Influence of Different Turbulence Models on Simulation of Lead-Bismuth Solidification
-
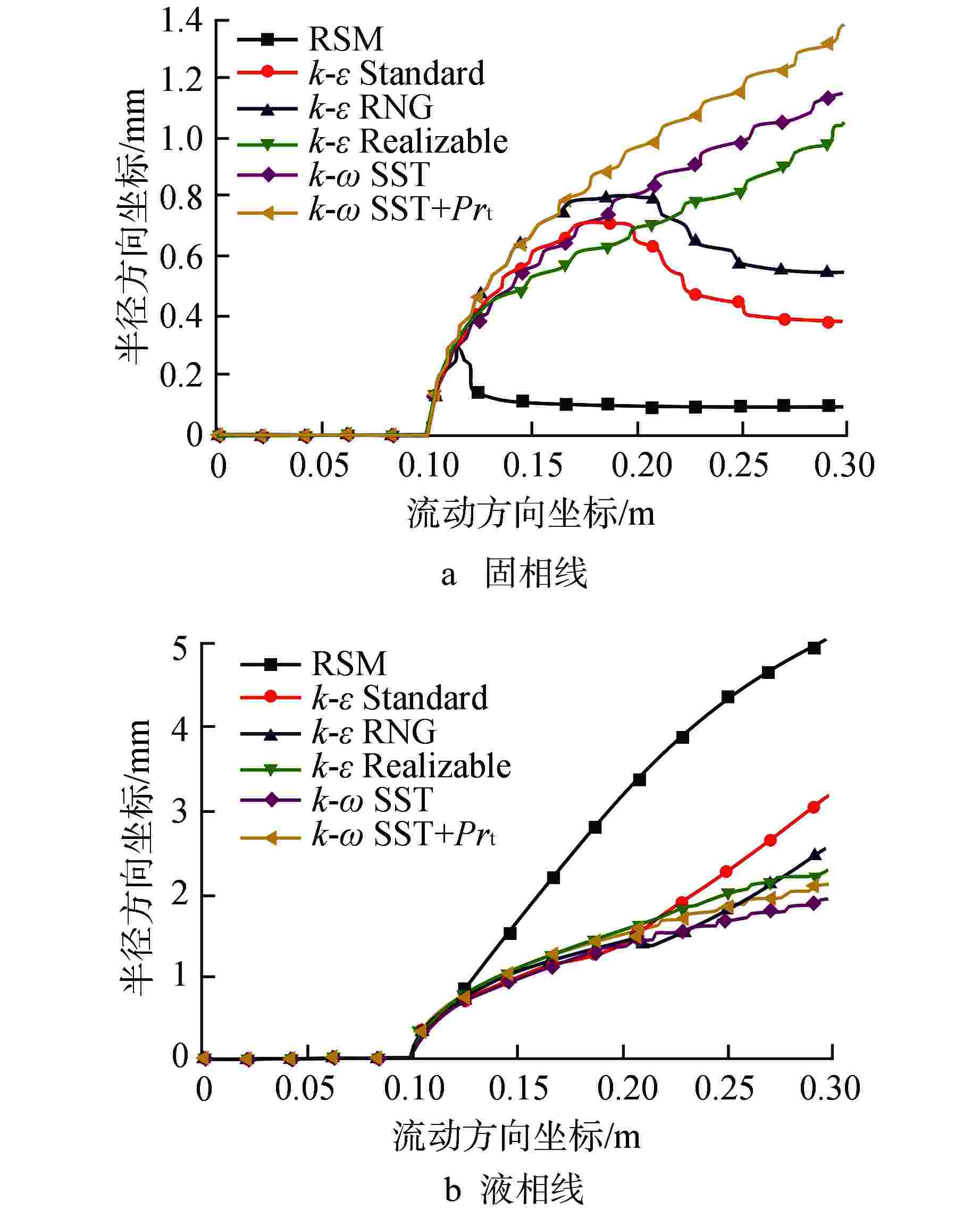
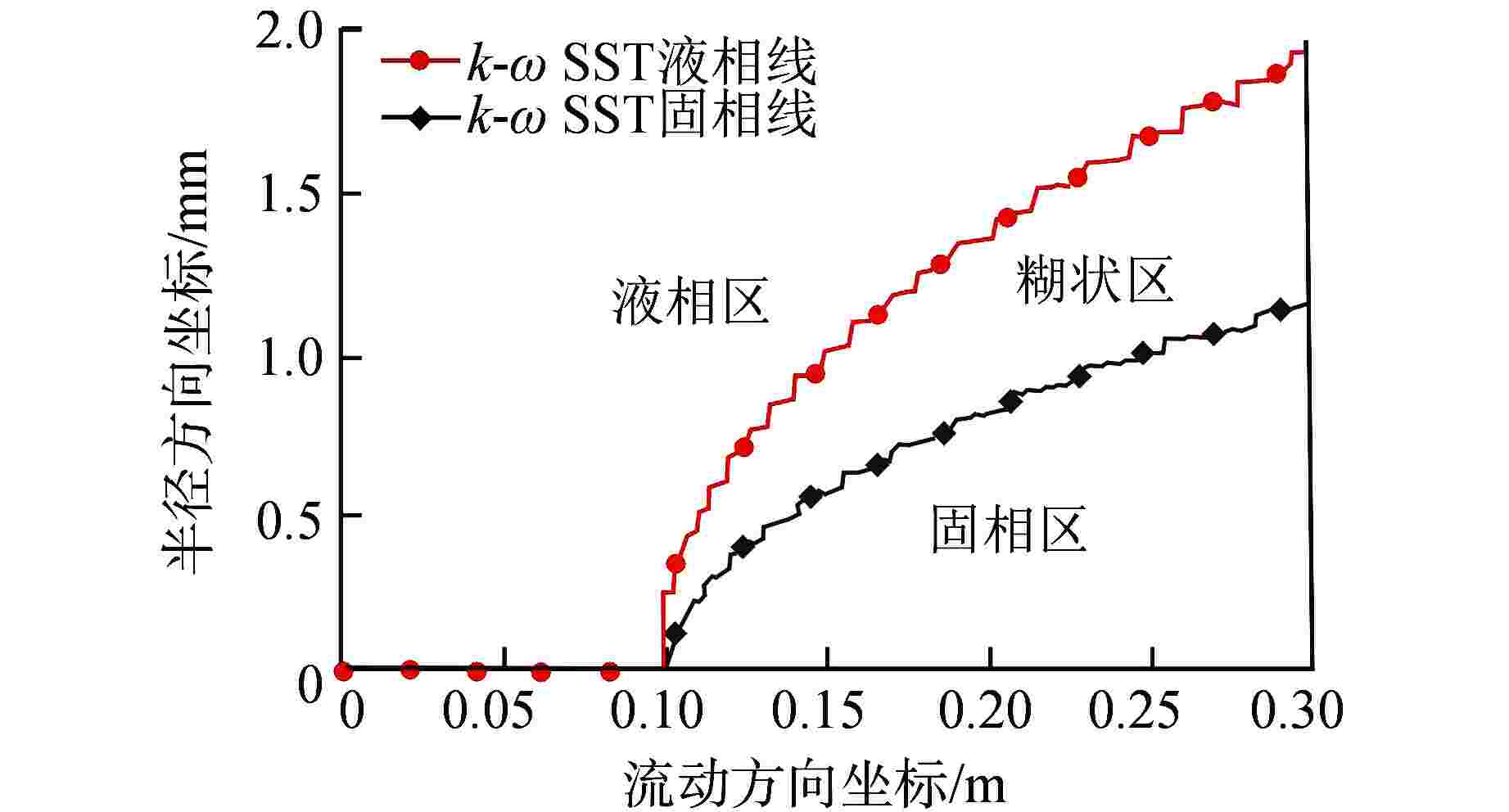
摘要: 为了研究不同湍流模型及湍流普朗特数(Prt)模型对模拟铅-铋凝固行为的影响,利用FLUENT对铅-铋管内流动凝固行为进行模拟研究。研究结果表明,尽管剪切应力传输(k-ω SST)模型、k-ε模型与雷诺应力(RSM)模型在模拟铅-铋传热时的差异可以忽略,但在相变过程中对温度场与压力场的模拟存在显著差异,应慎重选取湍流模型。另外对不同Prt模型对铅-铋的凝固行为模拟的研究表明,不同Prt模型对铅-铋的凝固行为模拟无明显差异。
-
关键词:
- 铅-铋快堆(LFR) /
- 安全分析 /
- 冷却剂凝固 /
- 湍流模型
Abstract: To study the influence of different turbulence models and turbulence Prandtl number (Prt) models on the simulation of lead-bismuth solidification behavior, this paper uses FLUENT to simulate the flow solidification behavior of lead-bismuth (Pb-Bi) inside a tube. The simulation results show that although the differences between the shear stress transfer (k-ω SST), k-ε and Reynolds stress (RSM) models in simulating Pb-Bi heat transfer can be ignored, there are significant differences in the simulation of the temperature and pressure fields during the phase change, thus the turbulence model should be carefully selected. In addition, the study on the simulation of Pb-Bi solidification using different Prt models shows no significant difference.-
Key words:
- LFR /
- Safety analysis /
- Coolant solidification /
- Turbulence models
-
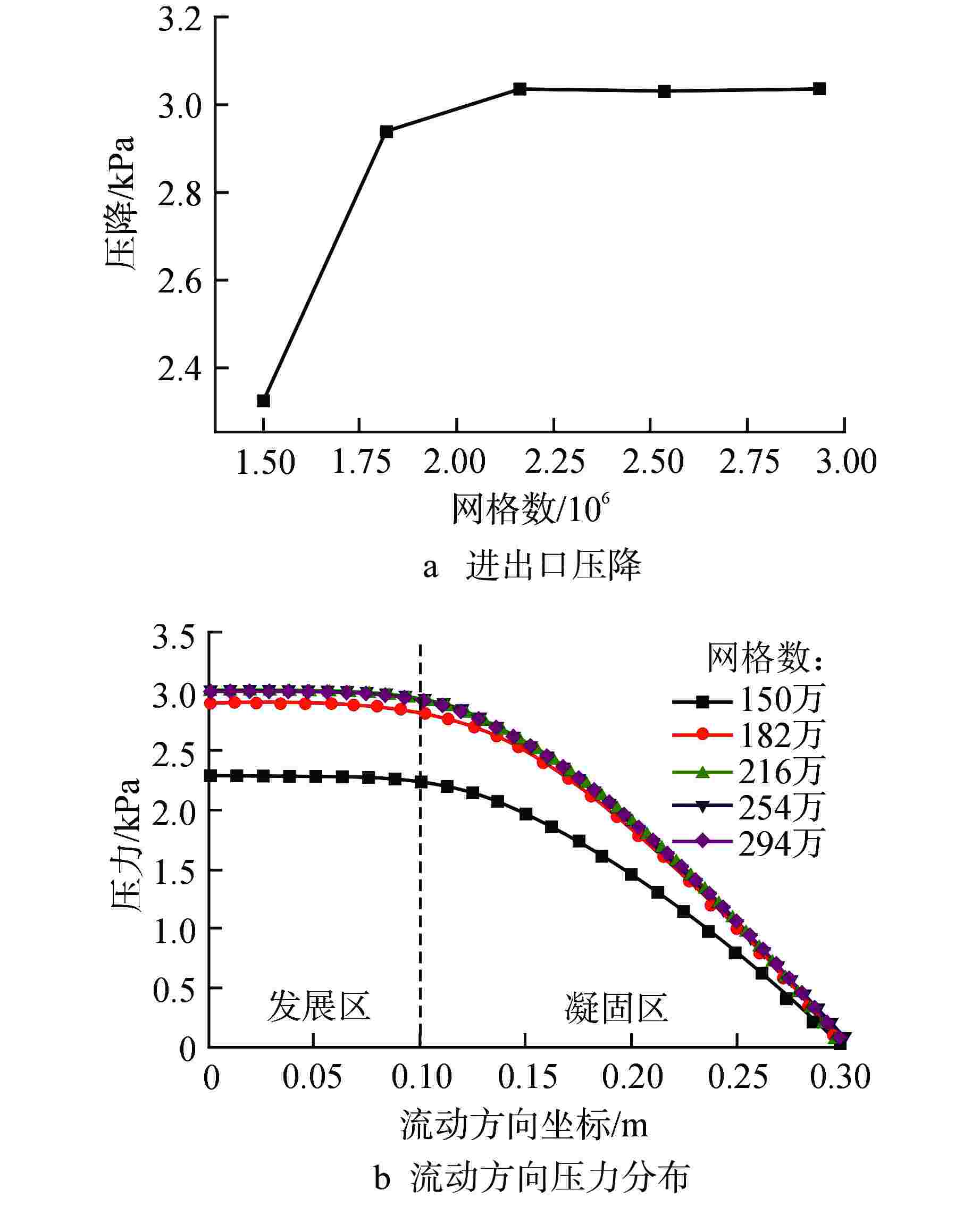
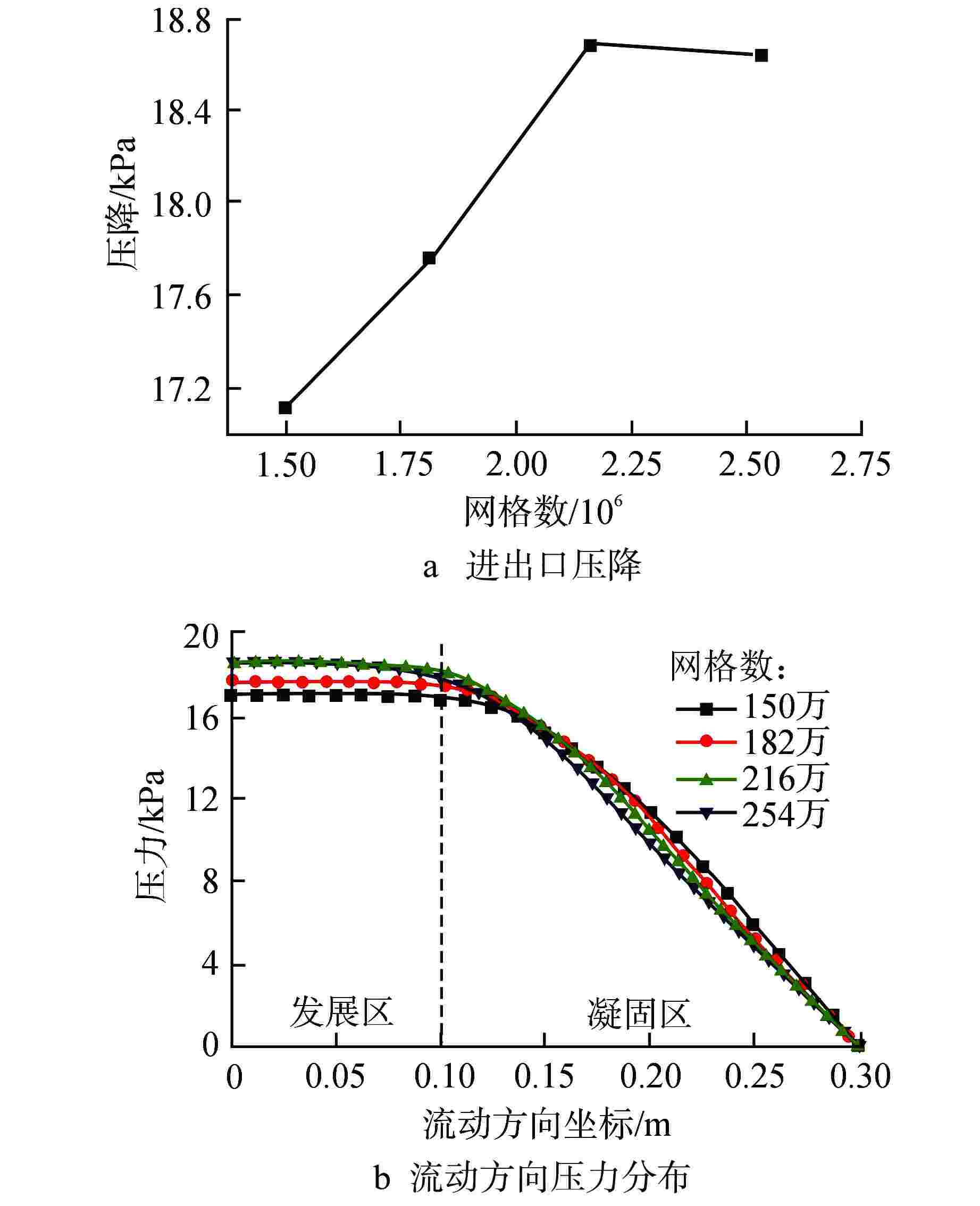
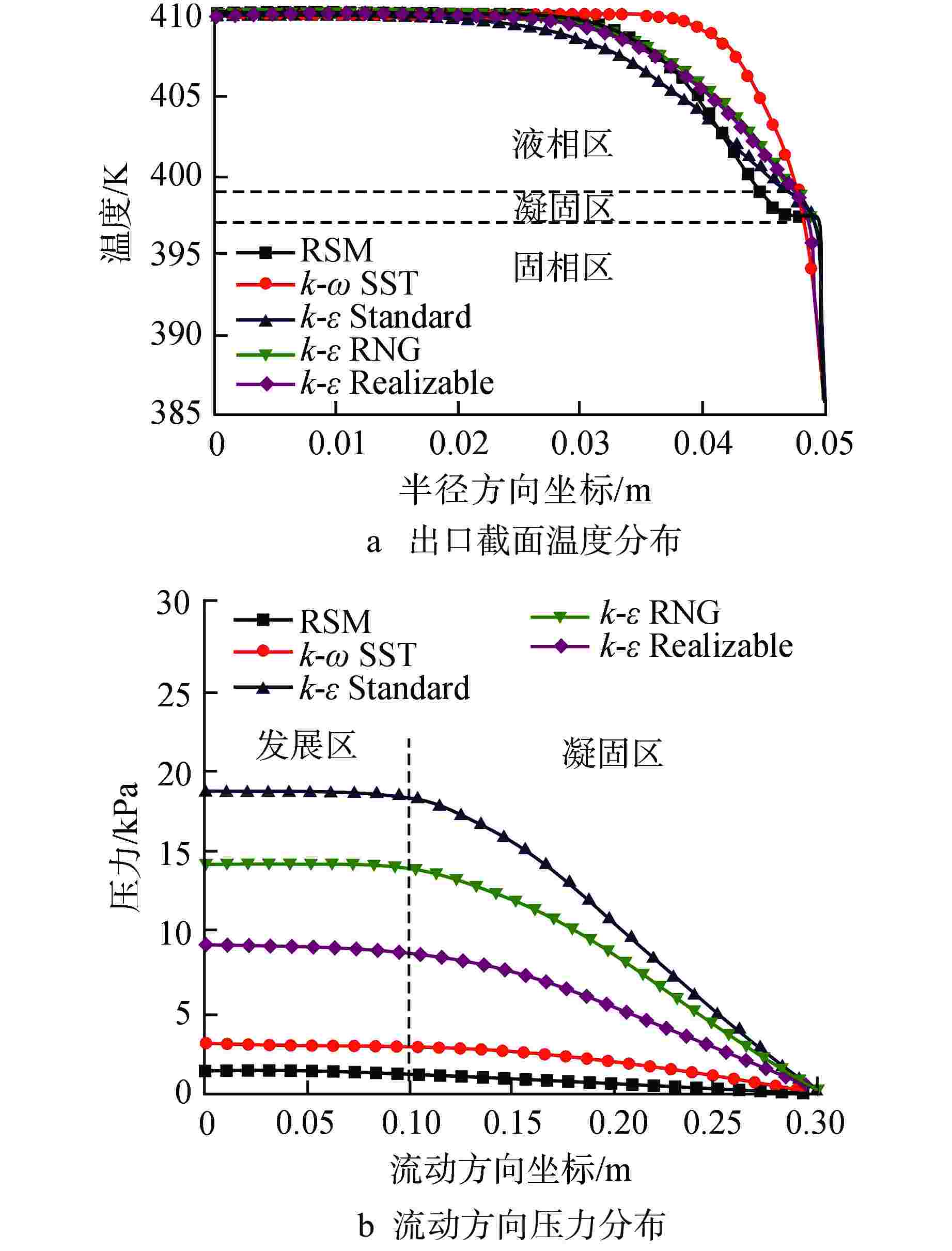
表 1 不同湍流模型计算结果对比
Table 1. Comparison of Results of Different Turbulence Models
模型 进出口压降 /Pa 出口平均温度 /K RSM 1443.8 405.6 k-ω SST 3033.5 407.4 k-ε Standard 18683.8 405.3 k-ε RNG 14149.0 406.2 k-ε 9144.4 405.3 表 2 不同湍流Pr模型计算结果对比
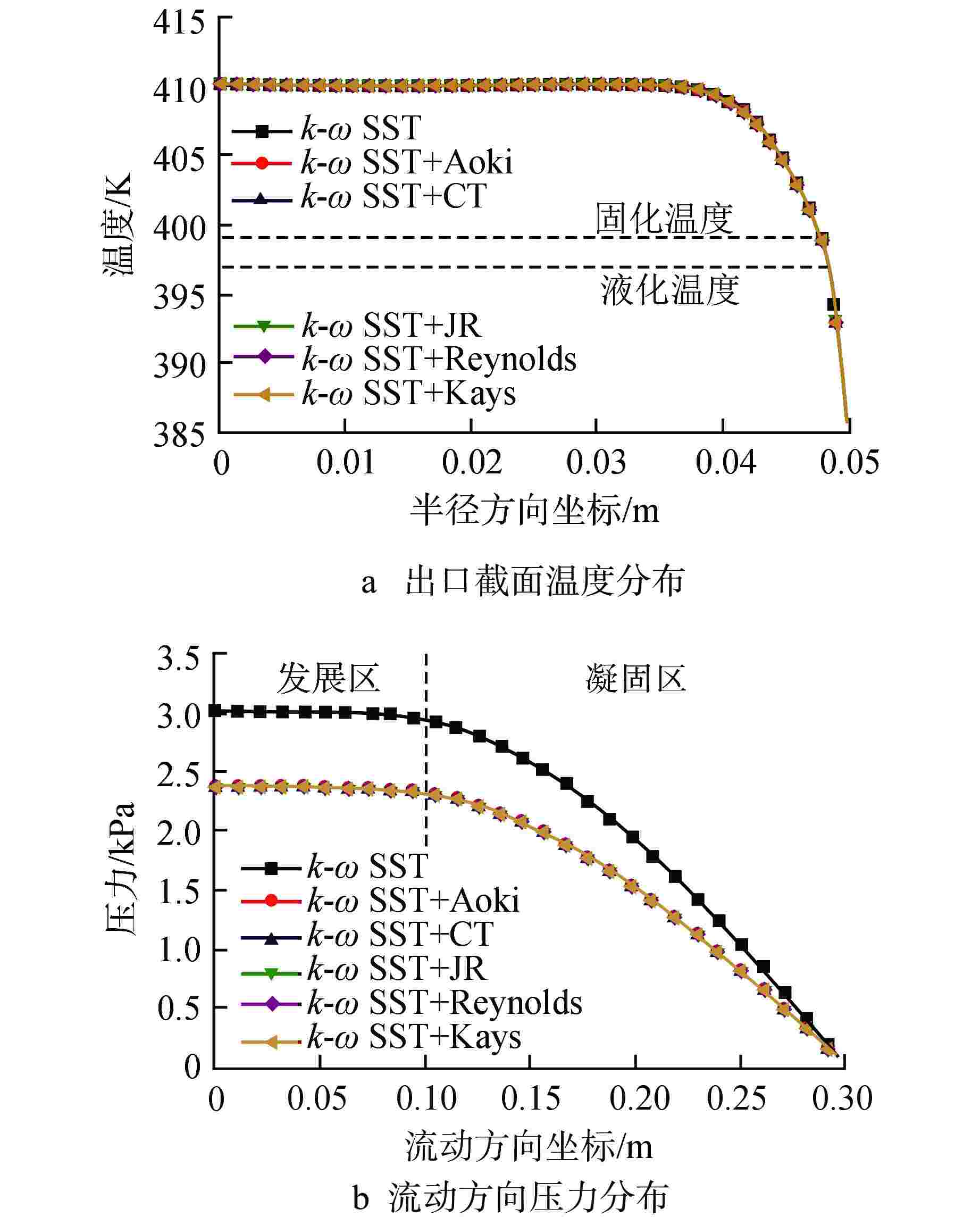
Table 2. Comparison of Results of Different Prt Models
模型 进出口压降 /Pa 出口平均温度 /K k-ω SST 3033.5 407.4 k-ω SST + Prt_Aoki 2396.6 407.3 k-ω SST +Prt_CT 2395.3 407.3 k-ω SST + Prt_JR 2396.8 407.3 k-ω SST + Prt_Reynolds 2396.3 407.3 k-ω SST + Prt_Kays 2394.6 407.3 -
[1] ALEMBERTI A, SMIRNOV V, SMITH C F, et al. Overview of lead-cooled fast reactor activities[J]. Progress in Nuclear Energy, 2014, 77: 300-307. doi: 10.1016/j.pnucene.2013.11.011 [2] WANG G, NIU S Q, CAO R F. Summary of severe accident issues of LBE-cooled reactors[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2018, 121: 531-539. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2018.08.015 [3] LE BRUN N, HEWITT G F, MARKIDES C N. Transient freezing of molten salts in pipe-flow systems: application to the direct reactor auxiliary cooling system (DRACS)[J]. Applied Energy, 2017, 186: 56-67. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.09.099 [4] ACHUTHAN N, MELICHAR T, PROFIR M, et al. Computational fluid dynamics modelling of lead natural convection and solidification in a pool type geometry[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2021, 376: 111104. doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2021.111104 [5] TARANTINO M, ROELOFS F, SHAMS A, et al. SESAME project: advancements in liquid metal thermal hydraulics experiments and simulations[J]. EPJ Nuclear Sciences & Technologies, 2020, 6: 18. [6] KÖNIG-HAAGEN A, FRANQUET E, PERNOT E, et al. A comprehensive benchmark of fixed-grid methods for the modeling of melting[J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2017, 118: 69-103. doi: 10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2017.04.008 [7] VOLLER V R, SWAMINATHAN C R, THOMAS B G. Fixed grid techniques for phase change problems: a review[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 1990, 30(4): 875-898. doi: 10.1002/nme.1620300419 [8] VOLLER V R, PRAKASH C. A fixed grid numerical modelling methodology for convection-diffusion mushy region phase-change problems[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 1987, 30(8): 1709-1719. doi: 10.1016/0017-9310(87)90317-6 [9] BENNON W D, INCROPERA F P. A continuum model for momentum, heat and species transport in binary solid-liquid phase change systems—I. Model formulation[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 1987, 30(10): 2161-2170. doi: 10.1016/0017-9310(87)90094-9 [10] BENNON W D, INCROPERA F P. A continuum model for momentum, heat and species transport in binary solid-liquid phase change systems—II. Application to solidification in a rectangular cavity[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 1987, 30(10): 2171-2187. doi: 10.1016/0017-9310(87)90095-0 [11] CARMAN P C. Fluid flow through granular beds[J]. Transactions of the Institution of Chemical Engineers, 1937, 15: 150-166. [12] MA Z H, ZHANG Y W. Solid velocity correction schemes for a temperature transforming model for convection phase change[J]. International Journal of Numerical Methods for Heat & Fluid Flow, 2006, 16(2): 204-225. [13] ROSE M E. A method for calculating solutions of parabolic equations with a free boundary[J]. Mathematics of Computation, 1960, 14(71): 249-256. doi: 10.1090/S0025-5718-1960-0115283-8 [14] VOLLER V R. An overview of numerical methods for solving phase change problems[M]//MINKOWYCZ W J, SPARROW E W. Advanced in Numerical Heat Transfer. Washington: Taylor & Francis, 1997: 341-380. [15] Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development. Handbook on lead-bismuth eutectic alloy and lead properties, materials compatibility, thermal-hydraulics and technologies-2015 edition: No. NEA-7268[R]. Paris: Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development, 2015. [16] LIU Z P, HUANG D S, WANG C L, et al. Flow and heat transfer analysis of lead–bismuth eutectic flowing in a tube under rolling conditions[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2021, 382: 111373. doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2021.111373 -





 下载:
下载: