Microstructure and Tensile Properties of ODS-310 Austenitic Steel
-
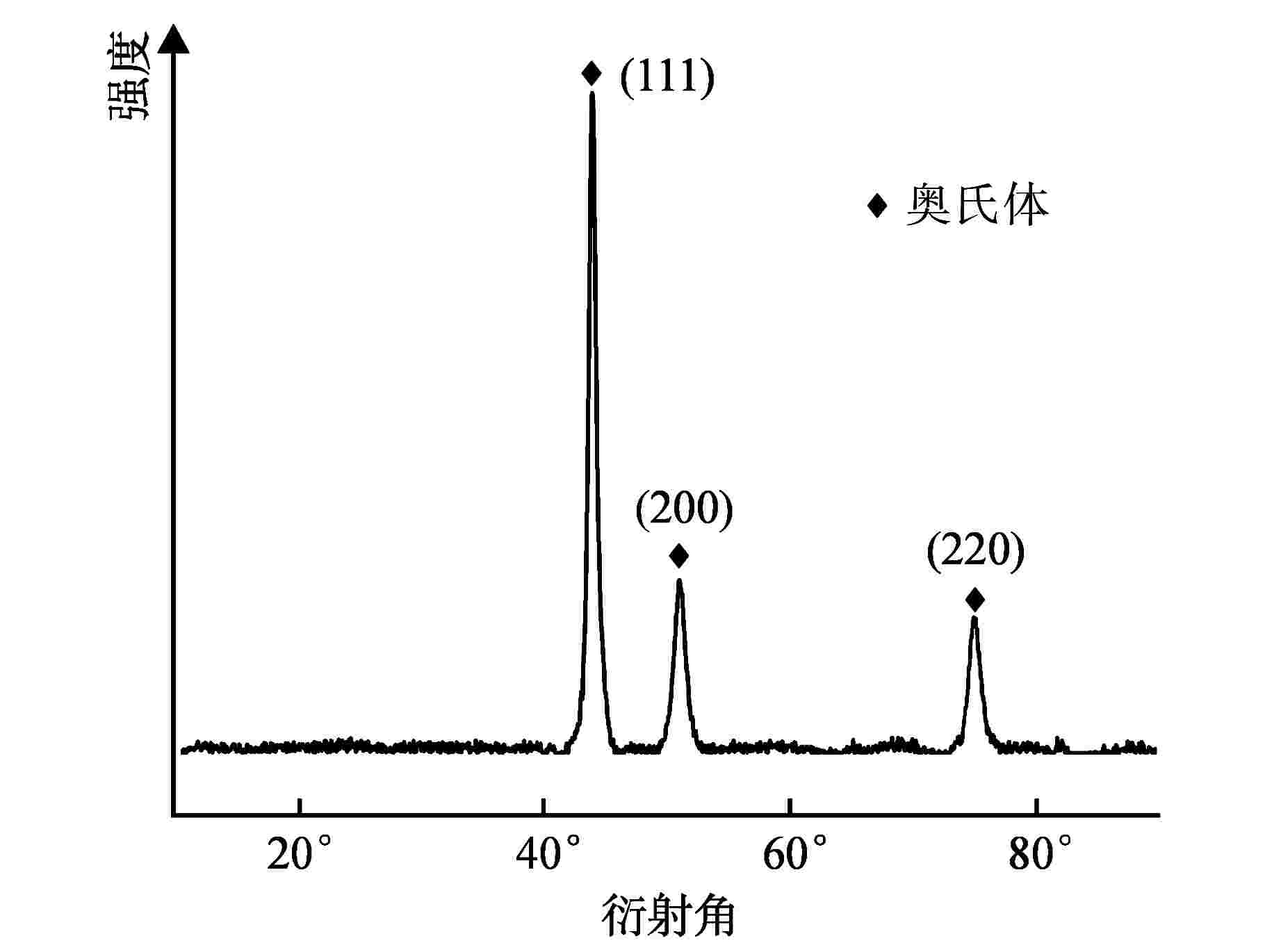
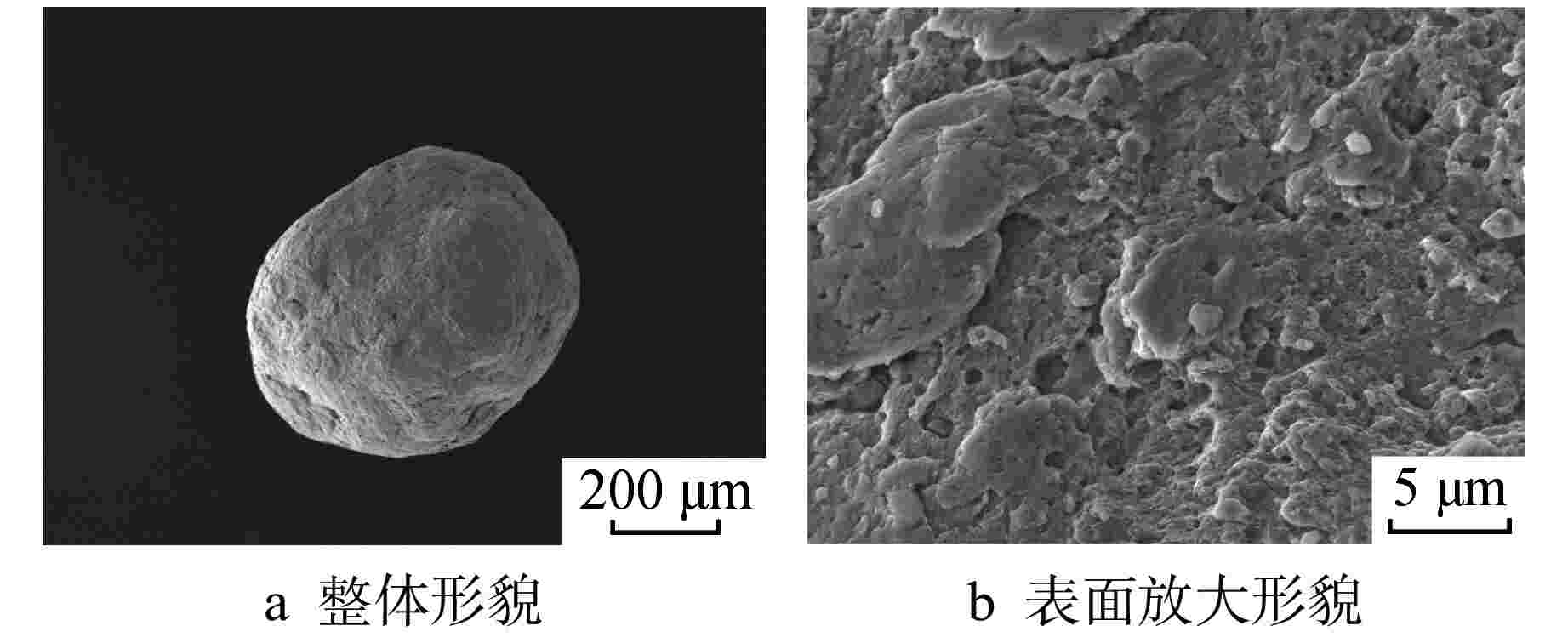
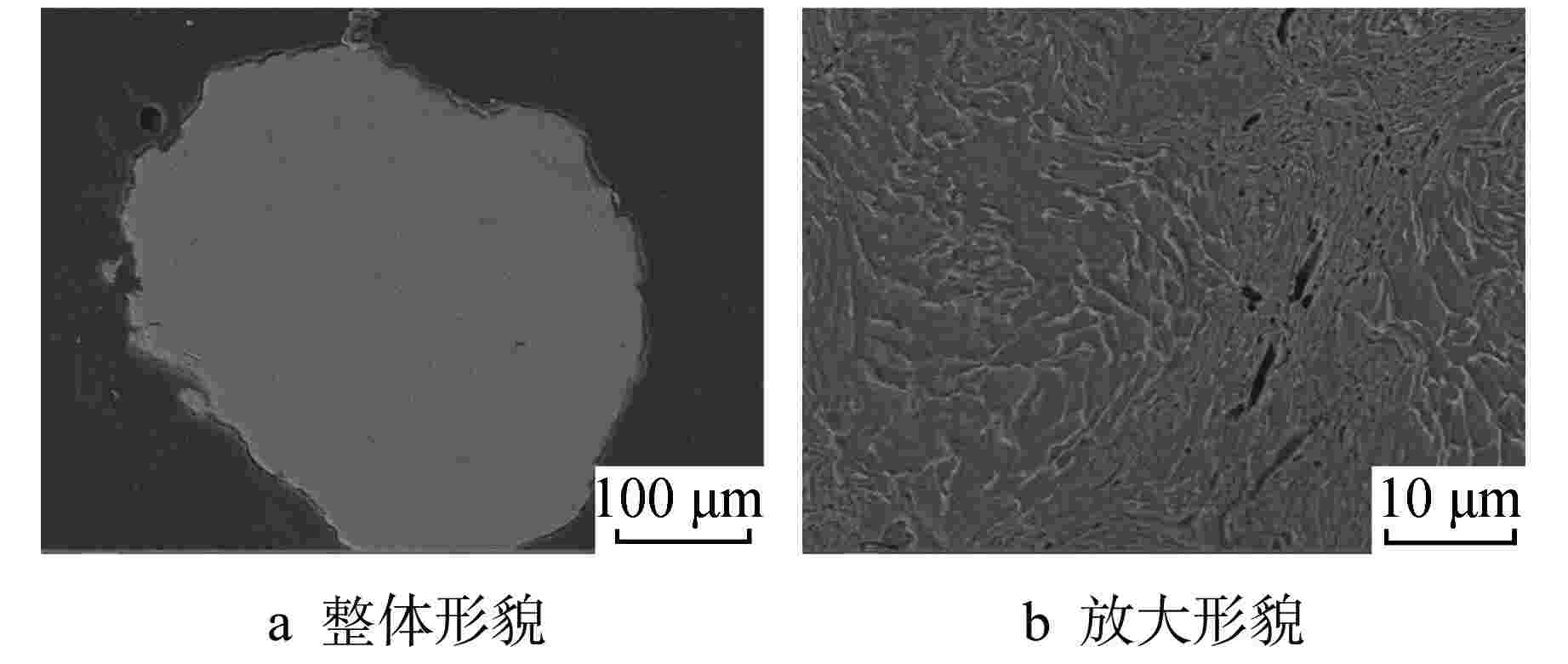
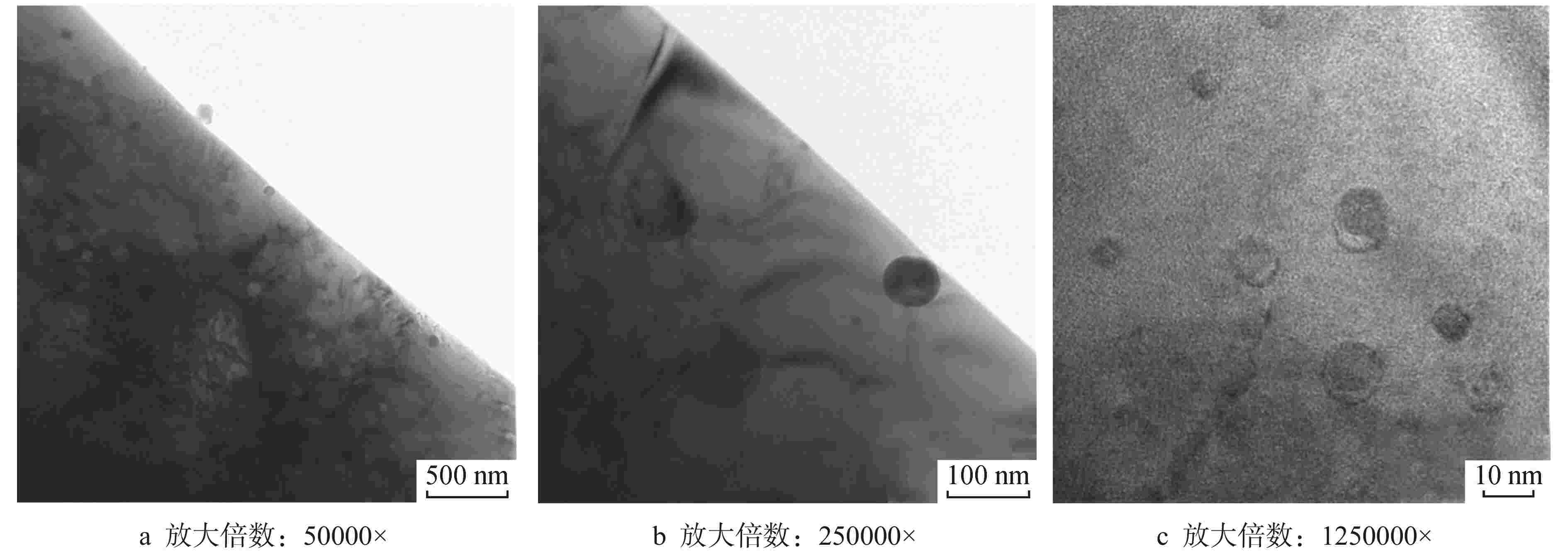
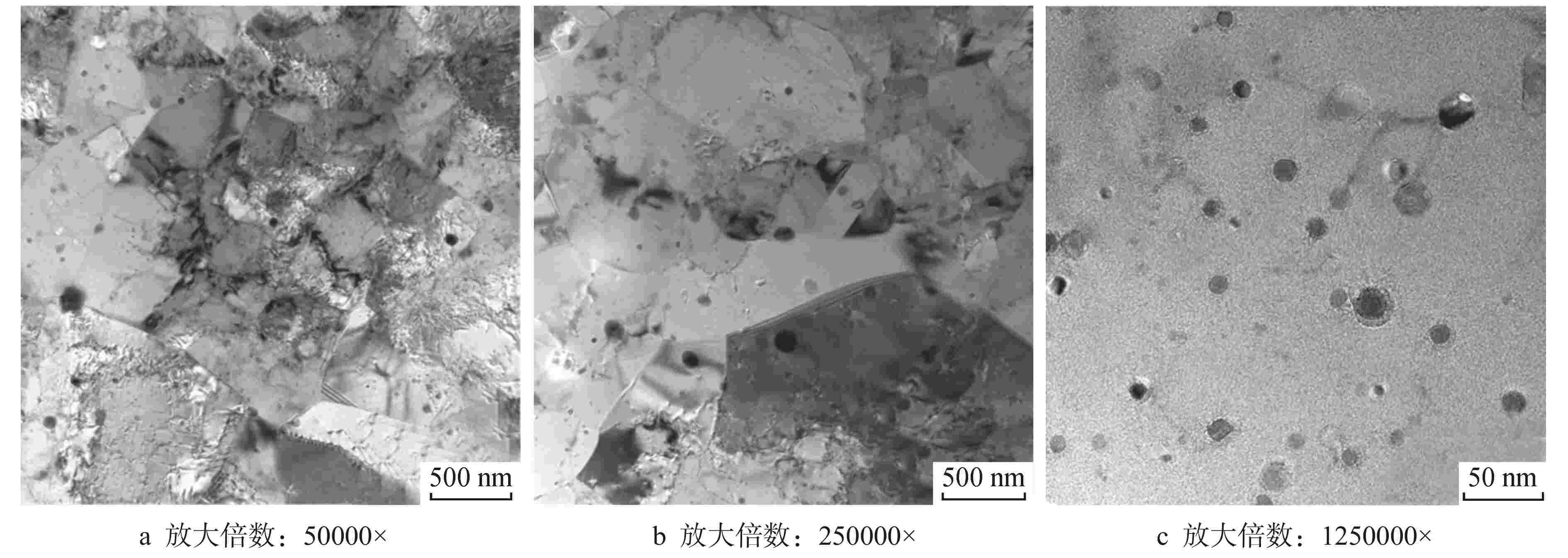
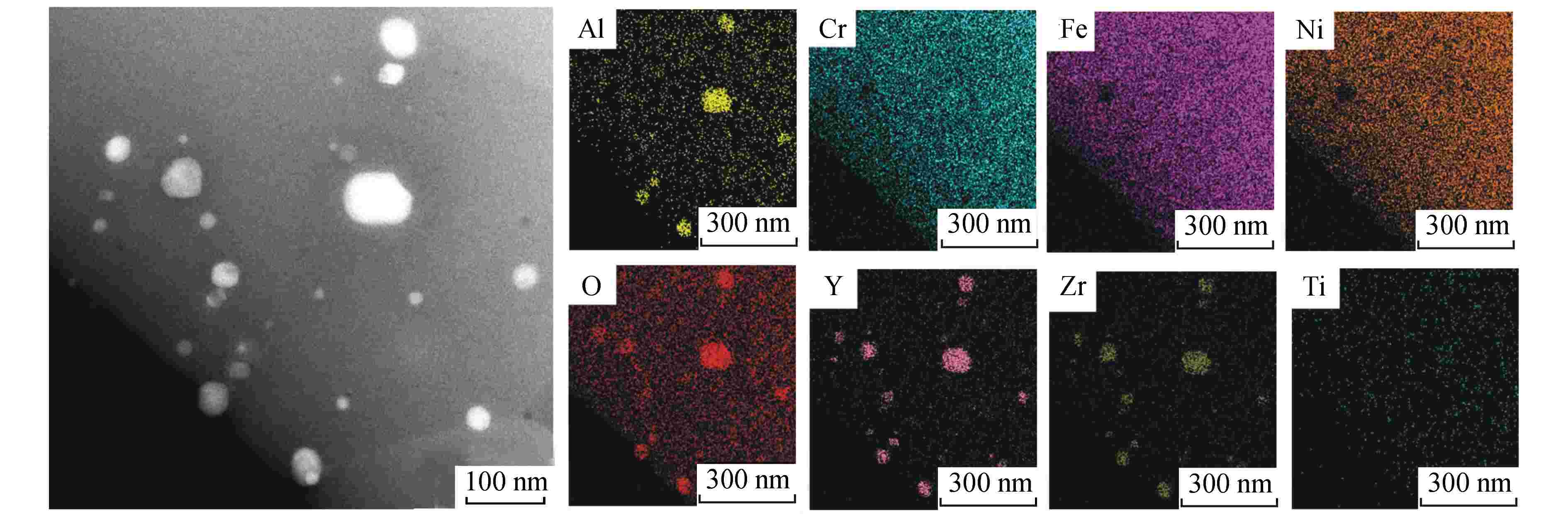
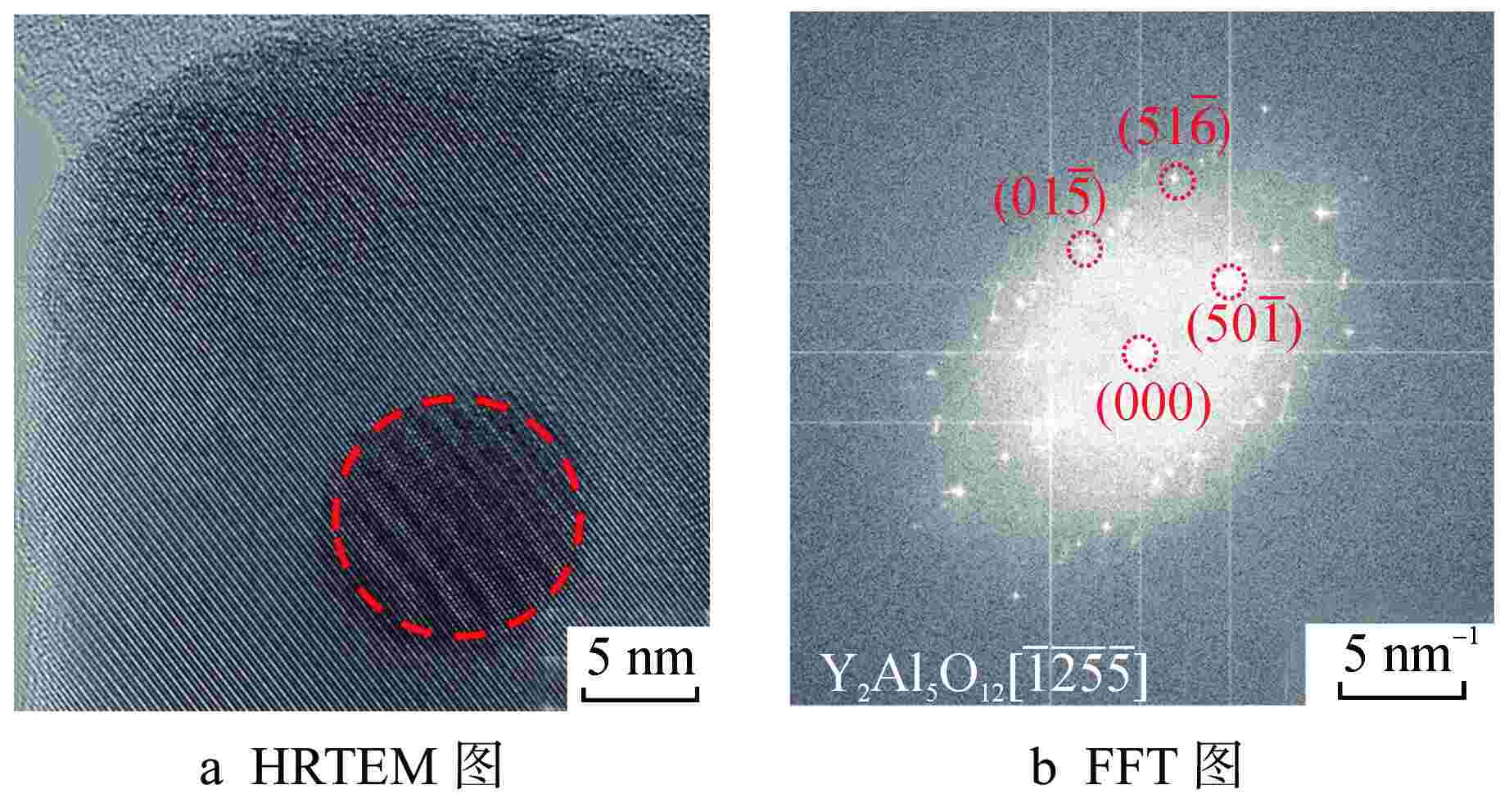
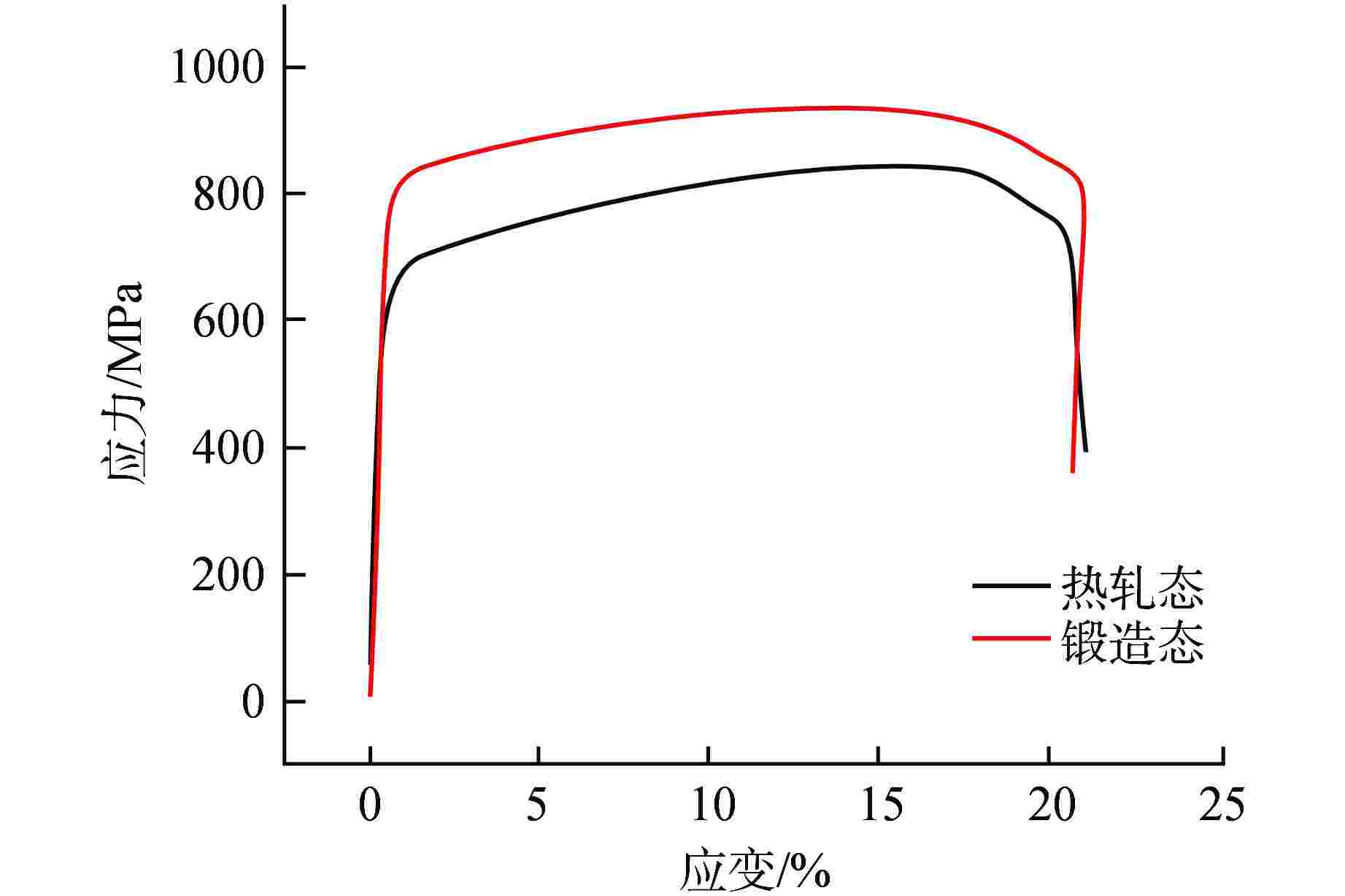
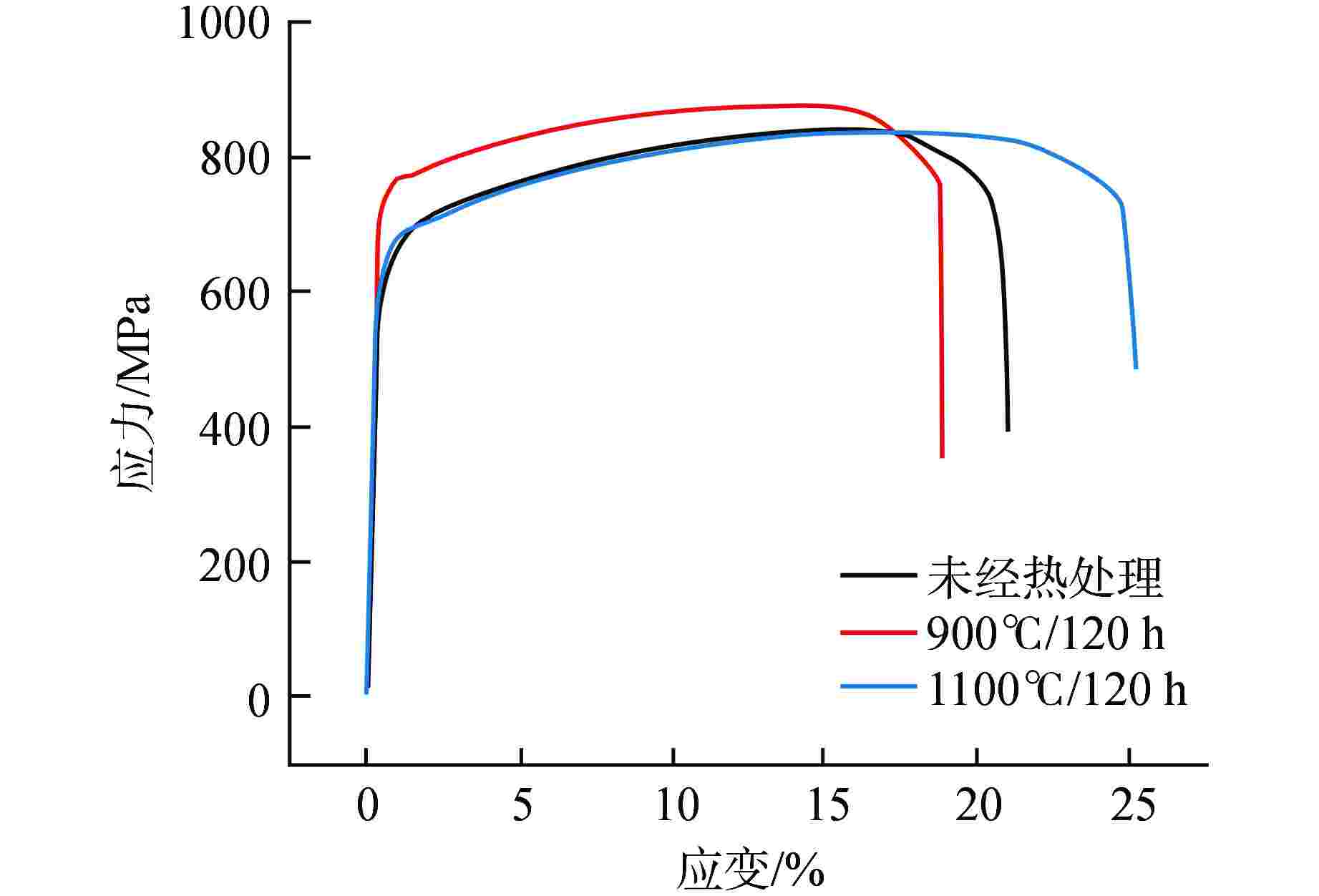
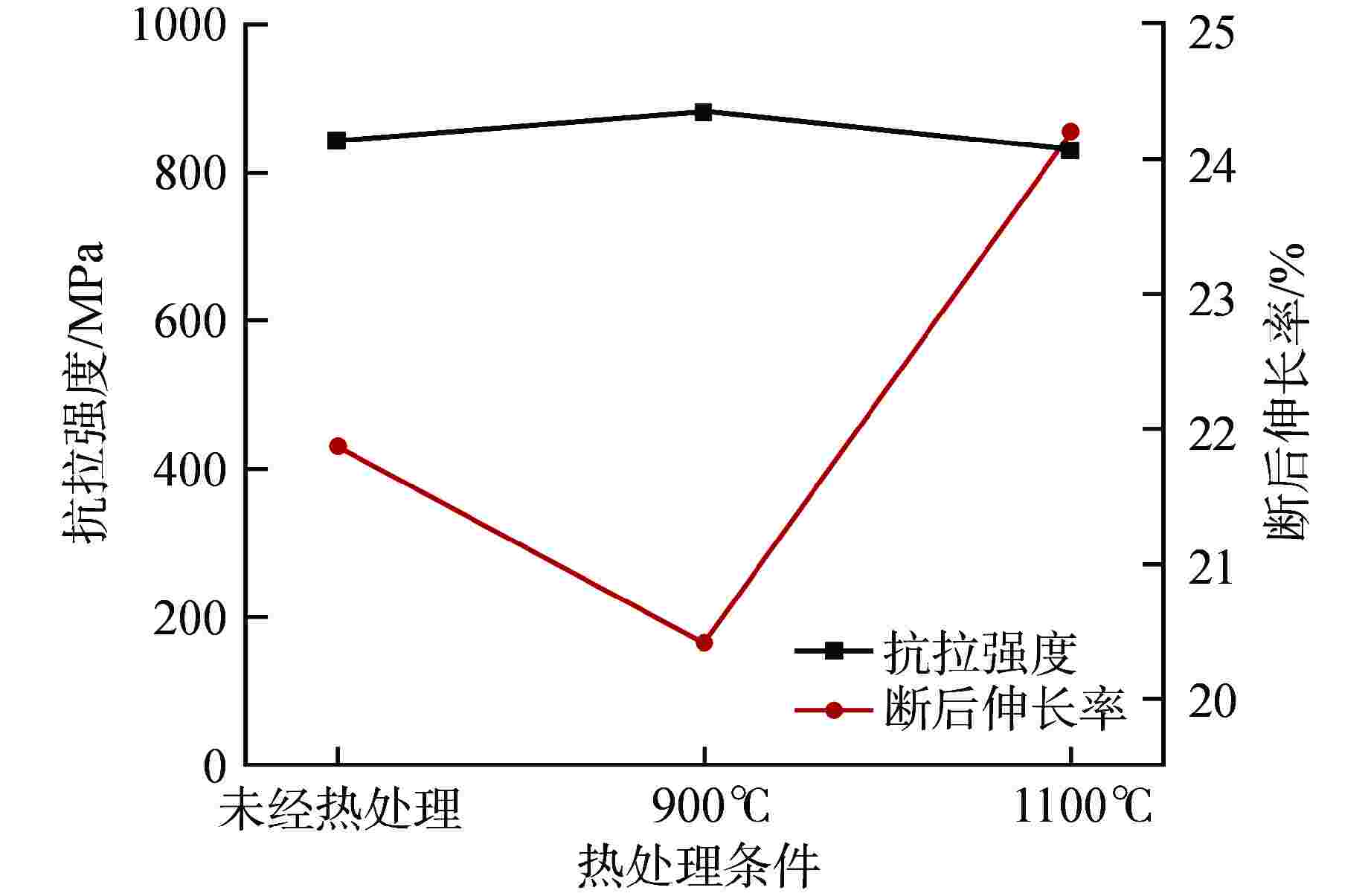
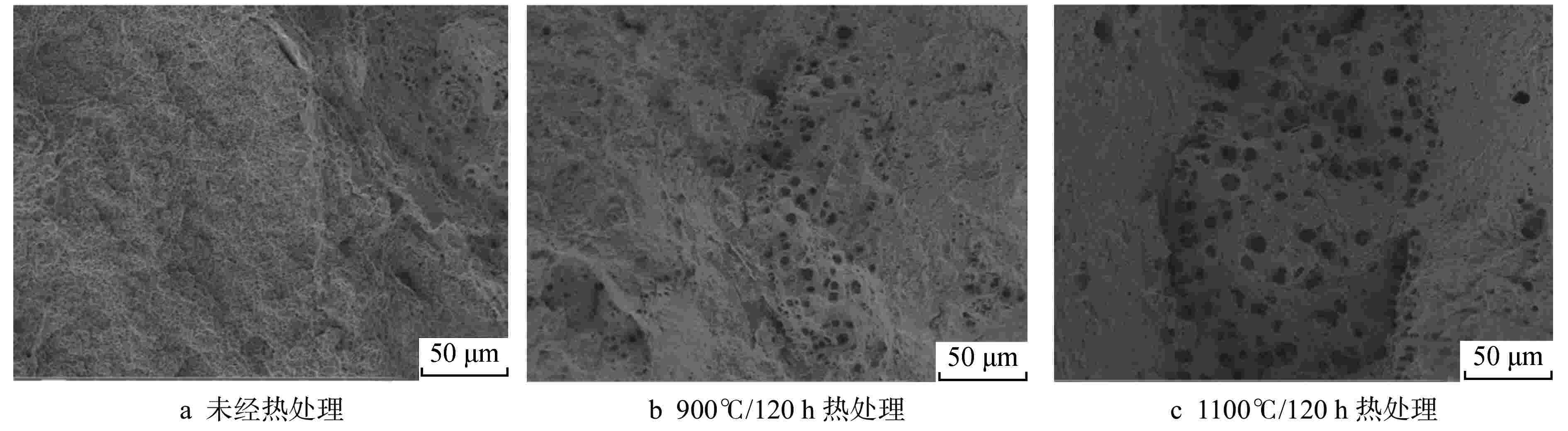
摘要: 为向超临界水冷堆提供可靠的核燃料包壳材料,通过机械合金化(MA)和热等静压法(HIP)制备了具有超细晶粒且弥散大量纳米氧化物颗粒的ODS-310奥氏体钢,采用扫描电镜(SEM)、能谱仪(EDS)和透射电镜(TEM)分析了经过不同热处理条件后材料的显微形貌,并测试了其拉伸性能。结果表明,材料中的弥散强化粒子呈球形,主要分布在晶粒内部及晶界处,其平均尺寸在10 nm以下,经成分分析及高分辨标定可确定为Y2Al5O12。热轧塑性变形加工配合热处理可明显调控样品的晶粒组织,经1100℃/120 h 热处理后,弥散颗粒尺寸和成分仍保持稳定,粒子对位错有明显的钉扎作用。所制备ODS-310奥氏体钢具有较高的抗拉强度,且其热稳定性良好,在不同温度下热处理前后样品的抗拉强度均在850 MPa左右,且经1100℃/120 h热处理后样品的塑性明显提高。本研究表明ODS-310奥氏体钢的拉伸性能良好,通过热处理可以调控晶粒组织,为ODS奥氏体钢的性能研究提供了宝贵的数据支持。
-
关键词:
- 纳米氧化物弥散强化 /
- ODS-310奥氏体钢 /
- 显微结构 /
- 拉伸性能
Abstract: In order to provide reliable nuclear fuel cladding materials for supercritical water-cooled reactors, ODS-310 austenitic steel with ultrafine grains and a large number of dispersed nano-oxide particles was prepared by mechanical alloying (MA) and hot isostatic pressing (HIP). The microstructure of the material after different heat treatment was analyzed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and its tensile properties were tested. The results show that the dispersion strengthening particles in the material are spherical and mainly distributed in the grain and at the grain boundary. The average size is below 10 nm. It can be determined as Y2Al5O12 by composition analysis and high resolution calibration. The grain structure of the sample can be obviously regulated by hot rolling plastic deformation combined with heat treatment. After heat treatment at 1100℃/120 h, the size and composition of the dispersed particles remain stable, and the particles have obvious pinning effect on dislocations. The prepared ODS-310 austenitic steel has high tensile strength and good thermal stability. The tensile strength of the samples before and after heat treatment at different temperatures is about 850 MPa, and the plasticity of the samples after heat treatment at 1100°C/120 h is significantly improved. This study shows that the tensile properties of ODS-310 austenitic steel are good, and the grain structure can be regulated by heat treatment. It can provide valuable data support for the study of ODS austenitic steel properties. -
表 1 ODS-310钢烧结坯实际成分
Table 1. Actual Composition of Sintered ODS-310 Steel
元素 Fe Cr Ni Ti Mo Y O Zr 质量分数/% 54.73 23.97 18.33 0.32 1.93 0.26 0.16 0.30 -
[1] BUCKTHORPE D. Introduction to generation IV nuclear reactors[M]//YVON P. Structural Materials for Generation IV Nuclear Reactors. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2017: 1-22. [2] NOVOTNY R, GUZONAS D. Material research for the supercritical water-cooled reactor—summary and open issues[M]//RITTER S. Nuclear Corrosion: Research, Progress and Challenges. Duxford: Woodhead Publishing, 2020: 403-435. [3] GUO X L, FAN Y, GAO W H, et al. Corrosion resistance of candidate cladding materials for supercritical water reactor[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2019, 127: 351-363. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2018.12.007 [4] VORONIN V I. Neutron diffraction study of samples of fuel element claddings made of austenitic steel[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2021, 547: 152798. doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2021.152798 [5] HURE J, COURCELLE A, TURQUE I. A micromechanical analysis of swelling-induced embrittlement in neutron-irradiated austenitic stainless steels[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2022, 565: 153732. doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2022.153732 [6] WANG M, SUN H Y, ZOU L, et al. Structural evolution of oxide dispersion strengthened austenitic powders during mechanical alloying and subsequent consolidation[J]. Powder Technology, 2015, 272: 309-315. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2014.12.008 [7] RAMAN L, GOTHANDAPANI K, MURTY B S. Austenitic oxide dispersion strengthened steels: a review[J]. Defence Science Journal, 2016, 66(4): 316-322. doi: 10.14429/dsj.66.10205 [8] RIBIS J, LOZANO-PEREZ S. Nano-cluster stability following neutron irradiation in MA957 oxide dispersion strengthened material[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2014, 444(1-3): 314-322. doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2013.10.010 [9] GAO J, CHEN F D, TANG X B, et al. Effects of grain boundary structures on primary radiation damage and radiation-induced segregation in austenitic stainless steel[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2020, 128(10): 105304. doi: 10.1063/5.0016404 [10] GRÄNING T, RIETH M, HOFFMANN J, et al. Production, microstructure and mechanical properties of two different austenitic ODS steels[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2017, 487: 348-361. doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2017.02.034 [11] LITVINOV D, CHAUHAN A, GRÄNING T, et al. Microstructure characterization of a novel austenitic ODS steel by transmission electron microscopy[J]. Materialia, 2019, 5: 100176. doi: 10.1016/j.mtla.2018.11.025 [12] WANG M, ZHOU Z J, SUN H Y, et al. Microstructural observation and tensile properties of ODS-304 austenitic steel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2013, 559: 287-292. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2012.08.099 [13] ZHOU Z J, SUN S Y, ZOU L, et al. Enhanced strength and high temperature resistance of 25Cr20Ni ODS austenitic alloy through thermo-mechanical treatment and addition of Mo[J]. Fusion Engineering and Design, 2019, 138: 175-182. doi: 10.1016/j.fusengdes.2018.11.020 [14] GRÄNING T, RIETH M, MÖSLANG A, et al. Investigation of precipitate in an austenitic ODS steel containing a carbon-rich process control agent[J]. Nuclear Materials and Energy, 2018, 15: 237-243. doi: 10.1016/j.nme.2018.05.005 [15] 王曼,周张健,闫志刚,等. ODS-316奥氏体钢显微结构及弥散相的TEM研究[J]. 金属学报,2013, 49(2): 153-158. [16] PENG Y Y, YU L M, LIU Y C, et al. Microstructures and tensile properties of an austenitic ODS heat resistance steel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2019, 767: 138419. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2019.138419 [17] WANG M, ZHOU Z J, SUN H Y, et al. Effects of plastic deformations on microstructure and mechanical properties of ODS-310 austenitic steel[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2012, 430(1-3): 259-263. doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2012.07.014 -





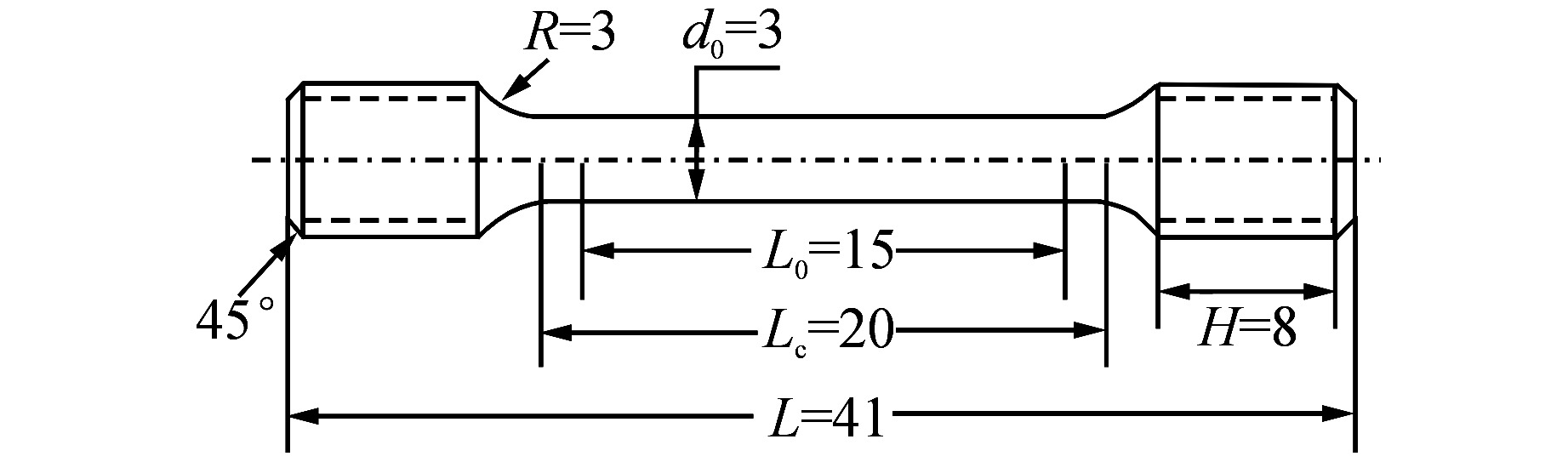
 下载:
下载: