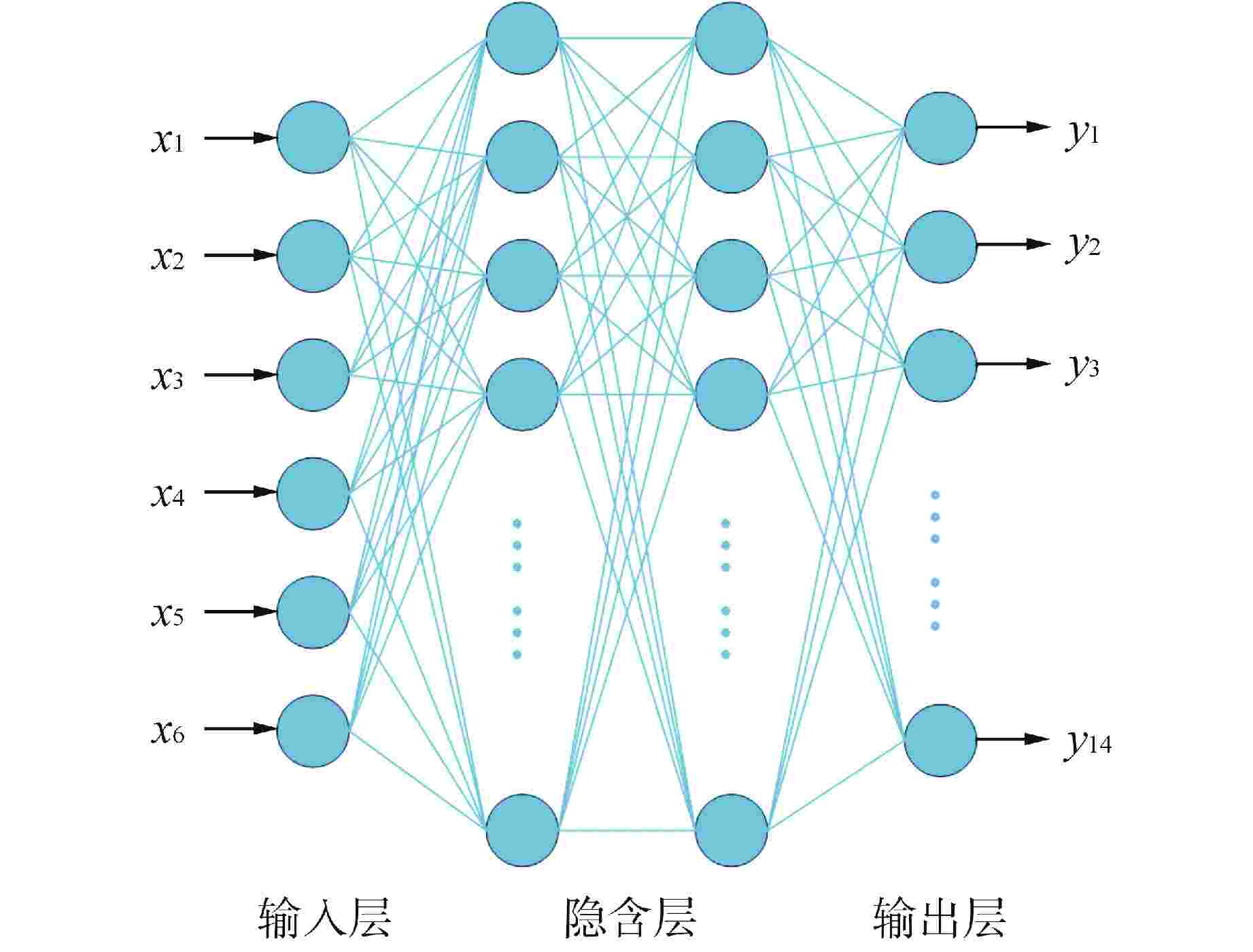
Development of Prediction Model for Two-phase Flow Regime in Nuclear Reactor Core Based on Artificial Neural Network
-
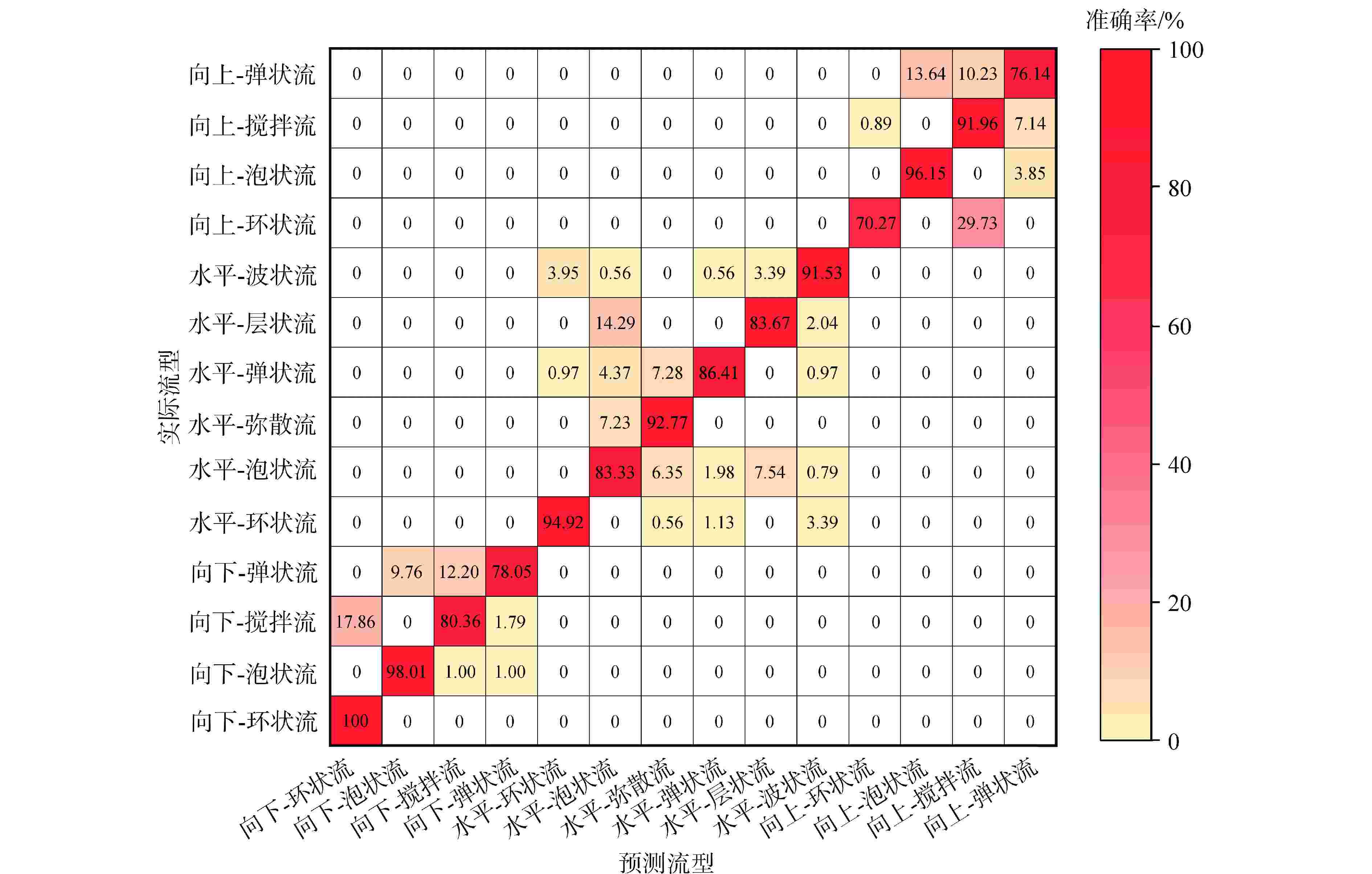
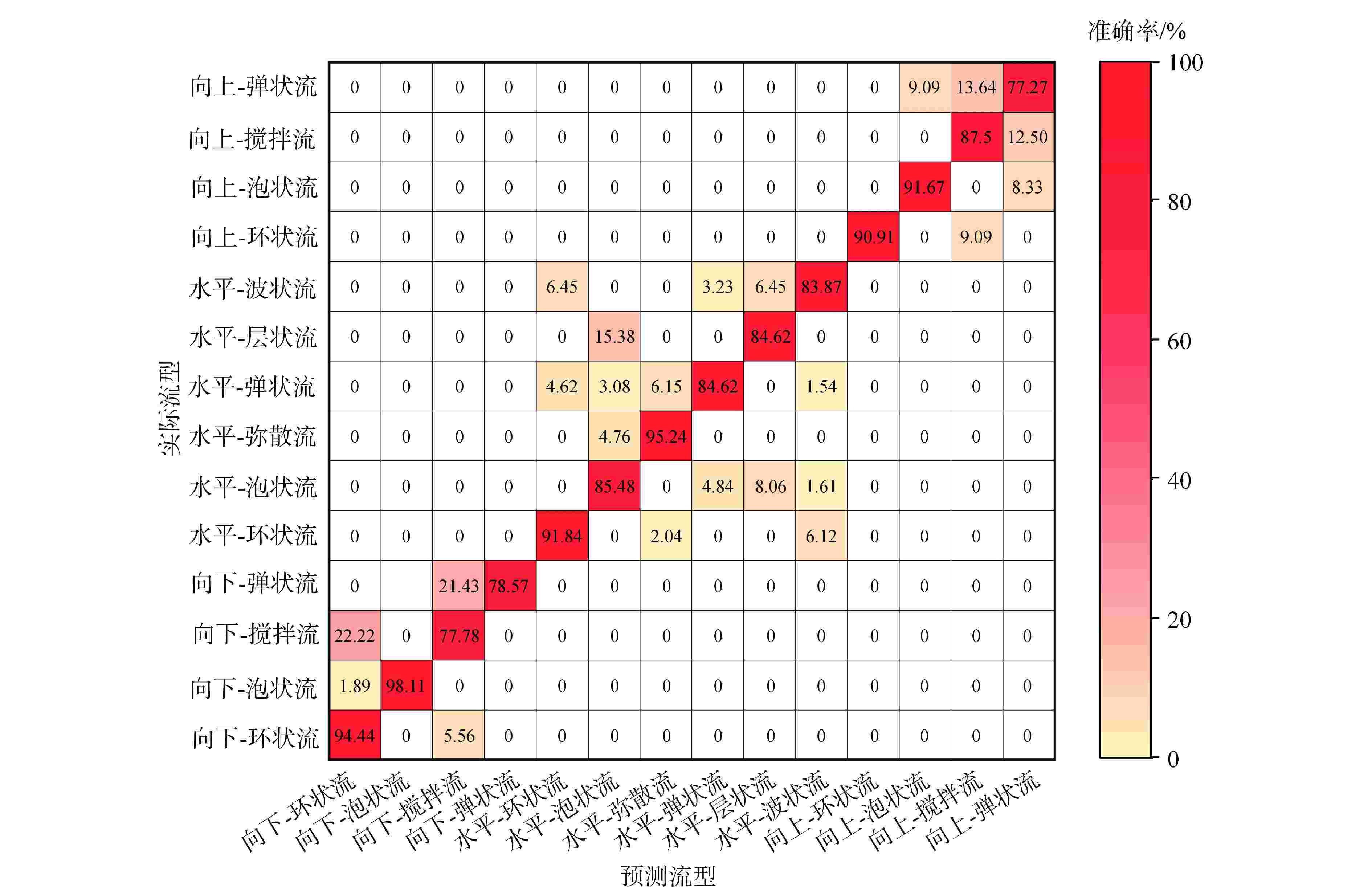
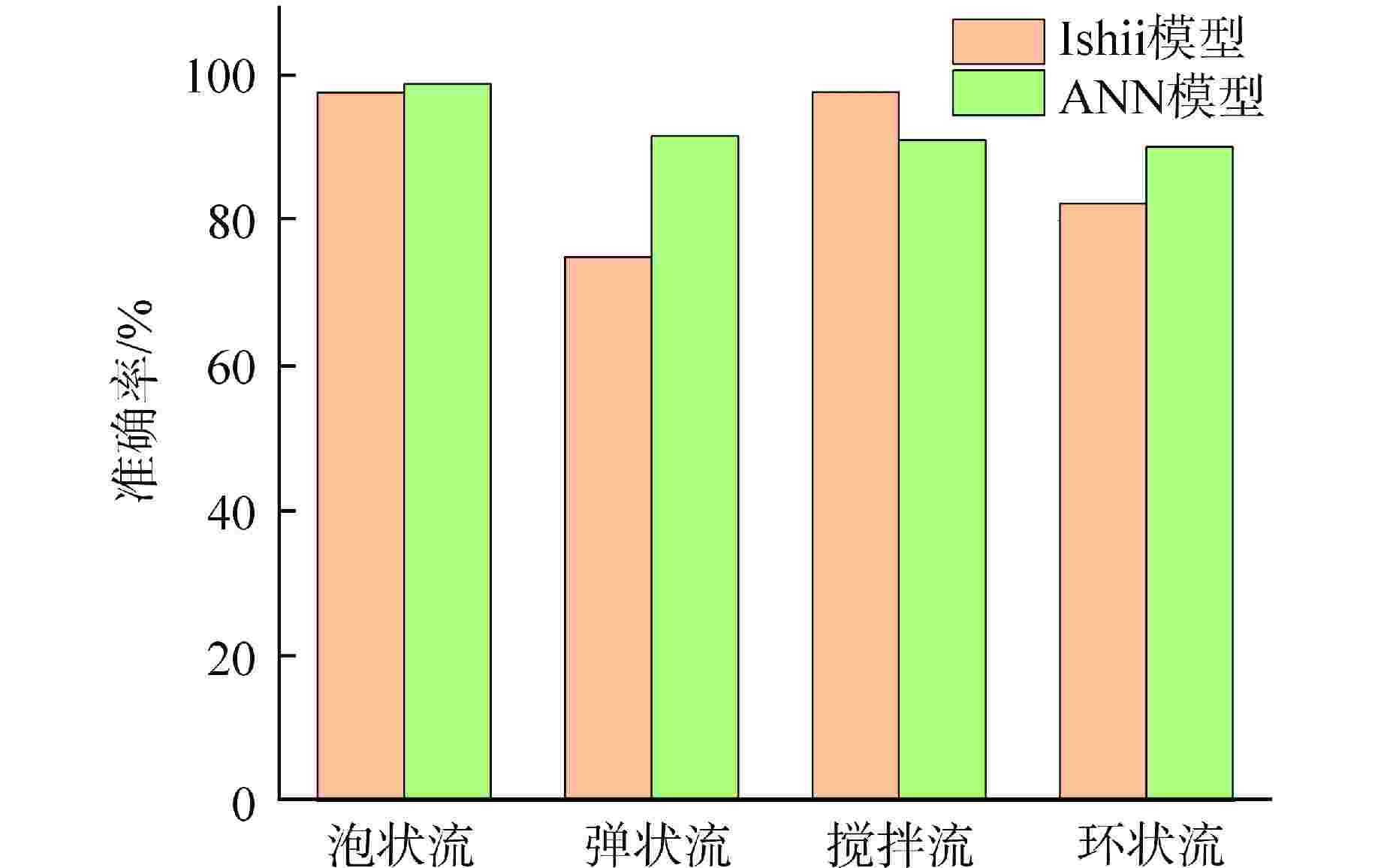
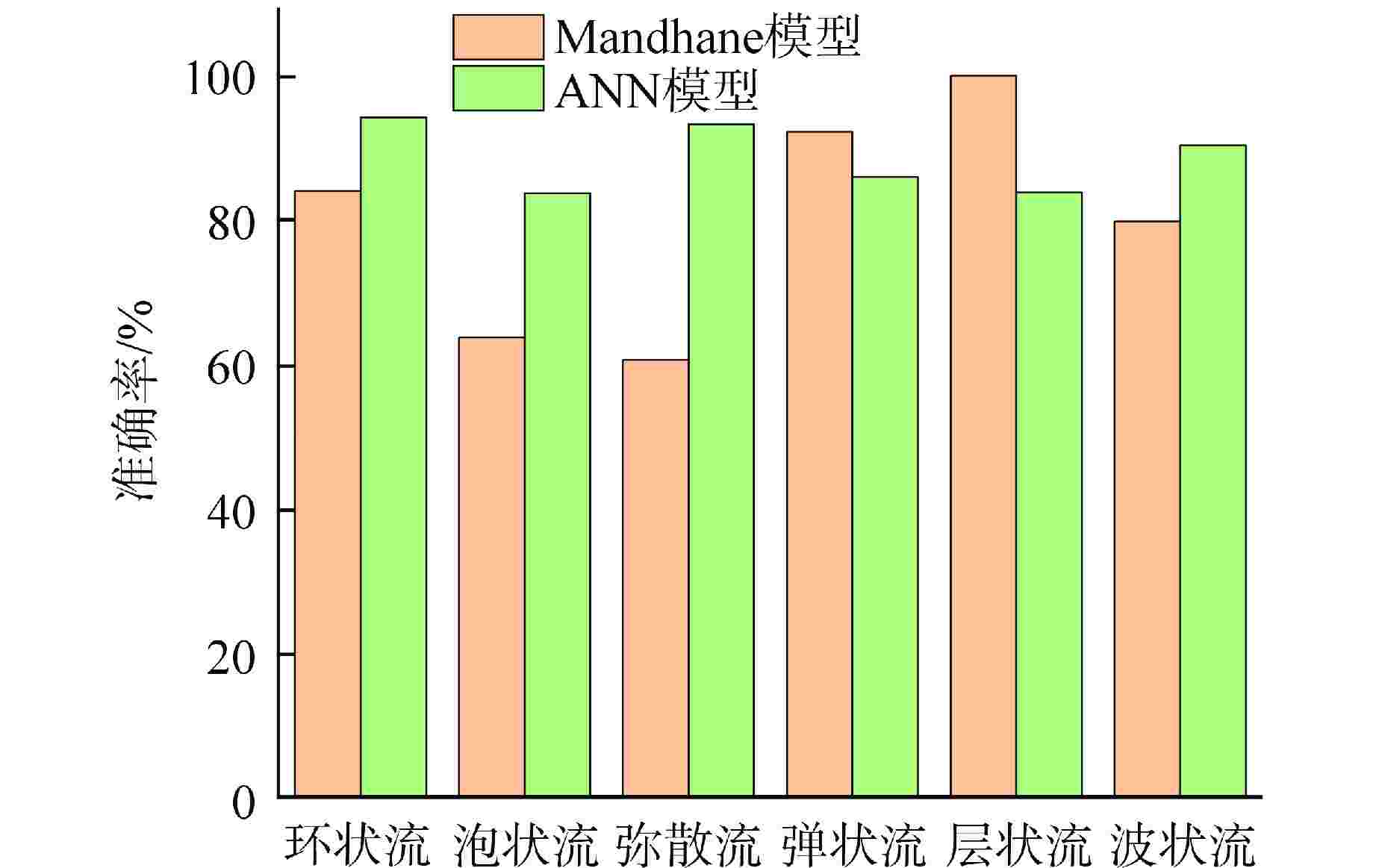
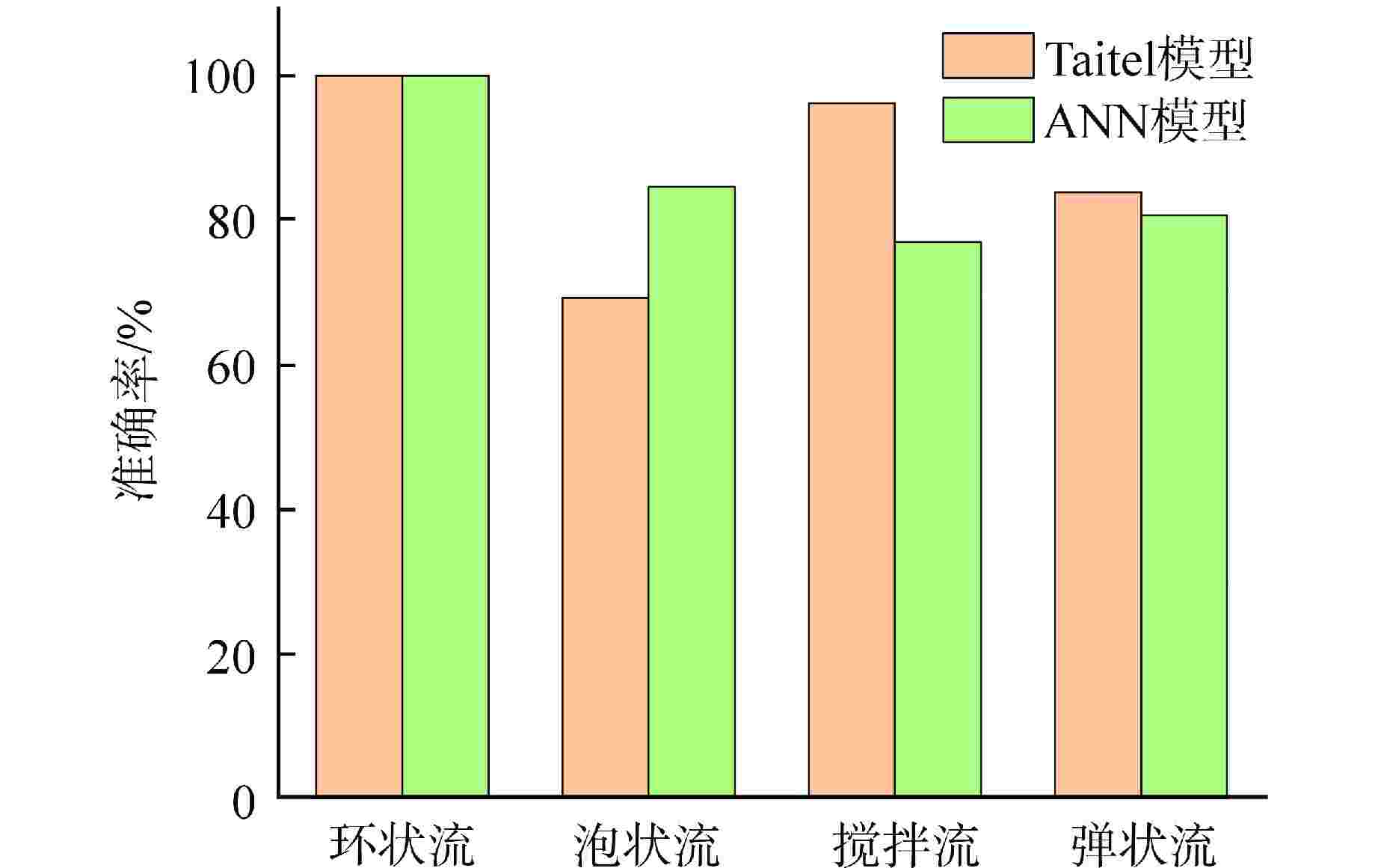
摘要: 为了充分利用不断增加的流型实验数据来扩大模型适用范围、提高模型预测精度,本研究收集实验数据建立了训练数据库并对数据进行了预处理,基于人工神经网络(ANN)算法开发了两相流型预测模型,分析了模型对不同方向上流型的预测精度并与传统流型预测模型进行对比。结果表明,建立的新模型对训练集的平均准确率为88.56%,对测试集的平均准确率为87.86%,新模型能直接用于各种不同工况,不会发生不同方向流型混淆的情况,相比于Ishii模型、Mandhane模型、Taitel模型,新模型具有更好的预测精度。本研究为流型预测提供了一种新方法,随着训练数据的更新,模型的适用范围和精度可以不断提高。
-
关键词:
- 反应堆堆芯 /
- 两相流型 /
- 机器学习 /
- 人工神经网络(ANN)
Abstract: To fully leverage the increasing experimental data on flow regimes to expand model applicability and improve prediction accuracy, this study collected experimental data, established a training database, and performed data preprocessing. A two-phase flow regime prediction model was developed based on the artificial neural network (ANN) algorithm. The model's prediction accuracy in various flow directions was analyzed and compared with traditional flow regime prediction models. The results show that the new model achieves an average accuracy of 88.56% on the training set and 87.86% on the test set. The proposed model can be directly applied to various operating conditions without causing misclassification of flow regimes in different directions. Compared to the Ishii model, Mandhane model, and Taitel model, the ANN-based model demonstrates superior prediction accuracy. This study provides a novel method for flow regime prediction, and with the continuous updating of training data, the applicability and accuracy of the model can be further improved. -
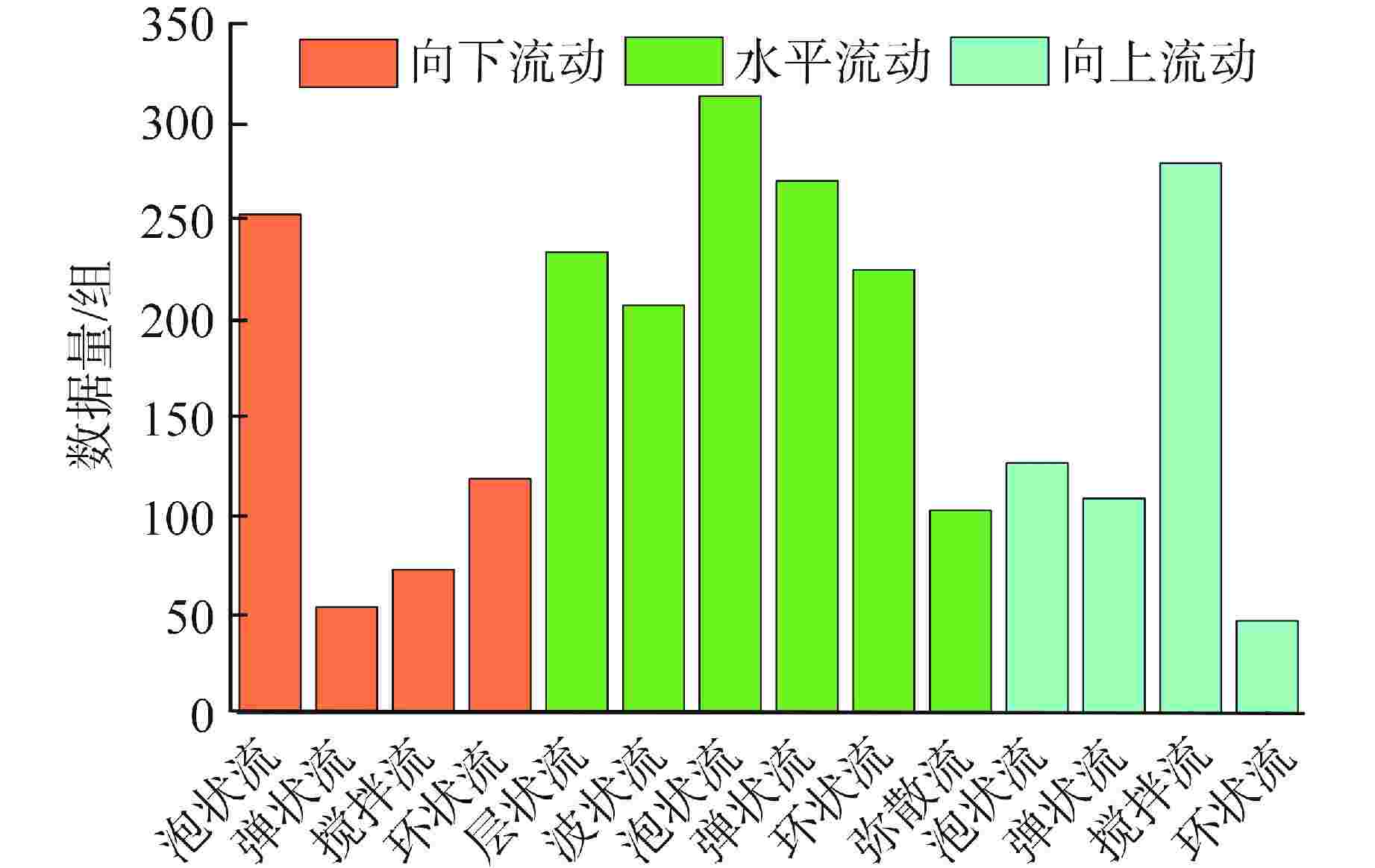
表 1 原始实验数据总结
Table 1. Summary of Original Experimental Data
数据来源 流动方向 表观气相
速度/(m·s−1)表观液相
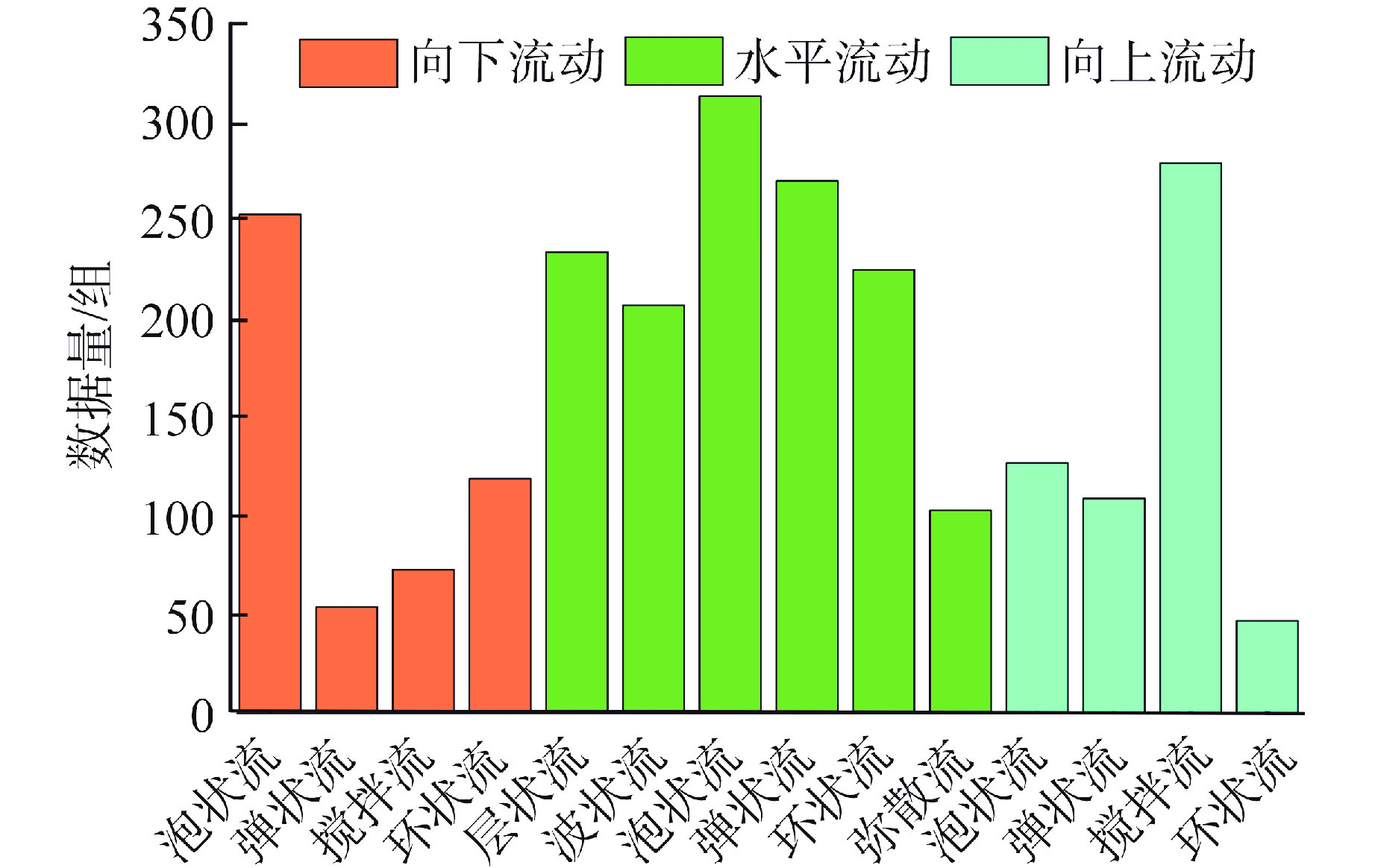
速度/(m·s−1)水力直径/m 数据量/组 流型种类 Mandhane[3] 水平流动 0.10~500 0.10~20 0.0127~0.1651 458 泡状流、层状流、波状流、弹状流、环状流、弥散流 Barnea[18] 水平流动 0.01~100 0.001~10 0.0040~0.1230 901 细长泡状流、弥散泡状流、弹状流、波状环状流、波状层状流、平滑层状流、环状流 Yang[19] 向下流动 0.01~10 0.10~10 0.1524 71 泡状流、帽状-泡状流、搅拌湍流、环状流 Lee[9] 向下流动 0.01~100 0.01~10 0.0254, 0.0508 197 泡状流、帽状-泡状流、弹状流、搅拌湍流、环状流 Pan[11] 向下流动 0.01~100 0.01~10 0.0254 119 泡状流、弹状流、搅拌湍流、环状流 Taitel[5] 向上流动 0.10~100 0.01~10 0.0250 108 泡状流、弹状流、搅拌流、环状流 Venkateswararao[8] 向上流动 0.01~50 0.01~1.0 0.0180 209 泡状流、弹状流、搅拌流、环状流 Mizutani[20] 向上流动 0.01~10 0.01~10 0.0093 67 泡状流、搅拌流、环状流、泡状-搅拌过渡流、搅拌-环状过渡流 Paranjape[10] 向上流动 0.01~100 0.01~10 0.0153 141 泡状流、帽状-泡状流、搅拌湍流、搅拌流 Zhou[21] 向上流动 0.01~100 0.01~1 0.0187 149 泡状流、搅拌流、环状流、泡状-搅拌过渡流 表 2 模型超参数选取范围及结果
Table 2. Selection Range and Results of Hyperparameters
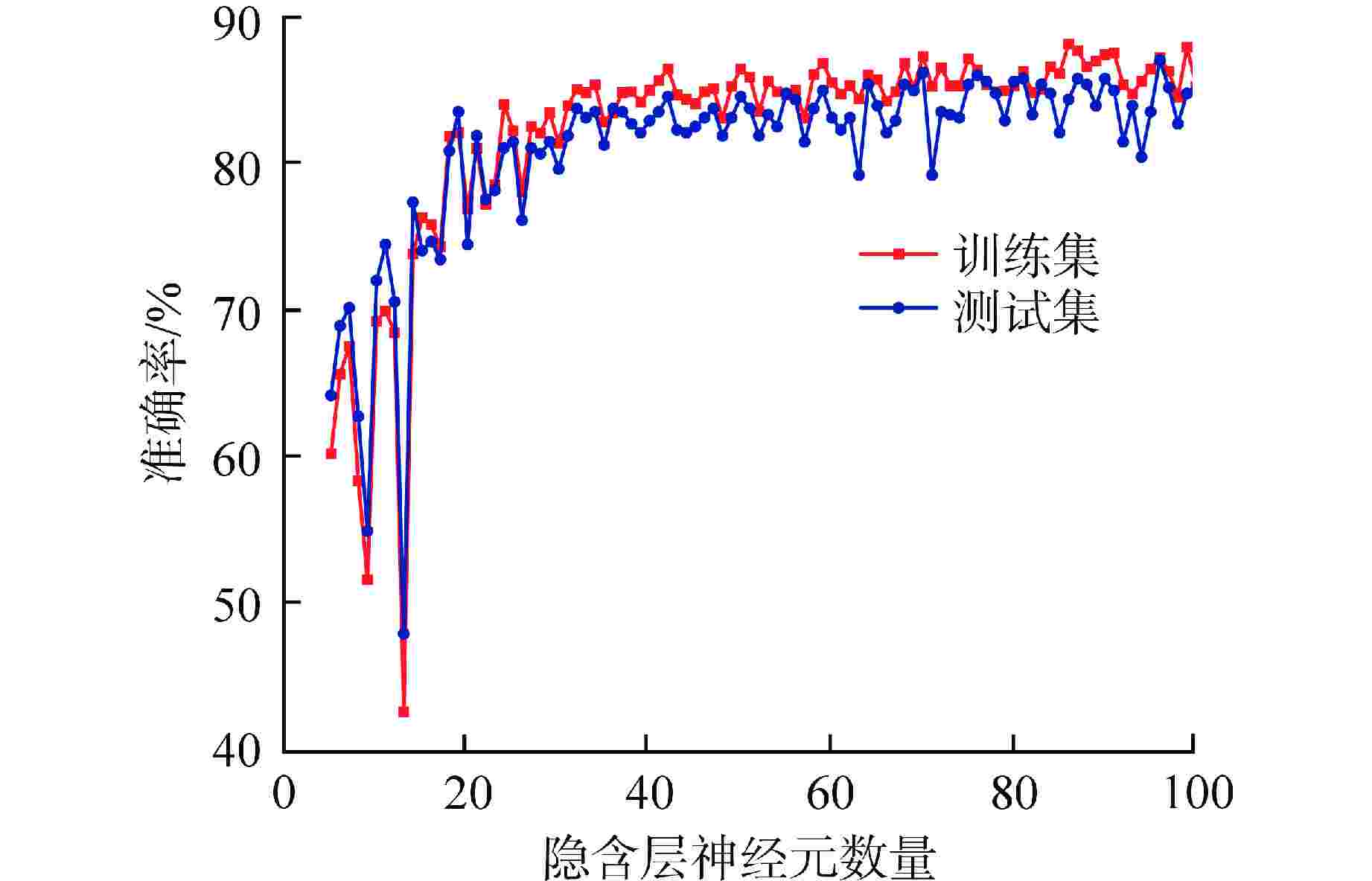
参数类型 选取范围 选取结果 激活函数 {'identity','logistic','tanh','ReLU'} ReLU 求解器 {'LBFGS','SGD','Adam'} Adam L2正则化参数 {1.0×10−3,1.0×10−4,1.0×10−5} 1.0×10−5 学习率 {0.0001,0.001,0.01,0.1} 0.01 最大迭代次数 {200,500,1000} 500 优化公差 {1.0×10−3,1.0×10−4,1.0×10−5} 1.0×10−5 -
[1] BAKER O. Design of pipelines for the simultaneous flow of oil and gas[C]//Fall Meeting of the Petroleum Branch of AIME. Dallas: OnePetro, 1953. [2] HEWITT G F, HALL-TAYLOR N S. Annular Two-Phase Flow[M]. New York: Pergamon Press, 1970: 4-20. [3] MANDHANE J M, GREGORY G A, AZIZ K. A flow pattern map for gas-liquid flow in horizontal pipes[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 1974, 1(4): 537-553. doi: 10.1016/0301-9322(74)90006-8 [4] TAITEL Y, DUKLER A E. A model for predicting flow regime transitions in horizontal and near horizontal gas-liquid flow[J]. AIChE Journal, 1976, 22(1): 47-55. doi: 10.1002/aic.690220105 [5] TAITEL Y, BARNEA D, DUKLER A E. Modelling flow pattern transitions for steady upward gas-liquid flow in vertical tubes[J]. AIChE Journal, 1980, 26(3): 345-354. doi: 10.1002/aic.690260304 [6] BARNEA D, SHOHAM O, TAITEL Y, et al. Flow pattern transition for gas-liquid flow in horizontal and inclined pipes. Comparison of experimental data with theory[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 1980, 6(3): 217-225. doi: 10.1016/0301-9322(80)90012-9 [7] BARNEA D. A unified model for predicting flow-pattern transitions for the whole range of pipe inclinations[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 1987, 13(1): 1-12. doi: 10.1016/0301-9322(87)90002-4 [8] VENKATESWARARAO P, SEMIAT R, DUKLER A E. Flow pattern transition for gas-liquid flow in a vertical rod bundle[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 1982, 8(5): 509-524. doi: 10.1016/0301-9322(82)90021-0 [9] LEE J Y, ISHII M, KIM N S. Instantaneous and objective flow regime identification method for the vertical upward and downward co-current two-phase flow[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2008, 51(13-14): 3442-3459. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2007.10.037 [10] PARANJAPE S, CHEN S W, HIBIKI T, et al. Flow regime identification under adiabatic upward two-phase flow in a vertical rod bundle geometry[J]. Journal of Fluids Engineering, 2011, 133(9): 091302. doi: 10.1115/1.4004836 [11] PAN L M, ZHANG M H, JU P, et al. Vertical co-current two-phase flow regime identification using fuzzy C-means clustering algorithm and ReliefF attribute weighting technique[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2016, 95: 393-404. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2015.11.081 [12] OUYANG L, JIN N D, REN W K. A new deep neural network framework with multivariate time series for two-phase flow pattern identification[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2022, 205: 117704. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2022.117704 [13] 张立峰,王智. 基于多元经验模态分解与卷积神经网络的气液两相流流型识别[J]. 计量学报,2023, 44(1): 73-79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1158.2023.01.11 [14] 朱隆祥,张卢腾,孙皖,等. 基于非监督机器学习方法的竖直环形流道流动沸腾流型研究[J]. 核动力工程,2023, 44(3): 112-120. [15] ROTH G A, AYDOGAN F. Theory and implementation of nuclear safety system codes–Part I: conservation equations, flow regimes, numerics and significant assumptions[J]. Progress in Nuclear Energy, 2014, 76: 160-182. doi: 10.1016/j.pnucene.2014.05.011 [16] The RELAP5-3D© Code Development Team. RELAP5-3D© code manual volume I: code structure, system models, and solution methods: Technical Report No. INEEL-EXT-98-00834[R]. Idaho Falls: Idaho National Laboratory, 2014. [17] PHUNG V A, KUDINOV P. Prediction of flow regimes and thermal hydraulic parameters in two-phase natural circulation by RELAP5 and TRACE codes[J]. Science and Technology of Nuclear Installations, 2015, 2015: 296317. [18] BARNEA D, LUNINSKI Y, TAITEL Y. Flow pattern in horizontal and vertical two phase flow in small diameter pipes[J]. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 1983, 61(5): 617-620. doi: 10.1002/cjce.5450610501 [19] YANG Z J, DANG Z R, YANG X H, et al. Downward two phase flow experiment and general flow regime transition criteria for various pipe sizes[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2018, 125: 179-189. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2018.03.072 [20] MIZUTANI Y, TOMIYAMA A, HOSOKAWA S, et al. Two-phase flow patterns in a four by four rod bundle[J]. Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 2007, 44(6): 894-901. doi: 10.1080/18811248.2007.9711327 [21] ZHOU Y L, HOU Y D, LI H W, et al. Flow pattern map and multi-scale entropy analysis in 3×3 rod bundle channel[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2015, 80: 144-150. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2015.02.006 [22] 苏光辉,秋穗正,田文喜,等. 核动力系统热工水力计算方法[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社,2013:201-204. [23] PEDREGOSA F, VAROQUAUX G, GRAMFORT A, et al. Scikit-learn: machine learning in Python[J]. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2011, 12: 2825-2830. [24] ISHII M, PARANJAPE S S, KIM S, et al. Interfacial structures and interfacial area transport in downward two-phase bubbly flow[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2004, 30(7-8): 779-801. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmultiphaseflow.2004.04.009 -





 下载:
下载: