Effect of Al Element on Thermal Aging Behavior of 20Cr25NiNb Heat-Resistant Steel
-
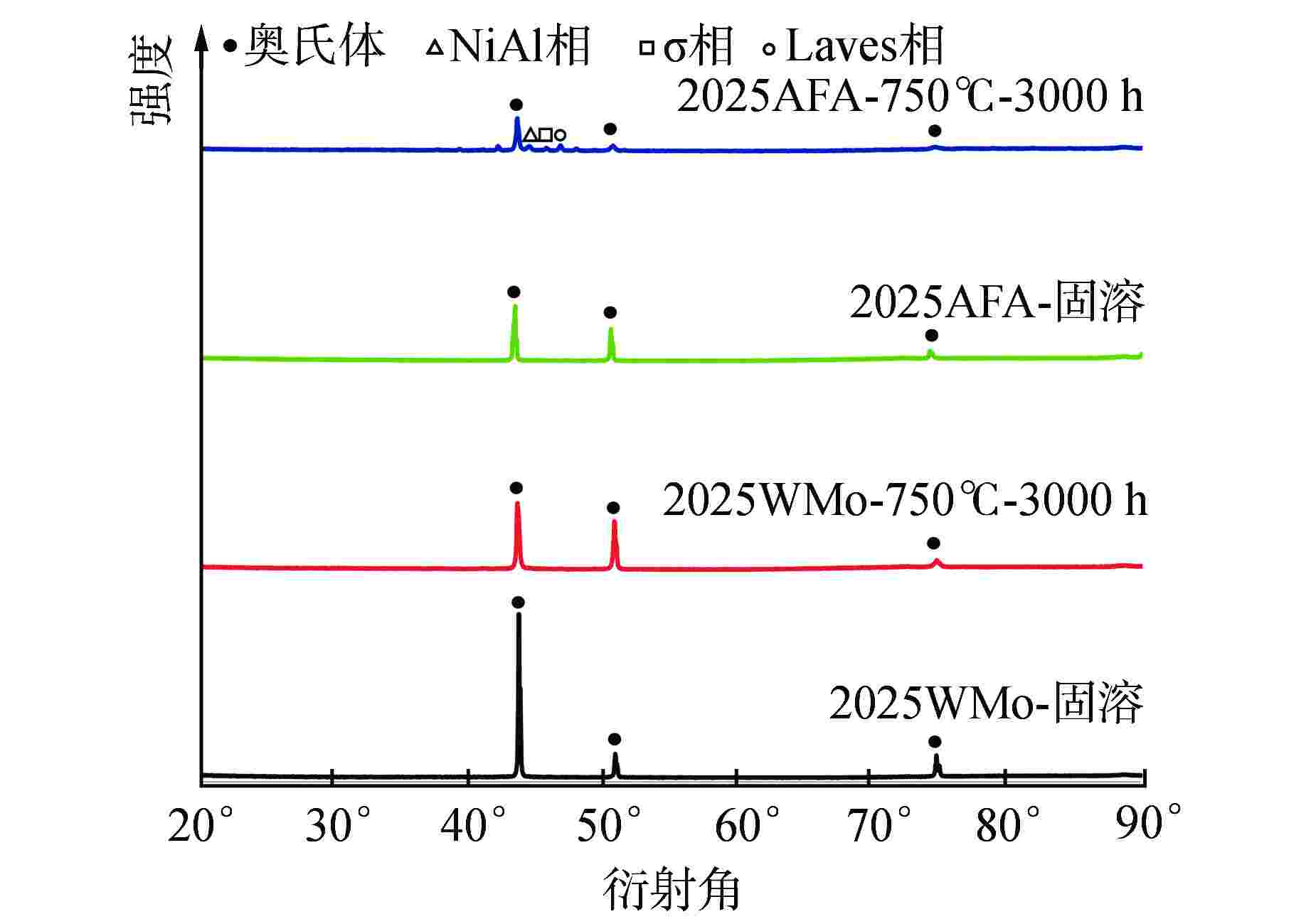
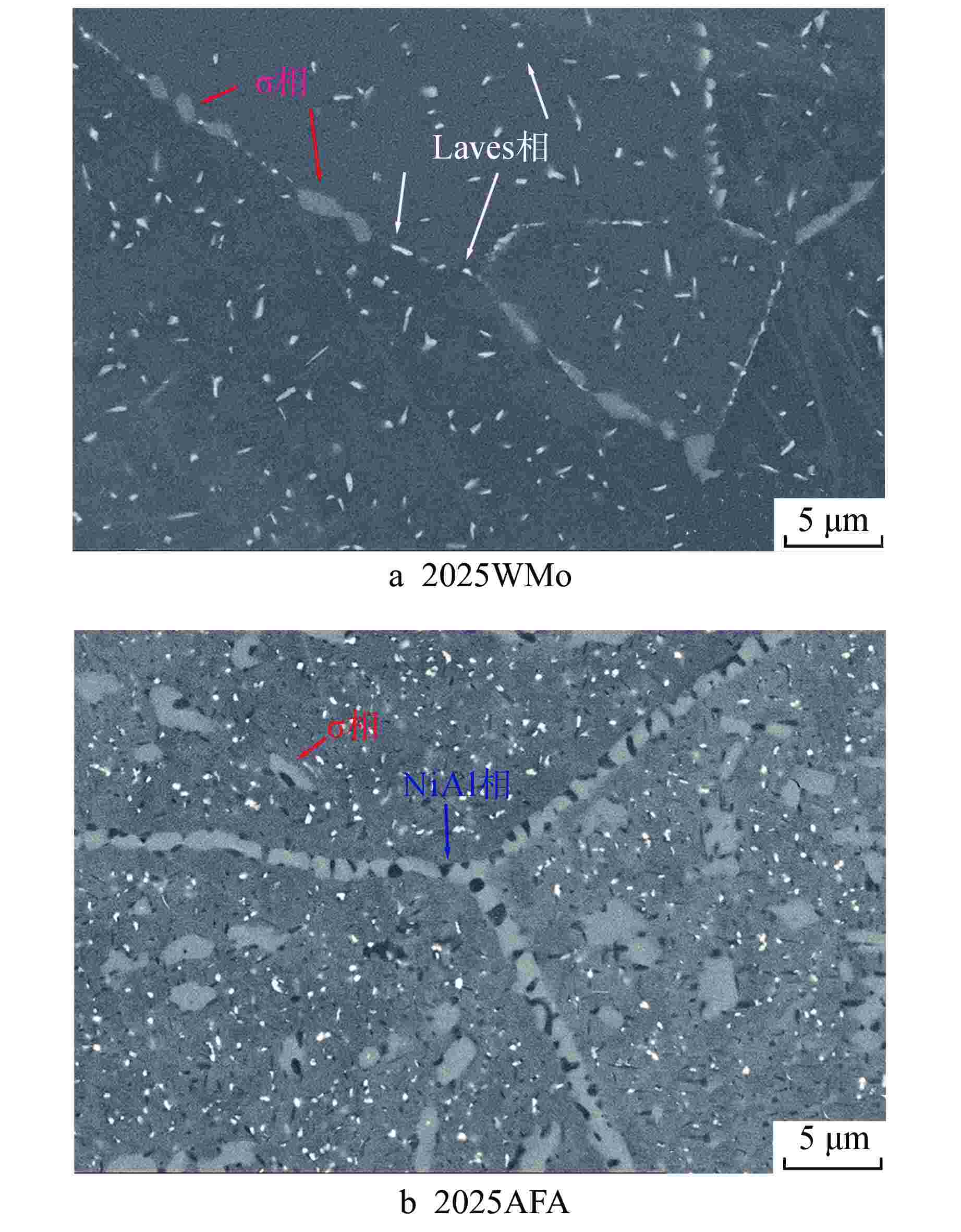
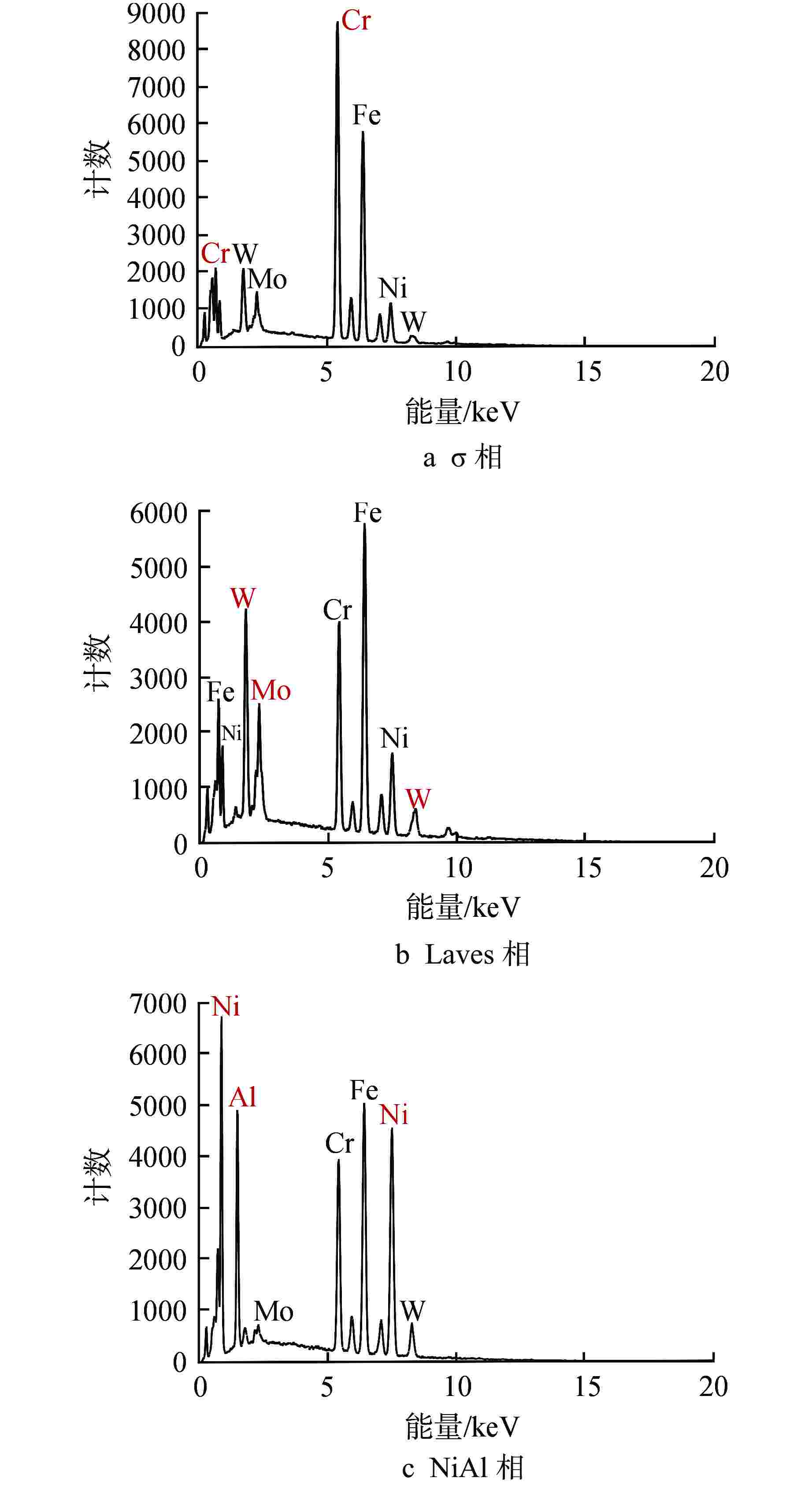
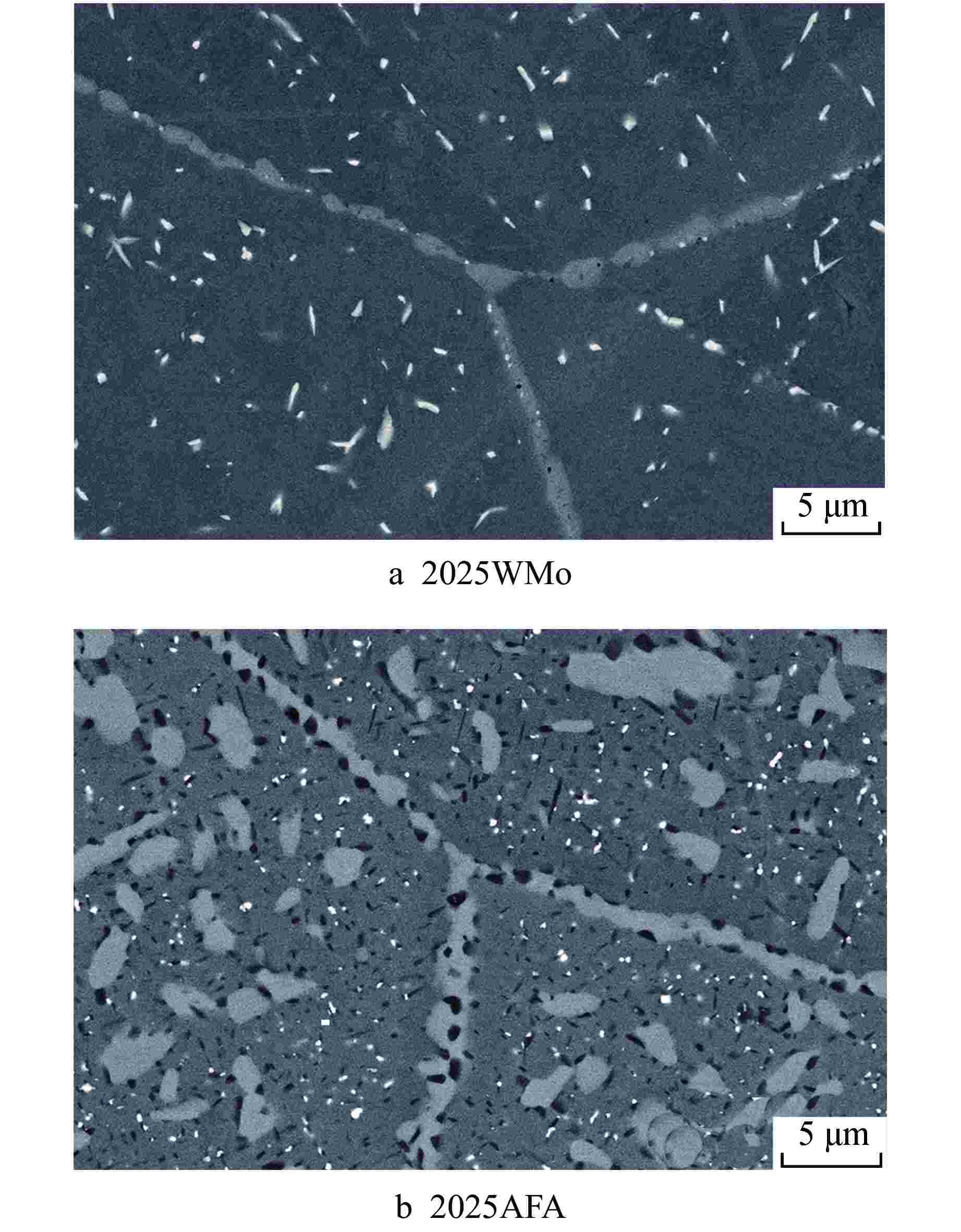
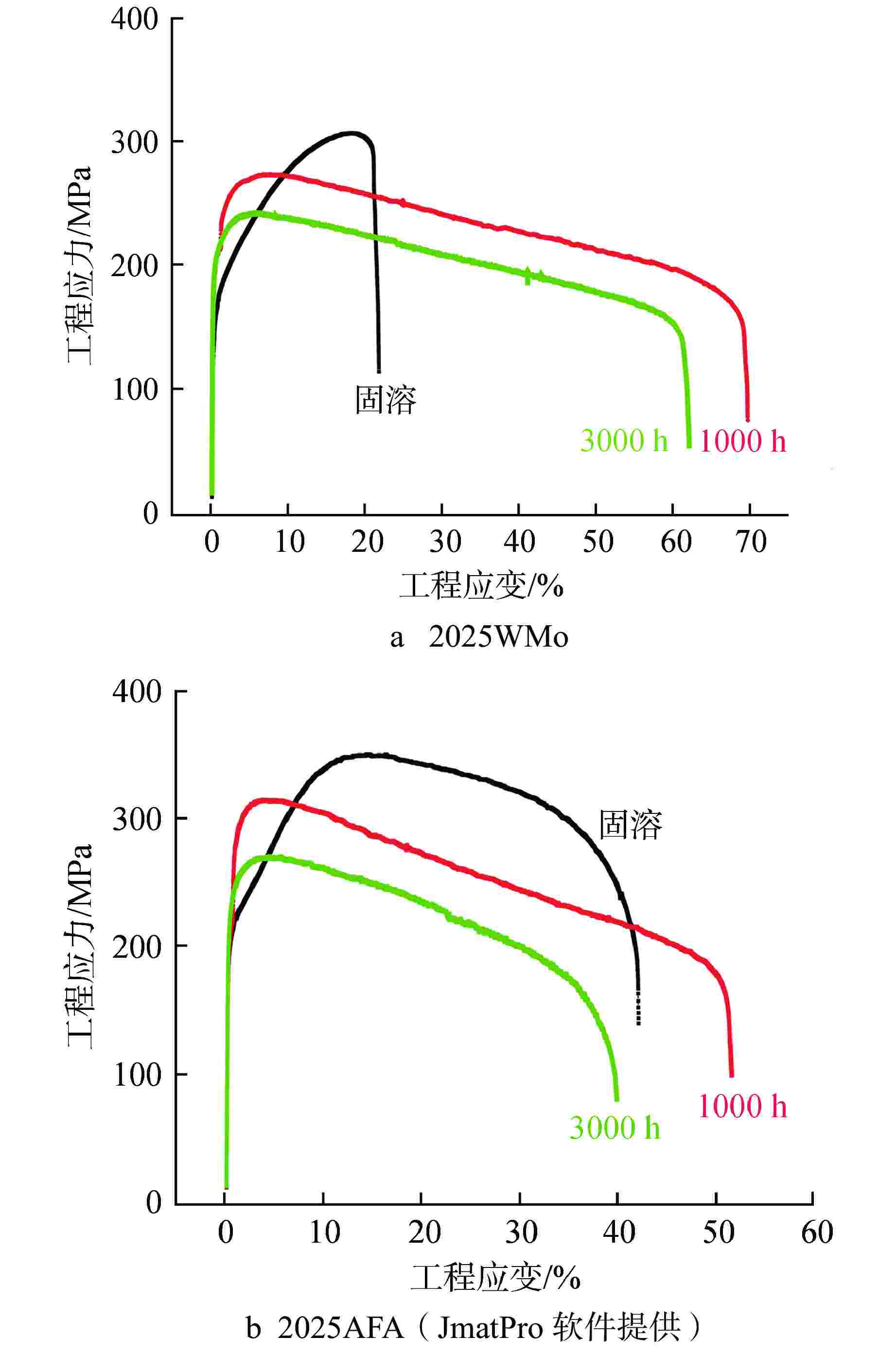
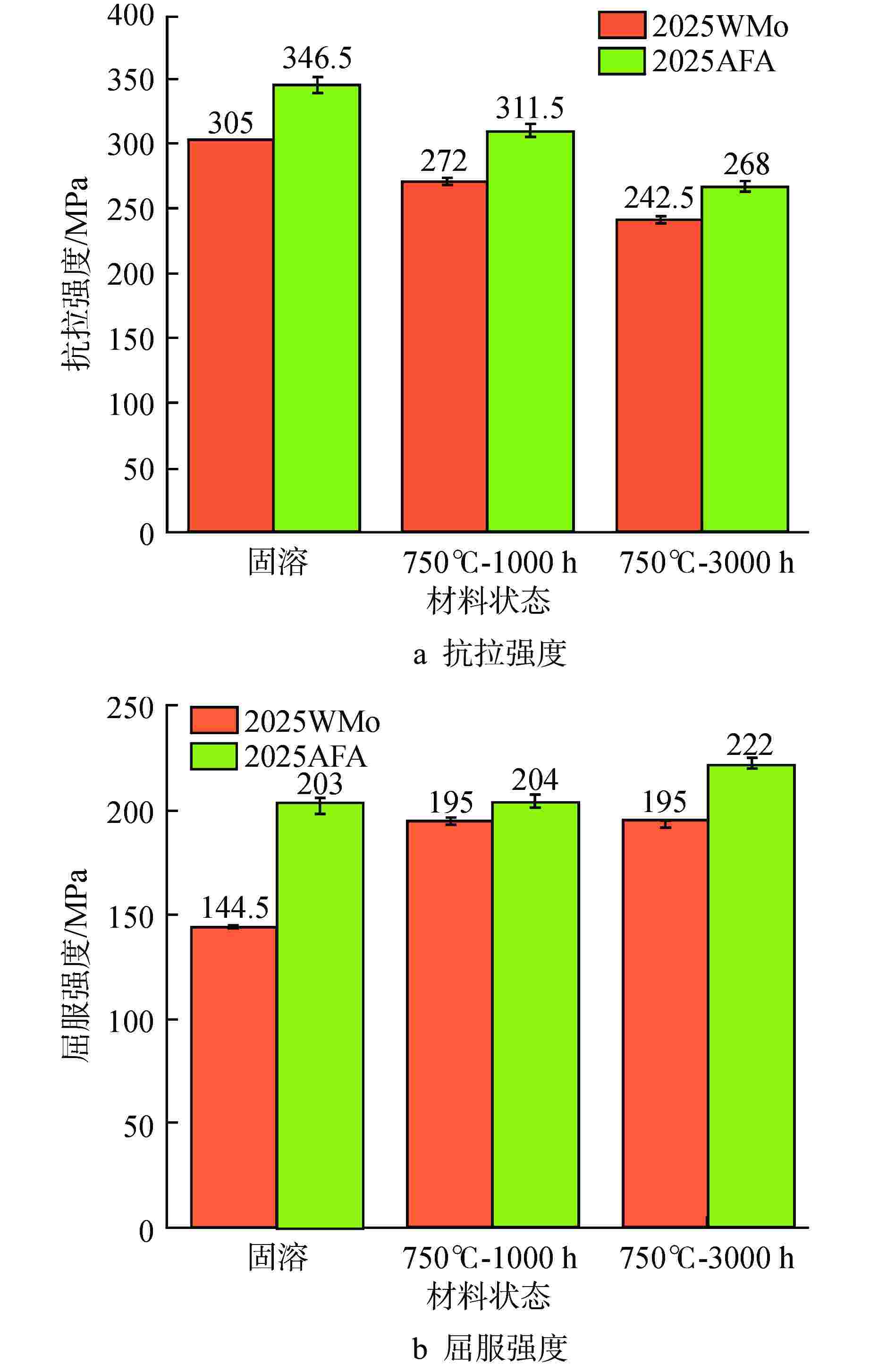
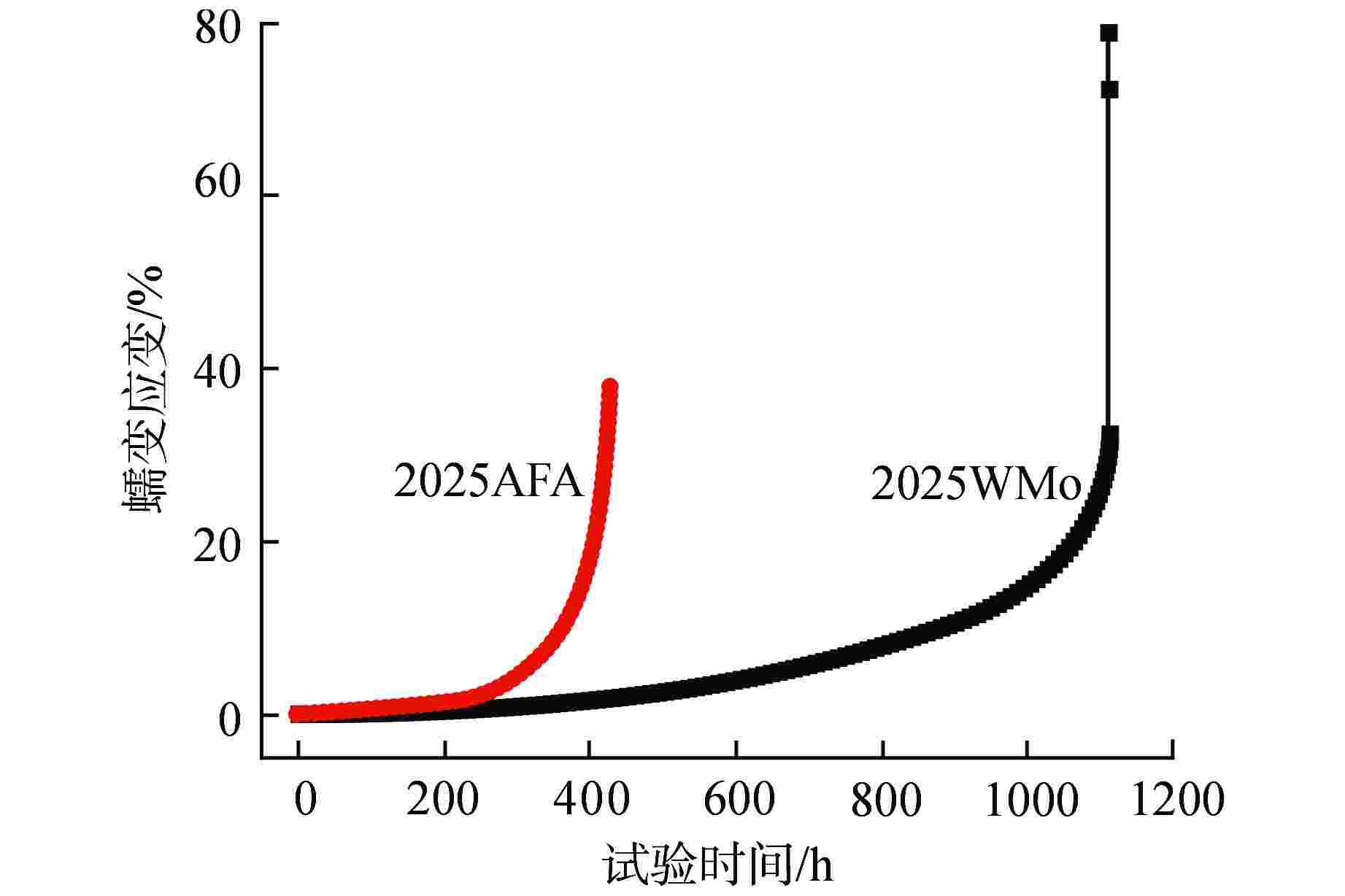
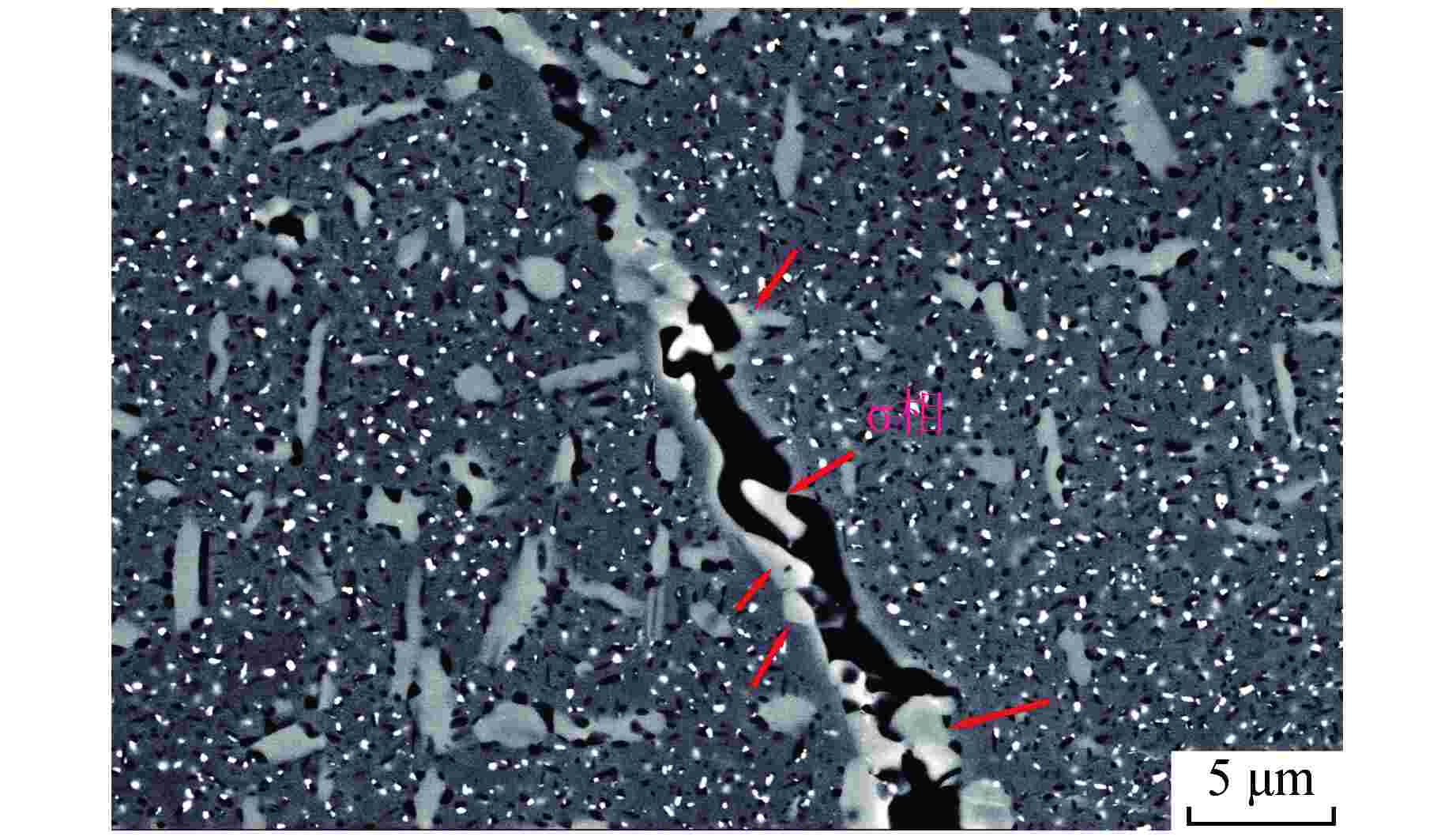
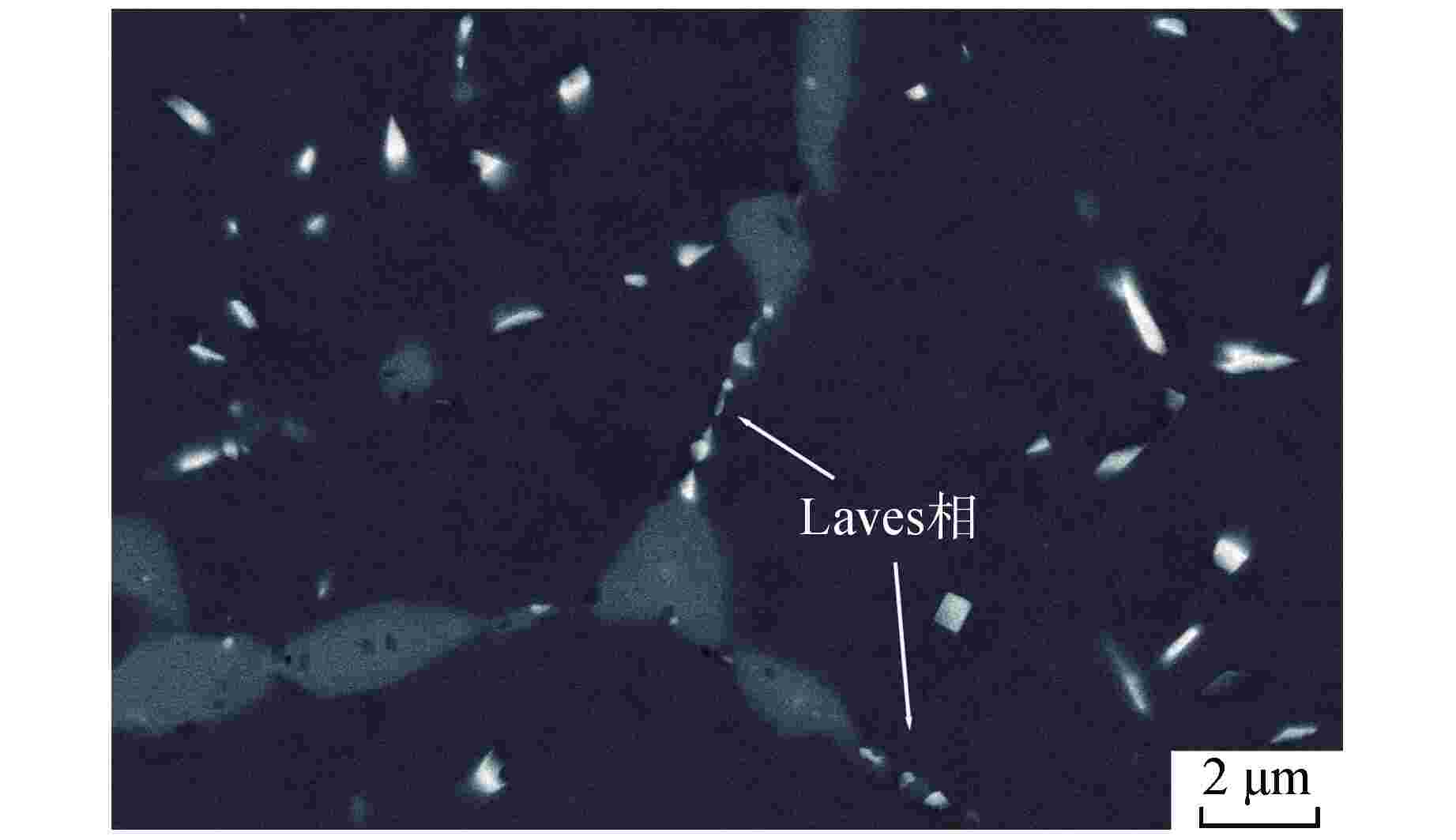
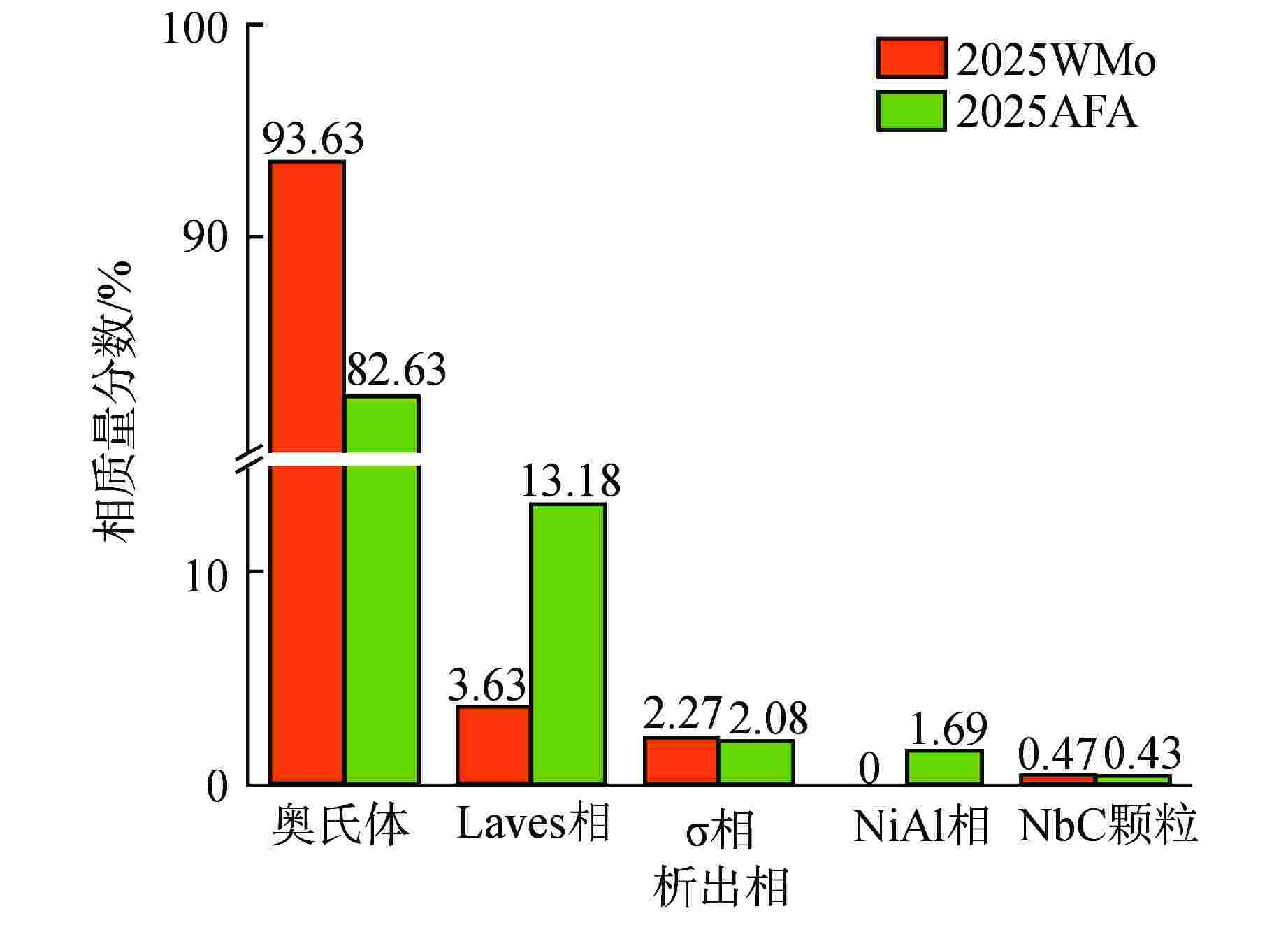
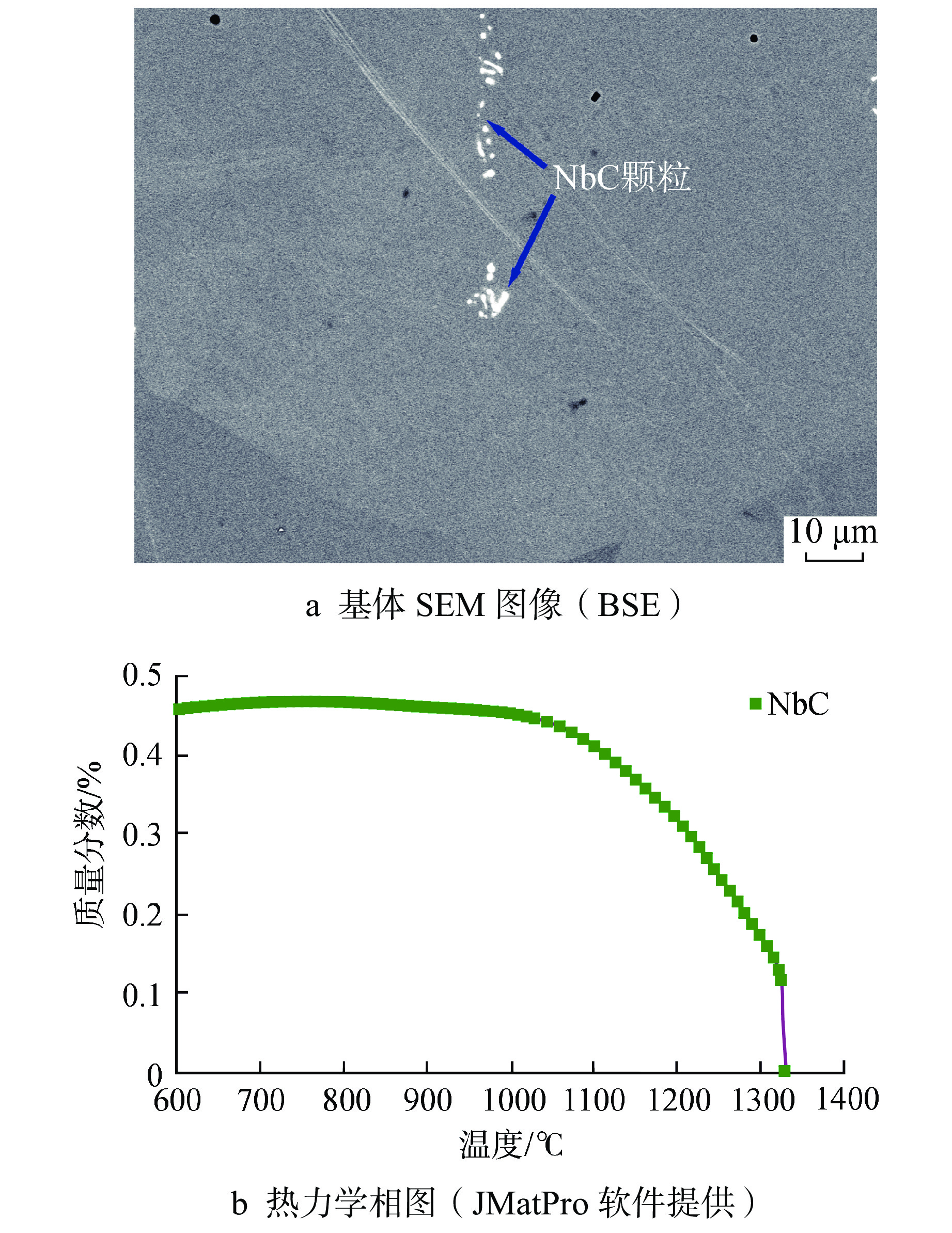
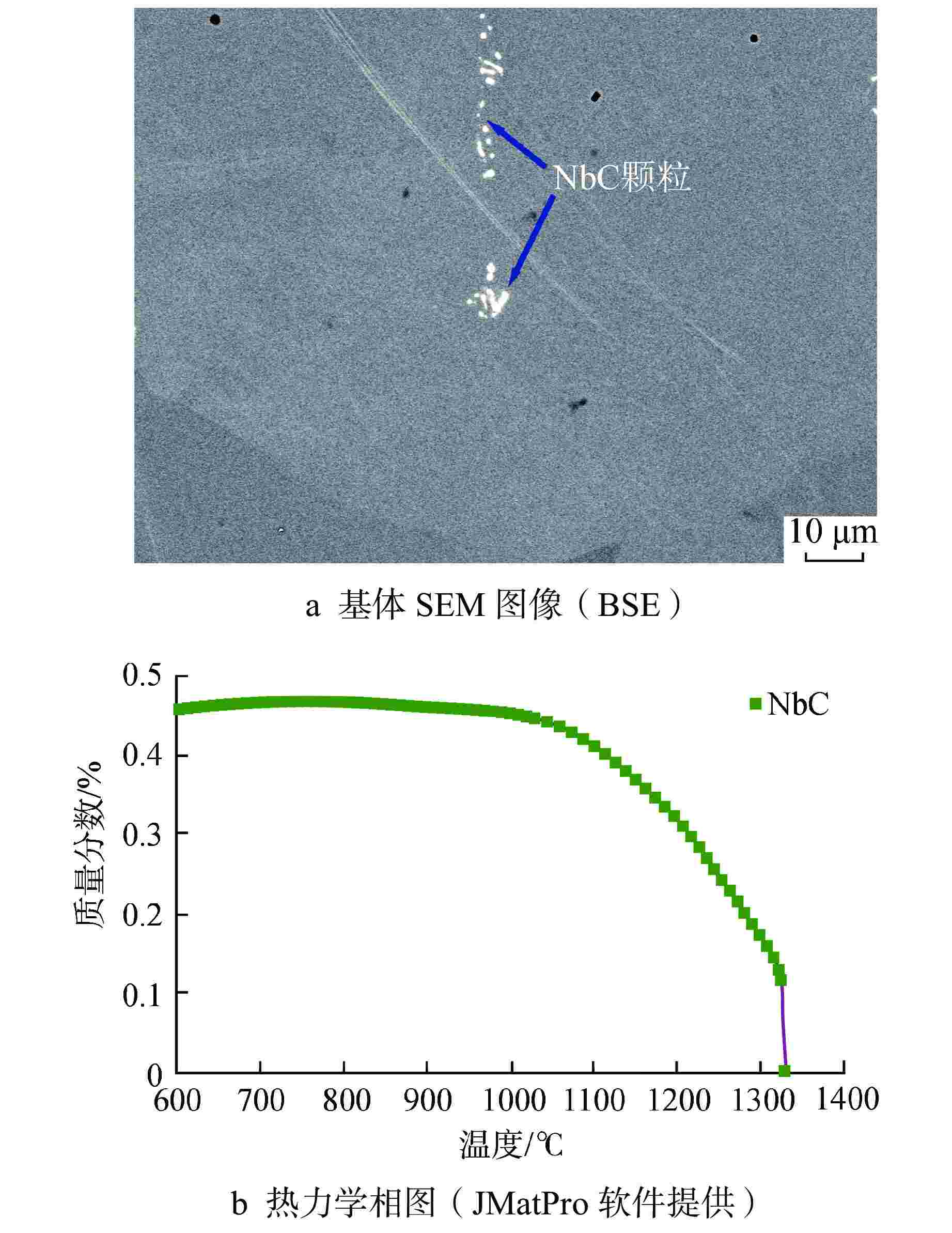
摘要: 为深入研究超临界气冷堆包壳材料的高温热老化行为以及Al元素对力学性能退化的影响,本文对添加Al元素和不含Al元素的2种20Cr25NiNb奥氏体耐热钢进行了750℃热老化试验,并开展了相应的微观组织分析和力学性能测试。研究发现,固溶态合金基体为奥氏体相,并含有少量微米级NbC。热老化后合金基体中析出了Laves相和σ相,而含Al钢中还观察到了NiAl相的析出。Al元素对20Cr25NiNb的热老化行为产生了双重影响,一方面,Al元素具有固溶强化效果,同时使得热老化后析出的Laves相尺寸更小、数密度更高,从而提升了高温拉伸强度;另一方面,蠕变裂纹主要沿晶界萌生并扩展,热老化后含Al合金中σ相体积分数更高,粗化更严重,严重降低了蠕变断裂寿命。不含Al合金晶界处析出的细小Laves相能有效阻止σ相生长,提升材料的蠕变性能。因此,本研究为超临界气冷堆包壳材料的成分优化提供了有力的支持。
-
关键词:
- 20Cr25NiNb /
- 热老化 /
- 高温强度 /
- 蠕变 /
- Al元素
Abstract: In order to comprehensively investigate the high-temperature thermal aging behavior of supercritical gas-cooled reactor (SCGCR) cladding materials and the impact of Al element on the degradation of material mechanical properties, the thermal aging experiments at 750℃ were conducted on two types of 20Cr25NiNb austenitic heat-resistant steels: the alloy doped with Al and the Al-free one. Subsequently, corresponding microstructure analysis and mechanical property tests were carried out. The results revealed that the as-solutionized steels consisted of austenite along with a minor amount of micro-sized NbC carbides. After thermal aging, the matrix exhibited the precipitation of Laves and σ phases, while the alloy containing Al additionally showed the emergence of NiAl precipitates. The presence of Al element induced dual effects on the thermal aging behavior of 20Cr25NiNb. On one hand, Al element exhibited a solid solution strengthening effect and led to a reduction in size and an increase in number density of Laves particles after thermal aging, thereby enhancing high-temperature tensile strength. On the other hand, creep cracks predominantly initiated and propagated along grain boundaries. After thermal aging, the volume fraction of σ phase in Al steel was higher and the coarsening was more serious, consequently resulting in a notable reduction in creep fracture life. The fine Laves phase precipitated at grain boundaries in the Al-free alloy effectively suppressed the growth of σ phase, thus enhancing creep resistance. As a conclusion, this study offers robust support for the optimization of cladding material composition for SCGCR applications.-
Key words:
- 20Cr25NiNb /
- Thermal aging /
- High temperature strength /
- Creep /
- Al element
-
表 1 试验用合金化学成分
Table 1. Chemical Composition of Alloys for Test
编号 元素质量分数/% Ni Cr Nb Si Mn W Mo C Al Fe 其他 2025WMo 23.50 20.0 0.76 0.5 0.7 2 1.0 0.047 余量 2025AFA 23.44 19.4 0.83 0.2 0.6 2 1.1 0.057 2.5 余量 B<0.0025 表 2 热老化后合金Laves相和σ相尺寸和体积分数
Table 2. Size and Volume Fraction of Laves and σ Phases of the Tested Alloys after Thermal Aging
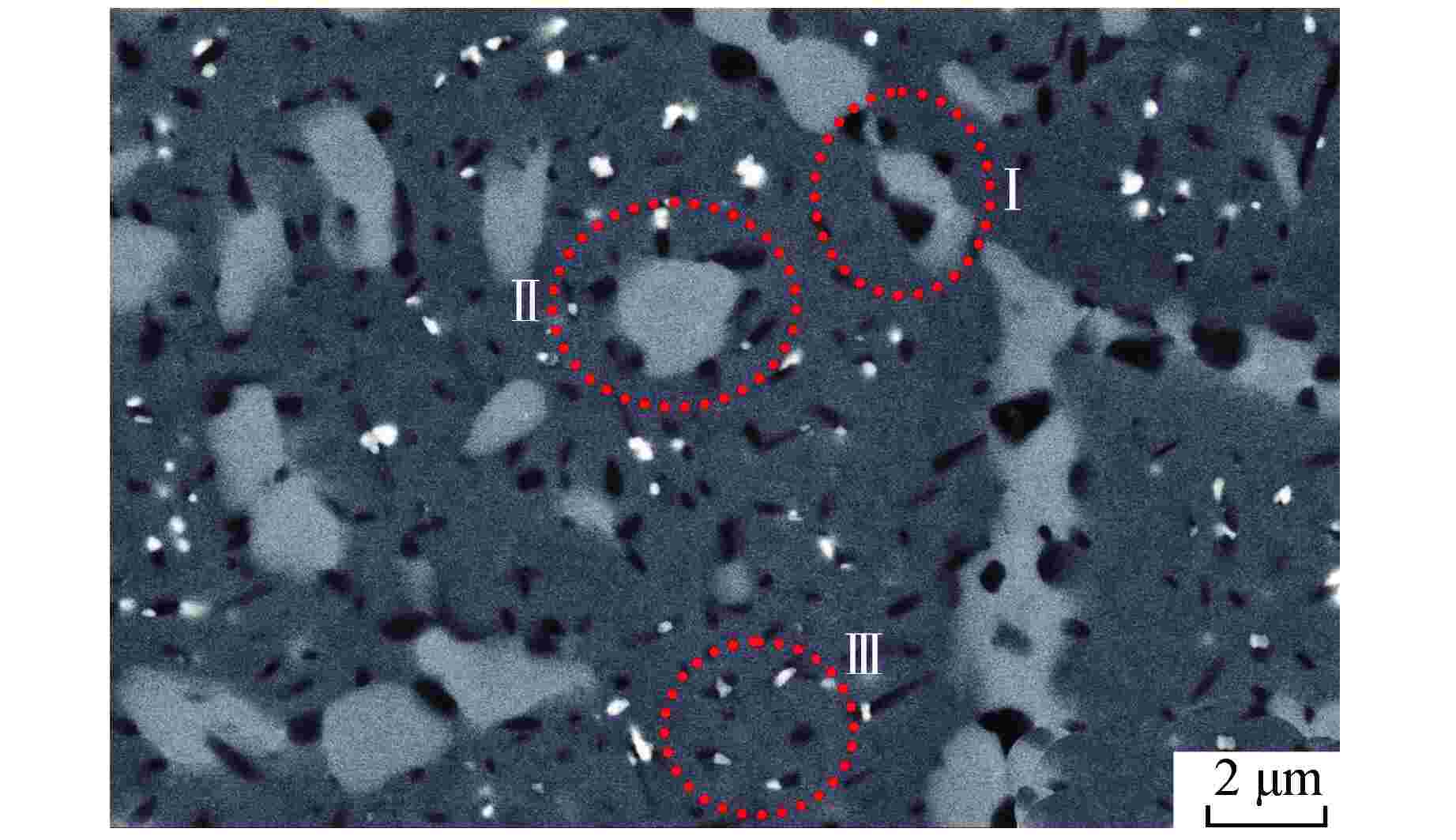
样品 2025WMo 2025AFA 热老化时间/h 1000 3000 1000 3000 Laves相 平均尺寸d/μm 0.2823 0.4107 0.2315 0.2480 f /% 1.03 1.82 1.28 1.34 σ相 平均尺寸d /μm 1.2779 1.2536 1.2251 1.4899 f /% 1.52 2.92 9.65 17.04 -
[1] 黄彦平,王俊峰. 超临界二氧化碳在核反应堆系统中的应用[J]. 核动力工程,2012, 33(3): 21-27. [2] 杨文斗. 反应堆材料学[M]. 北京: 中国原子能出版社, 2000: 232. [3] DAWSON J W, PHILLIPS M. Gas-cooled nuclear reactor designs, operation and fuel cycle[M]// CROSSLAND I. Nuclear Fuel Cycle Science and Engineering. Cambridge: Woodhead Publishing, 2012: 300-332. [4] AL-SHATER A, ENGELBERG D, LYON S, et al. Characterization of the stress corrosion cracking behavior of thermally sensitized 20Cr-25Ni stainless steel in a simulated cooling pond environment[J]. Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 2017, 54(7): 742-751. doi: 10.1080/00223131.2017.1309305 [5] SHU M, ZHOU Q, SHEN Y H, et al. Improved creep resistance of 20Cr25NiNb heat resistant steels through grain boundary intermetallic precipitation strengthening[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2023, 25: 3728-3743. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2023.06.213 [6] JANG M H, MOON J, KANG J Y, et al. Effect of tungsten addition on high-temperature properties and microstructure of alumina-forming austenitic heat-resistant steels[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2015, 647: 163-169. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2015.09.018 [7] JANG M H, KANG J Y, JANG J H, et al. Improved creep strength of alumina-forming austenitic heat-resistant steels through W addition[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2017, 696: 70-79. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2017.04.062 [8] YAMAMOTO Y, BRADY M P, SANTELLA M L, et al. Overview of strategies for high-temperature creep and oxidation resistance of alumina-forming austenitic stainless steels[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2011, 42(4): 922-931. doi: 10.1007/s11661-010-0295-2 [9] EVANS H E. Spallation of oxide from stainless steel AGR nuclear fuel cladding: mechanisms and consequences[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 1988, 4(5): 414-420. doi: 10.1179/mst.1988.4.5.414 [10] LOBB R C. Observations on the microstructure of 20Cr-25Ni-Nb stainless steel after exposure to iodine vapor during creep at 750℃[J]. Oxidation of Metals, 1981, 15(1): 147-167. [11] LOBB R C. The effect of iodine vapour on creep rupture properties of nitrided 20% Cr/25% Ni/Nb/1.5 Ti stainless steel[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 1978, 74(2): 212-220. doi: 10.1016/0022-3115(78)90360-4 [12] BENNETT M J, ROBERTS A C, SPINDLER M W, et al. Interaction between oxidation and mechanical properties of 20Cr–25Ni–Nb stabilised stainless steel[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 1990, 6(1): 56-68. doi: 10.1179/mst.1990.6.1.56 [13] JIANG Y J, GAO Q Z, ZHANG H L, et al. The effect of isothermal aging on microstructure and mechanical behavior of modified 2.5Al alumina-forming austenitic steel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2019, 748: 161-172. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2019.01.087 [14] JIANG J D, LIU Z Y, GAO Q Z, et al. The effect of isothermal aging on creep behavior of modified 2.5Al alumina-forming austenitic steel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2020, 797: 140219. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2020.140219 [15] SHU M, ZHOU Q, XIAO J, et al. Precipitates evolution during isothermal aging and its effect on tensile properties for an AFA alloy containing W and B elements[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2023, 58(27): 11252-11269. doi: 10.1007/s10853-023-08663-5 [16] YAMAMOTO Y, SANTELLA M L, BRADY M P, et al. Effect of alloying additions on phase Equilibria and Creep resistance of alumina-forming austenitic stainless steels[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2009, 40(8): 1868-1880. doi: 10.1007/s11661-009-9886-1 [17] HU B, TROTTER G, WANG Z W, et al. Effect of boron and carbon addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of the aged gamma-prime strengthened alumina-forming austenitic alloys[J]. Intermetallics, 2017, 90: 36-49. doi: 10.1016/j.intermet.2017.06.011 [18] ZHAO W X, ZHOU D Q, JIANG S H, et al. Ultrahigh stability and strong precipitation strengthening of nanosized NbC in alumina-forming austenitic stainless steels subjecting to long-term high-temperature exposure[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2018, 738: 295-307. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2018.09.081 [19] BEI H, YAMAMOTO Y, BRADY M P, et al. Aging effects on the mechanical properties of alumina-forming austenitic stainless steels[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2010, 527(7-8): 2079-2086. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2009.11.052 [20] ALOMARI A S. Serrated yielding and creep properties of an advanced austenitic stainless steel (Alloy 709) - application to next generation sodium fast reactors[D]. Raleigh: North Carolina State University, 2019. [21] MENG H J, WANG J, WANG L, et al. The precipitation control in aged alumina-forming austenitic stainless steels Fe-15Cr-25Ni-3Al-NbWCu by W addition and its effect on the mechanical properties[J]. Materials Characterization, 2020, 163: 110233. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2020.110233 [22] MA K K, WEN H M, HU T, et al. Mechanical behavior and strengthening mechanisms in ultrafine grain precipitation-strengthened aluminum alloy[J]. Acta Materialia, 2014, 62: 141-155. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2013.09.042 [23] WEN D H, LI Z, JIANG B B, et al. Effects of Nb/Ti/V/Ta on phase precipitation and oxidation resistance at 1073 K in alumina-forming austenitic stainless steels[J]. Materials Characterization, 2018, 144: 86-98. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2018.07.007 [24] NIKULIN I, KIPELOVA A, KAIBYSHEV R. Effect of high-temperature exposure on the mechanical properties of 18Cr–8Ni–W–Nb–V–N stainless steel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2012, 554: 61-66. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2012.06.011 -





 下载:
下载: