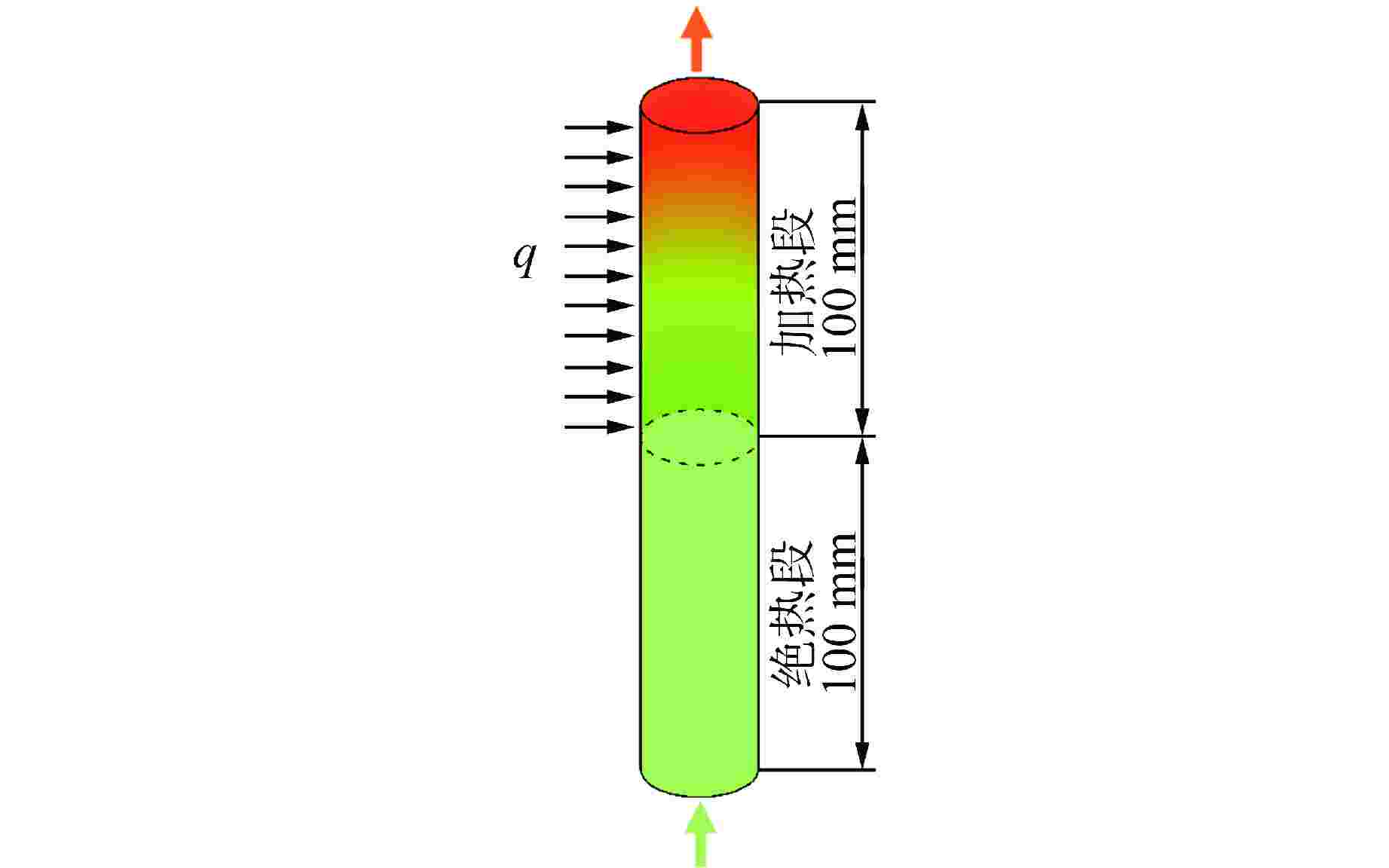
Numerical Study on DNB-Type Critical Heat Flux in Circular Tube under Rolling Condition
-
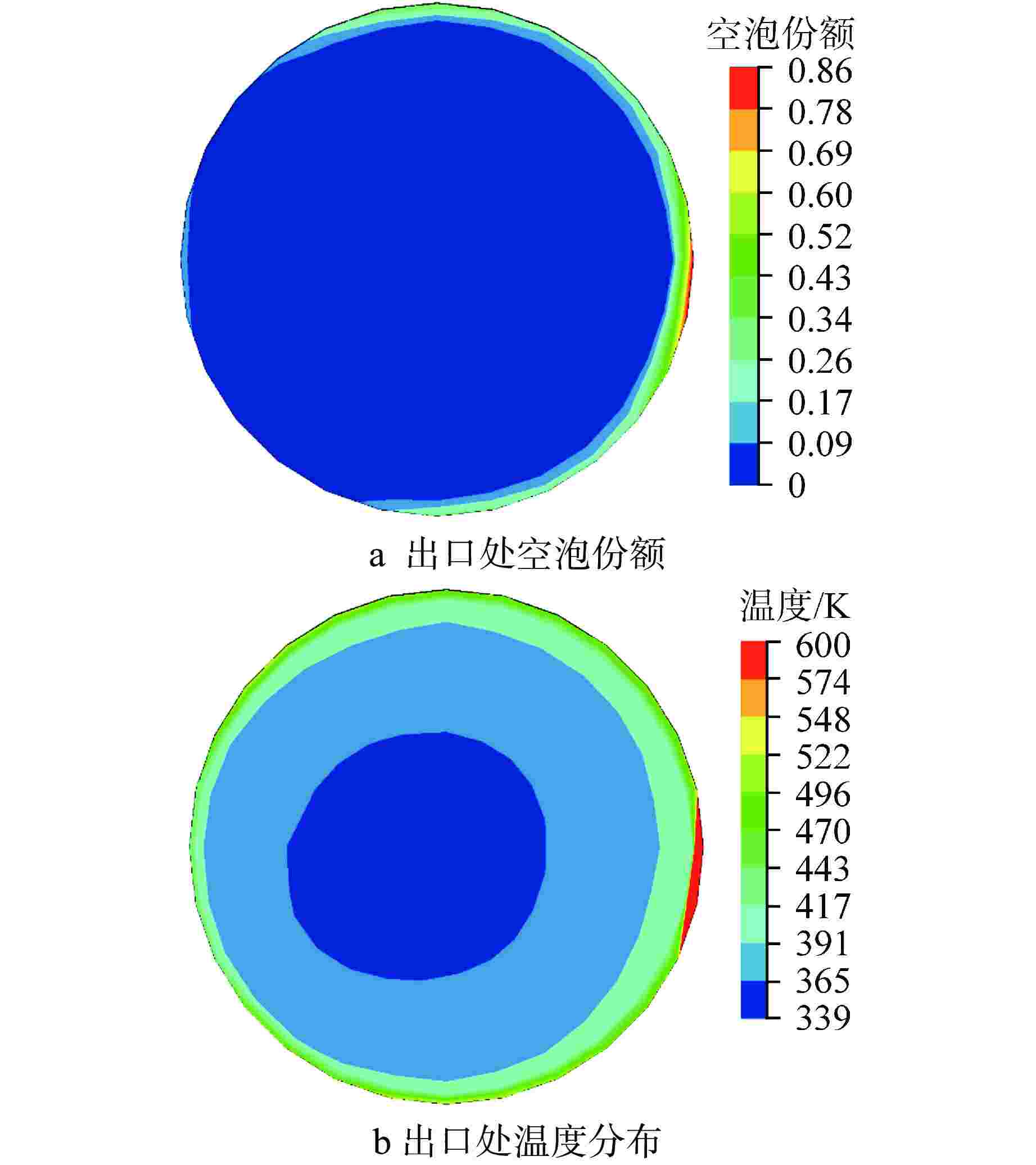
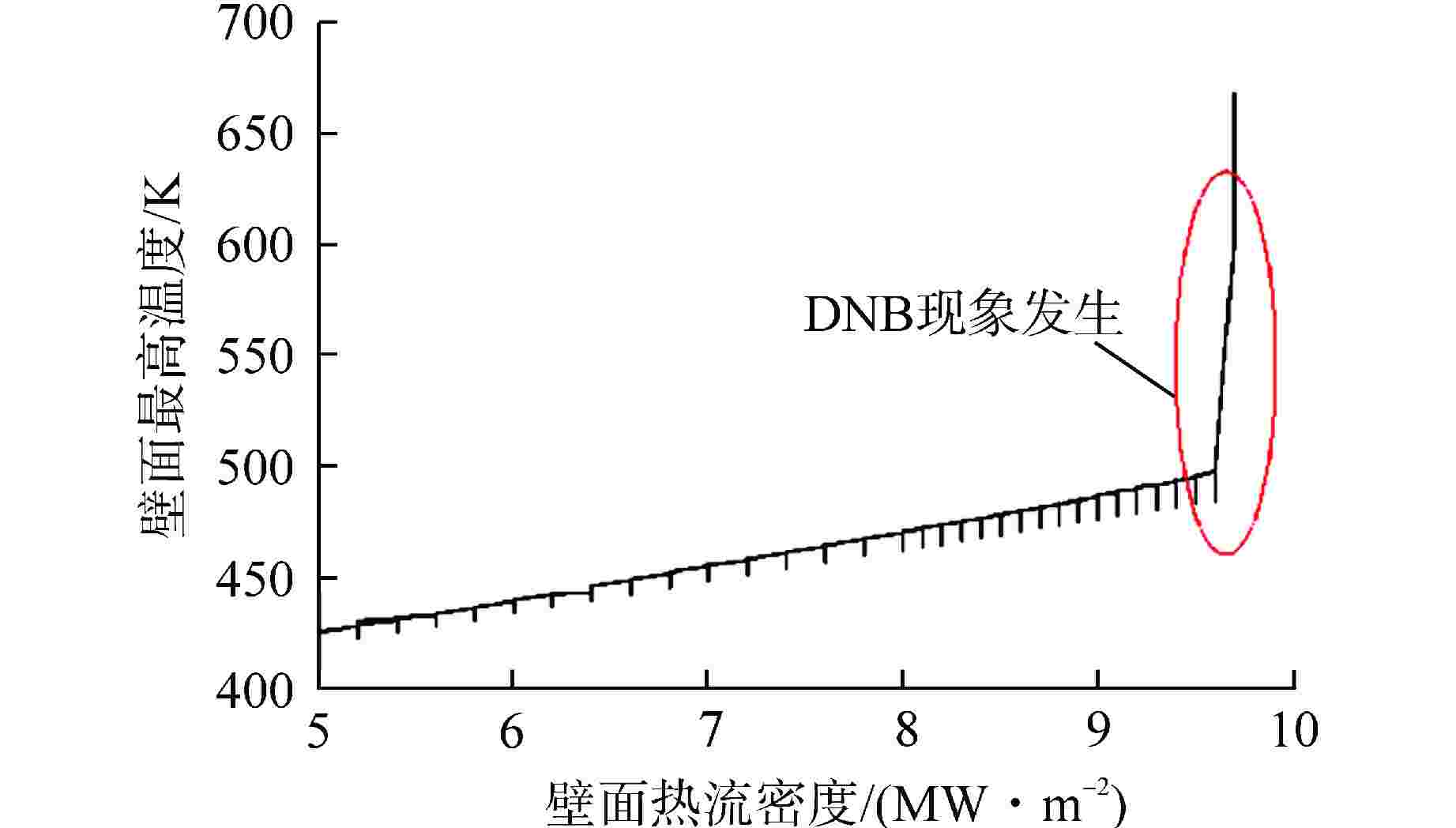
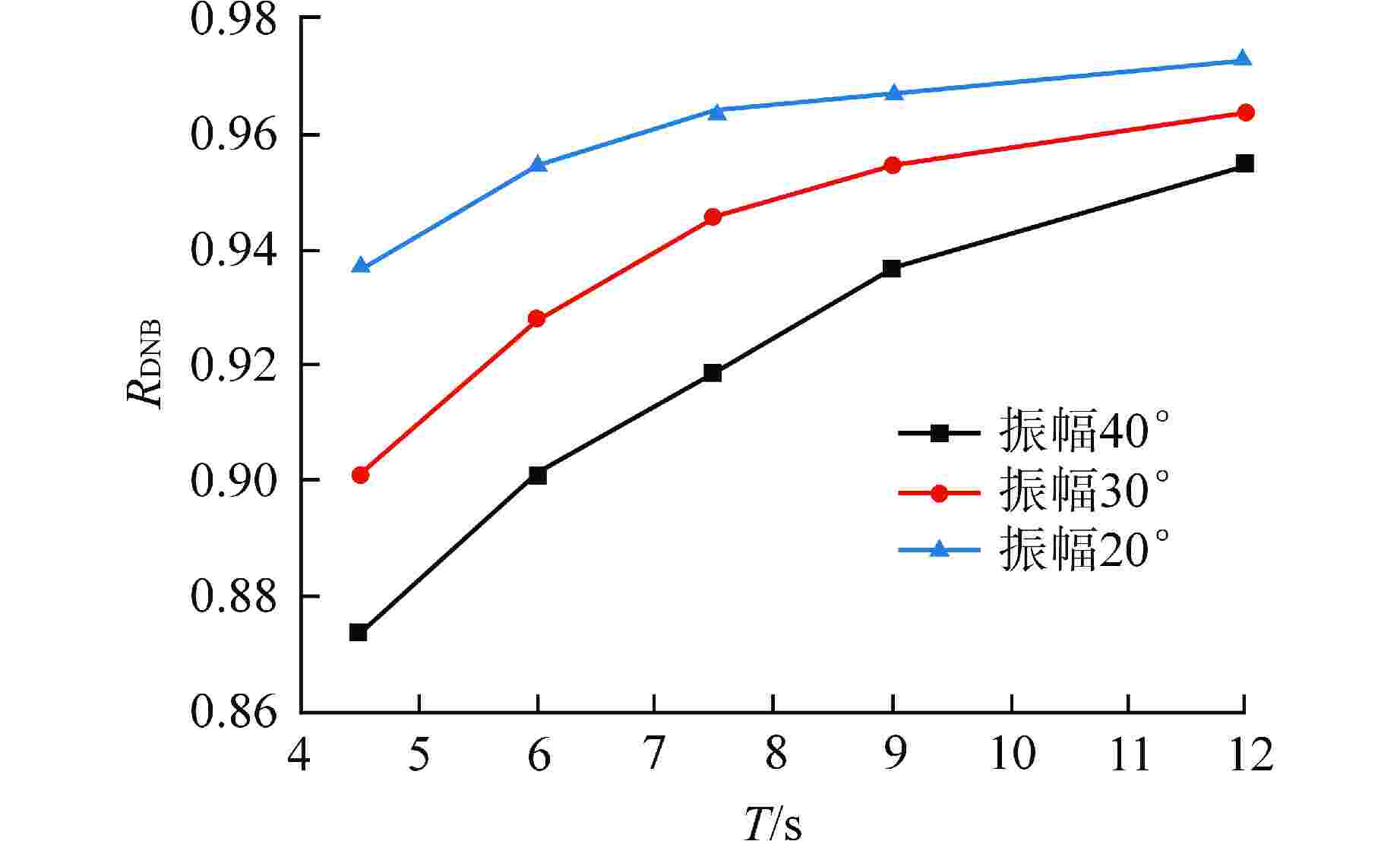
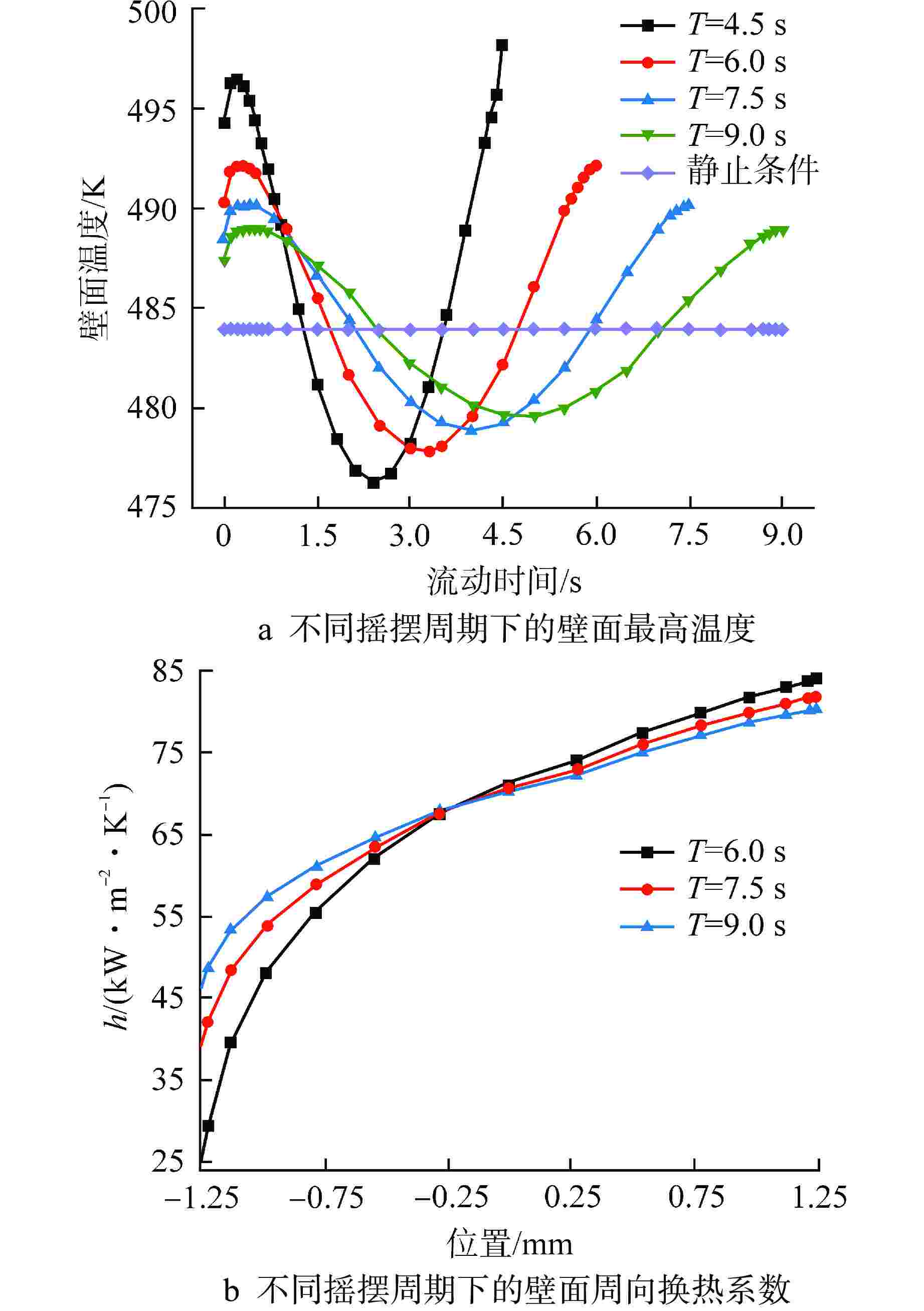
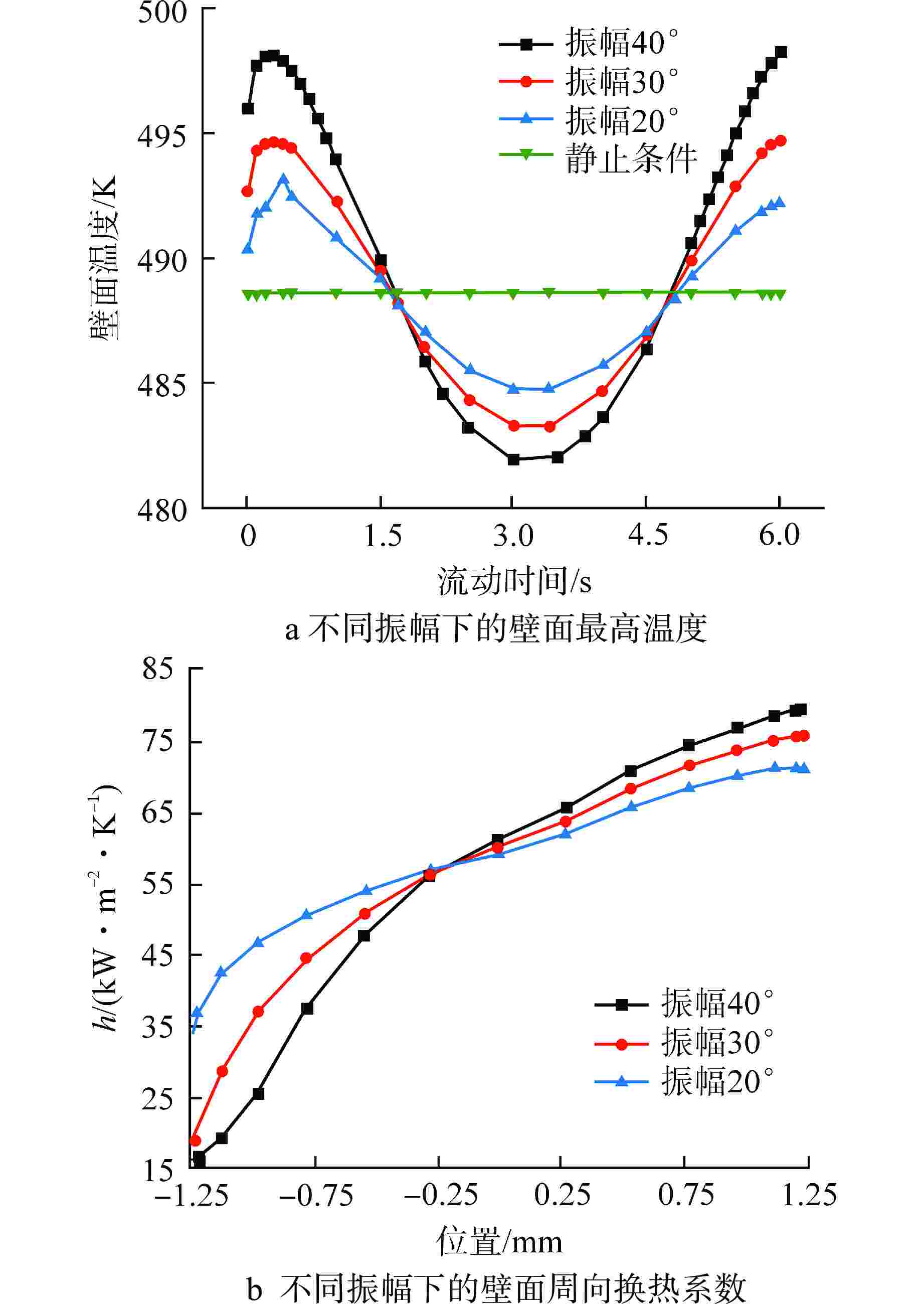
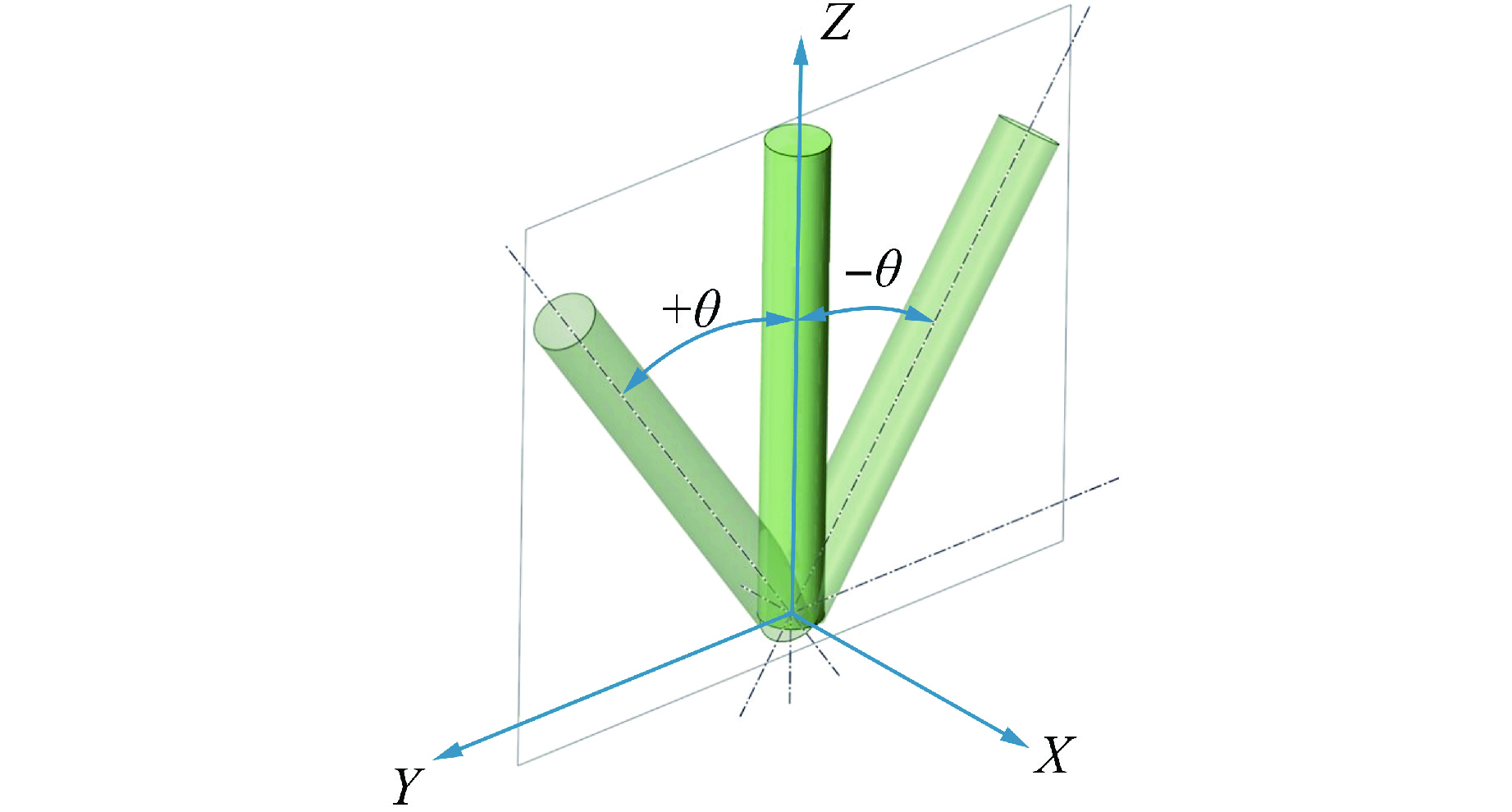
摘要: 针对摇摆条件下的竖直圆管内偏离核态沸腾(DNB)临界热流密度(CHF)进行了三维数值计算,采用欧拉两相流模型和非平衡壁面沸腾模型,通过将静止管道的CHF模拟值和实验值进行对比,完成了不同壁面沸腾子模型的敏感性分析。对15种振幅和周期组合的正弦简谐摇摆运动的竖直管道的CHF进行预测。结果表明:所有摇摆条件均导致了DNB现象的提前发生,在最“剧烈”的摇摆情况下,CHF的值最小。管道内的温度和换热系数会随着摇摆运动发生周期性的改变。在一个周期内,更大的振幅和更小的周期都会导致加热壁面在某时刻出现更小的换热系数,从而导致壁面最高温度上升。本研究可以为摇摆条件下DNB型CHF的数值预测提供参考。
-
关键词:
- 偏离核态沸腾(DNB) /
- 临界热流密度(CHF) /
- 摇摆条件 /
- 数值研究
Abstract: A three-dimensional numerical calculation was carried out on the departure from nucleate boiling (DNB) type critical heat flux (CHF) in a vertical circular tube under different rolling conditions. The Euler two-phase flow model and the non-equilibrium wall boiling model were used. By comparing the simulated CHF values of static tubes with experimental values, a sensitivity analysis of different wall boiling sub-models was completed. The CHF of a vertical tube with sinusoidal simple harmonic rolling motion is predicted for 15 combinations of amplitude and period. The results show that all rolling conditions lead to the early occurrence of DNB. In the most "violent" rolling situation, the value of CHF is the smallest. The temperature and heat transfer coefficient in the tube will change periodically with the rolling motion. Within a period, larger amplitude and smaller period will cause the heating wall to have a smaller heat transfer coefficient at a certain moment, resulting in an increase in the maximum temperature of the wall. This study can provide a reference for the numerical prediction of DNB-type CHF under rolling conditions. -
表 1 相间模型的选取
Table 1. Selection of Interphase Models
作用力模型 模型 曳力 Grace 升力 Tomiyama 湍流耗散力 Favre 壁面润滑力 Antal 虚拟质量力 — 表 2 实验工况
Table 2. Experimental Case
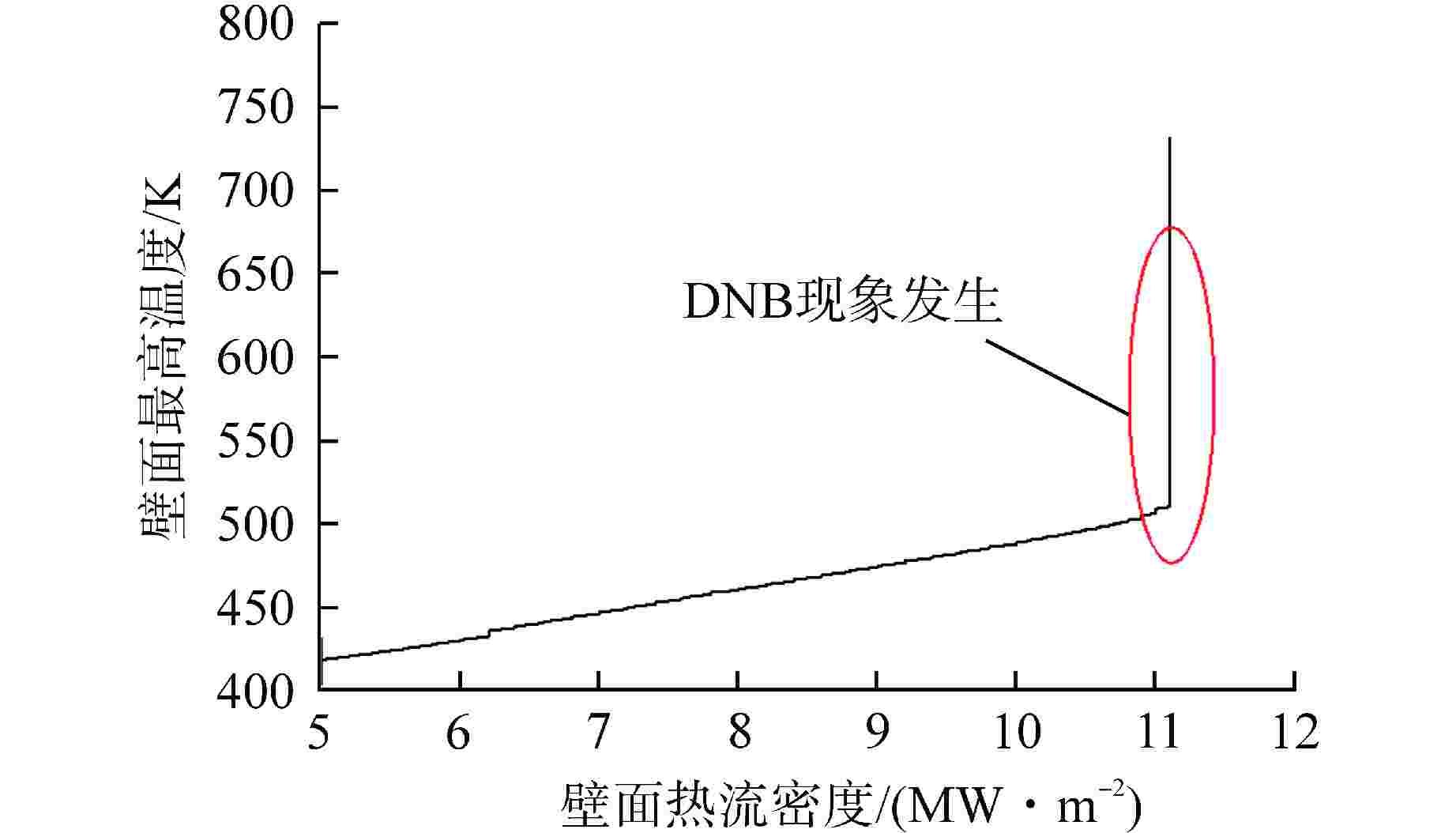
参数 数据 系统压力/MPa 0.58 饱和温度 /K 431 入口质量流量/(kg·m−2·s−1) 11479.8 入口温度/K 339.18 测的CHF/(MW·m−2) 12.1 表 3 壁面沸腾子模型敏感性分析
Table 3. Sensitivity Analysis on the Wall Boiling Sub-models
气泡脱离
直径模型核化
密度模型CHF发生
位置/m$q_{\mathrm{c}}/ $
(MW·m−2)与实验数据
的偏差/%T-K K-I 0.1995 8.4 30.57 K-I 0.1835 8.8 27.27 Unal 0.1980 11.1 8.26 T-K L-C 0.1920 6.6 45.45 K-I 0.1850 5.8 52.07 Unal 0.1910 8.6 28.93 表 4 摇摆工况
Table 4. Rolling Conditions
工况 T/s 振幅 工况 T/s 振幅 1 9 7.5 30° 2 4.5 40° 10 9.0 30° 3 6.0 40° 11 12.0 30° 4 7.5 40° 12 4.5 20° 5 9.0 40° 13 6.0 20° 6 12.0 40° 14 7.5 20° 7 4.5 30° 15 9.0 20° 8 6.0 30° 16 12.0 20° -
[1] 庞凤阁,高璞珍,王兆祥,等. 摇摆对常压水临界热流密度(CHF)影响实验研究[J]. 核科学与工程,1997, 17(4): 367-371. [2] 高璞珍,王兆祥,庞凤阁,等. 摇摆情况下水的自然循环临界热流密度实验研究[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报,1997, 18(6): 38-42. [3] HWANG J S, LEE Y G, PARK G C. Characteristics of critical heat flux under rolling condition for flow boiling in vertical tube[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2012, 252: 153-62. doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2012.06.032 [4] ZHANG R, CONG T L, TIAN W X, et al. Prediction of CHF in vertical heated tubes based on CFD methodology[J]. Progress in Nuclear Energy, 2015, 78: 196-200. doi: 10.1016/j.pnucene.2014.10.001 [5] 李权,焦拥军,于俊崇. 竖直加热圆管内过冷沸腾及CHF数值模拟[J]. 核动力工程,2015, 36(1): 168-172. [6] 陈丽娟. 竖直加热管道内干涸型临界沸腾数值分析[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学,2018. [7] PENG J, CHEN D Q, XU J J, et al. CFD simulation focusing on void distribution of subcooled flow boiling in circular tube under rolling condition[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2020, 156: 119790. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2020.119790 [8] 祁伟,步珊珊,李振中,等. 摇摆条件下竖直圆管内干涸型临界沸腾的数值研究[J]. 核动力工程,2022, 43(5): 63-69. [9] DEL VALLE V H, KENNING D B R. Subcooled flow boiling at high heat flux[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 1985, 28(10): 1907-1920. doi: 10.1016/0017-9310(85)90213-3 [10] COLE R. A photographic study of pool boiling in the region of the critical heat flux[J]. AIChE Journal, 1960, 6(4): 533-538. doi: 10.1002/aic.690060405 [11] TOLUBINSKY V I, KOSTANCHUK D M. Vapour bubbles growth rate and heat transfer intensity at subcooled water boiling[C]//International Heat Transfer Conference 4. Danbury, USA: Begell House Inc., 1970: 1-11. [12] KOCAMUSTAFAOGULLARI G, ISHII M. Interfacial area and nucleation site density in boiling systems[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 1983, 26(9): 1377-1387. doi: 10.1016/S0017-9310(83)80069-6 [13] ÜNAL H C. Maximum bubble diameter, maximum bubble-growth time and bubble-growth rate during the subcooled nucleate flow boiling of water up to 17.7 MN/m2[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 1976, 19(6): 643-649. doi: 10.1016/0017-9310(76)90047-8 [14] LEMMERT M, CHAWLA J M. Influence of flow velocity on surface boiling heat transfer coefficient[M]//HAHNE E, GRIGULL U. Heat Transfer in Boiling. New York: Academic Press and Hemisphere, 1977: 237-247. [15] KOCAMUSTAFAOGULLARI G, ISHII M. Foundation of the interfacial area transport equation and its closure relations[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 1995, 38(3): 481-493. doi: 10.1016/0017-9310(94)00183-V [16] CELATA G P, CUMO M, MARIANI A. Burnout in highly subcooled water flow boiling in small diameter tubes[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 1993, 36(5): 1269-1285. doi: 10.1016/S0017-9310(05)80096-1 -





 下载:
下载: