Analysis of Spent Fuel Cask Dropping Accident and Research on Relevant Improvement Measures
-
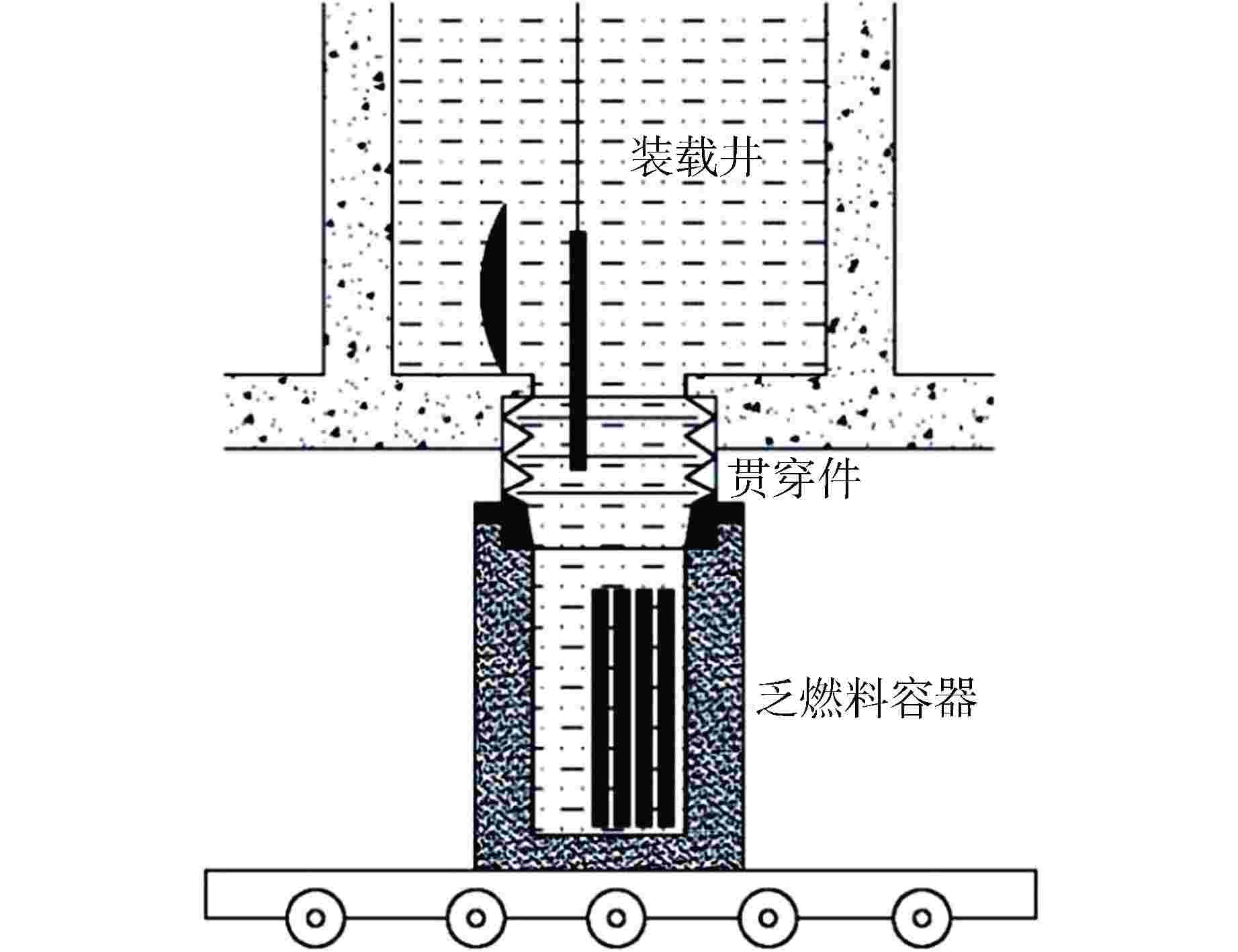
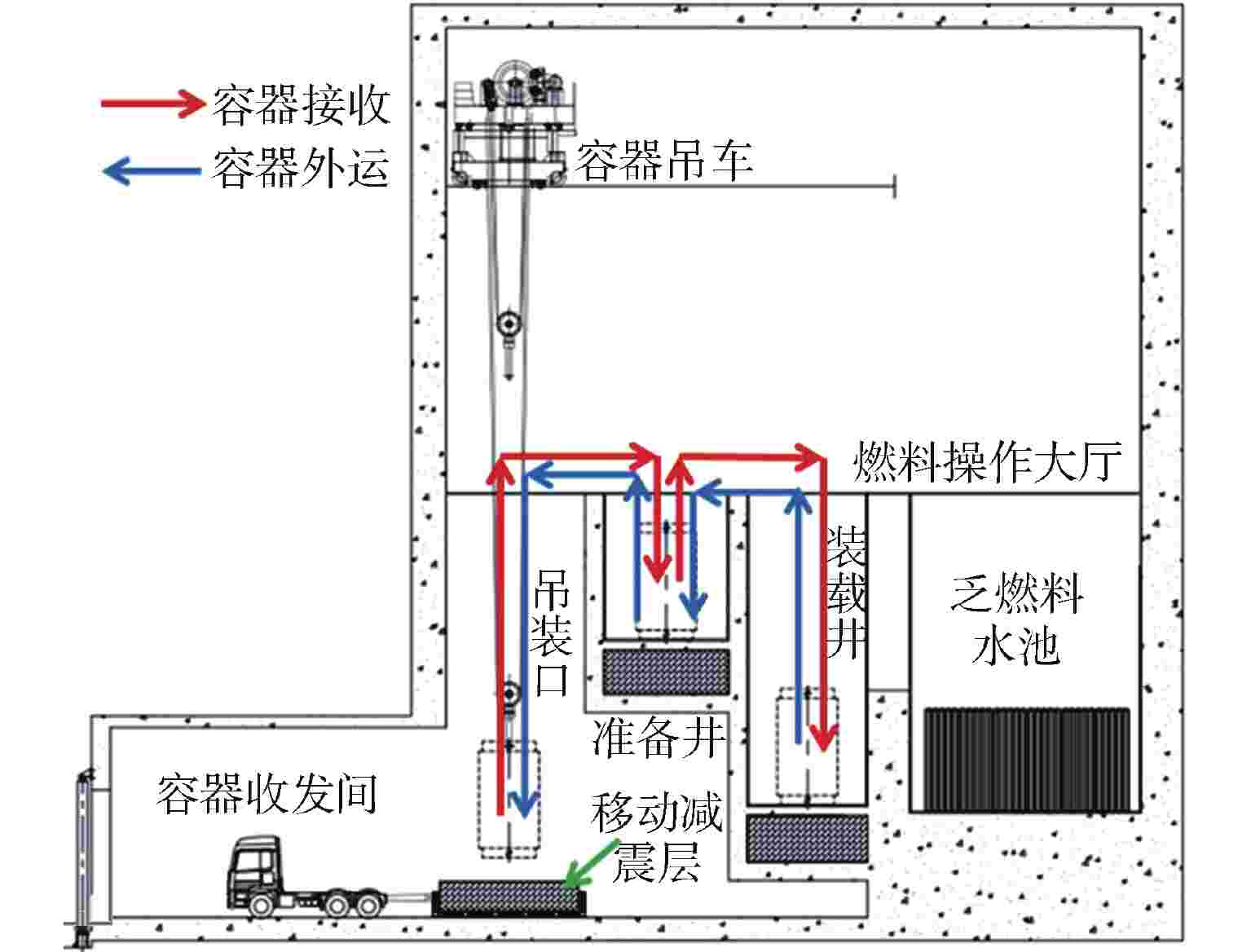
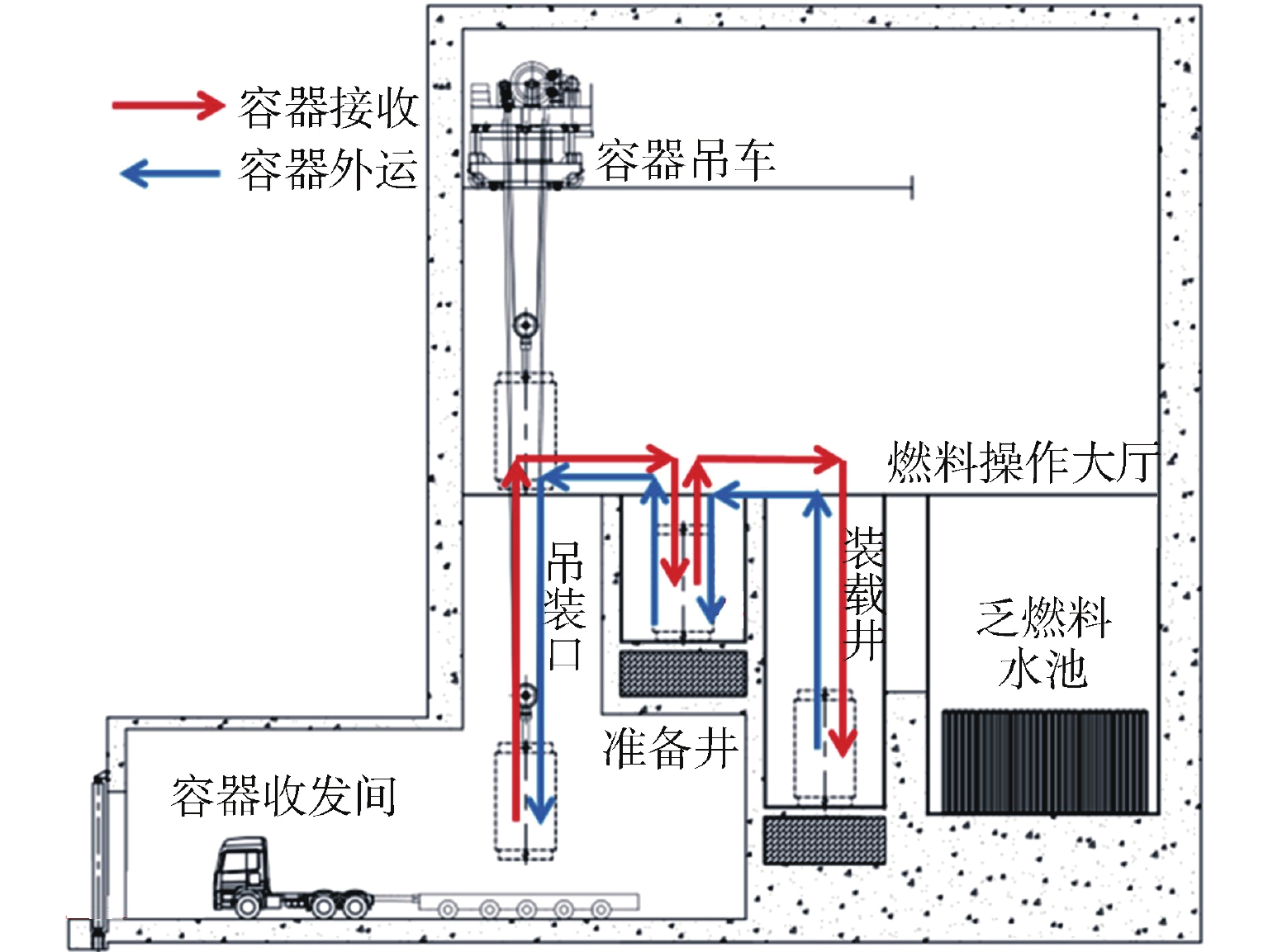
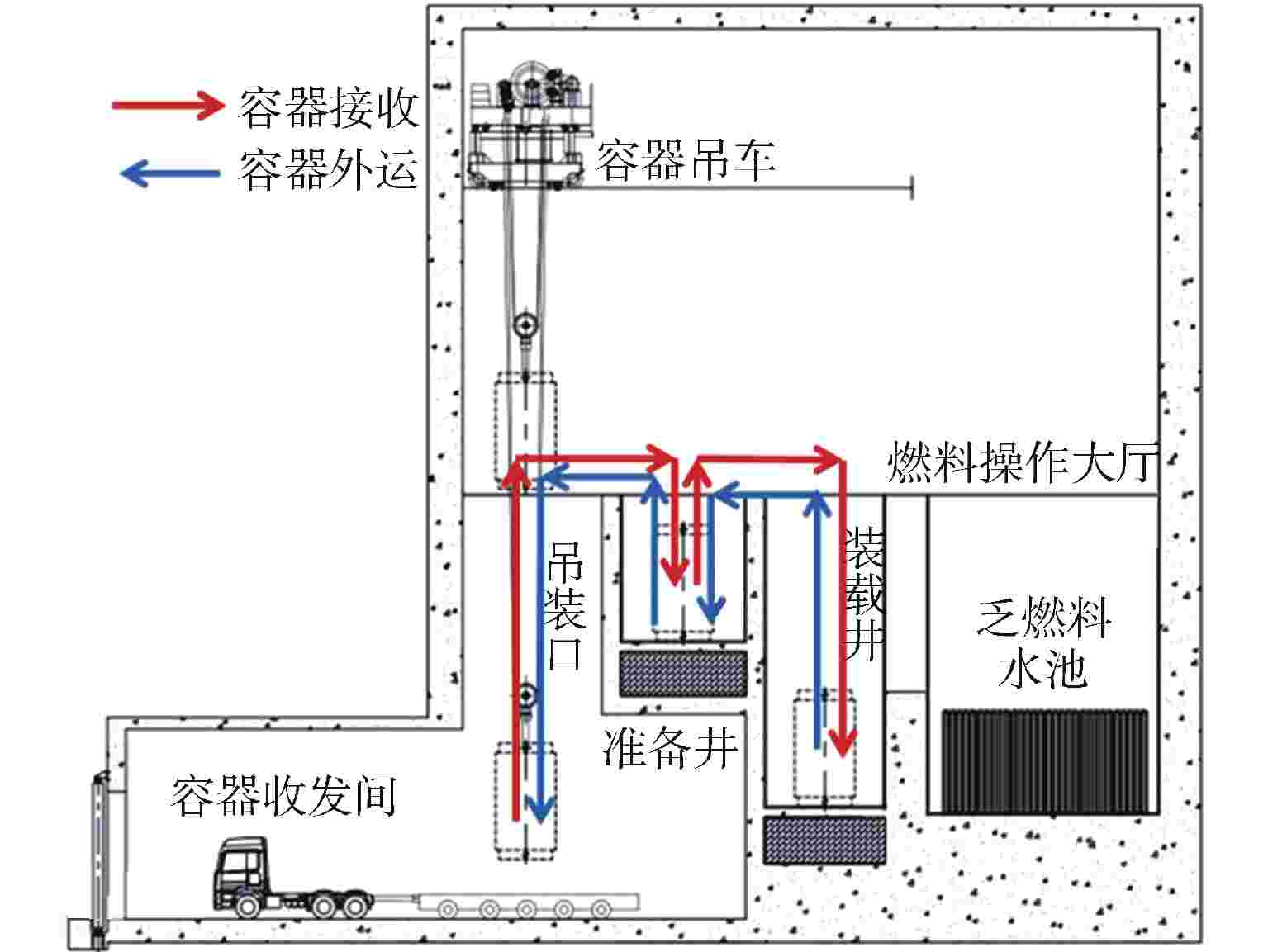
摘要: 国内核电厂普遍采用“容器浸没法”进行乏燃料外运,客观上无法完全消除乏燃料容器跌落风险。对乏燃料容器跌落事故后的放射性后果进行了分析计算,并对如何保证容器跌落后的完整性或实现容器完整性破损后放射性物质的包容进行了分析研究,提出了一系列缓解乏燃料容器跌落后果的改进措施,以降低放射性物质超限释放的风险,对于提升核电厂的乏燃料吊装操作安全具有积极指导意义。Abstract: "Cask immersion" is generally used in domestic nuclear power plants to deliver spent fuel, thus the risk of spent fuel cask dropping accident cannot be completely eliminated. The radioactive consequences of spent fuel cask dropping accident are analyzed and calculated, and how to ensure the integrity of the cask after dropping or how to contain radioactive materials after the cask integrity is broken is analyzed and studied. A series of improvement measures are put forward to alleviate the consequences of spent fuel ccask dropping, so as to reduce the risk of over-limit release of radioactive materials, which have positive guiding significance for improving the safety of spent fuel hoisting operation in nuclear power plants.
-
Key words:
- Spent fuel delivery /
- Spent fuel cask /
- Dropping /
- Release of radioactivity /
- Ventilation system
-
表 1 不同计算假设下的最大剂量值
Table 1. Maximum Dose for Different Calculation Assumptions
剂量 工况1 工况2 工况3 工况4 限值 有效剂量/Sv 12.7 3.16 0.65 0.33 0.1 甲状腺当量剂量/Sv 3.3 0.83 0.17 0.09 1.0 表 2 不同状态项目的推荐改进措施
Table 2. Recommended Improvements for Items in Different Status
改进措施 已固化核电项目 尚未开建项目 降低容器吊装高度 取消容器吊装 √ 降低池井整体标高 √ “台阶式”吊运 √ 提高抗跌落冲击能力 提高乏燃料容器筒体抗跌落能力 √ √ 装载井内完成容器密封 √ 移动式减震层 √ 固定式减震层 √ 缓解放射性物质的对外释放 临时充排水 √ 固定充排水管线 √ 关闭厂房大门 √ √ 提前开启事故通风系统 √ √ -
[1] 国家能源局. 核电厂专用起重机设计准则: NB/T 20234-2013[S]. 北京: 核工业标准化研究所,2013: 6-7. [2] LLOYD R L. A survey of crane operating experience at U. S. nuclear power plants from 1968 through 2002: NUREG-1774[R]. Washington, DC: U. S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission, 2003. [3] 程刚,郭全全,周耀,等. 乏燃料容器坠落事故工况下核燃料厂房的安全性分析[J]. 振动与冲击,2019, 38(6): 206-211. [4] 刘广东,吴维亮,朱贺,等. 事故工况下乏燃料运输容器跌落分析[J]. 包装工程,2017, 38(21): 31-34. [5] BLUMBERG M. Alternative radiological source terms for evaluating design basis accidents at nuclear power reactors: RG1.183[R]. Washington, DC: U. S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission, 2000. [6] SOFFER L, BURSON S B, FERRELL C M, et al. Accident source terms for light-water nuclear power plants: NUREG-1465[R]. Washington, DC: U. S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission, 1995. [7] STEPHENSON W, DUTTON L M C, HANDY B, et al. Realistic methods for calculating the releases and consequences of a large LOCA: EUR-14179[R]. Luxembourg: Commission of the European Communities, 1992. [8] WILMOT E L. Transportation accident scenarios for commercial spent fuel: SAND-80-2124[R]. Albuquerque: Sandia National Laboratories, 1981. [9] 环境保护部,中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 核动力厂环境辐射防护规定: GB 6249-2011[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社,2011: 4-5. [10] 李忠芳. 核乏燃料运输容器减震器填充材料的研究[D]. 淄博: 山东理工大学,2019. -





 下载:
下载: