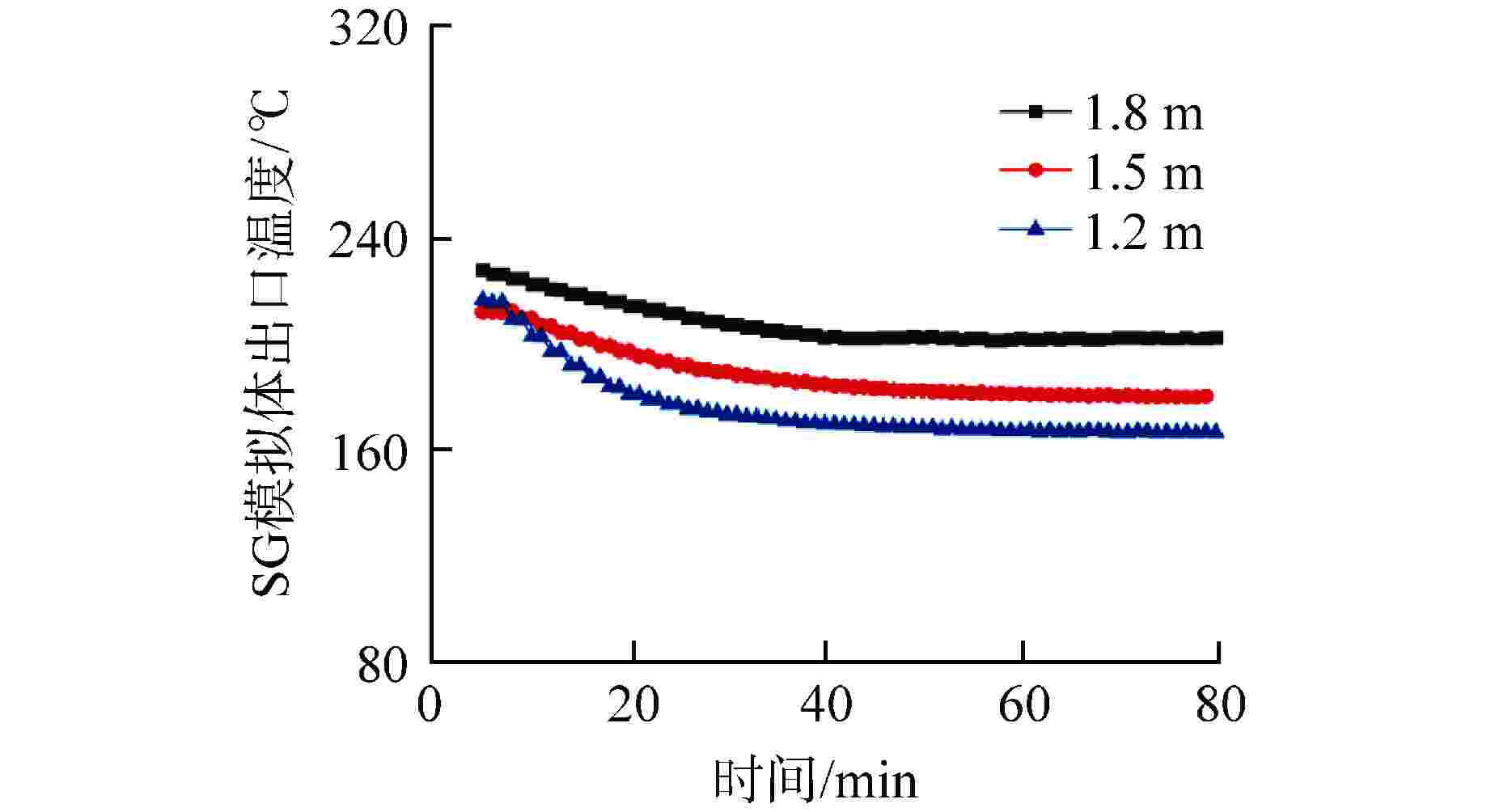
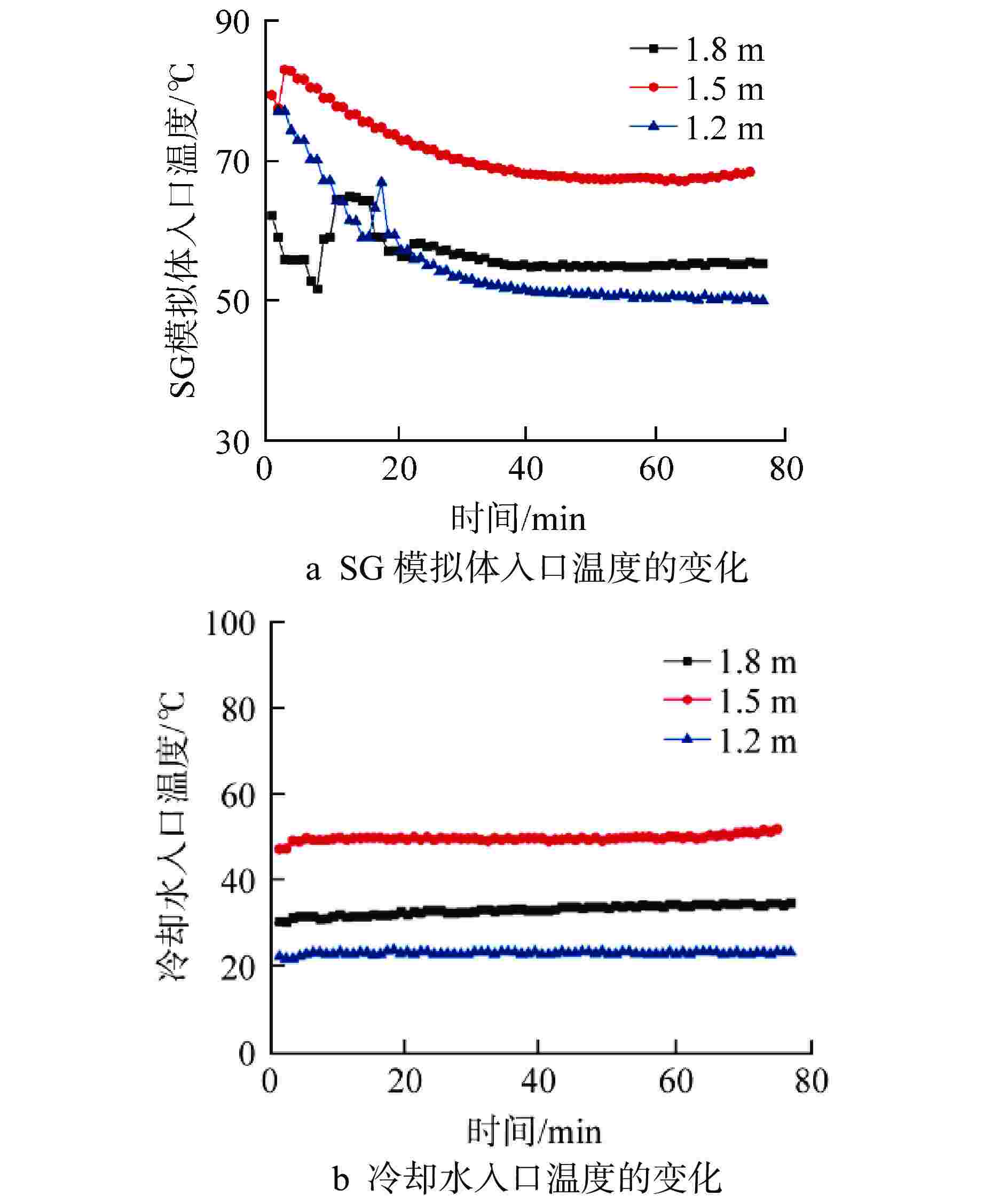
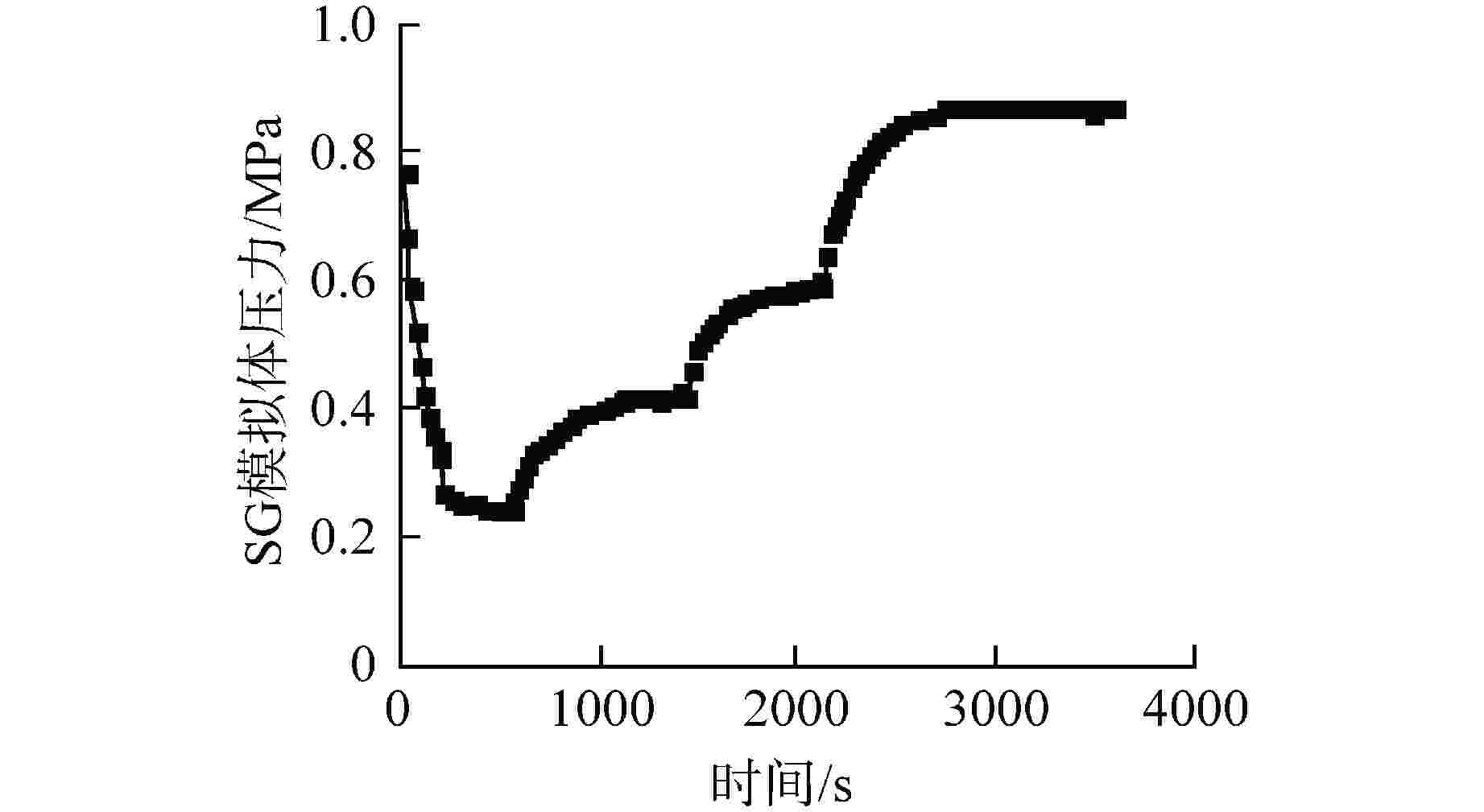
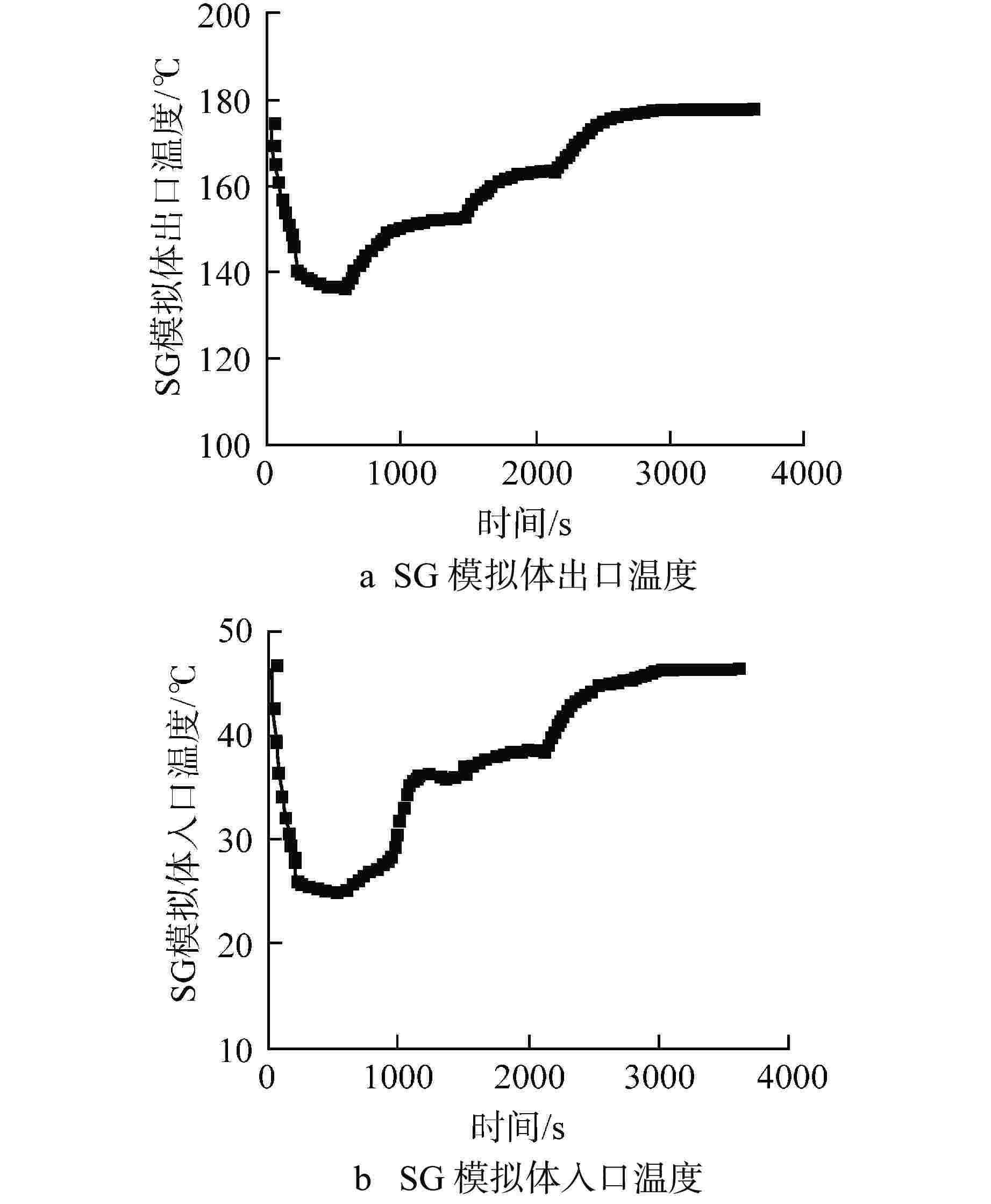
摘要: 相比于陆基核电厂,船用核动力装置的非能动安全系统运行压力较低,运行功率变化频繁,在两相自然循环条件下,非能动安全系统内的流动更加复杂多变。为了研究两相自然循环在低压、低功率条件下的循环特性,基于比例分析方法搭建了两相自然循环的原理试验台架,研究了低压条件下功率和初始液位高度对自然循环特性的影响。结果表明,在低压条件下,系统稳定运行后的压力、流量等均受初始液位高度和功率的影响。当功率为50 kW时,初始液位越高,系统稳定后的压力越大,但是流量相差较小;初始液位一定时,功率在40%满功率~100%满功率内,随着功率的增大,系统稳定后的压力也逐渐增大。这为试验台架后续两相自然循环的研究提供了方向,也为船用核动力装置非能动安全系统研究提供了参考。Abstract: Compared with the land-based nuclear power plant, the passive safety system of marine nuclear power plant has lower operating pressure and frequent changes in operating power. Under the condition of two-phase natural circulation, the flow in the passive safety system is more complex and changeable. In order to further study the circulation characteristics of two-phase natural circulation under the condition of low pressure and low power, the principle test bench of two-phase natural circulation is built based on the proportional analysis method, and the influence of power and initial liquid level height on the characteristics of natural circulation under the condition of low pressure is studied. The results show that under low pressure, the pressure and flow of the system after stable operation are affected by the initial liquid level and power. When the power is 50 kW, the higher the initial liquid level is, the greater the pressure after the system is stabilized, but the flow difference is small; When the initial liquid level is constant, the power is in the range of 40% full power to 100% full power. With the increase of power, the pressure after the system is stabilized also gradually increases. This provides a direction for the follow-up research of two-phase natural circulation of the test bench, and also provides a reference for the research of passive safety system of marine nuclear power plant.
-
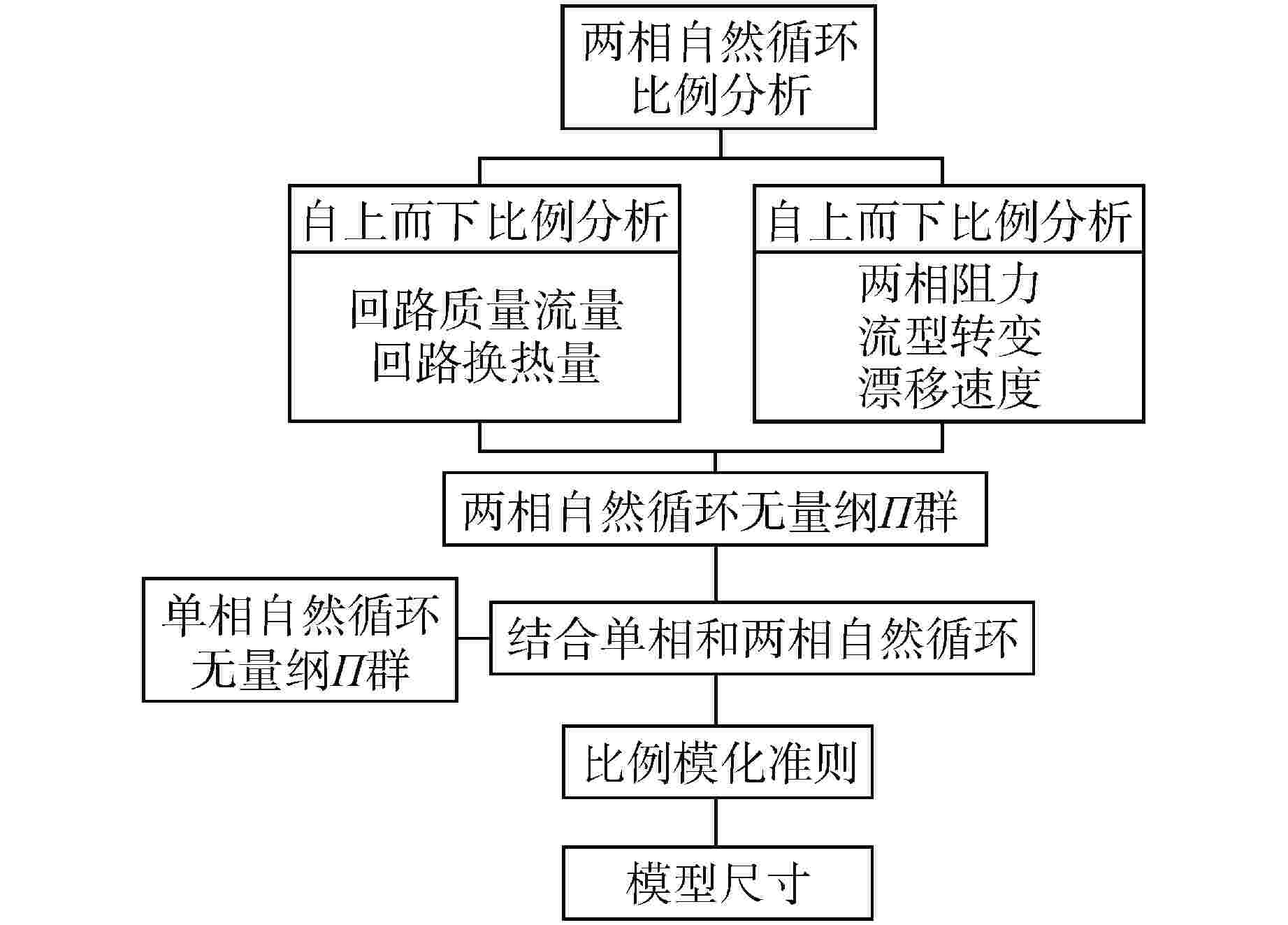
表 1 两相自然循环无量纲群
Table 1. Dimensionless Group of Two-phase Natural Circulation
序号 无量纲数 说明 1 ${\tau _{ { { {\rm{TP} },{\rm{o}}} } } } = \dfrac{ { {V_{ {\text{TP,o} } } } } }{ { {Q_{ {\text{TP,o} } } } } }$ 无量纲时间 2 ${\varPi _{Fr} } = \dfrac{ {u_{ {\text{TP} } }^2{\rho _{ {\text{TP} } } } } }{ {\alpha gl{ {\Delta } }\rho } }$ Froude数 3 $\varPi = \dfrac{ { {\rho _{\text{g} } }{\rho _{\text{l} } } } }{ {\alpha (1 - \alpha ){ {\Delta } }{\rho ^2} } }$ 4 ${\varPi _{ {\text{Nd} } } } = \dfrac{ { {v_{ {\text{gj} } } }\alpha { {\Delta } }\rho } }{ { {u_{ {\text{TP} } } }{\rho _{ {\text{TP} } } } } }$ drift flux数 5 ${\varPi _{\text{F} } } = \dfrac{ {fl} }{d} + K$ Friction数 6 ${\varPi _{ {\text{HT} } } } = \dfrac{ { {H_{\text{s} } }{A_{\text{s} } }({T_{\text{s} } } - {T_{ {\text{TP} } } })} }{ { {\rho _{ {\text{TP} } } }{h_{ {\text{TP} } } }{u_{ {\text{TP} } } }{a_{\text{c} } } }}$ 与传递热量相关比例准则数 7 ${\varPi _{\text{h} } } = \dfrac{ { {h_{\lg } }(1 - \alpha )\alpha { {\Delta } }\rho } }{ { {h_{ {\text{TP} } } }{\rho _{ {\text{TP} } } } } }$ 与焓相关比例准则数 8 ${\varPi _{ {\text{qf} } } } = \dfrac{ { {q_{\text{s} } }l} }{ { {u_{ {\text{TP} } } }{\rho _{\text{s} } }{c_{ {\text{vs} } } }({T_{\text{s} } } - {T_{ {\text{TP} } } }){V_{\text{s} } } }}$ 流体无量纲热量 9 ${\varPi _{\text{q} } } = \dfrac{ { {q_{\text{s} } } }}{ { {H_{\text{s} } }{A_{\text{s} } }({T_{\text{s} } } - {T_{ {\text{TP} } } })} }$ 固体无量纲热量 10 ${\varTheta _{\text{s} } } = \dfrac{ { {T_{\text{s} } } - {T_{ {\text{TP} } } } } }{ { {T_{\text{s} } } } }$ 无量纲温度 Hs—热传递系数, cvs—固体比热, qs—产热率;下标o表示相关物理量的初始参数 -
[1] IAEA. Passive safety systems and natural circulation in water cooled nuclear power plants: IAEA-TECDOC-1624[R]. Vienna: International Atomic Energy Agency, 2009: 6-7. [2] IAEA. Natural Circulation phenomena and modelling for advanced water cooled reactors: IAEA-TECDOC-1677[R]. Vienna: International Atomic Energy Agency, 2012: 286-298. [3] REYES JR J N, HOCHREITER L. Scaling analysis for the OSU AP600 test facility (APEX)[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 1998, 186(1-2): 53-109. doi: 10.1016/S0029-5493(98)00218-0 [4] ISHII M, KATAOKA I. Scaling laws for thermal-hydraulic system under single phase and two-phase natural circulation[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 1984, 81(3): 411-425. doi: 10.1016/0029-5493(84)90287-5 [5] FRIEND M T, WRIGHT R F, HUNDAL R, et al. Simulated AP600 response to small-break loss-of-coolant-accident and non-loss-of-coolant-accident events: analysis of SPES-2 integral test results[J]. Nuclear Technology, 1998, 122(1): 19-42. doi: 10.13182/NT98-A2848 [6] D'AMICO S, LOMBARDO C, MOSCATO I, et al. Transient analysis of “2 inch direct vessel injection line break” in SPES-2 facility by using TRACE code[J]. Journal of Physics:Conference Series, 2015, 655: 012059. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/655/1/012059 [7] 陈炳德,肖泽军,周仁明,等. AC600二次侧非能动应急堆芯余热排出系统实验装置及研究计划[J]. 核动力工程,1998, 19(2): 97-101. [8] 黄彦平,卓文彬,杨祖毛,等. 先进压水堆非能动余热排出技术试验研究[J]. 核动力工程,2003, 24(1): 18-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0926.2003.01.006 [9] 房芳芳,常华健,秦本科. 核反应堆试验台架比例分析方法的发展和应用[J]. 原子能科学技术,2012, 46(6): 658-664. [10] 武玉增,李常伟. 非能动余热排出系统模化及验证分析[J]. 船舶,2014(4): 75-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9855.2014.04.015 [11] 卢霞,匡波,孔浩铮,等. SBLOCA整体试验台架的比例模化分析与初步评估[J]. 应用科技,2019, 46(5): 80-87. [12] 卢冬华,肖泽军,陈炳德. 压水堆自然循环比例模化基本方程及相似准则数的研究[J]. 核动力工程,2009, 30(3): 72-84,94. [13] 卢冬华,肖泽军,陈炳德. 运动状态下压水堆自然循环比例模拟方法研究[J]. 核动力工程,2009, 30(6): 28-37. [14] WU J B, BI Q C, ZHOU C S. Experimental study on circulation characteristics of secondary passive heat removal system for Chinese pressurized water reactor[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2015, 77: 106-112. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2014.12.014 [15] 张金玲,郭玉君,秋穗正,等. 船用核动力装置自然循环载热能力的分析与计算[J]. 西安交通大学学报,1994, 28(6): 35-42. -





 下载:
下载: