Fault Detection for Reactor Coolant Pump Based on Moving Window Kernel Principal Component Analysis
-
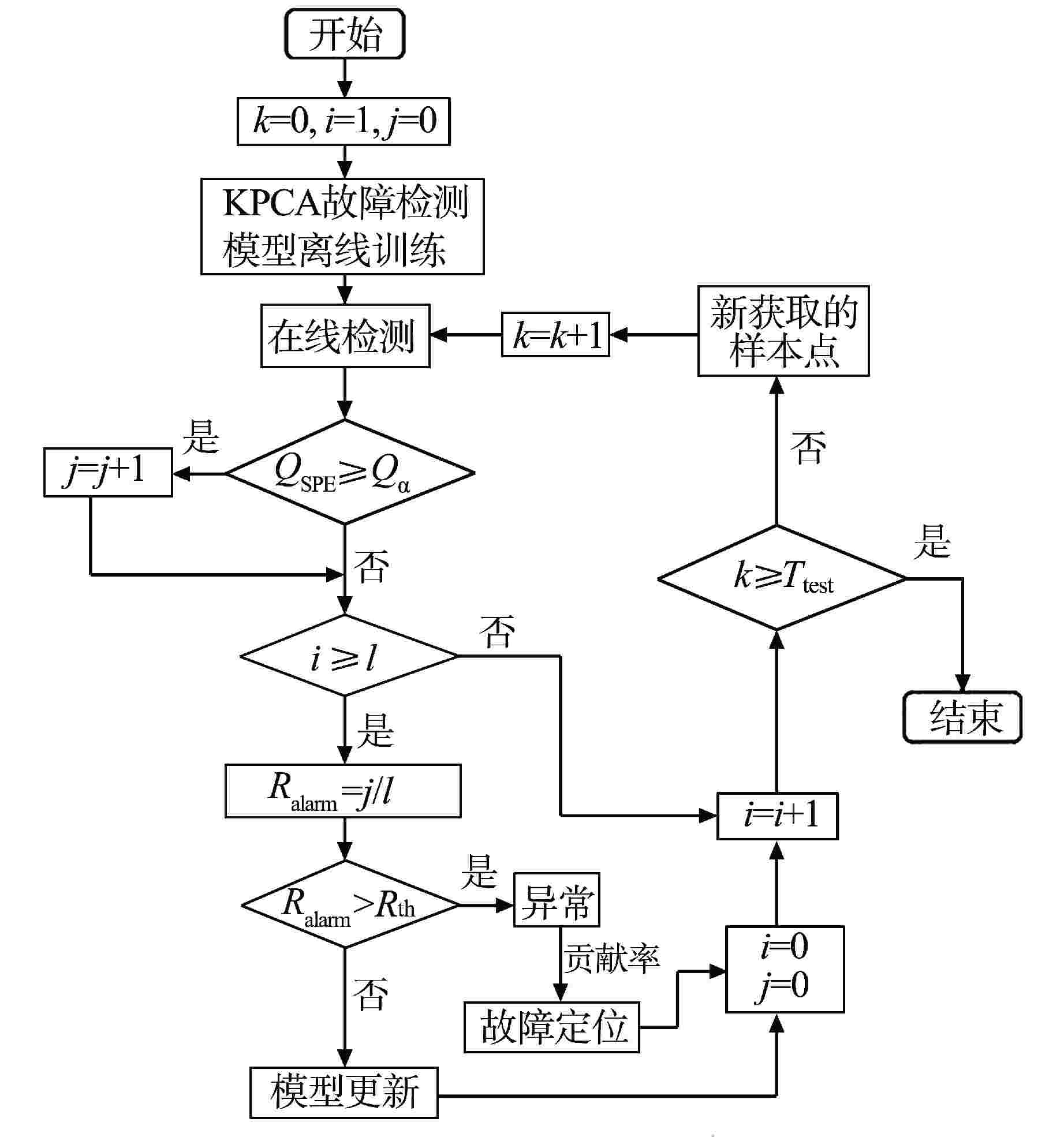
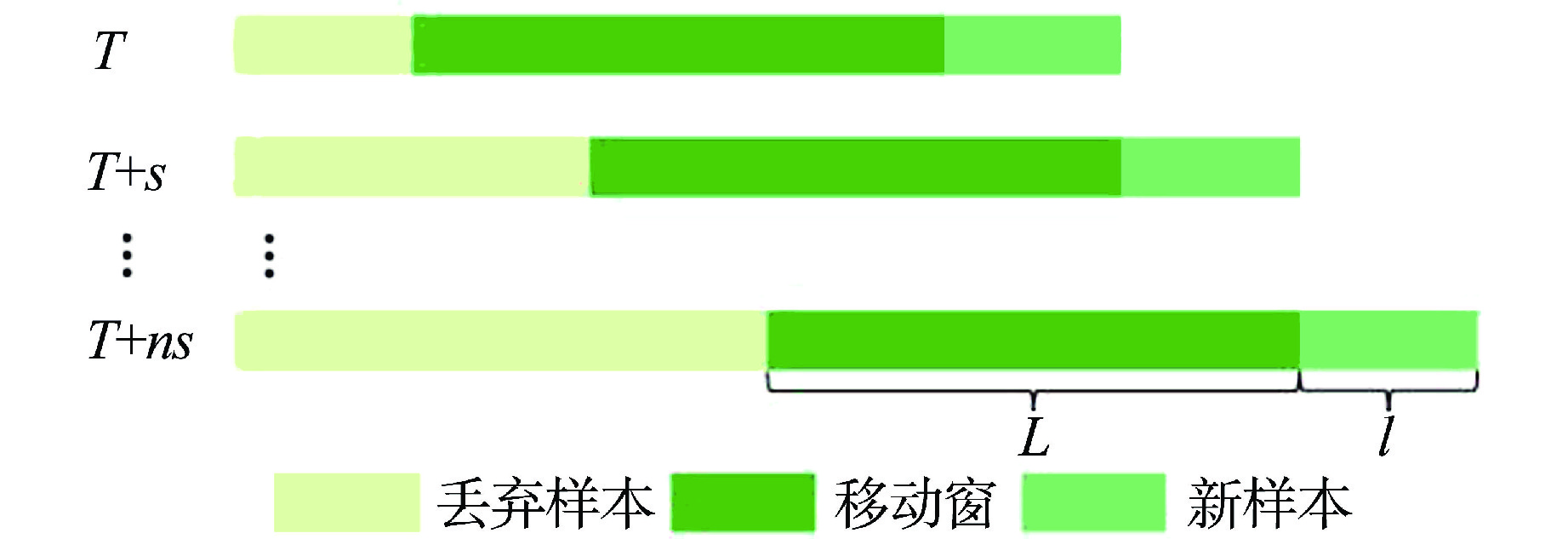
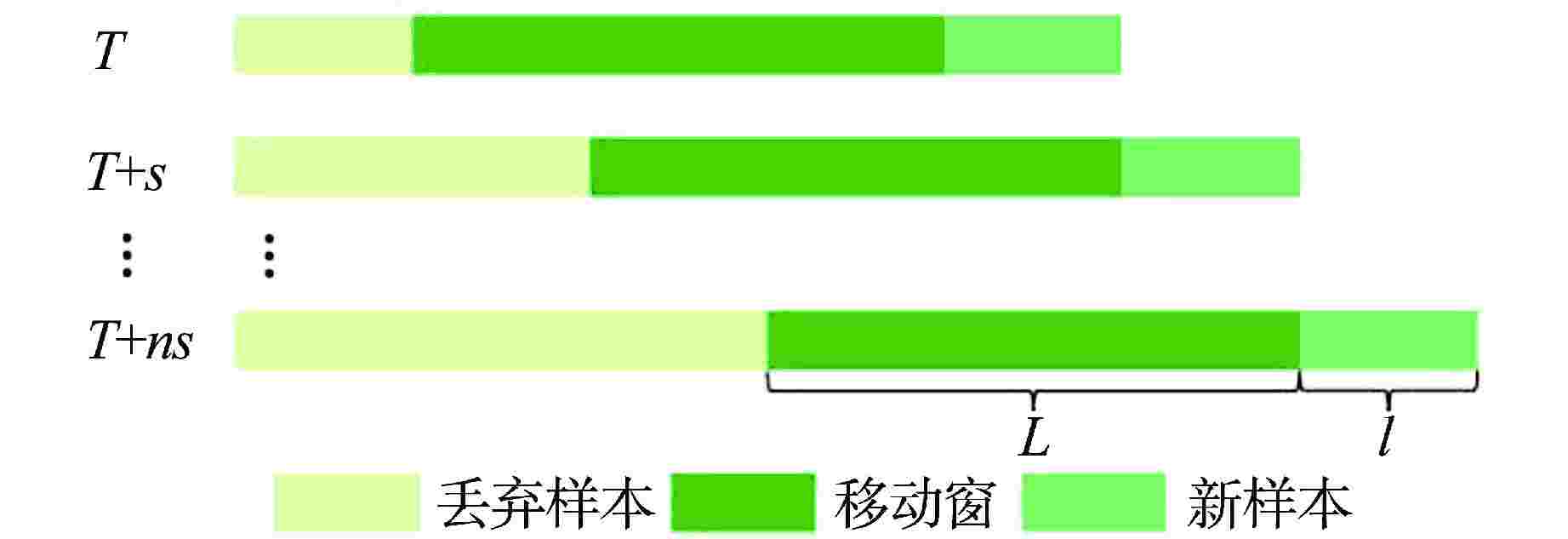
摘要: 由于部件性能衰退、工况变化等因素影响,核动力装置在运行过程中会表现出明显的时变性,进而造成故障检测模型失效。为了改善传统故障检测方法在时变工业过程中的性能和在役适应性,基于核主成分分析(KPCA)和移动窗技术,提出了一种用于核动力装置的长时故障检测方法。该方法通过移动窗技术可实现KPCA故障检测模型的自动更新,从而解决检测过程中信号的时变性问题。将移动窗KPCA方法应用于某核电厂主泵的长时监测中,结果表明,主泵在正常和异常状态下,移动窗KPCA方法在故障检测率(FDR)、误报率(FAR)等指标方面均表现出了良好的性能。
-
关键词:
- 核动力装置 /
- 核主成分分析(KPCA) /
- 移动窗 /
- 时变过程 /
- 故障检测
Abstract: Due to the influence of component performance decline and operation condition change, nuclear power plants (NPPs) show obvious time variability during operation, which leads to the failure of fault detection model. In order to improve the performance and in-service adaptability of traditional fault detection methods in time-varying industrial processes, this paper proposes a long-term fault detection strategy for NPPs based on kernel principal component analysis (KPCA) and moving window. In this method, the KPCA fault detection model is automatically updated by moving window technology, which solves the time-varying problem of signals in the detection process. The moving window KPCA method is applied to the long-term monitoring of the reactor coolant pump in a nuclear power plant. The results show that the moving window KPCA method has good performance in fault detection rate and false alarm rate under normal and abnormal conditions. -
表 1 主泵传感器布置
Table 1. Sensor Arrangement for Reactor Coolant Pump
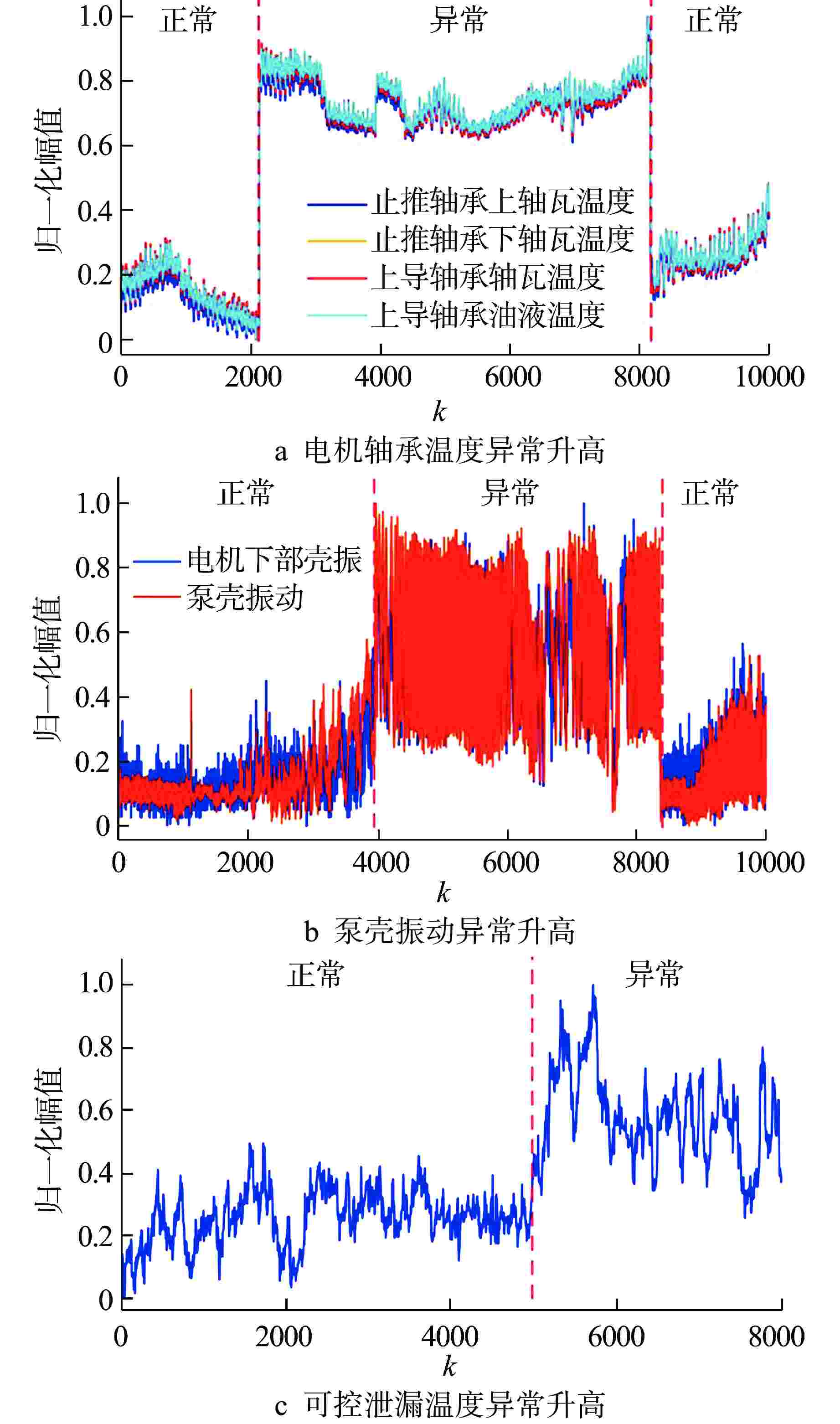
监测对象 测点监测参数 电机 ①定子绕组A相温度;②定子绕组B相温度;③ 定子绕组C相温度;④电机止推轴承上轴瓦温度;⑤电机止推轴承下轴瓦温度;⑥电机上导轴承轴瓦温度;⑦电机下导轴承轴瓦温度;⑧电机上导轴承油液温度;⑨电机下导轴承油液温度 转子系统 ①电机上部壳振;② 电机下部壳振;③泵轴X向位移;④泵轴Y向位移;⑤泵壳振动 轴封系统 ①轴封注入水温度;②可控泄漏温度;③第一级轴封前压力;④第二级轴封前压力;⑤第三级轴封前压力;⑥可控泄漏流量 注:①~⑨—测点位置编号 表 2 各类模型的FAR %
Table 2. False Alarm Rate of Different Models
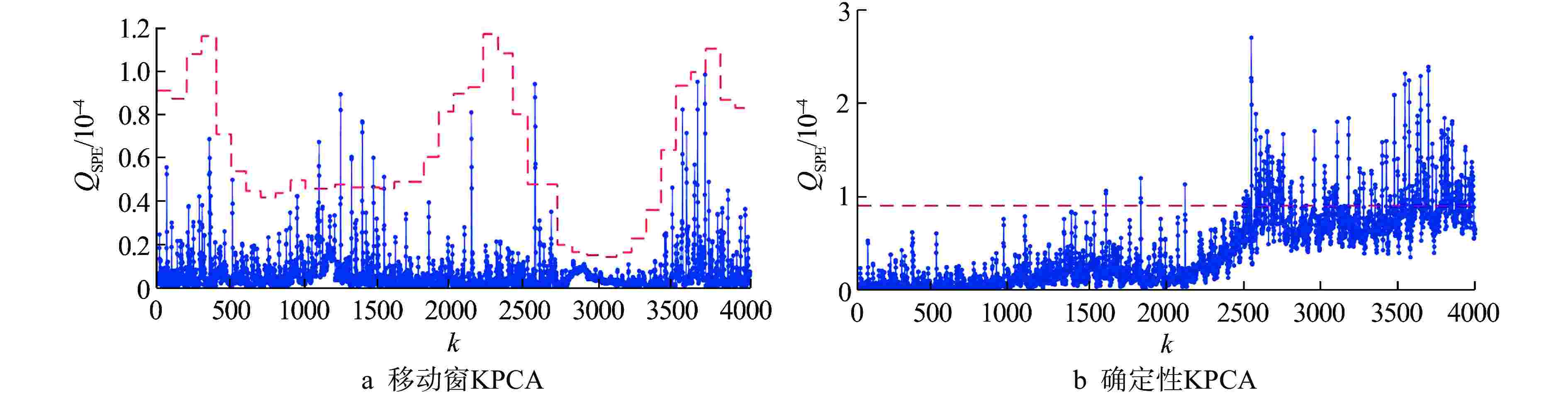
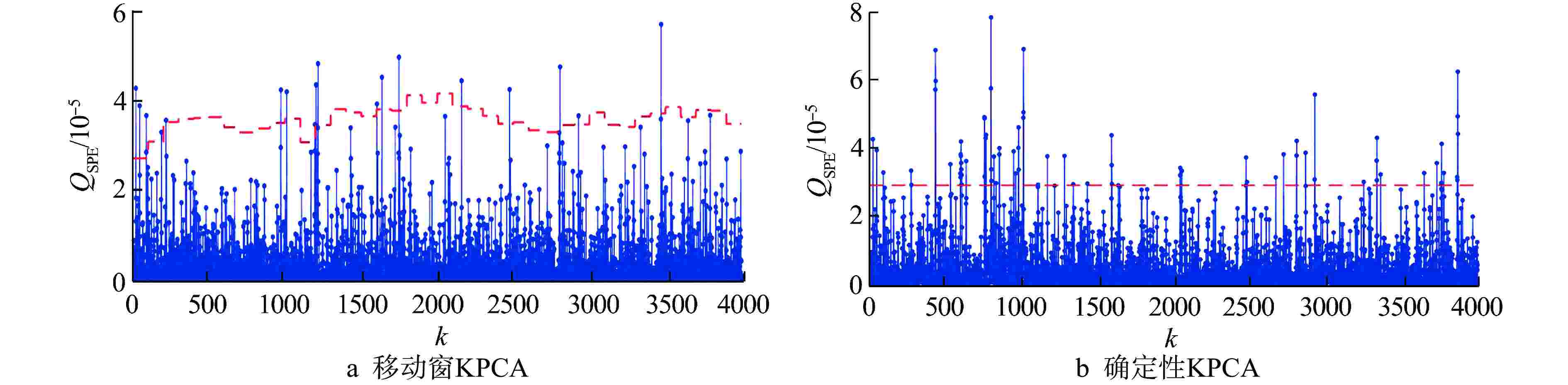
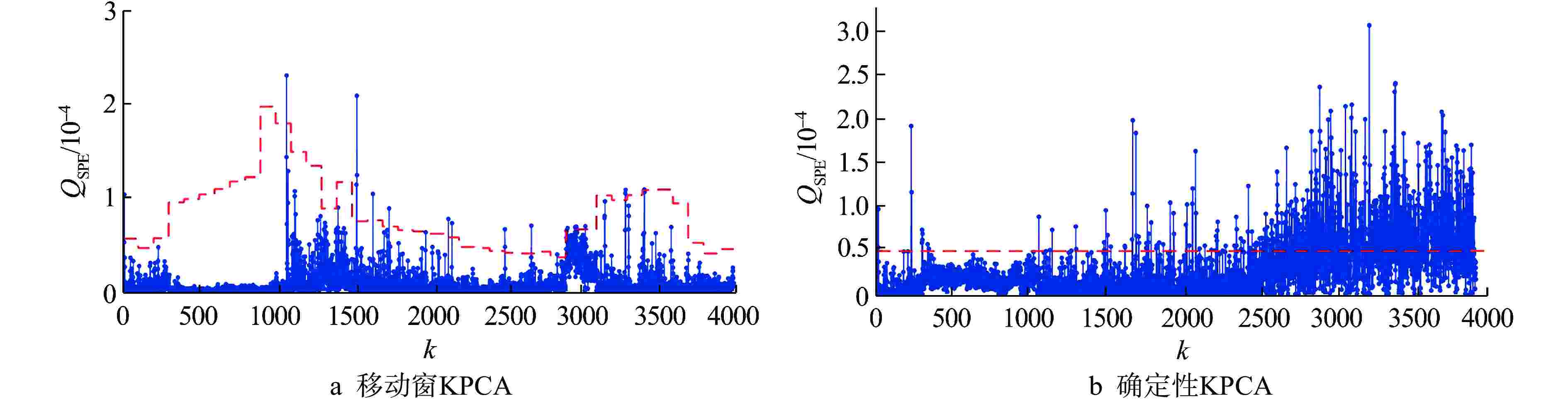
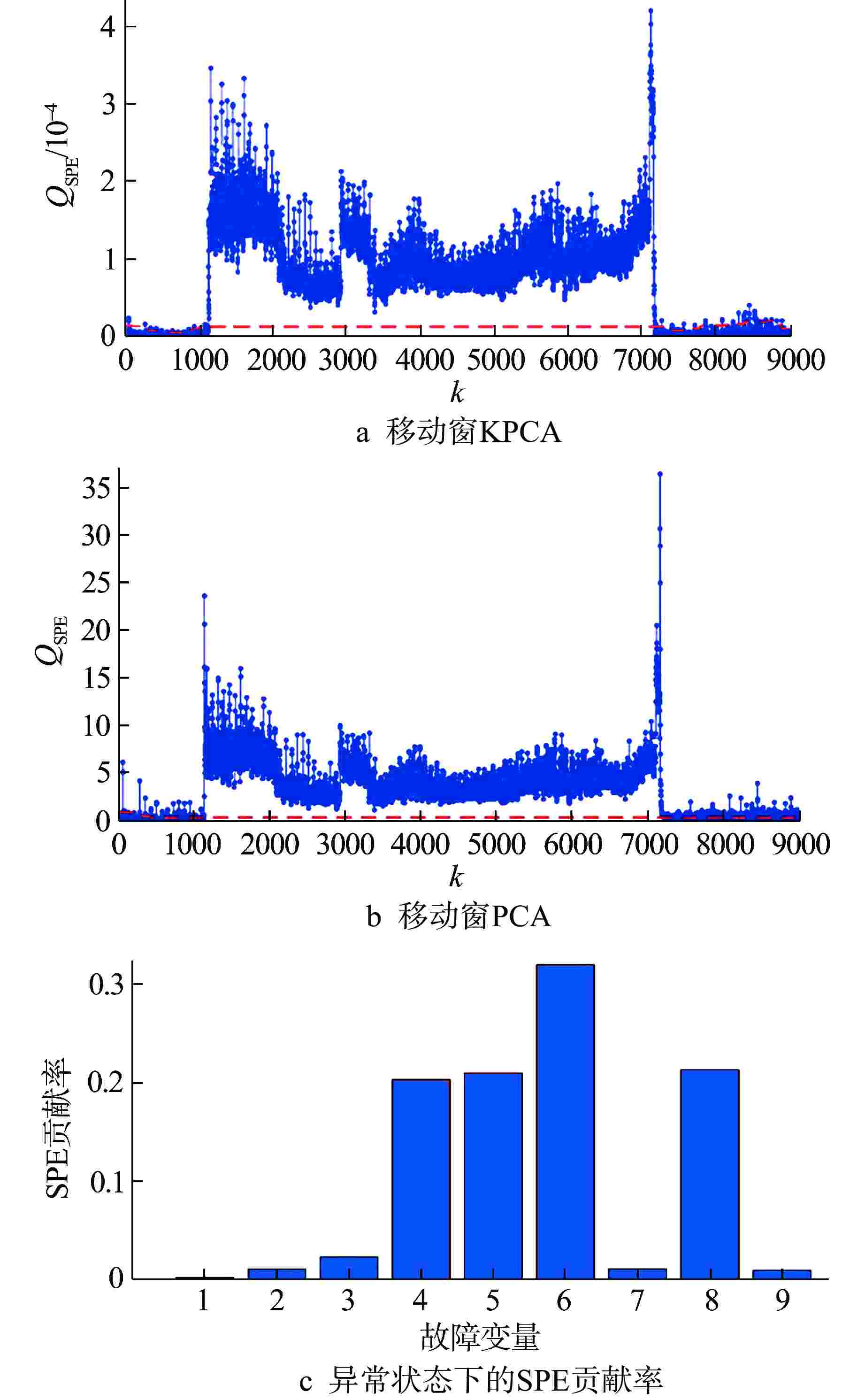
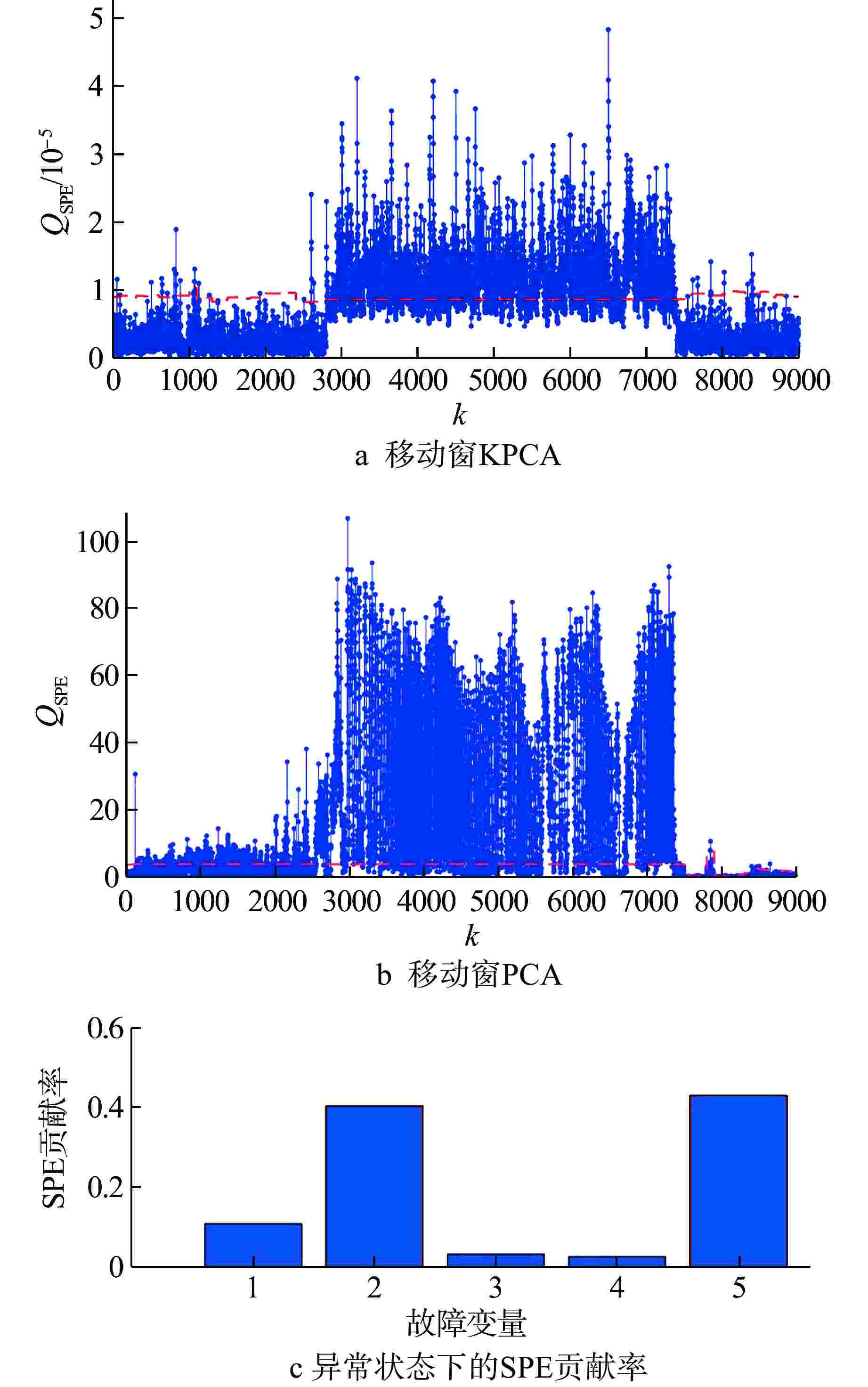
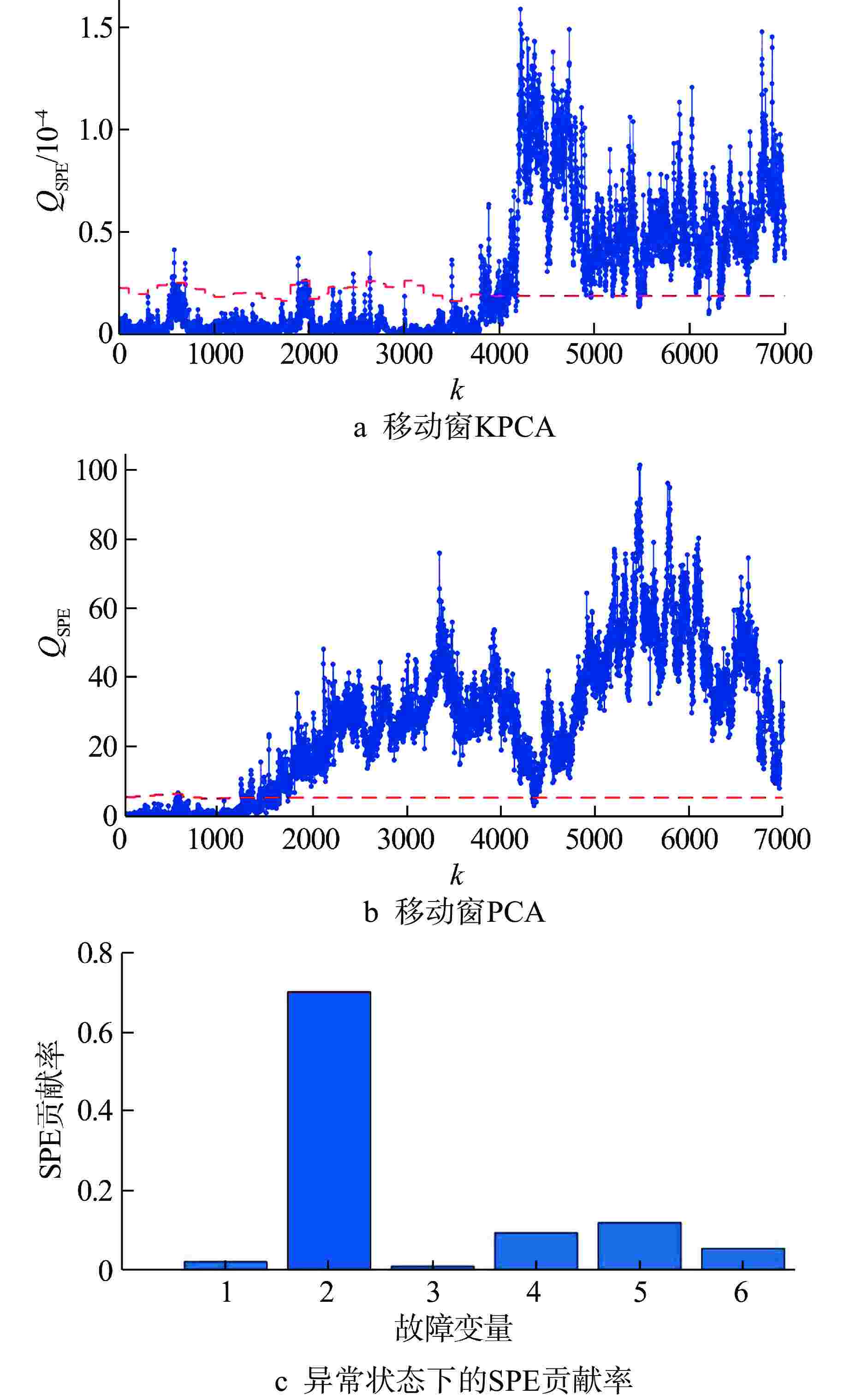
模型 电机 转子系统 轴封系统 确定性KPCA 11.58 1.87 20.62 移动窗KPCA 0.45 0.47 0.53 表 3 异常状态下各类模型的故障检测性能
Table 3. Fault Detection Performance of Models under Abnormal Conditions
异常事件子系统 方法 FDR/% FAR/% 电机 移动窗PCA 99.86 38.90 移动窗KPCA 99.87 2.72 转子系统 移动窗PCA 88.68 21.96 移动窗KPCA 78.79 1.83 轴封系统 移动窗PCA 99.74 62.31 移动窗KPCA 96.76 2.11 -
[1] HASHEMIAN H M. On-line monitoring applications in nuclear power plants[J]. Progress in Nuclear Energy, 2011, 53(2): 167-181. doi: 10.1016/j.pnucene.2010.08.003 [2] HUSSAIN M, DHIMISH M, TITARENKO S, et al. Artificial neural network based photovoltaic fault detection algorithm integrating two bi-directional input parameters[J]. Renewable Energy, 2020, 155: 1272-1292. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2020.04.023 [3] 彭彬森,夏虹,朱少民,等. 核动力装置运行数据的特征提取方法研究[J]. 原子能科学技术,2020, 54(3): 488-495. doi: 10.7538/yzk.2019.youxian.0229 [4] 孙英杰,彭敏俊. 基于MSET和SPRT的核动力装置异常状态监测技术研究[J]. 核动力工程,2015, 36(3): 57-61. [5] BARALDI P, DI MAIO F, TURATI P, et al. Robust signal reconstruction for condition monitoring of industrial components via a modified Auto Associative Kernel Regression method[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2015, 60-61: 29-44. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2014.09.013 [6] 朱少民,夏虹,彭彬森,等. 基于PCA的主泵传感器状态监测模型[J]. 核动力工程,2020, 41(3): 170-176. [7] BARALDI P, CAMMI A, MANGILI F, et al. An ensemble approach to sensor fault detection and signal reconstruction for nuclear system control[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2010, 37(6): 778-790. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2010.03.002 [8] 李伟,彭敏俊,刘永阔. 基于PCA的核电站传感器状态监测方法研究[J]. 核动力工程,2018, 39(1): 136-139. [9] SCHÖLKOPF B, SMOLA A, MÜLLER K R. Kernel principal component analysis[C]//Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks. Lausanne: Springer, 1997: 583-588. [10] 吴天昊,刘韬,施海宁,等. 基于核主元分析法的核电厂设备状态监测技术研究[J]. 核动力工程,2020, 41(5): 132-137. [11] WANG H, PENG M J, YU Y, et al. Fault identification and diagnosis based on KPCA and similarity clustering for nuclear power plants[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2021, 150: 107786. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2020.107786 [12] NAVI M, MESKIN N, DAVOODI M. Sensor fault detection and isolation of an industrial gas turbine using partial adaptive KPCA[J]. Journal of Process Control, 2018, 64: 37-48. doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2018.02.002 [13] DENG X G, TIAN X M. A new fault isolation method based on unified contribution plots[C]//Proceedings of the 30th Chinese Control Conference. Yantai: IEEE, 2011: 4280-4285. -





 下载:
下载: