Three-Dimensional Pin-by-pin Transient Analysis for PWR-Core
-
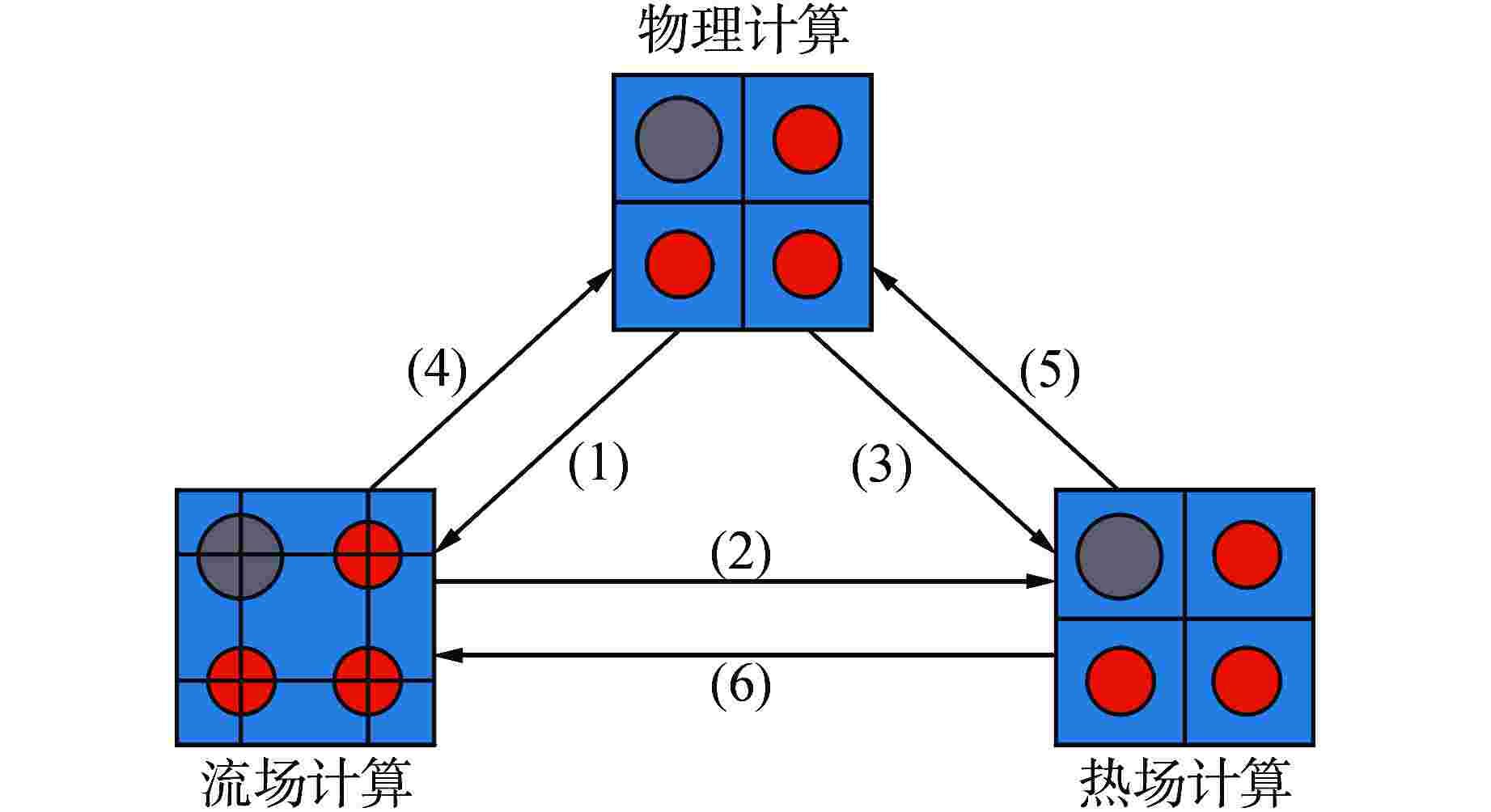
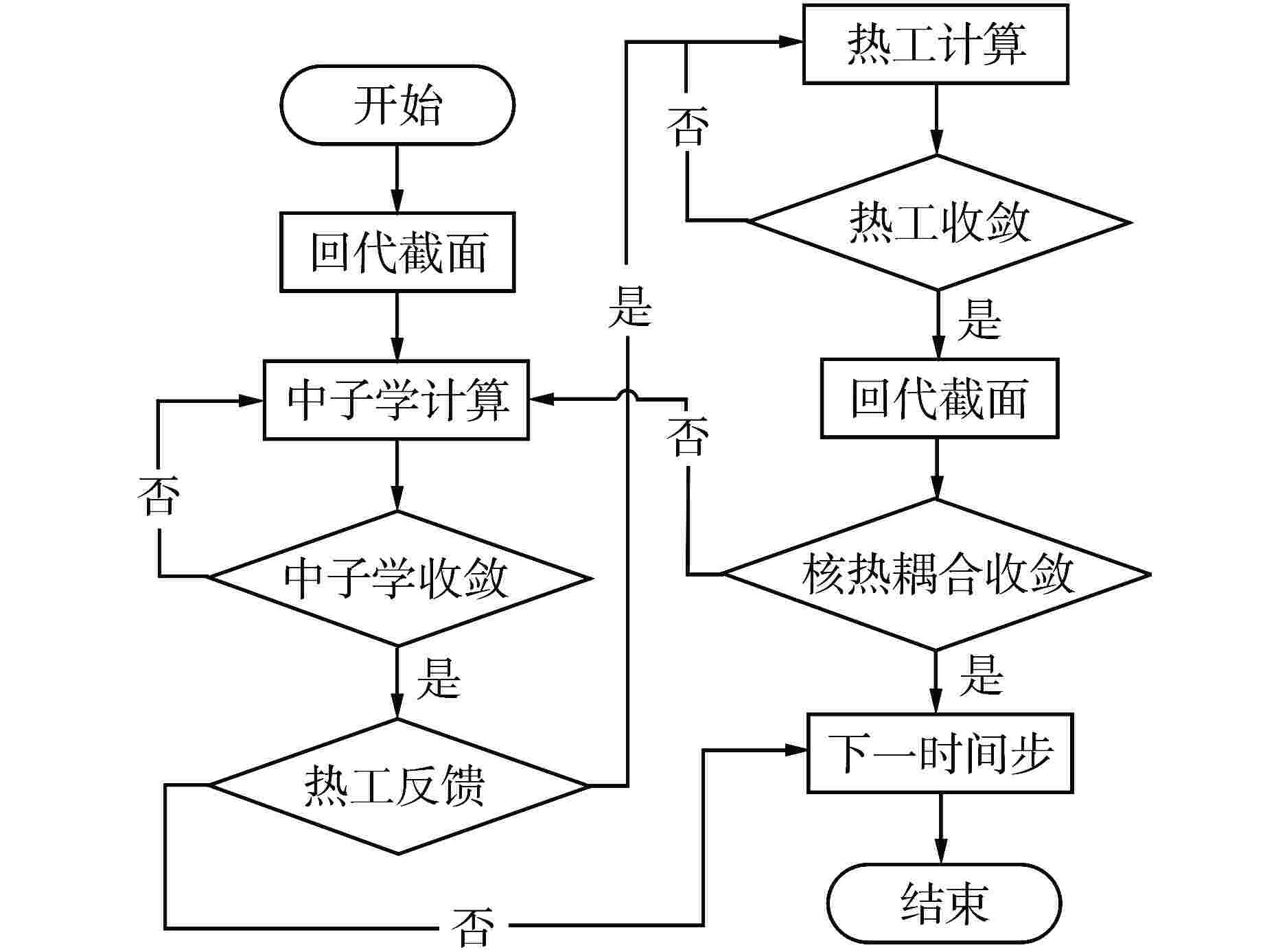
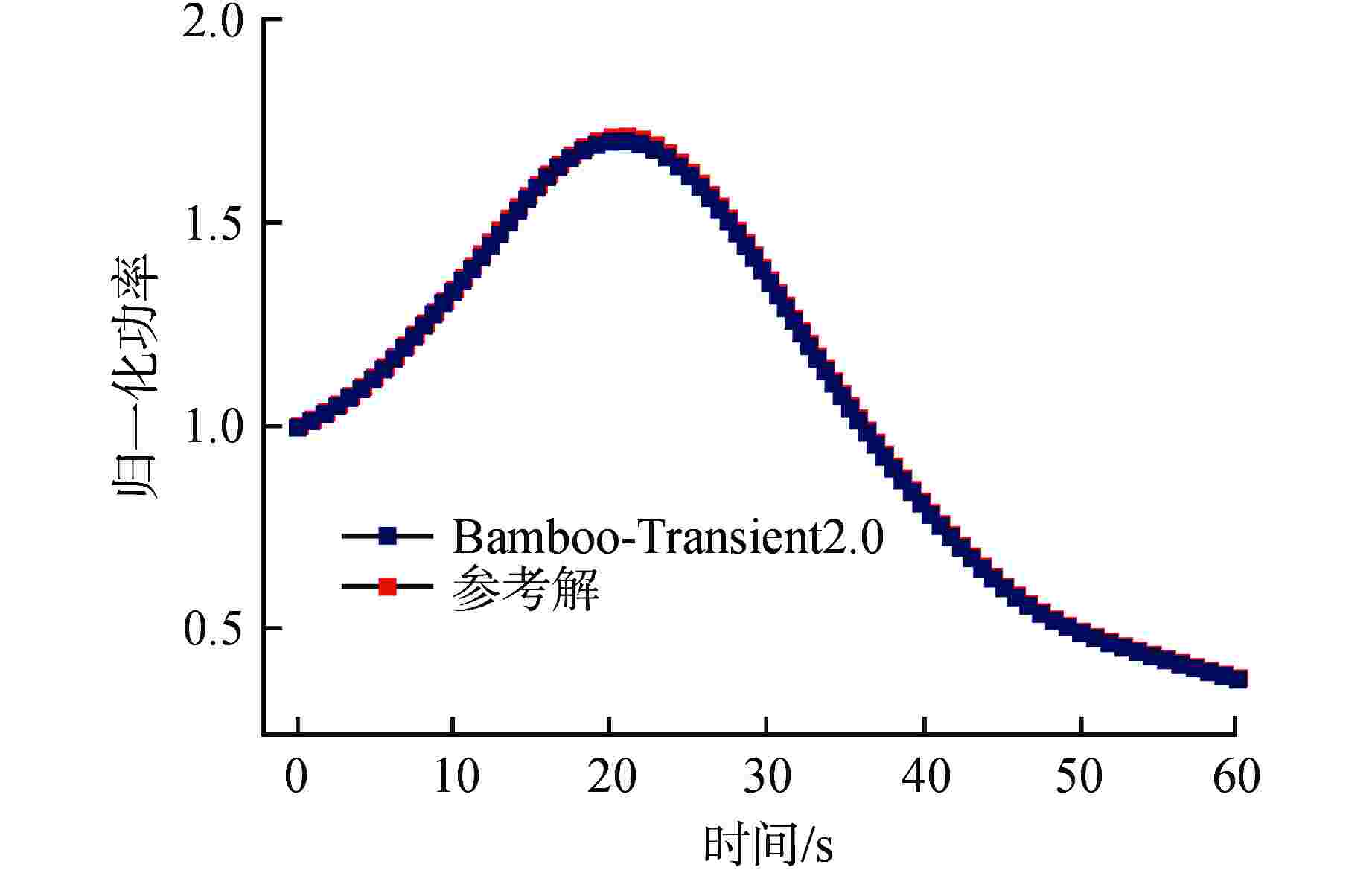
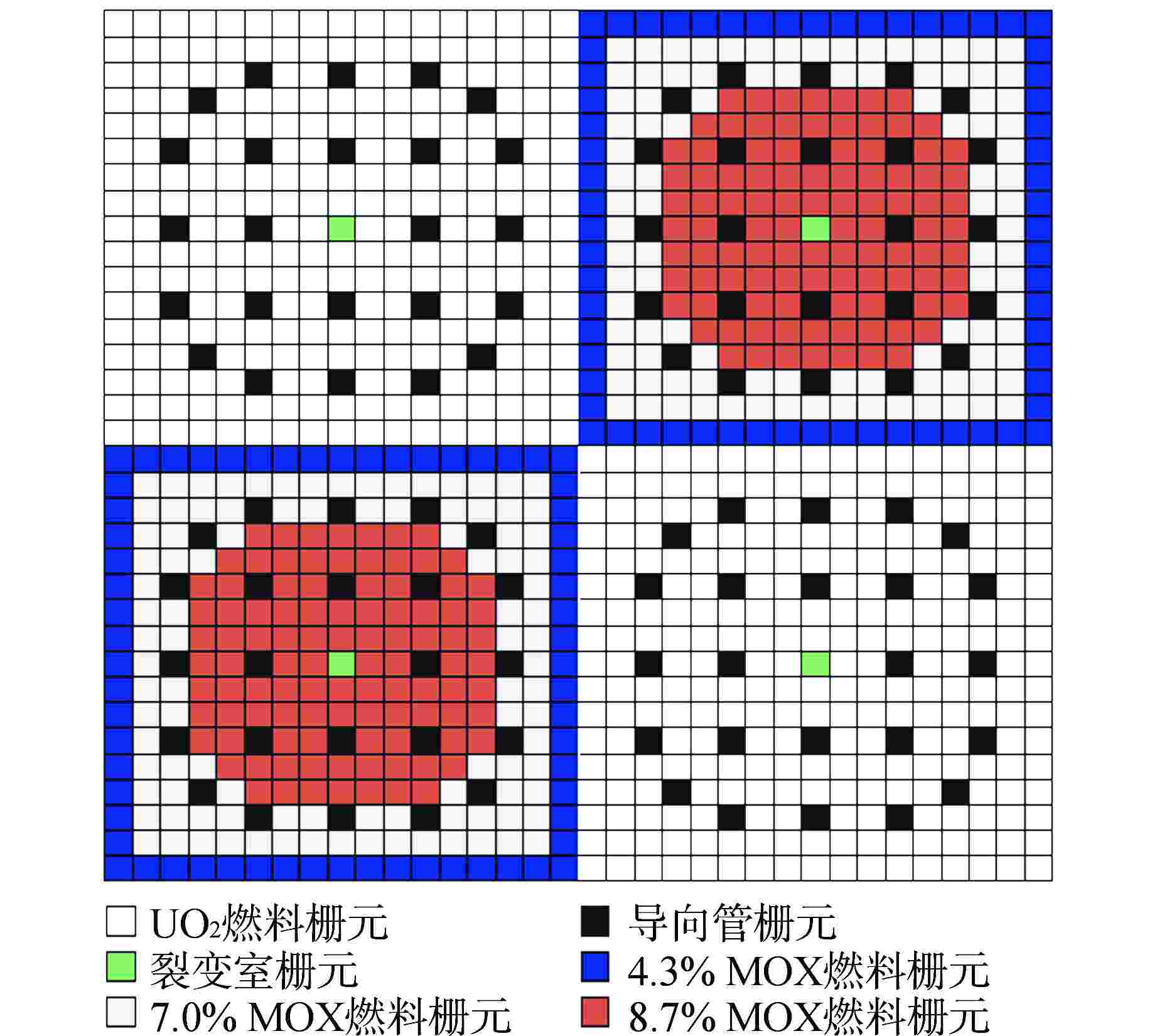
摘要: 为了保证核反应堆在瞬态过程中的安全性,需要进行三维全堆芯的瞬态分析,给出安全分析关注的燃料棒功率分布。本研究建立了压水堆三维全堆芯Pin-by-pin核热耦合瞬态分析的理论模型:采用全隐式向后差分方法和指数函数展开节块法实现了三维全堆芯Pin-by-pin时空中子动力学计算;采用栅元尺度的多通道模型进行三维全堆芯Pin-by-pin热工反馈计算;采用Picard迭代实现了核热紧耦合迭代计算;利用信息传递接口(MPI)并行技术,采用统一的空间区域分解方式,实现了核热耦合瞬态过程的并行计算。基于理论模型,开发了相应的程序Bamboo-Transient2.0,采用基准题和多组件问题对程序进行验证,并将其应用于商用压水堆瞬态分析。结果表明:Pin-by-pin瞬态分析程序较之组件均匀化的粗网扩散程序结果更加精细,有效改善了棒功率分布的偏差,同时能够给出栅元尺度下的各状态参数分布情况,可直接满足安全分析需求。
-
关键词:
- 压水堆 /
- NECP-Bamboo /
- Pin-by-pin /
- 瞬态分析
Abstract: In order to ensure the safety of nuclear reactor in transient process, it is necessary to carry out three-dimensional transient analysis of the whole core to obtain the power distribution of fuel rods concerned in the safety analysis. In this paper, a theoretical model of the pin-by-pin neutronic-thermohydraulic coupling transient analysis for PWR-core is established: the three-dimensional pin-by-pin spatio-temporal neutron dynamics calculation of PWR-core is realized by fully implicit backward difference method and exponential function expansion nodal method; the multi-channel model of cell scale is used to calculate the thermal feedback of three-dimensional full core pin-by-pin; the Picard iteration is used to realize the iterative calculation of neutronic-thermohydraulic tight coupling; using the parallel technology of message passing interface (MPI) and the unified spatial domain decomposition method, the parallel calculation of neutronic-thermohydraulic coupling transient process is realized. Based on the theoretical model, the corresponding code called Bamboo-Transient 2.0 was developed and verified by the benchmark and multi-assemblies questions, and it was then applied to the transient analysis for commercial PWRs. The results show that the pin-by-pin transient analysis code has more fine results than that of the traditional coarse-mesh diffusion code based on assembly homogenization, and it can reduce the deviation of power distribution of pin-cell. Meanwhile, it can provide the distribution of state parameters at cell scale, which can directly meet the requirements of safety analysis.-
Key words:
- PWR /
- NECP-Bamboo /
- Pin-by-pin /
- Transient analysis
-
表 1 不同CPU数目计算时间及并行效率
Table 1. Calculation Time and Parallel Efficiency for Different CPU Number
CPU数目 计算时间/s 并行效率/% 1 268.5 100 2 147.1 91.3 4 78.2 85.8 8 42.7 78.6 表 2 棒功率分布偏差随时间变化情况
Table 2. Deviation of Pin-cell Power Distribution at Different Time
时刻/s 最大偏差
(SP3)/%均方根偏差
(SP3)/%最大偏差
(扩散)/%均方根偏差
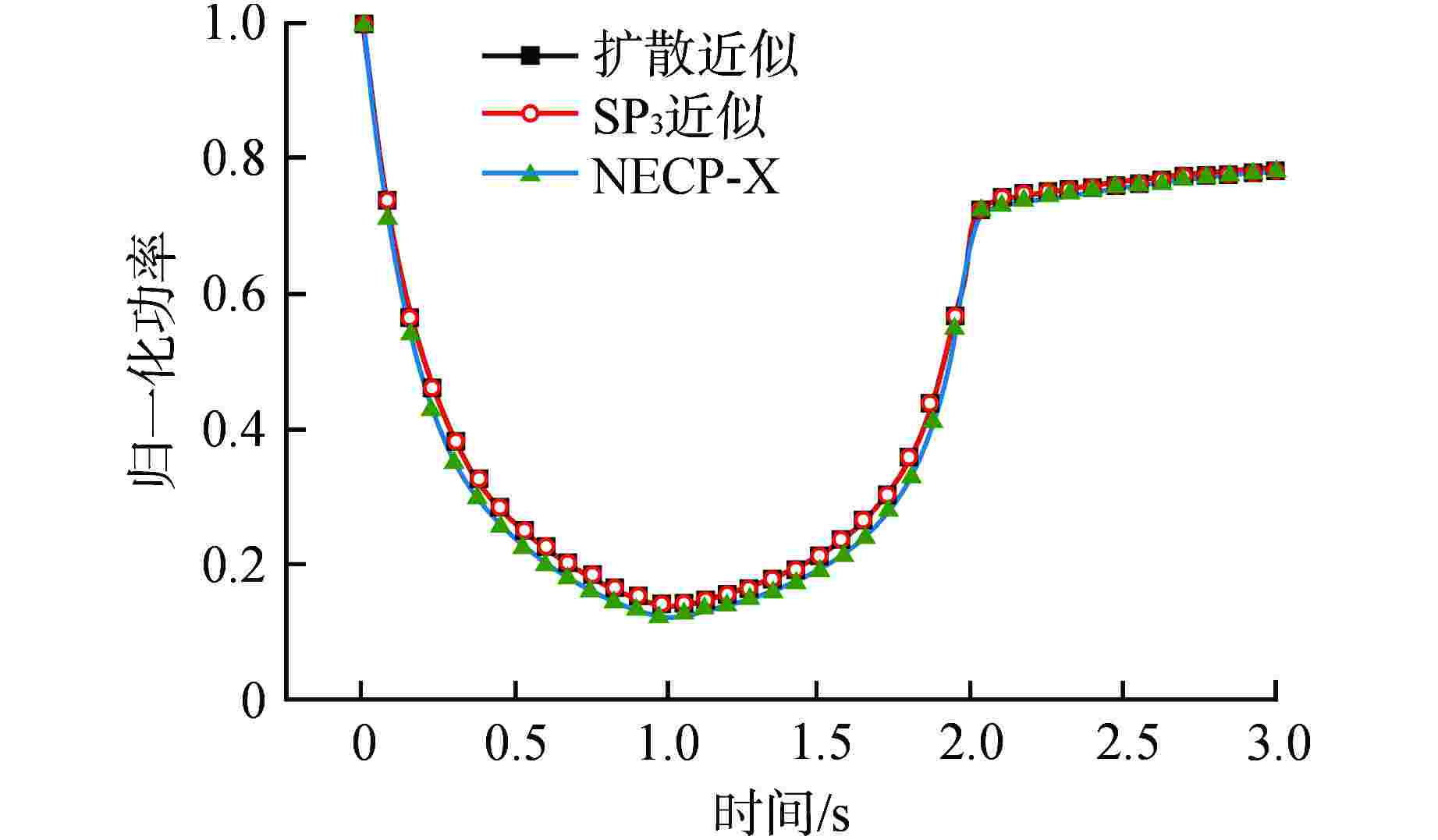
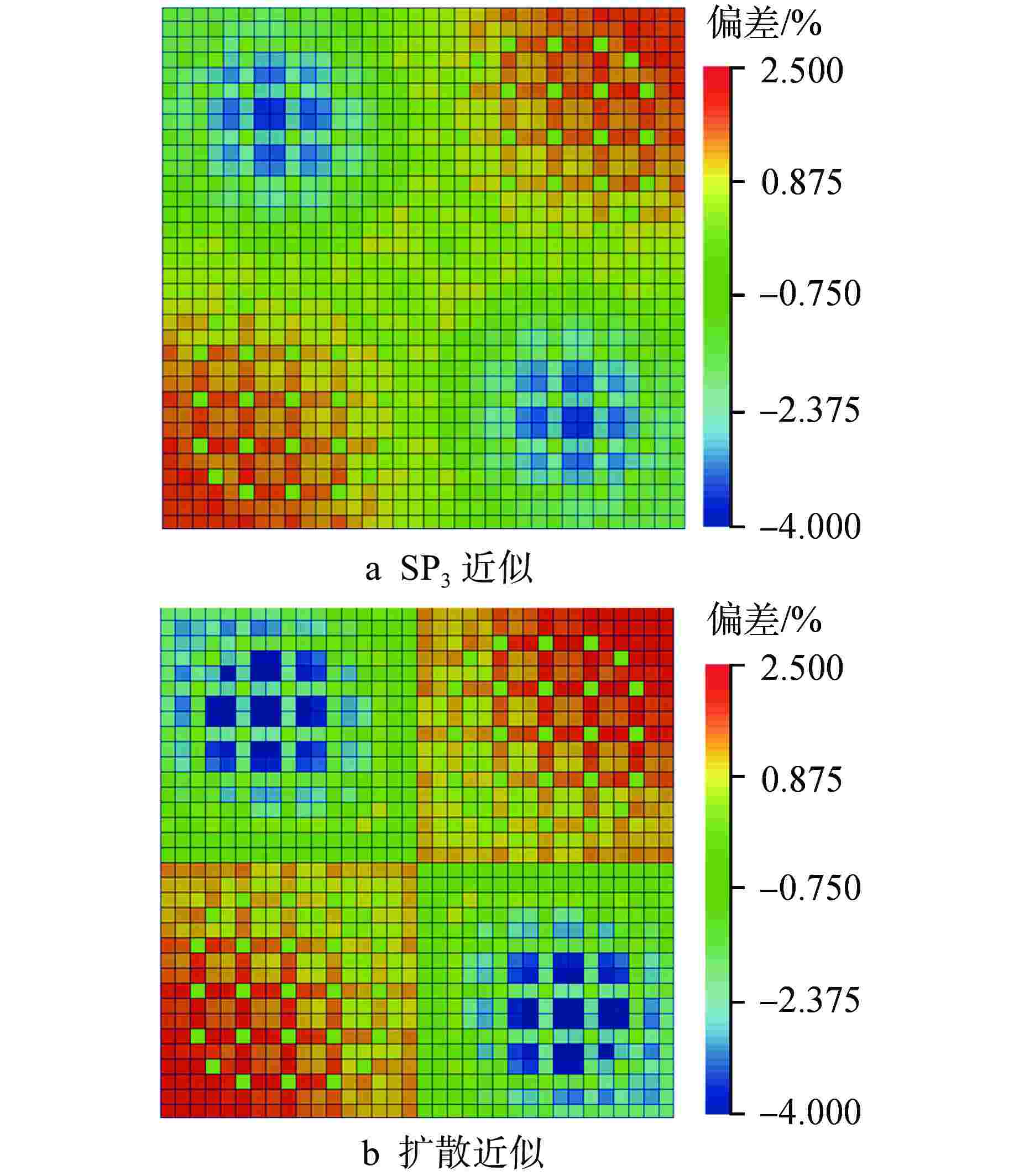
(扩散)/%0.5 −1.7861 0.6606 −2.6712 1.0025 1.0 −3.3670 1.3333 −4.0070 1.6127 2.0 0.9454 0.3019 −1.3593 0.5355 3.0 0.9433 0.3022 −1.3617 0.5354 -
[1] LI Y Z, HE T, LIANG B N, et al. Development and verification of PWR-core nuclear design code system NECP-Bamboo: Part III: Bamboo-transient[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 359: 110462. [2] GARCÍA-HERRANZ N, CUERVO D, SABATER A, et al. Multiscale neutronics/thermal-hydraulics coupling with COBAYA4 code for Pin-by-pin PWR transient analysis[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2017, 321: 38-47. doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2017.03.017 [3] GRAHN A, KLIEM S, ROHDE U. Coupling of the 3D neutron kinetic core model DYN3D with the CFD software ANSYS-CFX[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2015, 84: 197-203. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2014.12.015 [4] LEE D, KOZLOWSKI T, DOWNAR T J. Multi-group SP3 approximation for simulation of a three-dimensional PWR rod ejection accident[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2015, 77(mar.):94-100. [5] TADA K, YAMAMOTO A, YAMANE Y, et al. Applicability of the diffusion and simplified P3 theories for pin-by-pin geometry of BWR[J]. Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 2008, 45(10): 997-1008. doi: 10.1080/18811248.2008.9711885 [6] 谢伟华. 压水堆堆芯三维Pin-by-pin中子动力学计算方法研究[D]. 西安: 西安交通大学, 2018. [7] 杨文,郑友琦,吴宏春,等. EFEN-SP3方法的加速与并行计算研究[J]. 原子能科学技术,2013, 47(S2): 664-667. [8] WAND YQ, RABITI C, PALMIOTTI G. Parallelization of the red-black algorithm on solving the second-order PN transport equation with the hybrid finite element method[J]. Transactions of American Nuclear Society, 2011, 105: 319-321. [9] LI Y Z, ZHANG B, HE Q M, et al. Development and verification of PWR-core fuel management calculation code system NECP-Bamboo: Part I Bamboo-Lattice[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2018, 335: 432-440. doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2018.05.030 [10] YANG W, WU H C, LI Y Z, et al. Development and verification of PWR-core fuel management calculation code system NECP-Bamboo: Part II Bamboo-Core[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2018, 337: 279-290. doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2018.07.017 [11] GOLUOGLU S. A deterministic method for transient, three-dimensional neutron transport[D]. Knoxville, USA: The University of Tennessee, 1997. [12] SMITH M A, LEWIS E E, NA BC. Benchmark on deterministic 2-D MOX fuel assembly transport calculations without spatial homogenization[J]. Progress in Nuclear Energy, 2004, 45(2-4): 107-118 [13] HOU J, IVANOV K N, BOYARINOV V F, et al. OECD/NEA benchmark for time-dependent neutron transport calculations without spatial homogenization[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2017, 317: 177-189. doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2017.02.008 -





 下载:
下载: