Research on Correction Method of Pressure Spike at Gas-Liquid Interface Crossing Cells Based on RELAP5
-
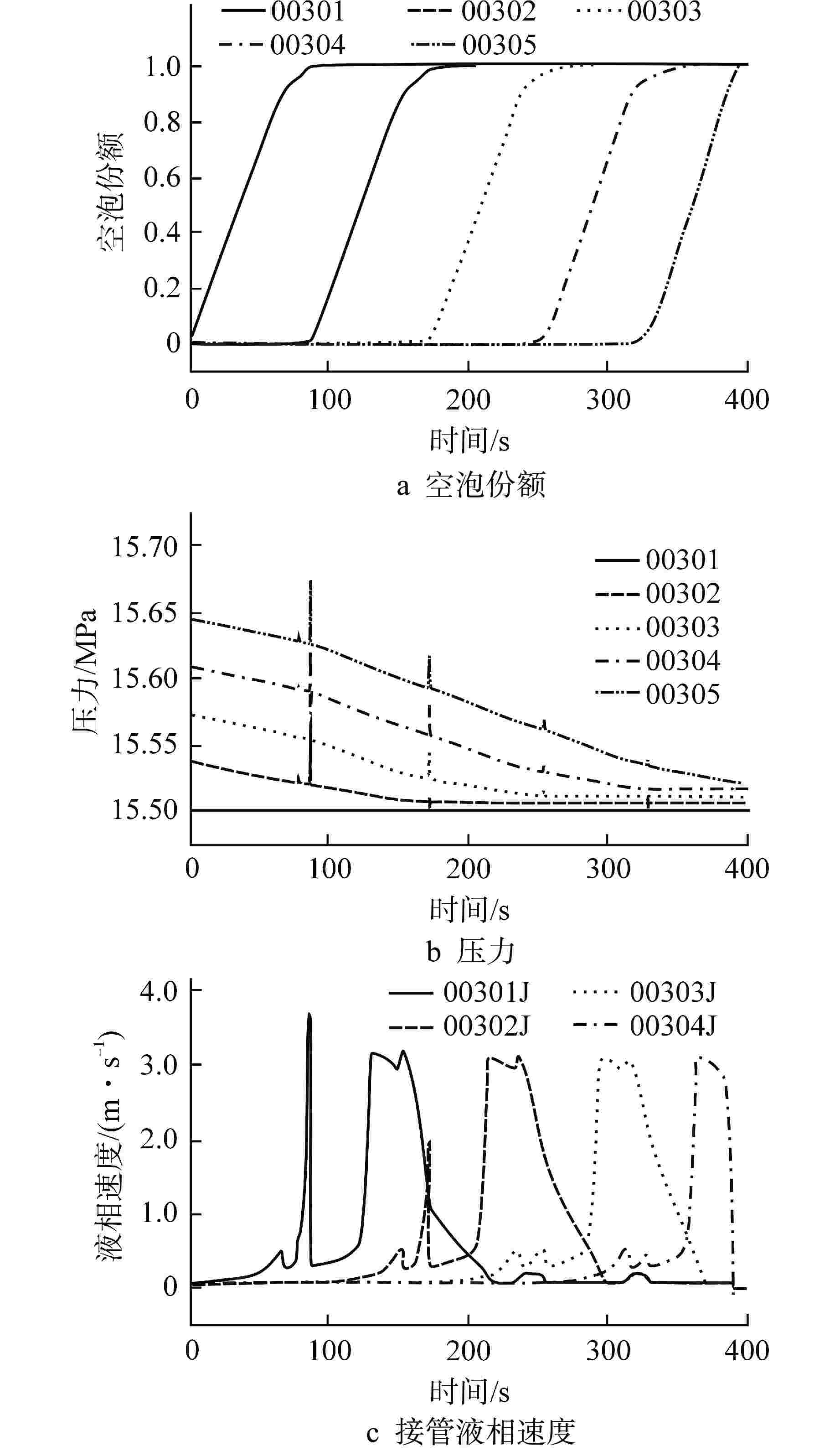
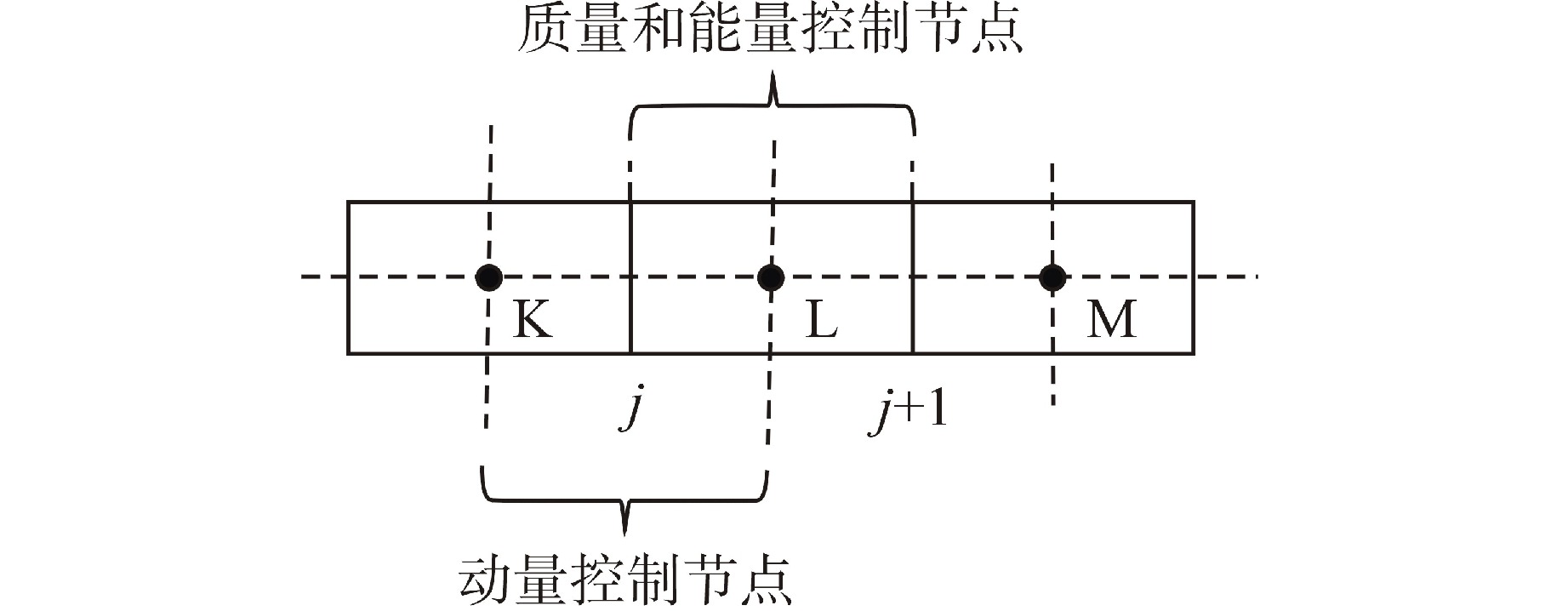
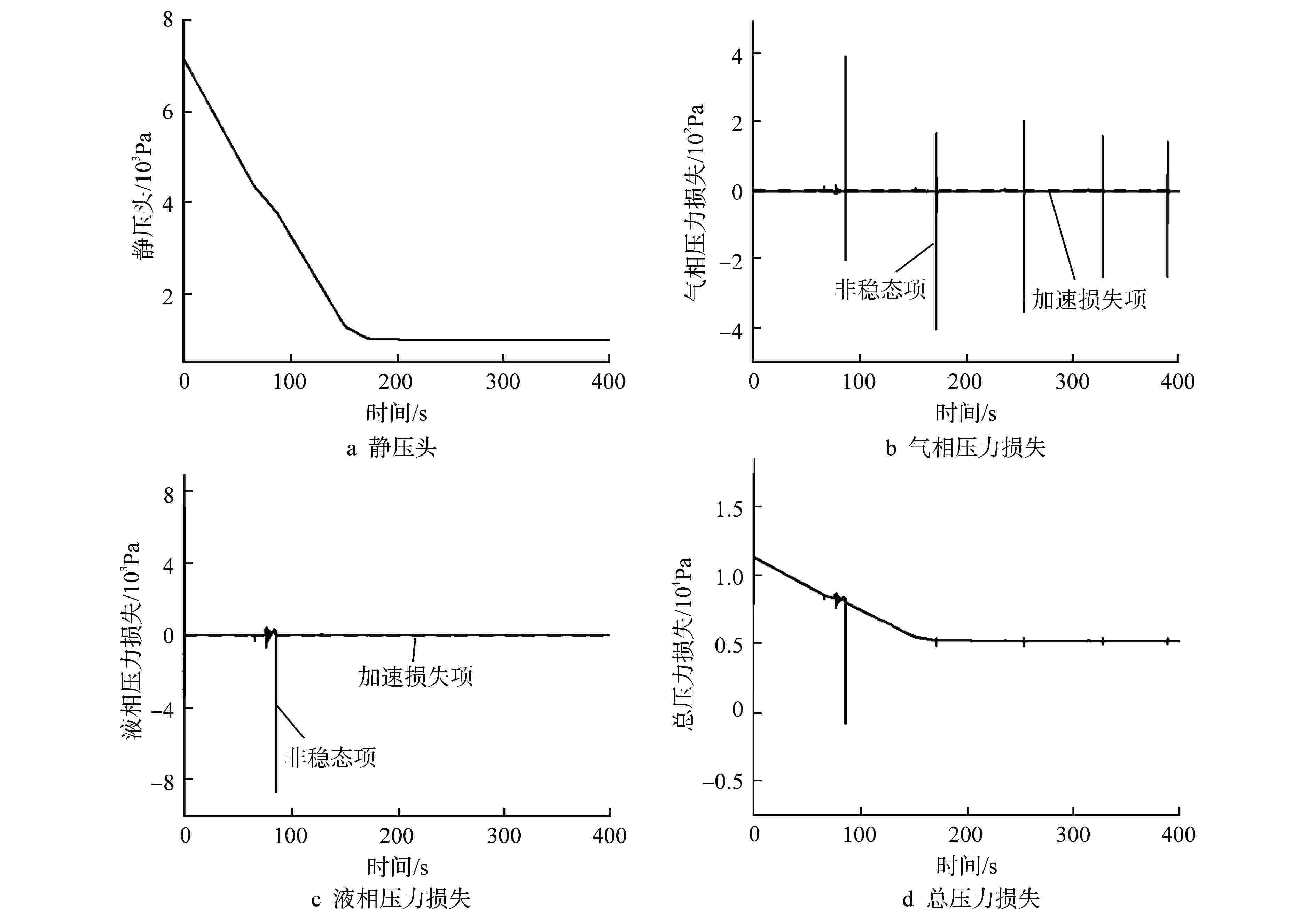
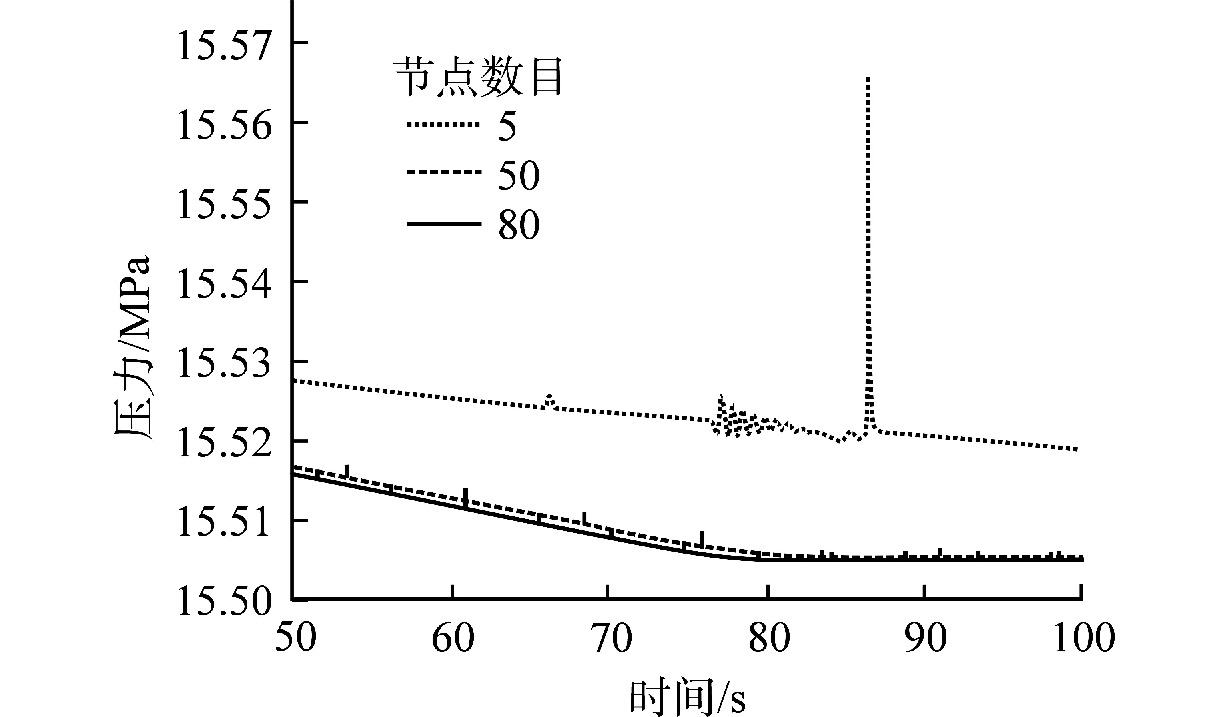
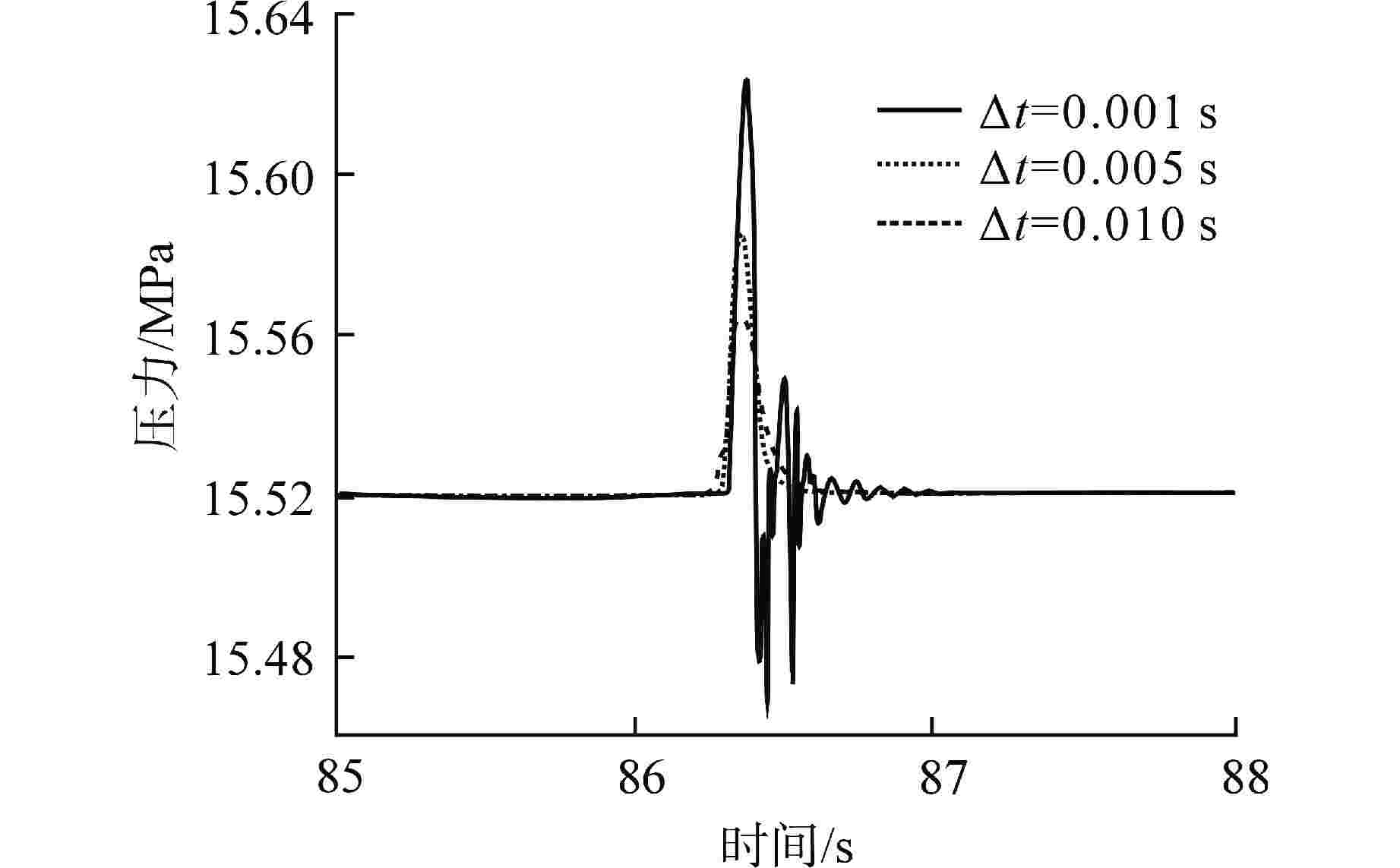
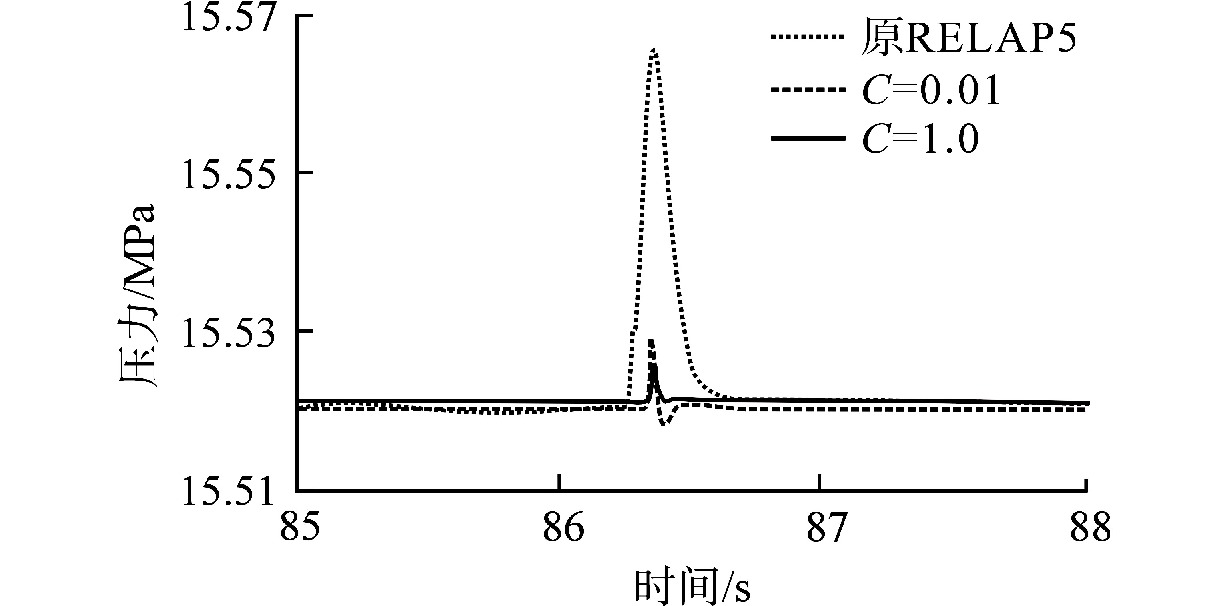
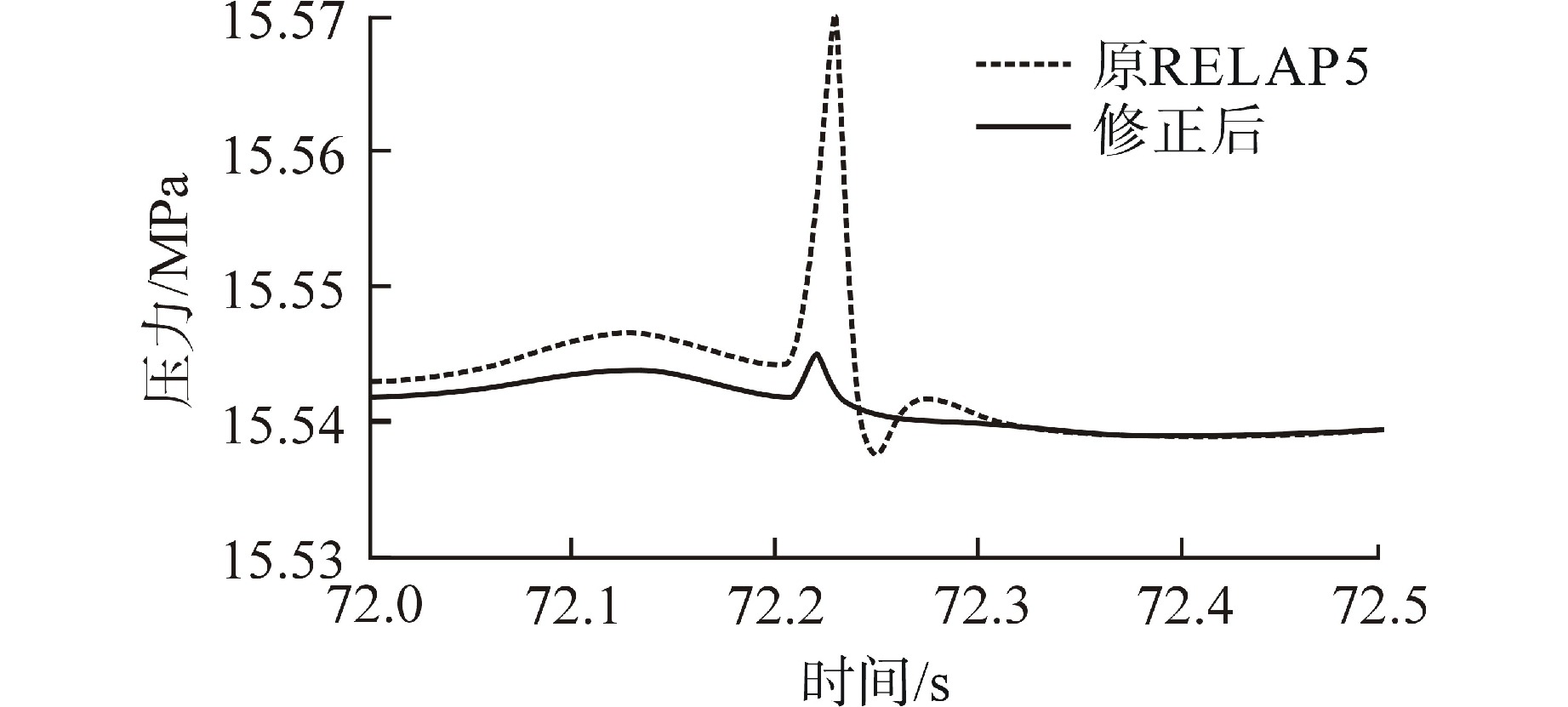
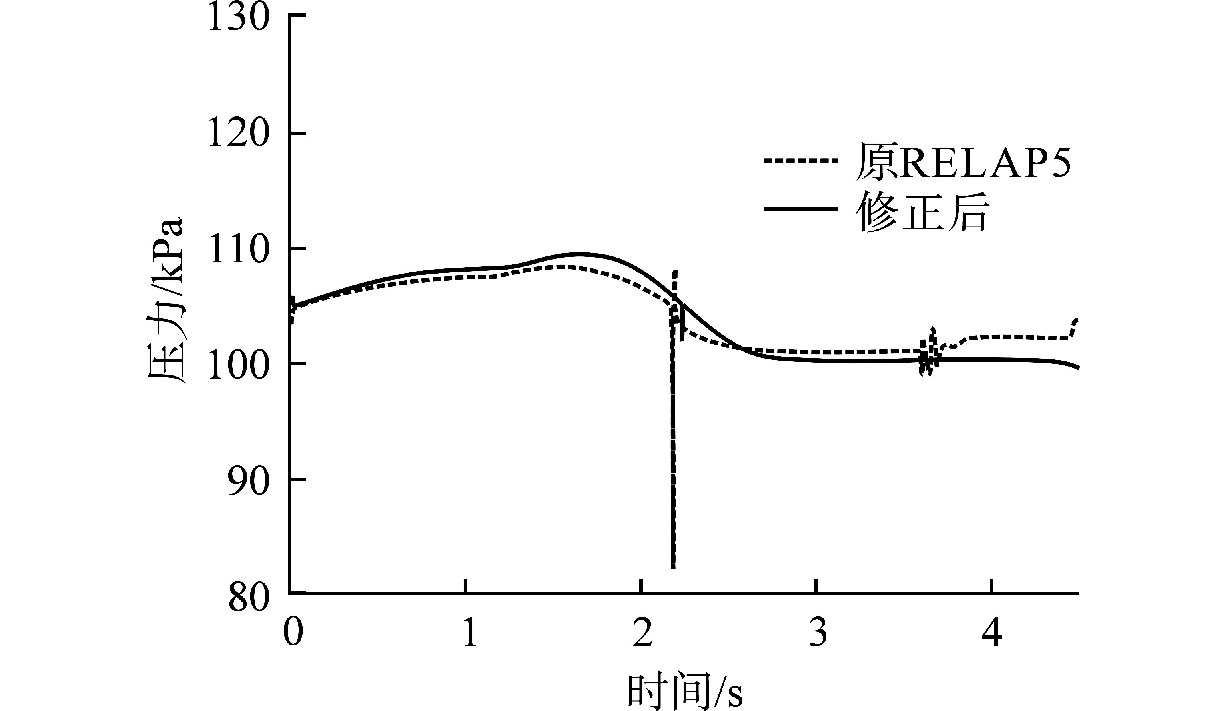
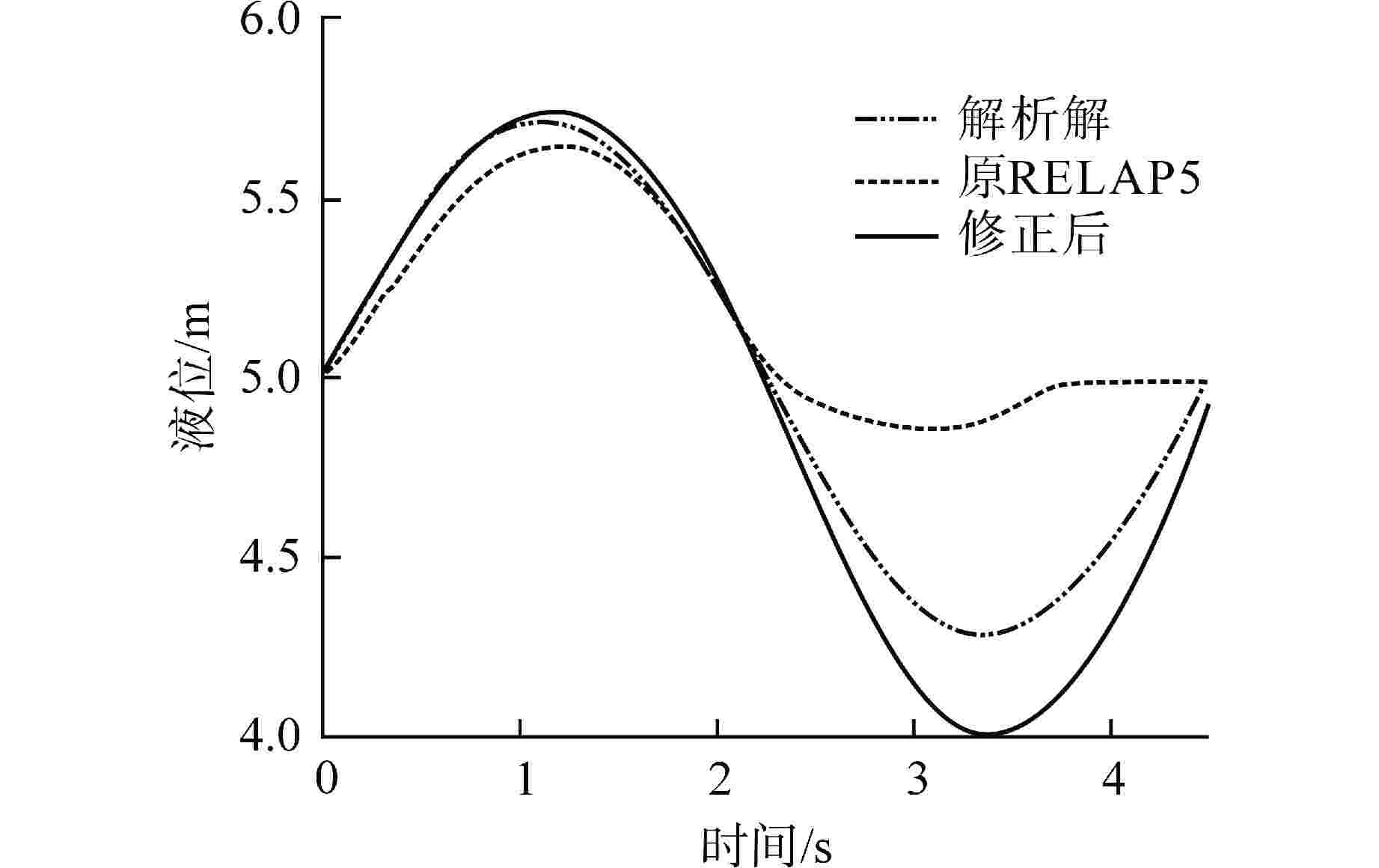
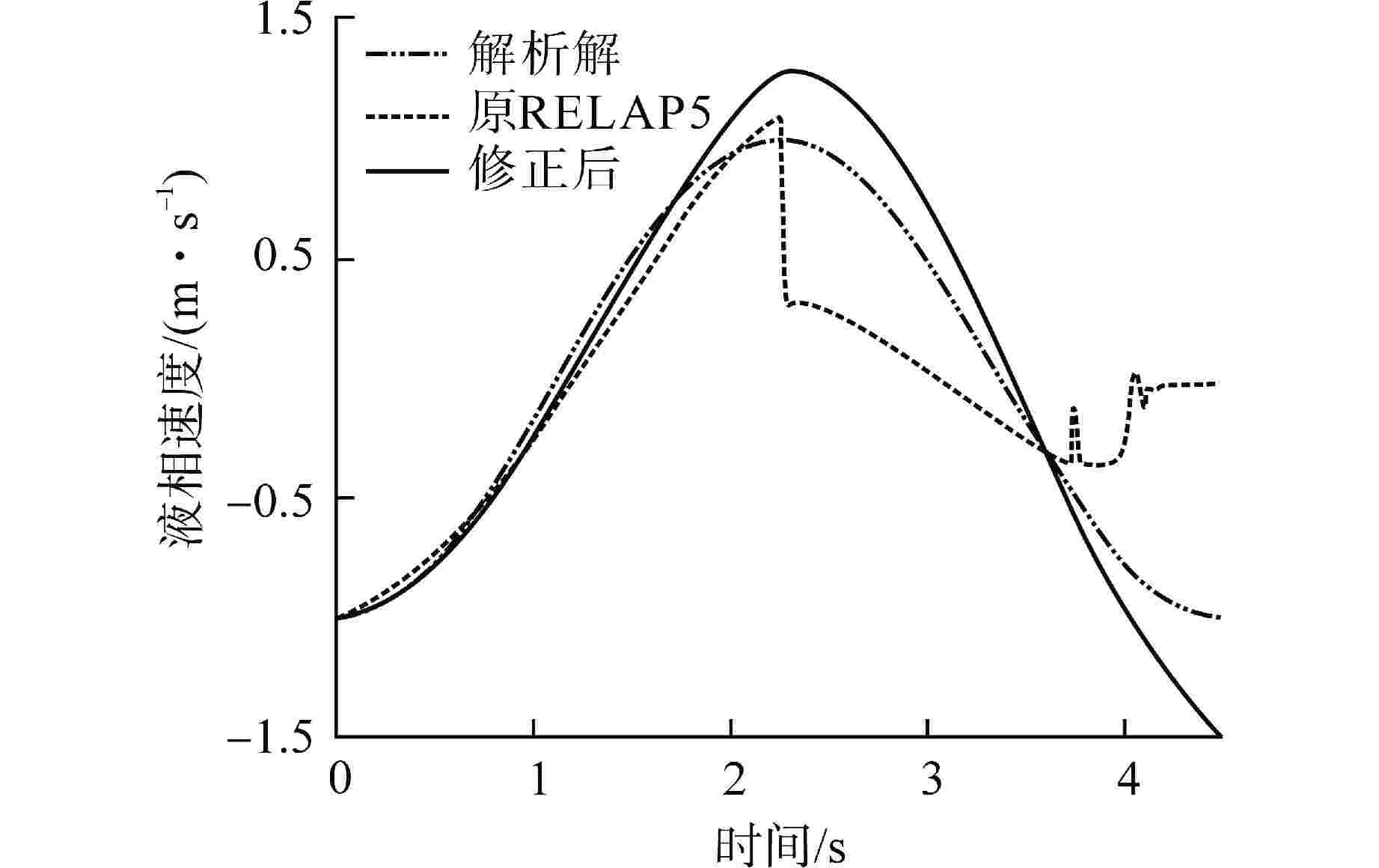
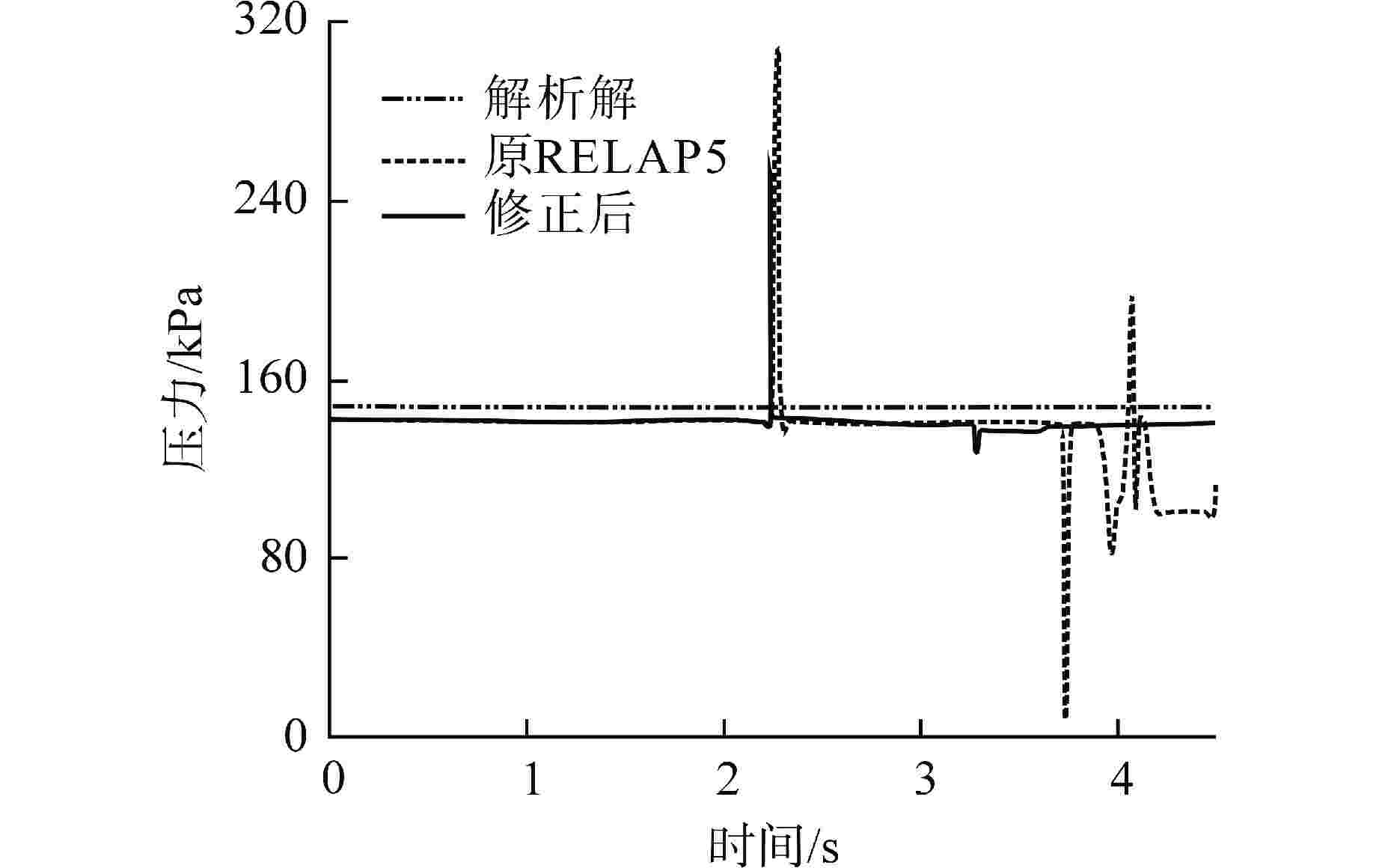
摘要: 为减小或消除RELAP5在垂直分层流动计算时气液相界面跨节点的非物理压力峰,提高计算的稳定性,从动量方程的角度出发,研究造成垂直单管排放算例中出现压力峰的原因,并提出了直接对动量方程进行修正从而减小压力峰的方法。研究发现,液相非稳态项是引起此类压力峰的主要原因。基于此,发展了用于修正液相非稳态项的数值方法,并且通过垂直单管的充排问题和压力计问题对该数值方法进行了验证。验证结果表明,该修正方法可以减小气液相界面跨节点时的非物理压力峰,有利于提高程序的计算稳定性。Abstract: In order to reduce or eliminate the non-physical pressure spike of gas-liquid interface crossing cell edges in vertical stratified flow calculation of RELAP5 and to improve the stability of the calculation, this study investigates the causes of pressure spikes in the vertical stratified flow from the perspective of momentum equations, and proposes a method to reduce the pressure spikes by directly correcting the momentum equations. It is found that the liquid phase unsteady term is the main cause of such pressure spikes. Based on this, a numerical method for correcting the liquid phase unsteady term is developed and validated with a vertical pipe filling and discharging problem and a manometer problem. The validation results show that the correction method can achieve the effect of reducing the non-physical pressure spikes in the process of the gas-water interface crossing cell edges, and therefore, it is beneficial to improve the stability of the code calculation.
-
Key words:
- Vertical stratified flow /
- Gas-liquid interface /
- RELAP5 /
- Pressure spikes /
- Momentum equations
-
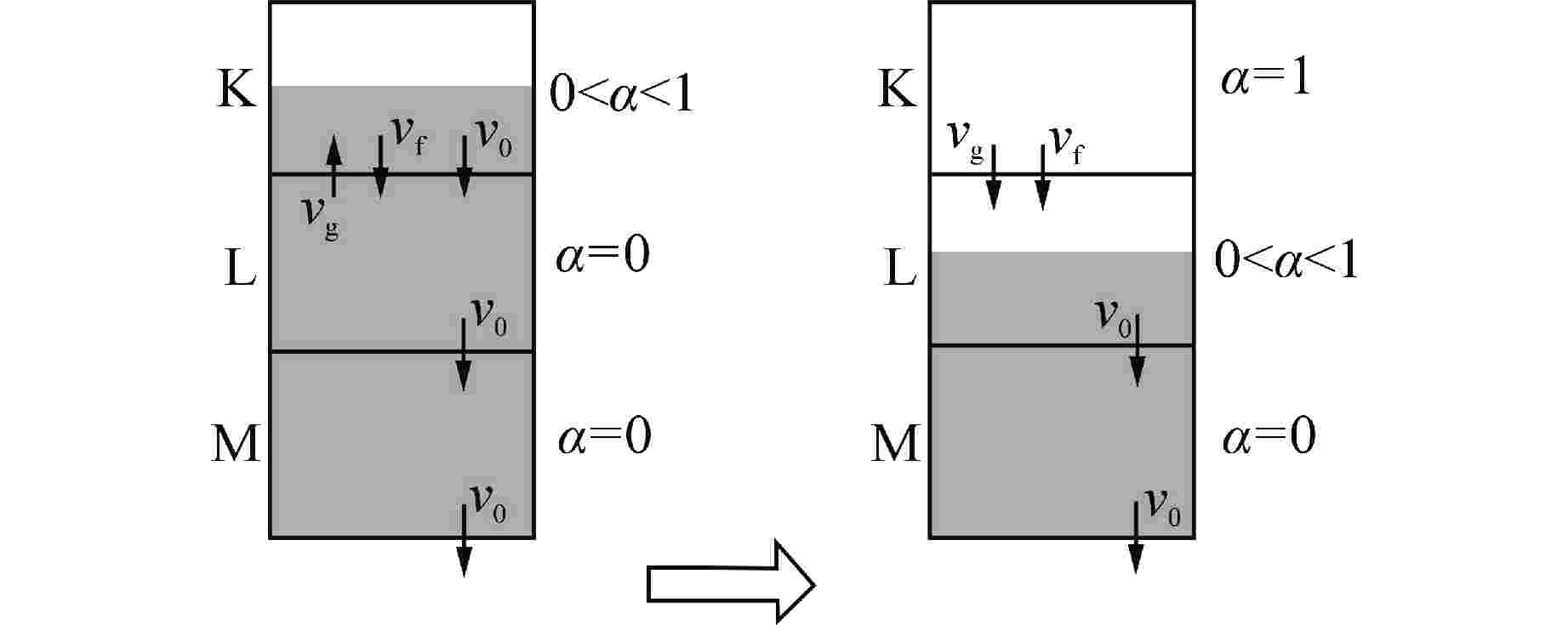
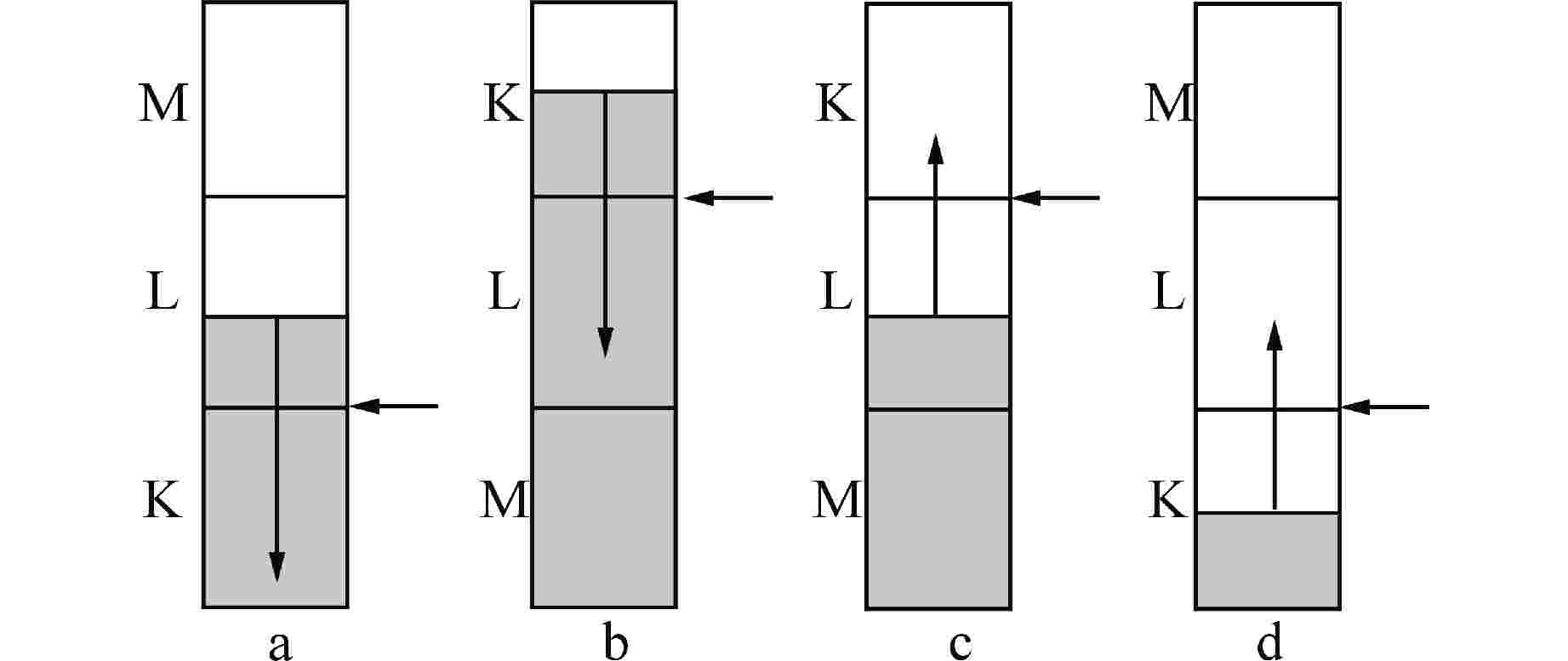
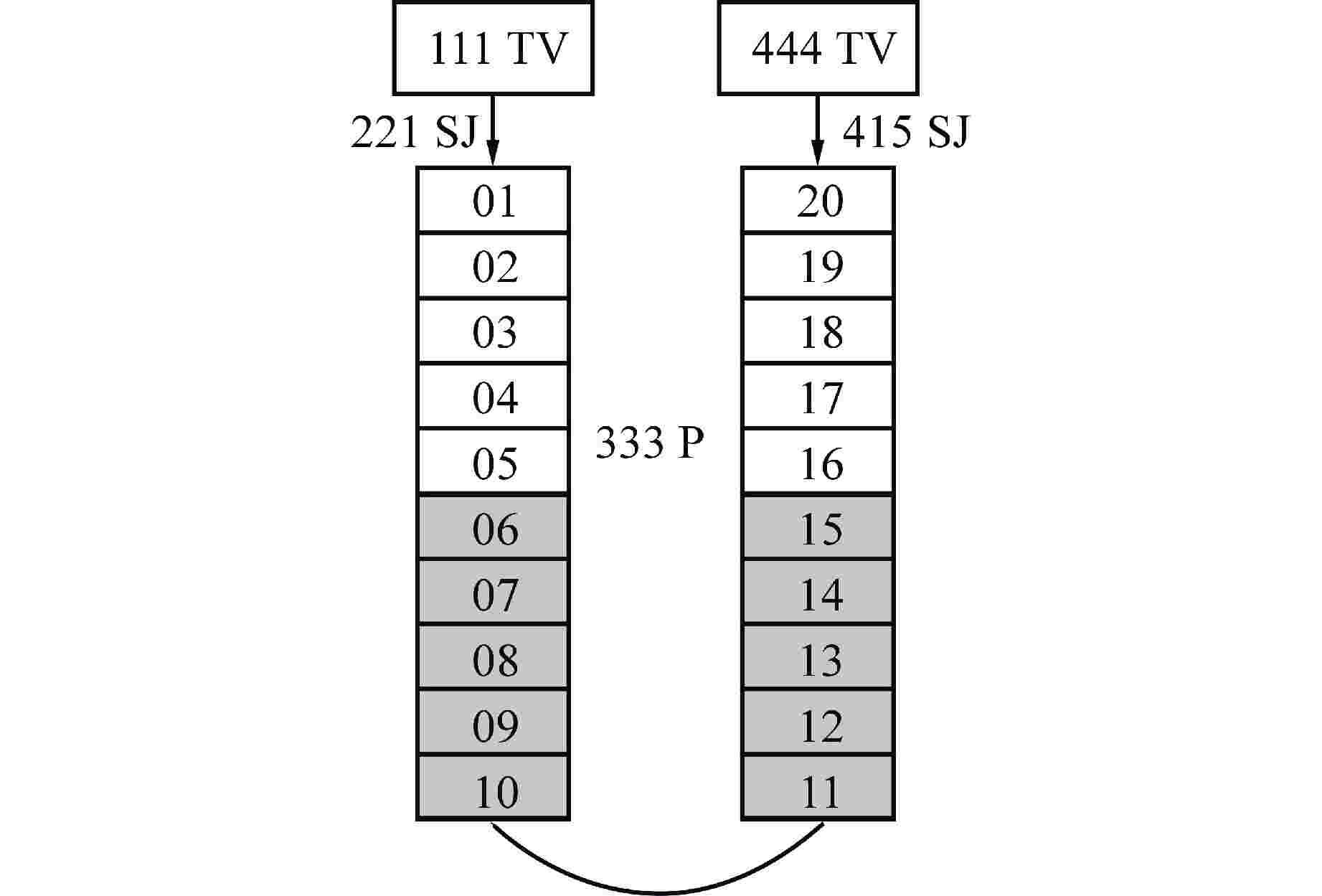
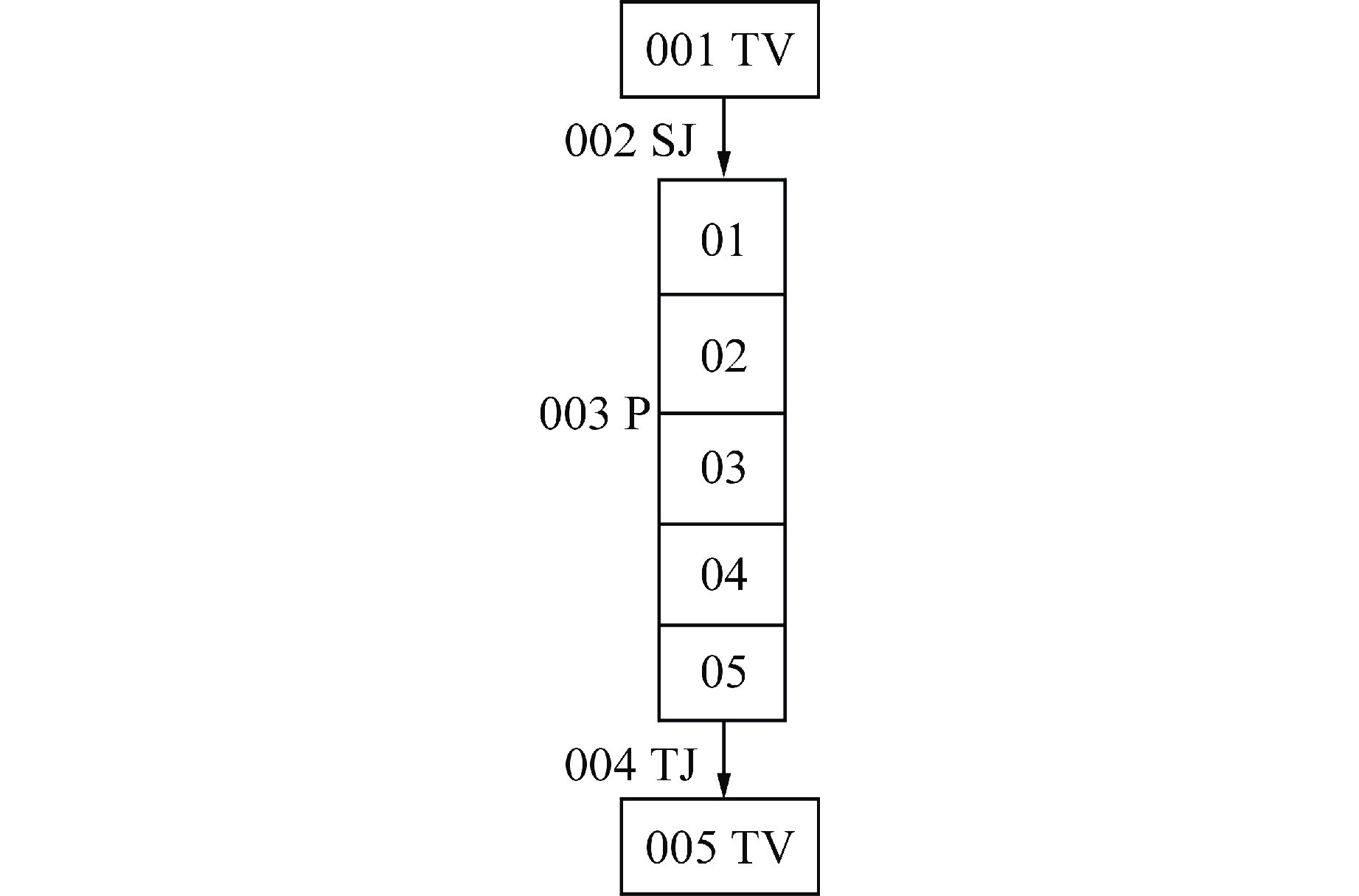
表 1 不同条件下对应的修正因子
Table 1. Correction Factor for Different Conditions
接管类型 接管连接的2个节点的
空泡份额条件接管处速
度条件修正因
子$ {S}_{\mathrm{f},{j}} $a $ {\alpha }_{\mathrm{g},\mathrm{K}}=0,\quad 0 < {\alpha }_{\mathrm{g},\mathrm{L}} < 1 $ $ {v}_{\mathrm{f},{j}} < 0,\quad {v}_{\mathrm{g},{j}} > 0 $ $ {\alpha }_{\mathrm{f},\mathrm{L}} $ b $ 0 < {\alpha }_{\mathrm{g},\mathrm{K}} < 1,\quad {\alpha }_{\mathrm{g},\mathrm{L}}=0 $ $ {v}_{\mathrm{f},{j}} > 0,\quad {v}_{\mathrm{g},{j}} < 0 $ $ {\alpha }_{\mathrm{f},\mathrm{K}} $ c $ {\alpha }_{\mathrm{g},\mathrm{K}}=1,\quad 0 < {\alpha }_{\mathrm{g},\mathrm{L}} < 1 $ $ {v}_{\mathrm{g},{j}} < 0,\quad {v}_{\mathrm{f},{j}} > 0 $ $ {\alpha }_{\mathrm{g},\mathrm{L}} $ d $ 0 < {\alpha }_{\mathrm{g},\mathrm{K}} < 1,\quad {\alpha }_{\mathrm{g},\mathrm{L}}=1 $ $ {v}_{\mathrm{g},{j}} > 0,\quad {v}_{\mathrm{f},{j}} < 0 $ $ {\alpha }_{\mathrm{g},\mathrm{K}} $ -
[1] CO L I T. RELAP5/MOD3 code manual. Volume 4, models and correlations: NUREG/CR-5535[R]. Washington: US Nuclear Regulatory Commission, 1995. [2] WEAVER W L. Improvements to mixture level tracking model: INEL-96/00097[R]. Idaho Falls: Idaho National Lab, 1996. [3] 巢飞,单建强,张勇,等. 两流体双压力模型半隐数值算法研究[J]. 核动力工程,2018, 39(2): 142-148. doi: 10.13832/j.jnpe.2018.01.0142 [4] ARAI M. Characteristics and stability analyses for two-phase flow equation systems with viscous terms[J]. Nuclear Science and Engineering, 1980, 74(2): 77-83. doi: 10.13182/NSE80-A19624 [5] LYCZKOWSKI R W, GIDASPOW D, SOLBRIG C W, et al. Characteristics and stability analyses of transient one-dimensional two-phase flow equations and their finite difference approximations[J]. Nuclear Science and Engineering, 1978, 66(3): 378-396. doi: 10.13182/NSE78-4 [6] HALEY T C, DREW D A, LAHEY JR R T. An analysis of the eigenvalues of bubbly two-phase flows[J]. Chemical Engineering Communications, 1991, 106(1): 93-117. doi: 10.1080/00986449108911538 [7] RAMSHAW J D, TRAPP J A. Characteristics, stability, and short-wavelength phenomena in two-phase flow equation systems[J]. Nuclear Science and Engineering, 1978, 66(1): 93-102. doi: 10.13182/NSE78-A15191 [8] ZOU L, ZHAO H H, ZHANG H B, et al. A revisit to the hicks' hyperbolic two-pressure two-phase flow model[C]//17th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-17). Xi’an, 2017. [9] ABE Y, AKIMOTO H, KAMO H, et al. Elimination of numerical pressure spikes induced by two-fluid model[J]. Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 1993, 30(12): 1214-1224. doi: 10.1080/18811248.1993.9734615 [10] ADACHI H. Multi-dimensional thermal-hydraulics in pressure vessel during reflood phase of a PWR-LOCA[J]. Ceskoslovenská Pediatrie, 1989, 45(6): 335-8. [11] AKIMOTO H, IGUCHI T, OKABE K, et al. Evaluation report on CCTF core-II reflood test C2-6, run 64; Effect of radial power profile[R]. Tokai-mura: Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute, 1985. [12] CO L I T. RELAP5/MOD3 code manual: code structure, system models, and solution methods. Volume 1: NUREG/CR-5535[R]. Washington: US Nuclear Regulatory Commission, 1995. [13] AKTAS B, MAHAFFY J H. A two-phase level tracking method[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 1996, 162(2-3): 271-280. doi: 10.1016/0029-5493(95)01132-3 [14] RANSOM V H. Course A---numerical modeling of two-phase flows for presentation at Ecole d'Ete d'Analyse Numerique: EGG-EAST-8546; CONF-8906249-1[R]. Idaho Falls: EG and G Idaho, 1989. [15] MOODY F J, WINTERBONE D E. Introduction to unsteady thermofluid mechanics[J]. International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow, 1991, 12(4): 384. -





 下载:
下载: