Effect of N and Al Addition on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Modified 25Ni-20Cr Austenitic Stainless Steel Aged at 700℃
-
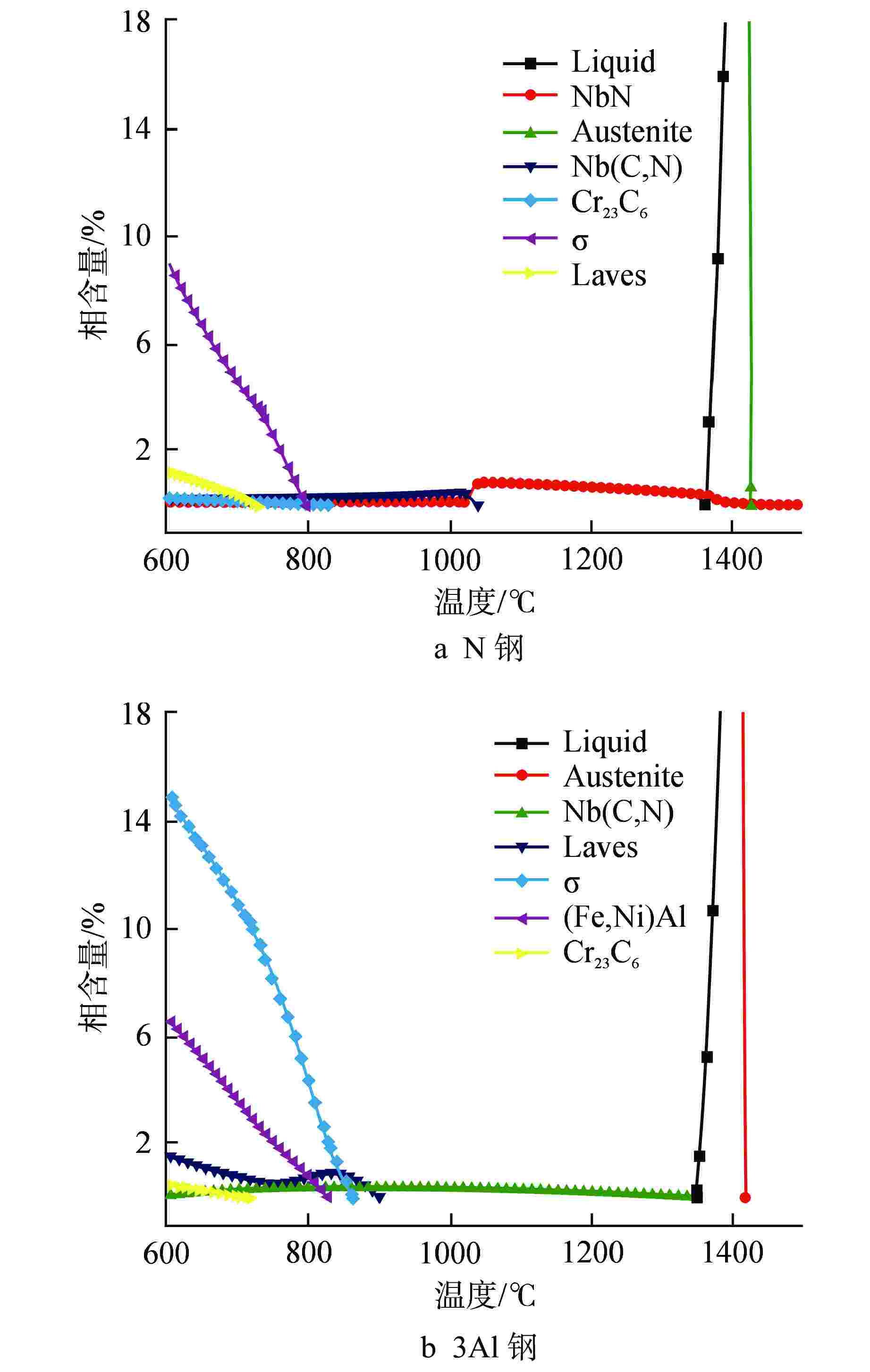
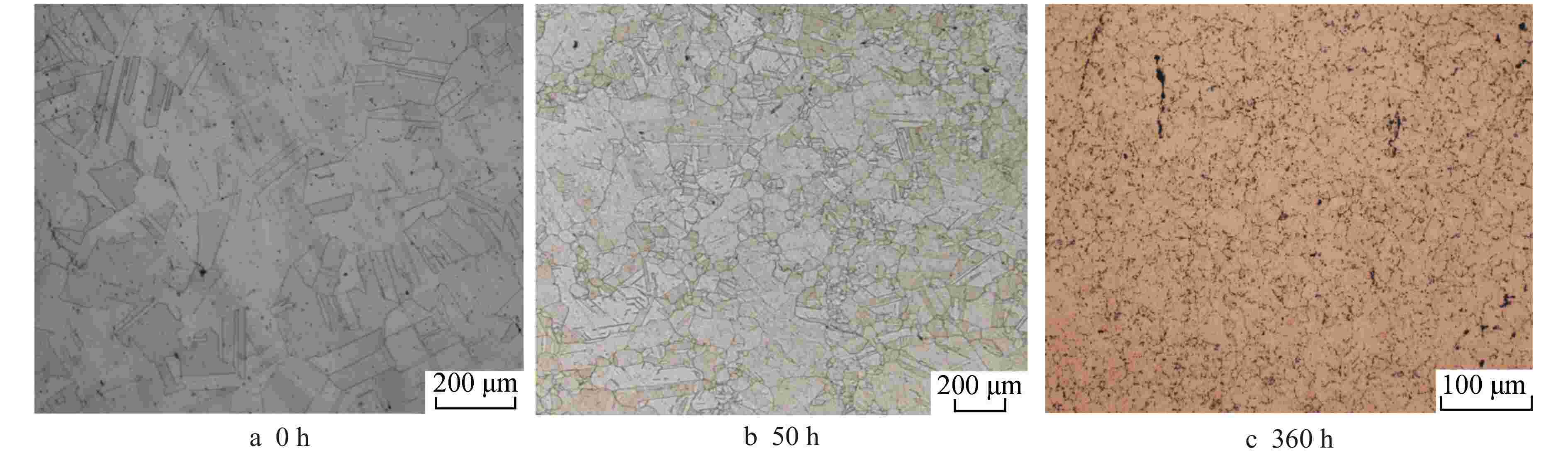
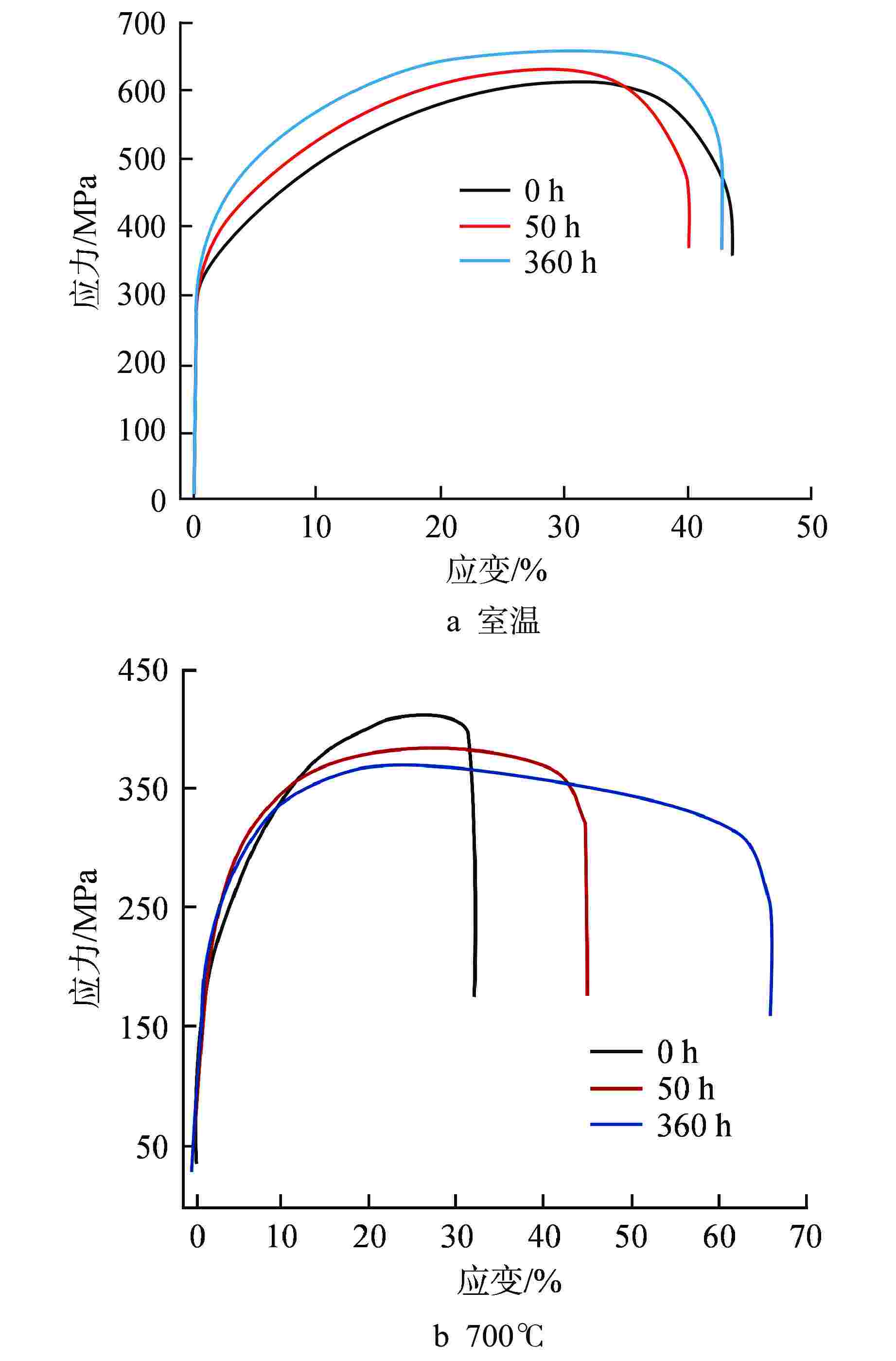
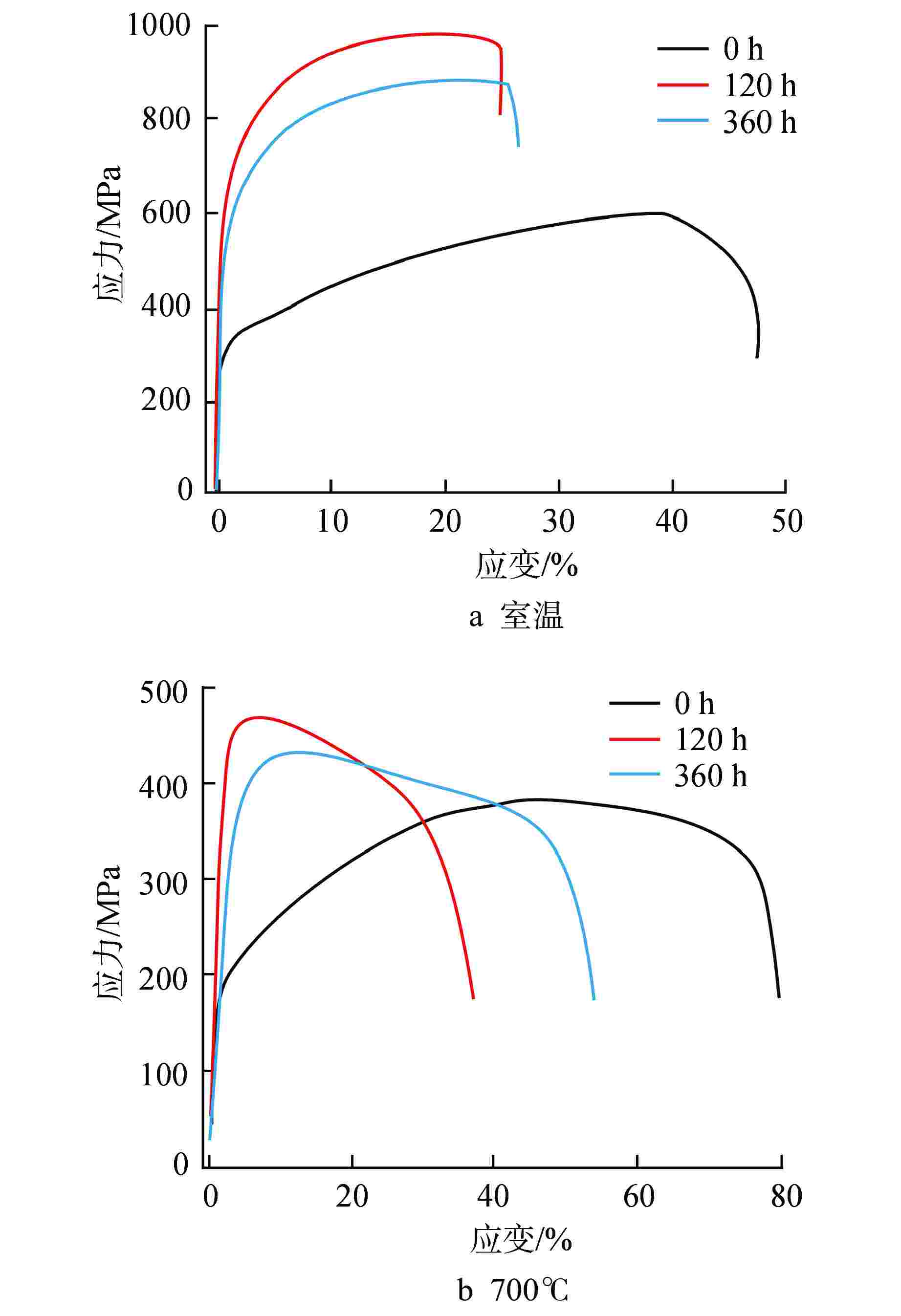
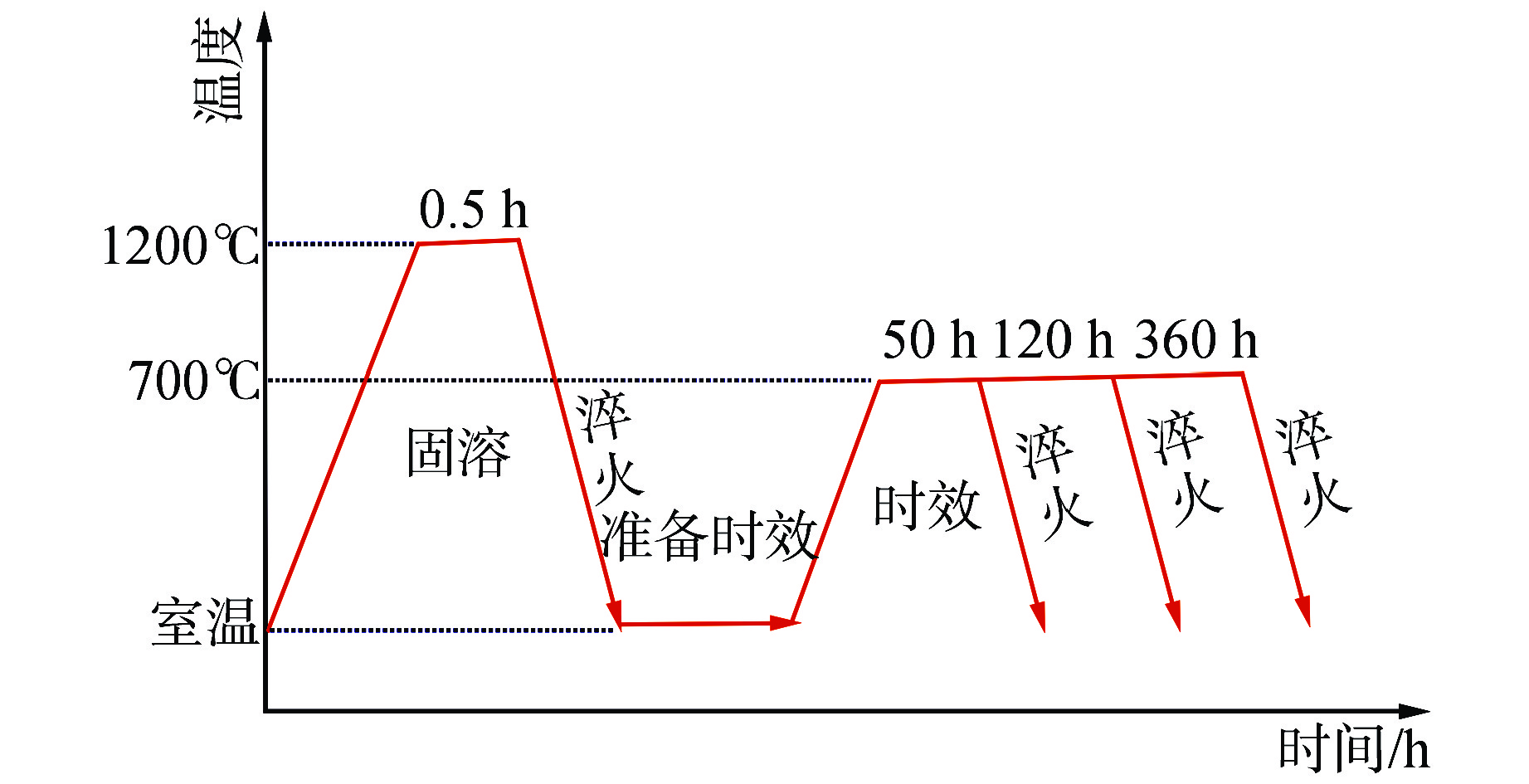
摘要: 为提高25Ni-20Cr(S35140)奥氏体不锈钢的高温强度,以满足超临界水堆(SCWR)对包壳材料的应用要求。采用微合金化方法,通过添加N和Al元素,并在700℃高温时效对S35140钢的性能进行改进。结果表明,加N钢中析出纳米级NbN相,钉扎位错,随时效进行,室温拉伸强度略有提高,室温延伸率几乎不变,高温拉伸强度略有降低,而高温延伸率提升至65%,时效120 h后冲击功仍然达到111.39 J;加Al钢中析出大量NiAl相和Laves相,随时效进行,室温和高温拉伸强度均显著提升,室温拉伸强度甚至达到1000 MPa,而塑性和冲击韧性下降明显。因此在S35140钢中,加N提高了塑韧性,加Al提高了强度,均显著改善S35140钢的力学性能。
-
关键词:
- S35140奥氏体钢 /
- 显微组织 /
- 力学性能 /
- 高温时效
Abstract: The high temperature strength of the 25Ni-20Cr (S35140) austenitic stainless steel needs to be improved to meet the application requirements of supercritical water reactor (SCWR) for cladding materials. In this study, the properties of S35140 Steel were improved by microalloying, adding N and Al and aging at 700℃. The results showed that nano-NbN phase precipitated in N-added steel, and dislocation was pinched. With aging, the tensile strength at room temperature increased slightly, the elongation at room temperature almost remained unchanged, and the tensile strength at high temperature decreased slightly; however, the elongation at high temperature increased to 65%, and the impact energy still reached 111.39 J after aging for 120 h. A large number of NiAl and Laves phases precipitated in Al-added steel. With aging, the tensile strength at room temperature and high temperature increased significantly, and the tensile strength at room temperature even reached 1000 MPa, while the ductility and impact toughness decreased significantly. Therefore, in S35140 steel, adding N increased the ductility and toughness, while adding Al increased the strength, both of which significantly improved the mechanical properties of S35140 steel.-
Key words:
- S35140 austenitic steel /
- Microstructure /
- Mechanical properties /
- Thermal aging
-
表 1 2种改进型S35140钢的实际成分
Table 1. Actual Composition of Two Kinds of Modified S35140 Steel
实验钢 元素质量分数/% Cr Ni Nb Al Si C Mo N Ti Fe N钢 19.59 24.20 0.77 0.02 0.4 0.03 1.69 0.1 0.04 Bal. 3Al钢 17.31 28.51 0.58 3.11 0.1 0.04 2.28 0 0.02 Bal. Bal.—Fe元素占比余量 表 2 时效360 h后N钢晶内析出相的EDS结果
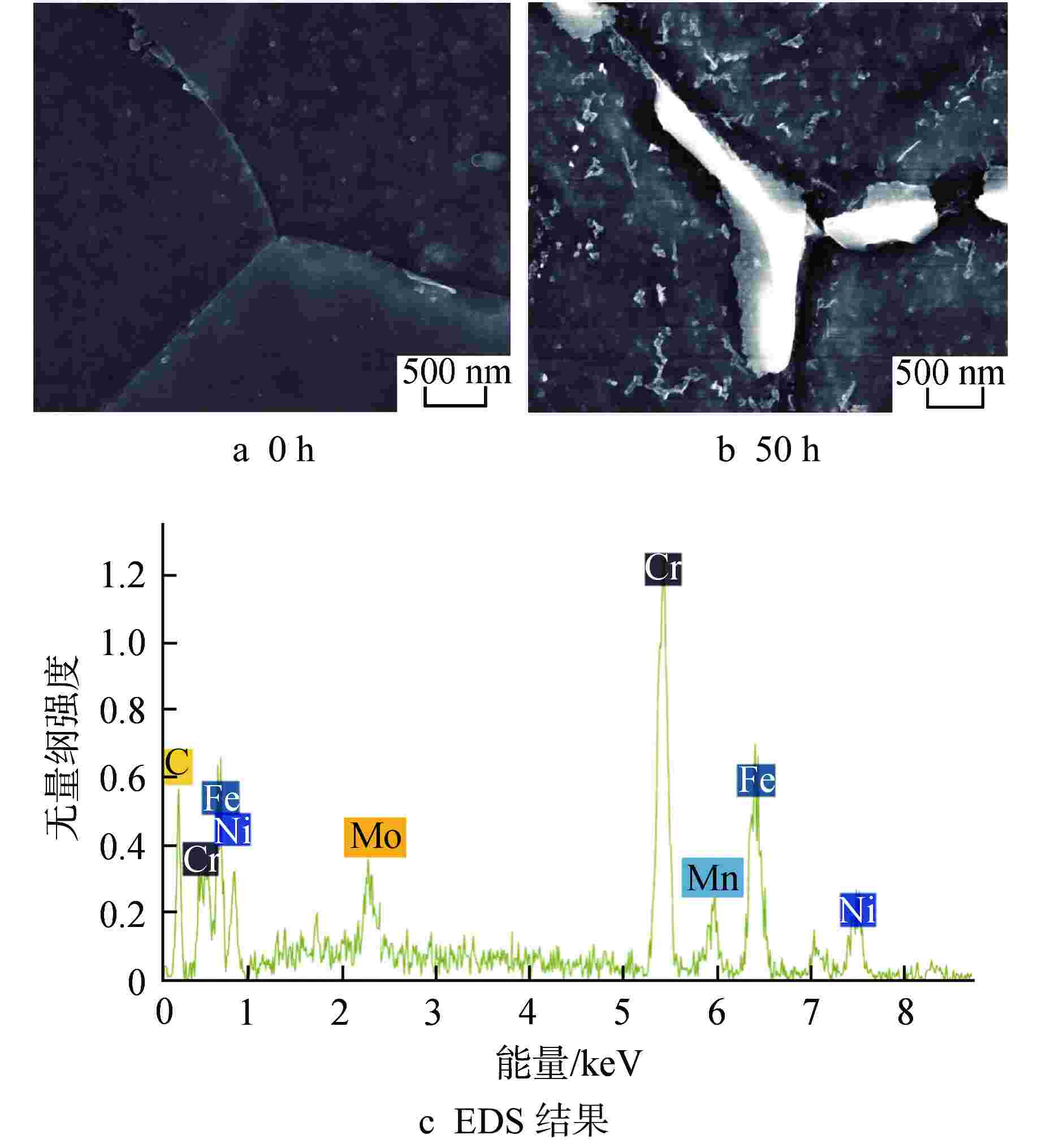
Table 2. EDS Results for Intragranular Precipitates in N Steel after 360 h Aging
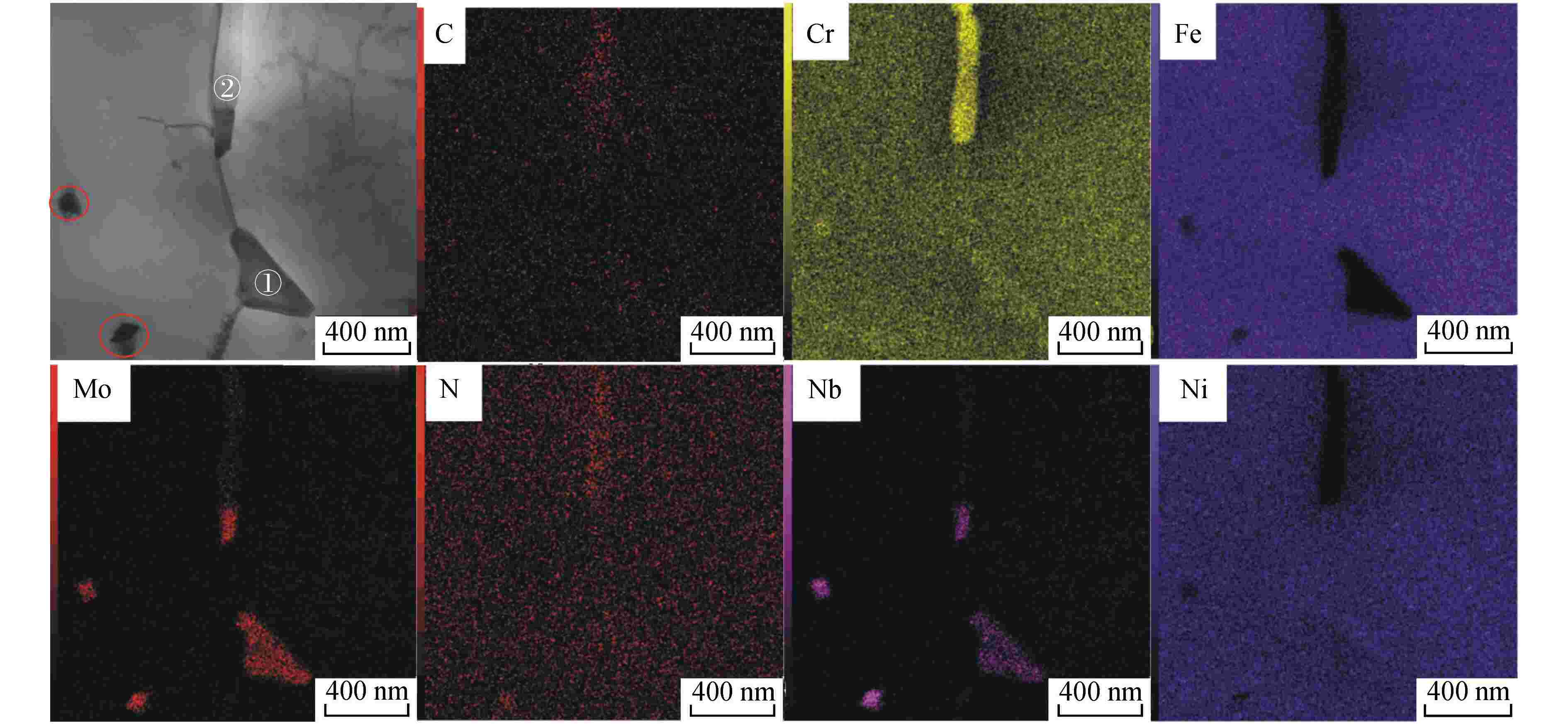
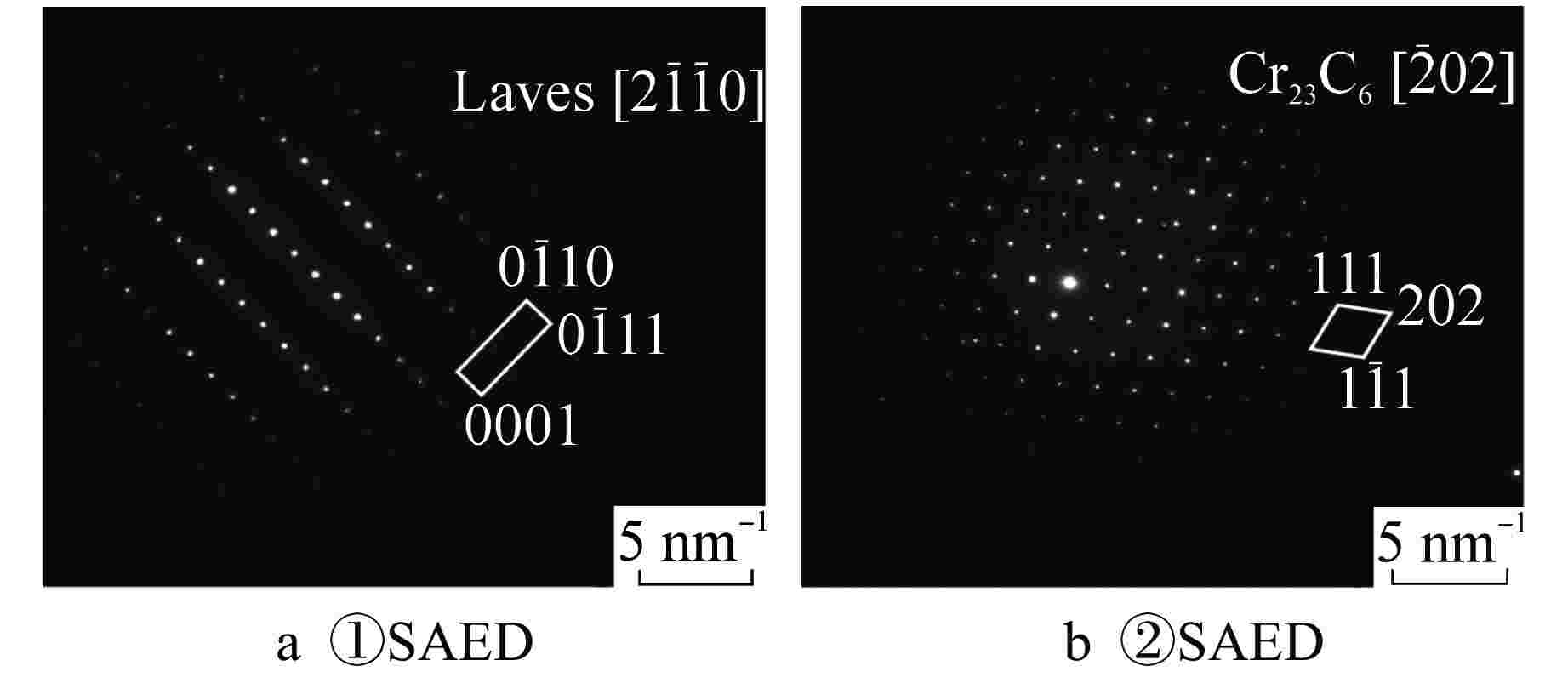
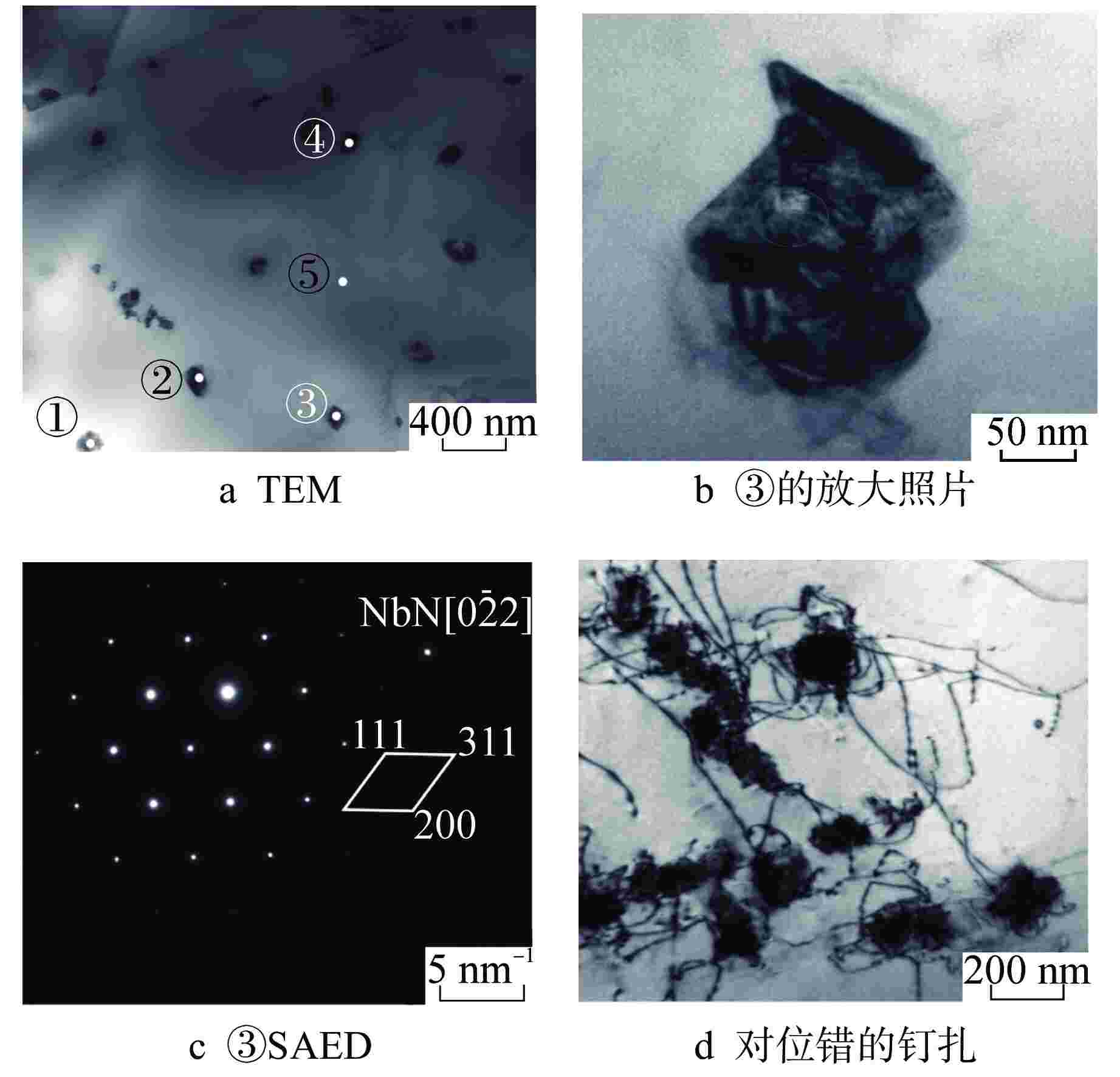
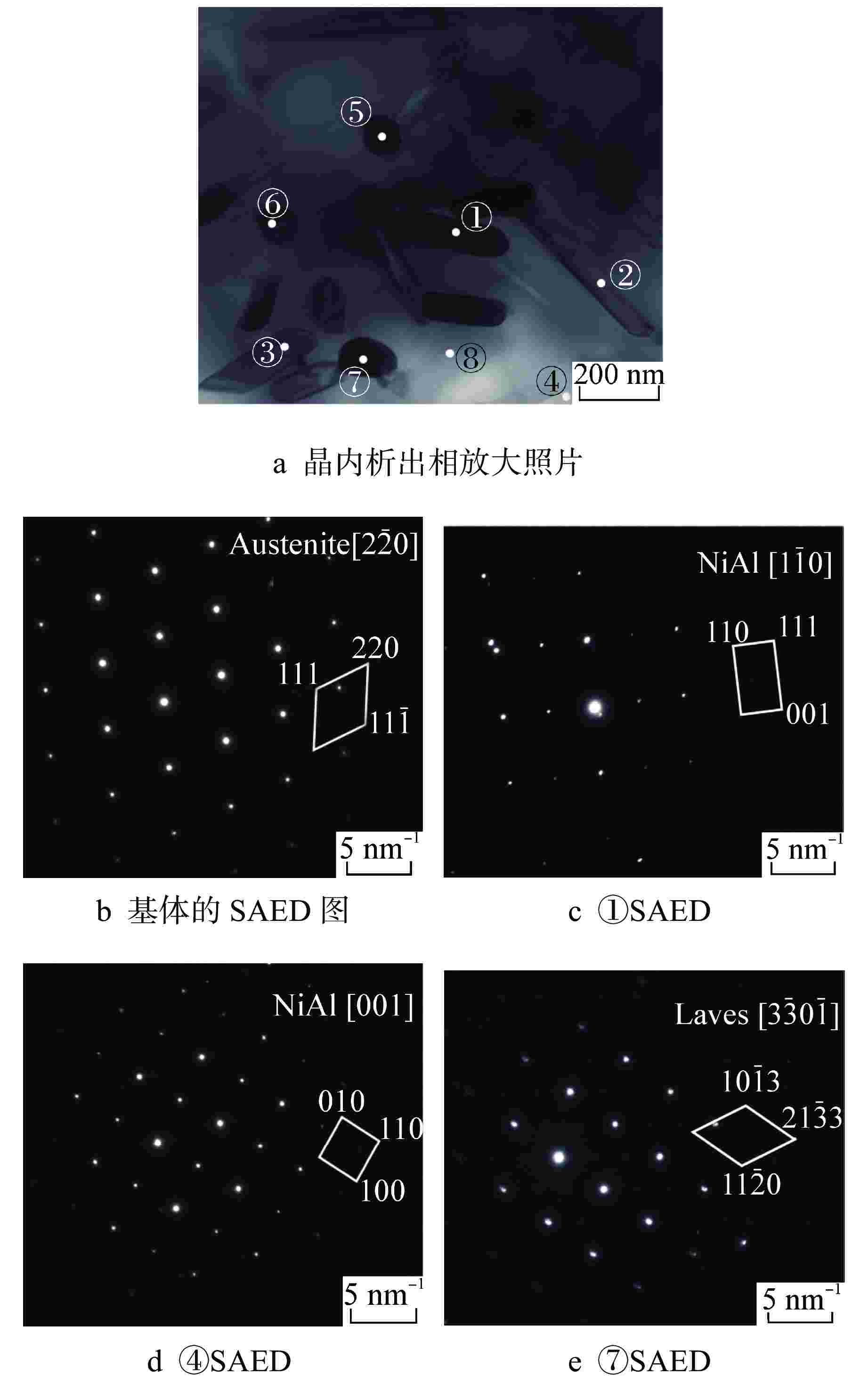
标记 元素原子百分比/% C N Cr Fe Ni Nb Mo ① 0 6.28 7.28 5.25 1.50 79.69 0 ② 0 2.43 18.43 5.01 1.64 66.81 5.69 ③ 0.15 3.30 17.64 26.00 12.24 39.36 1.32 ④ 0.83 2.74 10.08 9.71 3.26 72.57 0.81 ⑤ 0 2.60 20.09 50.22 24.59 0.10 2.39 表 3 时效360 h后3Al钢晶内析出相的EDS结果
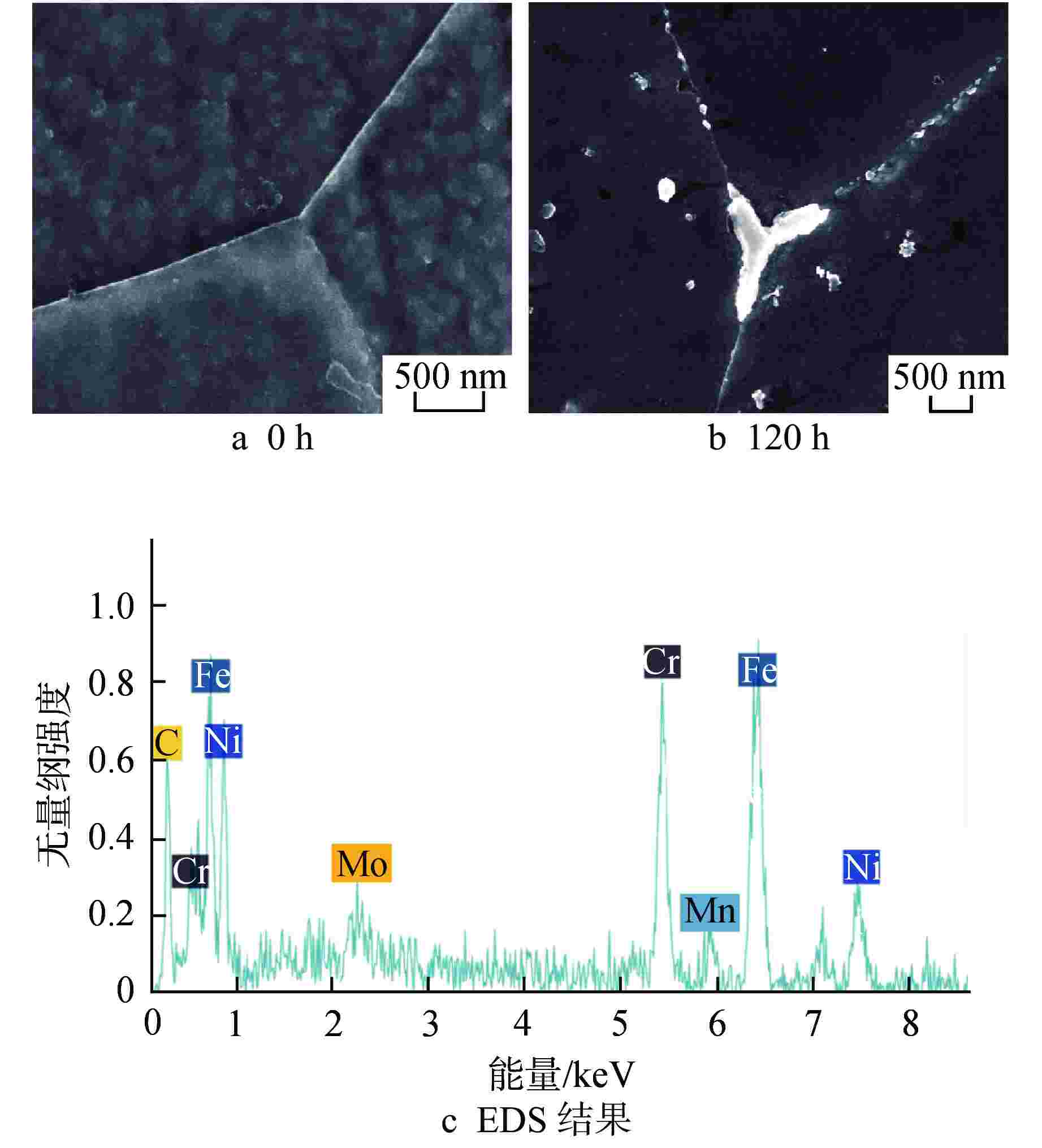
Table 3. EDS Results of Intragranular Precipitates in 3Al Steel after 360 h Aging
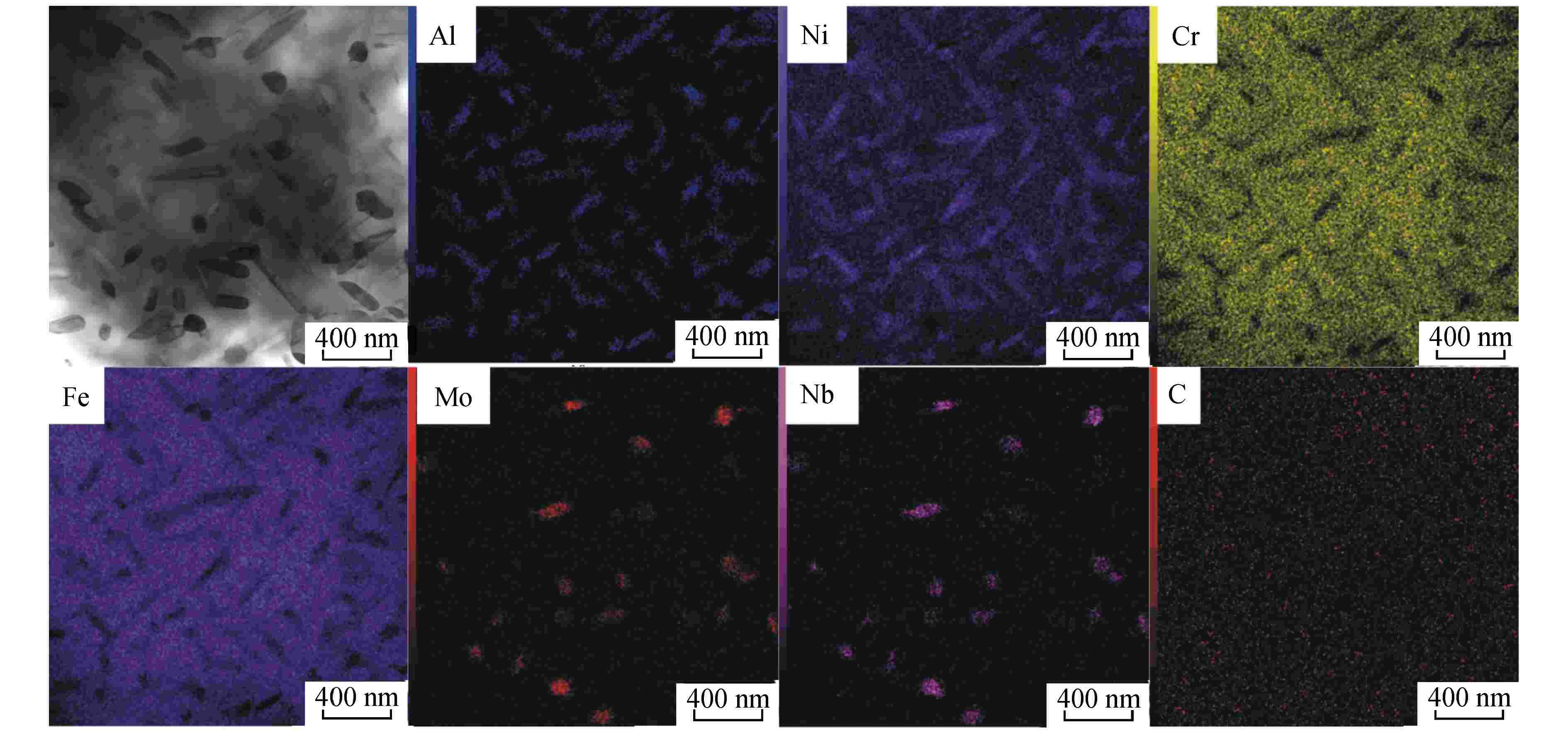
标记 元素原子百分比/% C Al Cr Fe Ni Nb Mo ① 0 28.91 2.43 13.68 54.51 0.18 0.26 ② 0 10.00 11.70 45.58 32.13 0.03 0.55 ③ 0 6.45 13.15 48.53 31.19 0.02 0.66 ④ 0.84 28.81 2.42 14.38 53.17 0.10 0.15 ⑤ 0 0.76 15.08 54.53 11.74 5.21 12.53 ⑥ 0.10 0.53 13.26 45.18 6.18 10.08 24.55 ⑦ 0 1.23 15.45 53.74 11.61 5.67 13.12 ⑧ 0 1.63 16.80 61.08 18.90 0.15 1.38 表 4 N钢和3Al钢时效态样品的室温冲击功
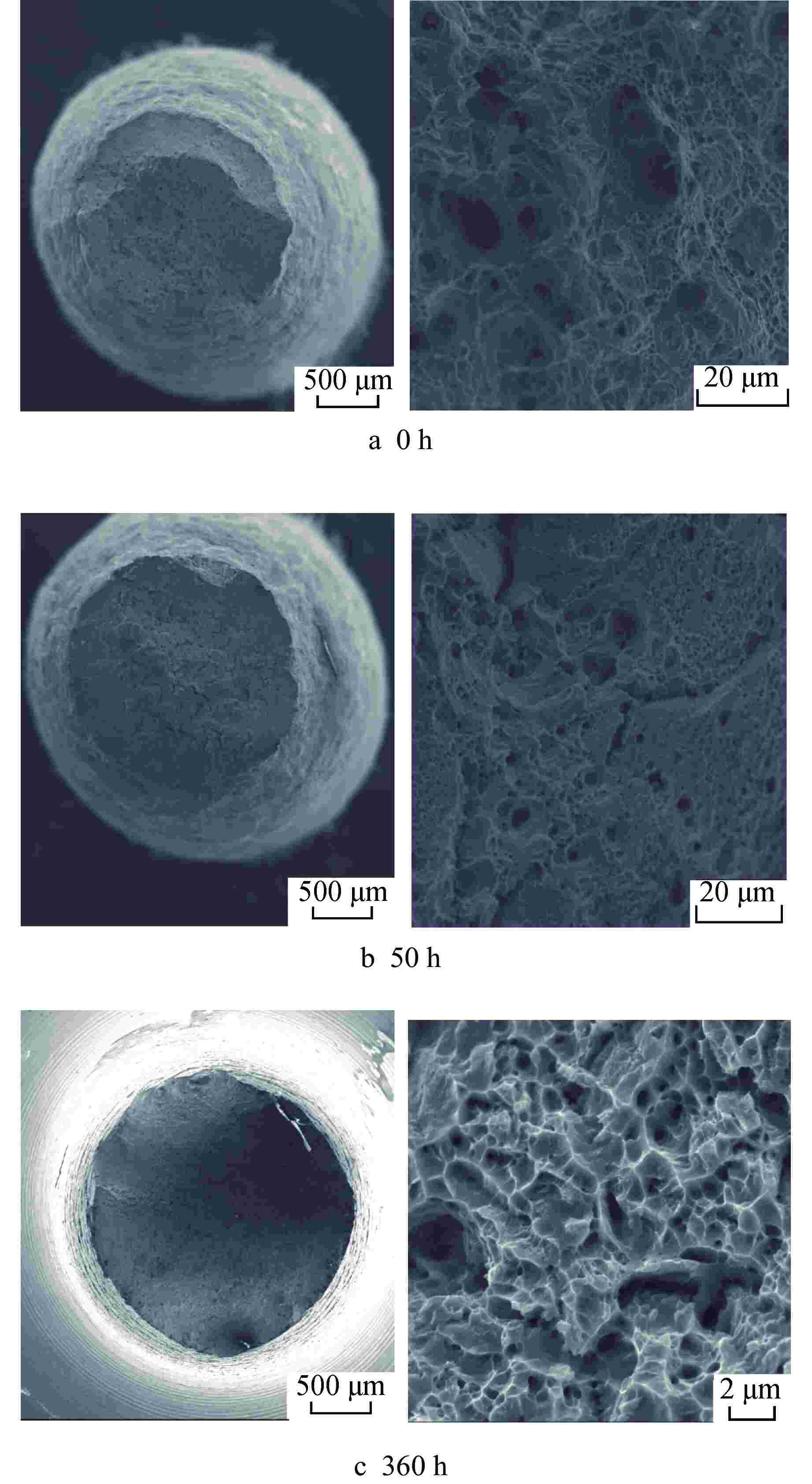
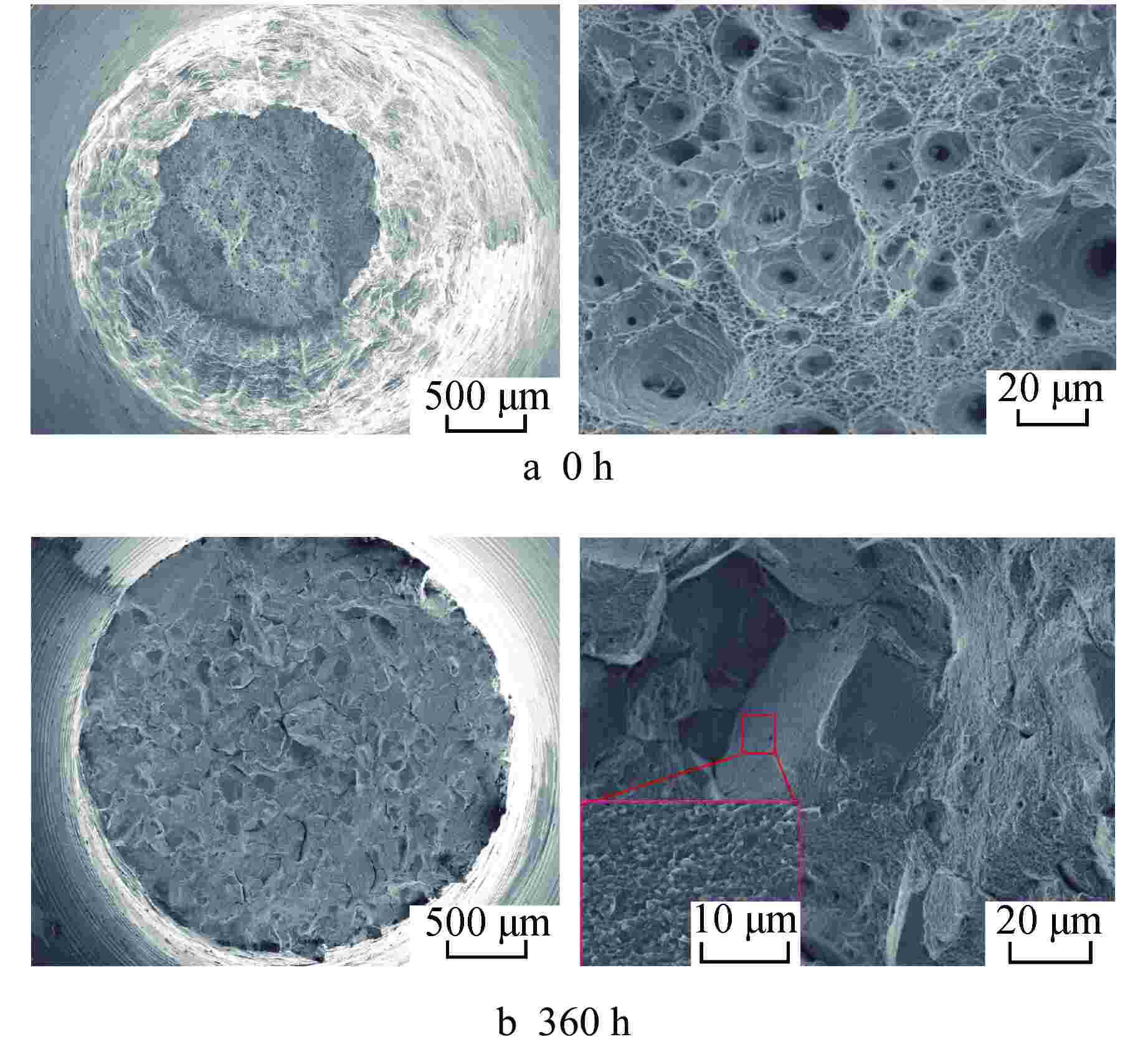
Table 4. Impact Energy of Aged N and 3Al Steel at Room Temperature
钢种 时效时间/h 冲击功/J N钢 0 264.47 50 166.87 360 111.39 3Al钢 0 357.76 120 44.81 360 48.24 -
[1] ISEDA A, OKADA H, SEMBA H, et al. Long term creep properties and microstructure of SUPER304H, TP347HFG and HR3C for A-USC boilers[J]. Energy Materials, 2007, 2(4): 199-206. doi: 10.1179/174892408X382860 [2] ZHANG N Q, LI B R, BAI Y, et al. Oxidation of austenitic steel TP347HFG exposed to supercritical water with different dissolved oxygen concentration[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2011, 148-149: 1179-1183. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.148-149.1179 [3] ODETTE G R, ALINGER M J, WIRTH B D. Recent developments in irradiation-resistant steels[J]. Annual Review of Materials Research, 2008, 38: 471-503. doi: 10.1146/annurev.matsci.38.060407.130315 [4] LINDAU R, MÖSLANG A, SCHIRRA M, et al. Mechanical and microstructural properties of a hipped RAFM ODS-steel[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2002, 307-311: 769-772. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3115(02)01045-0 [5] SAGARADZE V V, SHALAEV V I, ARBUZOV V L, et al. Radiation resistance and thermal creep of ODS ferritic steels[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2001, 295(2-3): 265-272. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3115(01)00511-6 [6] RAMAR A, SPÄTIG P, SCHÄUBLIN R. Analysis of high temperature deformation mechanism in ODS EUROFER97 alloy[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2008, 382(2-3): 210-216. doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2008.08.009 [7] MUKHOPADHYAY D K, FROES F H, GELLES D S. Development of oxide dispersion strengthened ferritic steels for fusion[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 1998, 258-263: 1209-1215. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3115(98)00188-3 [8] YUTANI K, KISHIMOTO H, KASADA R, et al. Evaluation of Helium effects on swelling behavior of oxide dispersion strengthened ferritic steels under ion irradiation[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2007, 367-370: 423-427. doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2007.03.016 [9] CHO H S, KIMURA A, UKAI S, et al. Corrosion properties of oxide dispersion strengthened steels in super-critical water environment[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2004, 329-333: 387-391. doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2004.04.040 [10] YOSHITAKE T, OHMORI T, MIYAKAWA S. Burst properties of irradiated oxide dispersion strengthened ferritic steel claddings[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2002, 307-311: 788-792. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3115(02)00947-9 [11] ALAMO A, BERTIN J L, SHAMARDIN V K, et al. Mechanical properties of 9Cr martensitic steels and ODS-FeCr alloys after neutron irradiation at 325℃ up to 42dpa[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2007, 367-370: 54-59. doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2007.03.166 [12] WAS G S, AMPORNRAT P, GUPTA G, et al. Corrosion and stress corrosion cracking in supercritical water[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2007, 371(1-3): 176-201. doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2007.05.017 [13] ZHANG Q, TANG R, YIN K J, et al. Corrosion behavior of Hastelloy C-276 in supercritical water[J]. Corrosion Science, 2009, 51(9): 2092-2097. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2009.05.041 [14] FULGER M, OHAI D, MIHALACHE M, et al. Oxidation behavior of Incoloy 800 under simulated supercritical water conditions[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2009, 385(2): 288-293. doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2008.12.004 [15] 胡本芙,余泉茂,高桥平七郎,等. 氦对Fe-Cr-Ni合金和Fe-Cr-Mn合金辐照损伤的影响[J]. 核科学与工程,2003, 23(2): 145-151. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-0918.2003.02.010 [16] 刘含莲,滕新营,王执福,等. Fe-Cr-Ni-N高温耐热钢的抗氧化性研究[J]. 铸造技术,2001, 22(6): 55-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8365.2001.06.023 [17] 王荣光,魏云,张清廉,等. 奥氏体不锈钢SUS316及SUS316L在含Cl−的饱和H2S水溶液中的应力腐蚀行为研究[J]. 中国腐蚀与防护学报,2000, 20(1): 47-53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4537.2000.01.008 [18] 周军,李中奎. 轻水反应堆(LWR)用包壳材料研究进展[J]. 中国材料进展,2014, 33(9-10): 554-559. [19] 张小可,纪仁峰,周灿栋. 超级奥氏体不锈钢00Cr20Ni25Mo6N0.15的时效析出相研究[J]. 宝钢技术,2021(6): 35-43,47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0716.2021.06.006 [20] BRADY M P, MAGEE J, YAMAMOTO Y, et al. Co-optimization of wrought alumina-forming austenitic stainless steel composition ranges for high-temperature creep and oxidation/corrosion resistance[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2014, 590: 101-115. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2013.10.014 [21] 徐向棋,吕昭平. 新一代新型抗高温氧化奥氏体耐热钢的研究进展[J]. 中国材料进展,2011, 30(12): 1-5+33. [22] VISWANATHAN R, BAKKER W. Materials for ultrasupercritical coal power plants-Turbine materials: part II[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2001, 10(1): 96-101. doi: 10.1361/105994901770345402 [23] VISWANATHAN R, COLEMAN K, RAO U. Materials for ultra-supercritical coal-fired power plant boilers[J]. International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 2006, 83(11-12): 778-783. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpvp.2006.08.006 [24] BRADY M P, YAMAMOTO Y, SANTELLA M L, et al. Composition, microstructure, and water vapor effects on internal/external oxidation of alumina-forming austenitic stainless steels[J]. Oxidation of Metals, 2009, 72(5): 311-333. [25] BRADY M P, UNOCIC K A, LANCE M J, et al. Increasing the Upper temperature oxidation limit of alumina forming austenitic stainless steels in air with water vapor[J]. Oxidation of Metals, 2011, 75(5): 337-357. [26] BRADY M P, YAMAMOTO Y, SANTELLA M L, et al. Effects of minor alloy additions and oxidation temperature on protective alumina scale Formation in creep-resistant austenitic stainless steels[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2007, 57(12): 1117-1120. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2007.08.032 [27] STOTT F H, WOOD G C, STRINGER J. The influence of alloying elements on the development and maintenance of protective scales[J]. Oxidation of Metals, 1995, 44(1-2): 113-145. doi: 10.1007/BF01046725 [28] 王曼. 新型奥氏体钢显微组织结构稳定性及力学性能的研究[D]. 北京: 北京科技大学, 2017. [29] 孙胜英. 新型奥氏体耐热钢的制备与性能优化[D]. 北京: 北京科技大学, 2014 -





 下载:
下载: