Research on Lattice Boltzmann Solution of Generalized Convection Diffusion Equation Based on Physical Fusion Neural Network
-
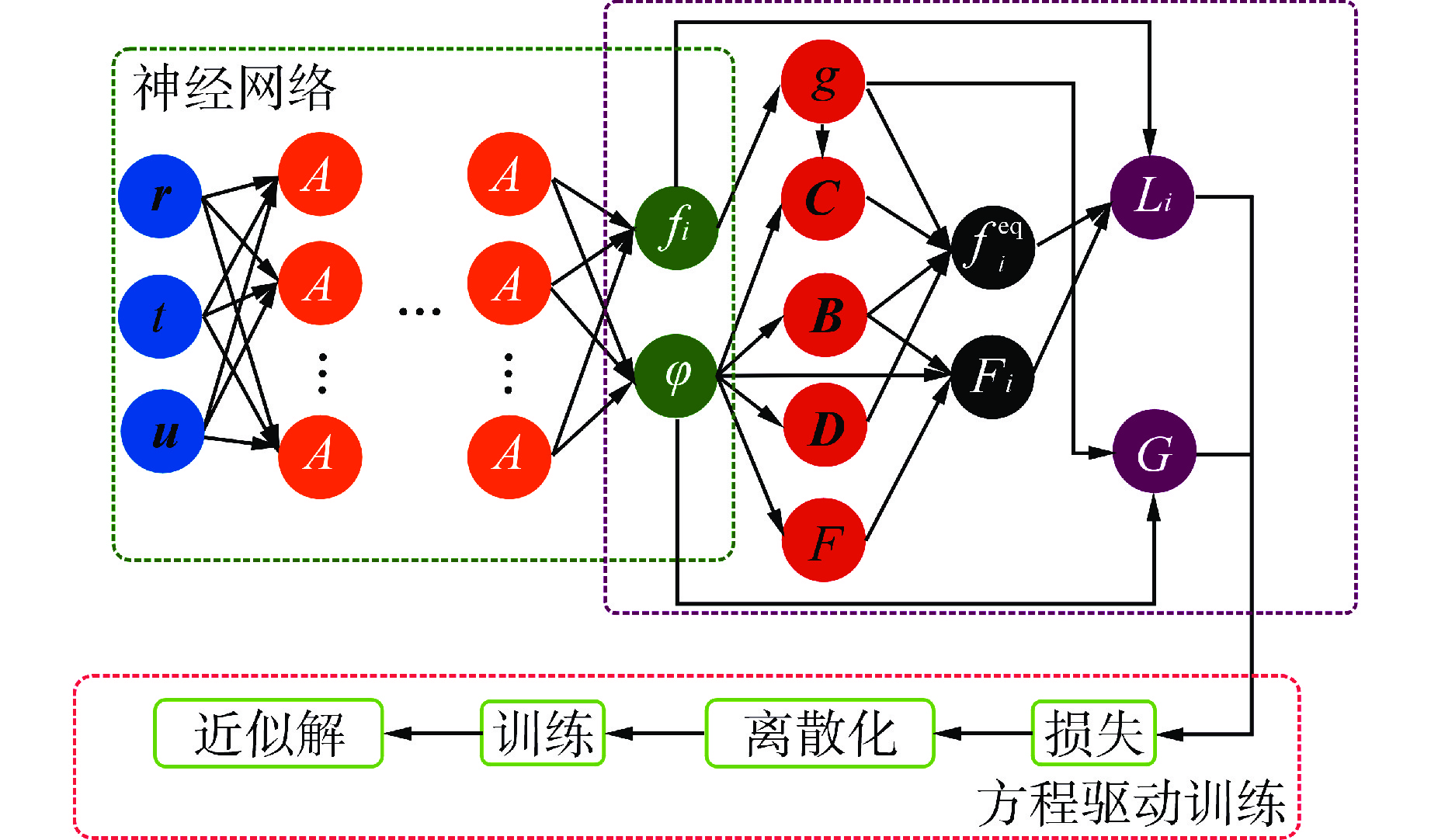
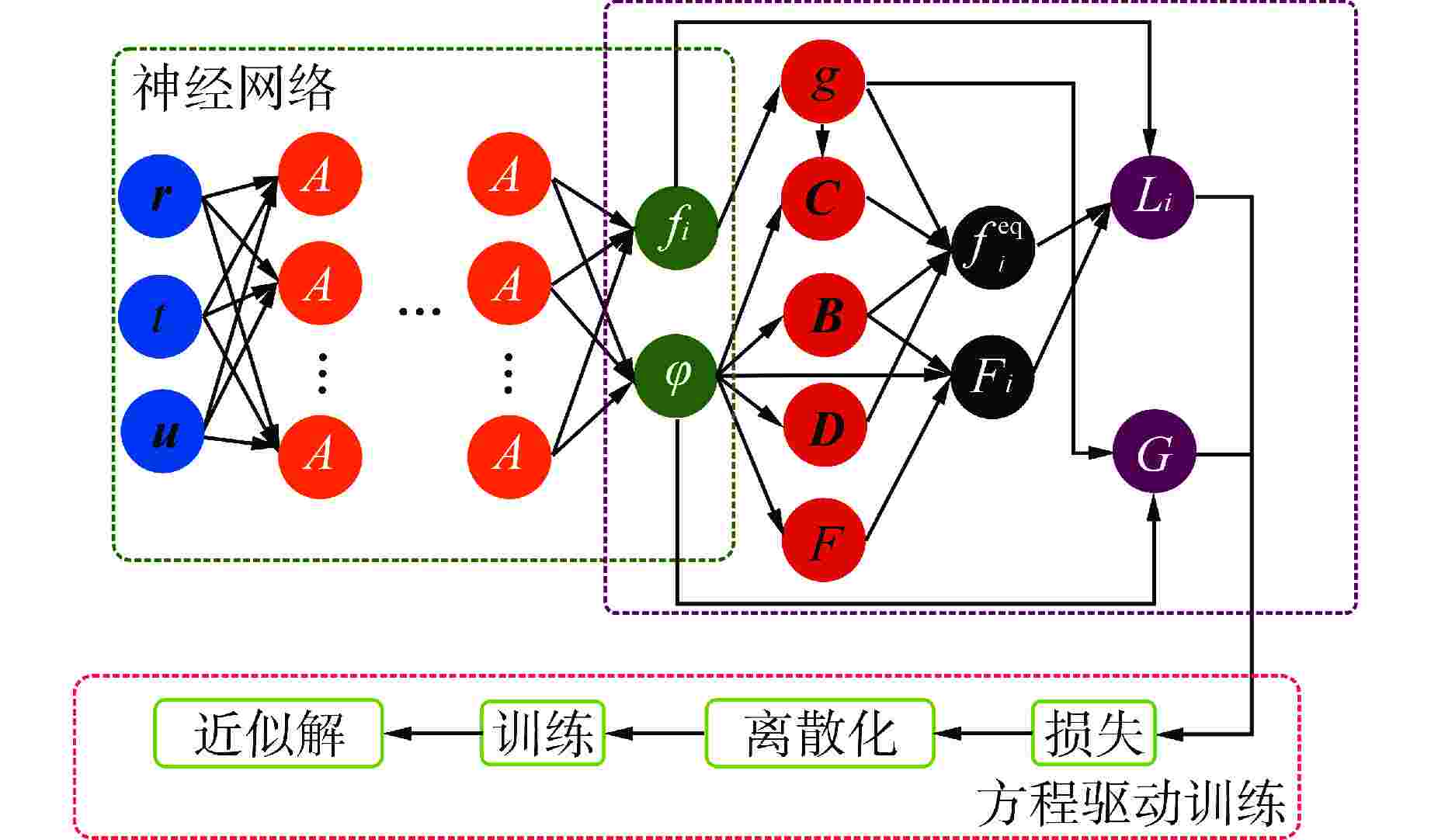
摘要: 为提高深度学习方法的网络复用性,构建一种适应于不同控制方程和不同物性参数条件的深度网络模型,本研究提出了基于物理融合神经网络的格子Boltzmann方法(PFNN-LBM)。在格子Boltzmann框架下建立了不同特征控制方程的统一格式离散速度Boltzmann方程,并使用单一网络的参数化物理信息约束神经网络求解,可以在一次训练后同时求解不同形式和不同物理参数的控制方程。为测试PFNN-LBM的准确性和适应性,选取了四种典型非线性对流扩散方程开展预测分析,包括扩散方程、非线性导热方程、Sine-Gordon方程和Burgers-Fisher方程,同时测试了不同物理参数条件的预测性能并对双群中子扩散问题进行了测试。计算结果表明,所提出的PFNN-LBM可以在一次训练后高精度地求解不同形式和不同物理参数的控制方程。这项工作可以为高效灵活地求解不同类型的方程提供一个新的框架,对于工程应用中的多物理场耦合计算方面可能具有突出优势。
-
关键词:
- 物理信息约束神经网络 /
- 格子Boltzmann /
- 深度学习 /
- 非线性对流扩散方程
Abstract: In order to improve the network reusability of the deep learning method and construct a deep network model suitable for different control equations and different physical parameters, a lattice Boltzmann method based on physical fusion neural network (PFNN-LBM) is proposed in this study. The unified discrete-velocity Boltzmann equation for equations with different characteristics is established under lattice Boltzmann method, and solved using the parameterize physics–informed neural network with a single network. The PFNN-LBM can simultaneously solve governing equations with different forms and different physical parameters within one single training. In order to test the accuracy and adaptability of PFNN-LBM, four types of macro-equations, including diffusion equation, nonlinear heat conduction equation, Sine-Gordon equation and Burgers-Fisher equation, are selected for prediction analysis. At the same time, the prediction performance under different physical parameters and the two-group neutron diffusion equations are tested. The calculation results show that the proposed PFNN-LBM can solve the control equations of different forms and different physical parameters with high accuracy after one training. This work can provide a novel framework for solving different types of equations efficiently and flexibly, and for engineering application, this work may have outstanding advantages in multi-physics coupling calculations. -
表 1 不同方程离散速度Boltzmann参数
Table 1. Discrete Velocity Boltzmann Parameters of Different Equations
参数 扩散
方程非线性
导热方程Sine-Gordon
方程Burgers-Fisher
方程B0 0 0 0 2 C11 0 0 0 36/5 C0 0 0 1 0 D11 1 0 1 1 D0 0 1 0 0 F0 0 0 −1 0 F1 1 1 0 1 F2 0 −1 0 0 F3 0 0 0 −1 g0 1 1 0 1 g1 0 0 1 0 表 2 PFNN-LBM在不同问题预测中的全局L2误差
Table 2. L2 Error of PFNN-LBM in Different Problems
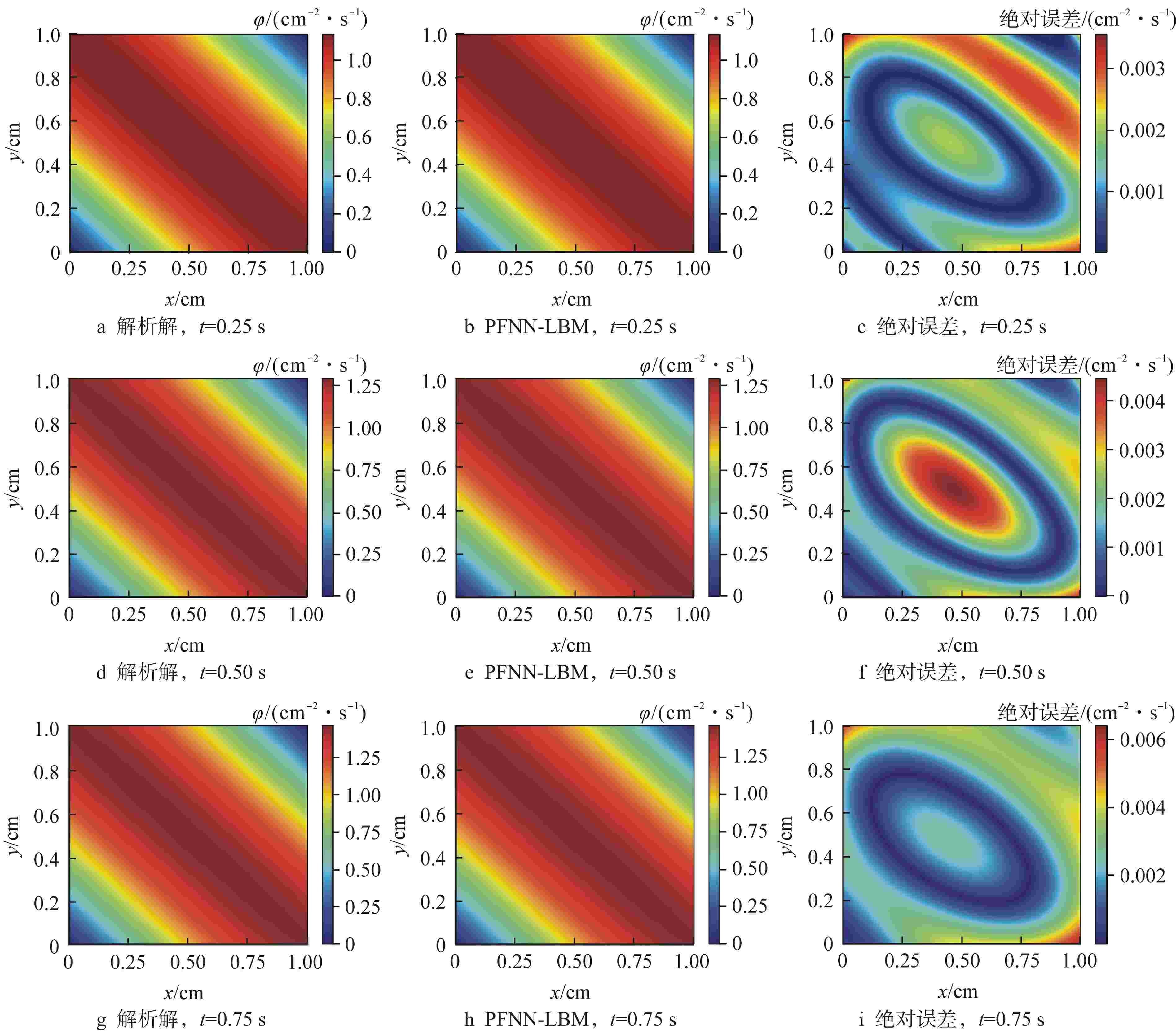
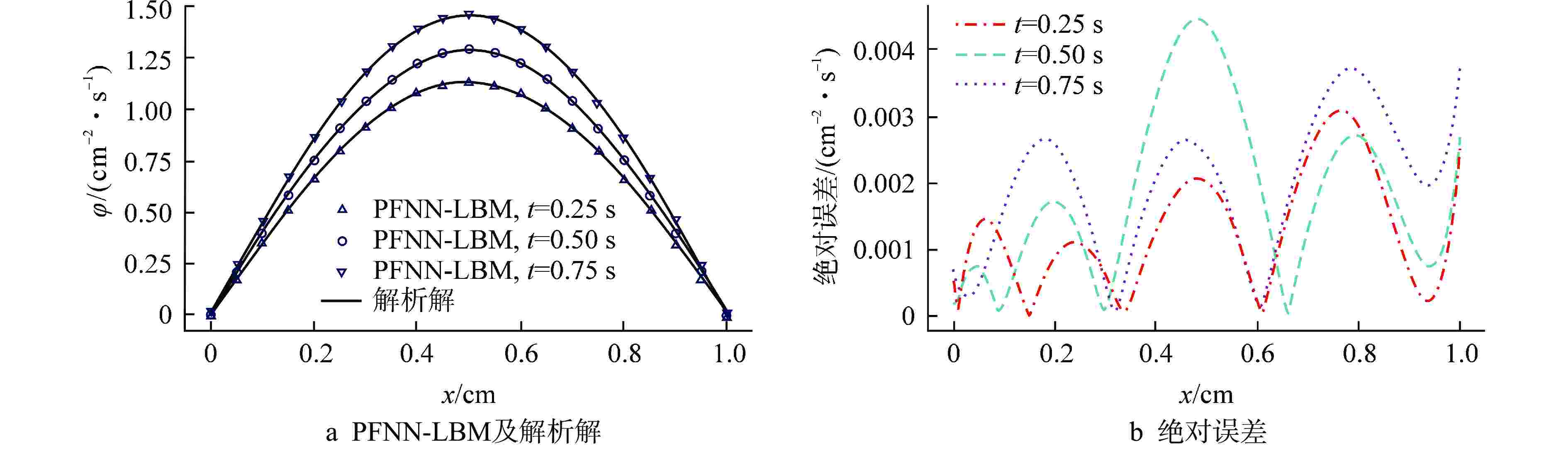
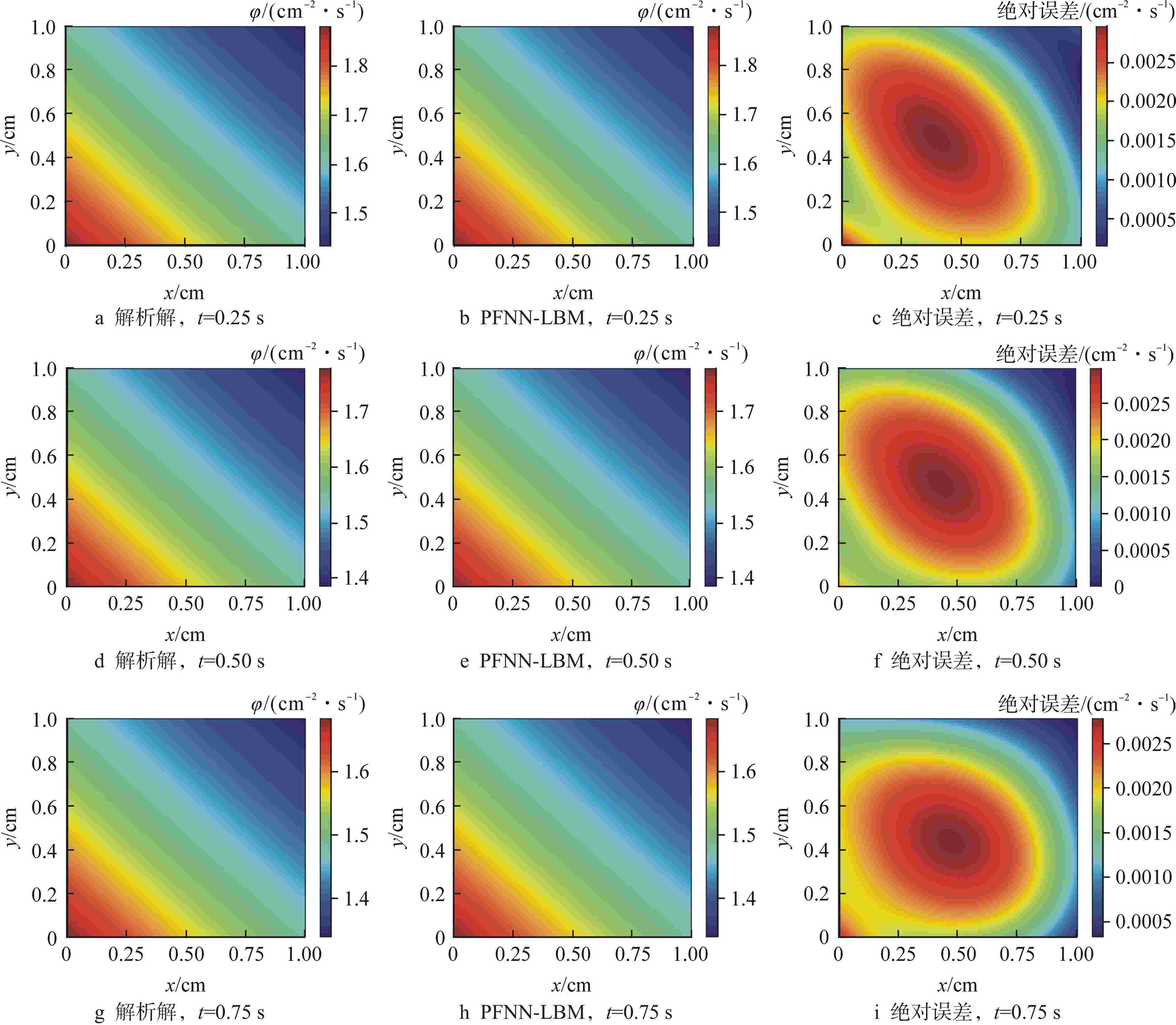
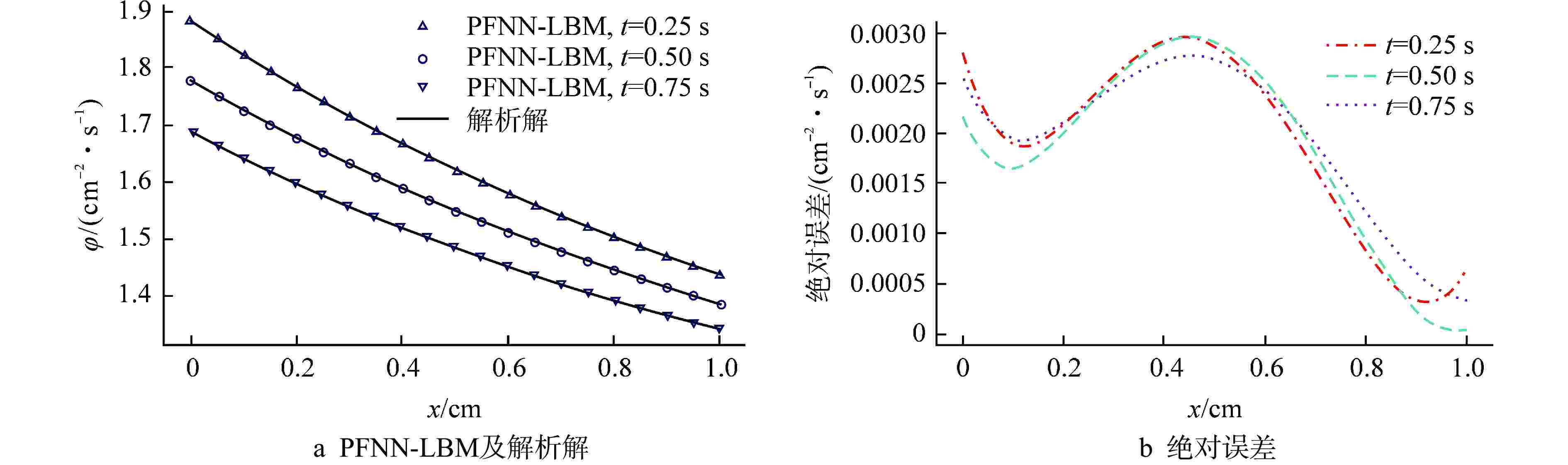
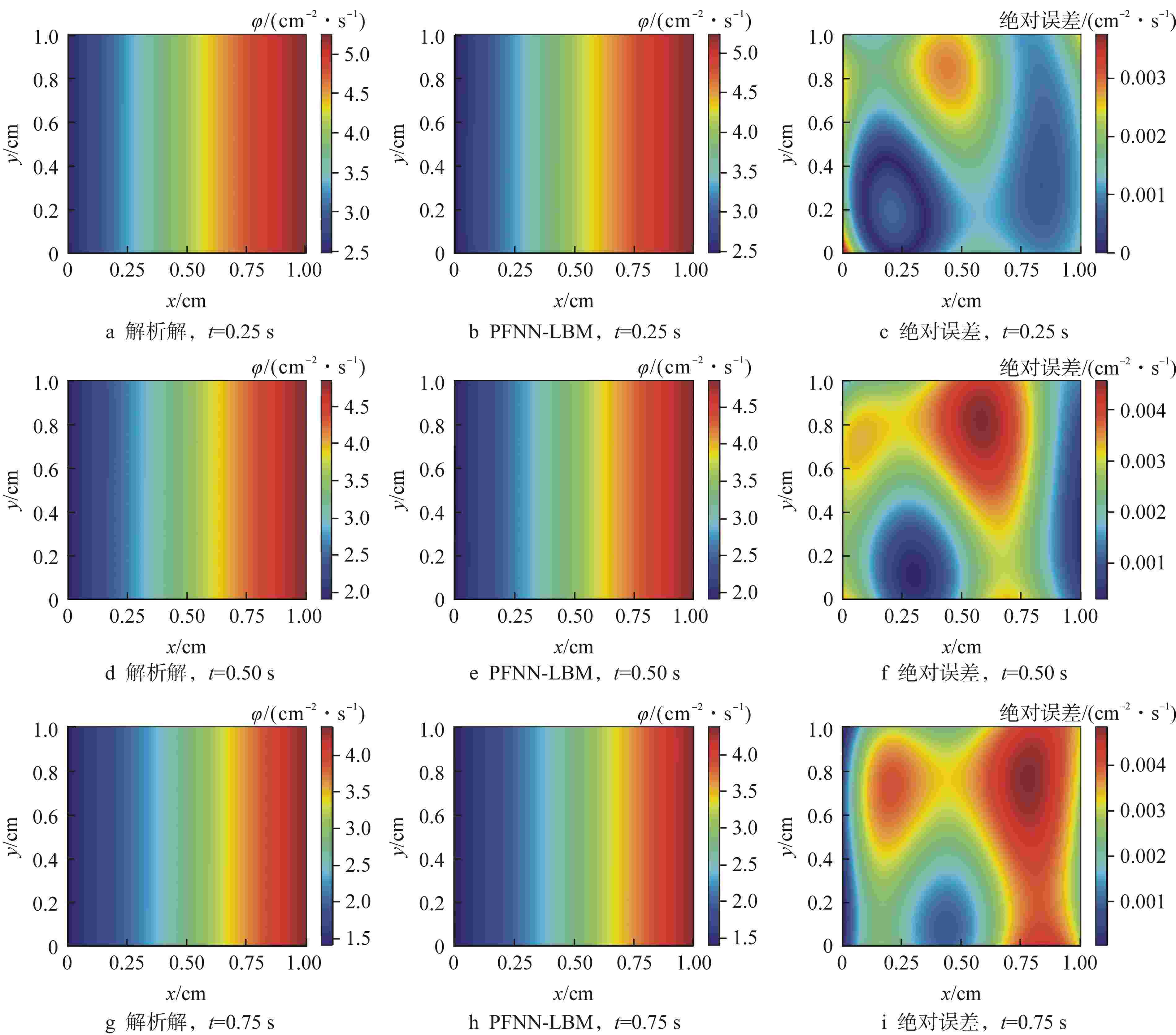
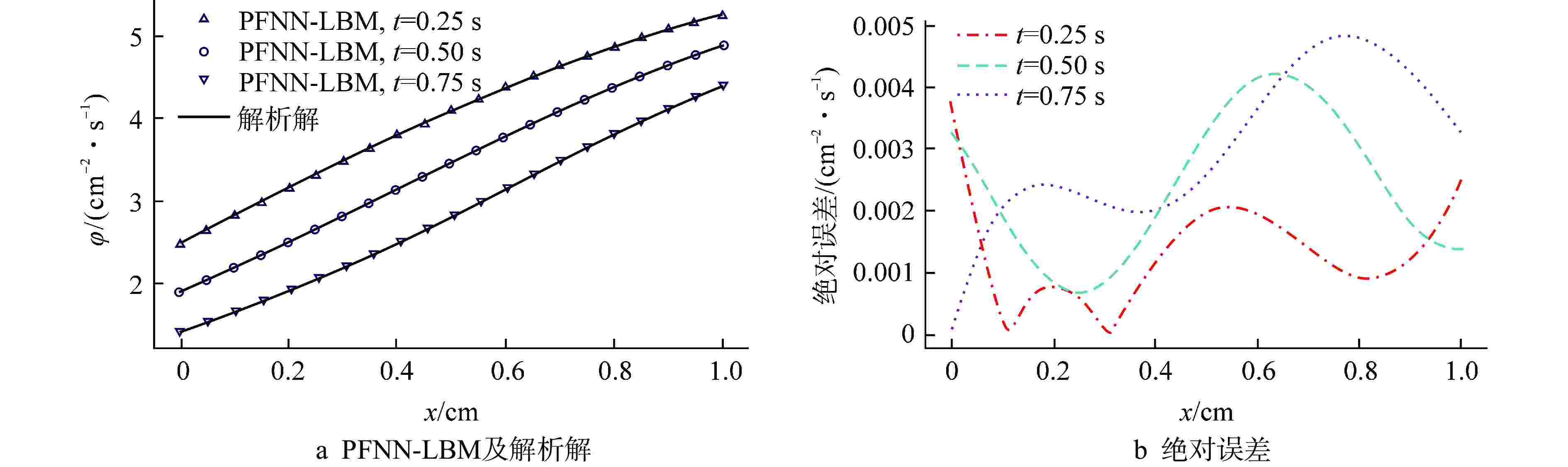
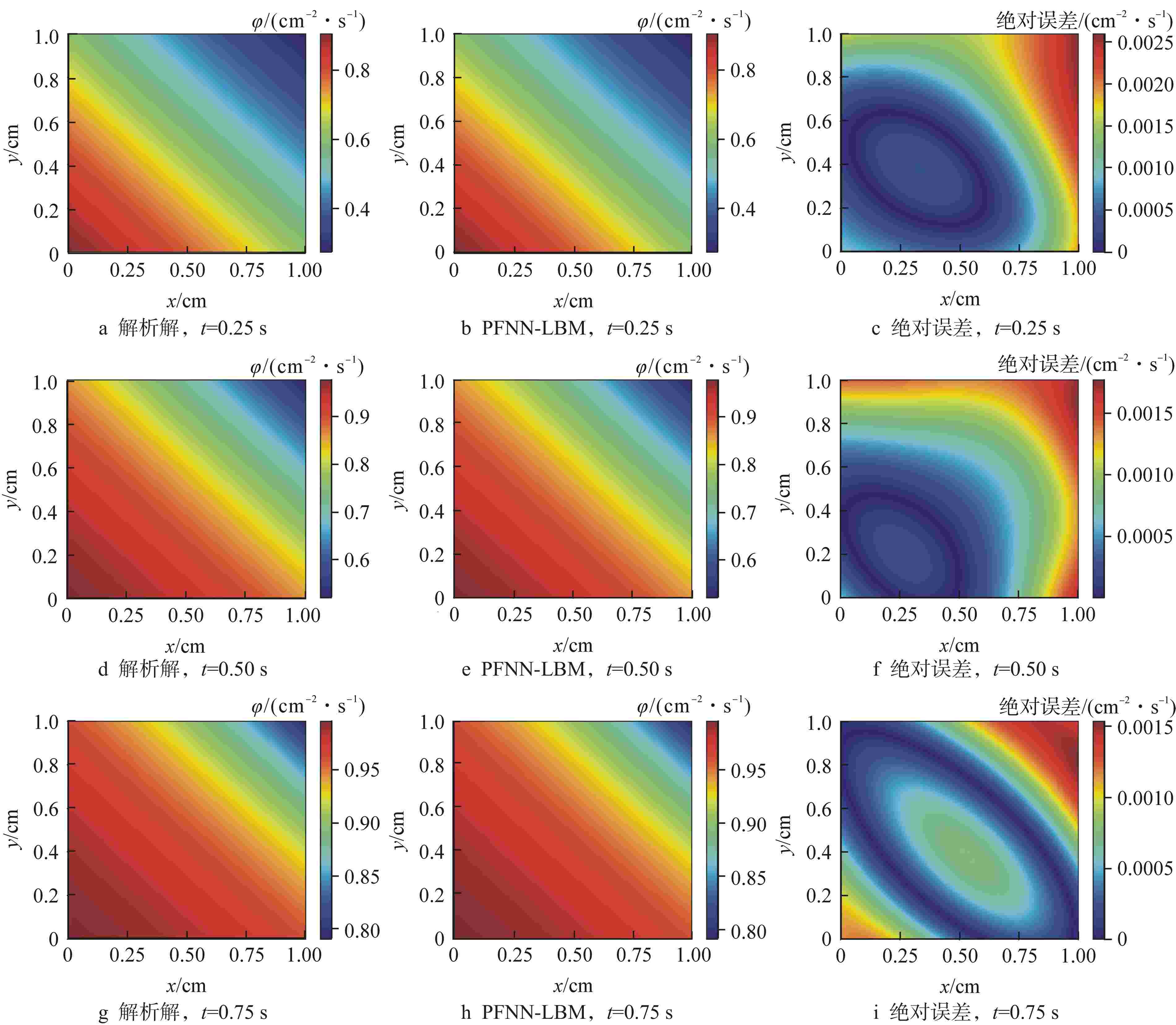
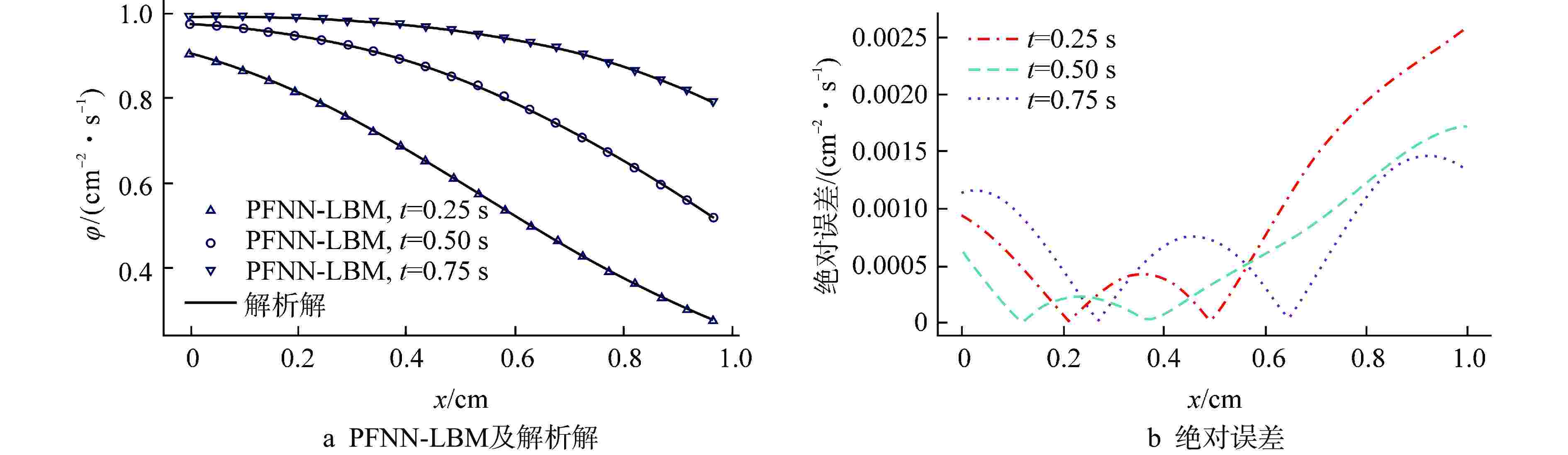
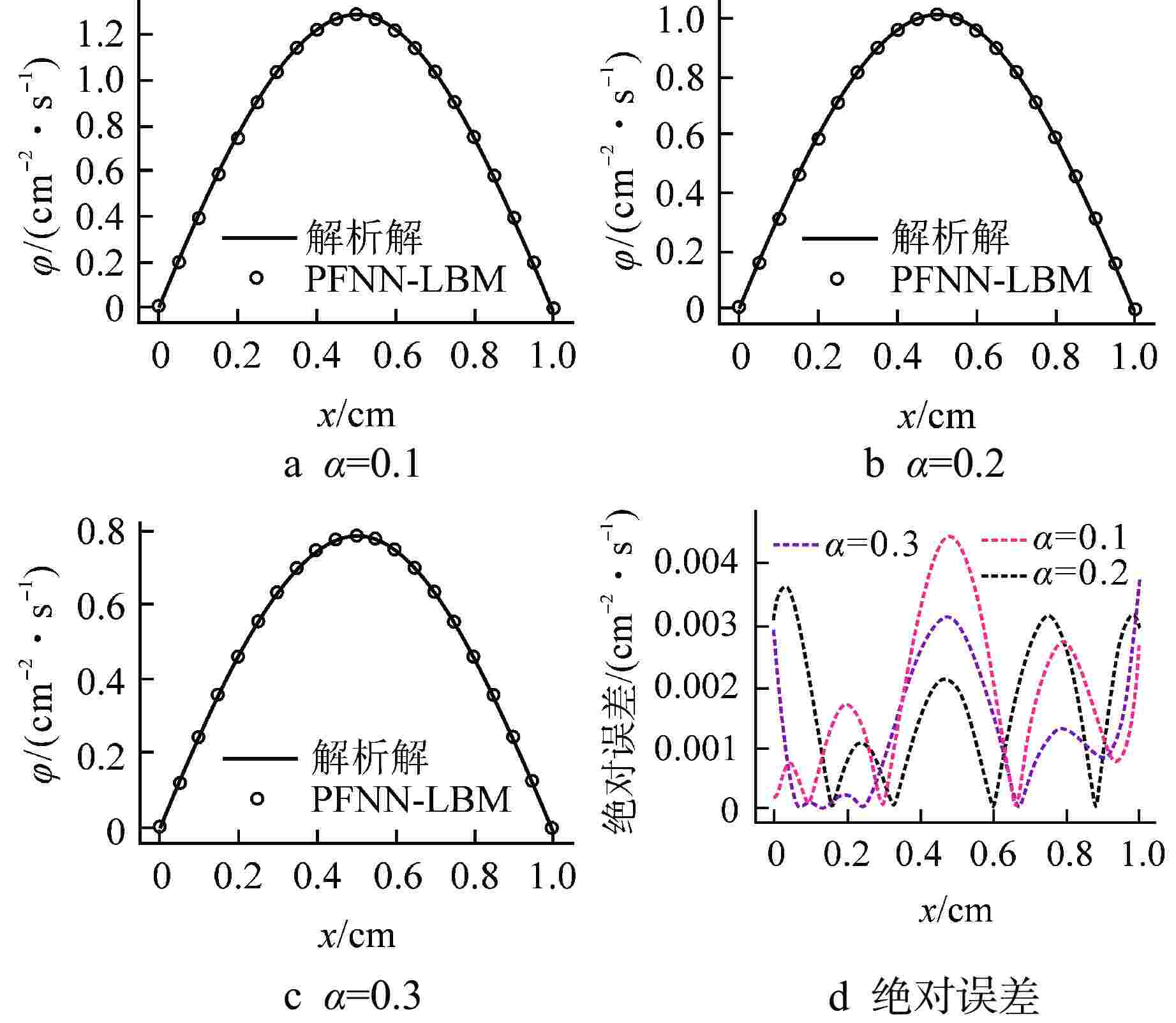
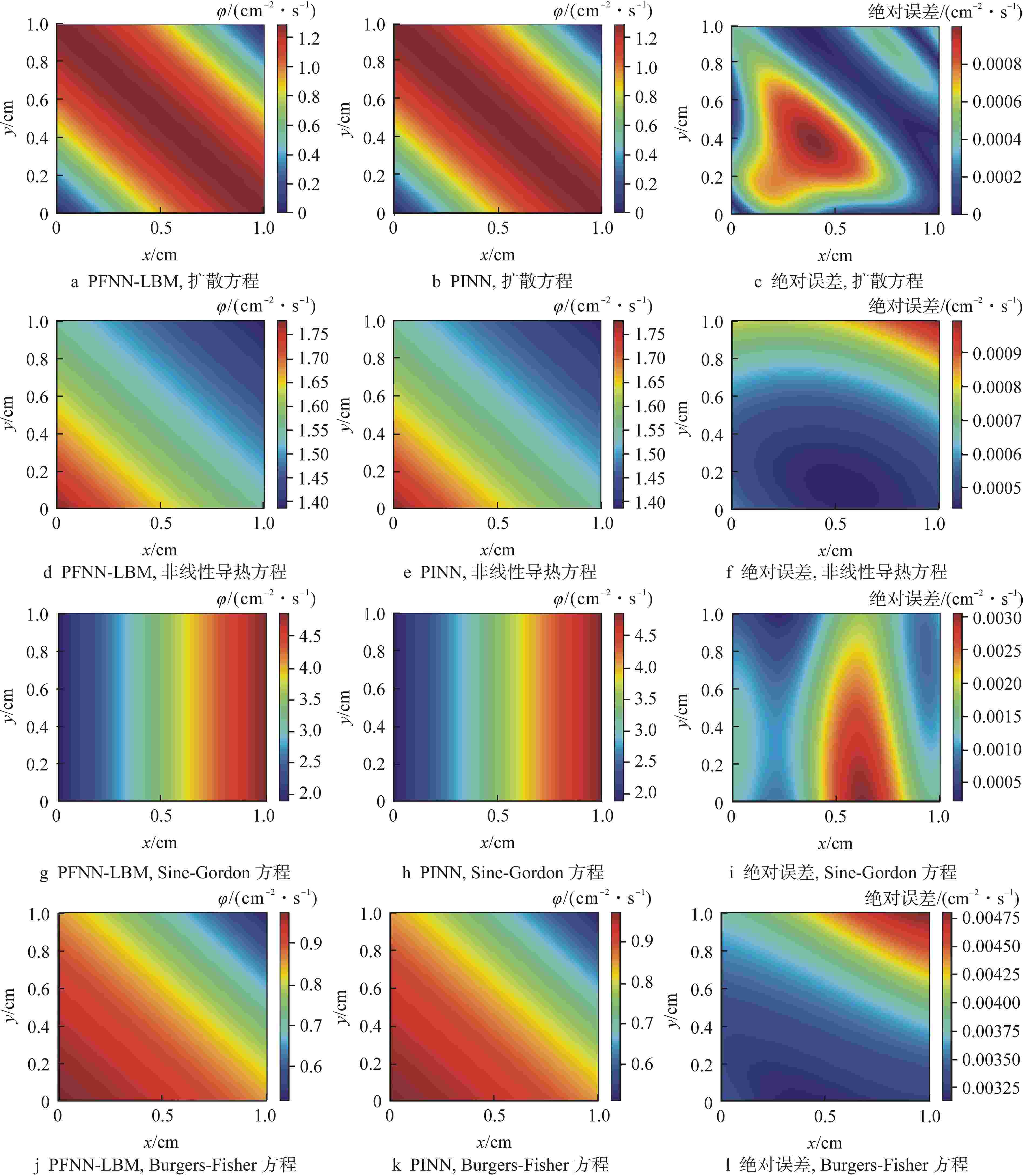
方程类型 全局L2误差/(cm–2·s–1) t=0.25 s t=0.50 s t=0.75 s 扩散方程 1.7×10−3 1.9×10−3 2.0×10−3 非线性导热方程 1.3×10−3 1.3×10−3 1.3×10−3 Sine-Gordon方程 3.6×10−3 7.7×10−3 1.1×10−3 Burgers-Fisher方程 1.8×10−3 9.8×10−3 6.6×10−3 表 3 沿对角线的中子注量率绝对误差对比
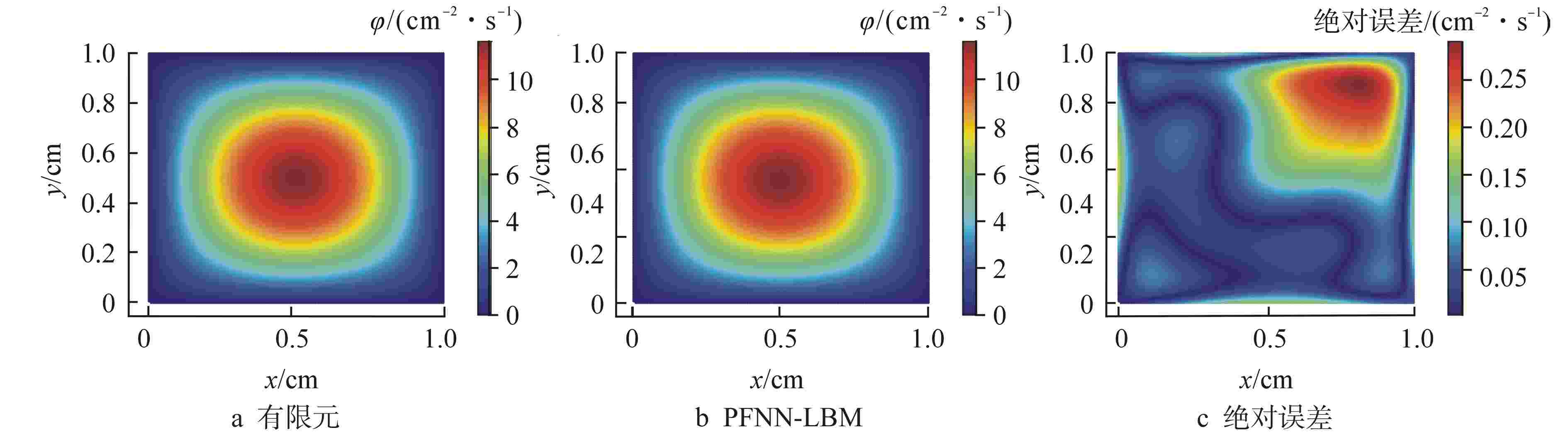
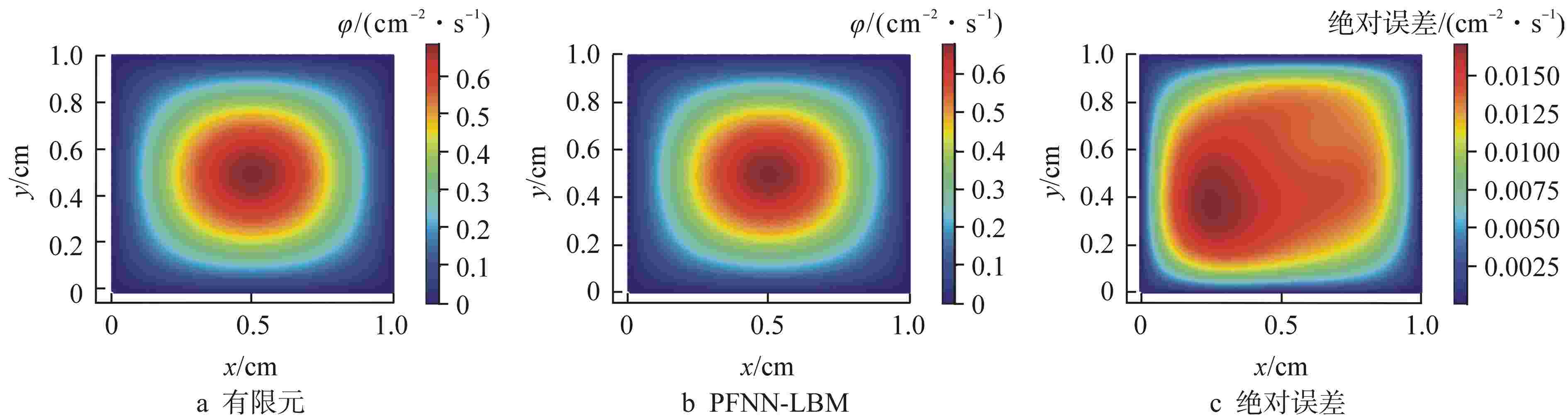
Table 3. Comparison of Absolute Error of Neutron Flux along Diagonal Lines
方程类型 绝对误差对比/(cm–2·s–1) PFNN-LBM PINN 扩散方程 4.35×10−3 9.990×10−4 非线性导热方程 2.96×10−3 4.796×10−3 Sine-Gordon方程 4.46×10−3 9.918×10−4 Burgers-Fisher方程 1.83×10−3 2.452×10−3 -
[1] GUO Z L, ZHENG C G, SHI B C. Discrete lattice effects on the forcing term in the lattice Boltzmann method[J]. Physical Review E, 2002, 65(4): 046308. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.65.046308 [2] HE Y L, LIU Q, LI Q, et al. Lattice Boltzmann methods for single-phase and solid-liquid phase-change heat transfer in porous media: a review[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2019, 129: 160-197. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2018.08.135 [3] CHEN H D, CHEN S Y, MATTHAEUS W H. Recovery of the Navier-Stokes equations using a lattice-gas Boltzmann method[J]. Physical Review A, 1992, 45(8): R5339-R5342. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.45.R5339 [4] CHEN T, WANG L P, LAI J, et al. Inverse design of mesoscopic models for compressible flow using the Chapman-Enskog analysis[J]. Advances in Aerodynamics, 2021, 3(1): 5. doi: 10.1186/s42774-020-00059-2 [5] YANG F, YANG H C, YAN Y H, et al. Simulation of natural convection in an inclined polar cavity using a finite-difference lattice Boltzmann method[J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2017, 31(6): 3053-3065. doi: 10.1007/s12206-017-0549-7 [6] 安博,孟欣雨,杨双骏,等. 非均匀矩形网格的局部网格细化LBM算法研究[J]. 力学学报,2023, 55(10): 2288-2296. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-23-062 [7] 邓书超,宋孝天,钟旻霄,等. 一种求解偏微分方程的动态平衡物理信息神经网络[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学,2024, 54(8): 1843-1859. [8] HE R, CHEN Y F, YANG Z H, et al. Phase field smoothing-PINN: a neural network solver for partial differential equations with discontinuous coefficients[J]. Computers & Mathematics with Applications, 2024, 171: 188-203. [9] ZHU Y H, ZABARAS N, KOUTSOURELAKIS P S, et al. Physics-constrained deep learning for high-dimensional surrogate modeling and uncertainty quantification without labeled data[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2019, 394: 56-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2019.05.024 [10] MENG X H, LI Z, ZHANG D K, et al. PPINN: parareal physics-informed neural network for time-dependent PDEs[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 370: 113250. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2020.113250 [11] WANG Y H, YAN L M, MA Y. Lattice Boltzmann solution of the transient Boltzmann transport equation in radiative and neutron transport[J]. Physical Review E, 2017, 95(6): 063313. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.95.063313 [12] WANG Y H, MA Y, JIANG N B, et al. Finite-difference lattice Boltzmann method for neutral particle transport solving[C]//The 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-30). Kyoto: The Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers,2023. -





 下载:
下载: