SPSA-based Performance Optimization Method for Steam Generator MPC System
-
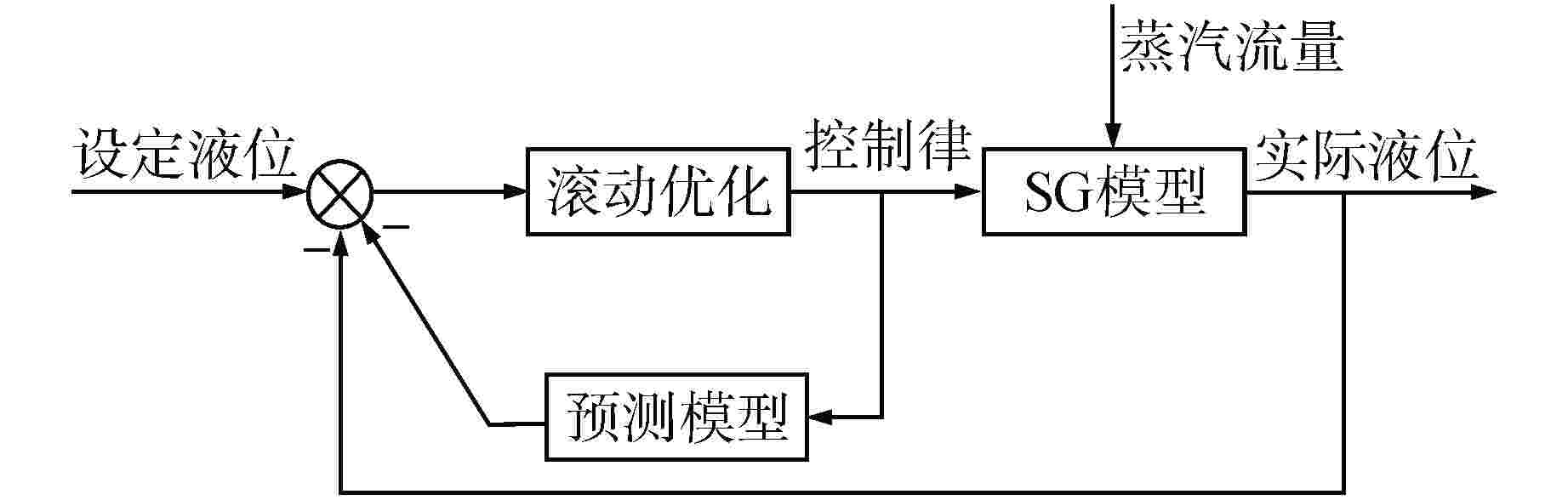
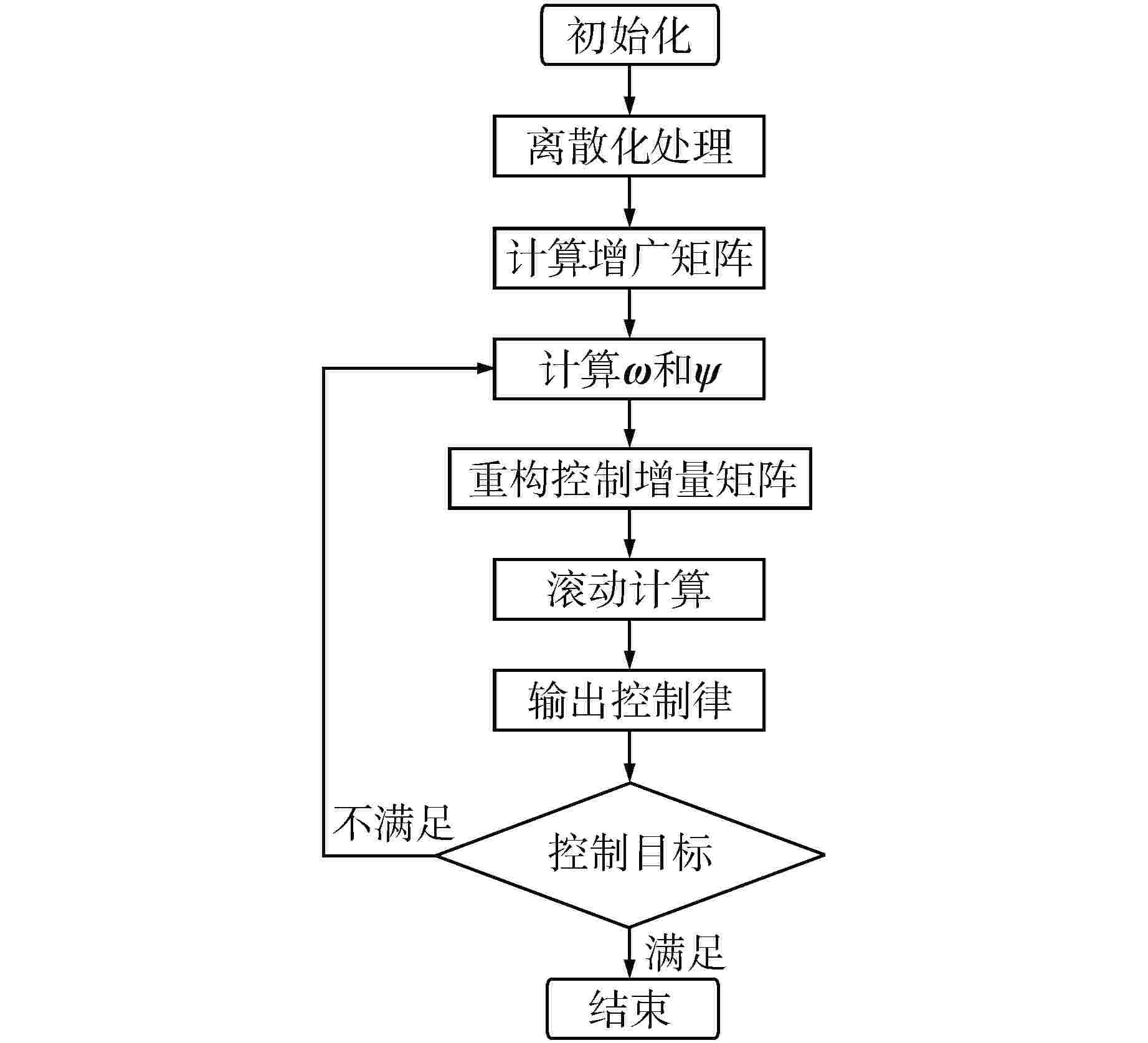
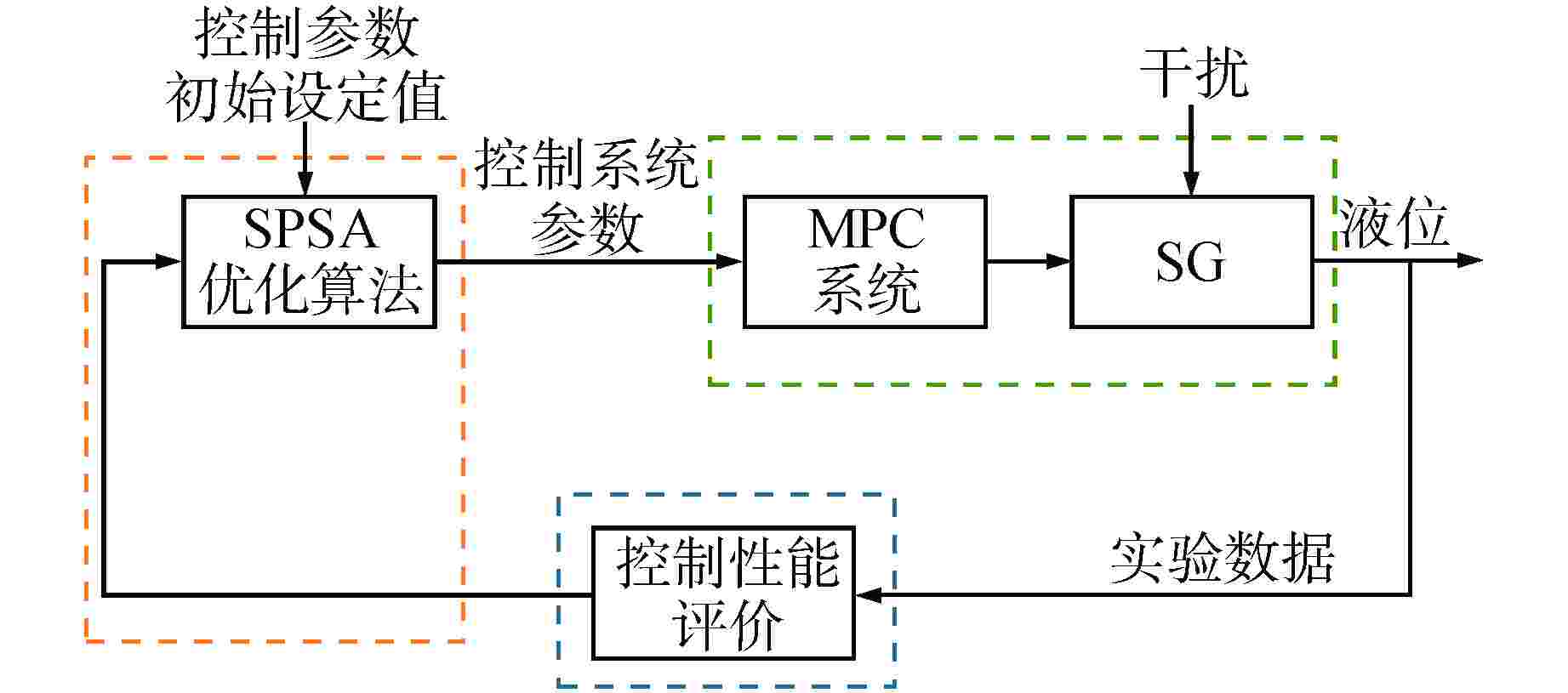
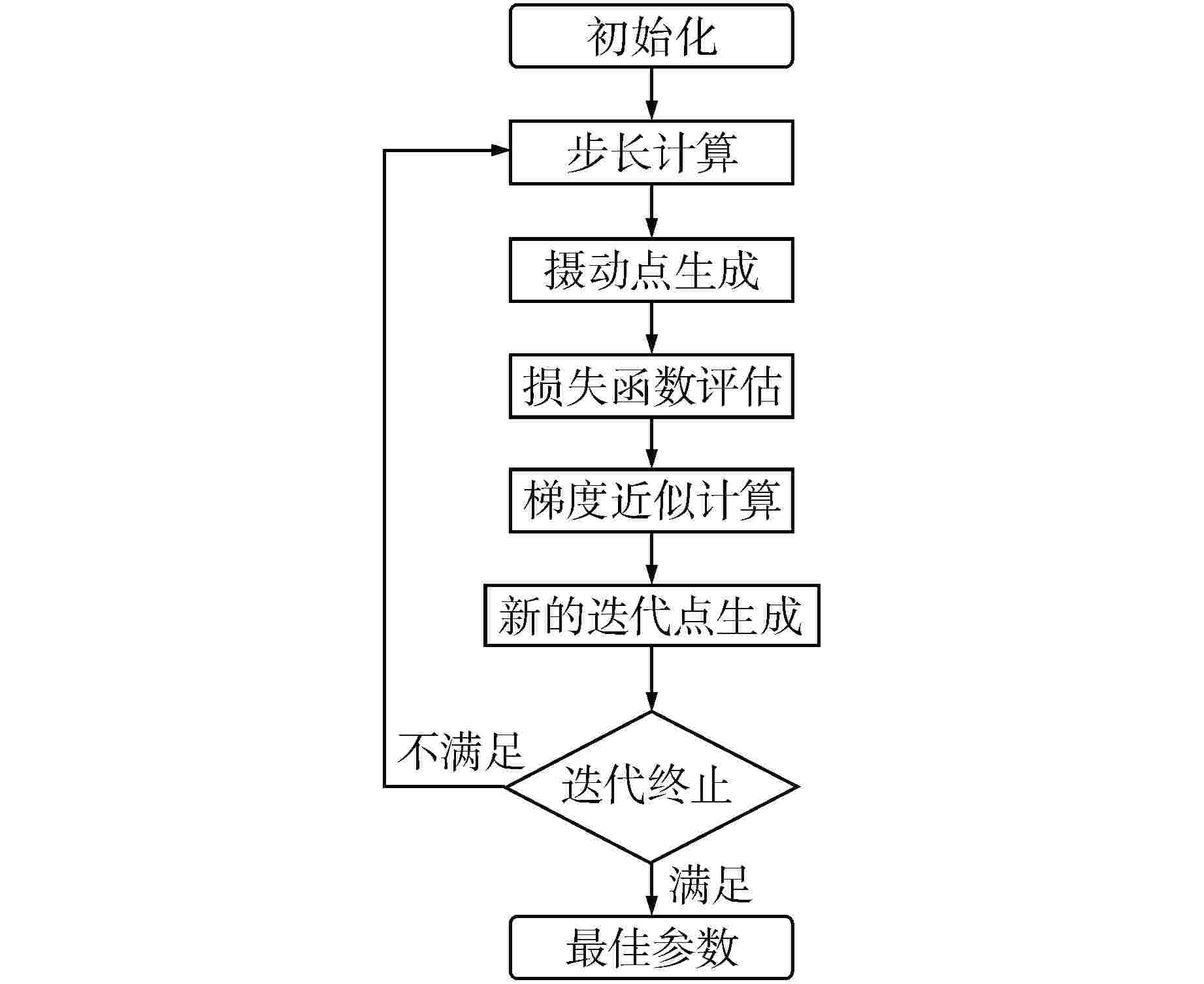
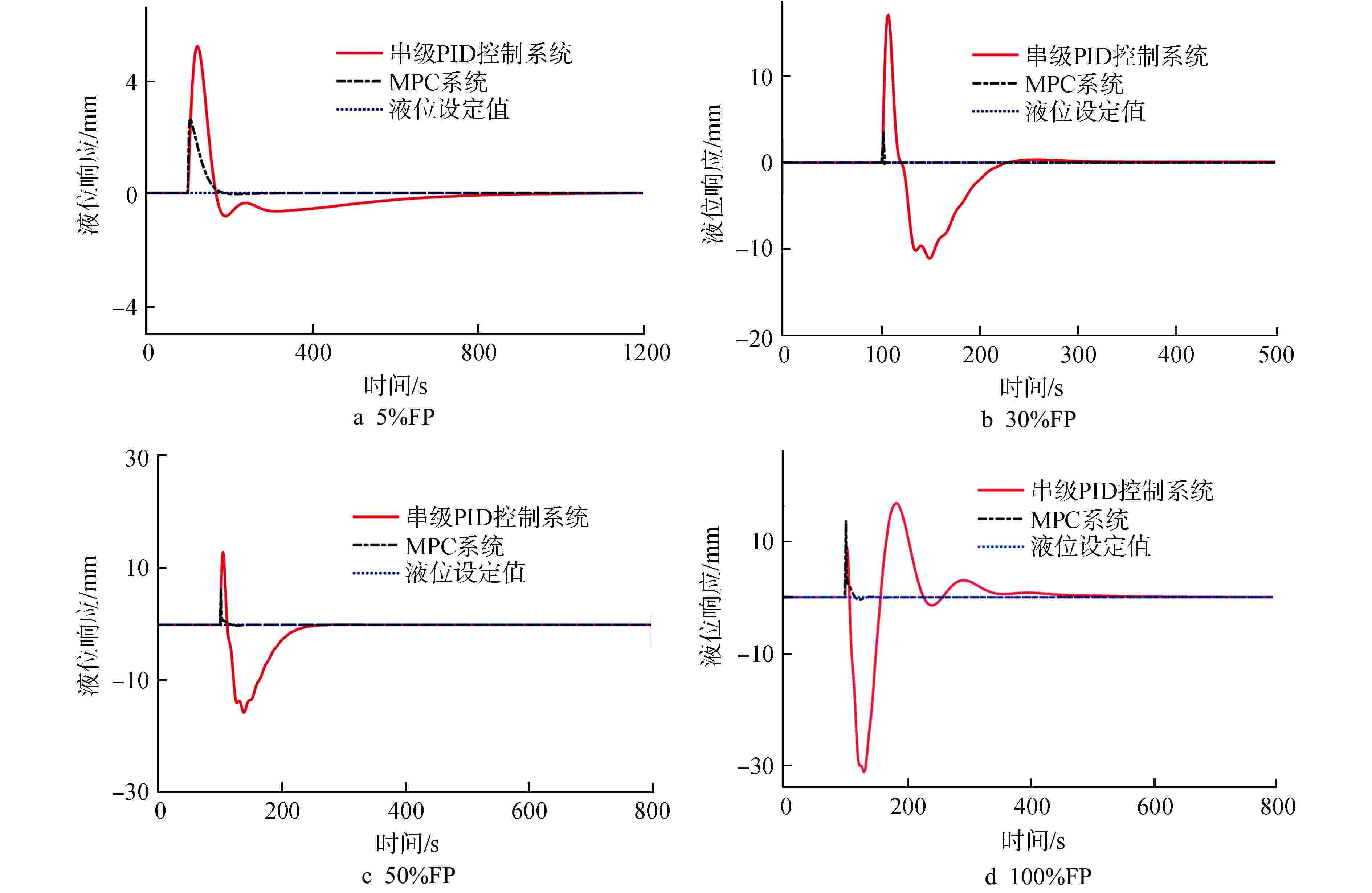
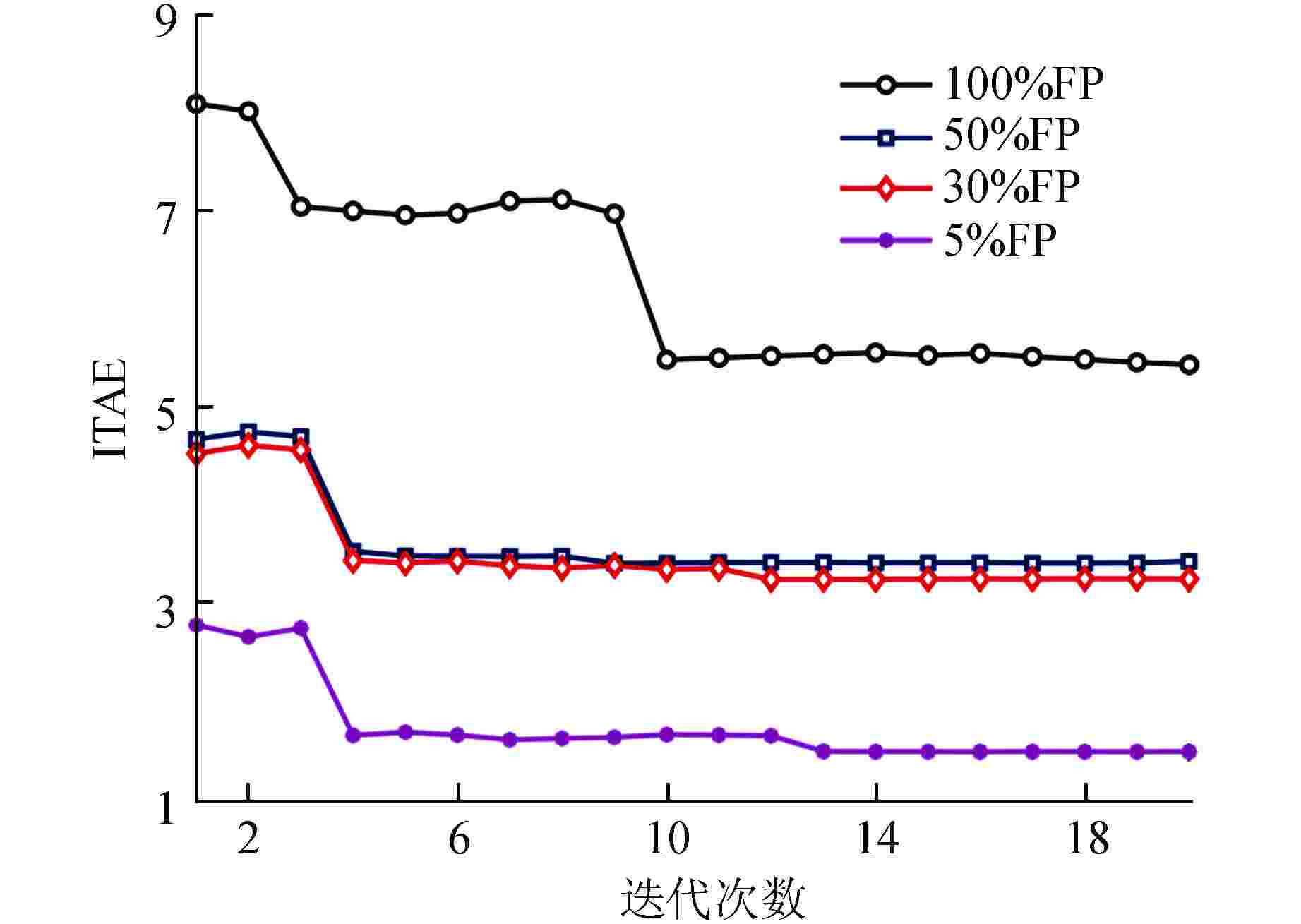
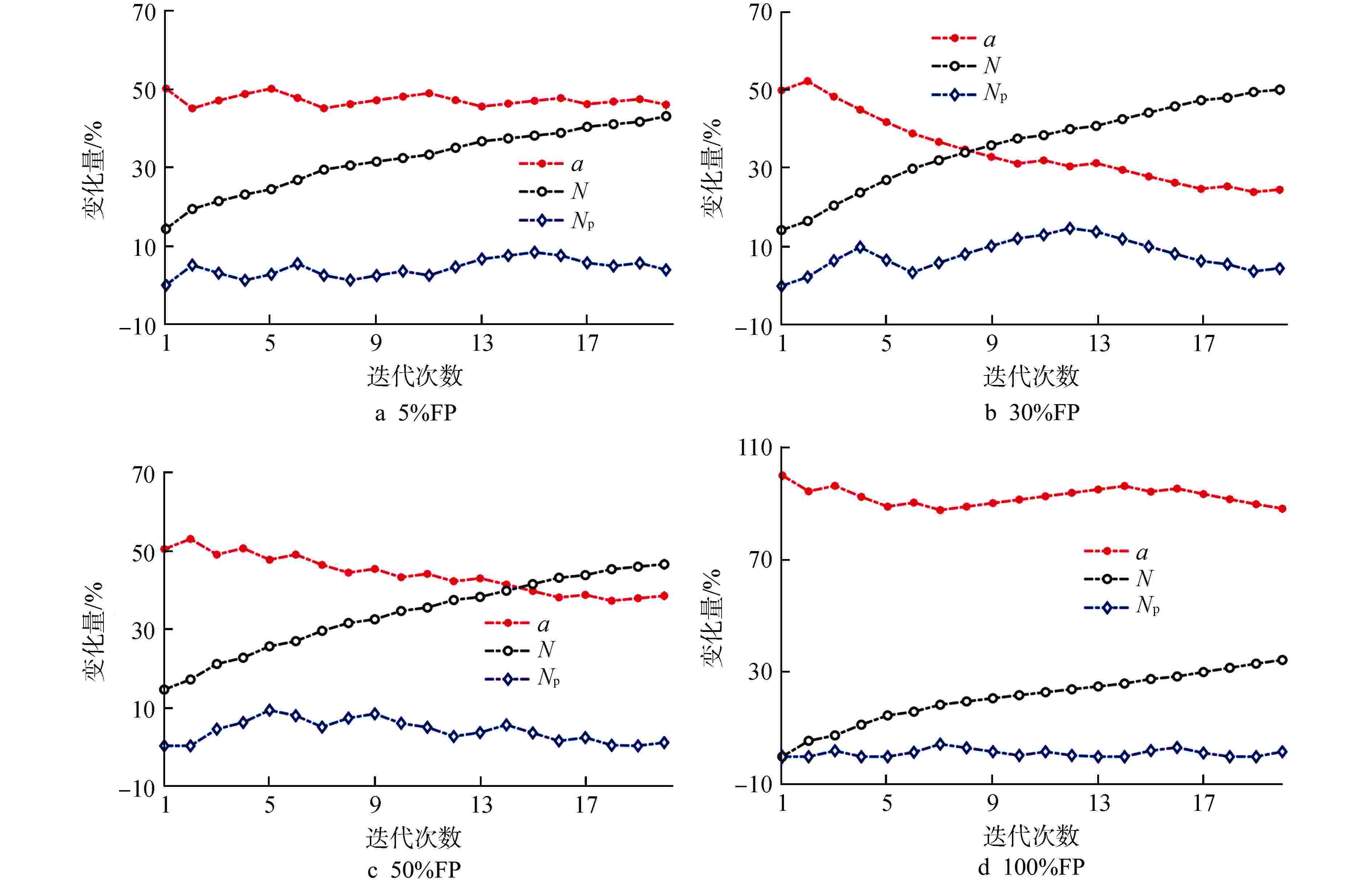
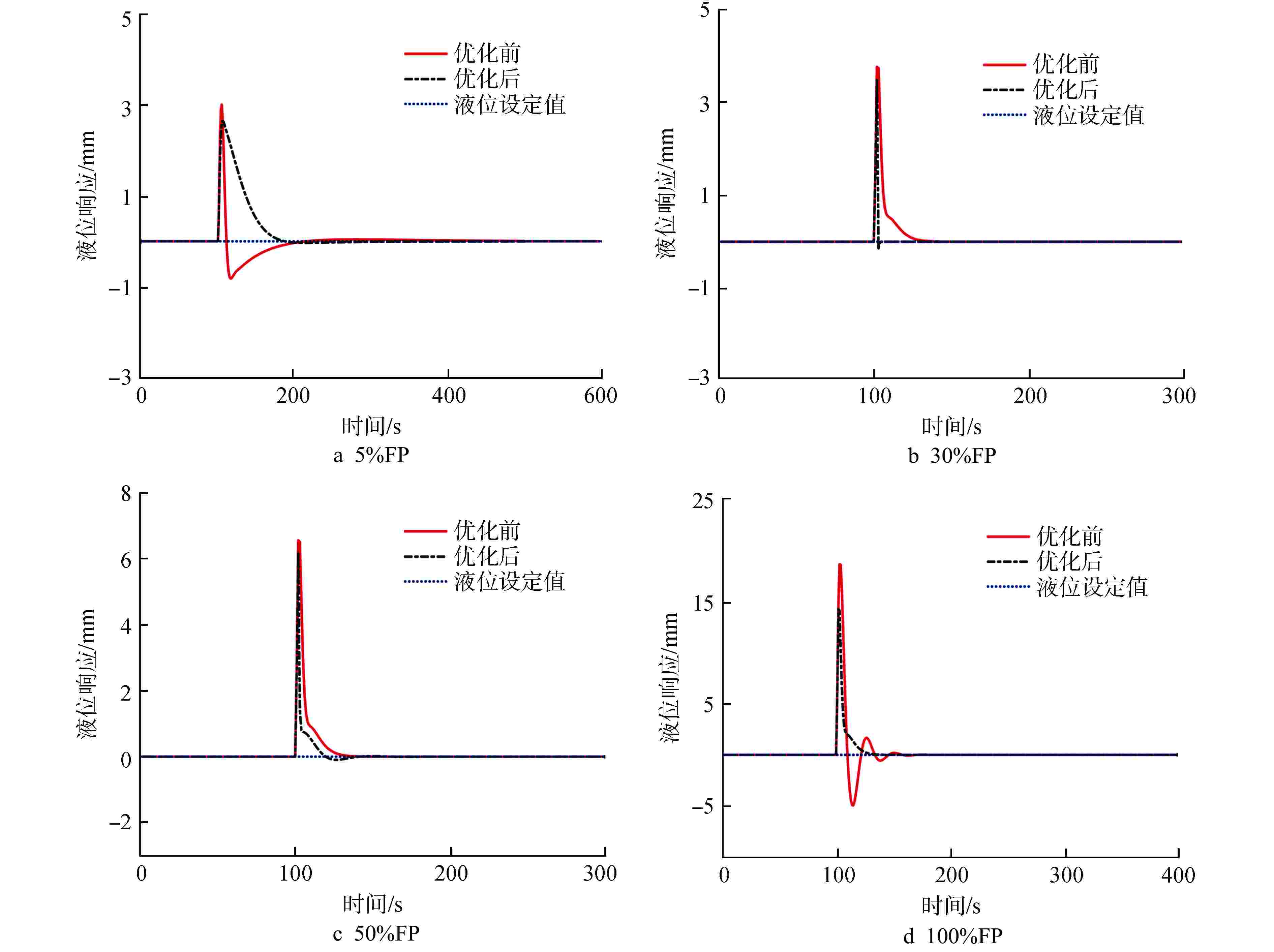
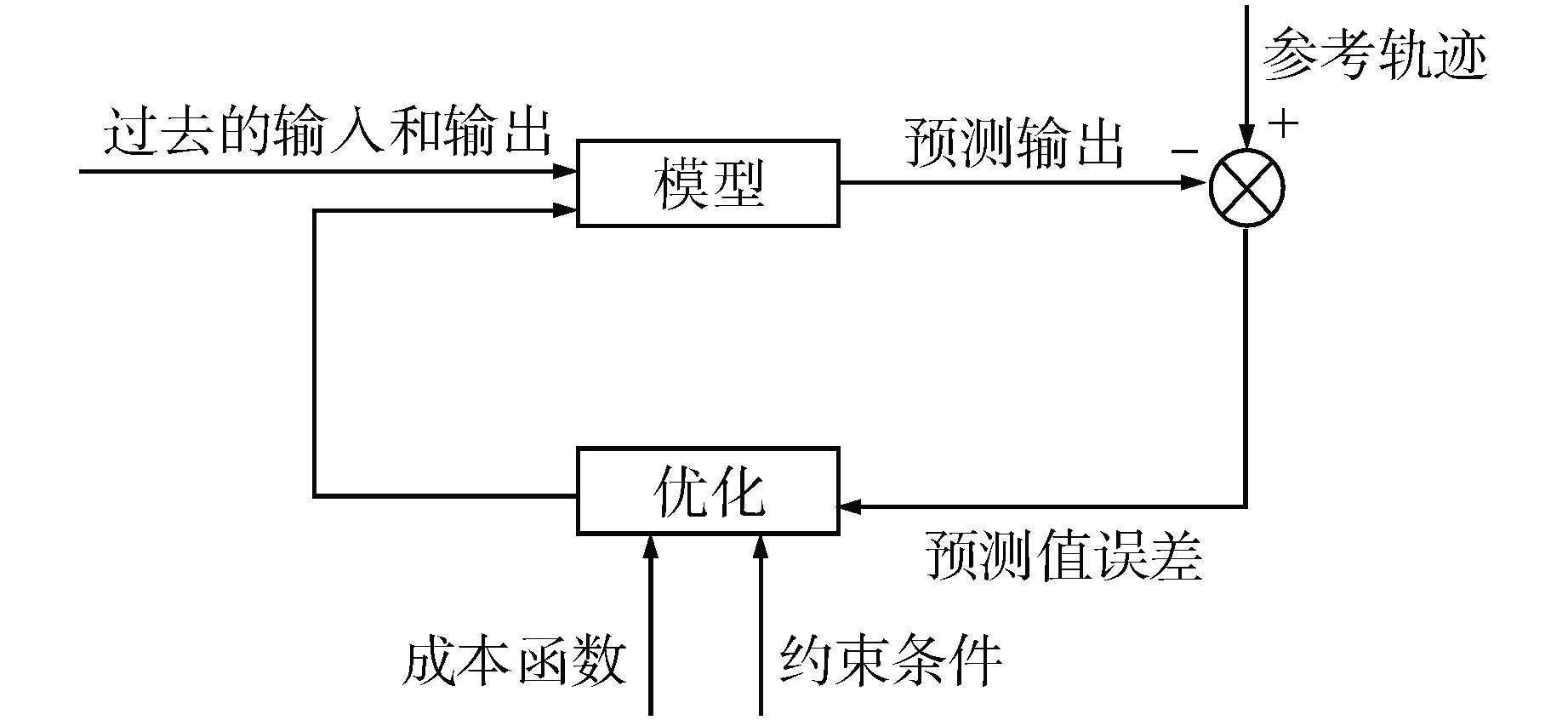
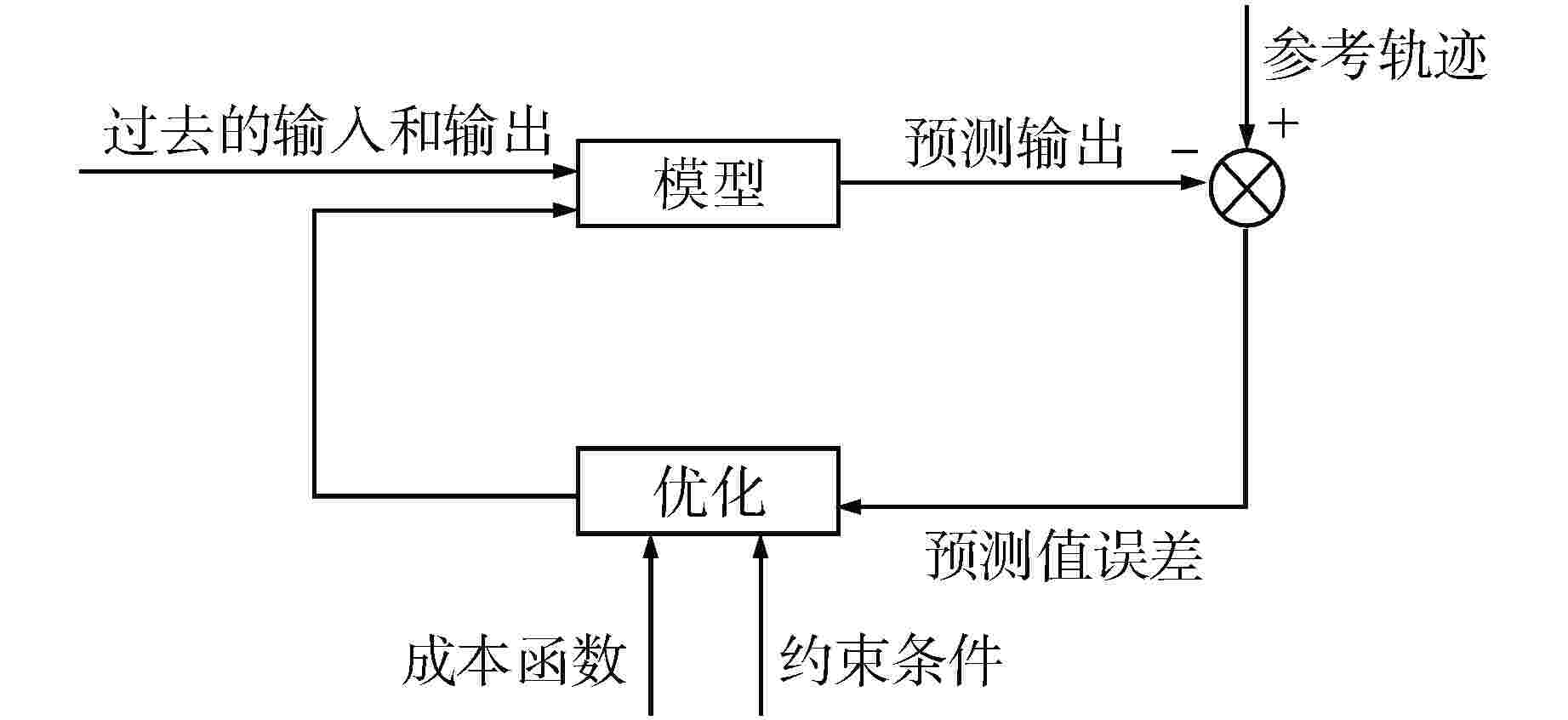
摘要: 核电厂蒸汽发生器(SG)液位变化过程具有强非线性且存在“虚假水位”现象,传统SG液位控制系统多采用固定参数比例-积分-微分(PID)控制器,但传统PID控制方法不具备自优化、自适应、自学习等能力,使得控制系统性能难以达到并保持最佳。为提高机组瞬态响应能力以及核电厂的稳定性、安全性和经济性,提出了一种基于并行摄动随机逼近(SPSA)算法的模型预测控制(MPC)方法。该方法采用MPC系统代替传统PID控制系统,并利用SPSA实现液位控制系统参数的整定优化,从而实现SG液位控制系统的性能优化。通过仿真试验验证了本方法能够有效提高SG液位控制参数的整定效率以及控制系统稳定性。
-
关键词:
- 蒸汽发生器(SG) /
- 模型预测控制 /
- 控制系统性能优化 /
- 并行摄动随机逼近算法
Abstract: The level change process of steam generator (SG) in nuclear power plant has strong nonlinearity and the phenomenon of "false water level" exists. Traditional SG level control systems mostly use fixed-parameter proportional-integral-derivative (PID) controllers, but traditional PID control methods do not have the capabilities of self-optimization, self-adaptation, and self-learning, making it difficult to achieve and maintain optimal control system performance. In order to improve the transient response ability of the unit and the stability, safety and economy of the nuclear power plant, a model predictive control (MPC) strategy based on simultaneous perturbation stochastic approximation (SPSA) algorithm is proposed. In this method, MPC system is used to replace the traditional PID control system, and SPSA is used to optimize and set the parameters of the level control system, so as to optimize the performance of the SG level control system. The simulation results show that this method can effectively improve the setting efficiency of SG level control parameters and the stability of the control system. -
表 1 串级PID和MPC控制系统仿真参数设置
Table 1. Simulation Parameter Setting of Cascade PID and MPC Control System
功率
控制参数5%FP 30%FP 50%FP 100%FP P1 0.009 0.078 0.11 0.28 I1 2.3×10−6 2.67×10−5 0 7.57×10−4 D1 0.7 0.2 0.5 0.79 P2 1.3 1.0 1.1 1.14 I2 5 0.52 0.4 0.59 D2 0.2 0 0.2 0.15 $ a $ 0.25 0.5 0.42 0.48 $ N $ 4 4.8 6.27 6.25 ${N_{\rm{p}}}$ 30 30 32 30 表 2 MPC系统控制参数约束范围
Table 2. Constraint Range of MPC System Control Parameters
参数 约束范围 $ a $ [0, 0.5] $ N $ [3, 10] ${N_{\rm{p}}}$ [30, 50] 表 3 MPC系统参数设置
Table 3. Parameters Setting of the MPC System
参数 设定值 液位目标设定值/mm 0 给水阀调节值 0.5 扰动比例/% 5 扰动设定时间/s 100 仿真总时长/s 1200 -
[1] 徐颖,陈坚才,于航,等. 蒸汽发生器液位控制系统手自动切换的前馈补偿研究[J]. 核动力工程,2021, 42(3): 140-144. [2] MAN G N, SIM Y R, LEE Y J. Design of an adaptive predictive controller for steam generators[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 2003, 50(1): 186-193. doi: 10.1109/TNS.2002.807854 [3] KOTHARE M V, METTLER B, MORARI M. Linear parameter varying model predictive contr for steam generator level control[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 1997, 21(S1): S861-S866. [4] 张登,蔡宛睿,谢成龙,等. 核电数字化控制系统PID参数自动寻优软件研制[J]. 核动力工程,2020, 41(S1): 77-81. doi: 10.13832/j.jnpe.2020.S1.0077 [5] 项洪一,冯晓露,刘建光,等. 核电站蒸汽发生器水位模型预测控制方法研究[J]. 科技创新导报,2017, 14(14): 167-170. doi: 10.16660/j.cnki.1674-098X.2017.14.167 [6] 董化平,张建民. 秦山第二核电厂蒸汽发生器液位控制系统PID参数整定[J]. 核动力工程,2005, 26(3): 272-276. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0926.2005.03.014 [7] 项洪一,陈坚才,黄振广,等. ACPR1000核电厂SG水位控制调试方法研究[J]. 核科学与工程,2019, 39(5): 758-764. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0918.2019.05.013 [8] SALEHI A, SAFARZADEH O, KAZEMI M H. Fractional order PID control of steam generator water level for nuclear steam supply systems[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2019, 342: 45-59. doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2018.11.040 [9] 杜琛鑫. 时滞系统的PID稳定域及参数整定研究[D]. 大连: 大连海事大学, 2019. [10] 张宇声,郭立峰,蔡猛. 基于模糊自适应参数整定的直流蒸汽发生器PID控制系统研究[J]. 核动力工程,2008, 29(4): 93-96. [11] WU S F, WANG P F, WAN J S, et al. Parameter optimization for AP1000 steam generator feedwater control system using particle swarm optimization algorithm[C]//Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering. Charlotte: ASME, 2016. [12] 孔祥松,郭佳明,郑东斌,等. 基于一种改进型SPSA的中压绝缘件质量控制方法[J]. 高校化学工程学报,2020, 34(6): 1500-1510. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9015.2020.06.022 [13] KONG X S, ZHENG D B. A knowledge-informed simplex search method based on historical quasi-gradient estimations and its application on quality control of medium voltage insulators[J]. Processes, 2021, 9(5): 770. doi: 10.3390/pr9050770 [14] KONG X S, WANG X, MA Z C. A novel method for controller parameters optimization of steam generator level control[C]//Proceedings of the 2013 21st International Conference on Nuclear Engineering. Chengdu: ASME, 2013. [15] KONG X S, ZHANG J, XIAO Y N, et al. Performance optimization for steam generator level control based on a revised simultaneous perturbation stochastic approximation algorithm[C]//Proceedings in the 3rd International Conference on Intelligent Green Building and Smart Grid. Yilan, China: IEEE, 2018. [16] RADAC M B, PRECUP R E, PETRIU E M, et al. Application of IFT and SPSA to servo system control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2011, 22(12): 2363-2375. doi: 10.1109/TNN.2011.2173804 [17] XUN Z, SPALL J C. A modified second-order SPSA optimization algorithm for finite samples[J]. International Journal of Adaptive Control and Signal Processing, 2002, 16(5): 397-409. doi: 10.1002/acs.715 [18] WANG L P. Model predictive control system design and implementation using MATLAB®[M]. London: Springer, 2009: 185-192. [19] KWON W H, HAN S. Receding horizon control: model predictive control for state models[M]. London: Springer, 2005: 20-25. [20] WANG L P. Discrete model predictive controller design using Laguerre functions[J]. Journal of Process Control, 2004, 14(2): 131-142. doi: 10.1016/S0959-1524(03)00028-3 [21] 江绍波. 基于数据驱动的蒸汽发生器液位控制系统性能优化方法研究[D]. 厦门: 厦门理工学院, 2021. [22] IRVING E, MIOSSEC C, TASSART J. Towards efficient full automatic operation of the PWR steam generator with water level adaptive control[C]//Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Boiler Dynamics and Control in Nuclear Power Stations 2. Bournemouth: ICE, 1980: 309-329. [23] 郑艳秋,张英,尤恺,等. 基于相角裕度的PID控制器自整定改进算法的研究[J]. 核动力工程,2020, 41(S2): 108-113. -





 下载:
下载: