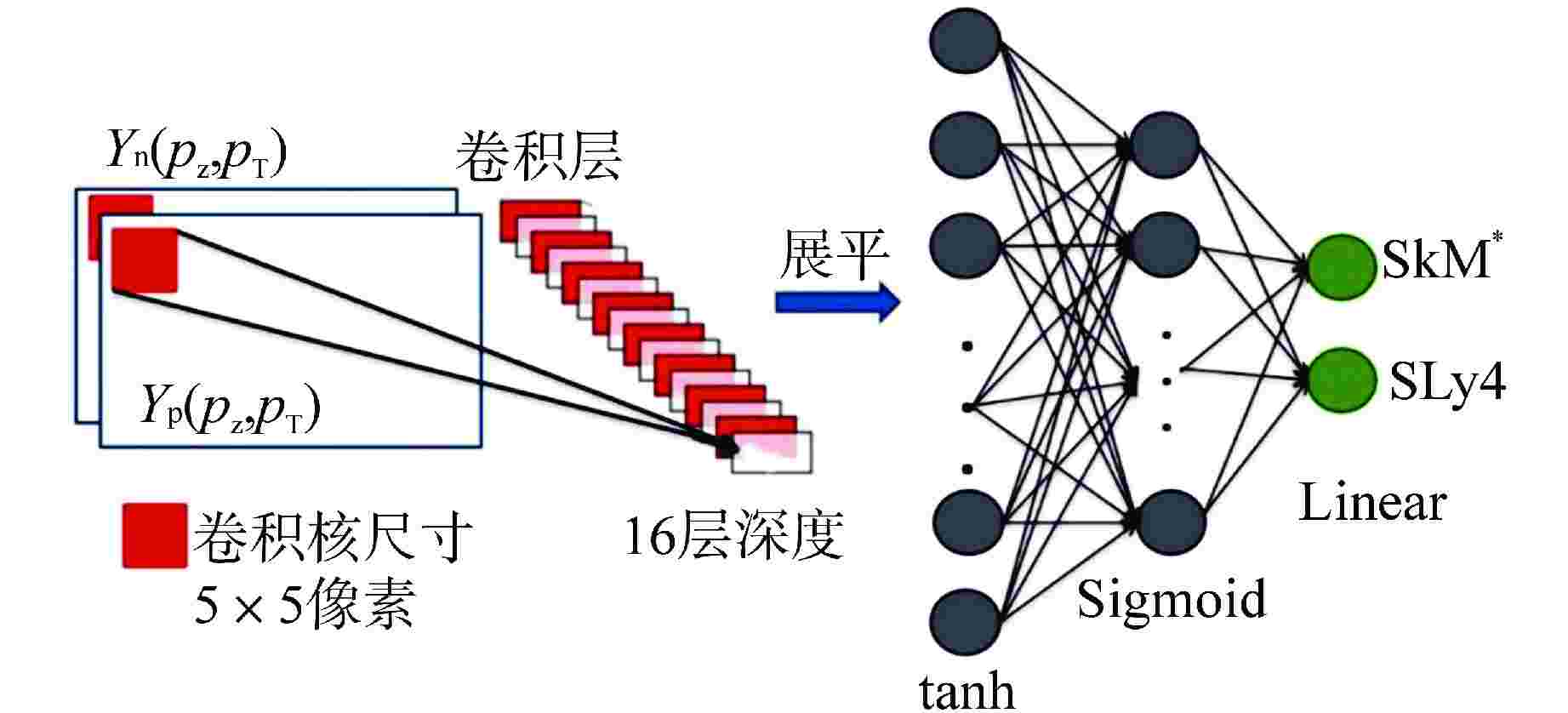
Using Convolutional Neural Networks to Distinguish Nucleon Effective Mass Splitting
-
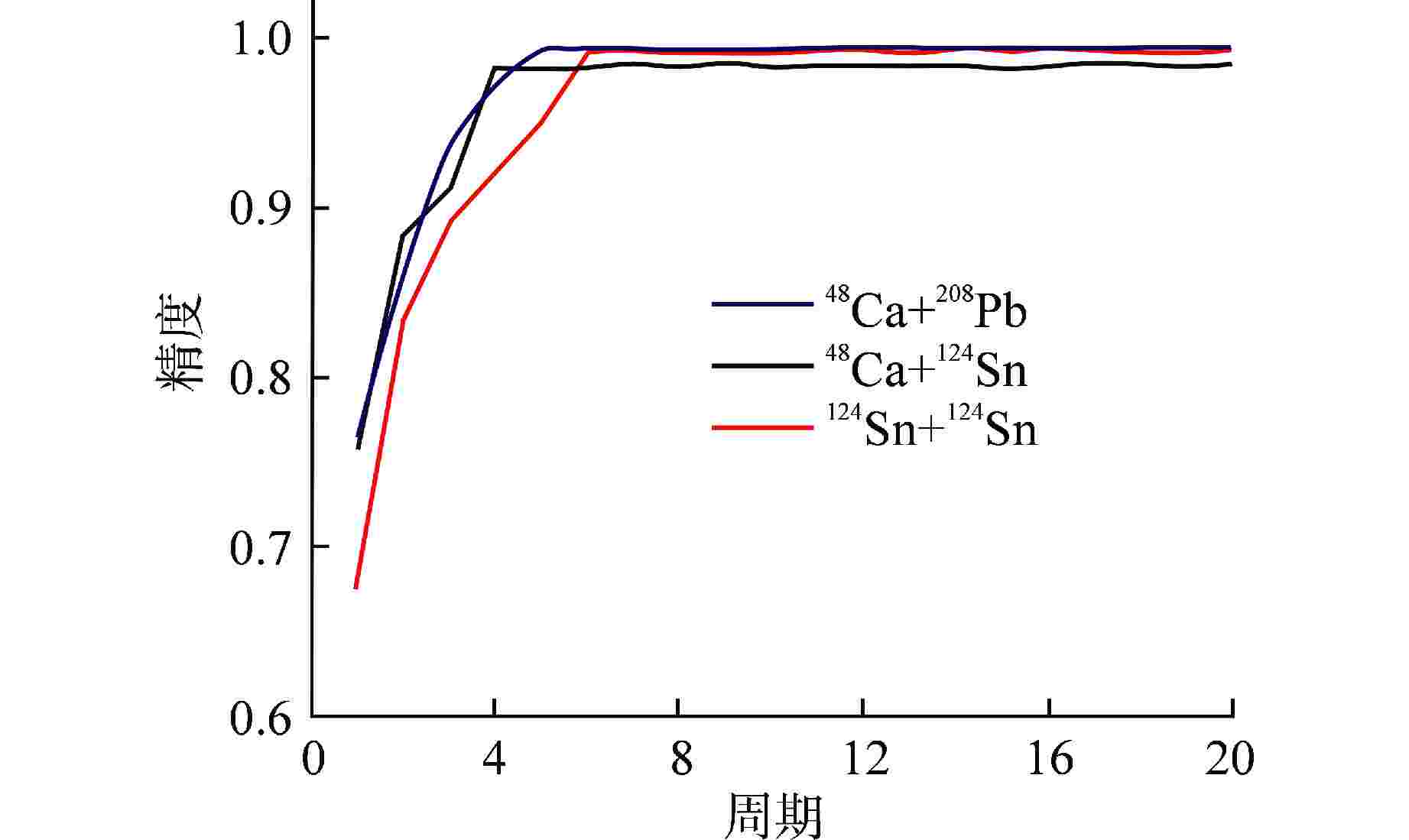
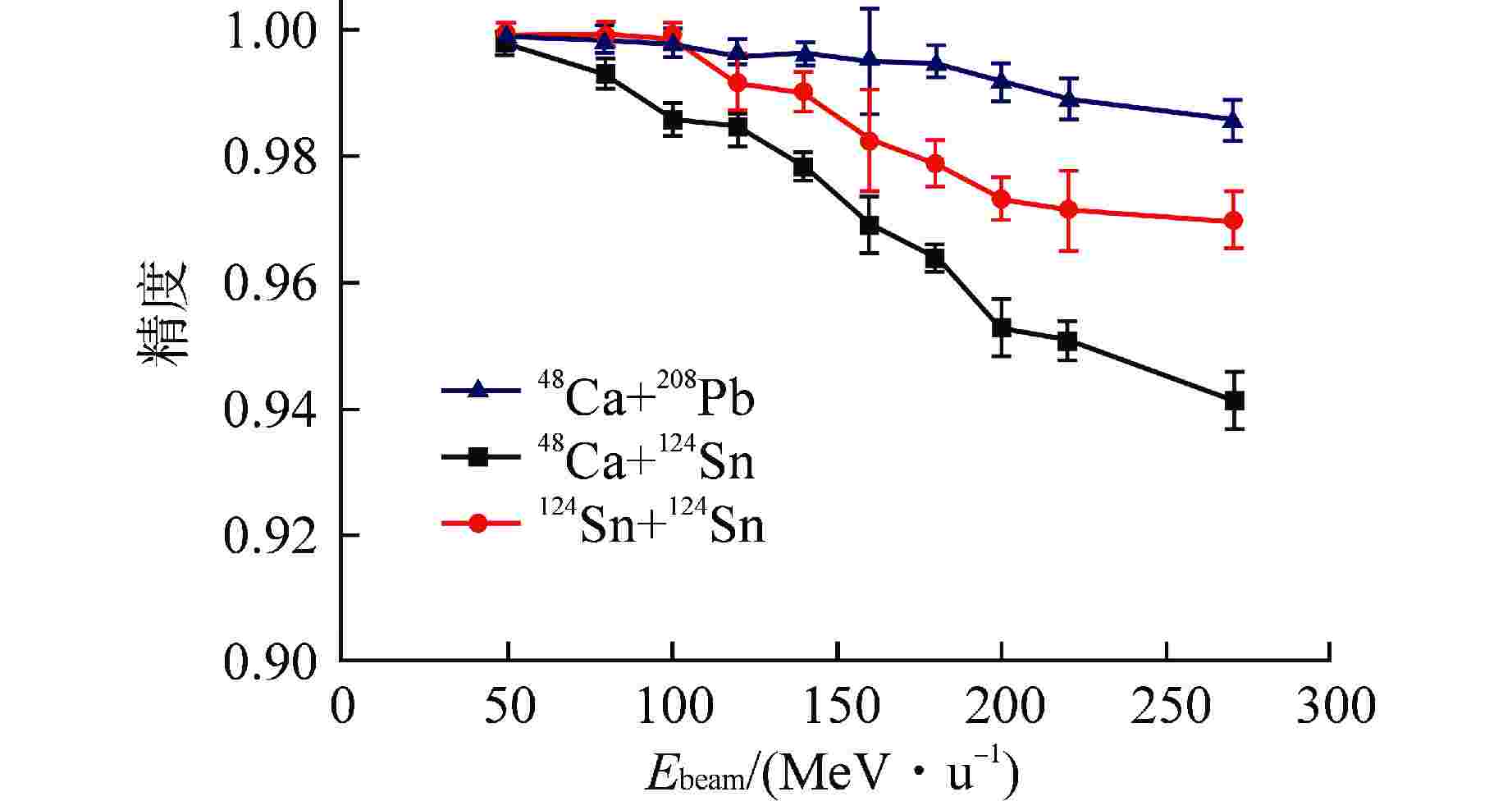
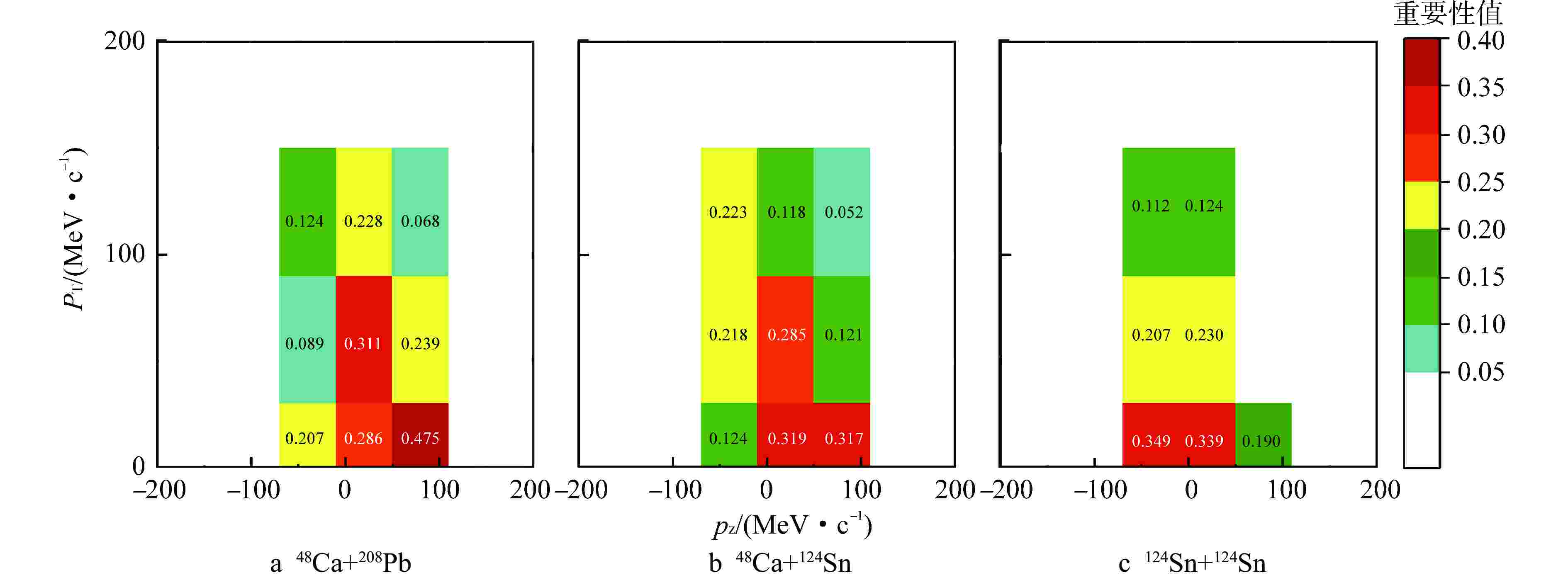
摘要: 为精确分辨核物质中质子与中子有效质量劈裂,本研究提出一种使用双通道输入的卷积神经网络(CNN)确定核子有效质量劈裂的新方法。该方法的主要思想是利用CNN学习理论模型计算质子、中子产额的纵、横动量分布。研究采用的理论模型为改进的量子分子动力学模型(ImQMD),有效相互作用参数为SkM*与SLy4两套参数,分别对应于中子有效质量大于质子有效质量和中子有效质量小于质子有效质量。通过对大量模型数据的学习,建立了利用CNN分辨核子有效质量劈裂的方法。对3套丰中子弹靶系统48Ca+208Pb、48Ca+124Sn和124Sn+124Sn的分析表明,3套系统均在束流能量为50 MeV/u时分辨精度最高,均超过99.5%。在束流能量为270 MeV/u时,3套系统的分辨精度仍均高于93%。通过遮挡法对质子、中子产额的纵、横动量分布图像重要性区域进行了考查,给出了3套系统在50 MeV/u时的重要性图分析,指出二维动量图像中,低横动量区域对于有效质量劈裂的分辨有更大的重要性。
-
关键词:
- 核子有效质量劈裂 /
- 卷积神经网络(CNN) /
- 丰中子系统 /
- 机器学习 /
- 重要性图
Abstract: In order to accurately distinguish the effective mass splitting of protons and neutrons in nuclear matter, a dual-channel-input convolutional neural network (CNN) is proposed for determining the effective mass splitting of nucleons. The main idea of this method is to use CNN learning theoretical model to calculate the longitudinal and transverse momentum distributions of proton and neutron yields. The theoretical model used in this study is an improved quantum molecular dynamics model (ImQMD), and the effective interaction parameters are SkM* and SLy4, which correspond to the effective mass of neutrons being larger than the effective mass of protons and the effective mass of neutrons being smaller than the effective mass of protons respectively. Through the learning of a large number of model data, a method to distinguish the effective mass splitting of nucleons by CNN is established. The analysis of the three sets of neutron-rich target systems—48Ca+208Pb, 48Ca+124Sn, and 124Sn+124Sn—shows that all three systems achieve the highest resolution accuracy at a beam energy of 50 MeV/u, exceeding 99.5%. At a beam energy of 270 MeV/u, the resolution accuracy of all three systems remains above 93%. Using the blocking method, the importance regions of the longitudinal and transverse momentum distribution of proton and neutron yields were investigated. An analysis of the importance maps for the three systems at 50 MeV/u was provided, indicating that the two-dimensional energy spectra of nucleons in the low transverse momentum region are more sensitive to the effective mass splitting of nucleons. -
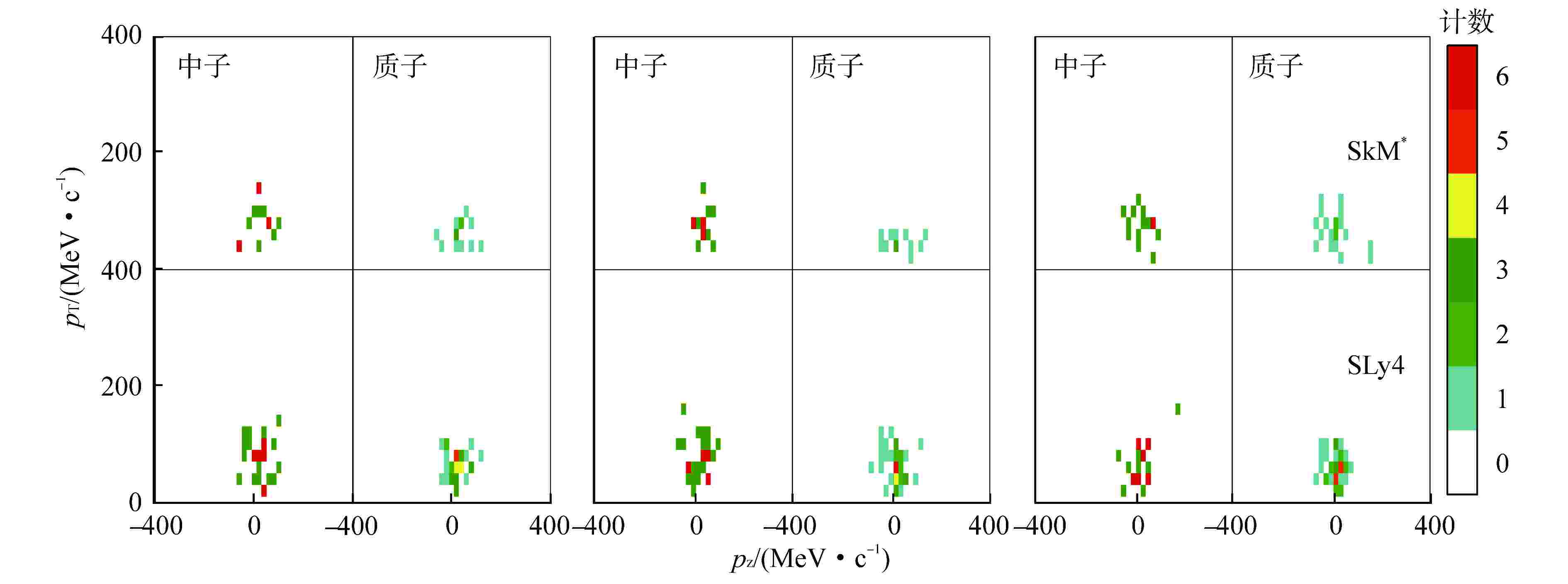
图 4 48Ca+208Pb系统在束流能量Ebeam= 50 MeV/u情况下参数SkM*与SLy4的3个随机碰撞事件的$ {Y}_{\mathrm{p}}({p}_{\mathrm{z}},{p}_{\mathrm{T}}) $和$ {Y}_{\mathrm{n}}({p}_{\mathrm{z}},{p}_{\mathrm{T}}) $图像对比
Figure 4. Comparison of $ {Y}_{\mathrm{p}}({p}_{\mathrm{z}},{p}_{\mathrm{T}}) $ and $ {Y}_{\mathrm{n}}({p}_{\mathrm{z}},{p}_{\mathrm{T}}) $ Maps of Three Pairs of Random Events for Parameters SkM* and SLy4 in System 48Ca+208Pb at a Beam Energy of 50 MeV/u
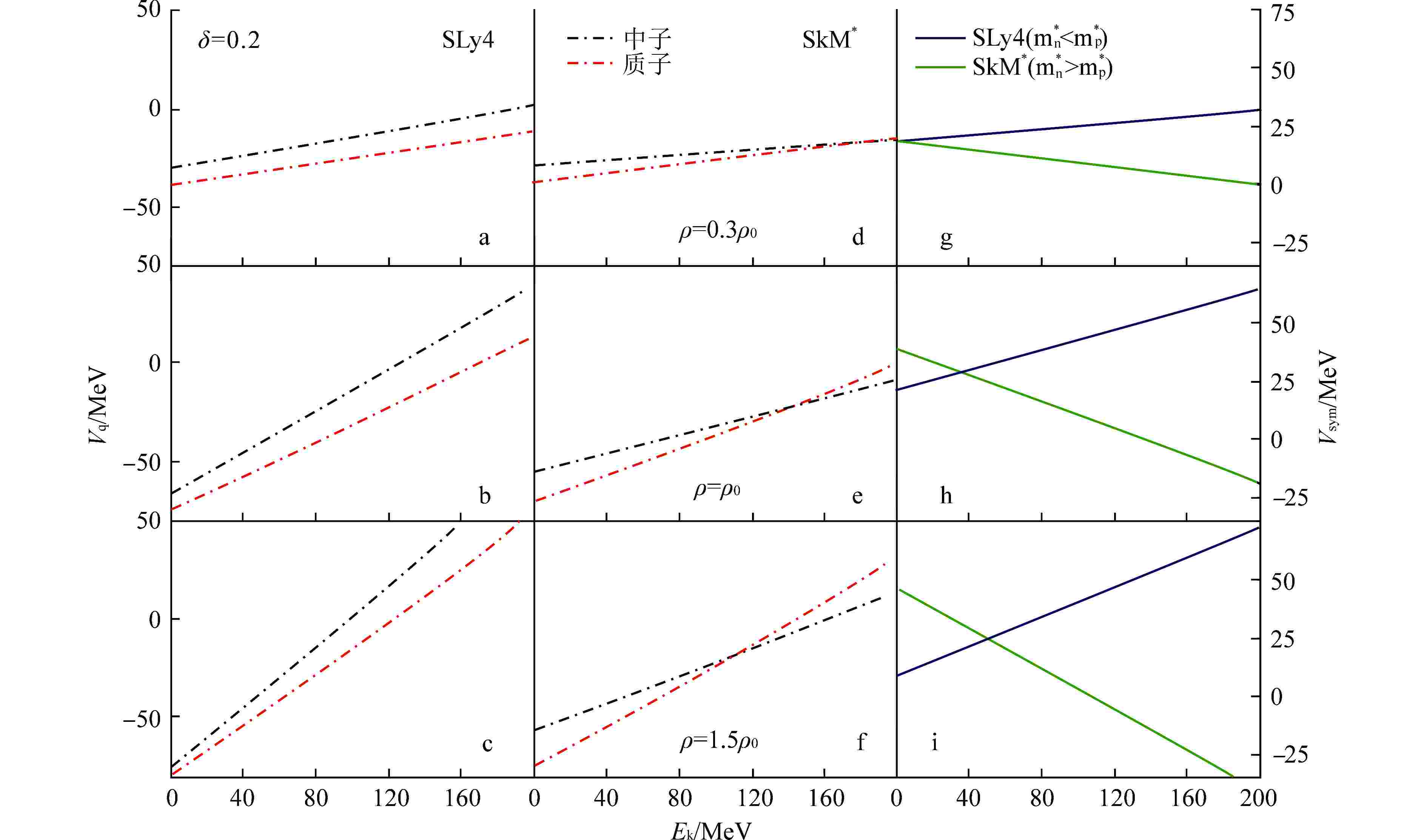
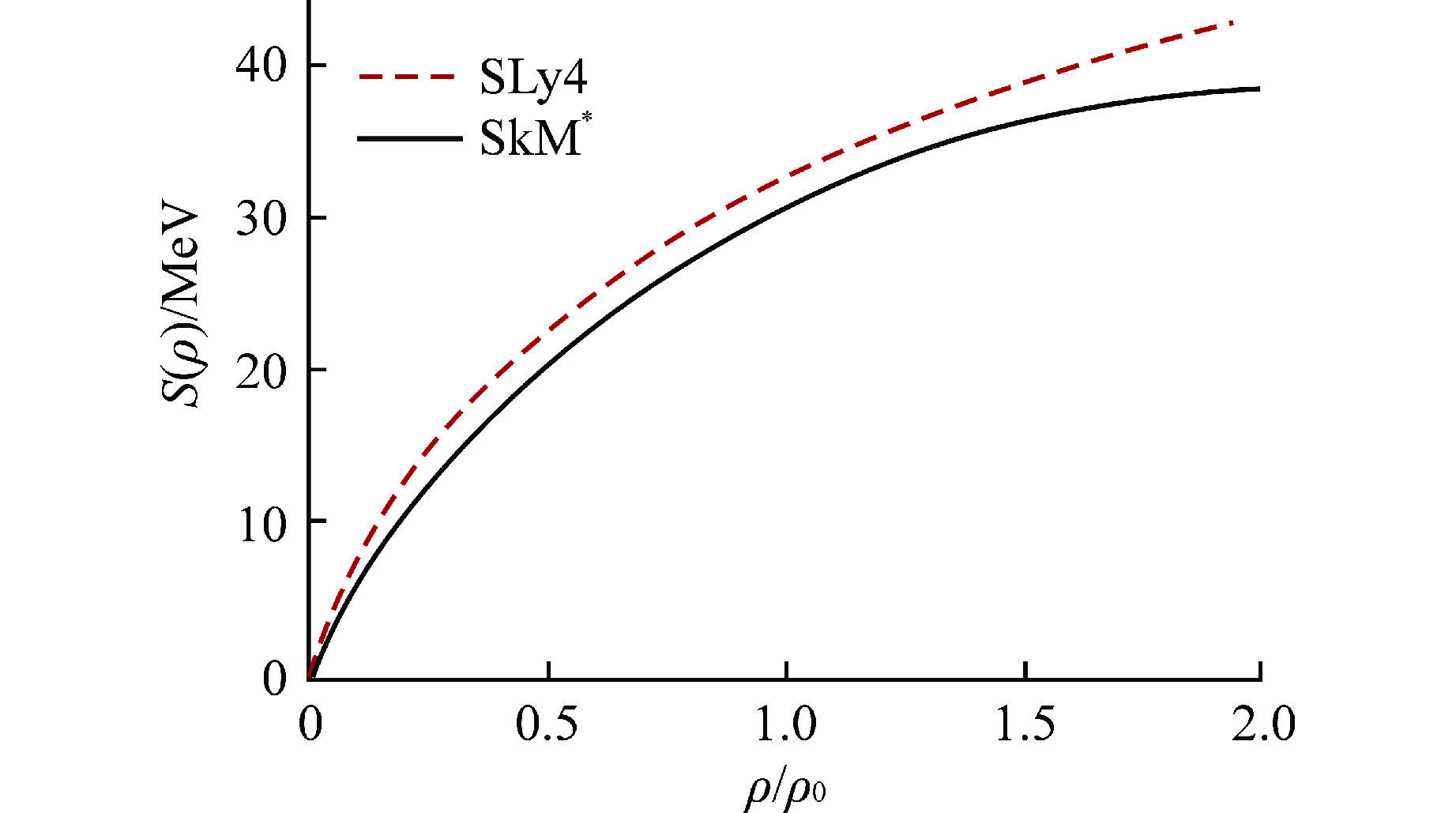
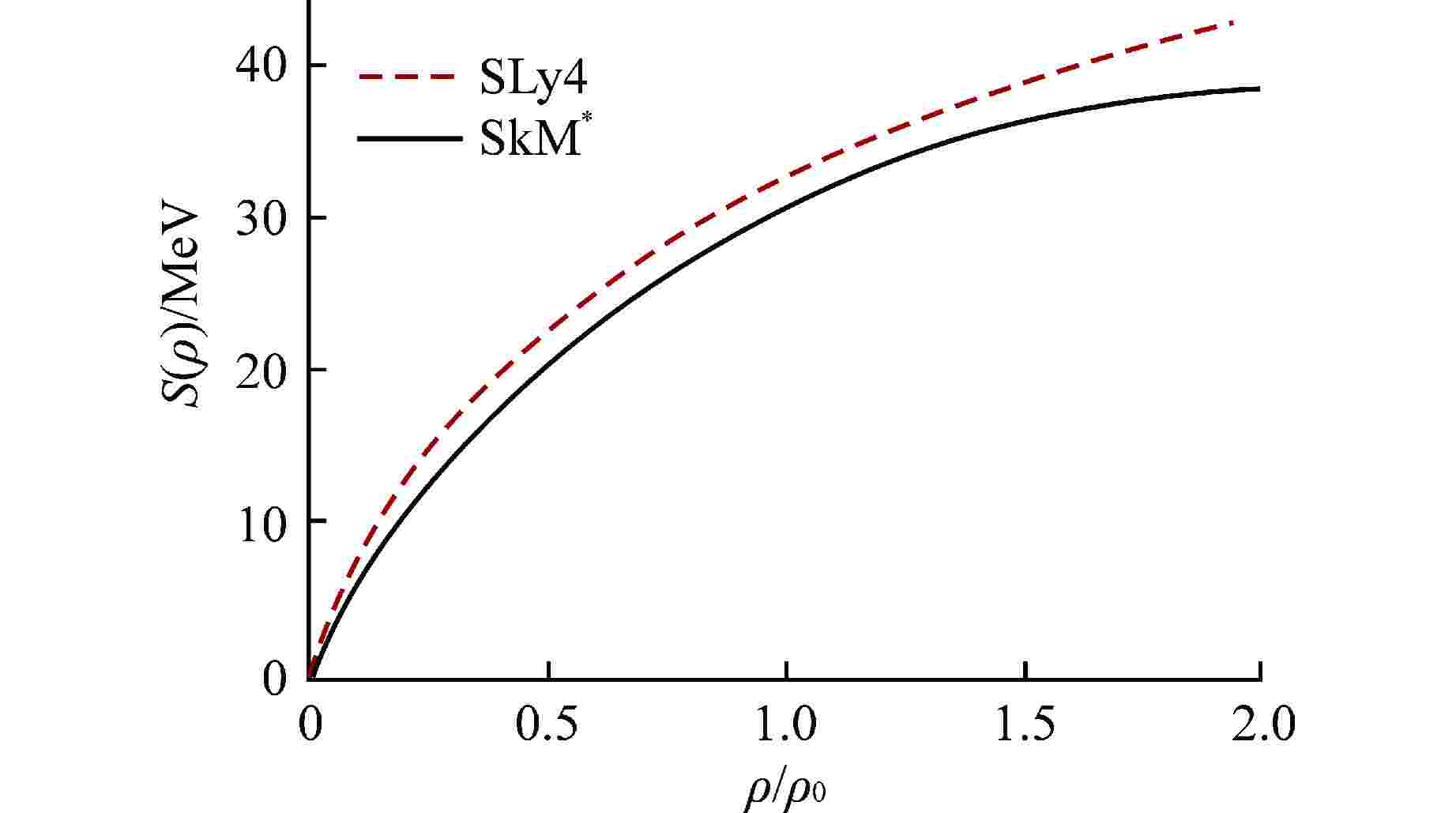
表 1 两套参数SLy4与SkM*对应的参数与核物质参数(δ=0.2)
Table 1. Parameters and Nuclear Matter Parameters (δ=0.2) Corresponding to the Two Sets of Parameters SLy4 and SkM*
参数 ρ0/fm−3 E0/MeV S0/MeV L/MeV $ \mathrm{\Delta }{m}_{\mathrm{n}\mathrm{p}}^{\mathrm{*}} $ SLy4 0.16 15.97 32 46 $ < 0 $ SkM* 0.16 15.77 30 46 $ > 0 $ -
[1] LI B A, CAI B J, CHEN L W, et al. Nucleon effective masses in neutron-rich matter[J]. Progress in Particle and Nuclear Physics, 2018, 99: 29-119. doi: 10.1016/j.ppnp.2018.01.001 [2] FENG Z Q. Effective mass splitting of neutron and proton and isospin emission in heavy-ion collisions[J]. Nuclear Physics A, 2012, 878: 3-13. doi: 10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2012.01.014 [3] ZHANG Y X, TSANG M B, LI Z X, et al. Constraints on nucleon effective mass splitting with heavy ion collisions[J]. Physics Letters B, 2014, 732: 186-190. doi: 10.1016/j.physletb.2014.03.030 [4] COUPLAND D D S, YOUNGS M, CHAJECKI Z, et al. Probing effective nucleon masses with heavy-ion collisions[J]. Physical Review C, 2016, 94(1): 011601. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevC.94.011601 [5] SU J, ZHU L, HUANG C Y, et al. Effects of symmetry energy and effective k-mass splitting on central 96Ru(96Zr)+96Zr(96Ru) collisions at 50 to 400 MeV/nucleon[J]. Physical Review C, 2017, 96(2): 024601. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevC.96.024601 [6] SU J, ZHU L, GUO C C. Constraints on the effective mass splitting by the isoscalar giant quadrupole resonance[J]. Physical Review C, 2020, 101(4): 044606. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevC.101.044606 [7] ZHANG F, SU J. Probing neutron–proton effective mass splitting using nuclear stopping and isospin mix in heavy-ion collisions in GeV energy region[J] Nuclear Science and Techniques, 2022, 31(8): 77. [8] LI B A, CAI B J, XIE W J, et al. Progress in constraining nuclear symmetry energy using neutron star observables since GW170817[J]. Universe, 2021, 7(6): 182. doi: 10.3390/universe7060182 [9] STEIGMAN G. Primordial nucleosynthesis: successes and challenges[J] International Journal of Modern Physics E, 2006, 15(1): 1-35. [10] MEIßNER U G, RAKHIMOV A M, WIRZBA A, et al. Neutron-proton mass difference in isospin-asymmetric nuclear matter[J]. The European Physical Journal A, 2007, 32(3): 299-309. doi: 10.1140/epja/i2007-10390-9 [11] LI A, HU J N, SHANG X L, et al. Nonrelativistic nucleon effective masses in nuclear matter: Brueckner-Hartree-Fock model versus relativistic Hartree-Fock model[J]. Physical Review C, 2016, 93(1): 015803. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevC.93.015803 [12] SHANG X L, LI A, MIAO Z Q, et al. Nucleon effective mass in hot dense matter[J]. Physical Review C, 2020, 101(6): 065801. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevC.101.065801 [13] OU L, LI Z X, ZHANG Y X, et al. Effect of the splitting of the neutron and proton effective masses on the nuclear symmetry energy at finite temperatures[J]. Physics Letters B, 2011, 697(3): 246-250. doi: 10.1016/j.physletb.2011.01.062 [14] VAN DALEN E N E, MÜTHER H. Off-shell behavior of nucleon self-energy in asymmetric nuclear matter[J]. Physical Review C, 2010, 82(1): 014319. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevC.82.014319 [15] WANG S B, TONG H, ZHAO Q, et al. Neutron-proton effective mass splitting in neutron-rich matter[J]. Physical Review C, 2023, 108(3): L031303. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevC.108.L031303 [16] ZUO W, CAO L G, LI B A, et al. Isospin splitting of the nucleon mean field[J]. Physical Review C, 2005, 72(1): 014005. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevC.72.014005 [17] MANSOUR H, GAD K, HASSANEEN K S A. Self-consistent green function calculations for isospin asymmetric nuclear matter[J]. Progress of Theoretical Physics, 2010, 123(4): 687-700. doi: 10.1143/PTP.123.687 [18] MARGUERON J, CASALI R H, GULMINELLI F. Equation of state for dense nucleonic matter from metamodeling. I. Foundational aspects[J]. Physical Review C, 2018, 97(2): 025805. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevC.97.025805 [19] LI X H, GUO W J, LI B A, et al. Neutron–proton effective mass splitting in neutron-rich matter at normal density from analyzing nucleon–nucleus scattering data within an isospin dependent optical model[J]. Physics Letters B, 2015, 743: 408-414. doi: 10.1016/j.physletb.2015.03.005 [20] ZHANG Z, CHEN L W. Isospin splitting of the nucleon effective mass from giant resonances in 208Pb[J]. Physical Review C, 2016, 93(3): 034335. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevC.93.034335 [21] XU J, XIE W J, LI B A. Bayesian inference of nuclear symmetry energy from measured and imagined neutron skin thickness in 116, 118, 120, 122, 124, 130, 132Sn, 208Pb and 48Ca[J]. Physical Review C, 2020, 102(4): 044316. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevC.102.044316 [22] MORFOUACE P, TSANG C Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Constraining the symmetry energy with heavy-ion collisions and Bayesian analyses[J]. Physics Letters B, 2019, 799: 135045. doi: 10.1016/j.physletb.2019.135045 [23] TSANG C Y, KURATA-NISHIMURA K, TSANG M B, et al. Constraining nucleon effective masses with flow and stopping observables from the SπRIT experiment[J]. Physics Letters B, 2024, 853: 138661. doi: 10.1016/j.physletb.2024.138661 [24] ZHANG Y X, WANG N, LI Q F, et al. Progress of quantum molecular dynamics model and its applications in heavy ion collisions[J]. Frontiers of Physics, 2020, 15(5): 54301. doi: 10.1007/s11467-020-0961-9 [25] SAGAWA H, YOSHIDA S, ZENG G M, et al. Isospin dependence of incompressibility in relativistic and nonrelativistic mean field calculations[J]. Physical Review C, 2007, 76(3): 034327. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevC.76.034327 [26] 邢凤竹,崔建坡,高永浩,等. 超重核296Og的结构和α衰变[J]. 原子核物理评论,2023, 40(4): 511-518. -





 下载:
下载: