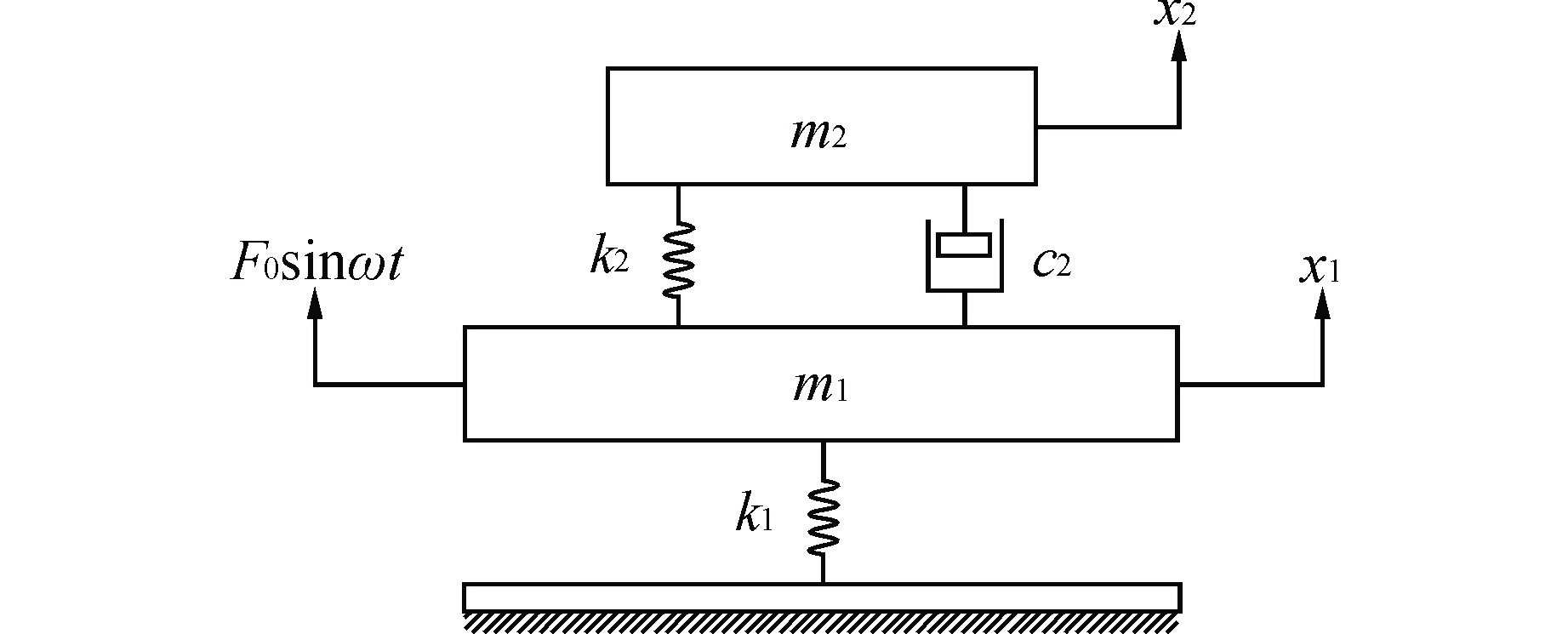
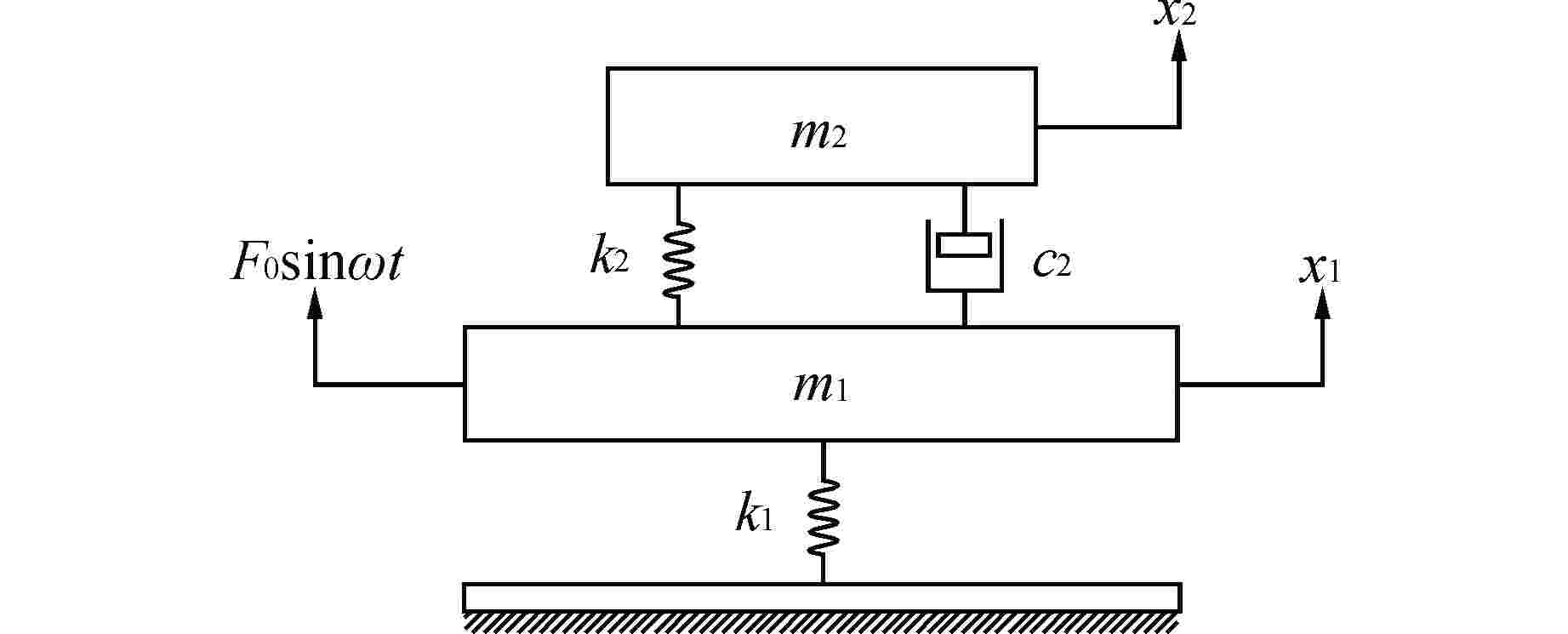
Design and Experimental Study of Dynamic Vibration Absorber for Small Branch Pipe of Complex Pipeline of Nuclear Power Unit
-
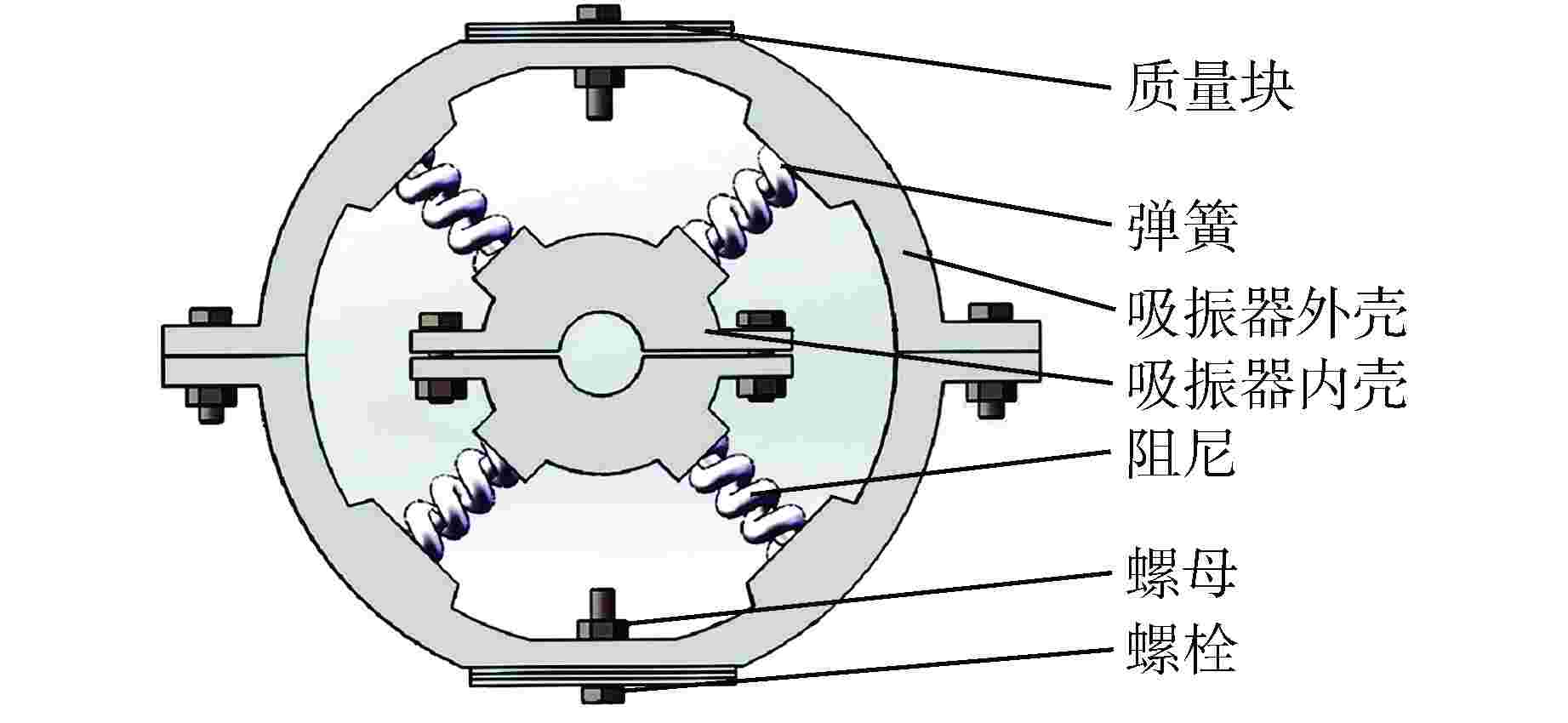
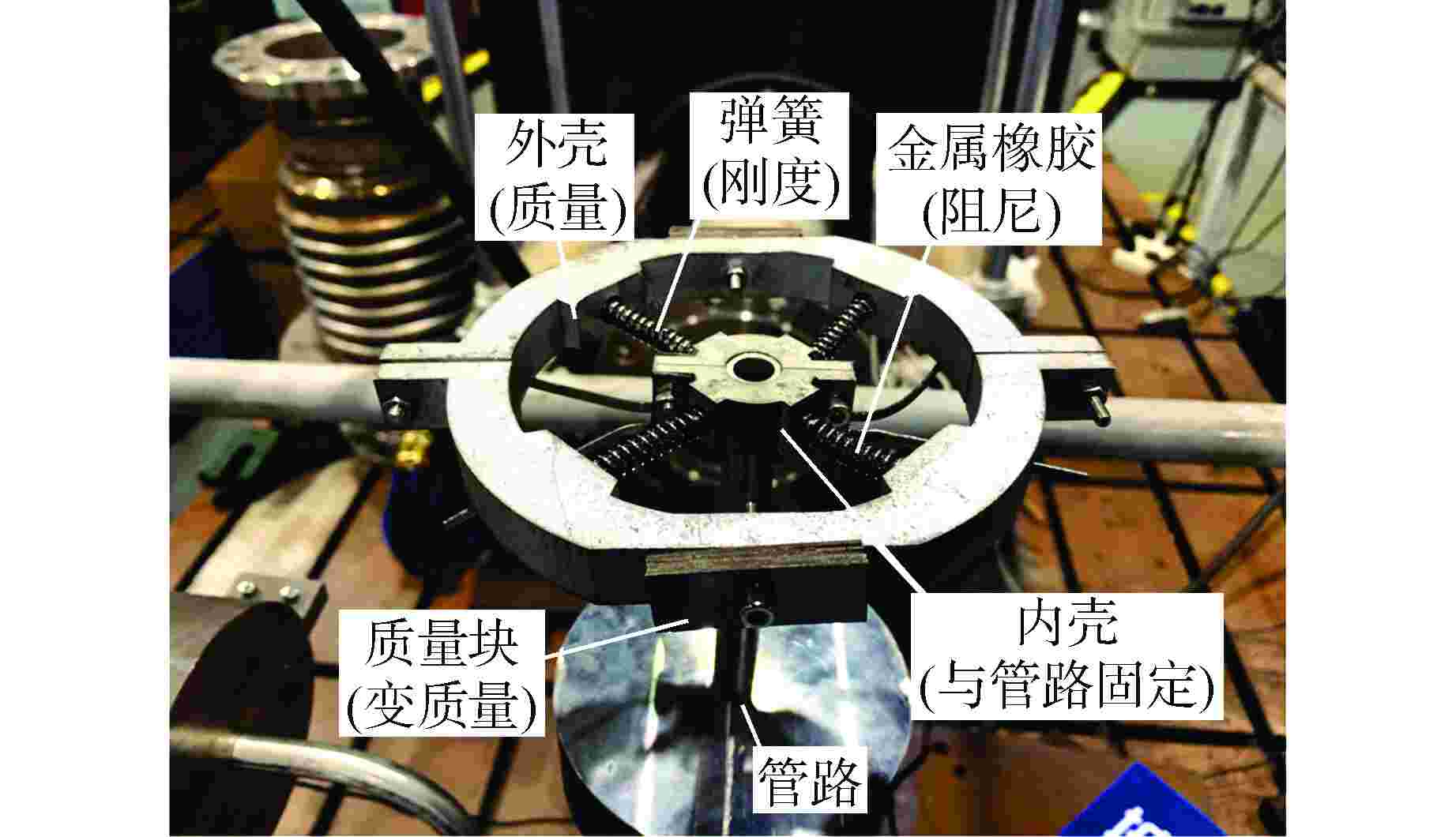
摘要: 核电机组复杂管线小支管长期无规律地振动会导致管道疲劳断裂、破损而引发泄漏,甚至发生核电安全事故。目前常采用加固或减振的方式,但效果不佳,某些频率下的振动峰值难以降低。针对上述问题,本论文设计了一种结构简单、安装方便且质量可调的动力吸振器。通过模拟实际振动工况参数,然后对有无动力吸振器的小支管进行动力学建模分析,并以加速度传递率为参考对动力吸振器相关参数进行设计,获得动力吸振器的最优质量、刚度以及阻尼。最后实物制作并进行试验验证,结果表明,本论文所设计的动力吸振器将小支管在共振频率下的三向振动降低了60%以上(大于工程要求的5 dB);通过微调质量块个数扩大了吸振频段的可调节范围,能够满足不同工况的需求;增加金属橡胶材料进一步增强了动力吸振器的吸振效果,相比无阻尼结构可以将减振性能提高10%以上。本研究为核电机组复杂管线小支管的减振提供了有效方法。Abstract: The long-term irregular vibration of small branches in the complex pipelines of nuclear power units can lead to fatigue fracture and damage, causing leaks and even nuclear safety accidents. Currently, reinforcement or vibration reduction methods are commonly used, but the effectiveness is limited, and reducing the vibration peak at certain frequencies is challenging. To address these issues, this paper proposes the design of a structurally simple, easy-to-install, and adjustable-quality dynamic absorber. By simulating actual vibration conditions, the dynamic modeling and analysis of small branches with and without dynamic absorbers are conducted. Using the acceleration transfer rate as a reference, the relevant parameters of the dynamic absorber are designed to obtain the optimal mass, stiffness, and damping of the dynamic absorber. Finally, the physical prototype is produced and experimentally verified. The results show that the designed dynamic absorber in this paper reduces the three-axis vibration of small branches at resonance frequencies by more than 60% (exceeding the engineering requirement of 5 dB). Fine-tuning the number of mass blocks expands the adjustable range of the absorption frequency band, meeting the requirements of different operating conditions. Adding metal rubber material further enhances the absorption effect of the dynamic absorber, improving the damping performance by more than 10% compared to the structure without damping. This research provides an effective method for vibration reduction in the small branches of complex pipelines in nuclear power units.
-
表 1 小支管模态结果
Table 1. Modal Results of Small Branch Pipes
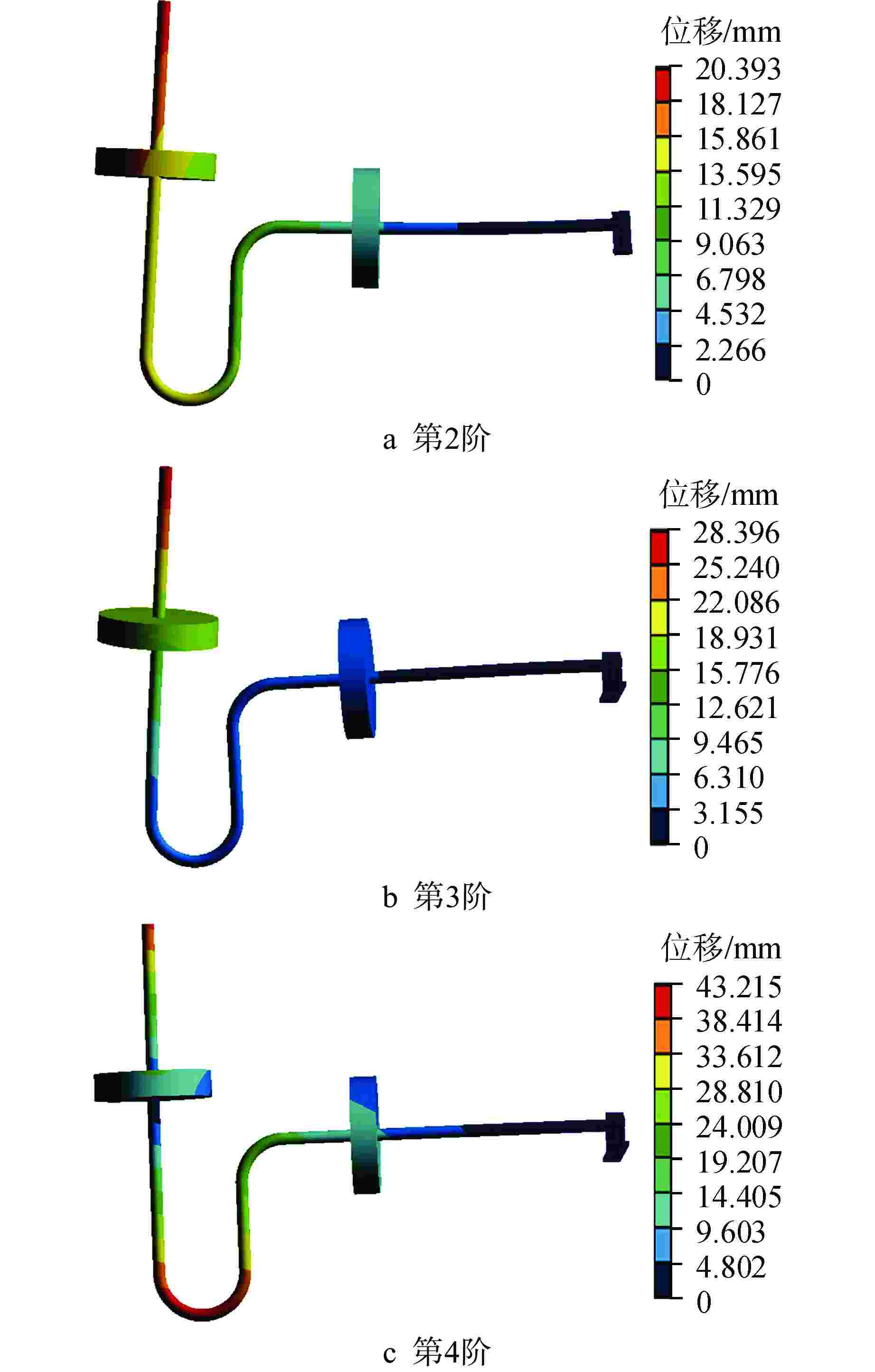
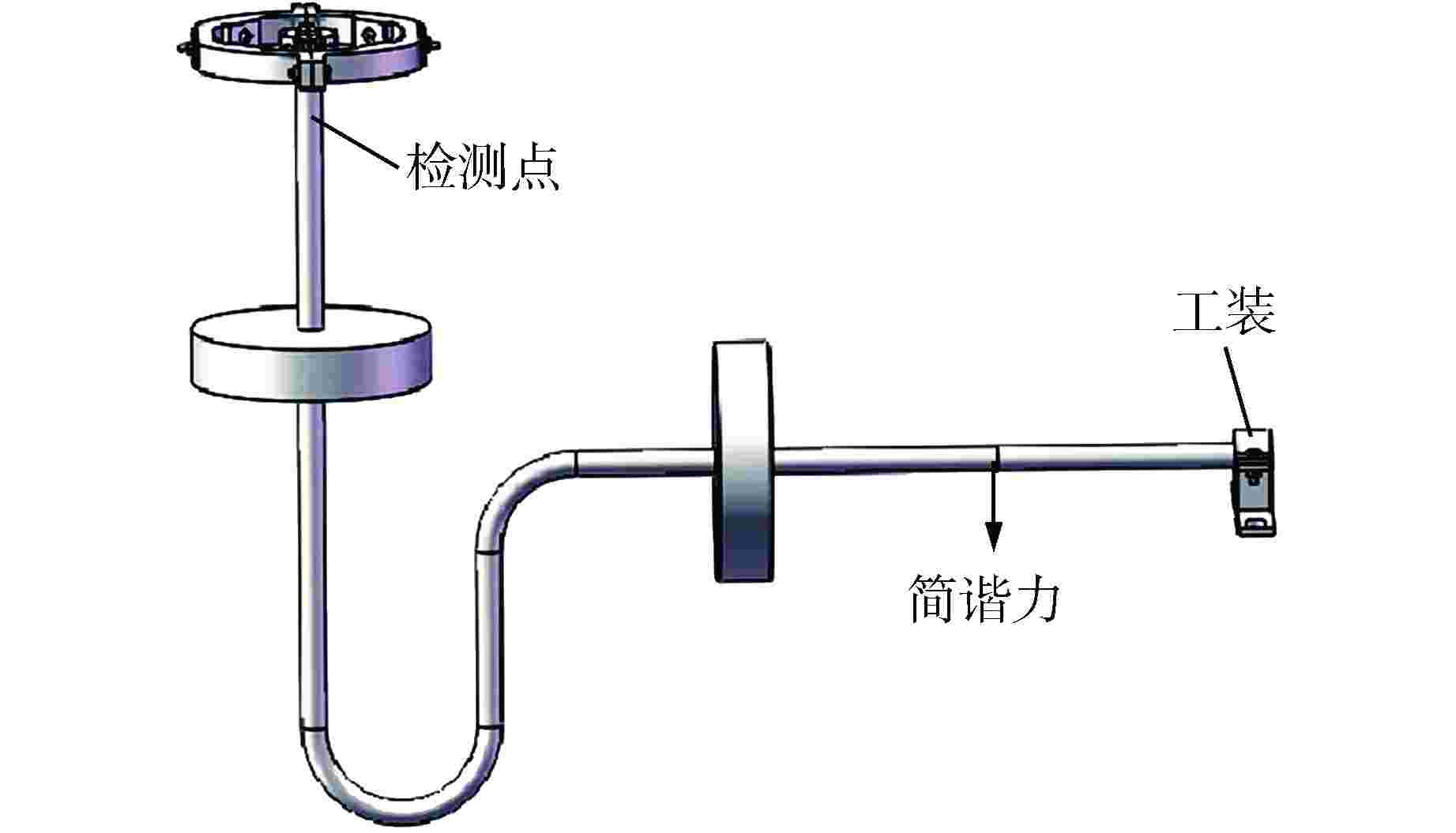
模态 频率/Hz 模态 频率/Hz 1 5.0081 6 40.4570 2 5.5217 7 43.1480 3 11.1970 8 84.6370 4 19.5220 9 118.9400 5 32.6730 10 173.2800 表 2 检测点X、Y、Z方向最大加速度
Table 2. Maximum Acceleration of Measuring Points in X, Y and Z Directions
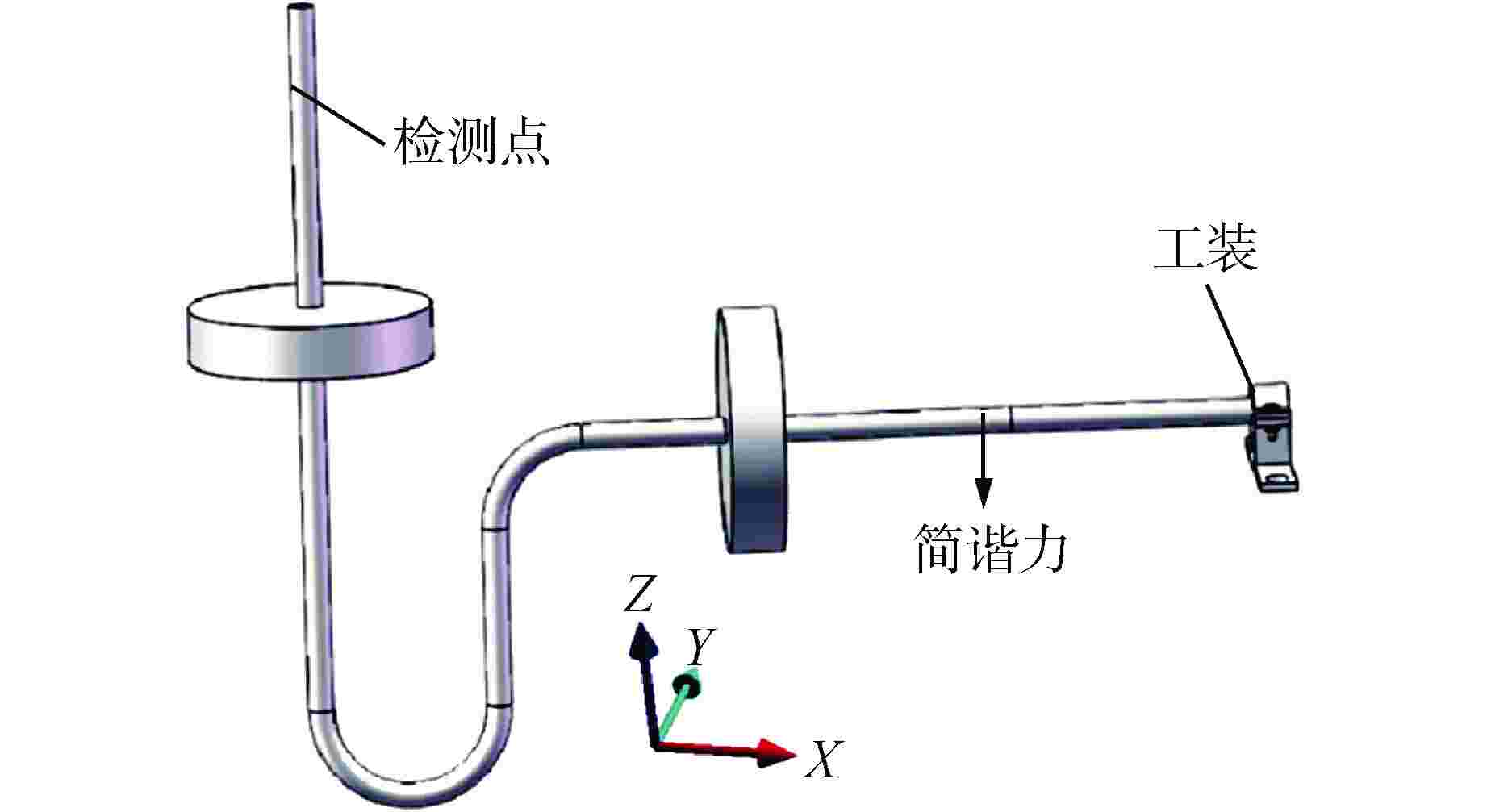
设备名称 加速度/(m·s−2) X方向 Y方向 Z方向 027YP 174 3 10 表 3 不同方向上有无动力吸振器的吸振效果
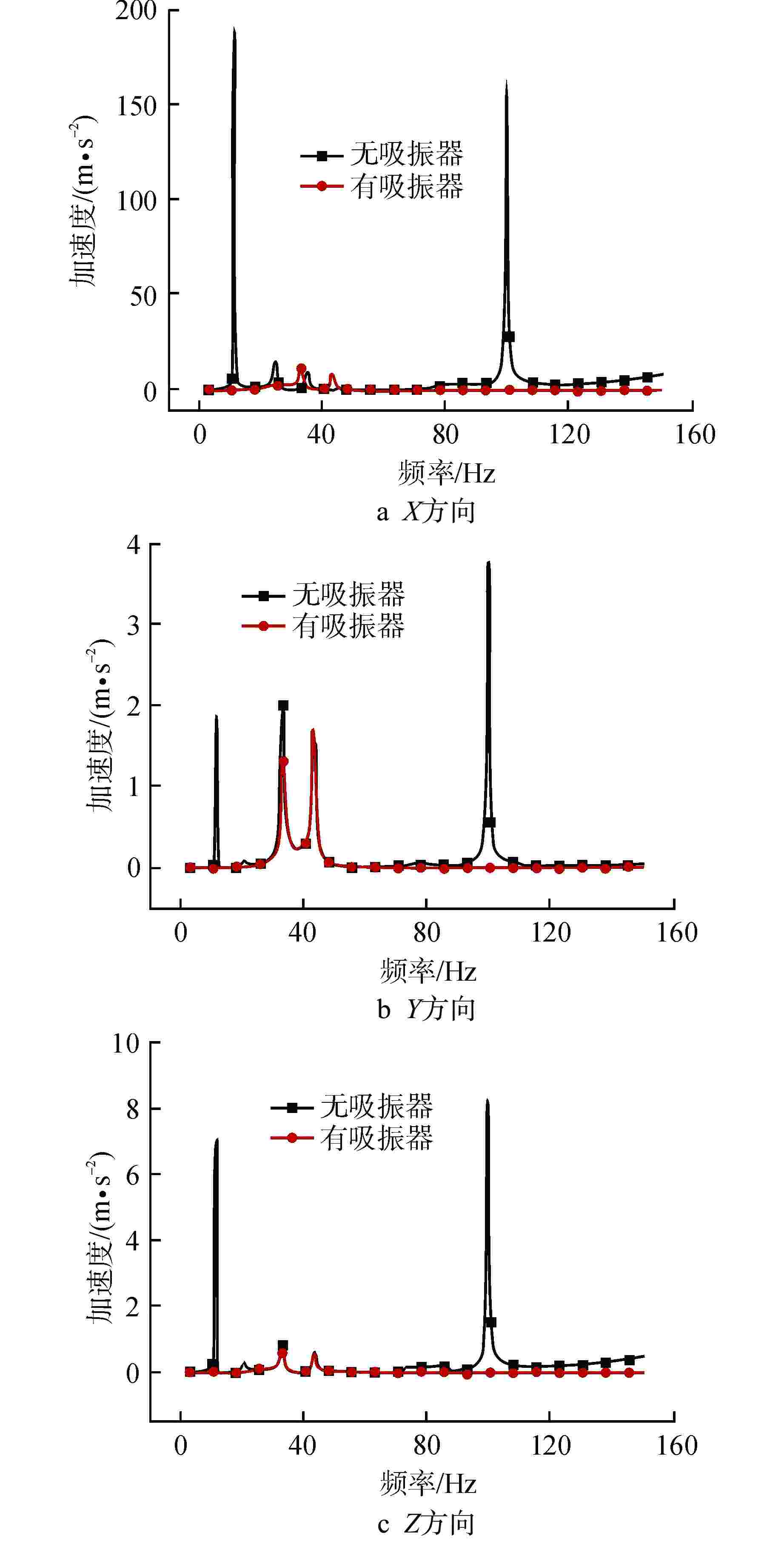
Table 3. Vibration Absorption Effects in Different Directions with or without Dynamic Vibration Absorber
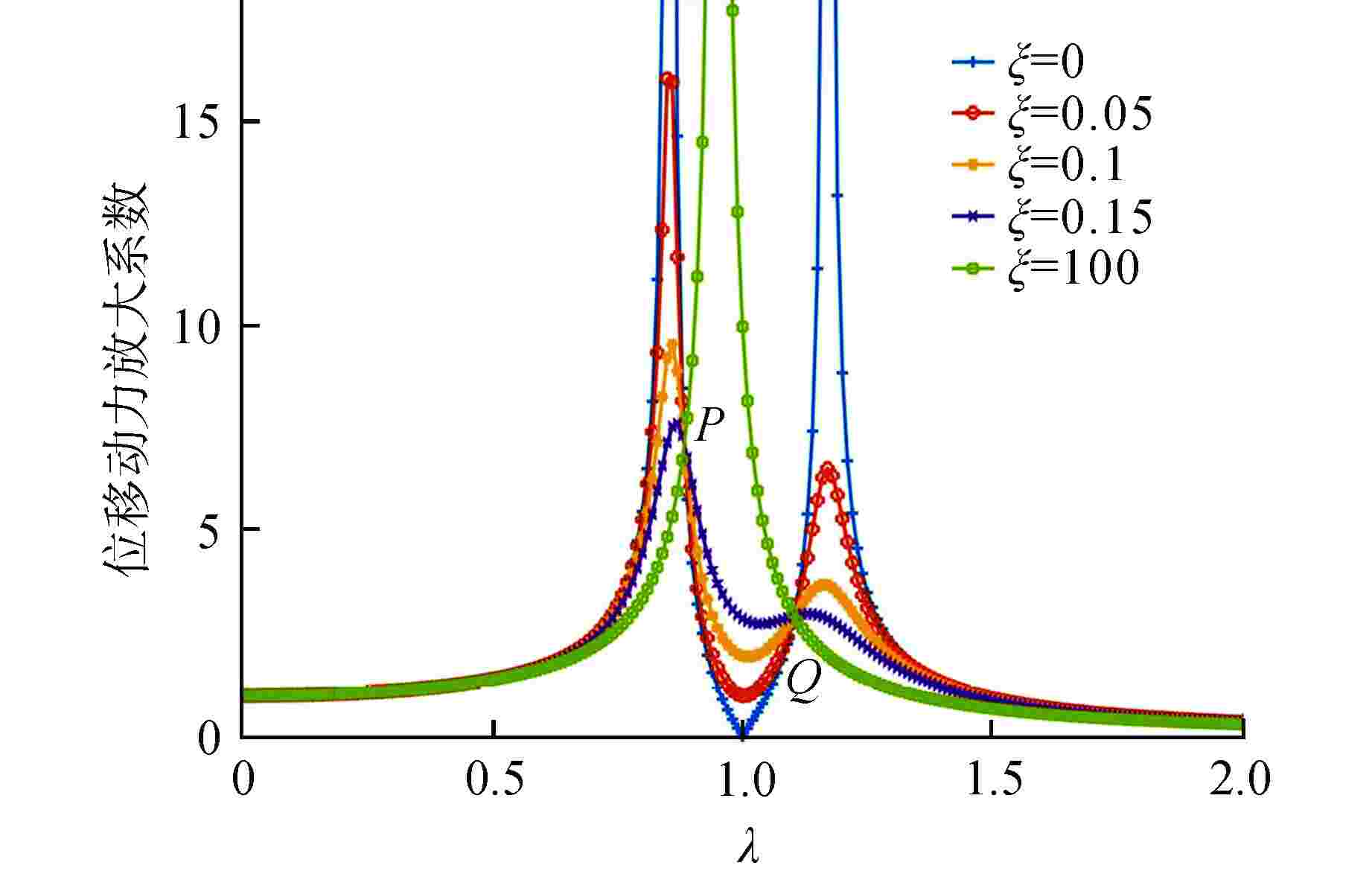
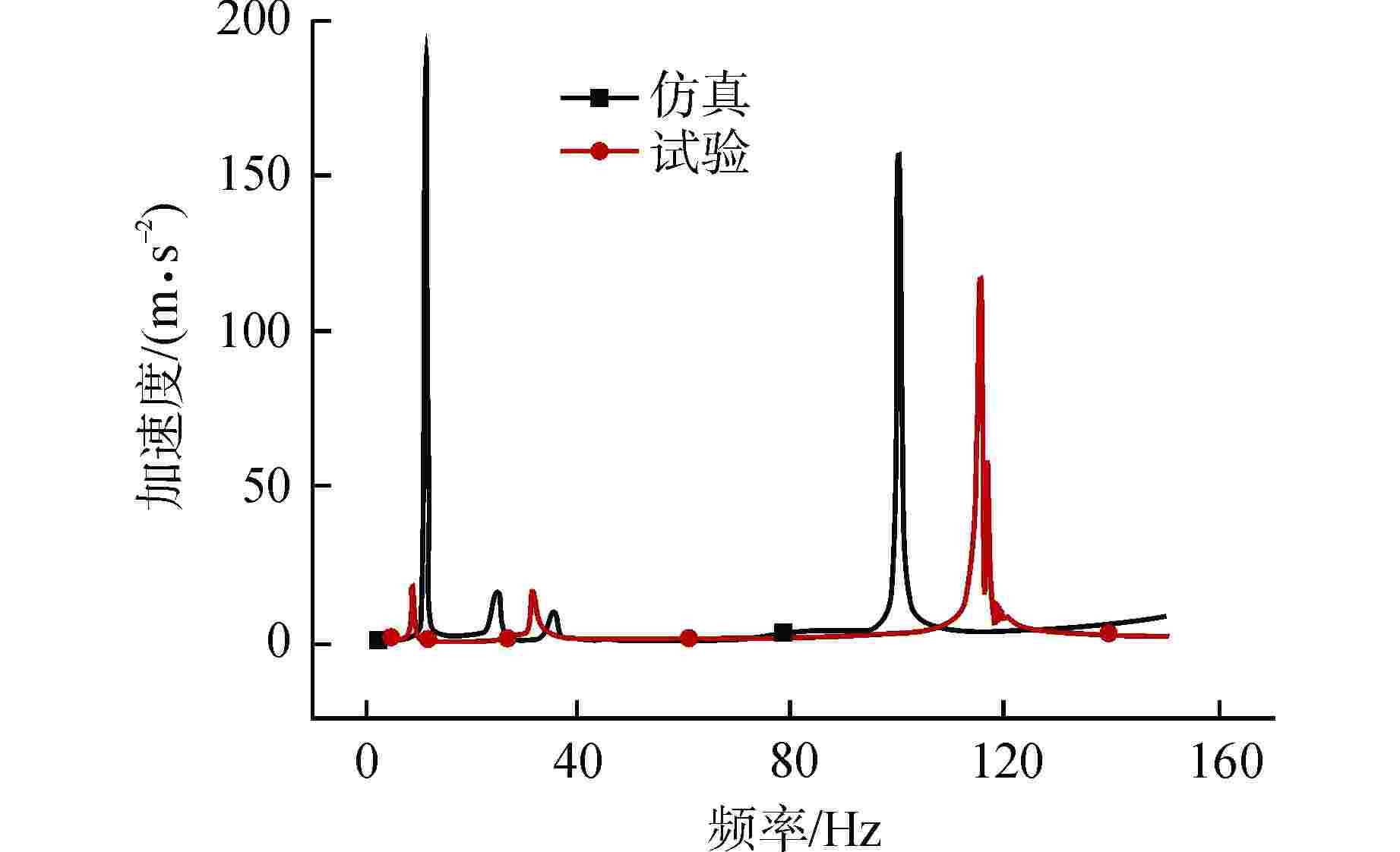
方向 11.25 Hz处加速度/(m·s−2) η1/% η2/dB 无动力吸振器 有动力吸振器 X 187.6500 11.5570 93.8 24.2 Y 1.8756 0.0285 98.5 36.4 Z 7.0064 0.1042 98.5 36.6 方向 99.75 Hz处加速度/(m·s−2) η1/% η2/dB 无动力吸振器 有动力吸振器 X 156.4300 0.1390 99.9 61.0 Y 3.7806 0.0032 99.9 61.4 Z 8.1623 0.0103 99.9 58.0 表 4 33 Hz处有无阻尼管路吸振效果对比
Table 4. Comparison of Vibration Absorption Effects at 33 Hz for Pipelines with or without Damping
方向 加速度/(m·s−2) η1/% 无阻尼 有阻尼 X 81.3370 11.5570 85.6 Y 3.1842 1.3213 58.5 Z 4.1715 0.5957 85.7 表 5 测试仪器型号及参数
Table 5. Test Instrument Model and Parameters
序号 设备名称 设备型号 技术参数 1 激振器 E-JZK-100 激振力≤1000 N 2 功率放大器 E5874A AC:220 V/50 Hz/8 A 3 力传感器 ECL-YD-312A 灵敏度:2.72 pC/N 4 加速度传感器 1A102E 灵敏度:2 mV/g 5 数据采集器 DH5922N 表 6 不同激振力下有无动力吸振器的吸振效果
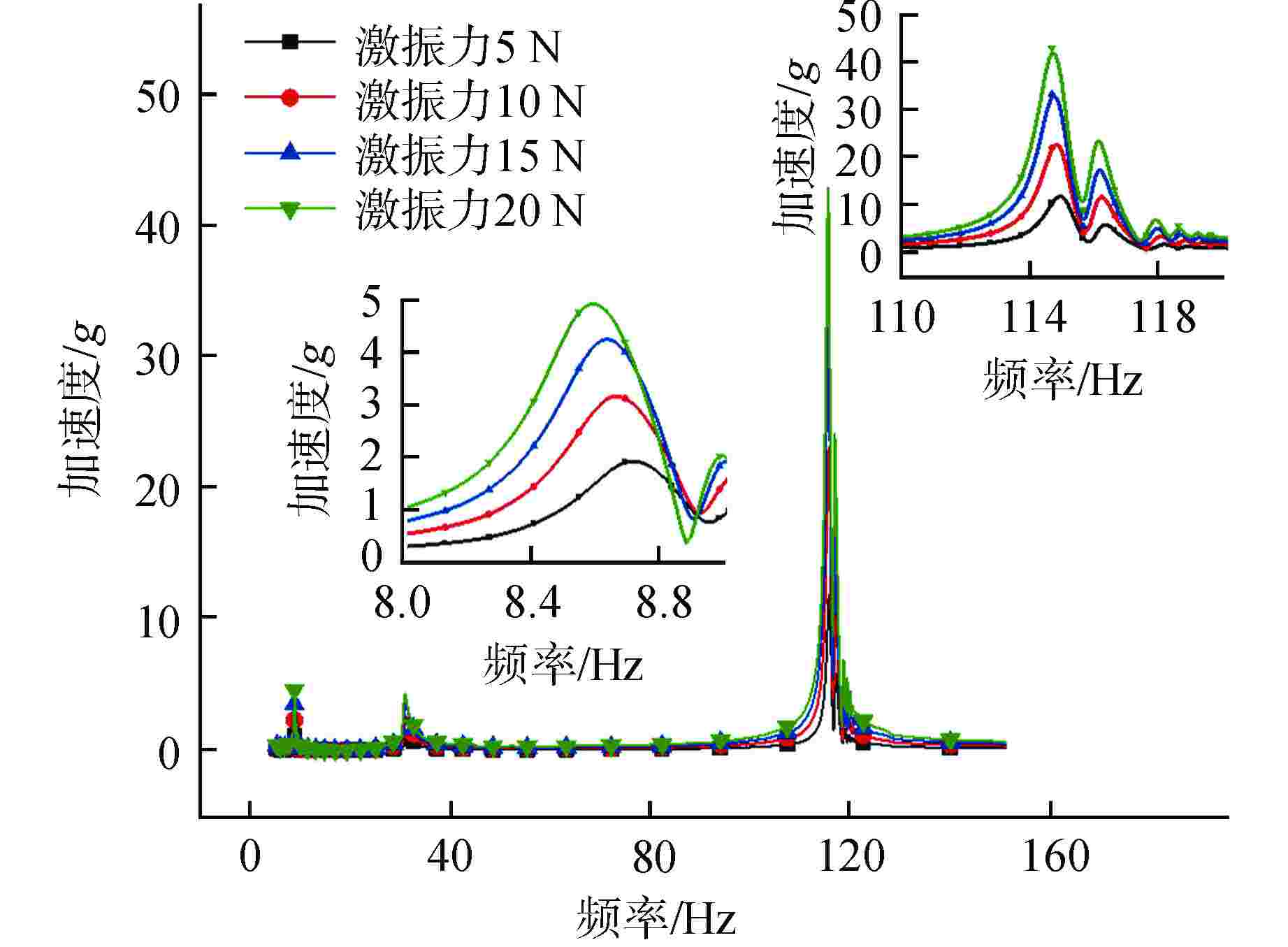
Table 6. Vibration Absorption Effects under Different Excitation Forces with or without Dynamic Vibration Absorber
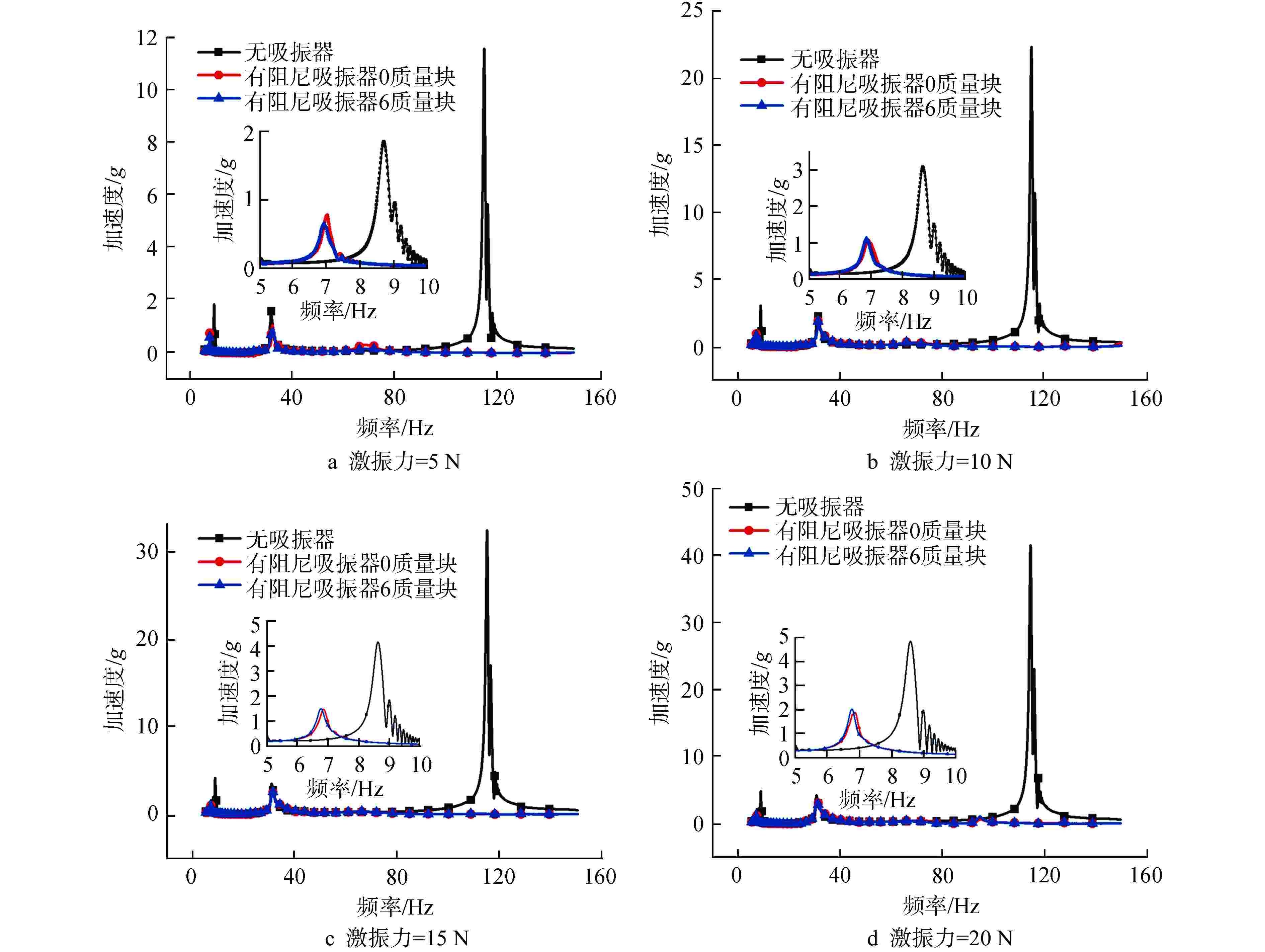
激振力/N 8.7 Hz处加速度/g η1/% η2/dB 无动力吸振器 有动力吸振器 5 1.8456 0.6473 64.9 9.1 10 3.0816 1.0742 65.1 9.2 15 4.1657 1.4763 64.6 9.0 20 4.8326 1.8484 61.8 8.3 激振力/N 115 Hz处加速度/g η1/% η2/dB 无动力吸振器 有动力吸振器 5 11.7424 0.0220 99.8 54.5 10 22.9346 0.0376 99.8 55.7 15 32.9543 0.0781 99.8 52.5 20 42.4867 0.2012 99.5 46.5 表 7 30 Hz处有无阻尼吸振效果对比
Table 7. Comparison of Vibration Absorption Effects at 30 Hz with or without Damping
激振力/N 无阻尼加速度 有阻尼加速度 η1/% 5 1.1g 0.9g 18 10 2.3g 2.0g 13 15 3.1g 2.7g 13 20 3.8g 3.4g 11 -
[1] 王超. 管路振动主动控制方法及实验研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学,2021. [2] DONG W, MUGGERIDGE D. Virbration characteristics of reinforced plastic pipes in a fluid medium[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Engineering in the Ocean Environment. Halifax: IEEE, 1974: 232-232. [3] PAIDOUSSIS M P. Flow-induced instabilities of cylindrical structures[J]. Applied Mechanics Reviews, 1987, 40(2): 163-175. doi: 10.1115/1.3149530 [4] 背户一登. 动力吸振器及其应用[M]. 任明章,译. 北京: 机械工业出版社,2013: 161-164. [5] 王文初,尹志勇,陈科,等. 新型三向管路动力吸振器设计方法研究[J]. 船舶力学,2015, 19(S1): 191-197. [6] 张琳,李华峰,陈勇,等. 基于动柔度方法的管路动力吸振器设计研究[J]. 中国舰船研究,2019, 14(5): 138-144. doi: 10.19693/j.issn.1673-3185.01394 [7] 姚伍平,彭旭,唐文兵,等. 基于欧拉梁的管路吸振器振动特性研究[J]. 舰船科学技术,2020, 42(15): 48-54. [8] 王碧浩,熊夫睿,黄茜,等. 管道系统动力吸振器布置多目标优化设计[J]. 机械,2020, 47(6): 10-16,31. [9] 刘彬彬,陈果,赵正大,等. 一种新型动力吸振器的液压管道减振试验研究[J]. 噪声与振动控制,2017, 37(1): 152-157,187. [10] 郭吉祥. 轮毂加工机床主轴动力吸振器设计及实验研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江工业大学,2020. [11] 李拓,白鸿柏. 编织-嵌槽型金属橡胶在不同温度下的压缩性能[J]. 机械工程材料,2018, 42(10): 58-61. doi: 10.11973/jxgccl201810011 -





 下载:
下载: