Research on Vibration-induced Noise Simulation of Main Control Room of High-temperature Gas-cooled Reactor
-
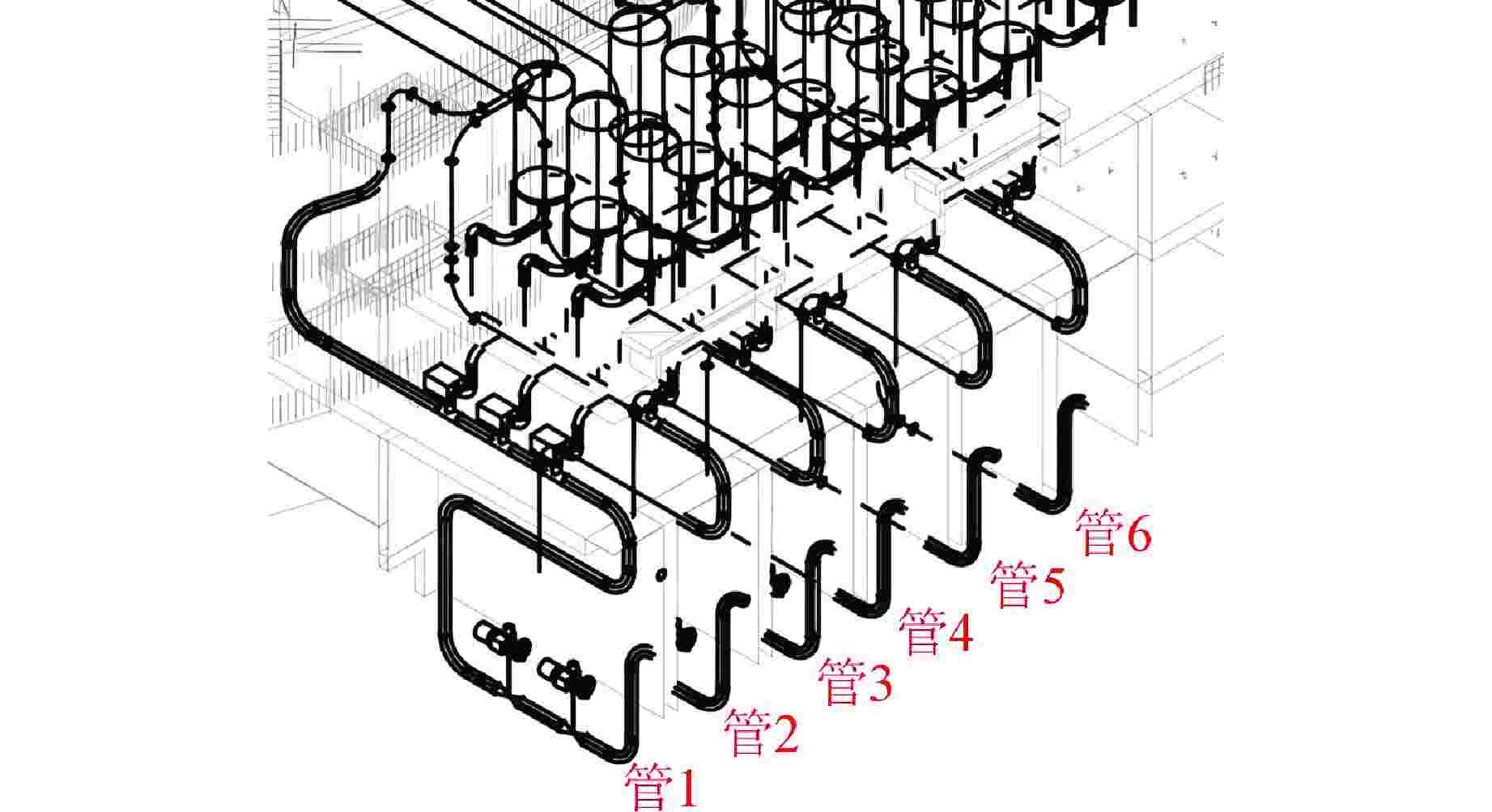
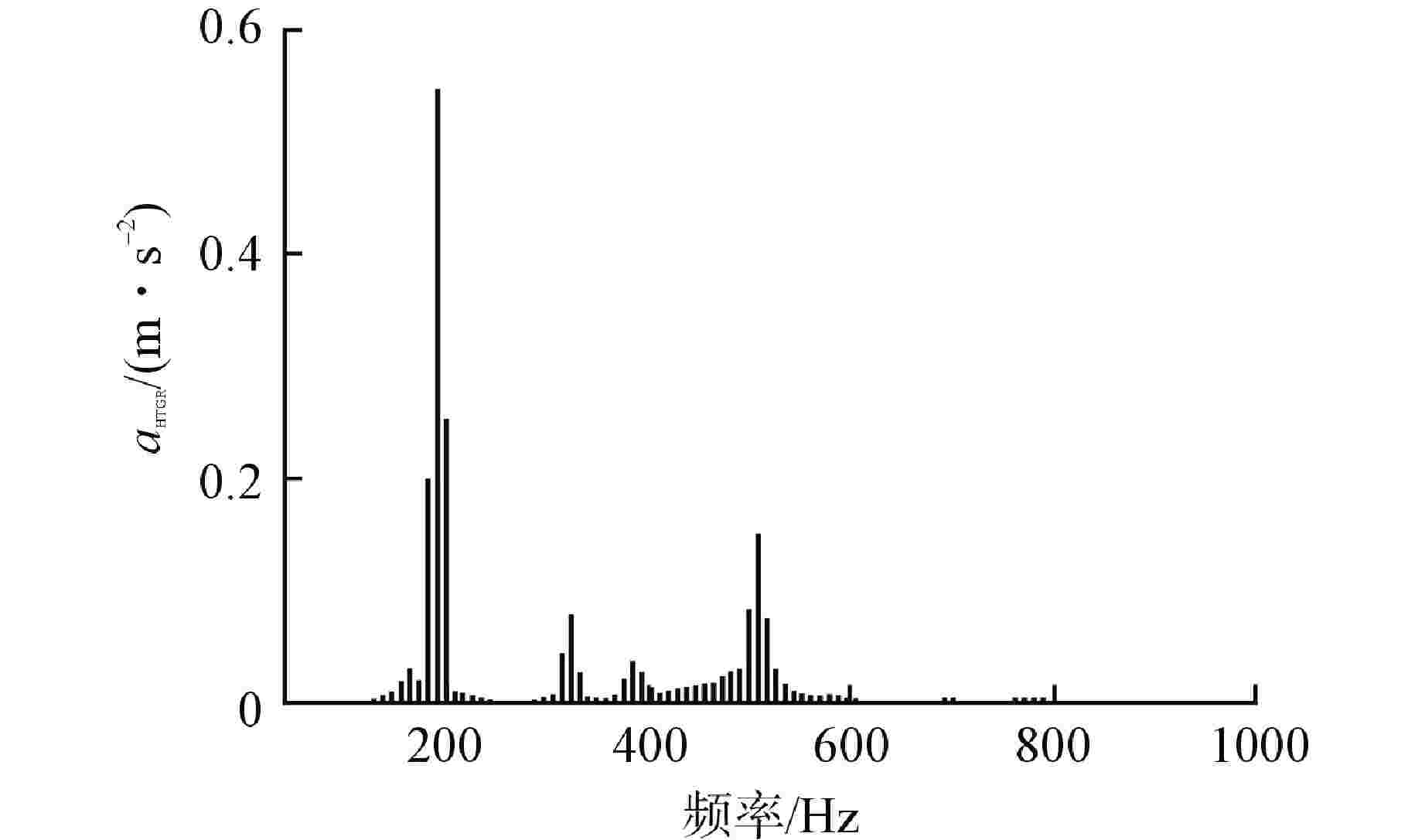
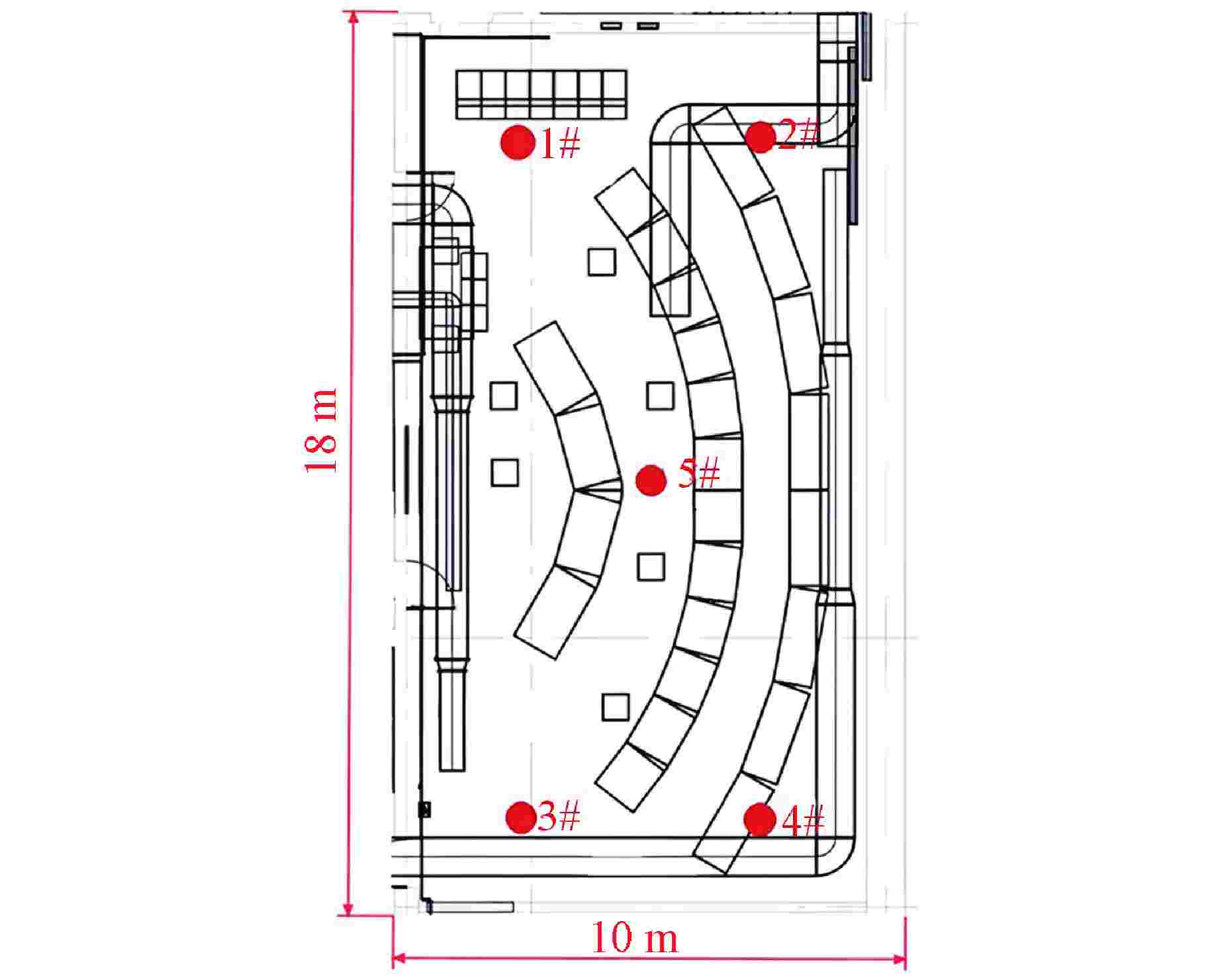
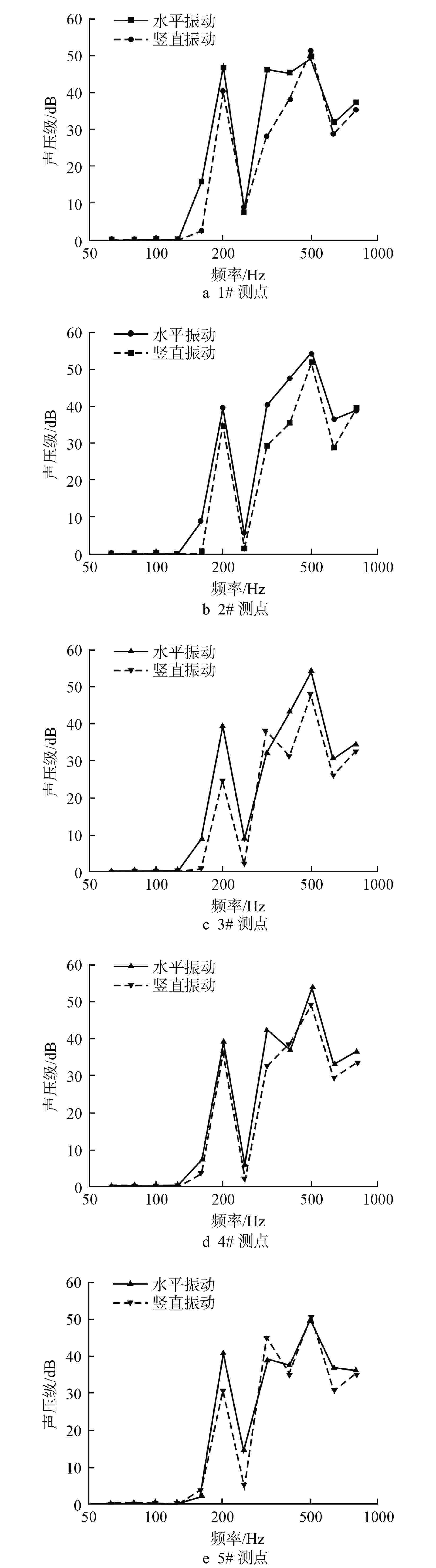
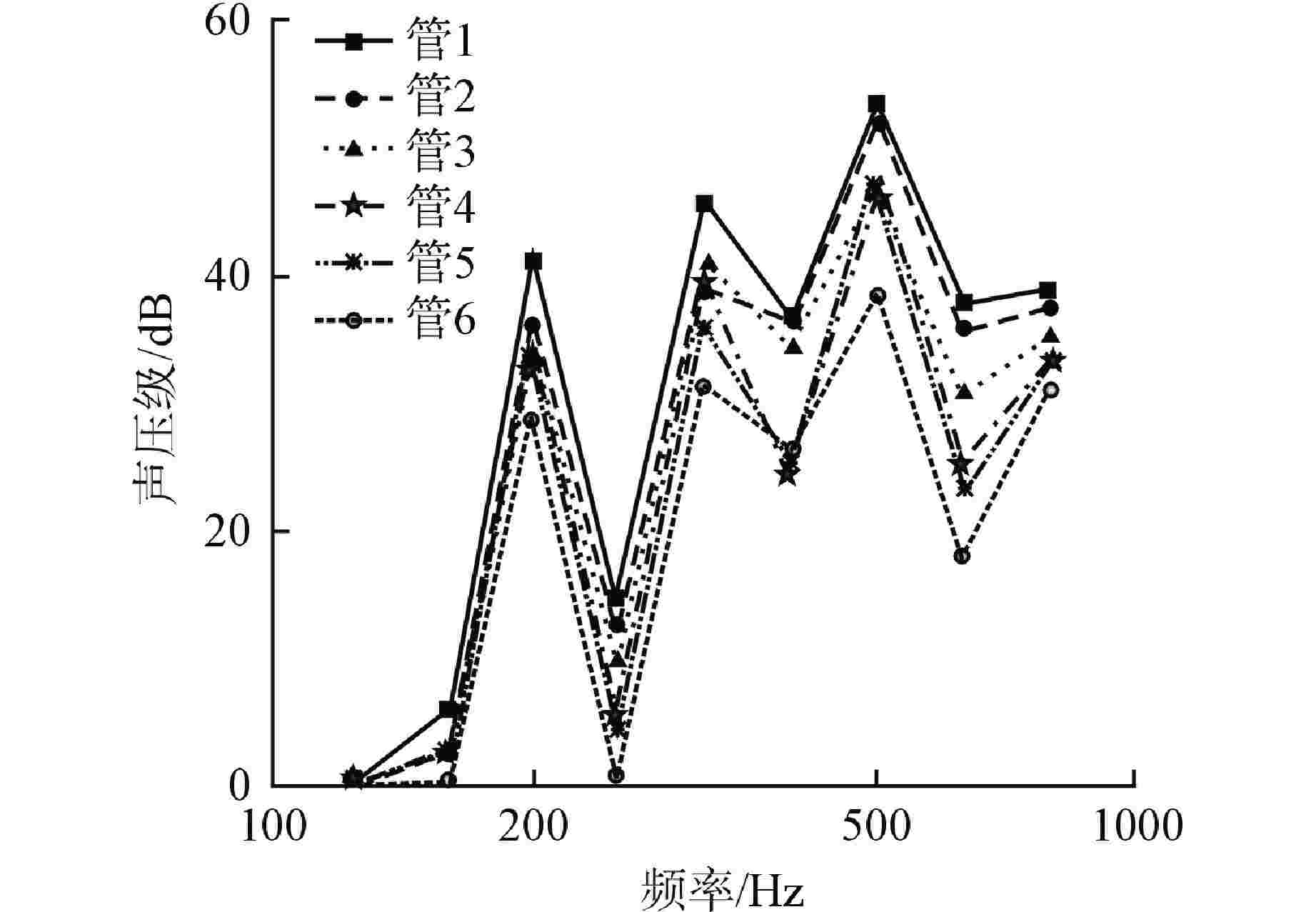
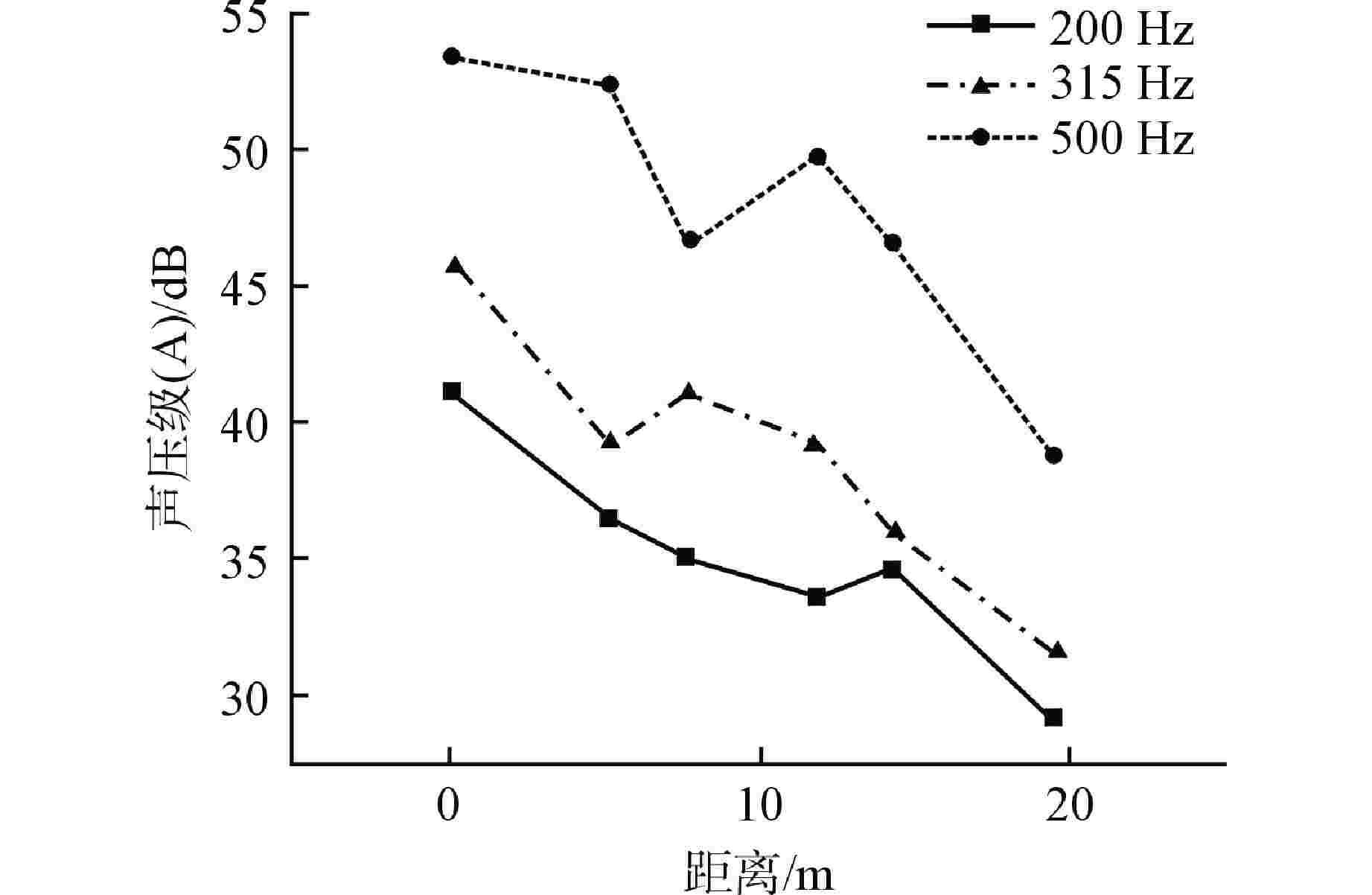
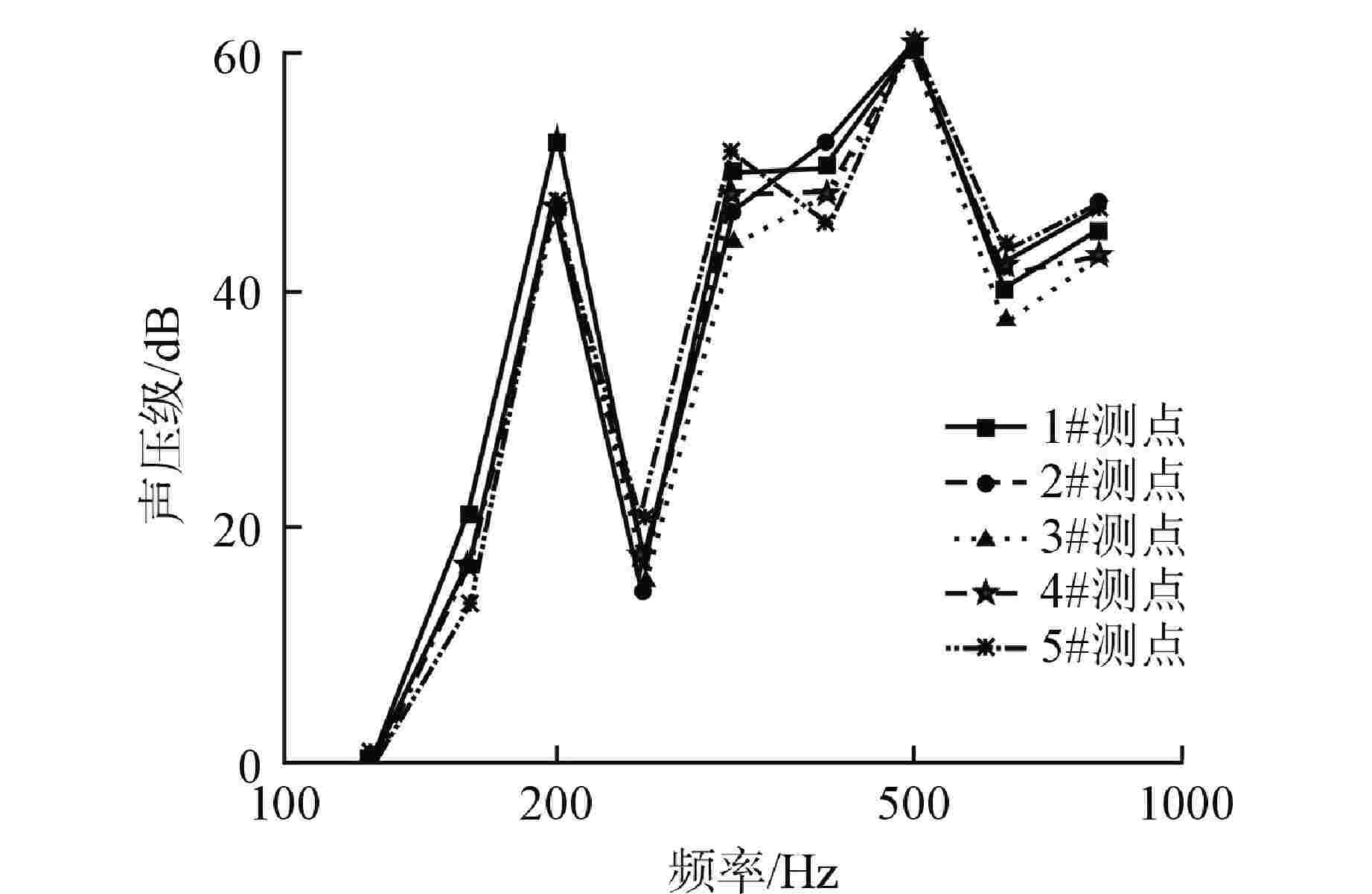
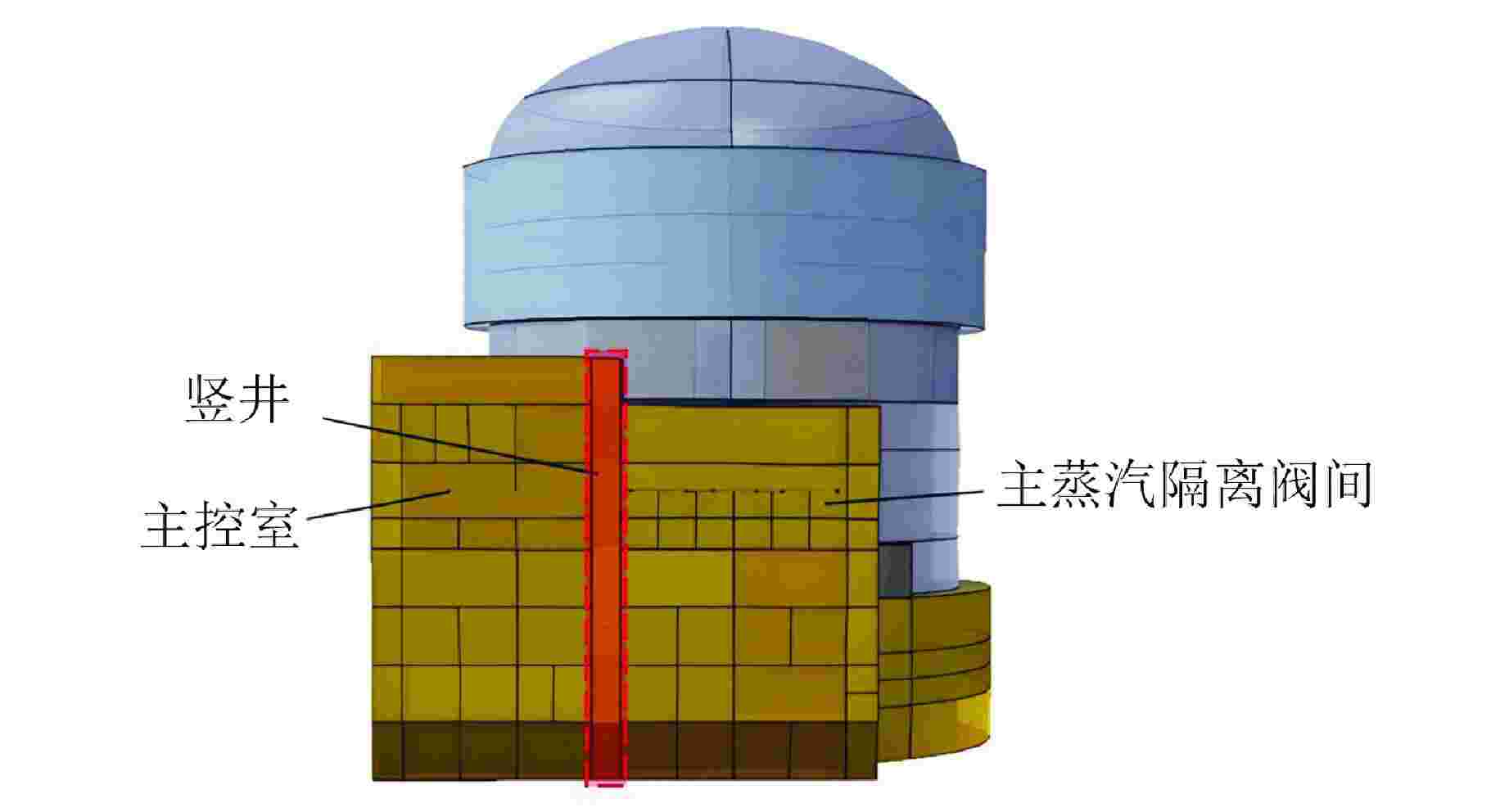
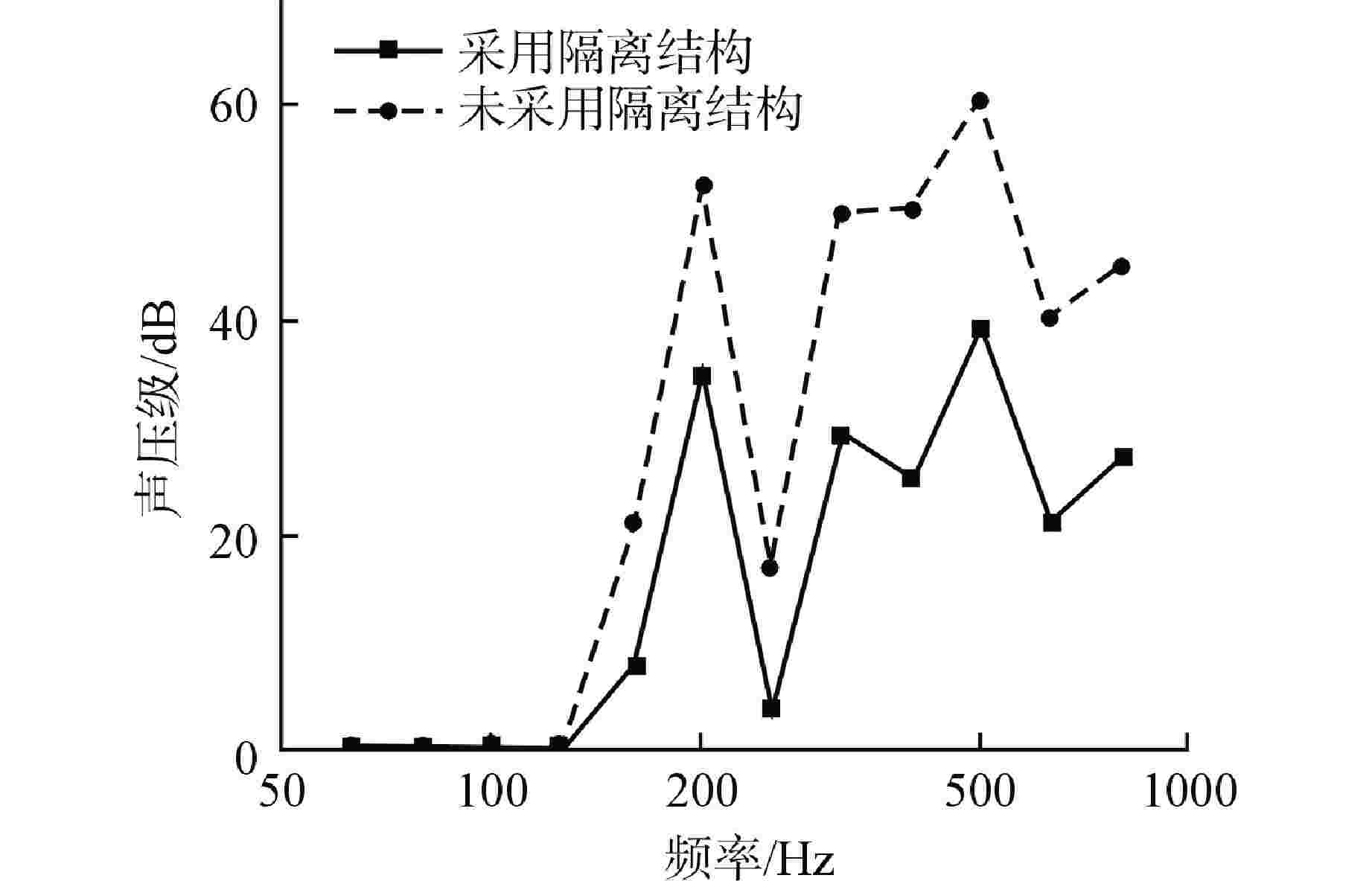
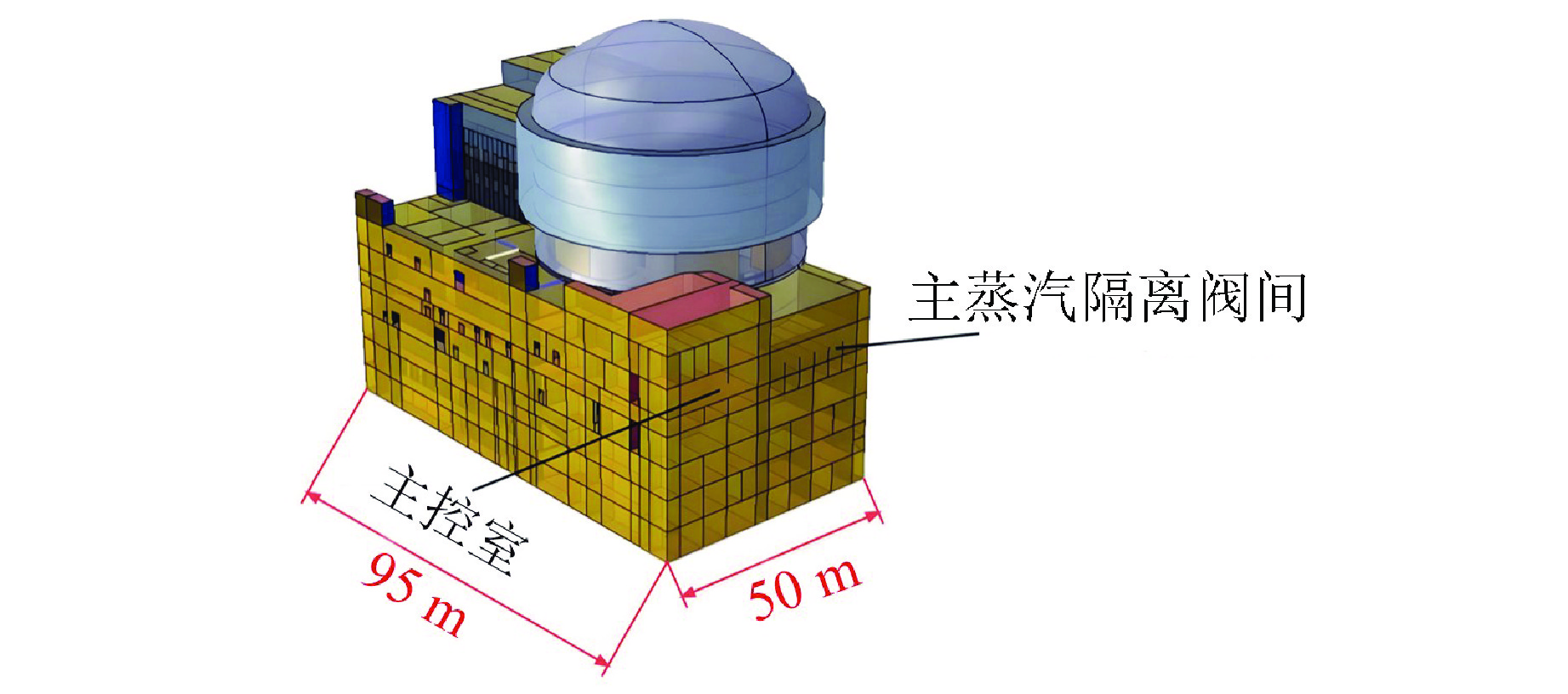
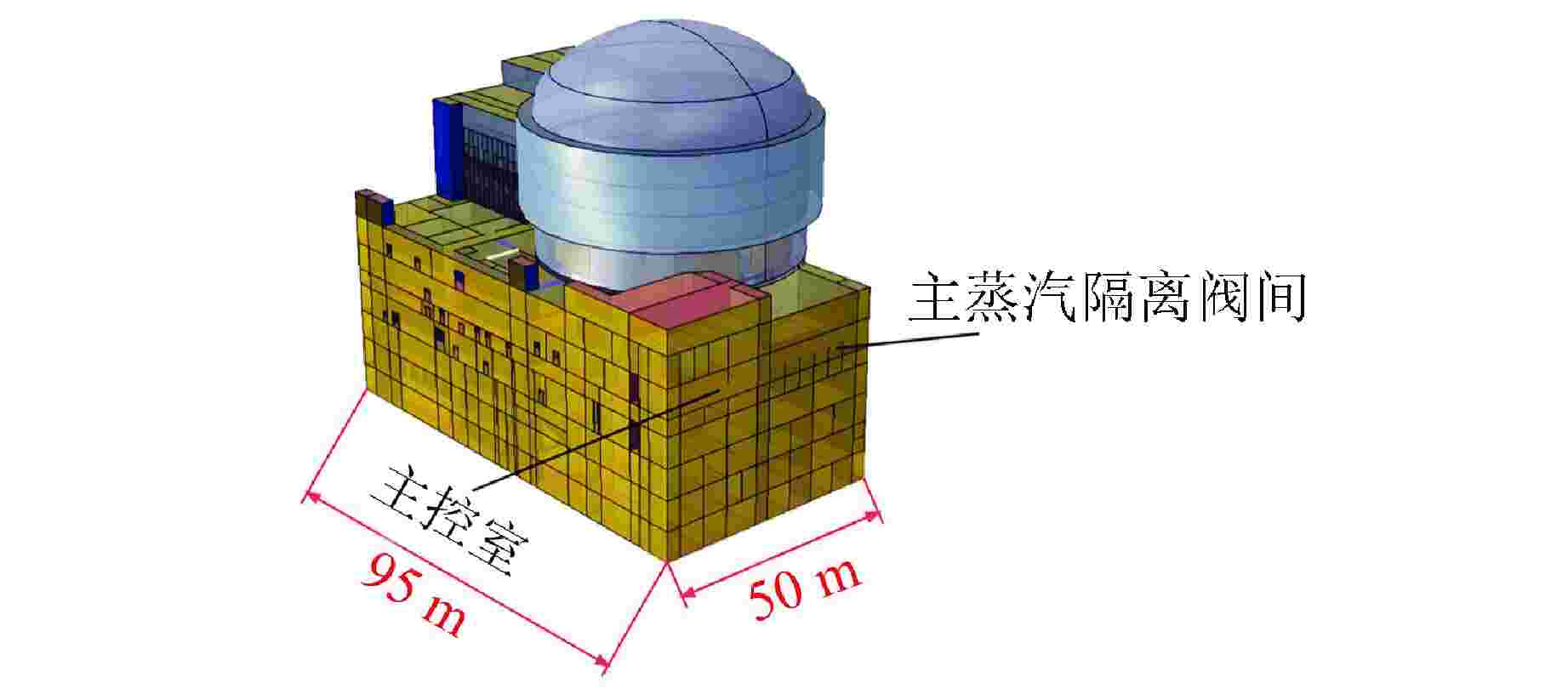
摘要: 主控室噪声是核电厂运行安全关注的重要问题之一。本文基于结构有限元模型和声学边界元模型,探究主蒸汽管道振动对高温气冷堆主控室内噪声的影响。建立了某高温气冷堆概念设计核岛厂房的频响分析有限元模型与主控室频域声学边界元模型,预测结构传递主蒸汽管道振动主导的主控室噪声水平;探究不同主蒸汽管道对主控室内声压级的影响规律,并基于声学贡献量分析,识别对主控室噪声贡献最大的墙壁振动;提出了通过物理隔断进行主控室振动噪声优化的方法。结果表明,主蒸汽管道水平振动在主控室内产生的噪声高于竖直振动;主蒸汽管道振动引起的最大噪声超过60 dB;主控室靠近主蒸汽管道隔离阀间的墙壁与天花板对室内噪声的声学贡献量最大;通过物理隔断可大幅降低主控室内部噪声水平。Abstract: Noise in the main control room is one of the major concerns for operational safety of the nuclear power plant. In this paper, the impact of the main steam pipeline vibration on the noise level in the main control room of the high temperature gas-cooled reactor (HTGR) is investigated by using a structural finite element model and an acoustic boundary element model. A finite element model for frequency response analysis of the nuclear island of one HTGR conceptual design, and a boundary element model for acoustic analysis of the main control room in the frequency domain, are established respectively, to predict the noise levels in the main control room dominated by vibration transfer from the main steam pipelines. The influence patterns of various main steam pipes are explored, and the wall vibration that contributes most to the noise level of the main control room is identified based on acoustic contribution analysis. A method for optimizing the main control room noise through physical partitioning is proposed. The results show that, horizontal vibrations of the main steam pipeline generate higher noise levels in the control room compared to vertical vibrations. The maximum noise caused by the vibration of the main steam pipeline exceeds 60 dB. The walls near the main steam isolation valve room and the ceiling contribute the most to the indoor noise in the control room. Through physical partitioning, the noise level of the control room can be reduced significantly.
-
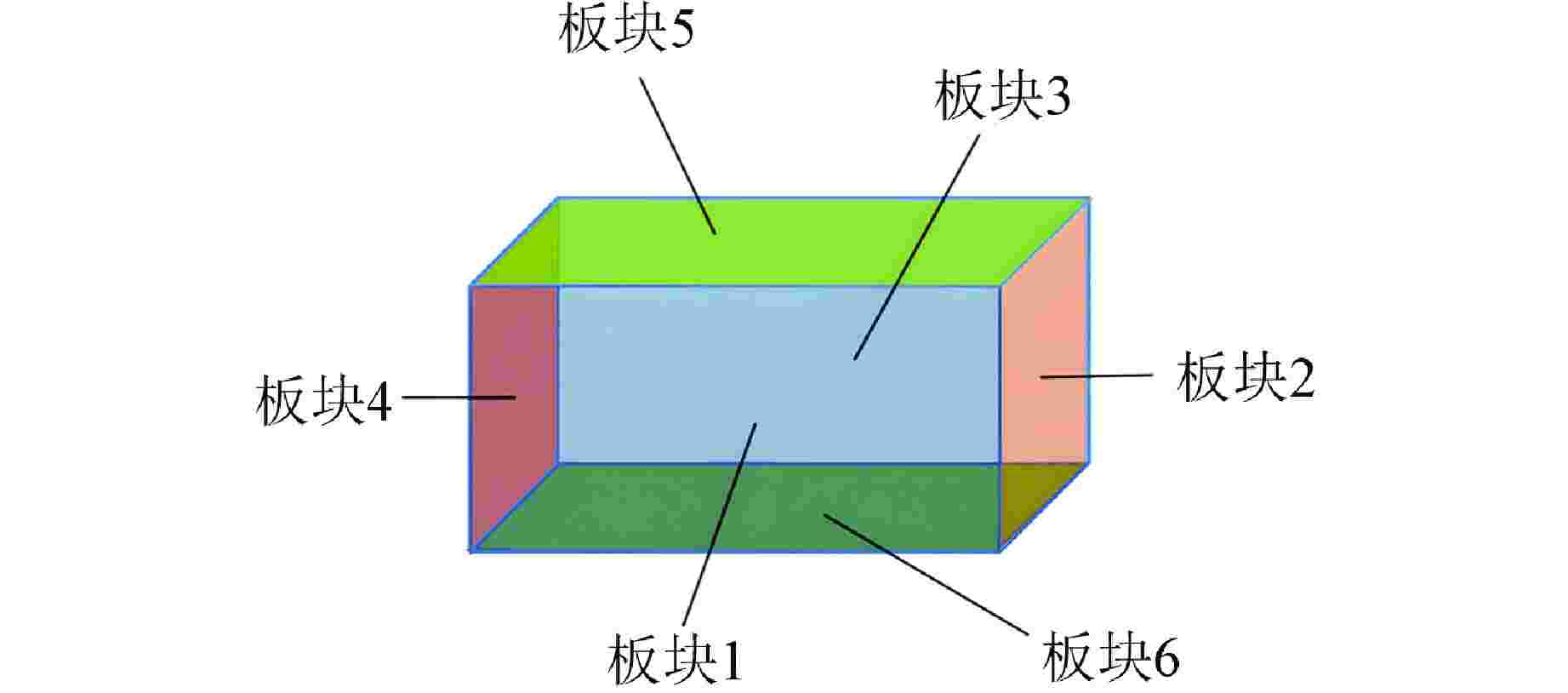
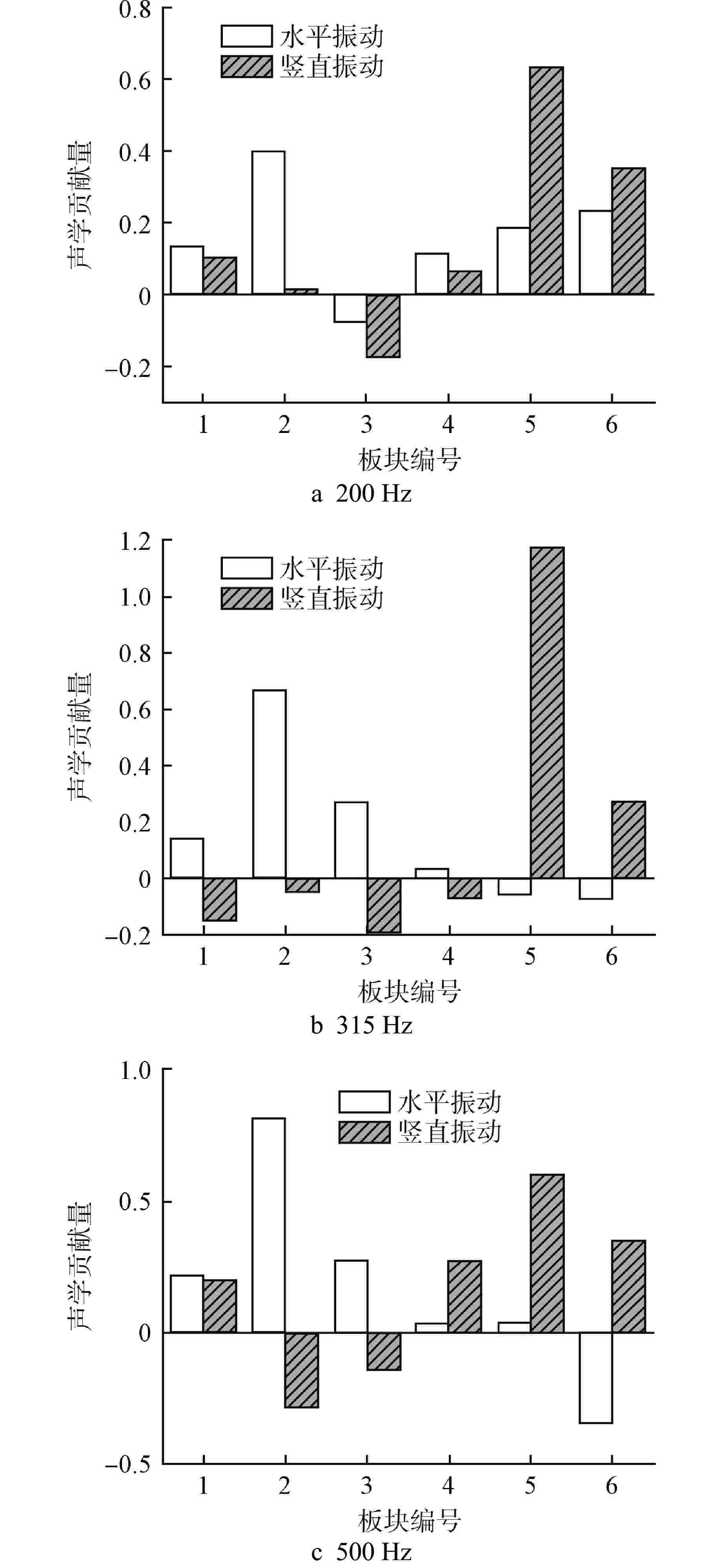
表 1 板块编号
Table 1. Panel Number
板块编号 板块 1 主控室外墙 2 靠近主蒸汽隔离阀间墙壁 3 主控室内墙 4 远离主蒸汽隔离阀间墙壁 5 主控室天花板 6 主控室地板 -
[1] LIHUA G, HUIZHEN H. Air conditioning noise analysis and calculation in nuclear power plant[C]//Proceedings of 2019 Chinese Automation Congress (CAC). Hangzhou: IEEE, 2019: 4512-4514. [2] 夏栓,詹敏明,陈星文,等. 某核电厂主蒸汽管道振动原因分析及解决方案探讨[J]. 核动力工程,2021, 42(5): 138-142. [3] 胡小洁. AP系列核电厂主控制室噪声控制设计[J]. 科学技术创新,2018(34): 53-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1328.2018.34.028 [4] 陈星文,蔡奕霖,秦洁. 核电厂主蒸汽管道流致声振动优化方法研究[J]. 振动与冲击,2021, 40(24): 299-304. [5] 张然. 高温气冷堆核电站主控制室建筑噪声控制设计研究[J]. 中国住宅设施,2022(5): 30-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5093.2022.5.zgzzss202205011 [6] ZHANG Z Y, DONG Y J, LI F, et al. The Shandong Shidao Bay 200 MWe High-temperature gas-cooled reactor pebble-bed module (HTR-PM) demonstration power plant: an engineering and technological innovation[J]. Engineering, 2016, 2(1): 112-118.ZHANG Z Y, DONG Y J, LI F, et al. The Shandong Shidao Bay 200 MWe High-temperature gas-cooled reactor pebble-bed module (HTR-PM) demonstration power plant: an engineering and technological innovation[J]. Engineering, 2016, 2(1): 112-118. [7] TOMIKU R, OTSURU T, OKAMOTO N, et al. Direct and modal frequency response analysis of sound fields in small rooms by finite element method[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2008, 123(S5): 3092. [8] KIRKUP S. The boundary element method in acoustics: a survey[J]. Applied Sciences, 2019, 9(8): 1642. doi: 10.3390/app9081642 [9] 欧开宽,雷晓燕,罗锟,等. 混凝土箱梁相似模型面板声学贡献对比分析[J]. 振动工程学报,2019, 32(6): 1011-1018. -





 下载:
下载: