Research on Intelligent Accident Diagnosis Model of Nuclear Reactor Coolant System
-
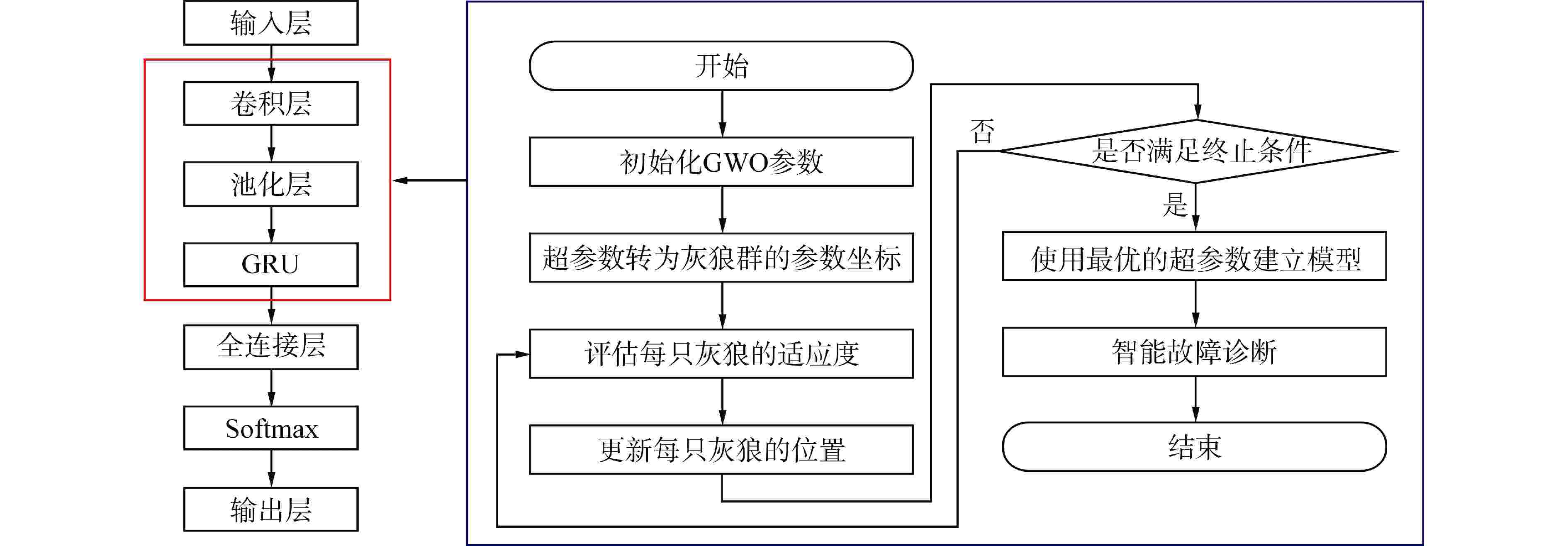
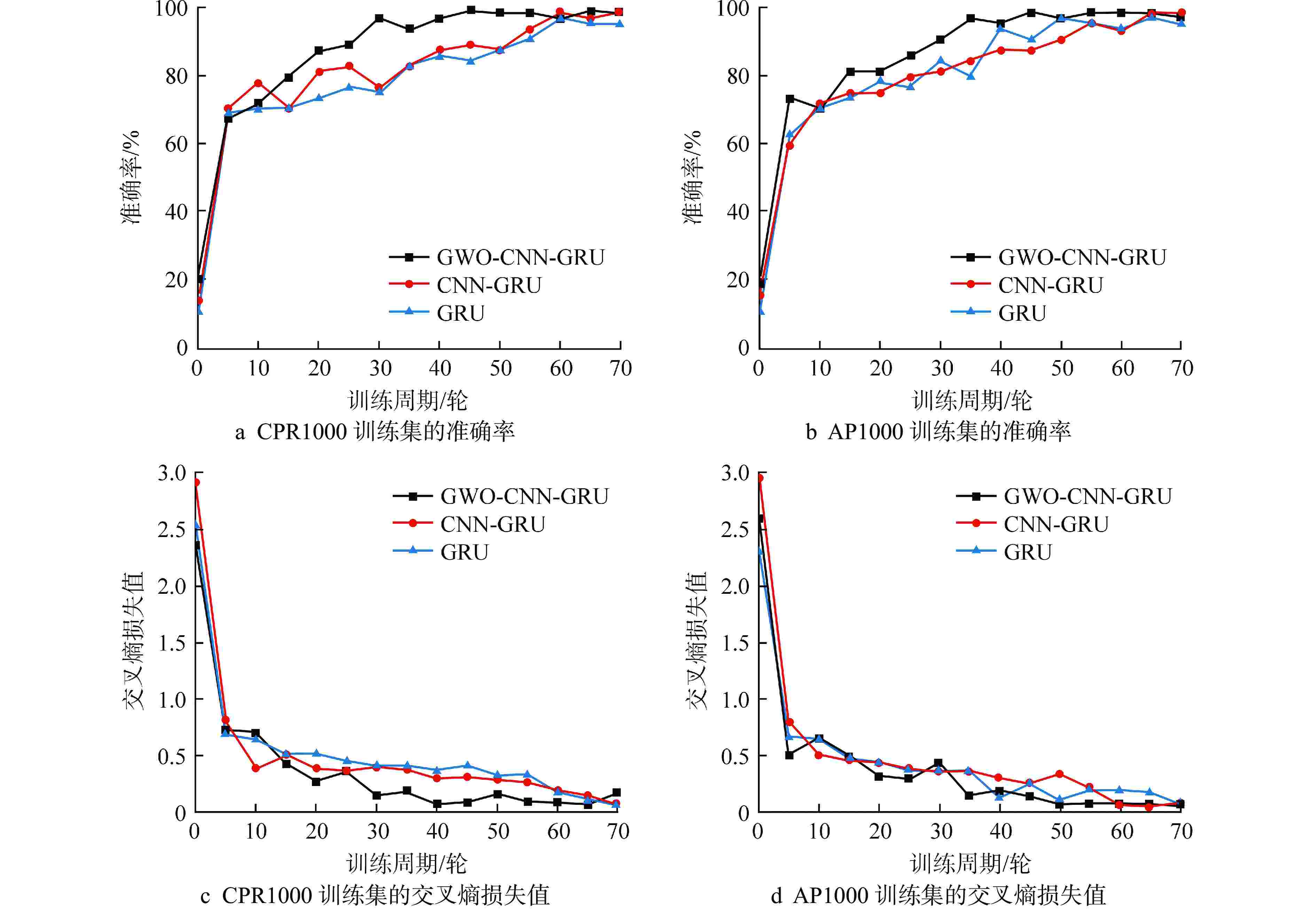
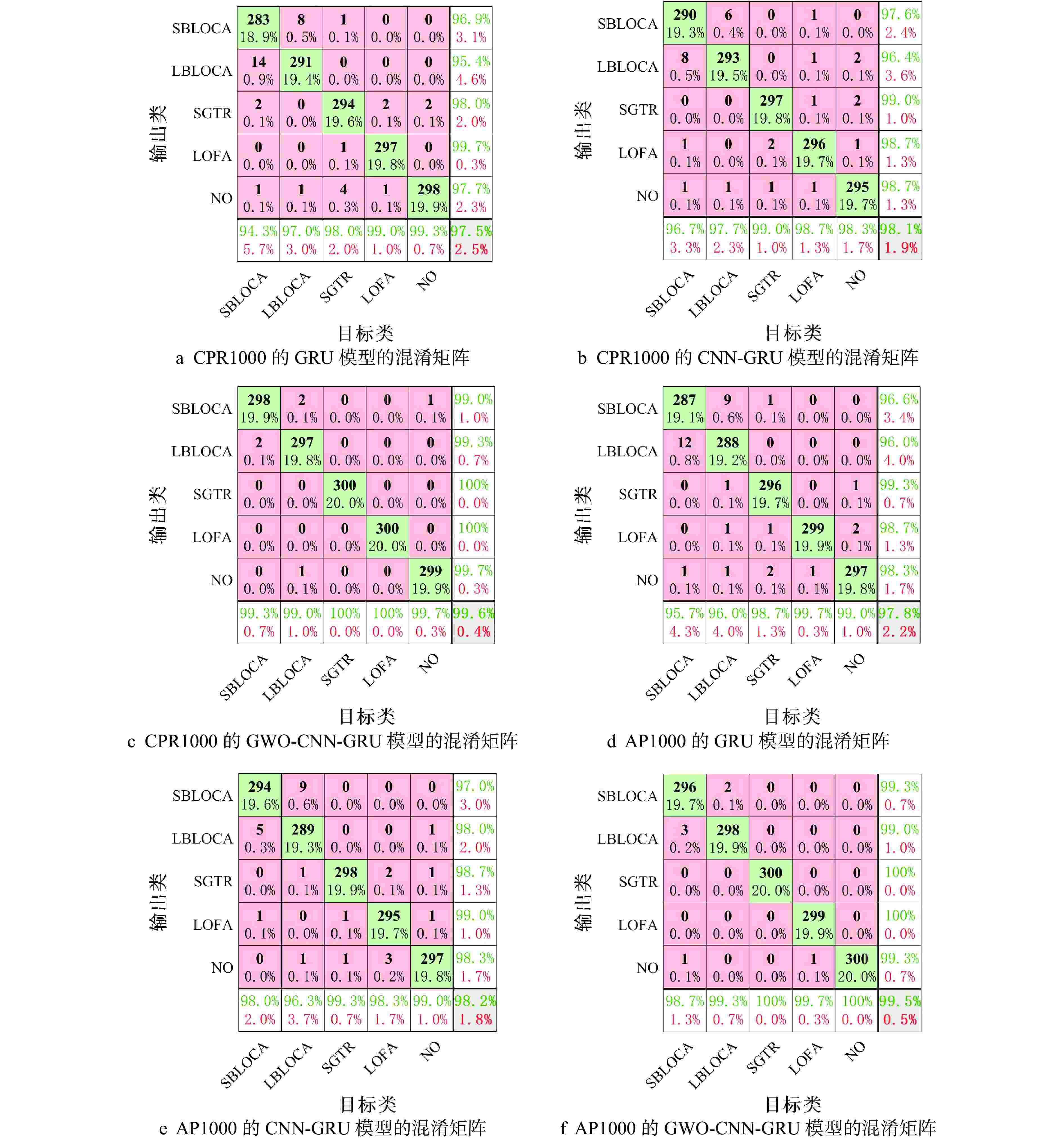
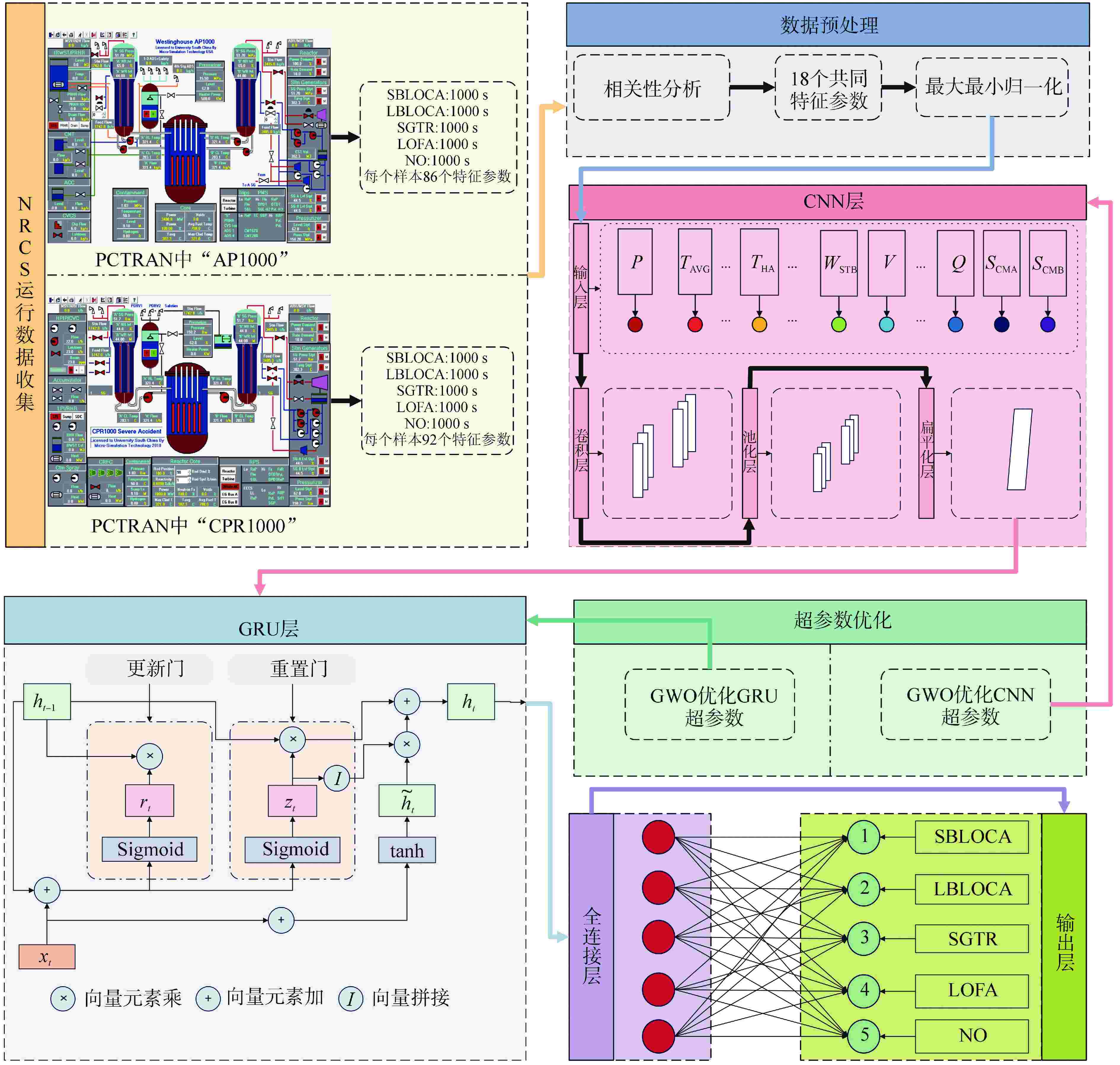
摘要: 尽管人工智能技术在核电厂的事故诊断领域中已被广泛应用,但传统模型存在诊断准确性不足、泛化性较弱等缺陷,难以满足核反应堆冷却剂系统(NRCS)对于事故诊断的高要求。本研究建立了一种NRCS智能事故诊断新模型。首先,为提高模型事故诊断的准确性,应用了卷积神经网络(CNN)和门控循环单元(GRU),结合CNN强大的特征提取能力和GRU高效的时序数据分类能力,建立了NRCS事故诊断模型(CNN-GRU模型);其次,为提高模型的泛化性,应用灰狼优化(GWO)算法,在CNN-GRU模型中自适应优化超参数,建立了NRCS智能事故诊断模型(GWO-CNN-GRU模型);最后,为验证所提出模型的性能,本研究以核电厂仿真与严重事故分析仪(PCTRAN)中的NRCS为研究对象,模拟测试了1 种正常工况和4 种典型事故工况的诊断过程。结果显示,在CPR1000堆型的NRCS测试集上,所提出模型的事故诊断平均准确率为99.6%,相较于GRU和CNN-GRU模型分别提高了2.1%和1.5%;同时,在AP1000堆型的NRCS测试集上,所提出模型的事故诊断平均准确率为99.5%,相较于其他两种模型分别提高了1.7%和1.3%。因此,本文提出的模型在准确性和泛化性方面均表现出优异性能,为NRCS智能事故诊断提供了重要参考。
-
关键词:
- 核反应堆冷却剂系统(NRCS) /
- 智能事故诊断 /
- 卷积神经网络(CNN) /
- 门控循环单元(GRU) /
- 灰狼优化(GWO)算法
Abstract: Although artificial intelligence technology has been extensively employed in the field of accident diagnosis for nuclear power plants, conventional models often suffer from shortcomings such as insufficient accuracy and poor generalizability, which fail to meet the stringent requirements for accident diagnosis of the nuclear reactor coolant system (NRCS). This study establishes a new intelligent accident diagnosis model for NRCS. Firstly, to enhance the accuracy of accident diagnosis, an NRCS accident diagnosis model (CNN-GRU) integrating convolutional neural network (CNN) and gated recurrent unit (GRU) is proposed; Firstly, to enhance the diagnostic accuracy of the model, convolutional neural networks (CNN) and gated recurrent unit (GRU) were integrated. The powerful feature extraction capabilities of CNN and the efficient time-series data classification abilities of GRU were combined to establish the NRCS accident diagnosis model (CNN-GRU). Secondly, to enhance the generalizability of the model, the grey wolf optimizer (GWO) algorithm was used to adaptively optimize the hyperparameters within the CNN-GRU model, thereby establishing the NRCS intelligent accident diagnosis model (GWO-CNN-GRU). Finally, to validate the performance of the proposed model, the NRCS in personal computer transient analyzer (PCTRAN) was used as the object of study, and the diagnostic process of one normal operating condition and four typical accident conditions was simulated. The results demonstrated that the proposed model achieved an average accident diagnosis accuracy of 99.6% on the NRCS test set for the CPR1000 reactor type, which is an improvement of 2.1% and 1.5% compared to the GRU and CNN-GRU models, respectively; Similarly, on the NRCS test set for the AP1000 reactor type, the proposed model achieved an average accident diagnosis accuracy of 99.5%, representing an increase of 1.7% and 1.3% over the other two models, respectively. Therefore, the model proposed in this paper demonstrates superior performance in terms of accuracy and generalizability, providing a valuable reference for intelligent accident diagnosis of NRCS. -
表 1 特征参数的名称和符号
Table 1. Names and Symbols of Feature Parameters
参数名称及单位 参数符号 反应堆冷却剂系统压力/105 Pa P 反应堆冷却剂系统平均温度/℃ TAVG 热管A温度/℃ THA 热管B温度/℃ THB 冷管A温度/℃ TCA 冷管B温度/℃ TCB 反应堆冷却剂循环A管流量/(t·h−1) WRCA 反应堆冷却剂循环B管流量/(t·h−1) WRCB 蒸汽发生器A管压力/105 Pa PSGA 蒸汽发生器B管压力/105 Pa PSGB 蒸汽发生器A管给水流量/(t·h−1) WFWA 蒸汽发生器B管给水流量/(t·h−1) WFWB 蒸汽发生器A管蒸汽流量/(t·h−1) WSTA 蒸汽发生器B管蒸汽流量/(t·h−1) WSTB 反应堆冷却剂系统液体体积/m−3 V 总热功率/MW Q 环路A过冷裕度的温度/℃ SCMA 环路B过冷裕度的温度/℃ SCMB 表 2 仿真测试的样本数据集
Table 2. Sample Dataset for Simulation Testing
样本类型 运行工况 样本数量 标签型号 标签数量 训练集 SBLOCA 700 1 700 LBLOCA 700 2 700 SGTR 700 3 700 LOFA 700 4 700 NO 700 5 700 测试集 SBLOCA 300 1 300 LBLOCA 300 2 300 SGTR 300 3 300 LOFA 300 4 300 NO 300 5 300 表 3 仿真测试所需条件
Table 3. Conditions for Simulation Test
仿真测试的条件名称 型号参数 仿真设备 联想拯救者R9000P(2023款) 处理器 AMD Ryzen 9 7945HX 显卡 NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4060 操作系统 Windows 11 仿真软件 MATLAB R2023b 表 4 需要优化的超参数及其初始化随机范围
Table 4. Hyperparameters for Optimization and Initialization Random Ranges
超参数 未优化的值 初始化随机范围 优化后的值 卷积核的数量 128 [2, 128] 32 GRU单元的数量 32 [10, 200] 64 学习率 0.0001 [0.0001, 0.1] 0.0006 批大小 64 [16, 128] 32 训练轮数 100 [10, 100] 70 表 5 不同模型5折交叉验证准确率对比
Table 5. Comparison of Accuracy Using 5-Fold Cross-Validation for Different Models
模型5折交叉验证准确率/% 第1折 第2折 第3折 第4折 第5折 平均值 SVM 94.5 93.9 97.3 96.6 97.3 95.92 BPNN 93.2 89.7 94.6 94.2 93.4 93.02 GRU 97.0 97.6 97.5 97.0 97.7 97.36 CNN-GRU 97.9 98.2 98.1 97.8 98.4 98.08 GWO-CNN-GRU 99.3 99.6 99.3 99.5 99.5 99.44 表 6 不同模型5折交叉验证精度对比
Table 6. Comparison of Precision Using 5-Fold Cross-Validation for Different Models
模型5折交叉验证精度/% 第1折 第2折 第3折 第4折 第5折 平均值 SVM 96.4 95.5 95.7 96.9 93.6 95.56 BPNN 94.3 94.0 94.1 93.8 94.2 94.10 GRU 97.2 97.1 96.9 97.4 96.7 97.06 CNN-GRU 97.5 97.2 98.8 97.6 98.6 97.94 GWO-CNN-GRU 98.9 99.4 99.6 99.3 99.6 99.36 表 7 不同模型5折交叉验证召回率对比
Table 7. Comparison of Recall Using 5-Fold Cross-Validation for Different Models
模型5折交叉验证召回率/% 第1折 第2折 第3折 第4折 第5折 平均值 SVM 93.8 94.5 95.4 93.9 93.6 94.24 BPNN 93.3 94.8 93.1 93.6 92.2 93.40 GRU 97.2 96.9 96.4 96.4 97.3 96.84 CNN-GRU 98.2 97.9 98.4 97.8 98.6 98.18 GWO-CNN-GRU 99.1 99.3 99.1 99.2 98.9 99.12 -
[1] 潘军,黎义斌,瞿泽晖,等. 华龙一号主泵卡轴事故工况瞬态过渡过程数值分析[J]. 核动力工程,2024, 45(1): 201-209. [2] GAO Z W, CECATI C, DING S X. A survey of fault diagnosis and fault-tolerant techniques-part I: fault diagnosis with model-based and signal-based approaches[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2015, 62(6): 3757-3767. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2015.2417501 [3] TIAN J L, JIANG Y C, ZHANG J S, et al. High-performance fault classification based on feature importance ranking-XgBoost approach with feature selection of redundant sensor data[J]. Current Chinese Science, 2022, 2(3): 243-251. doi: 10.2174/2210298102666220318100051 [4] 陈志辉,夏虹,刘邈. 核电系统故障诊断专家系统研究[J]. 核动力工程,2005, 26(5): 523-527. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0926.2005.05.023 [5] 张燕,周志伟,董秀臣. 核电厂实时故障诊断专家系统的设计与实现[J]. 原子能科学技术,2006, 40(4): 420-423. [6] OH C H, LEE J I. Real time nuclear power plant operating state cognitive algorithm development using dynamic Bayesian network[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2020, 198: 106879. [7] WU G H, TONG J J, ZHANG L G, et al. Framework for fault diagnosis with multi-source sensor nodes in nuclear power plants based on a Bayesian network[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2018, 122: 297-308. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2018.08.050 [8] ISERMANN R. Model-based fault-detection and diagnosis -status and applications[J]. Annual Reviews in Control, 2005, 29(1): 71-85. doi: 10.1016/j.arcontrol.2004.12.002 [9] BAKHTIARIDOUST M, YADEGAR M, MESKIN N. Data-driven fault detection and isolation of nonlinear systems using deep learning for Koopman operator[J]. ISA Transactions, 2023, 134: 200-211. doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2022.08.030 [10] ZHANG W T, YANG D, WANG H C. Data-driven methods for predictive maintenance of industrial equipment: a survey[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2019, 13(3): 2213-2227. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2019.2905565 [11] AYODEJI A, LIU Y K. Support vector ensemble for incipient fault diagnosis in nuclear plant components[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 2018, 50(8): 1306-1313. doi: 10.1016/j.net.2018.07.013 [12] WANG H, PENG M J, HINES J W, et al. A hybrid fault diagnosis methodology with support vector machine and improved particle swarm optimization for nuclear power plants[J]. ISA Transactions, 2019, 95: 358-371. doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2019.05.016 [13] NAIMI A, DENG J M, SHIMJITH S R, et al. Fault detection and isolation of a pressurized water reactor based on neural network and k-nearest neighbor[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 17113-17121. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3149772 [14] 刘永阔,夏虹,谢春丽,等. BP-RBF神经网络在核电厂故障诊断中的应用[J]. 原子能科学技术,2008, 42(3): 193-199. doi: 10.7538/yzk.2008.42.03.0193 [15] GUO H, HU S, WANG F, et al. A novel method for quantitative fault diagnosis of photovoltaic systems based on data-driven[J]. Electric Power Systems Research, 2022, 210: 108121. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgr.2022.108121 [16] WEN L, LI X Y, GAO L, et al. A new convolutional neural network-based data-driven fault diagnosis method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2018, 65(7): 5990-5998. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2017.2774777 [17] LEE G, LEE S J, LEE C. A convolutional neural network model for abnormality diagnosis in a nuclear power plant[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2021, 99: 106874. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106874 [18] 王天舒,余刃,刘笑凡. 核动力装置运行故障诊断系统设计研究[J]. 核动力工程,2018, 39(2): 176-179. [19] 吴琼,李永飞,李铭洋. 异常数据实时检测方法研究综述[J]. 现代计算机,2022, 28(16): 9-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1423.2022.16.002 [20] 宋群,袁青霞,王俊江. 基于自动机器学习的运动过程心电检测算法[J]. 西北大学学报: 自然科学版,2023, 53(5): 771-781. [21] ZHOU D X. Theory of deep convolutional neural networks: downsampling[J]. Neural Networks, 2020, 124: 319-327. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2020.01.018 [22] 陈雨欣,刘章鑫,刘欣谊,等. 基于机器学习算法的扬州市冬小麦遥感分类提取[J]. 中国农机化学报,2024, 45(8): 154-161,169. [23] 孙超. 基于岭回归的地铁车载设备故障预测[J]. 铁路通信信号工程技术,2024, 21(8): 74-79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4440.2024.08.012 -





 下载:
下载: