The Deep Learning Method to Search Effective Multiplication Factor of Nuclear Reactor Directly
-
摘要: 求解有效增殖系数(keff)是核反应堆临界计算的基本问题,目前业界普遍采用源迭代方法进行求解。本文基于人工智能深度学习方法求解微分方程的基础理论,提出将keff与神经网络各神经元权重共同作为机器学习优化参数,针对将神经网络函数代入中子学微分方程形成的加权损失函数进行深度学习计算,同时进行中子注量率逼近与keff直接搜索求解的新方法。讨论了中子学微分方程特征值数理形式、初始神经网络设定方法、损失函数加权因子、收敛准则等影响深度学习性能的重要因素及相应的性能提升策略;通过多种算例的数值计算验证了该方法的正确性,以及学习性能提升策略的有效性。研究成果为核反应堆求解keff这一中子学物理重要科学问题探索出了一条新的技术途径。
-
关键词:
- 有效增殖系数 /
- 人工智能深度学习方法 /
- 中子学微分方程 /
- 加权损失函数 /
- 性能提升策略
Abstract: It's a basic problem in the reactor criticality calculation to determine the effective multiplication factor keff. At present, the source iteration method is widely used in the industry. Based on the theory of artificial intelligence deep learning method to solve differential equations, this paper puts forward a new method, which takes keff and the weights of neural network neurons as machine learning optimization parameters, calculates the weighted loss function formed by substituting neural network functions into neutron differential equations, and simultaneously approaches neutron fluence rate and searches for keff directly. The mathematical form of eigenvalue of neutron differential equation, the setting method of initial neural network, the weighting factor of loss function, convergence criterion and other important factors affecting deep learning performance and the corresponding performance improvement schemes are discussed. The correctness of the method and the effectiveness of the learning performance improvement schemes are verified by numerical calculation of various examples. The results have explored a new technical way to calculate the keff of nuclear reactors, which is an important scientific problem in neutron physics. -
表 1 一维平板几何单群单材料扩散问题计算结果
Table 1. Calculation Results of One-Dimensional Slab Single Group Single Material Diffusion Problem
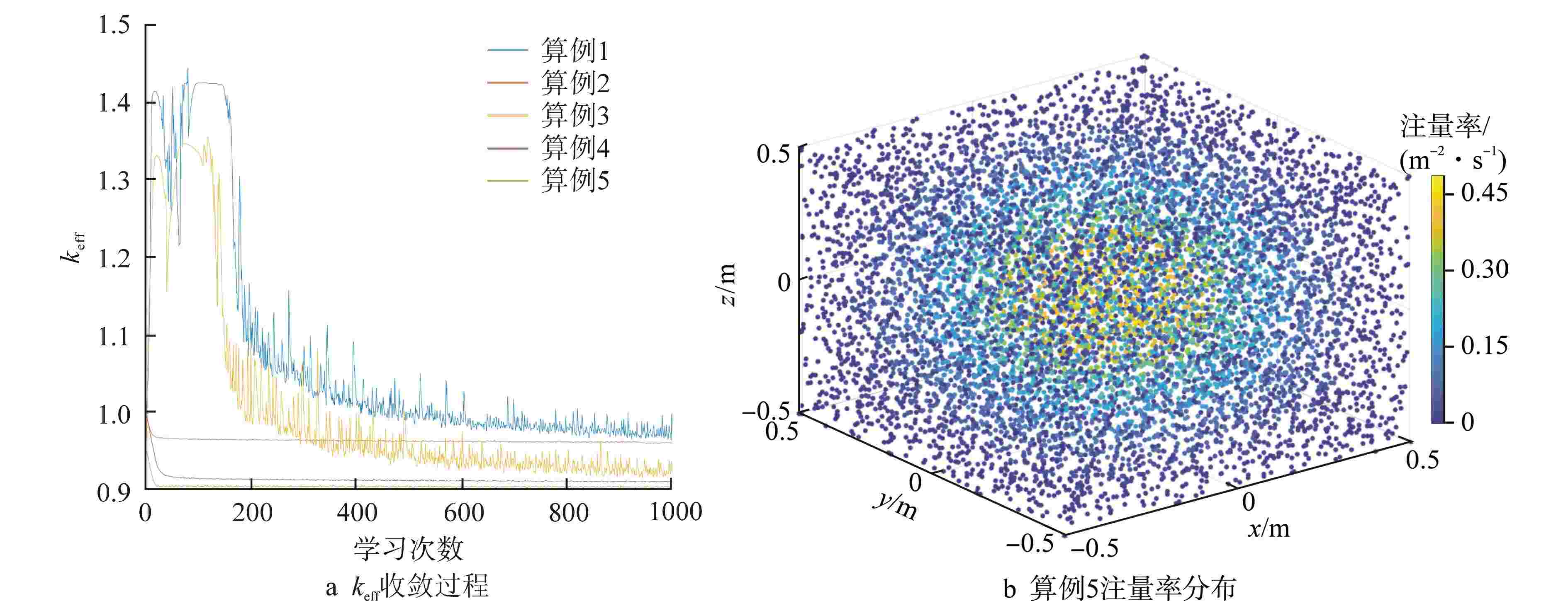
算例 k∞ keff_r Pb Pt keff_s keff_rel DLoss σMSE σSEi,max 1 1.425 0.95 50 50 0.9777 0.0292 0.0179 1.0054×10−4 4.4461×10−4 2 1.425 0.95 30 30 0.9856 0.0375 0.0229 2.1839×10−4 9.7300×10−4 3 1.425 0.95 10 10 0.9852 0.0371 0.0110 3.1139×10−4 0.00142 4 1.425 0.95 50 10 0.9596 0.0101 0.0035 1.7543×10−5 5.2826×10−5 5 1.425 0.95 10 50 0.9886 0.0406 0.0108 4.4073×10−4 0.0018 6 1.425 0.95 10~50* 10~50* 0.9499 −1.0526×10−4 1.2418×10−4 2.3044×10−8 1.0789×10−7 7 1.575 1.05 50 50 1.0983 0.0460 0.0439 2.3015×10−4 0.0011 8 1.575 1.05 30 30 1.0546 0.0044 9.5737×10−4 3.6342×10−6 1.5015×10−5 9 1.575 1.05 10 10 1.0522 0.0021 1.7608×10−4 1.266×10−6 5.2569×10−6 10 1.575 1.05 50 10 1.0674 0.0166 0.0075 3.3881×10−5 1.4986×10−4 11 1.575 1.05 10 50 1.0538 0.0036 2.7161×10−4 3.9332×10−6 1.5473×10−5 12 1.575 1.05 10~50* 10~50* 1.0501 9.5238×10−5 1.7485×10−4 1.3314×10−8 5.7686×10−8 *—权重随机;keff_r —keff理论值;keff_s— keff实际求解值;keff_rel —keff相对偏差,keff_rel =(keff_s−keff_r)/keff_r;σMSE—中子注量率平均方差,即机器学习方法求出的各空间离散点注量率数值解与解析解的方差平均值;σSEi,max—中子注量率最大方差,即空间离散点中注量率数值解与解析解方差的最大值 表 2 两维圆柱几何单群单材料扩散问题计算结果
Table 2. Calculation Results of Two-Dimensional Cylindrical Geometry Single Group Single Material Diffusion Problem
算例 k∞ keff_r Pb Pt keff_s keff_rel DLoss σMSE σSEi,max 1 1.350 0.900 50 50 0.9025 0.0028 4.6361×10−4 1.3725×10−6 2.4390×10−5 2 1.350 0.900 30 30 0.9005 5.5555×10−4 4.7125×10−5 6.7853×10−8 1.3253×10−6 3 1.350 0.900 10 10 0.9095 0.0106 0.0027 4.3597×10−5 6.3004×10−4 4 1.350 0.900 10~50* 10~50* 0.9009 0.0010 0.0084 2.6671×10−6 3.8331×10−5 5 1.650 1.100 50 50 1.1095 0.0086 0.0113 3.8655×10−5 6.5992×10−4 6 1.650 1.100 30 30 1.1070 0.0064 0.0024 1.4379×10−5 2.2977×10−4 7 1.650 1.100 10 10 1.1024 0.0022 5.1359×10−4 5.7976×10−6 4.1215×10−5 8 1.650 1.100 10~50* 10~50* 1.1034 0.0031 0.0016 2.3881×10−6 2.1793×10−5 表 3 三维立方体几何单群单材料扩散问题计算结果
Table 3. Calculation Rresults of Three-dimensional Cubic Geometry Single Group Single Material Diffusion Problem
算例 k∞ keff_r 初始网络 keff_s keff_rel DLoss σMSE σSEi,max 1 1.425 0.95 k=1,随机网络 0.9588 0.0093 0.0013 2.3236×10−5 2.0309×10−4 2 1.425 0.95 k=1,已收敛网络 0.9549 0.0052 0.0021 1.5792×10−5 1.2297×10−4 3 1.350 0.90 k=1,随机网络 0.9039 0.0043 0.0070 1.2244×10−4 9.5364×10−4 4 1.350 0.90 k=1,已收敛网络 0.9046 0.0051 0.0033 4.4672×10−5 2.4292×10−4 5 1.350 0.90 算例2已收敛网络与k 0.9038 0.0042 0.0017 2.1639×10−5 1.4398×10−4 表 4 计算区域材料特性
Table 4. Calculate Area Material Properties
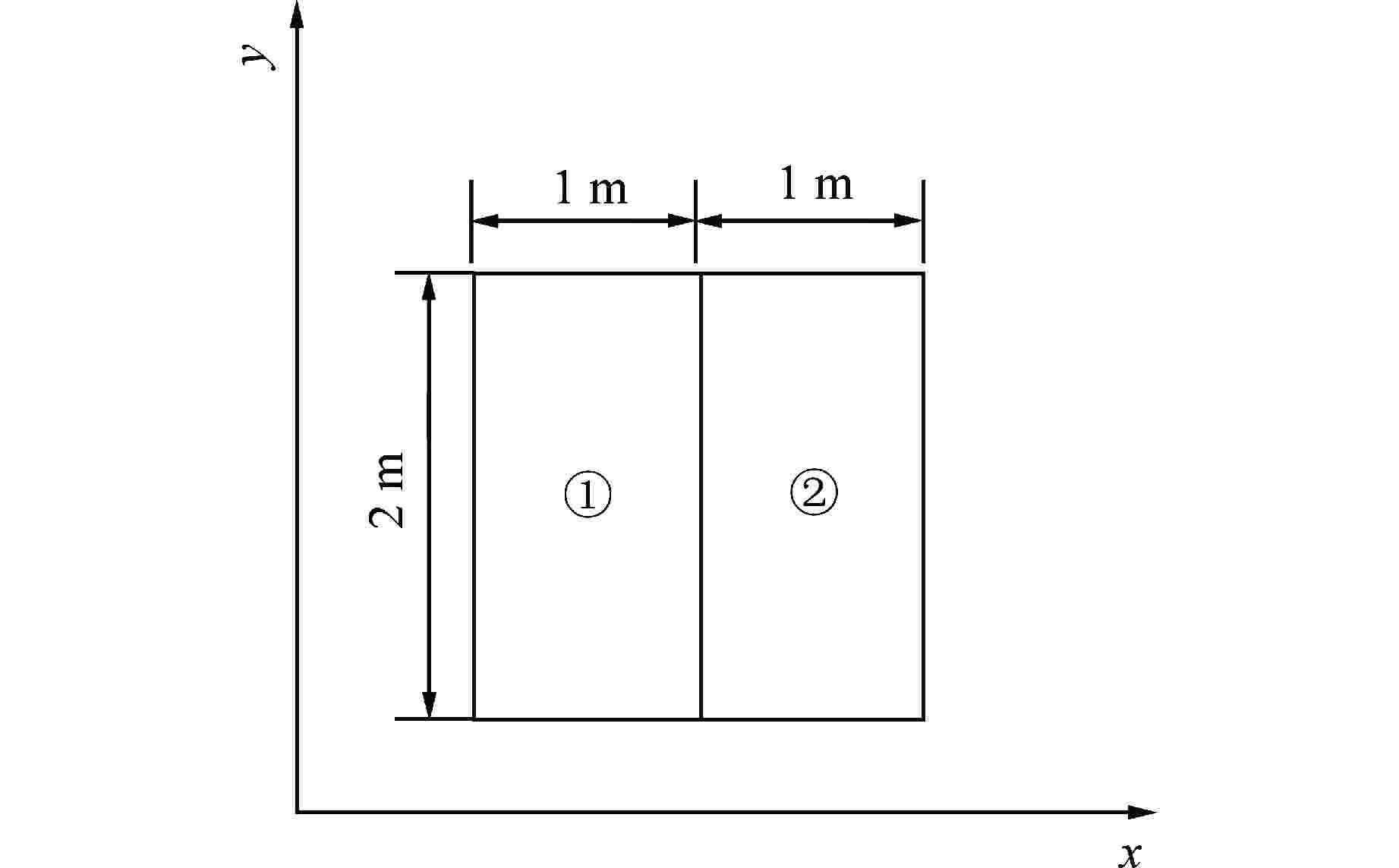
材料号 能群 Dg/cm $ {\varSigma _{\text{a}}} $/cm−1 $ \nu {\varSigma _{\text{f}}} $/cm−1 ${\varSigma _{{1 \to 2} } }$/cm−1 ① 1 1.268 0.007181 0.004609 0.02767 2 0.1902 0.07047 0.08675 ② 1 1.255 0.008252 0.004602 0.02533 2 0.211 0.1003 0.1091 表 5 两维长方形几何多群多材料扩散问题计算结果
Table 5. Calculation Results of Two-Dimensional Rectangular Geometry Multi Group Multi Material Diffusion Problem
机器学习获得的keff_s 快群DLoss的MSE 热群DLoss的MSE CORCA-3D PARCS DNTR keff计算值 相对偏差 keff计算值 相对偏差 keff计算值 相对偏差 1.0660 2.0985×10−4 4.5409×10−5 1.0690 0.0028 1.0710 0.0047 1.0712 0.0049 MSE—均方误差 表 6 一维平板几何单群输运问题特征值计算结果
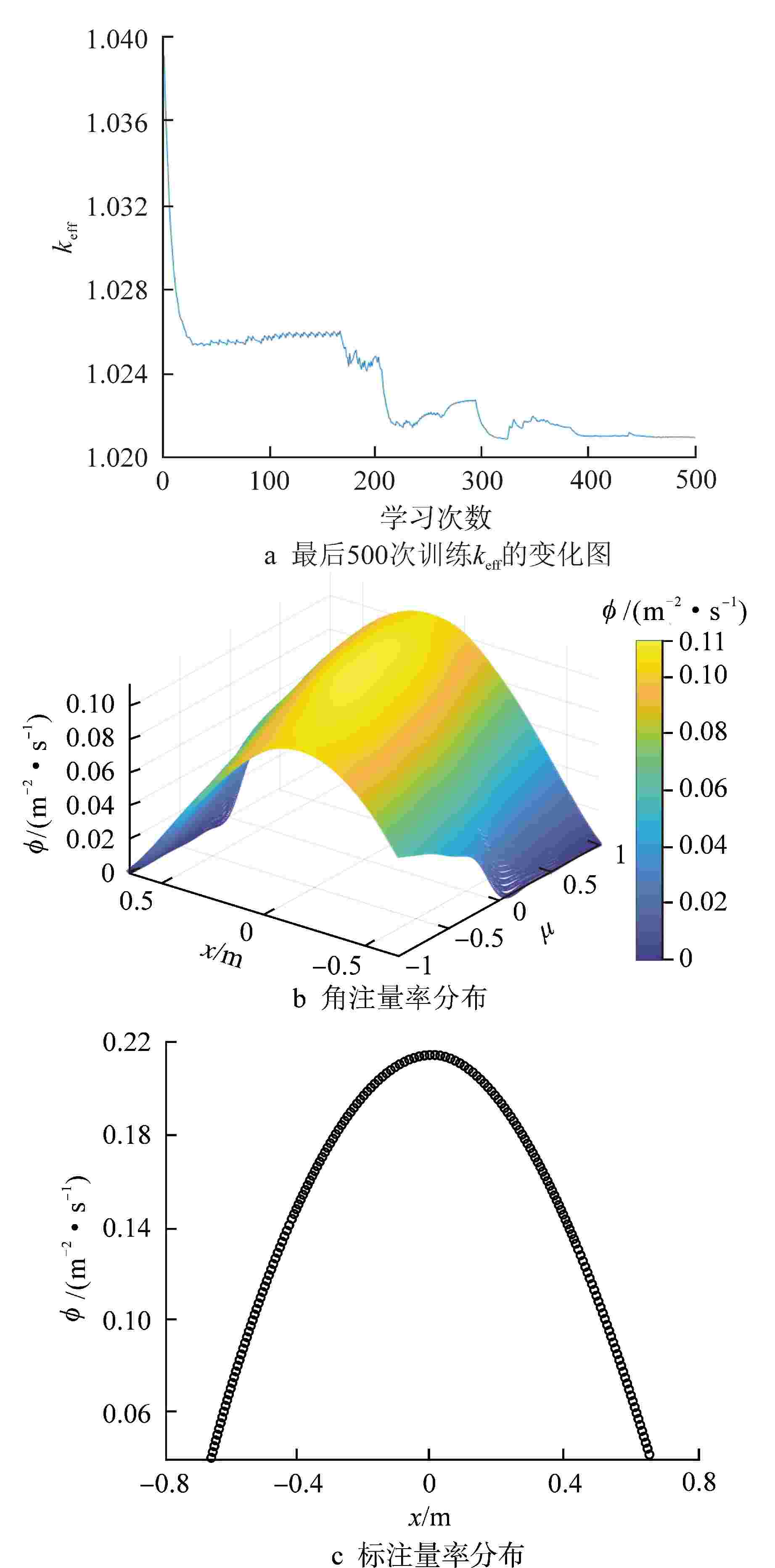
Table 6. Eigenvalue Calculation Result of One-Dimensional Slab Geometry Single Group Transport Problem
机器学习获得的keff Δ 相对偏差 结束时DLoss函数σMSE 1.0210 1.0200 0.00098039 1.2538×10−5 -
[1] 谢仲生, 曹良志, 张少泓. 核反应堆物理分析[M]. 第五版. 西安: 西安交通大学出版社, 2020: 69-90. [2] 谢仲生, 邓力. 中子输运理论数值计算方法[M]. 西安: 西北工业大学出版社, 2005: 11-50. [3] XIE Y C, WANG Y H, MA Y, et al. Neural network based deep learning method for multi-dimensional neutron diffusion problems with novel treatment to boundary[J]. Journal of Nuclear Engineering, 2021, 2(4): 533-552. doi: 10.3390/jne2040036 [4] RAISSI M, PERDIKARIS P, KARNIADAKIS G E. Physics-informed neural networks: a deep learning framework for solving forward and inverse problems involving nonlinear partial differential equations[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2019, 378: 686-707. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2018.10.045 [5] 刘东,罗琦,唐雷,等. 基于PINN深度机器学习技术求解多维中子学扩散方程[J]. 核动力工程,2022, 43(2): 1-8. doi: 10.13832/j.jnpe.2022.02.0001 [6] GALIB S M, BHOWMIK P K, AVACHAT A V, et al. A comparative study of machine learning methods for automated identification of radioisotopes using NaI gamma-ray spectra[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 2021, 53(12): 4072-4079. doi: 10.1016/j.net.2021.06.020 [7] 周蜀林. 偏微分方程[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 2005: 1-16. [8] HAGAN M T, DEMUTH H B, BEALE M H, et al. Neural network design[M]. 2nd ed. Oklahoma: Martin Hagan, 2014: (2-1)-(2-25). [9] BYRD R H, GILBERT J C, NOCEDAL J. A trust region method based on interior point techniques for nonlinear programming[J]. Mathematical Programming, 2000, 89(1): 149-185. doi: 10.1007/PL00011391 [10] DUMOUCHEL W H, O'BRIEN F L. Integrating a robust option into a multiple regression computing environment[C]//Computer Science and Statistics: Proceedings of the 21st Symposium on the Interface. Alexandria, VA: American Statistical Association, 1989: 41-48. [11] KINGMA D P, BA J. Adam: a method for stochastic optimization[C]//Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations. San Diego, 2014: 1-15. [12] 杨强, 张宇, 戴文渊, 等. 迁移学习[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2020: 2-79. [13] AN P, MA Y Q, XIAO P, et al. Development and validation of reactor nuclear design code CORCA-3D[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 2019, 51(7): 1721-1728. doi: 10.1016/j.net.2019.05.015 [14] DOWNAR T, XU Y, SEKER V. PARCS v3.0 US NRC core neutronics simulator theory manual[M]. Rockville, MD: US NRC, 2012: 5-98. [15] 卢皓亮,吴宏春,曹良志,等. 中子输运方程的三角形节块SN方法研究[J]. 核动力工程,2006, 27(5): 6-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0926.2006.05.002 [16] 杜书华. 输运问题的计算机模拟[M]. 长沙: 湖南科学技术出版社, 1988: 130-150, 304-345. -





 下载:
下载: