Optimization and Thermal Safety Analysis of CFETR Advanced Small Sample Irradiation Capsule
-
摘要: 中国聚变工程试验堆(CFETR)先进材料辐照考验样品所在胶囊结构较为复杂,其内部填充氦气,胶囊肋条尺寸、位置以及胶囊内部填充材料对样品温度影响大。基于STAR-CCM+程序建立CFETR先进小样品辐照装置内胶囊全尺寸模型,针对样品的目标温度,对胶囊的肋条和填充材料进行了调整。对于胶囊内整体样品释热率较低的情况,采用释热率较大的钨材料作为填充材料,可以明显提高整体样品温度;对于局部样品释热率差别较大的情况,调整局部肋条的尺寸和位置,能够很好控制样品间的温度,使样品计算温度满足目标温度范围。结果表明:采用上述方法进行优化后,样品中心温度能够满足目标温度范围,且满足入高通量工程试验堆(HFETR)辐照的热工安全,保证整个辐照任务能够顺利开展。Abstract: The capsule structure of the advanced material irradiation test sample in China Fusion Engineering Experimental Reactor (CFETR) is relatively complicated, and the capsule is filled with helium. The size and location of the capsule rib and the material of the filling inside the capsule have great influence on the sample temperature. Based on the STAR-CCM+ code, a full-scale capsule model was established in the CFETR advanced small sample irradiation device, and the rib and filler materials of the capsule were adjusted according to the target temperature of the sample. For the problem that the heat release rate of the whole sample in the capsule is low, using tungsten material with higher heat release rate as filling material can significantly increase the overall sample temperature. For the case that the heat release rate of local samples is quite different, the temperature between samples can be well controlled by adjusting the size and position of the local rib, so that the calculated temperature of the sample can meet the target temperature range. The results show that after optimization with the above method, the sample center temperature can meet the target temperature range and meet the thermal safety of irradiation in the High Flux Engineering Test Reactor (HFETR), ensuring the smooth development of the entire irradiation task.
-
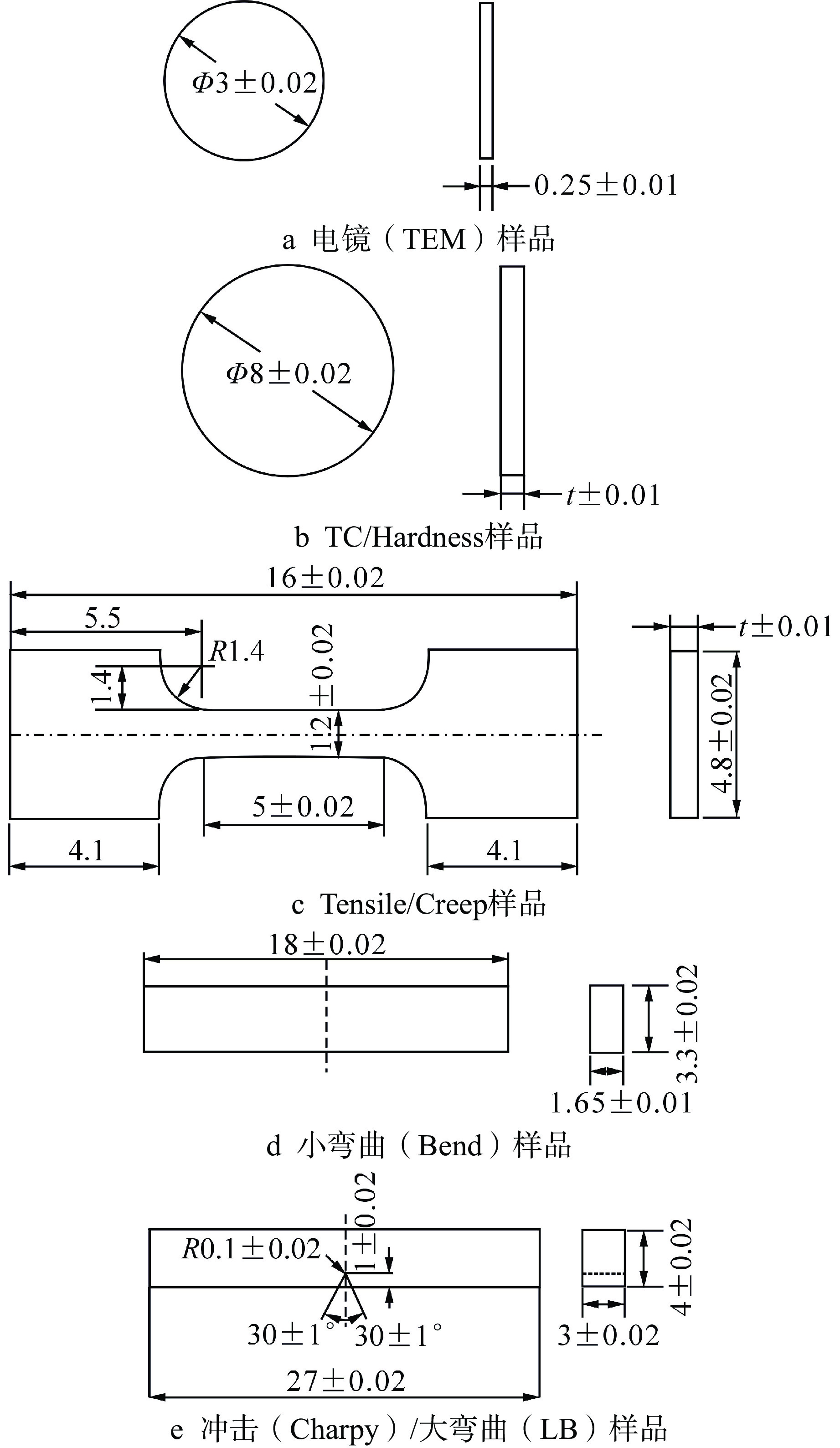
表 1 胶囊内样品材料、数量和辐照目标温度
Table 1. Material, Quantity and Irradiation Target Temperature of Each Capsule Sample
胶囊类型 区域 样品类型 材料 数量 目标温度/℃ I-01 Section A Hardness 铜合金 1 200~300 TC 2 Section B Tensile 不锈钢 4 铜合金 4 Section C Tensile 不锈钢 8 Section D TEM 不锈钢 16 铜合金 8 钨合金 4 涂层 4 Section E Hardness 钨合金 1 铜合金 1 不锈钢 3 I-02 SectionA TC 铜合金 2 200~300 钨合金 2 Section B Tensile 铜合金 4 钨合金 4 Section C Bend 钨合金 6 Section D TC 铜合金 2 不锈钢 10 I-03 Section A TC 铜合金 2 400~450 Hardness 1 Section B Tensile 铜合金 4 不锈钢 4 Section C Tensile 不锈钢 8 Section D Hardness 不锈钢 3 Section E TC 不锈钢 10 Section F TEM 不锈钢 20 铜合金 4 I-04 SectionA TC 不锈钢 4 500~550 Section B Tensile 不锈钢 8 Section C Tensile 不锈钢 8 Section D Hardness 不锈钢 3 钨合金 2 Section E TC 不锈钢 6 Section F TEM 不锈钢 16 钨合金 8 I-05 Section A TC 钨合金 4 500~550 Section B Tensile 钨合金 8 Section C Bend 钨合金 6 Section D Bend 钨合金 6 表 2 I-04样品材料释热率与目标温度
Table 2. Heat Release Rate and Target Temperature of Sample I-04
胶囊类型 材料类型 释热率/(W·g−1) 目标温度/℃ I-04 钨合金 18.98~19.67 500~550 不锈钢 12.96~13.52 表 3 各样品温度及其对应目标温度
Table 3. Temperature of Each Sample and Corresponding Target Temperature
样品位置 样品计算温度/℃ 样品目标温度/℃ Section A 379~427 500~550 Section B 353~451 Section C 331~484 Section D 469~519 Section E 420~481 Section F 396~429 表 4 肋条所在位置和尺寸
Table 4. Location and Dimensions of Ribs
类型 位置/mm 肋条宽度/mm 肋管结构1 0 5 30 2 48 1 75 5 肋管结构2 48 2 肋管结构3 按结构图从左至右,以肋左侧标定其所在位置 表 5 优化调整后肋条所在位置和尺寸
Table 5. Position and Size of Rib after Optimization Adjustment
类型 位置/mm 肋条宽度/mm 优化调整1 0 5 30.5 1 49 2 75 5 优化调整2 0 5 30.5 1 49 2 75 5 优化调整3 0 5 22.5 1 38.5 1 48 2 75 5 表 6 I-04样品计算温度与热熔丝温度
Table 6. Calculated Temperature and Hot Fuse Temperature of Sample in I-04
样品所在区域 样品计算
温度/℃热熔丝计算
温度/℃外侧铝管
温度/℃Section A 499~523 70~79 Section B 497~535 553~557 551~554 Section C 485~532 551~554 547~550 Section D 500~542 Section E 488~515 Section F 489~504 -
[1] 刘水清,刘红倩,向玉新,等. HFETR辐照孔道中子特性研究[J]. 核动力工程,2017, 38(6): 31-35. [2] 马立勇,向玉新,王皓,等. HFETR辐照石墨材料中子注量验证试验[J]. 核动力工程,2017, 38(S1): 157-159. [3] 刘红倩,刘水清,康长虎,等. HFETR辐照孔道内中子注量率敏感性分析[J]. 核科学与工程,2021, 41(6): 1130-1137. [4] 曾科,陶文铨,贾斗南,等. HFETR燃料元件稳态三维流场和温度场数值模拟程序的研制和应用[J]. 核动力工程,2003, 24(S2): 30-33. [5] 张维忠,秋穗正,曾科,等. 高通量工程试验堆堆芯流量分配计算[J]. 核动力工程,2001, 22(2): 97-100,112. [6] 杨文华,童明炎,孙胜. 模块式套管型随堆辐照考验装置Ansys CFX热工分析[J]. 核动力工程,2013, 34(4): 153-156. -






 下载:
下载: