Study on Neutron Diffusion Calculation Method Based on hp-VPINN
-
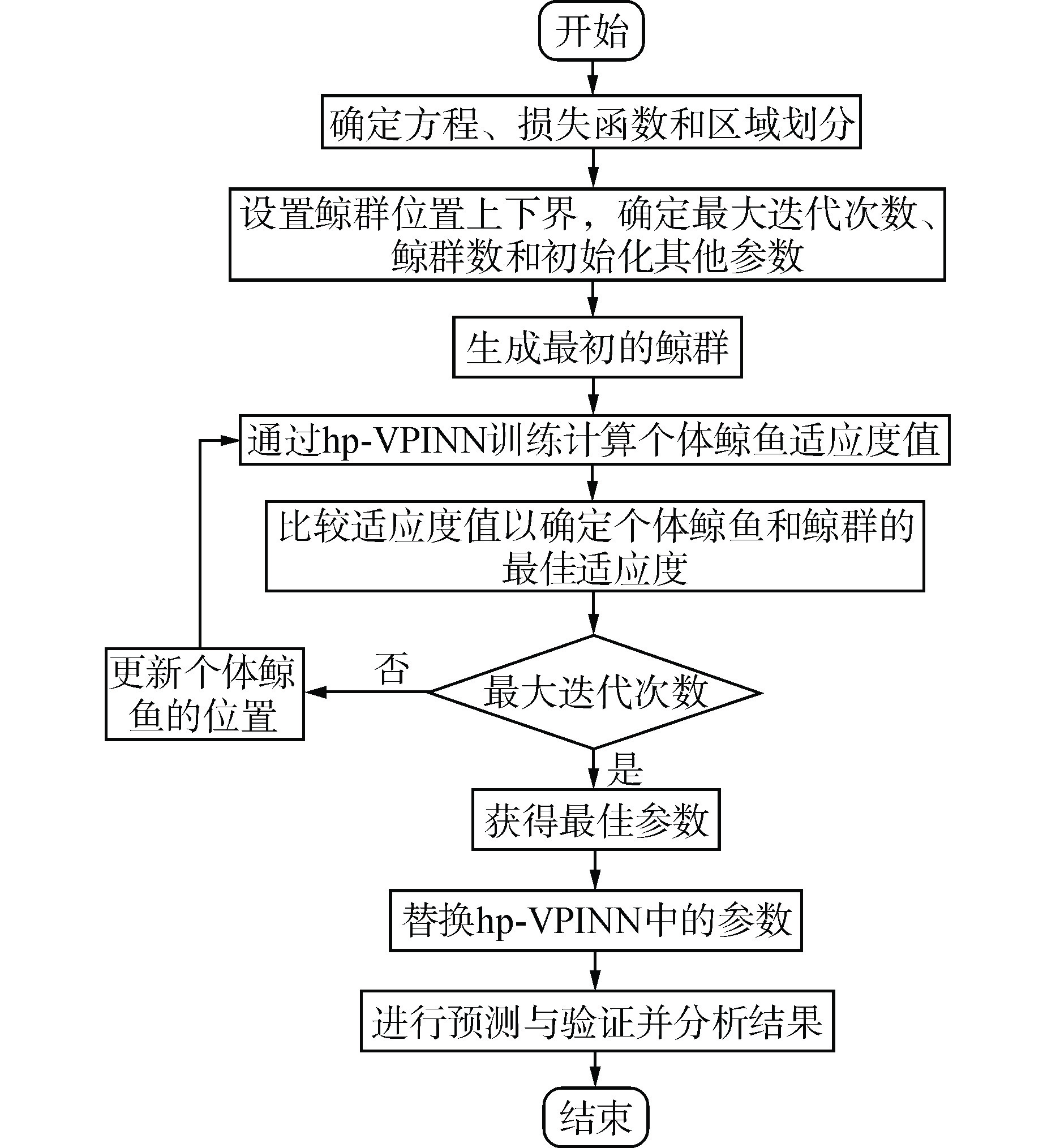
摘要: 先进的反应堆模拟技术需要基于较少的实际探测数据反演全堆关键参数。针对这一需要,本文基于具有高阶多项式域分解功能的变分残差物理信息神经网络(hp-VPINN)构建计算模型,用于正向、反向求解中子扩散方程。该模型使用神经网络作为试函数,并将其代入中子扩散方程形成变分残差作为损失函数进行梯度下降。为了提高求解精度及效率,本文还根据中子扩散方程的物理特性提出了有效增殖系数智能搜索与反演等创新型关键技术,并基于鲸鱼优化算法(WOA)实现了神经网络超参数自优化。最后通过多个算例进行验证,结果表明该方法在具有较高精度的同时,实现了较低的训练数据依赖,为先进反应堆模拟技术提供了一条少量输入数据且较高精度输出的中子扩散求解途径。
-
关键词:
- 变分残差物理信息神经网络(hp-VPINN) /
- 鲸鱼优化算法(WOA) /
- 中子扩散方程 /
- 有效增殖系数 /
- 反应堆模拟技术
Abstract: Advanced reactor simulations require the inversion of key parameters of the whole reactor based on less actual detection data. To meet this need, this paper constructs a computational model based on variational residual physics-informed neural network (hp-VPINN) with high-order polynomial domain decomposition function, which is used to solve the neutron diffusion equation forward and backward. The model uses neural network as trial function, and substitutes it into the neutron diffusion equation to form variational residual as loss function for gradient descent. In order to improve the accuracy and efficiency of the solution, this paper also proposes some innovative key technologies such as effective multiplication factor intelligent search and inversion based on the physical characteristics of neutron diffusion equation, and realizes the self-optimization of neural network hyperparameters based on whale optimization algorithm (WOA). Finally, several examples are verified, and the results show that the method has high accuracy and low dependence on training data, providing a solution with less training data and higher accuracy output for advanced reactor simulations. -
表 1 分区截面参数
Table 1. Zonal Cross-section Parameters
区域 g ${D_g}/{\text{cm}}$ $ \mathrm{\mathit{\Sigma}}_{\mathrm{a},g}/\text{c}\text{m}^{-1} $ $ v\mathit{\mathrm{\mathit{\Sigma}}}_{\mathrm{f},g}/\text{c}\text{m}^{-1} $ ${{{\varSigma}} _{1 \to 2}}/{\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 1}}$ ①,② 1 1.4 0.01 0.007 0.01 ①,② 2 0.4 0.015 0.2 ③ 1 1.3 0.008 0.003 0.01 ③ 2 0.5 0.05 0.06 -
[1] 杨戴博,李昆,黎刚,等. “华龙一号”堆芯中子通量测量系统设计[J]. 核电子学与探测技术,2021, 41(01): 146-150. [2] 谢仲生,曹良志,张少泓. 核反应堆物理分析[M]. 第五版. 西安: 西安交通大学出版社,2020: 69-90,89-91. [3] 周琴. 堆芯安全性在线分析[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学,2014. [4] 余红星,李文杰,柴晓明,等. 数字反应堆发展与挑战[J]. 核动力工程,2020, 41(4): 1-7. [5] 龚禾林,陈长,李庆,等. 基于物理指引和数据增强的反应堆物理运行数字孪生研究[J]. 核动力工程,2021, 42(S2): 48-53. [6] RAISSI M, PERDIKARIS P, KARNIADAKIS G E. Physics-informed neural networks: a deep learning framework for solving forward and inverse problems involving nonlinear partial differential equations[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2019, 378: 686-707. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2018.10.045 [7] 刘东,罗琦,唐雷,等. 基于PINN深度机器学习技术求解多维中子学扩散方程[J]. 核动力工程,2022, 43(2): 1-8. [8] WANG J Y, PENG X J, CHEN Z, et al. Surrogate modeling for neutron diffusion problems based on conservative physics-informed neural networks with boundary conditions enforcement[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2022, 176: 109234. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2022.109234 [9] YANG Y, GONG H L, ZHANG S Q, et al. A data-enabled physics-informed neural network with comprehensive numerical study on solving neutron diffusion eigenvalue problems[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2023, 183: 109656. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2022.109656 [10] PRANTIKOS K, TSOUKALAS L H, HEIFETZ A. Physics-informed neural network solution of point kinetics equations for a nuclear reactor digital twin[J]. Energies, 2022, 15(20): 7697. doi: 10.3390/en15207697 [11] ELHAREEF M H, WU Z Y. Physics-informed neural network method and application to nuclear reactor calculations: a pilot study[J]. Nuclear Science and Engineering, 2023, 197(4): 601-622. doi: 10.1080/00295639.2022.2123211 [12] KHARAZMI E, ZHANG Z Q, KARNIADAKIS G E M. hp-VPINNs: variational physics-informed neural networks with domain decomposition[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2021, 374: 113547. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2020.113547 [13] MIRJALILI S, LEWIS A. The whale optimization algorithm[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2016, 95: 51-67. doi: 10.1016/j.advengsoft.2016.01.008 [14] 刘欣. 无网格方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社,2011: 45-47. [15] 马丁 T. 哈根,霍华德 B. 德姆斯,马克 H. 比勒,等. 神经网络设计[M]. 章毅,译. 第二版. 北京: 机械工业出版社,2018: 1-25. [16] MISHKIN D, SERGIEVSKIY N, MATAS J. Systematic evaluation of convolution neural network advances on the Imagenet[J]. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2017, 161: 11-19. doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2017.05.007 [17] HAGEMAN L A, YASINSKY J B. Comparison of alternating-direction time-differencing methods with other implicit methods for the solution of the neutron group-diffusion equations[J]. Nuclear Science and Engineering, 1969, 38(1): 8-32. doi: 10.13182/NSE38-8 [18] IMRON M. Development and verification of open reactor simulator ADPRES[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2019, 133: 580-588. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2019.06.049 [19] GE J, ZHANG D L, TIAN W X, et al. Steady and transient solutions of neutronics problems based on finite volume method (FVM) with a CFD code[J]. Progress in Nuclear Energy, 2015, 85: 366-374. doi: 10.1016/j.pnucene.2015.07.012 -






 下载:
下载: