Prediction of RPV Irradiation Embrittlement Performance and Life Evaluation of Extended Operation in a Nuclear Power Plant
-
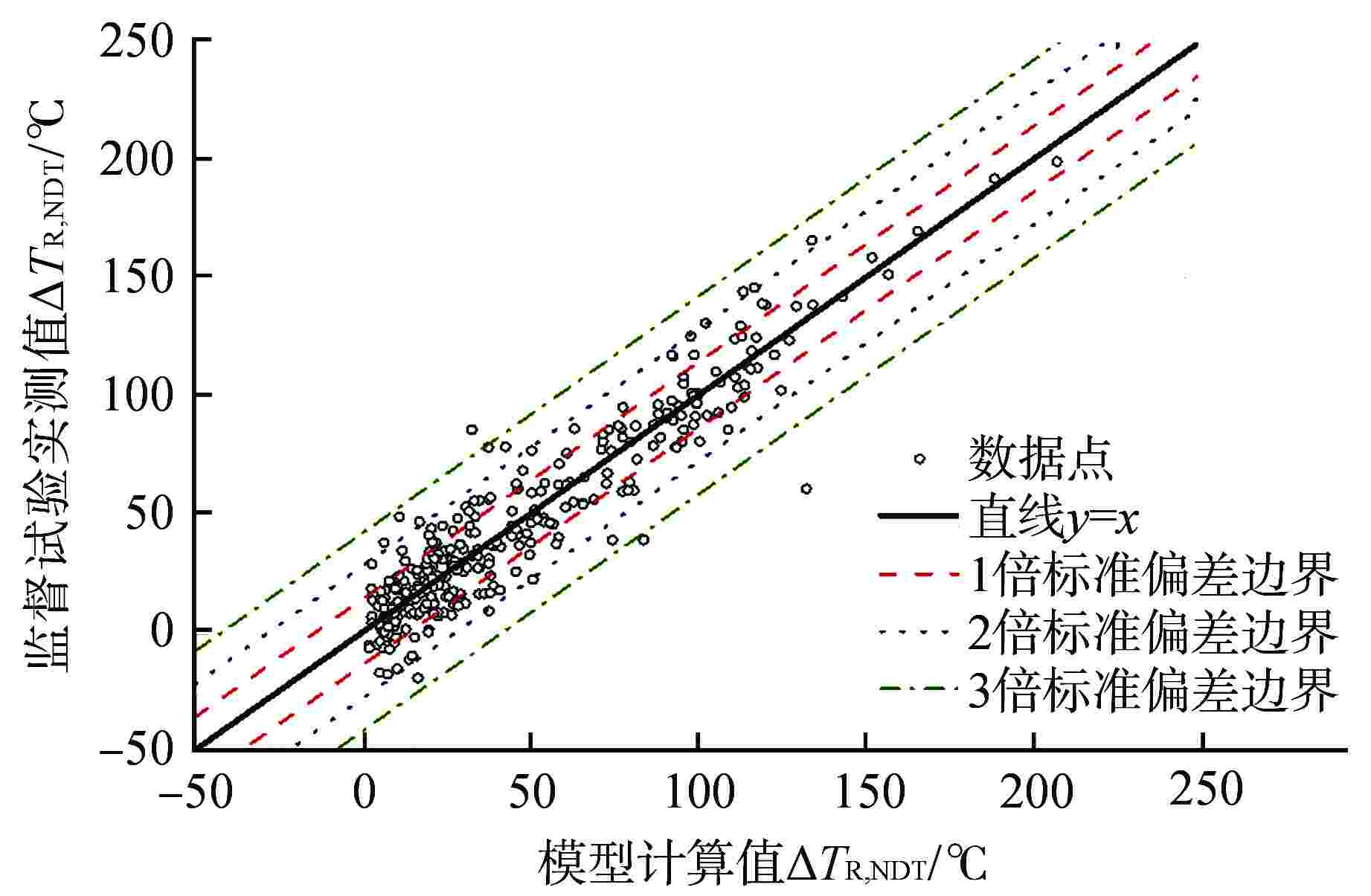
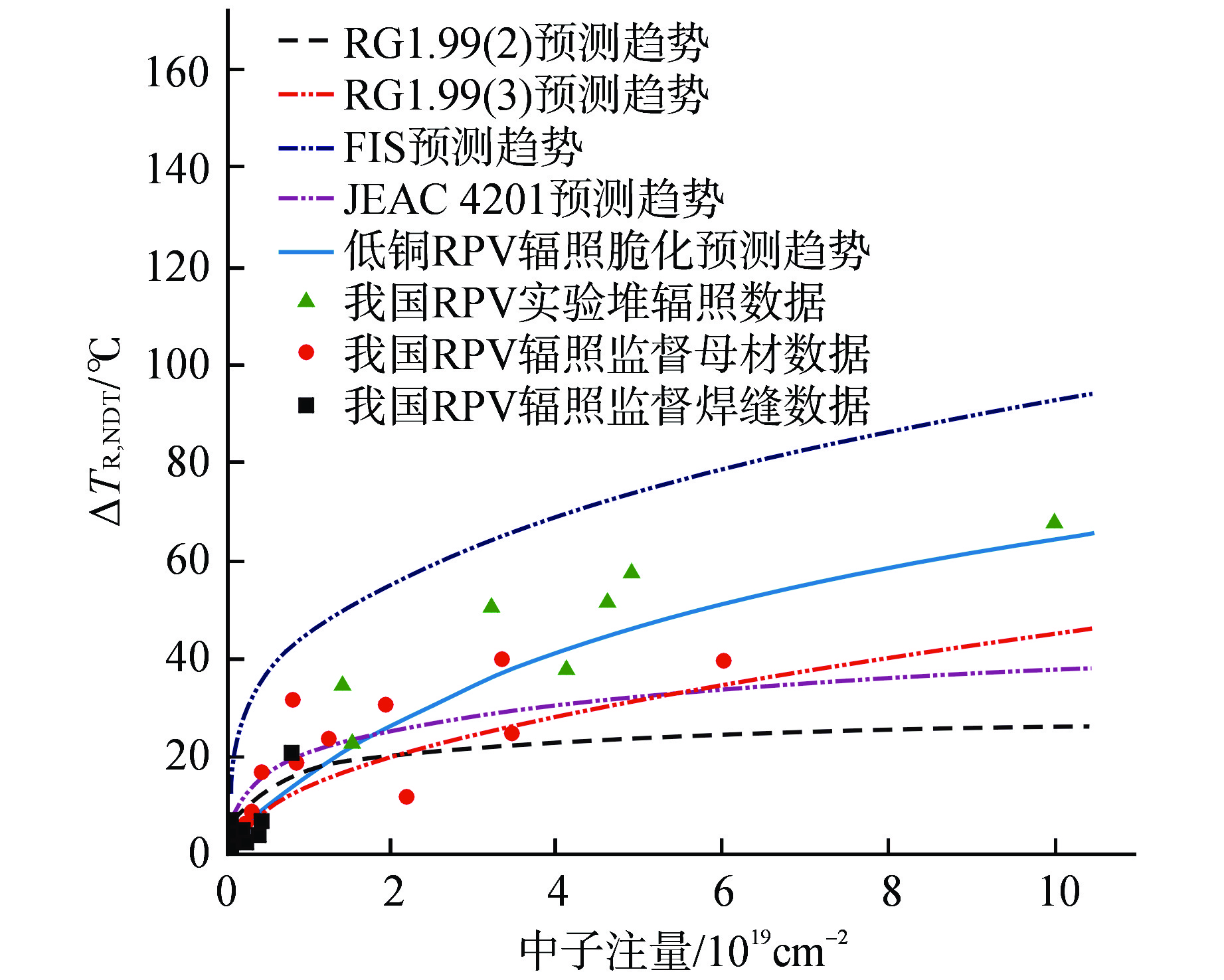
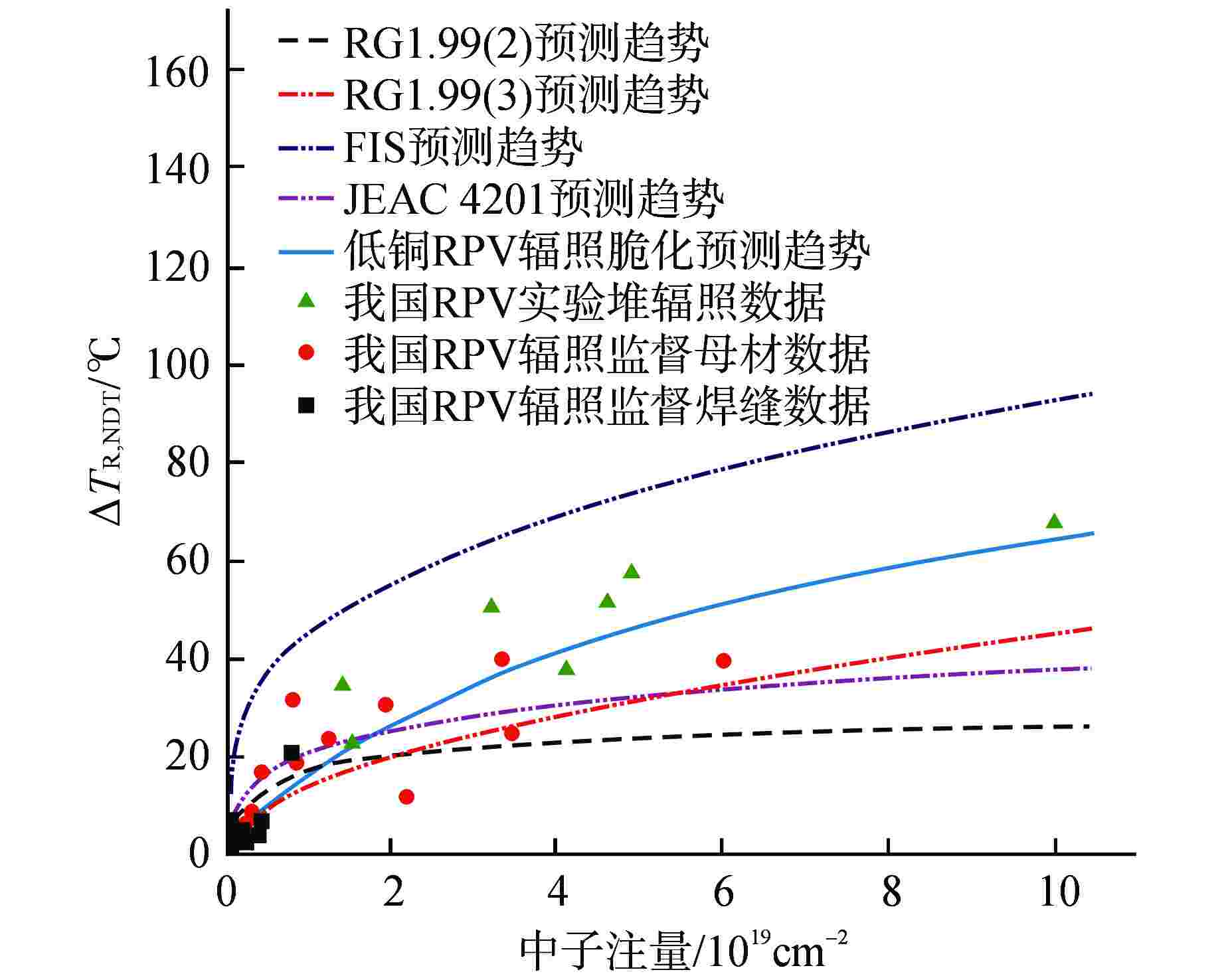
摘要: 我国自主设计建造的某核电厂已进入延续运行阶段,作为反应堆核心部分的压力容器辐照脆化性能评价采用了国外的辐照脆化预测模型,但该模型基于的辐照数据不能有效代表我国反应堆压力容器(RPV)材料的辐照脆化性能,尤其是针对延续运行阶段。本文基于国内外RPV辐照脆化预测模型及其开发机理,构建了适用于我国工程应用的自主低Cu RPV辐照脆化预测模型,该模型考虑了稳定基体缺陷和合金元素析出沉淀等辐照脆化关键因素,同时根据国产低Cu RPV材料的辐照脆化数据,开展了自主模型的标准偏差和裕量分析,结果表明模型预测置信度较高。最后依据自主模型评估该核电厂RPV的辐照脆化性能,证明其延续运行至60 等效满功率年(EFPY)具有可行性。Abstract: A domestic self-designed and built nuclear power plant has entered the stage of extended operation. A foreign prediction model was adopted for the irradiation embrittlement evaluation of the reactor pressure vessel, however, the irradiation data on which the foreign prediction model was based cannot effectively represent the irradiation embrittlement performance of domestic RPV materials, especially for the extended operation stage. Based on the radiation embrittlement prediction models of RPV at home and abroad and their development mechanisms, an independent low-Cu RPV radiation embrittlement prediction model suitable for domestic engineering applications has been formed, which considers the key factors of irradiation embrittlement such as stable matrix defects and alloy element precipitation. According to the irradiation embrittlement data of domestic low-Cu RPV materials, the standard deviation and margin analysis of the independent model were carried out, and the results indicated a high level of confidence in prediction. Based on the model, the irradiation performance of the RPV was evaluated, and the feasibility of extended operation to 60 equivalent full power years (EFPY) was demonstrated.
-
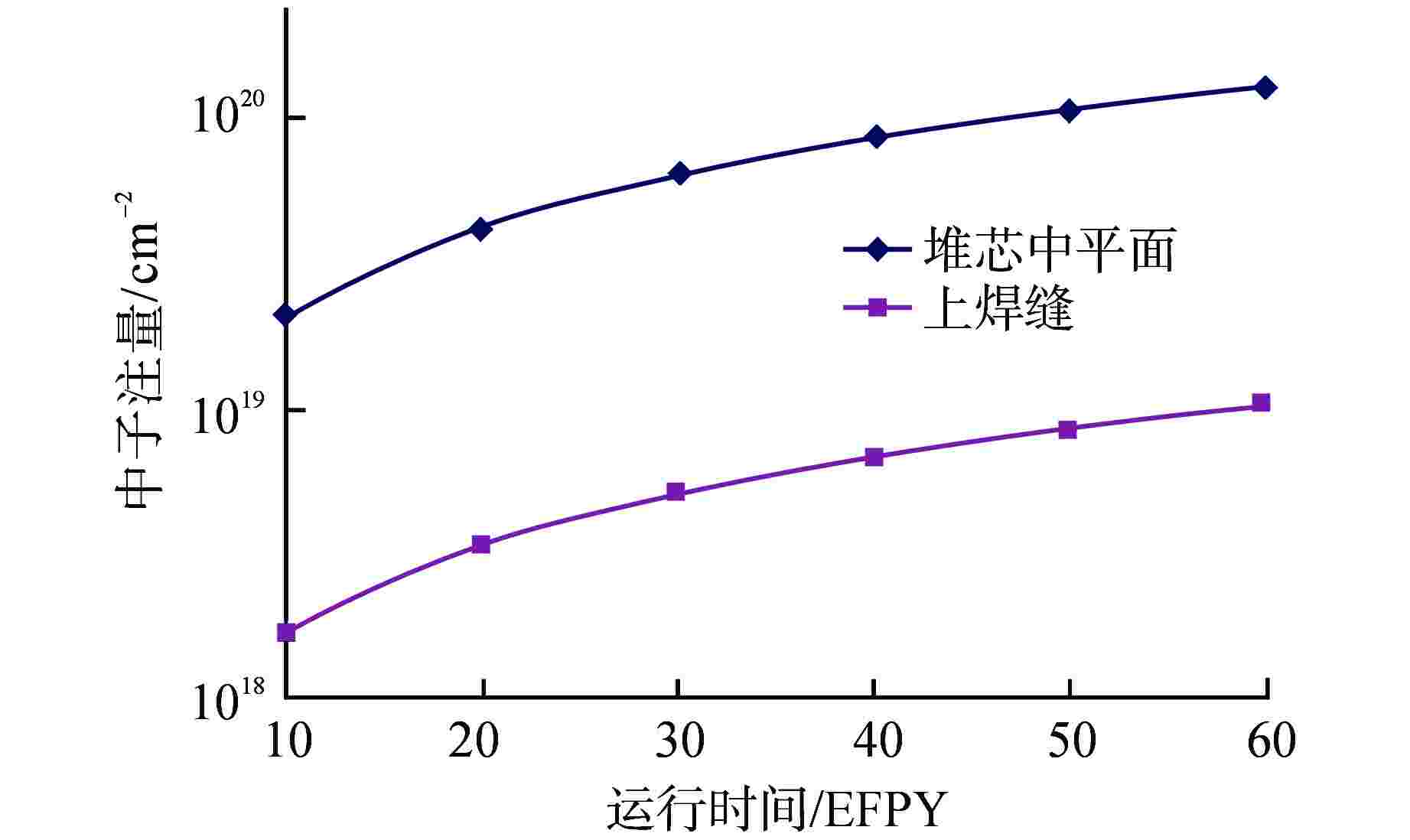
表 1 不同运行时间RPV内表面及1/4壁厚处的中子注量
Table 1. Neutron Fluence at the Inner Surface and 1/4 Wall Thickness of RPV at Different Operating Periods
运行时间
/
EFPY中子注量/1019 cm−2 堆芯
中
平面
内表面上焊缝 堆芯中平面
1/4壁厚上焊缝
1/4壁厚40 8.37 0.68 5.54 0.45 50 10.46 0.84 6.92 0.56 60 12.56 1.01 8.30 0.67 表 2 压力容器内表面
$ \Delta {T_{{\text{R,NDT}}}} $ 和ART的计算值Table 2.
$ \Delta {T_{{\text{R,NDT}}}} $ and ART at RPV Internal Surface运行时间/EFPY $ \Delta {T_{{\text{R,NDT}}}} $/℃ ART/℃ 堆芯
中平面上焊缝 堆芯带状区1/4壁厚 上焊缝1/4壁厚 堆芯
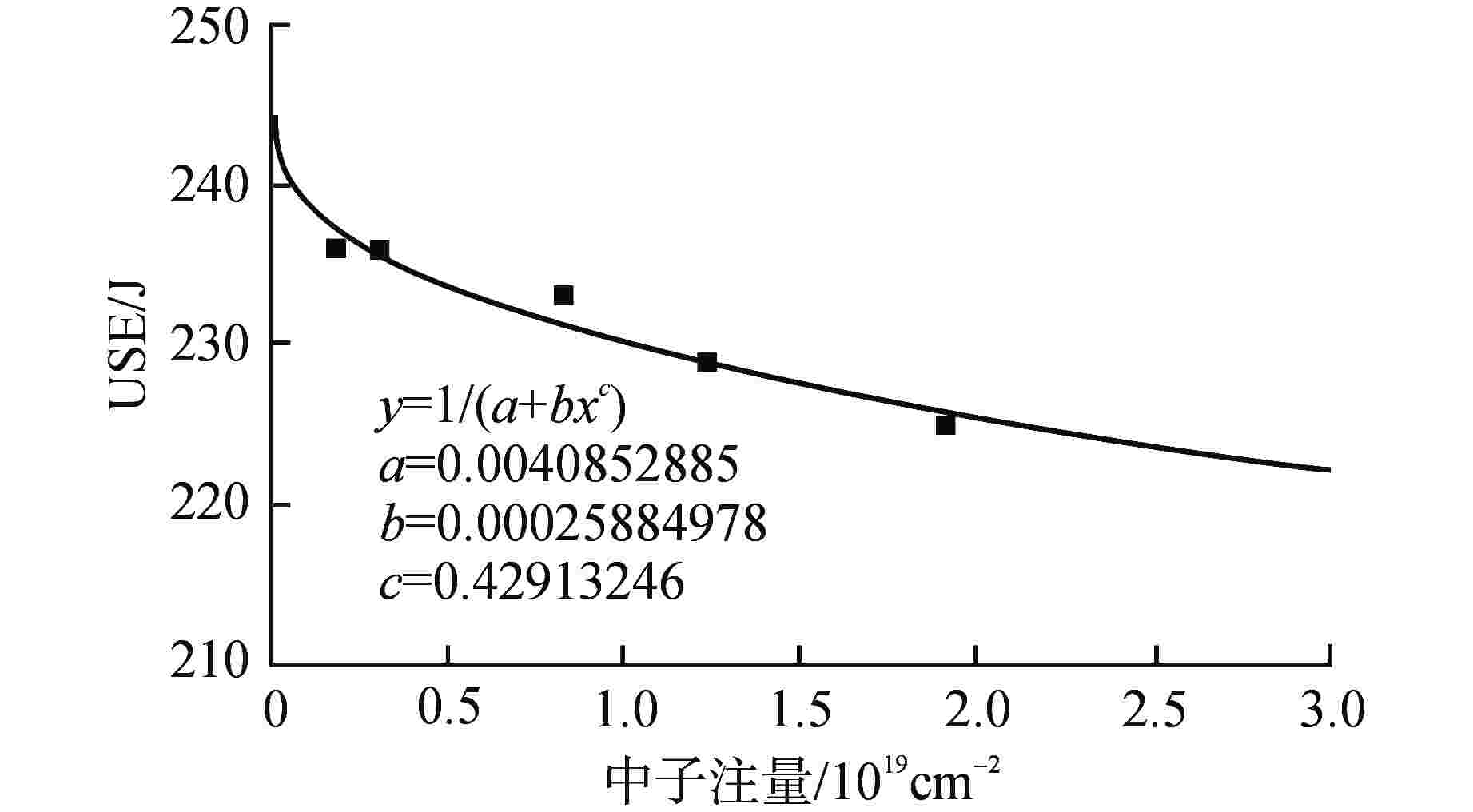
中平面上焊缝 堆芯带状区1/4壁厚 上焊缝1/4壁厚 40 66 15 56 12 70 19 60 16 50 72 18 61 14 76 22 65 18 60 77 20 66 15 81 24 70 19 表 3 不同运行时期RPV的USE
Table 3. USE of RPV at Different Operating Periods
参数名 参数值 运行时间/EFPY 40 50 60 USE/J 211 209 206 表 4 运行60 EFPY后RPV材料性能
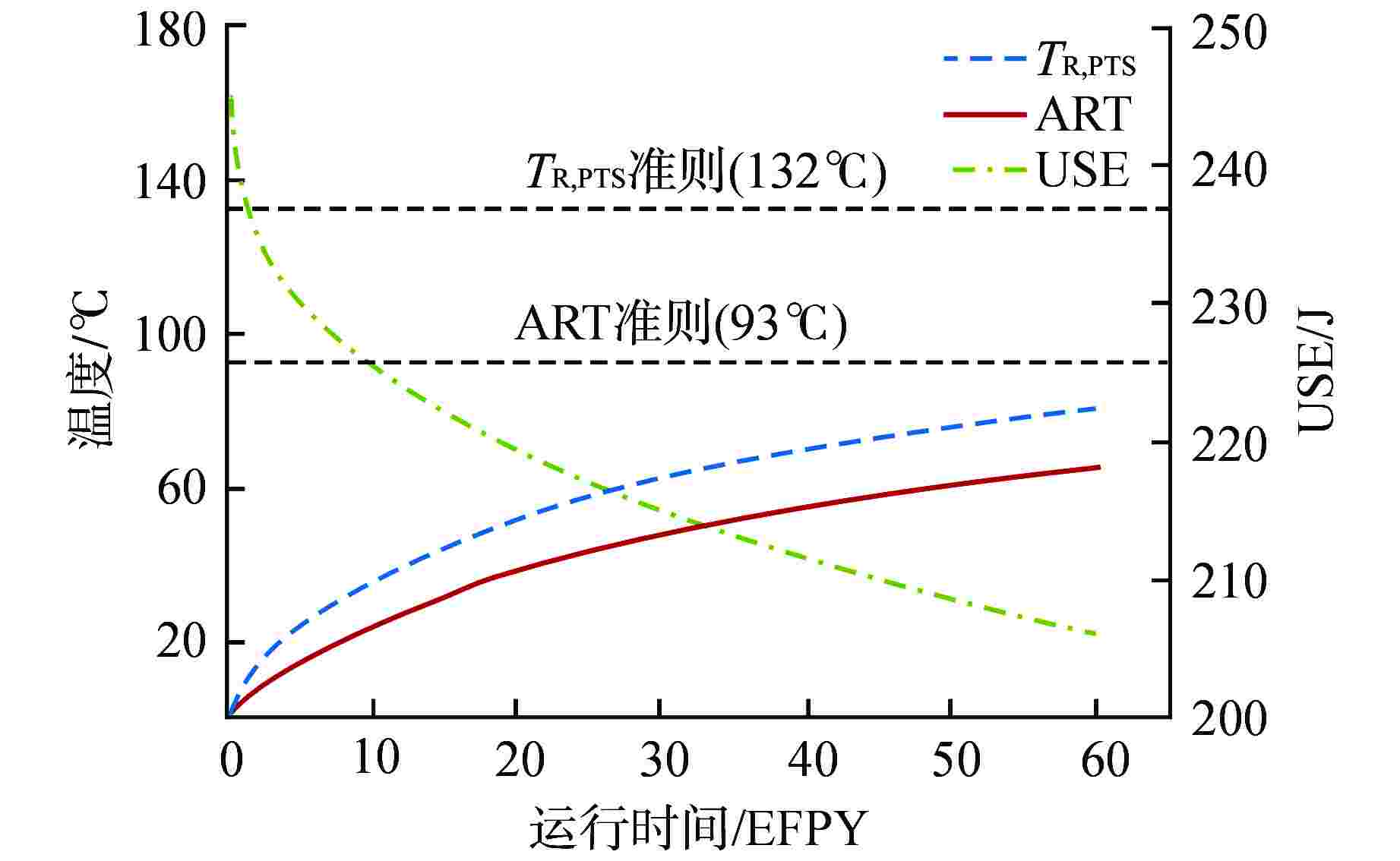
Table 4. RPV Material Properties at the End of 60 EFPY
RPV性能指标 预测
计算值寿期限值 引用规范 1/4壁厚处ART/℃ 70 93 RG1.99(2)
第三章USE/J 206 68 10CFR50 TR,PTS /℃ 81 132 10CFR50 -
[1] 杨文斗. 反应堆材料学[M]. 北京: 原子能出版社, 2006: 328. [2] American Society for Testing and Materials. Standard practice for design of surveillance programs for light-water moderated nuclear power reactor vessels: ASTM E185[S]. USA: ASTM Committee, 1982: 1-8. [3] U. S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission. Radiation embrittlement of reactor vessel materials, regulatory guide 1.99 revision 2: TASK ME 305-4[R]. Washington: U. S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission, 1988. [4] 日本原子力规则委员会. 核反应堆压力容器材料监督试验方法: JEAC 4201[S]. 日本: 日本电气协会, 1991:12-58. [5] TANON A P, GRANDEMANGE J, HOUSSIN B, et al. French verification of PWR vessel integrity: EPRI-NP--6713[R]. Palo Alto: Research Reports Center, 1990. [6] EASON E D, WRIGHT J E, ODETTE G R. Improved embrittlement correlations for reactor pressure vessel steels: NUREG/CR-6551[R]. Washington: U. S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission, 1998. [7] SERVER W L, ENGLISH C A, NAIMAN D Q, et al. Charpy embrittlement correlations – status of combined mechanistic and statistical bases for U. S. RPV steels: EPRIMRP-45[R]. Palo Alto: Electric Power Research Institute, 2001. [8] EASON E D, ODETTE G R, NANSTAD R K. A Physically based correlation of irradiation-induced transition temperature shifts for RPV steels: ORNL/TM-2006/530[R]. Tennessee: Oak Ridge National Laboratory, 2006 [9] ERICKSONKIRK M. A review of ∆T30 data for reactor pressure vessel steels obtained at high fluence[J]. J ASTM Intl., 2009: JAI102000-8. [10] 佟振峰,林虎,宁广胜,等. 低铜合金反应堆压力容器钢辐照脆化预测评估模型[J]. 原子能科学技术,2009, 43(S1): 103-108. [11] American Society for Testing and Materials. Standard practice for extrapolating reactor vessel surveillance dosimetry results: ASTM E560[S]. USA: ASTM Committee, 2001: 1-5 [12] U. S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission. 10CFR Part50 domestic licensing of production and utilization facilities, appendix A[Z]. USA: Nuclear Regulatory Commission, 2021. -





 下载:
下载: