Safety Characteristics Analysis of Helium-Xenon Cooled Reactor System under LOCA
-
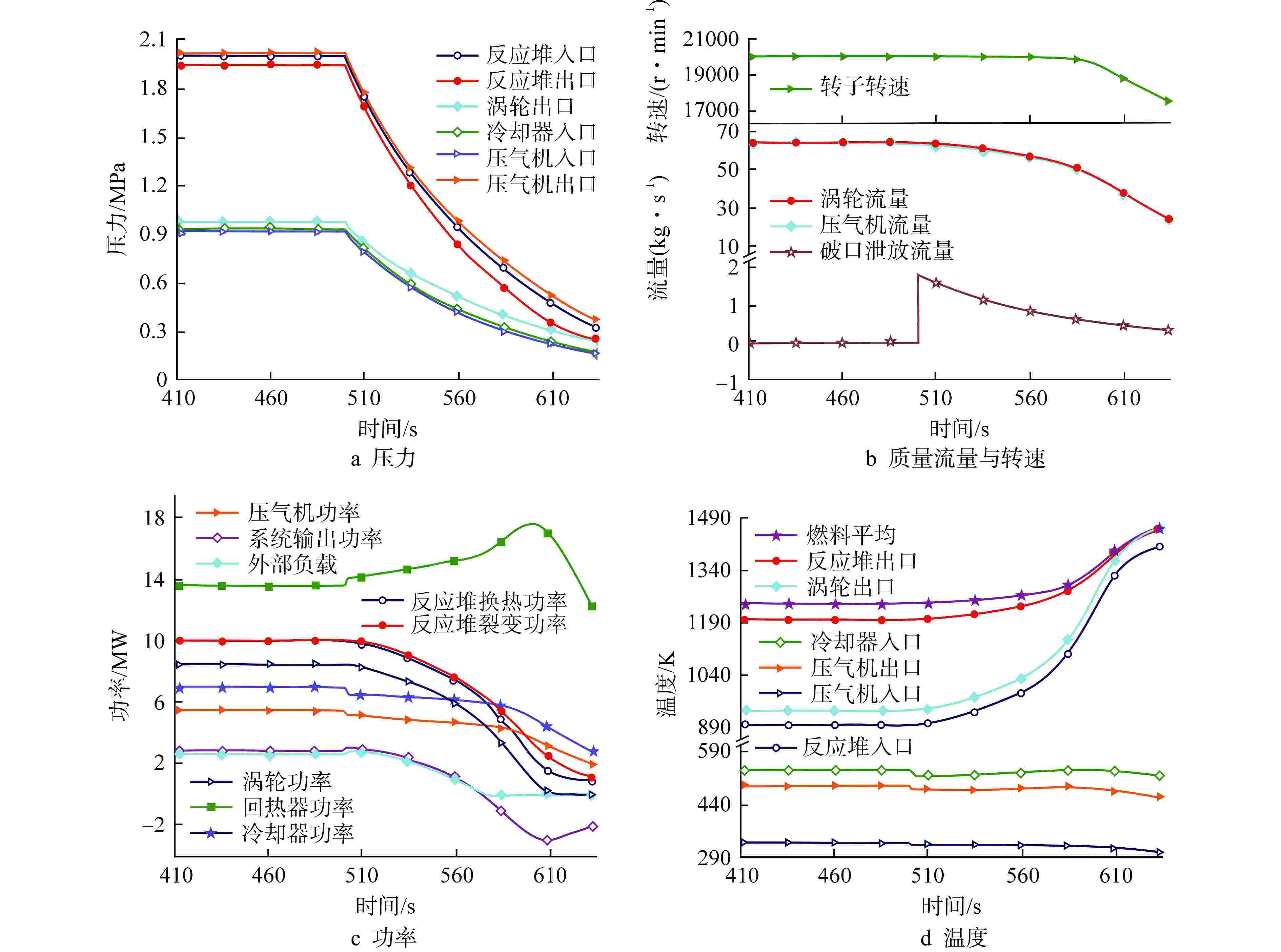
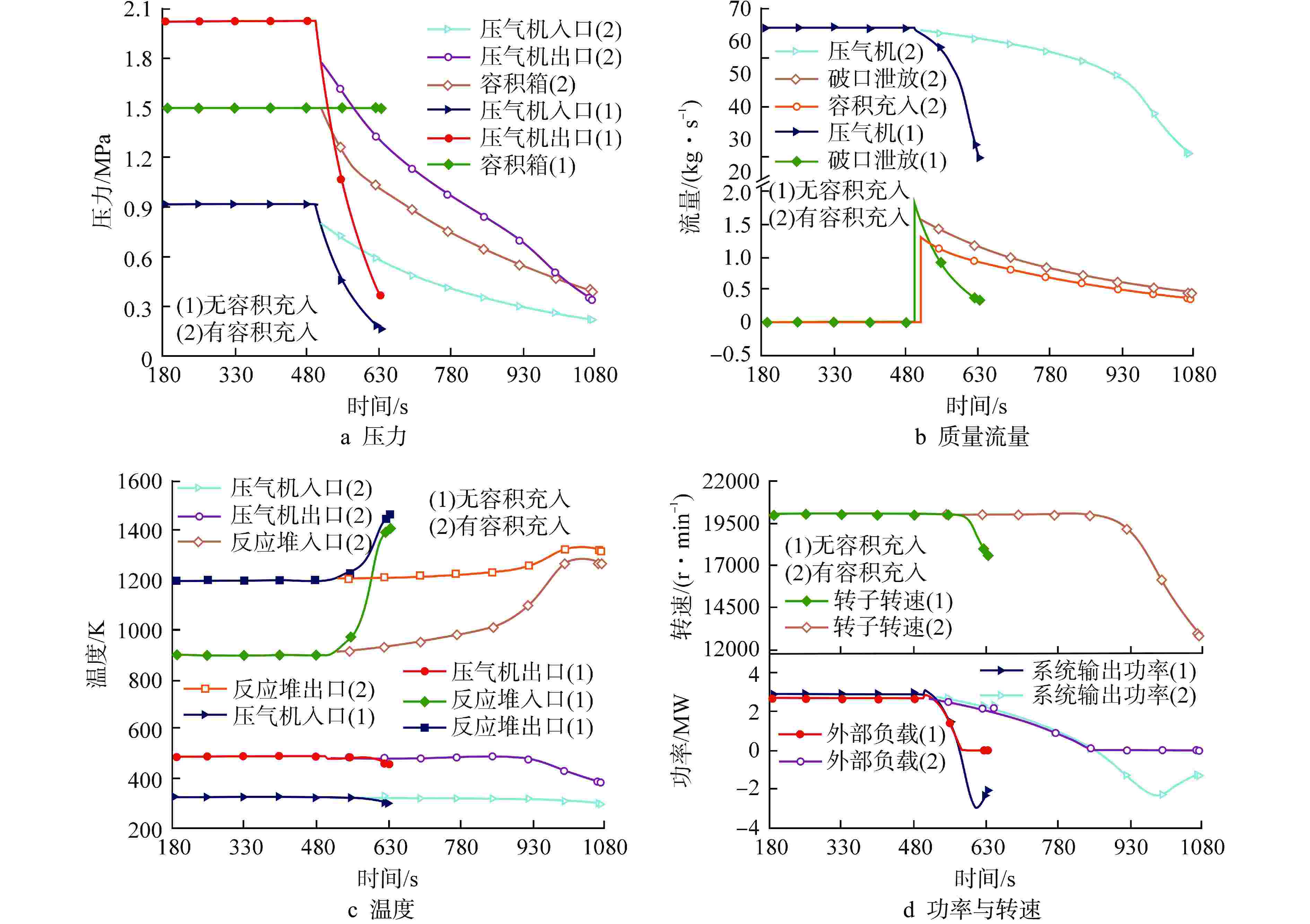
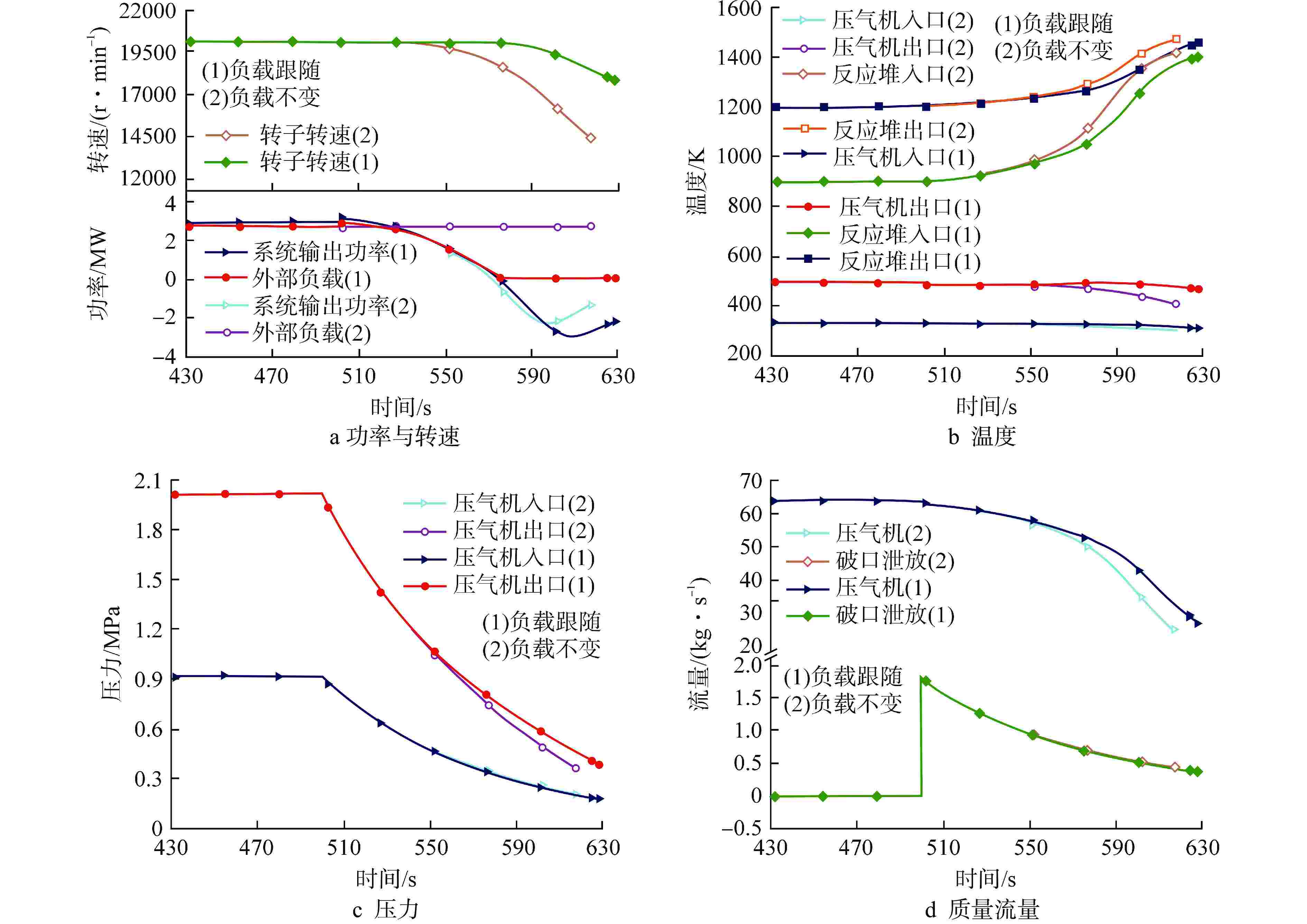
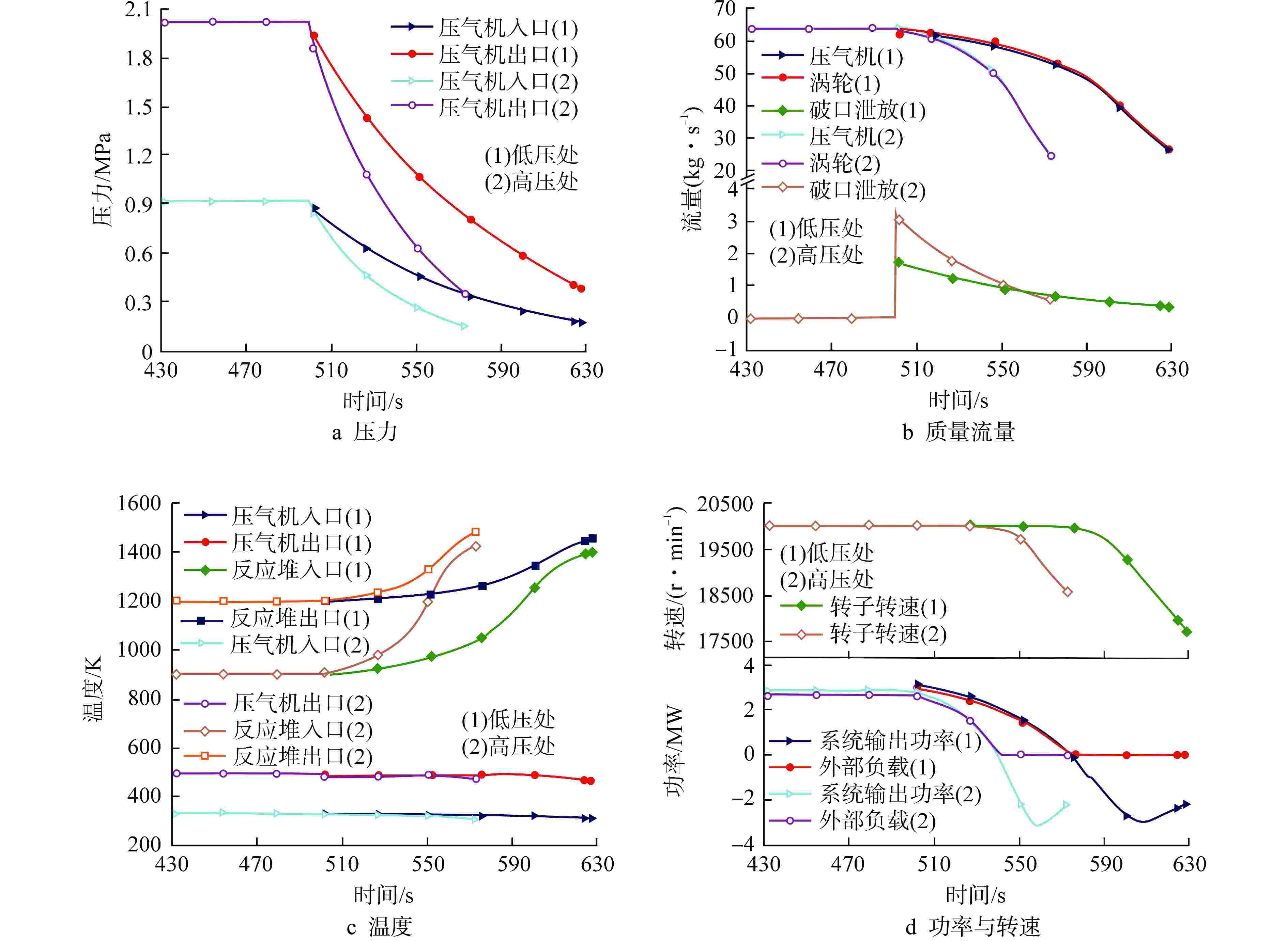
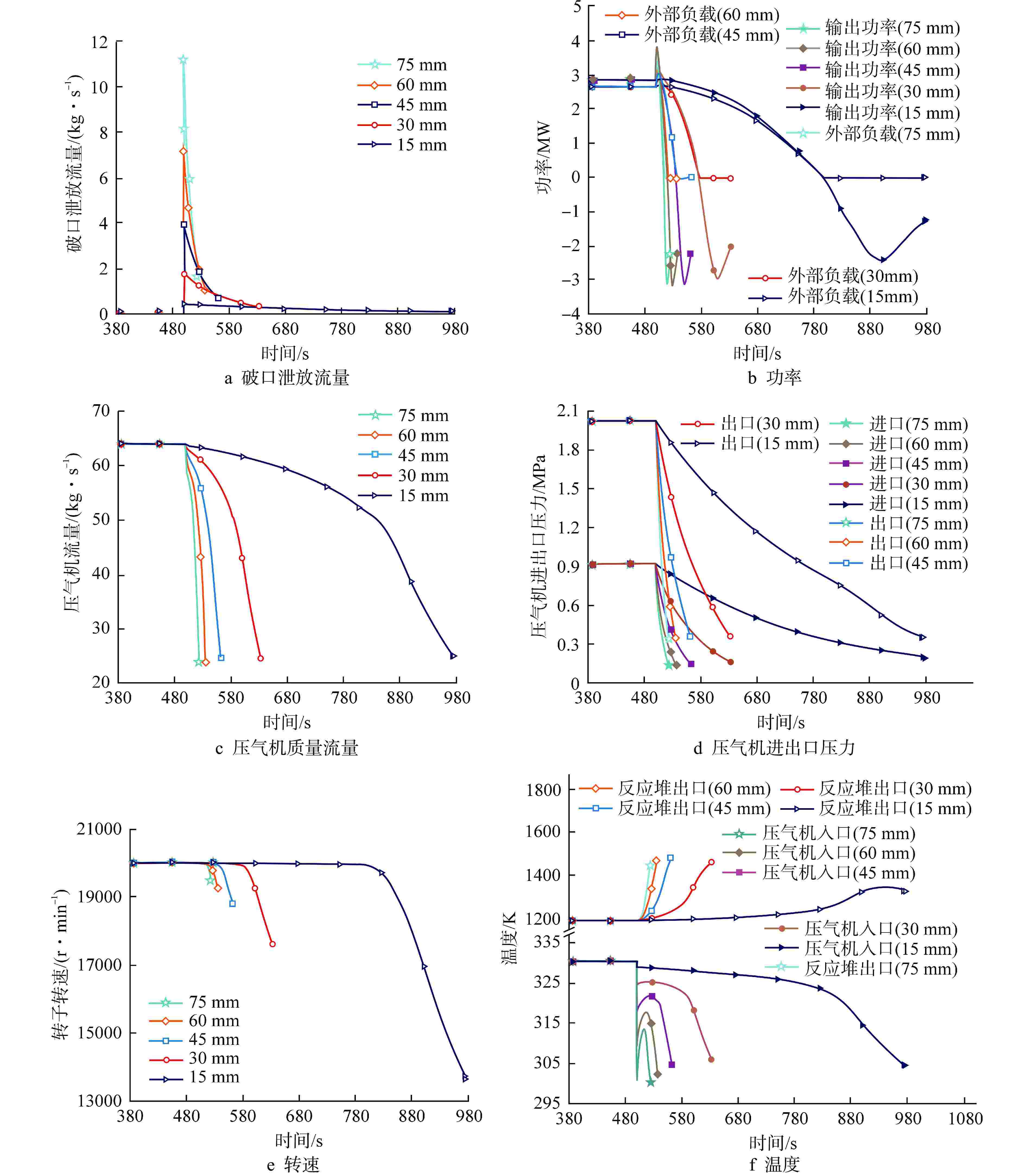
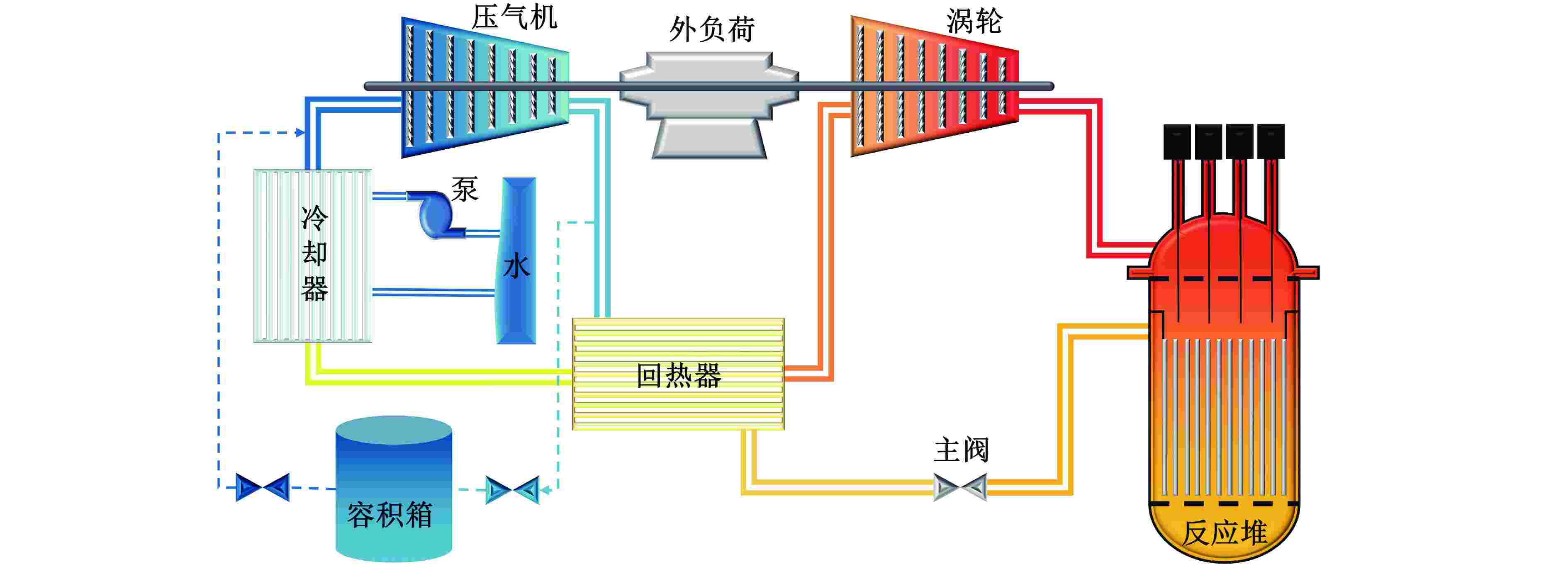
摘要: 为规避反应堆系统破口冷却剂丧失事故(LOCA)带来的高风险和高危害性,本文通过已开发的氦氙气冷反应堆系统LOCA分析程序,模拟了多种LOCA瞬态工况,分析了系统瞬态特性、容积充入影响特性、负载跟随失效影响特性、破口位置影响特性和破口尺寸影响特性。结果表明:在发生LOCA后,系统压力与流量将迅速下降;容积充入对LOCA具有缓解作用,使得流量下降速率和反应堆出口温度上升速率分别降低77.15%和90.27%;负载不变和高压处破口均对LOCA具有负面影响,使得流量下降速率分别提高13.85%和79.83%,反应堆出口温度上升速率分别提高15.84%和96.06%;系统压力和流量下降速率随着破口尺寸增加而增加,尤其破口尺寸从15 mm到30 mm,流量下降速率与反应堆出口温度上升速率的增加幅度显著,分别为258.84%和595.91%。
-
关键词:
- 直接布雷顿循环 /
- 氦氙混合气体 /
- 冷却剂丧失事故(LOCA) /
- 系统仿真程序
Abstract: In order to avoid the high risk and harm caused by the loss of coolant accident (LOCA) in the reactor system, the developed LOCA analysis code for helium-xenon cooled reactor system was used to simulate a variety of LOCA transient conditions, and the system transient characteristics, volume filling influence characteristics, load following failure influence characteristics, break location influence characteristics and break size influence characteristics were analyzed. The results show that the system pressure and mass flow rate decrease rapidly after the LOCA. Volume filling can alleviate LOCA, reducing the rate of mass flow rate decline and the rate of reactor outlet temperature rise by 77.15% and 90.27%, respectively. Both the constant load and the break at high pressure have a negative impact on LOCA, resulting in an increase in the rate of mass flow rate decline by 13.85% and 79.83% respectively, and an increase in the rate of reactor outlet temperature rise by 15.84% and 96.06% respectively. The decrease rates of system pressure and mass flow rate rise with the increase of the break size. Especially between 15 mm and 30 mm of the break size, the flow rate decreases and the reactor outlet temperature increases significantly by 258.84% and 595.91%, respectively. -
表 1 LOCA瞬态工况序列表
Table 1. LOCA Transient Condition Sequence
工况序号 破口尺寸/mm 破口位置 容积系统是否投入 负载状态 1 30 压气机入口 否 负载跟随 2 30 压气机入口 是 负载跟随 3 30 压气机入口 否 负载不变 4 30 压气机出口 否 负载跟随 5 15 压气机入口 否 负载跟随 6 45 压气机入口 否 负载跟随 7 60 压气机入口 否 负载跟随 8 75 压气机入口 否 负载跟随 表 2 系统LOCA分析程序稳态验证
Table 2. Steady State Verification of System LOCA Analysis Code
参数 设计值 计算值 相对误差/% 反应堆入口温度/K 907.00 910.09 0.34 反应堆出口温度/K 1200.00 1208.38 0.70 涡轮出口温度/K 966.30 966.69 0.04 冷却器入口温度/K 553.70 565.12 2.06 压气机入口温度/K 340.00 343.76 1.11 压气机出口温度/K 501.60 502.41 0.16 反应堆入口压力/MPa 1.41 1.41 0 反应堆出口压力/MPa 1.40 1.39 −0.71 涡轮出口压力/MPa 0.73 0.72 −1.37 冷却器入口压力/MPa 0.70 0.69 −1.43 压气机入口压力/MPa 0.67 0.68 1.49 压气机出口压力/MPa 1.41 1.43 1.42 循环质量流量/(kg·s−1) 11.20 11.20 0 压气机增压比 2.11 2.10 −0.47 涡轮膨胀比 1.91 1.92 0.47 表 3 LOCA瞬态特性分析与验证案例的初始稳态条件差异分析表
Table 3. Initial Steady State Conditions Difference Analysis Table of LOCA Analysis and Validation Cases
参数 LOCA分析 验证案例 比例 参数 LOCA分析 验证案例 差值 反应堆功率/MW 10.00 1.75 5.71 反应堆入口压力/MPa 2.00 1.41 0.59 涡轮功率/MW 8.49 1.49 5.70 反应堆出口压力/MPa 1.95 1.39 0.56 压气机功率/MW 5.45 0.95 5.73 涡轮出口压力/MPa 0.97 0.72 0.25 冷却器功率/MW 7.00 1.22 5.73 冷却器入口压力/MPa 0.93 0.69 0.24 回热器功率/MW 13.58 2.37 5.73 压气机入口压力/MPa 0.92 0.68 0.24 循环质量流量/(kg·s–1) 63.98 11.20 5.71 压气机出口压力/MPa 2.02 1.43 0.59 -
[1] YU J C. Accident and safety analysis[M]//YU J C. Marine Nuclear Power Technology. Singapore: Springer, 2020: 341-360. [2] LI Z G, SUN J, LIU M L, et al. Design of a hundred-kilowatt level integrated gas-cooled space nuclear reactor for deep space application[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2020, 361: 110569. doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2020.110569 [3] LU D G, DING H, SUI D, et al. Safety analysis of a supercritical carbon dioxide cooled reactor system coupled with Brayton cycle under loss-of-coolant accident[J]. Progress in Nuclear Energy, 2023, 161: 104718. doi: 10.1016/j.pnucene.2023.104718 [4] 张元东. 超临界二氧化碳反应堆运行与安全特性研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学,2021: 125-131. [5] 孟涛. 700 kWe气冷空间反应堆特性分析及系统瞬态特性研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学,2020: 126-128. [6] QIN H, ZHANG R, GUO K L, et al. Thermal-hydraulic analysis of an open-grid megawatt gas-cooled space nuclear reactor core[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2021, 45(8): 11616-11628. doi: 10.1002/er.5329 [7] EL-GENK M S, TOURNIER J M P, GALLO B M. Dynamic simulation of a space reactor system with closed brayton cycle loops[J]. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 2010, 26(3): 394-406. doi: 10.2514/1.46262 [8] MING Y, LIU K, ZHAO F L, et al. Dynamic modeling and validation of the 5 MW small modular supercritical CO2 brayton-cycle reactor system[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2022, 253: 115184. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2021.115184 [9] MING Y, TIAN R F, ZHAO F L, et al. Control strategies and transient characteristics of a 5MWth small modular supercritical CO2 Brayton-cycle reactor system[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2023, 235: 121302. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2023.121302 [10] 明杨,易经纬,方华伟,等. 直接布雷顿循环气冷反应堆系统运行特性分析[J]. 原子能科学技术,2020, 54(7): 1168-1175. doi: 10.7538/yzk.2020.youxian.0013 [11] 王庚,孙永伟,邓欣. 高压大容积全缠绕气瓶的Workbench ACP参数化结构分析[J]. 材料开发与应用,2023, 38(3): 73-76. [12] 王庚,孙永伟,邓欣. 高压大容积碳纤维全缠绕气瓶的设计研究[J]. 材料开发与应用,2023, 38(2): 63-66,83. [13] 章静,田文喜,朱大欢,等. 超临界流体的泄压过程研究[J]. 原子能科学技术,2015, 49(3): 440-446. doi: 10.7538/yzk.2015.49.03.0440 [14] WANG X B, ZHAO F L, HE Y H, et al. Development and verification of helium–xenon mixture cooled small reaction system[J]. Progress in Nuclear Energy, 2023, 160: 104679. doi: 10.1016/j.pnucene.2023.104679 -





 下载:
下载: