Analysis of Correlation Between Reaction and Flow Loss of Helium Compressor
-
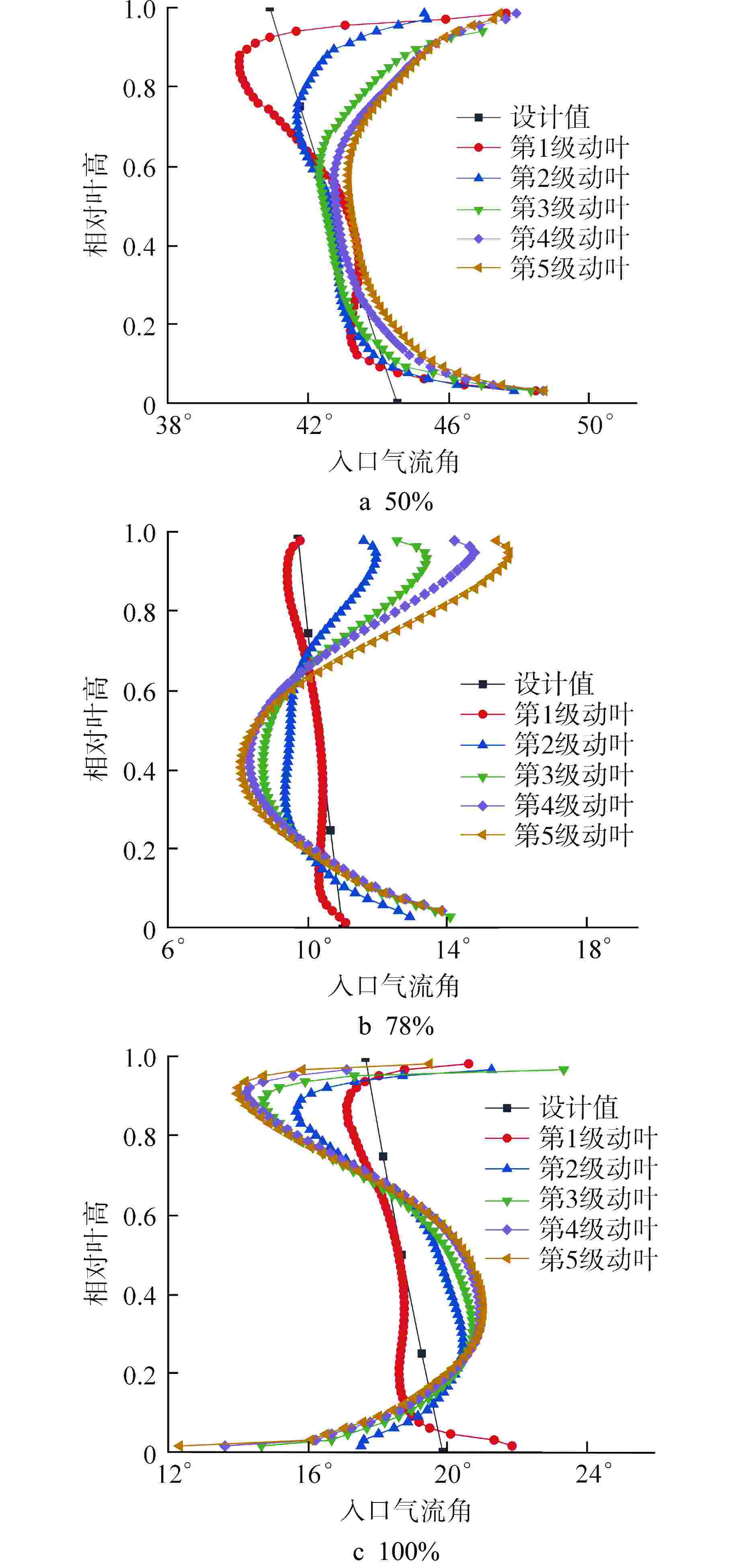
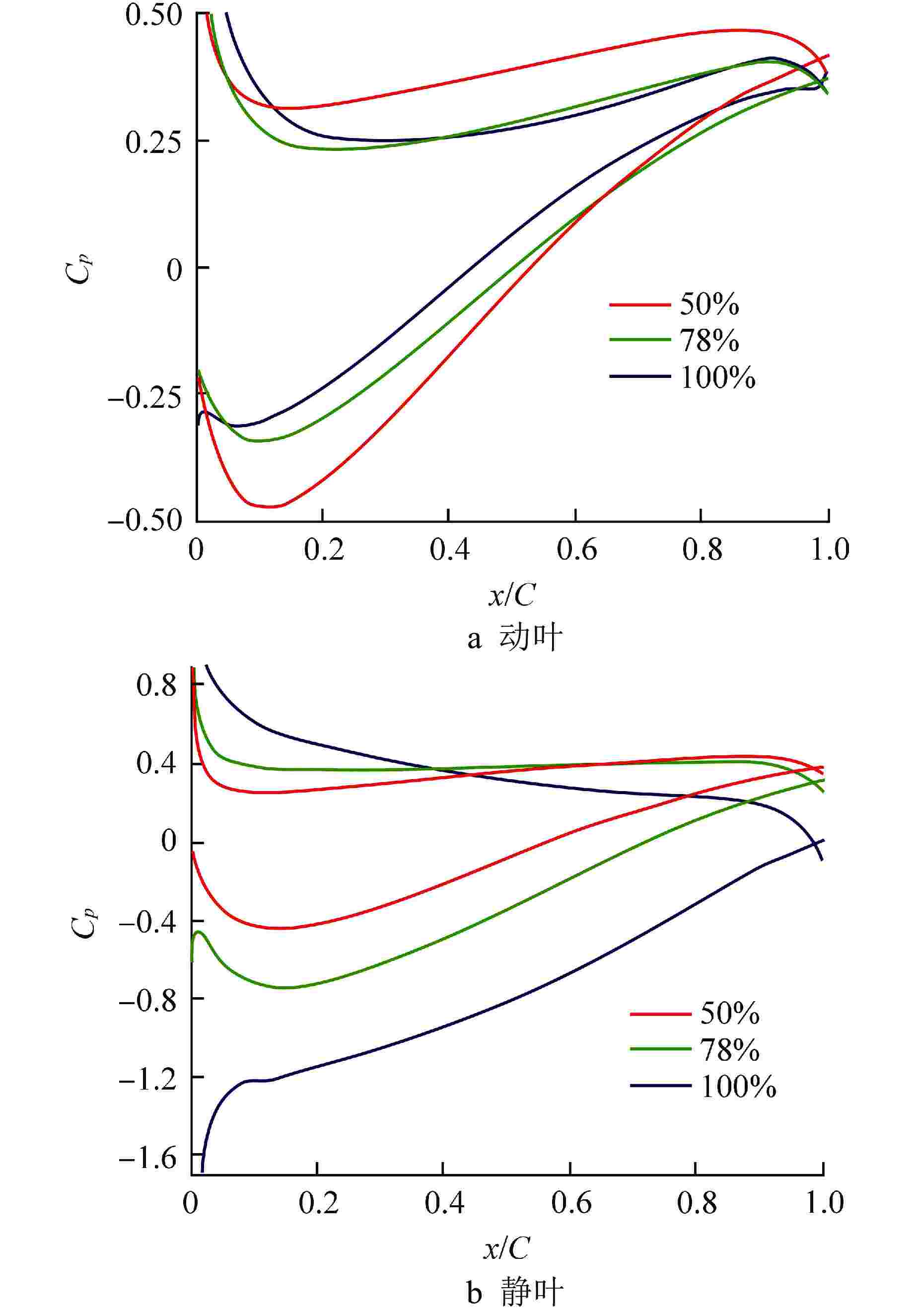
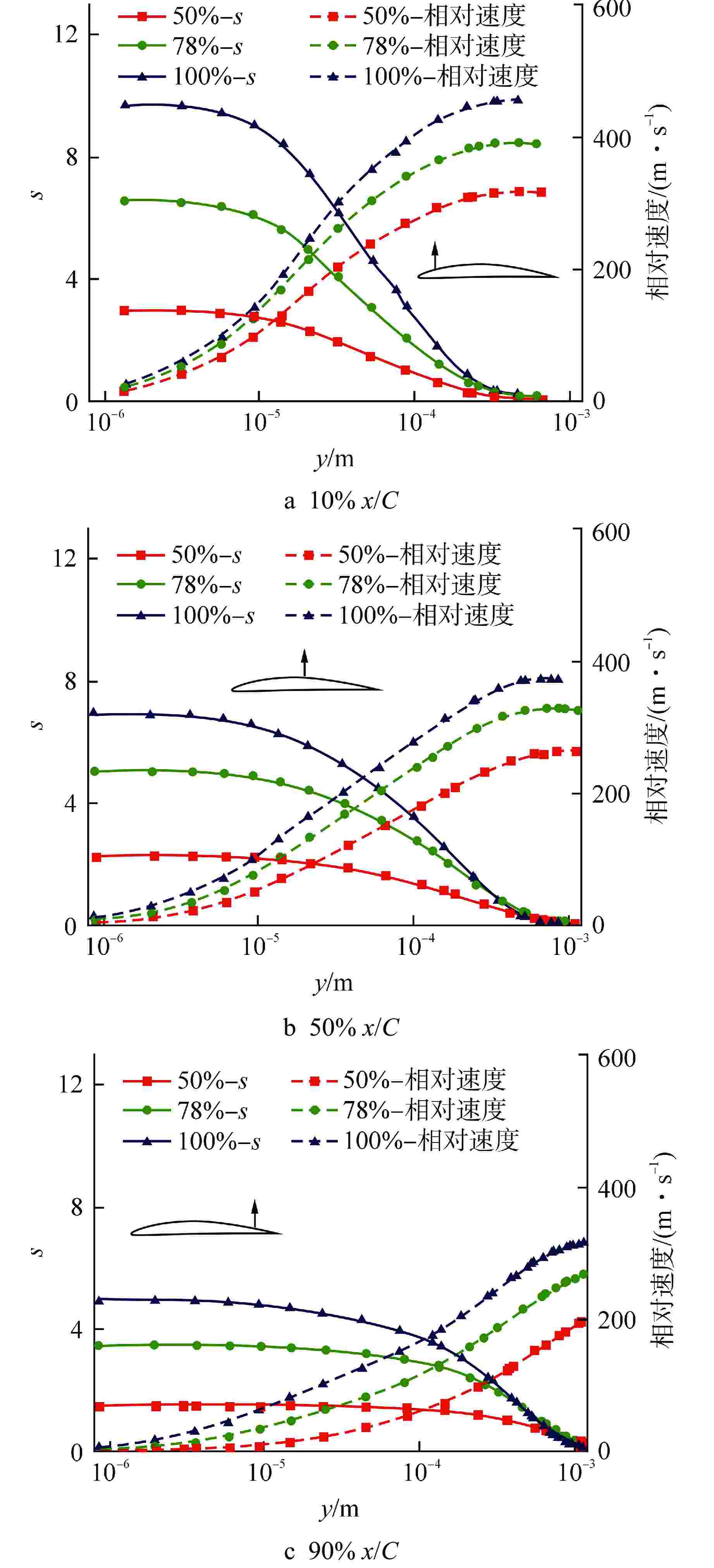
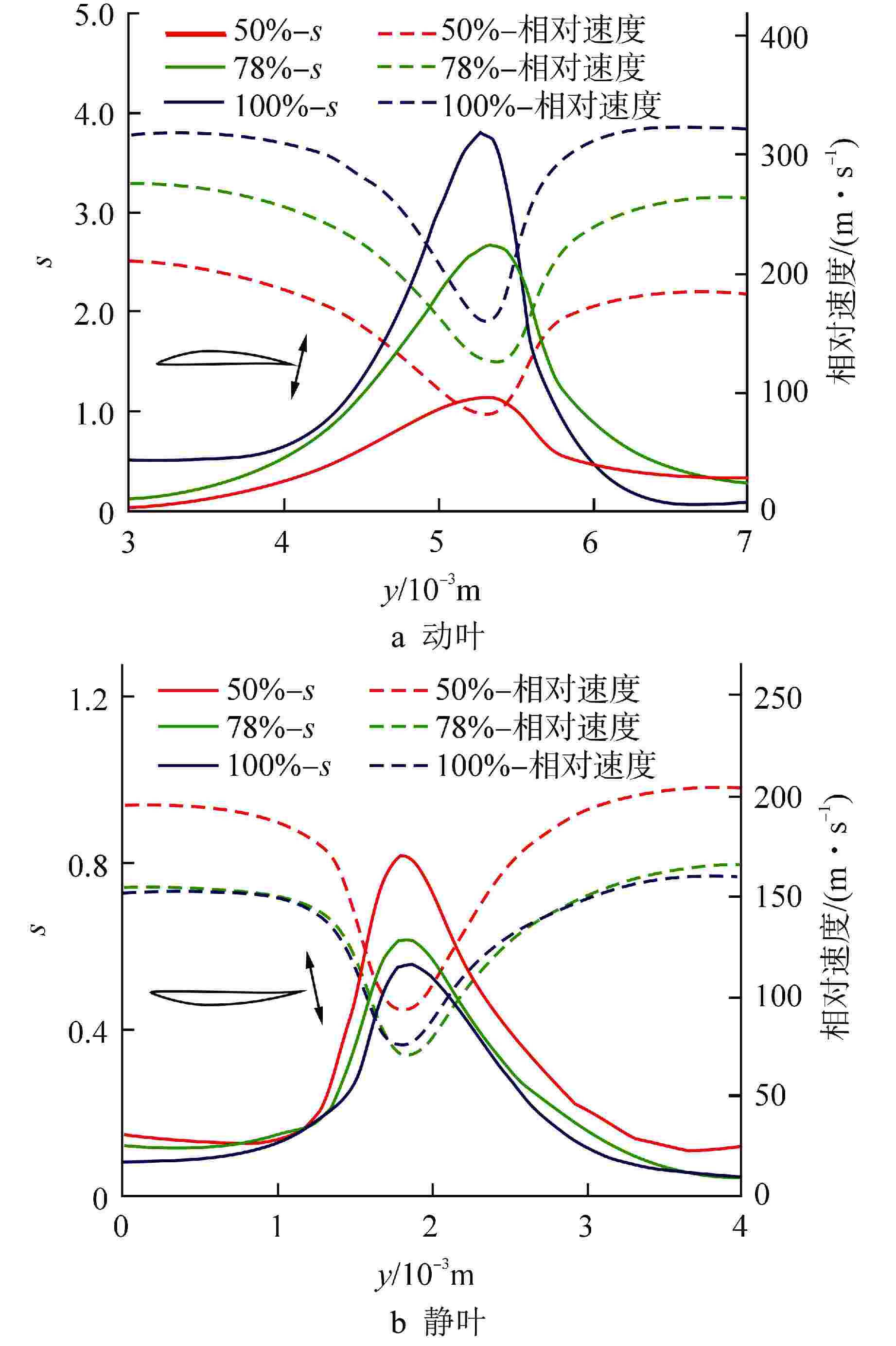
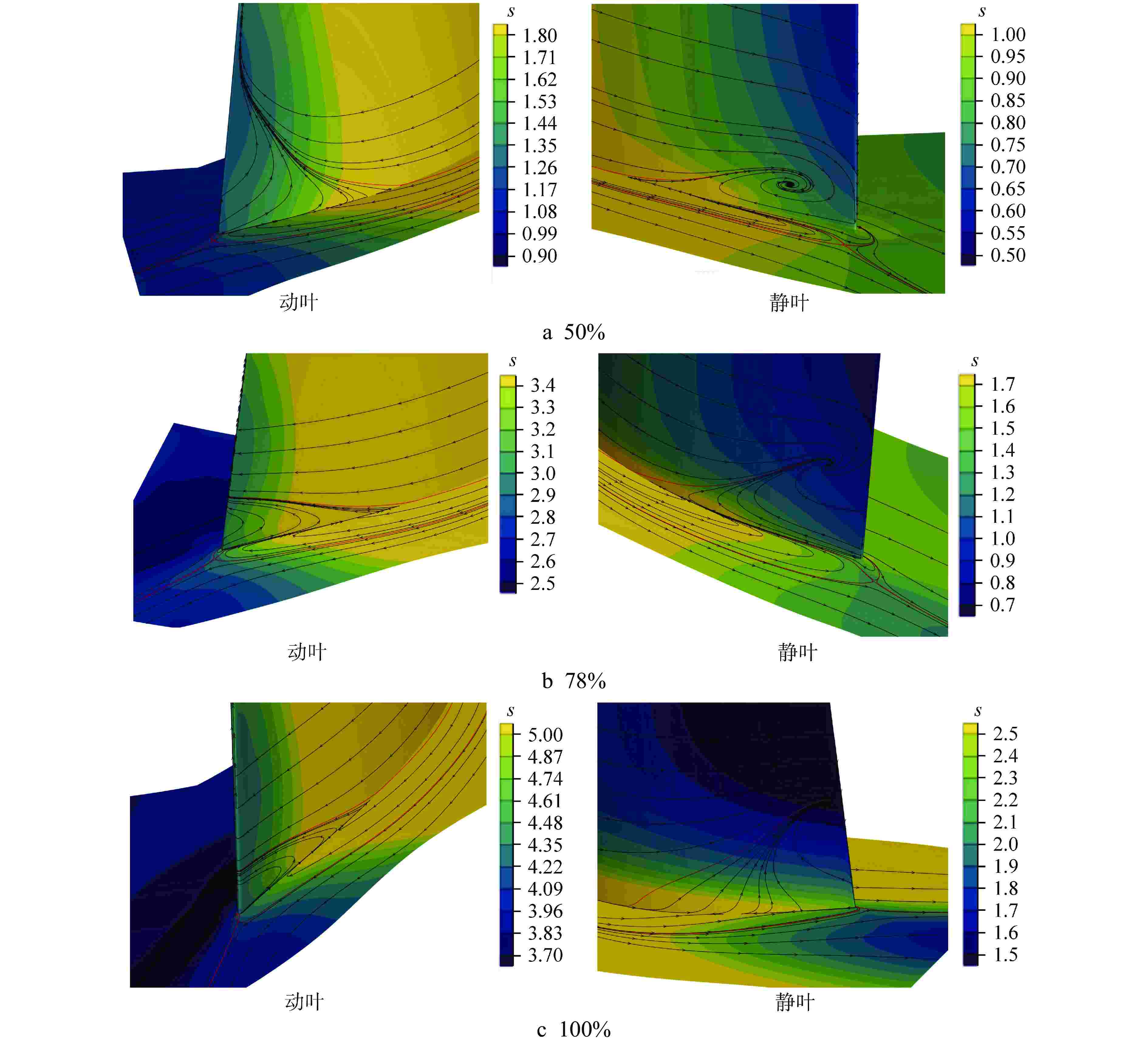
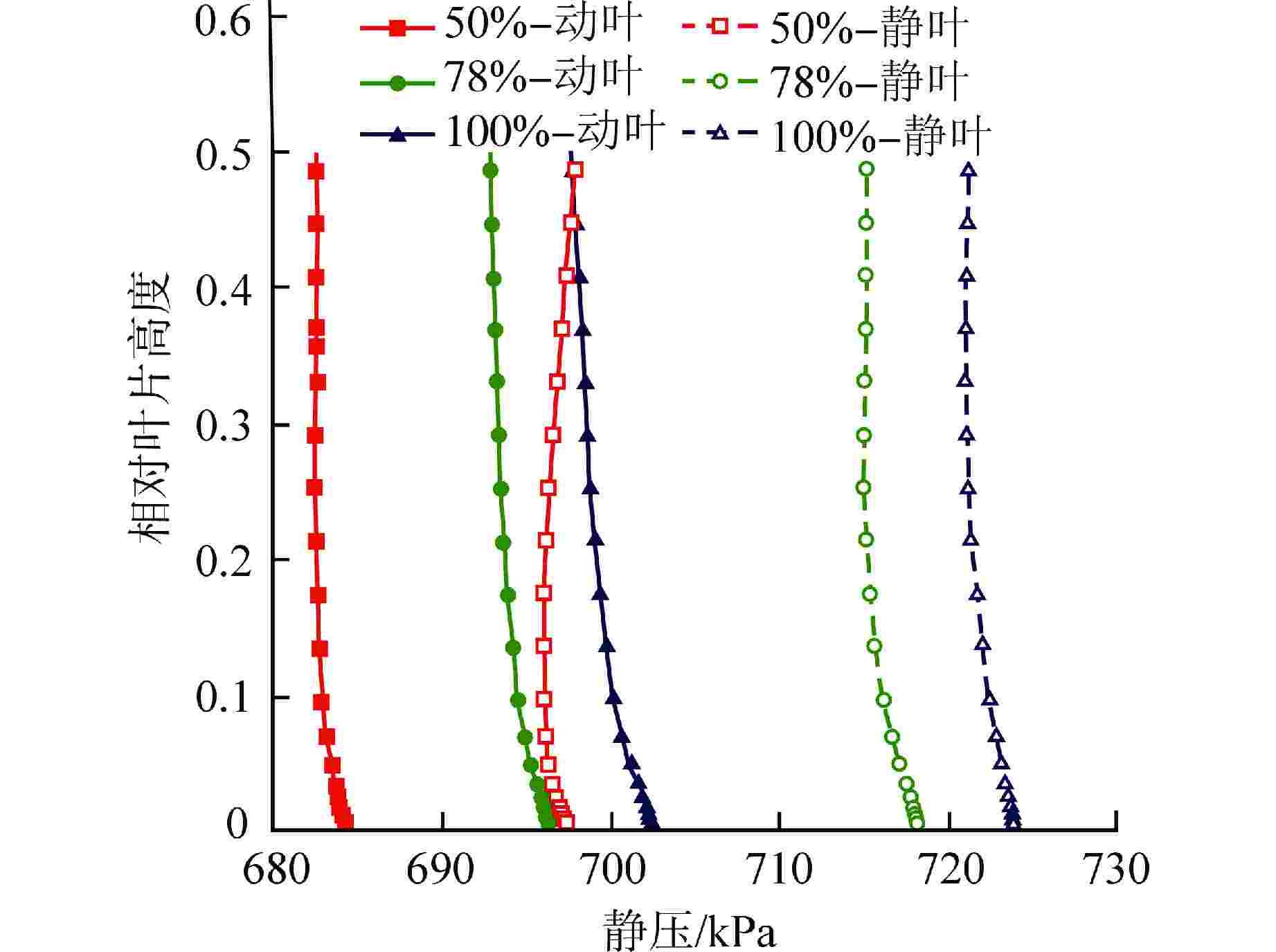
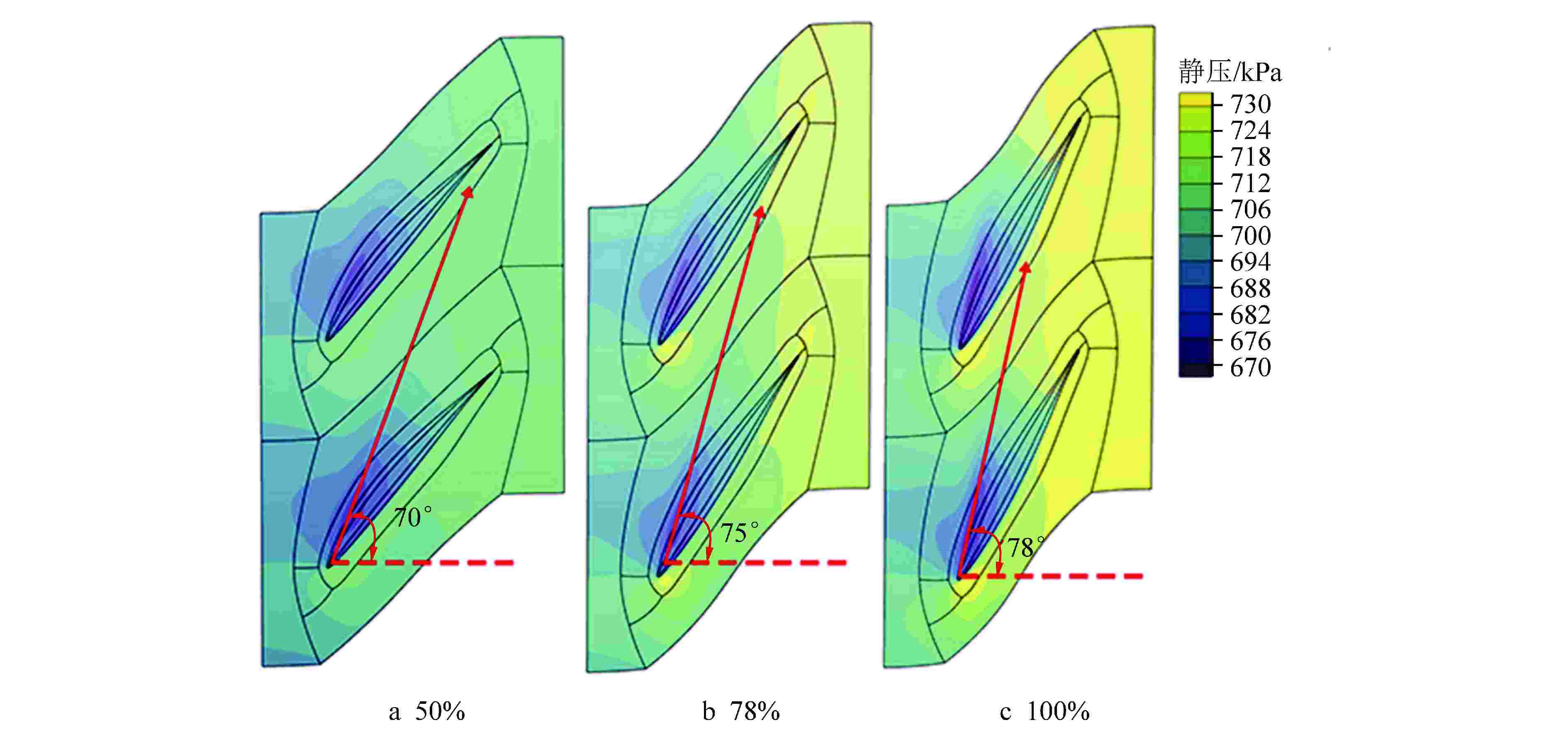
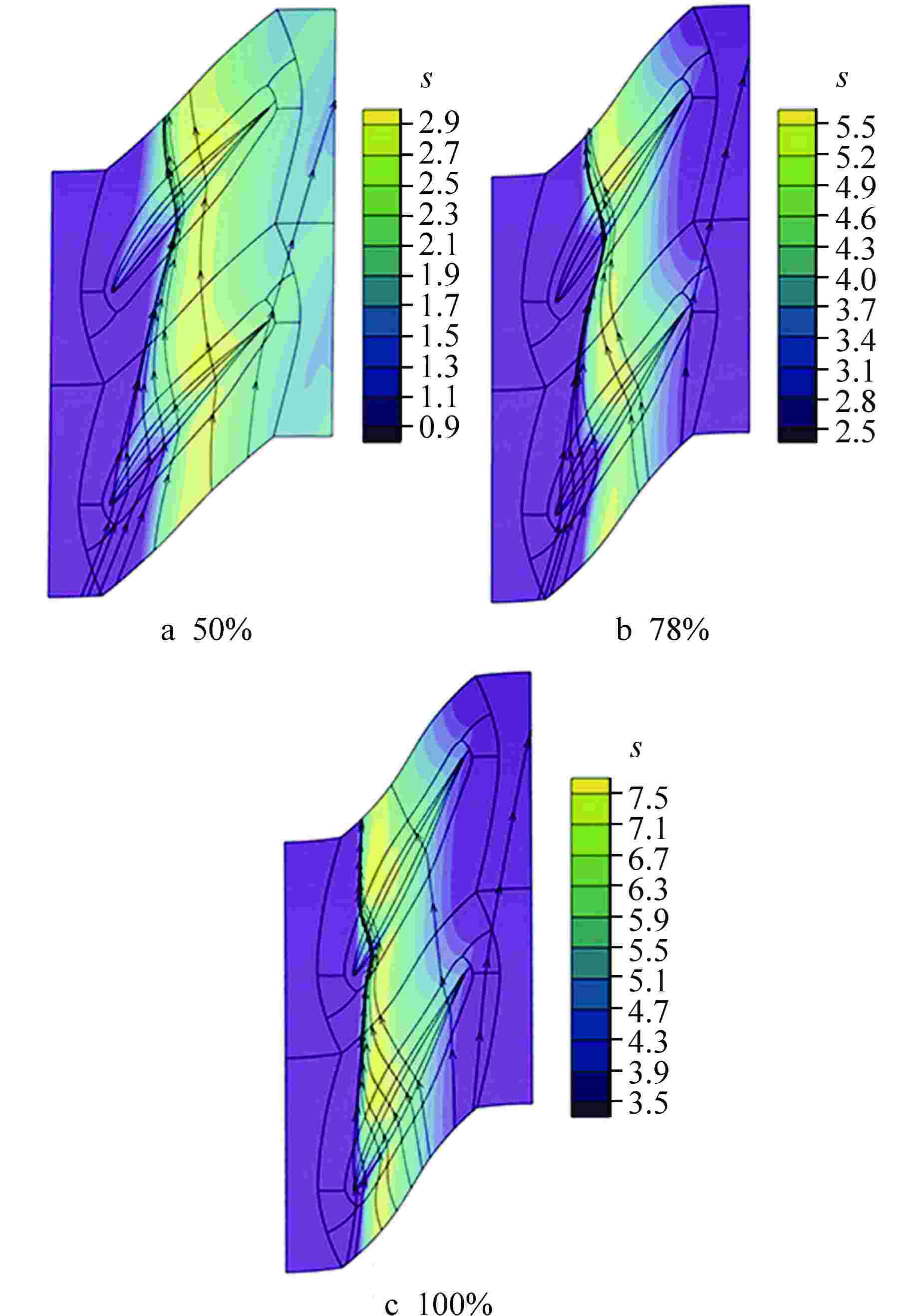
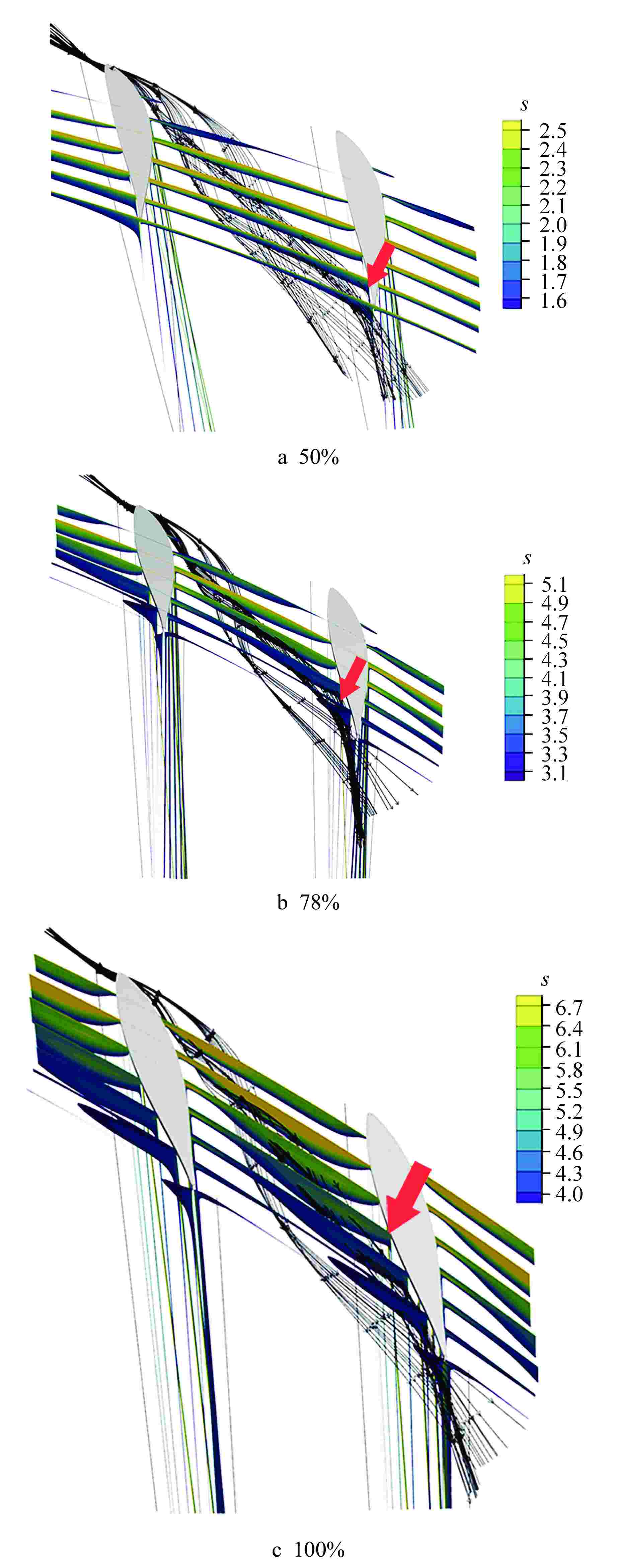
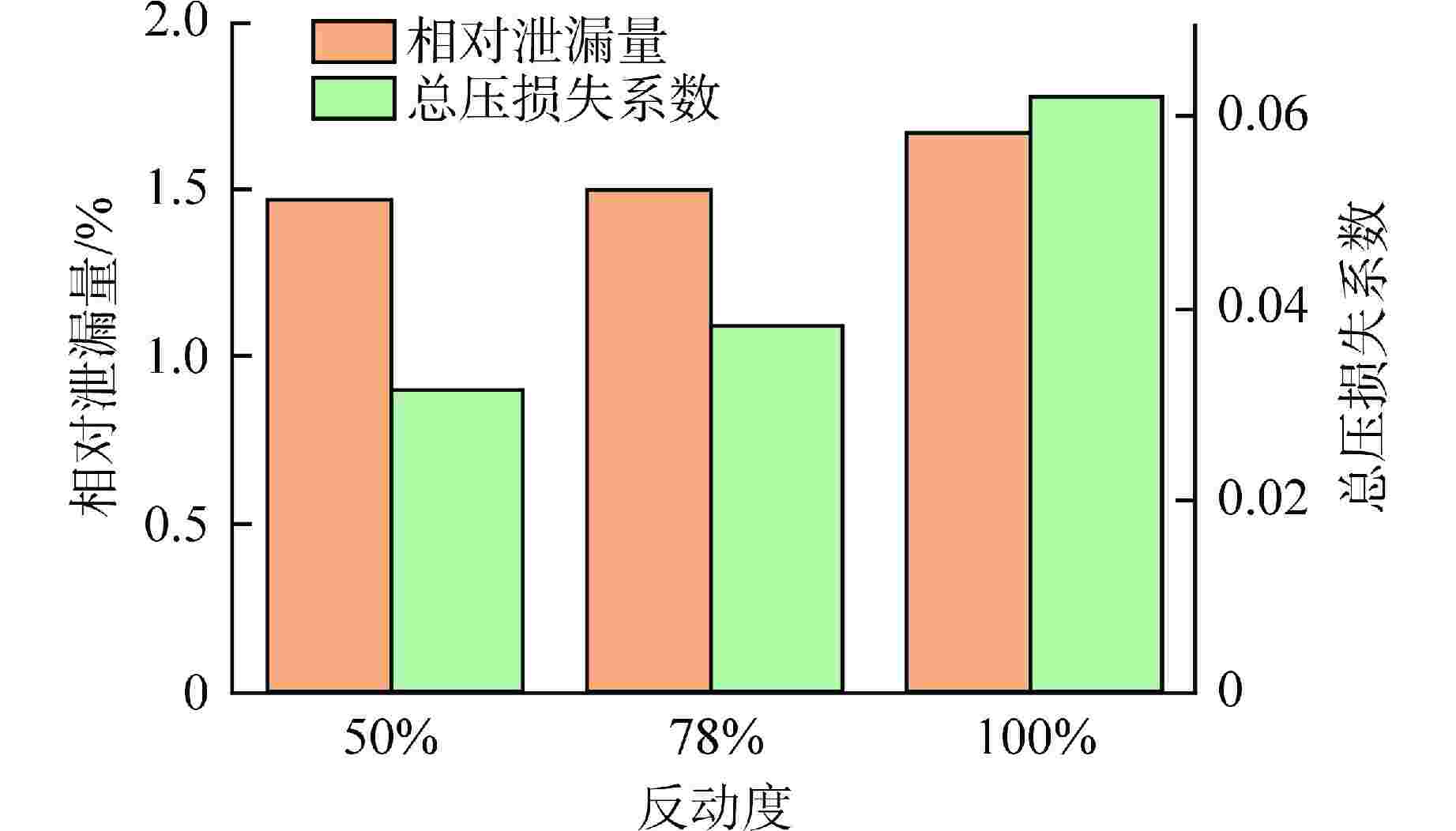
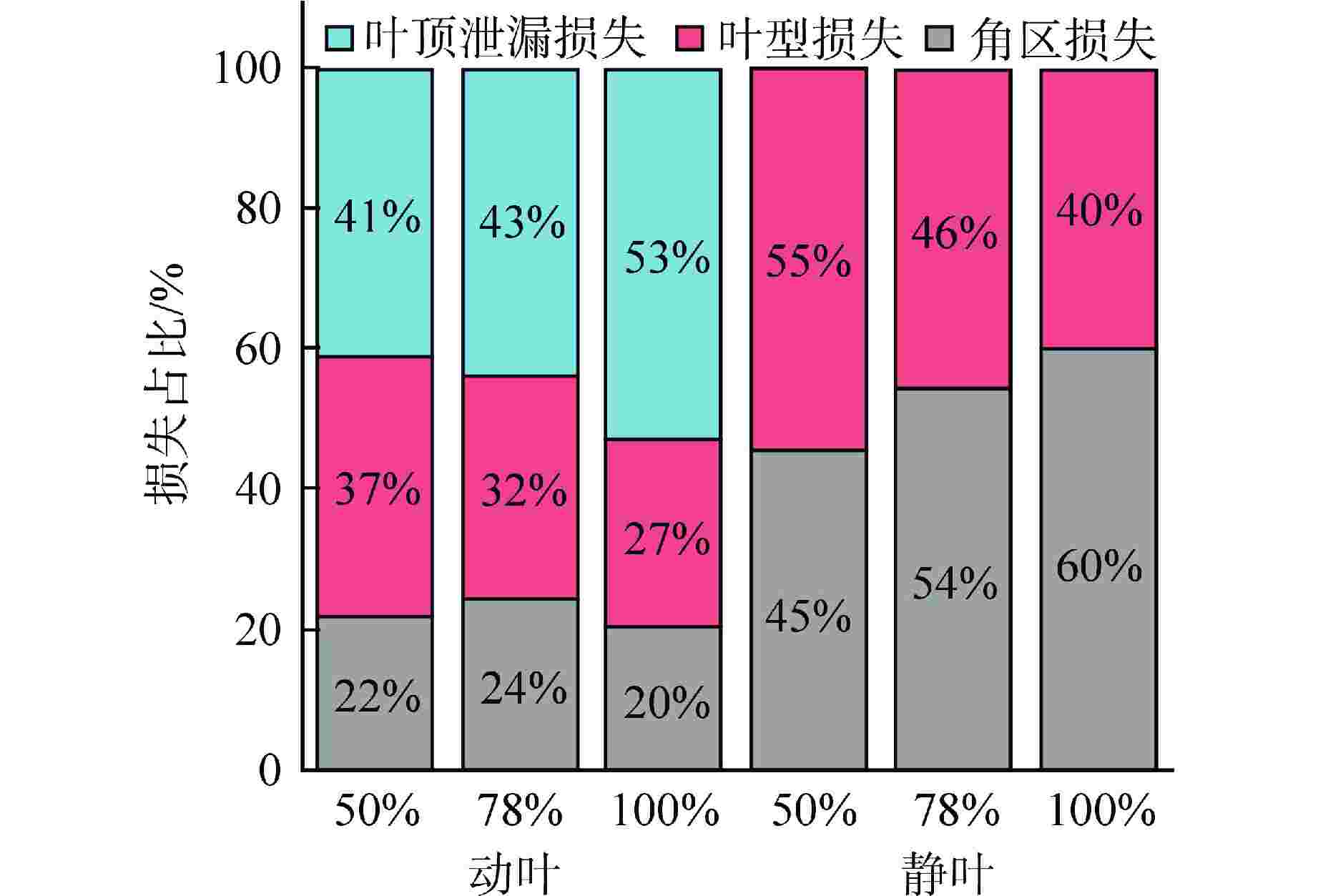
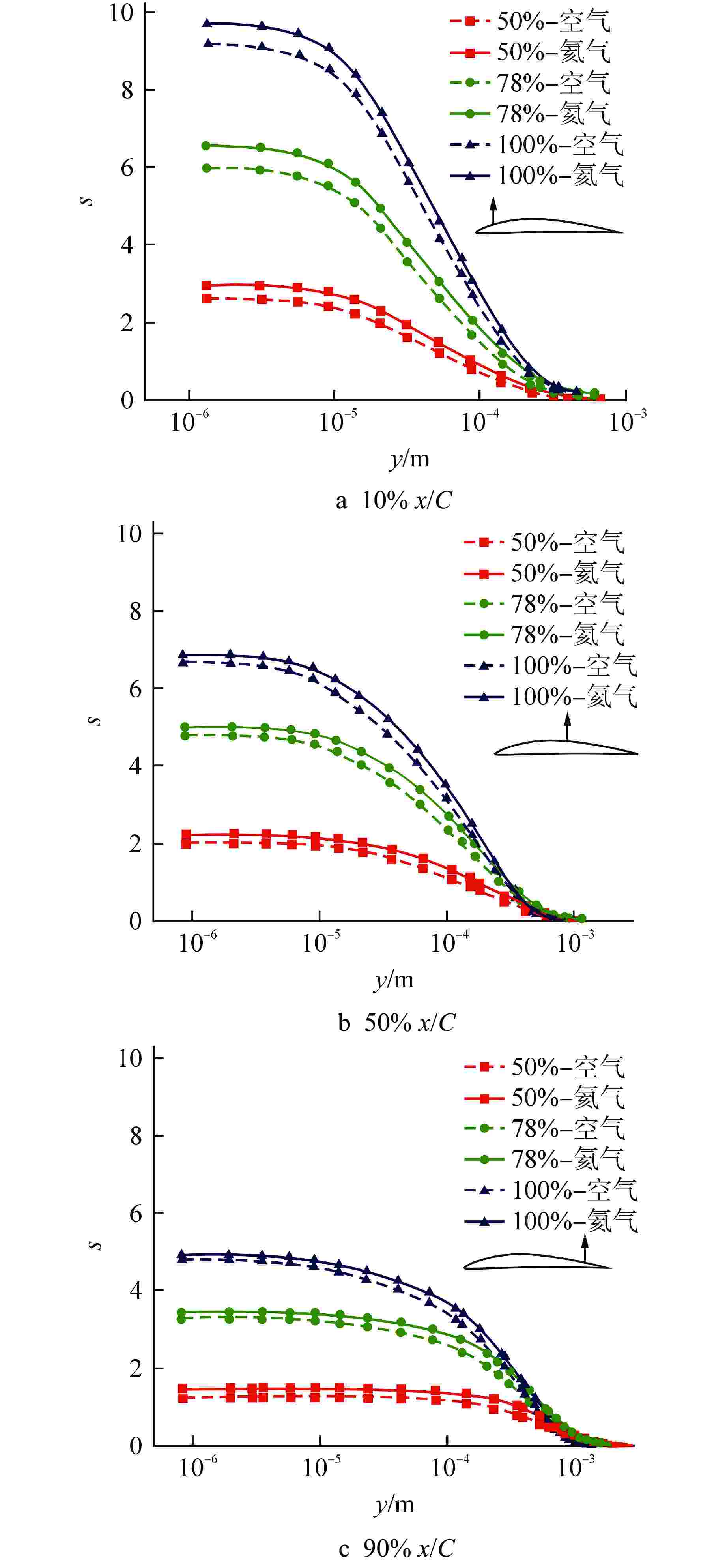
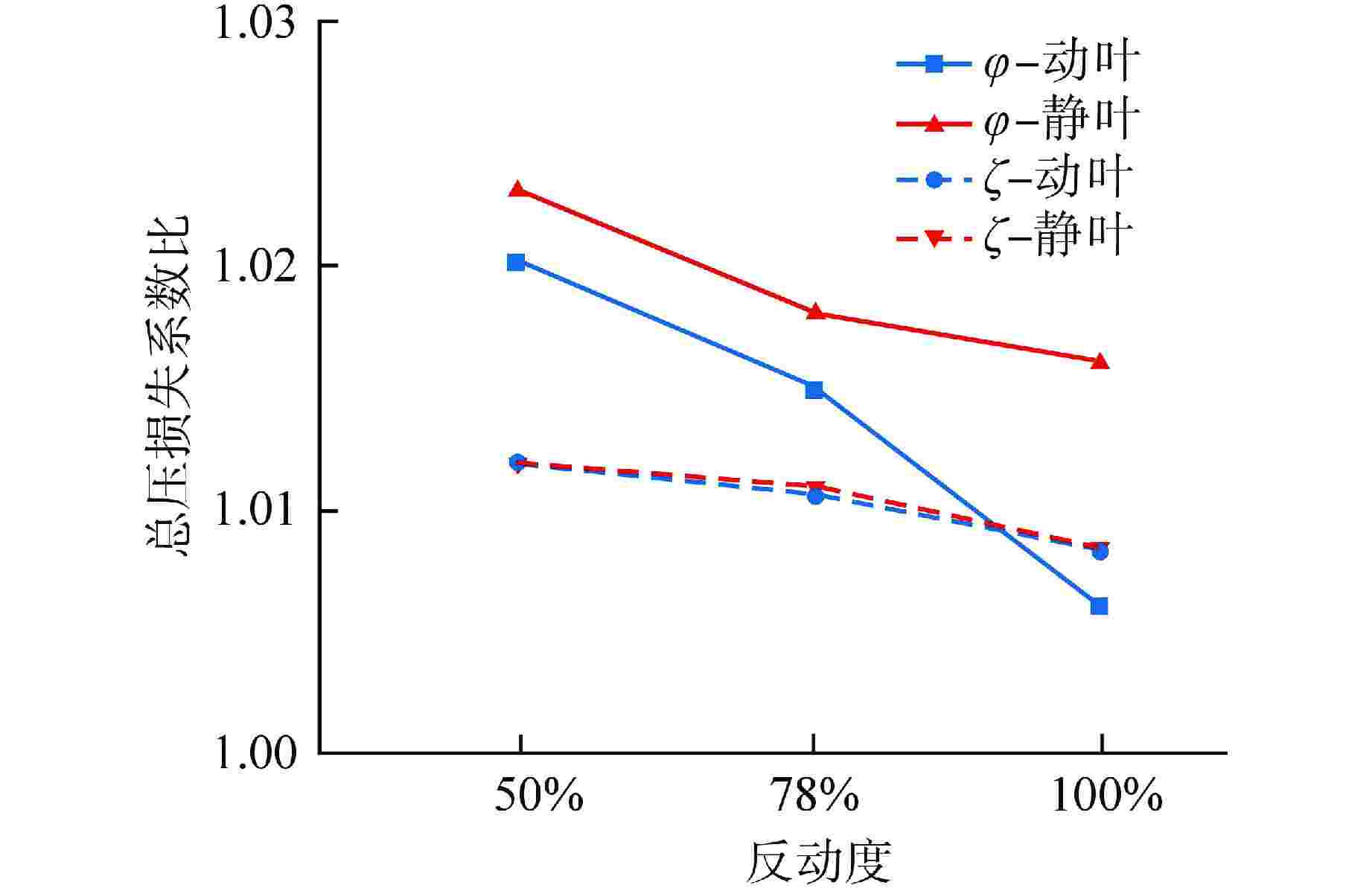
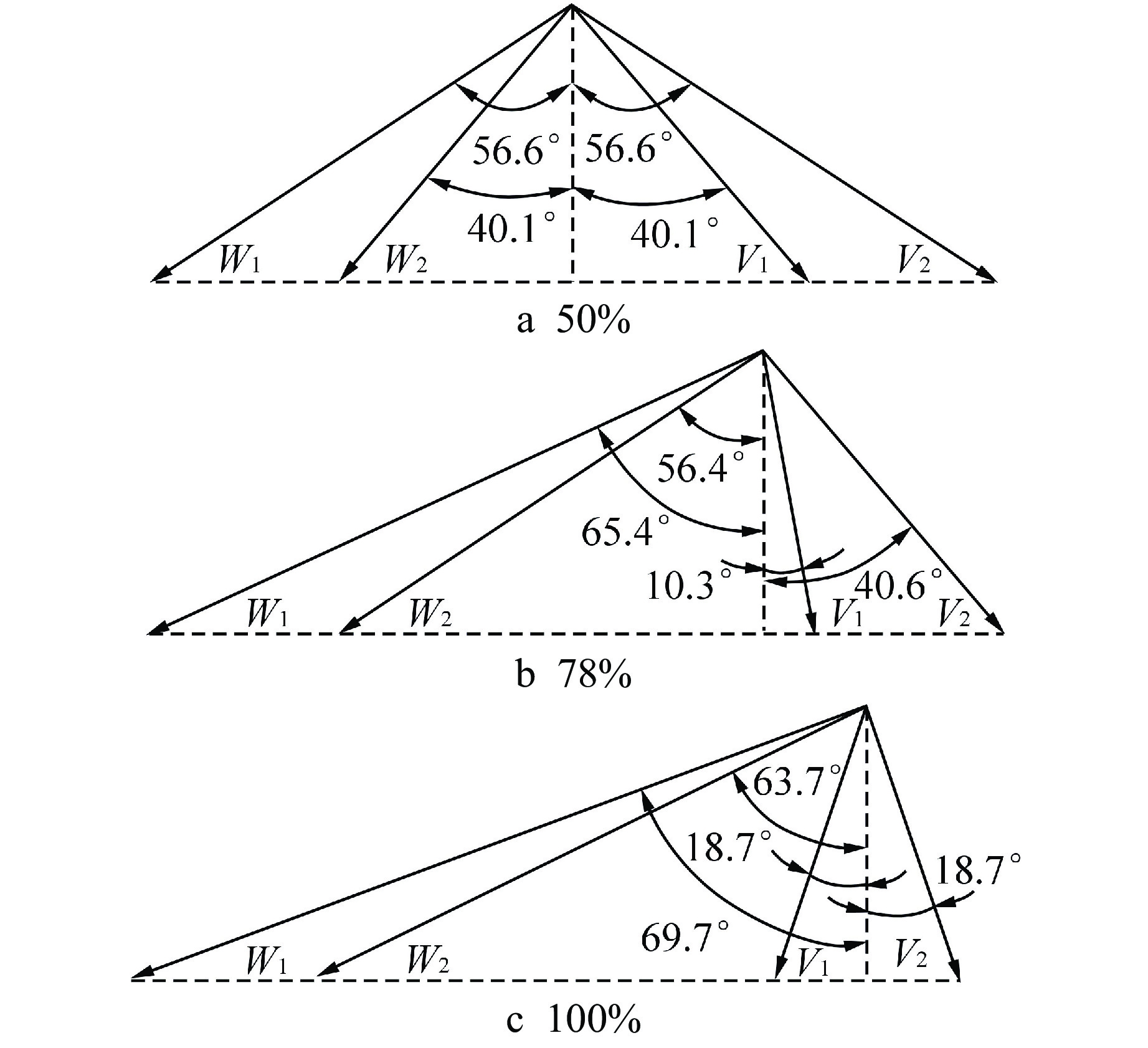
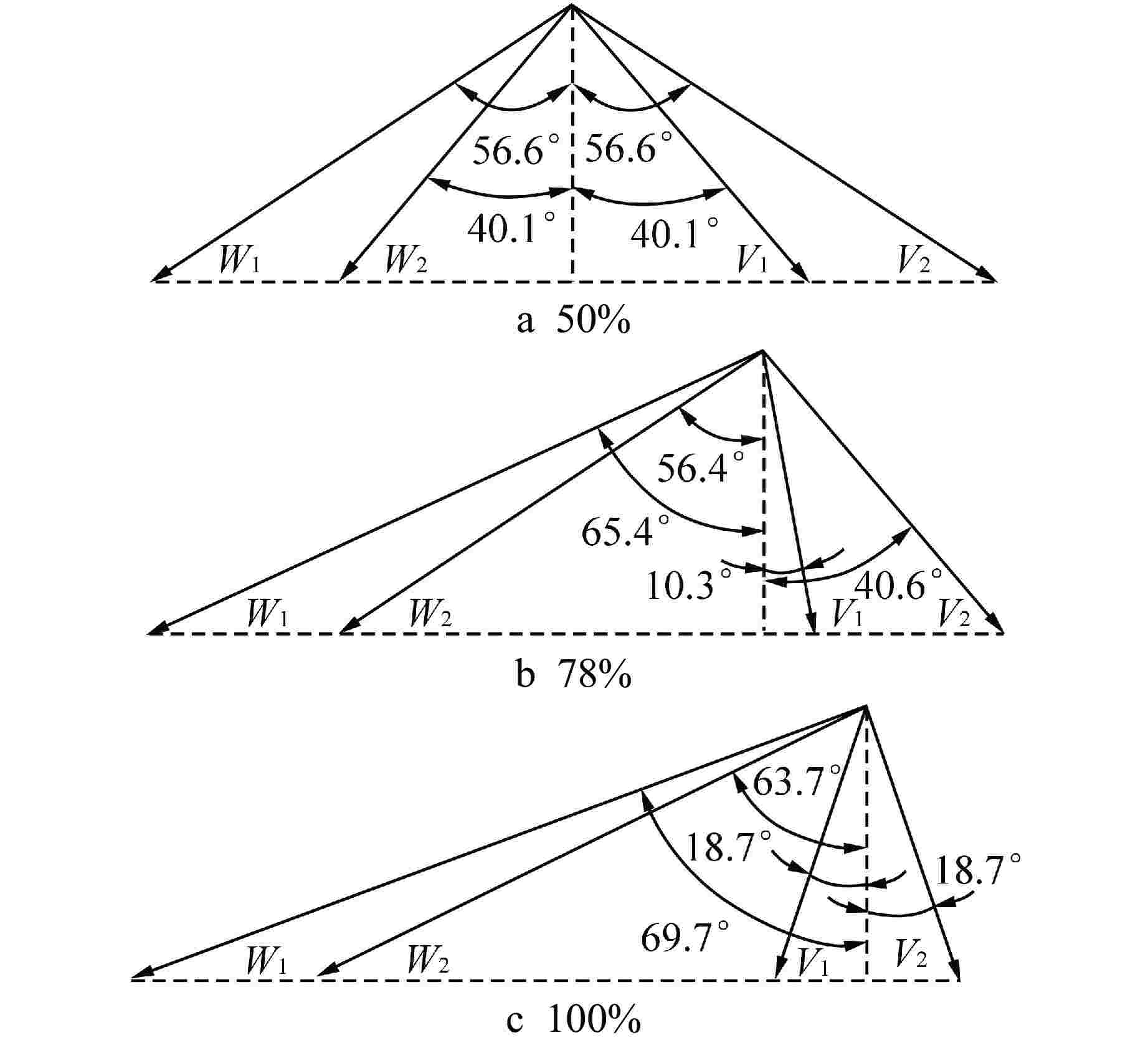
摘要: 多级轴流氦气压气机是氦气轮机的关键部件之一,通常采用高反动度设计提升单级焓增以减少级数,但经验表明高反动度往往导致效率降低,因此在采用高反动设计时有必要澄清反动度对流动损失的影响。本文以不同反动度的氦气压气机为研究对象,利用计算流体动力学(CFD)方法详细分析了基于氦气流动的压气机叶片通道内部的叶型损失、角区损失和叶顶泄漏损失与反动度的关联性。结果表明,在100%反动度动叶和50%反动度静叶中,由于通道内相对速度较高,导致叶型损失更大,且随着反动度增高,动叶中的负荷提高导致叶顶泄漏处的损失加大,同时,静叶弯曲角的增大和展向压差使得静叶角区分离流更为严重。在100%反动度下,叶顶泄漏损失占动叶栅损失的53%,角区损失占静叶栅损失的60%。此外,本研究基于空气压气机叶型损失模型,通过物性分析优化了适用于氦气压气机的叶型损失模型。Abstract: Multi-stage axial helium compressor is one of the key components of helium turbine. High reaction design is usually used to enhance the enthalpy gain of a single stage to reduce the number of stages, but experience shows that high reaction often leads to a reduction in efficiency, so it is necessary to clarify the effect of reaction on flow loss when using high reaction designs. In this paper, the correlation between the profile loss, corner loss and tip leakage loss inside the compressor vane channel based on helium flow and the reaction degree is analyzed in detail using CFD method for helium compressors with different reactions. The results show that the profile loss of 100% reaction rotor and 50% reaction stator increases due to the high relative velocity. As the reaction increases, the high load in the rotor leads to the increase of the loss at the tip leakage of the rotor. And, the increase of the stator bending angel and spanwise differential pressure make the separation of the stator angle more serious. At 100% reaction, the tip leakage loss accounts for 53% of the rotor loss and the corner loss accounts for 60% of the stator loss. Based on the air compressor profile loss model, the profile loss model suitable for helium compressor is optimized through physical property analysis.
-
Key words:
- Helium compressor,
- Degree of reaction,
- Loss model,
- Numerical simulation
-
表 1 氦气压气机设计参数
Table 1. Design Parameters of Helium Compressor Model
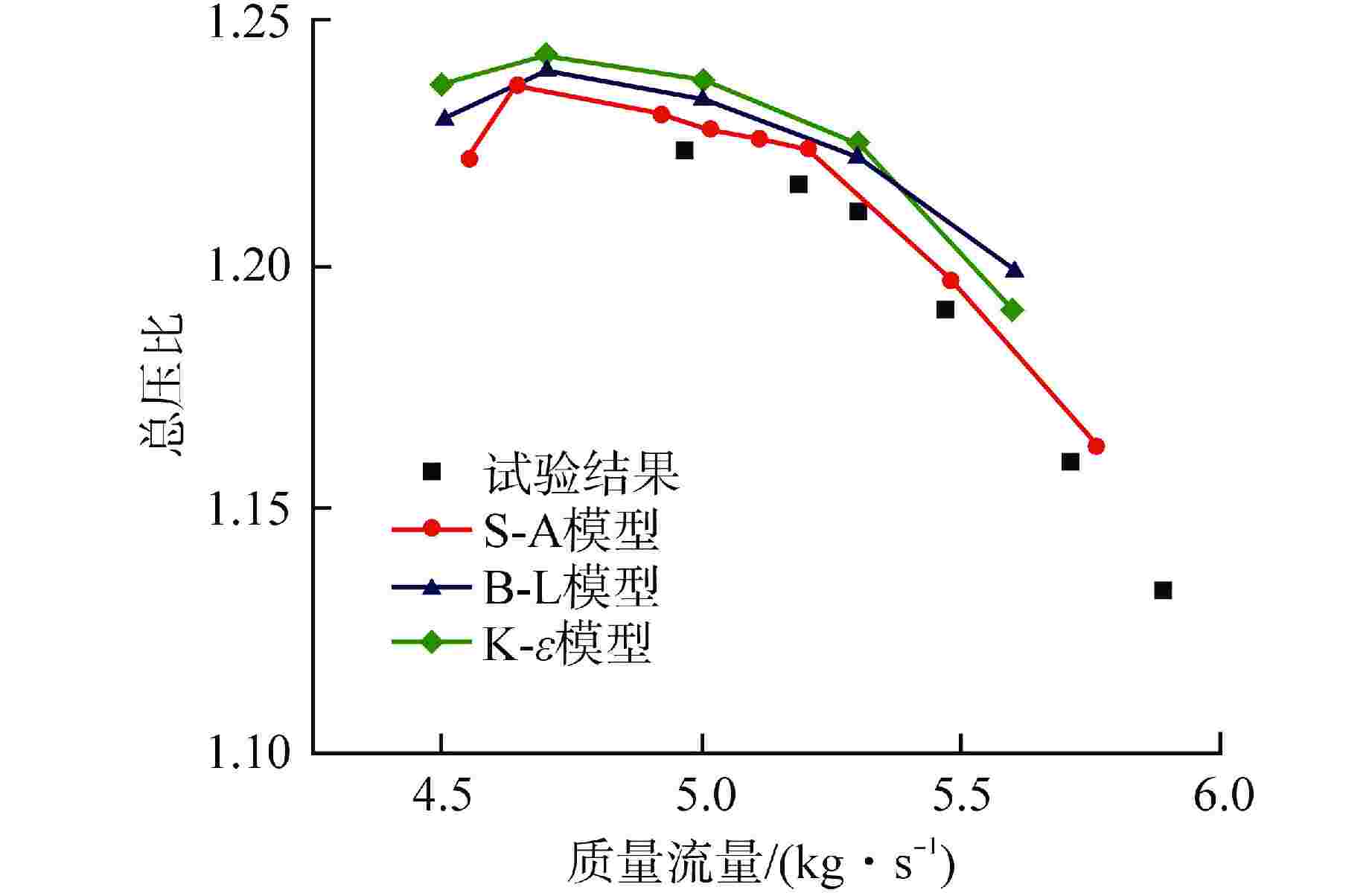
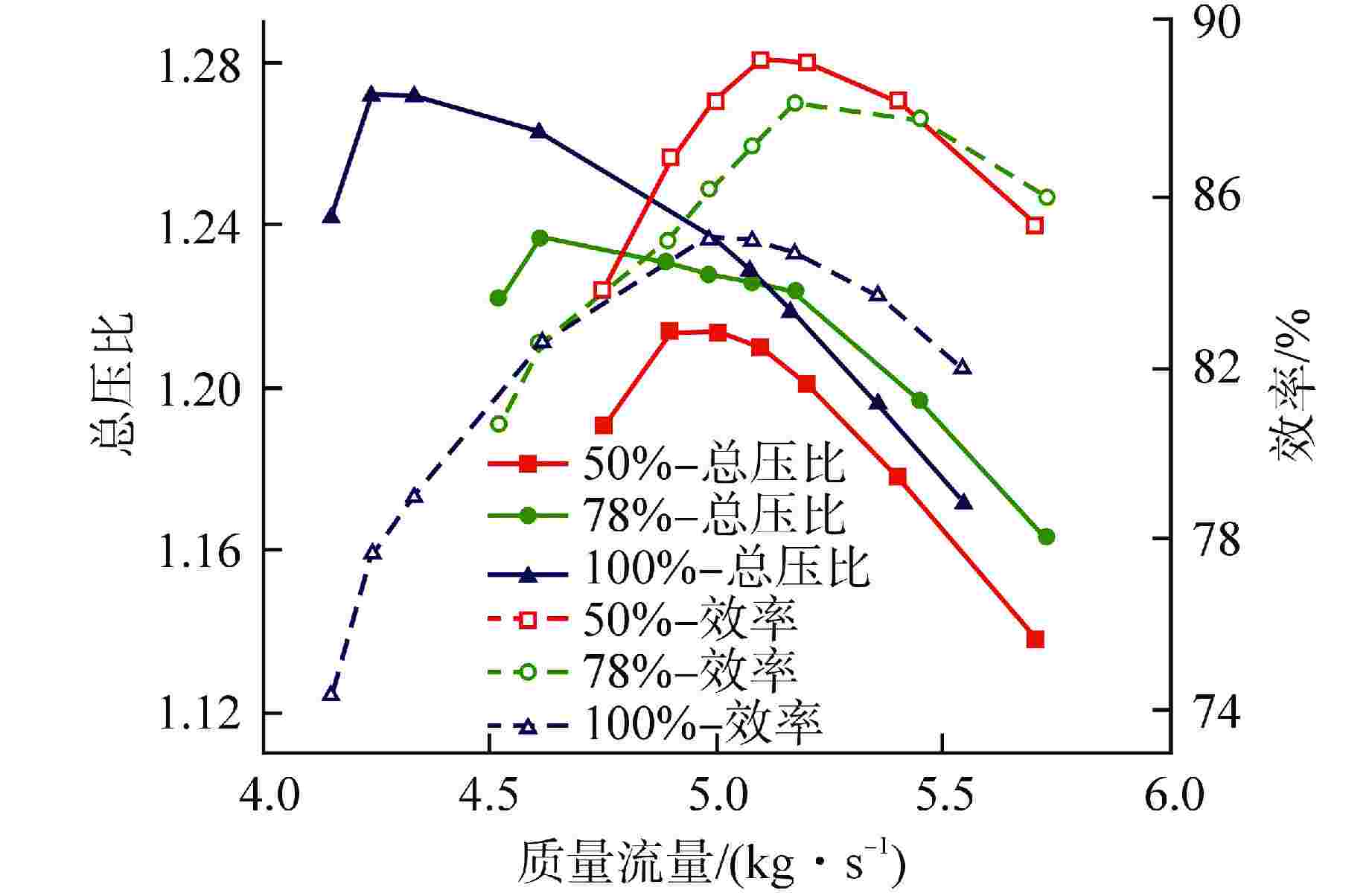
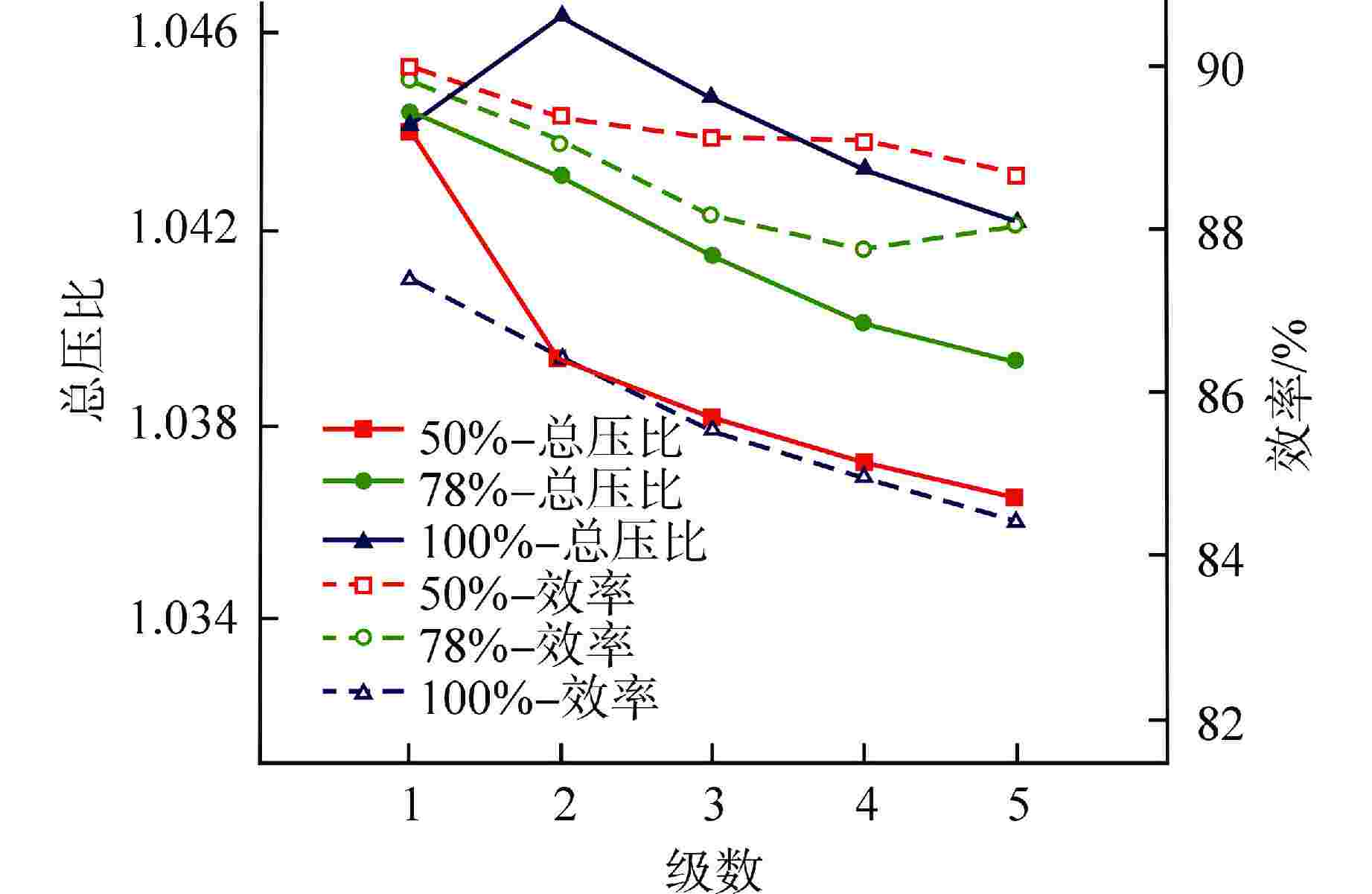
设计参数 数值 质量流量/(kg·s−1) 5.0 进口总压/MPa 0.71 进口总温/K 320 总压比 1.2 级数 5 转速/(r·min−1) 15000 动叶数量 77 静叶数量 102 第1级动叶高度/mm 27 叶顶间隙 1% 叶高 流量系数 0.4233 载荷系数 0.286 表 2 氦气和空气压气机参数对比
Table 2. Parameter Comparison of Helium and Air Compressors
参数 氦气 空气 进口总温/K 320 320 进口总压/Pa 709275 239531 转速/(r·min−1) 15000 5576 -
[1] BAMMERT K, BUENDE R. Comparison of nuclear power plants with closed-cycle helium turbine and with steam turbine cycle for combined power and steam generation[J]. Journal of Engineering for Power, 1973, 95(1): 11-18. doi: 10.1115/1.3445688 [2] 周佳慧. 高温气冷堆氦气轮机基本特性的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2006. [3] GUT W. Comparison of the relative losses and characteristics of axialflow compressor stages[J]. Escher Wyss News, 1960, 22(23): 3-13. [4] TIAN Z T, REN P, MALIK A, et al. Research on the influence of highly loaded design method on the stability of helium compressor[J]. Progress in Nuclear Energy, 2021, 132: 103599. doi: 10.1016/j.pnucene.2020.103599 [5] MALIK A, ZHENG Q, LIN A Q. The design and performance analysis of highly loaded compressor of closed Brayton cycle HTGR power plant with helium xenon gas mixture as working fluid[J]. Progress in Nuclear Energy, 2019, 117: 103084. doi: 10.1016/j.pnucene.2019.103084 [6] 明亮, 杨小勇, 张佑杰, 等. 叶顶间隙与轴向间隙对氦气压气机气动特性的影响[J]. 清华大学学报: 自然科学版. 2017, 57(8): 832-837. [7] 田志涛,郑群,姜斌,等. 氦压气机转子叶顶间隙结构研究[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报,2019, 40(5): 938-943. [8] 苏洋,黄伟光,张靖煊,等. 多级轴流氦气压气机流动失稳实验研究[J]. 热能动力工程,2018, 33(1): 12-19. doi: 10.16146/j.cnki.rndlgc.2018.01.003 [9] LIEBLEIN S. Loss and stall analysis of compressor cascades[J]. Journal of Basic Engineering, 1959, 81(3): 387-397. doi: 10.1115/1.4008481 [10] 朱荣凯. 氦气轴流压气机相似模化研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2008. [11] BROWN L E. Axial flow compressor and turbine loss coefficients: a comparison of several parameters[J]. Journal of Engineering for Power, 1972, 94(3): 193-201. doi: 10.1115/1.3445672 [12] SAKIADIS B C. Boundary‐layer behavior on continuous solid surfaces: II. The boundary layer on a continuous flat surface[J]. AIChE Journal, 1961, 7(2): 221-225. doi: 10.1002/aic.690070211 -





 下载:
下载: