Study on the Selection Method of Probability Density Distribution in Nuclear Data Stochastic Sampling
-
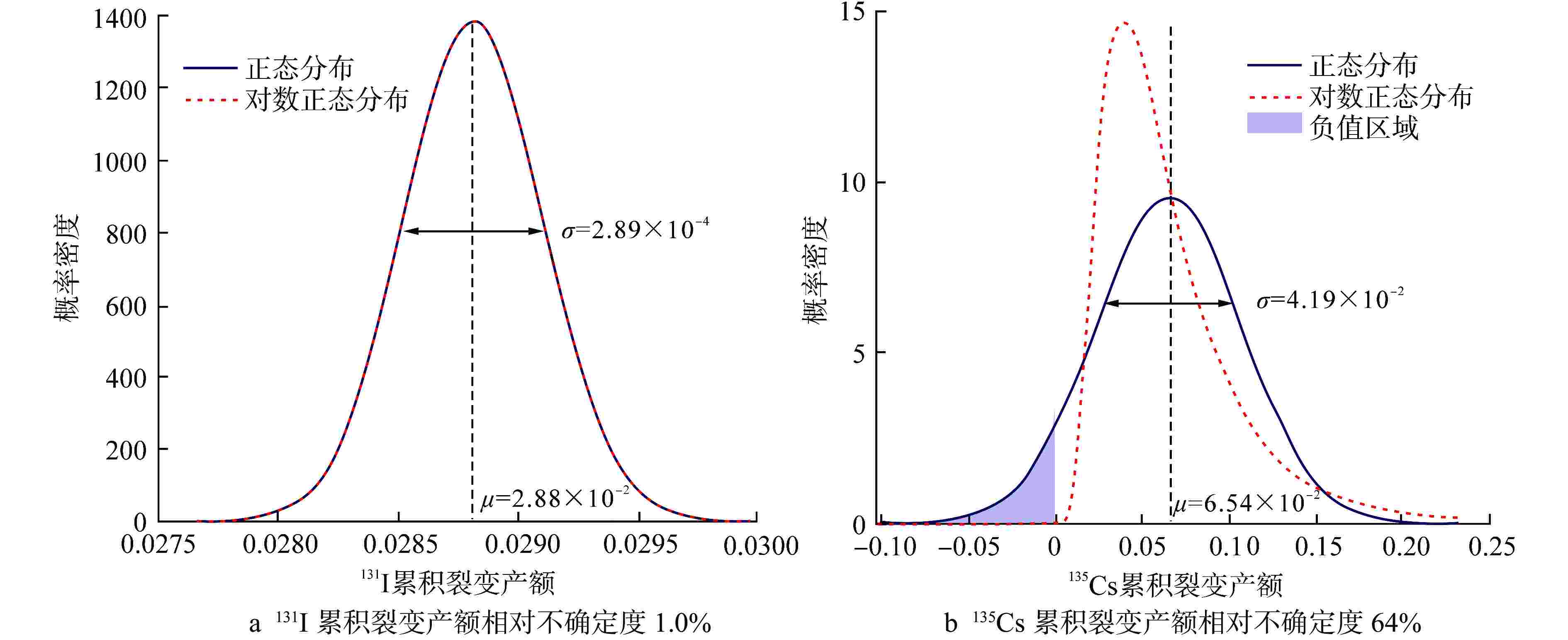
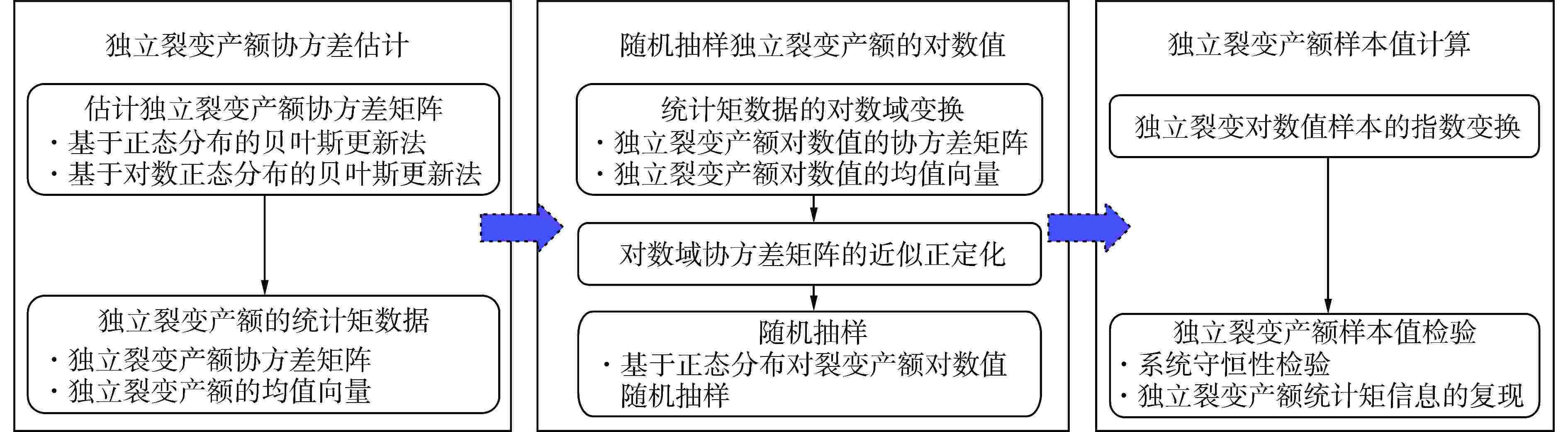
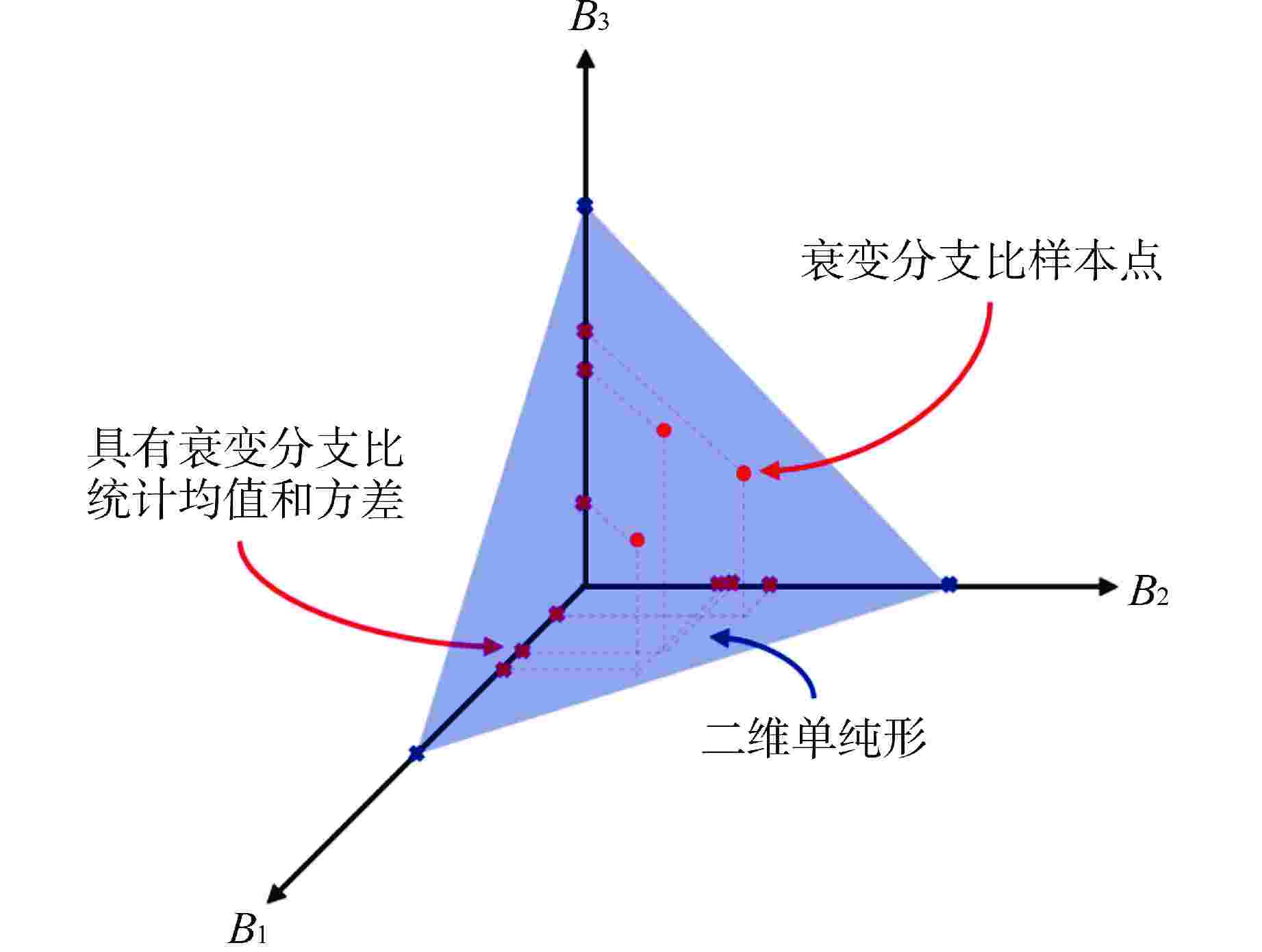
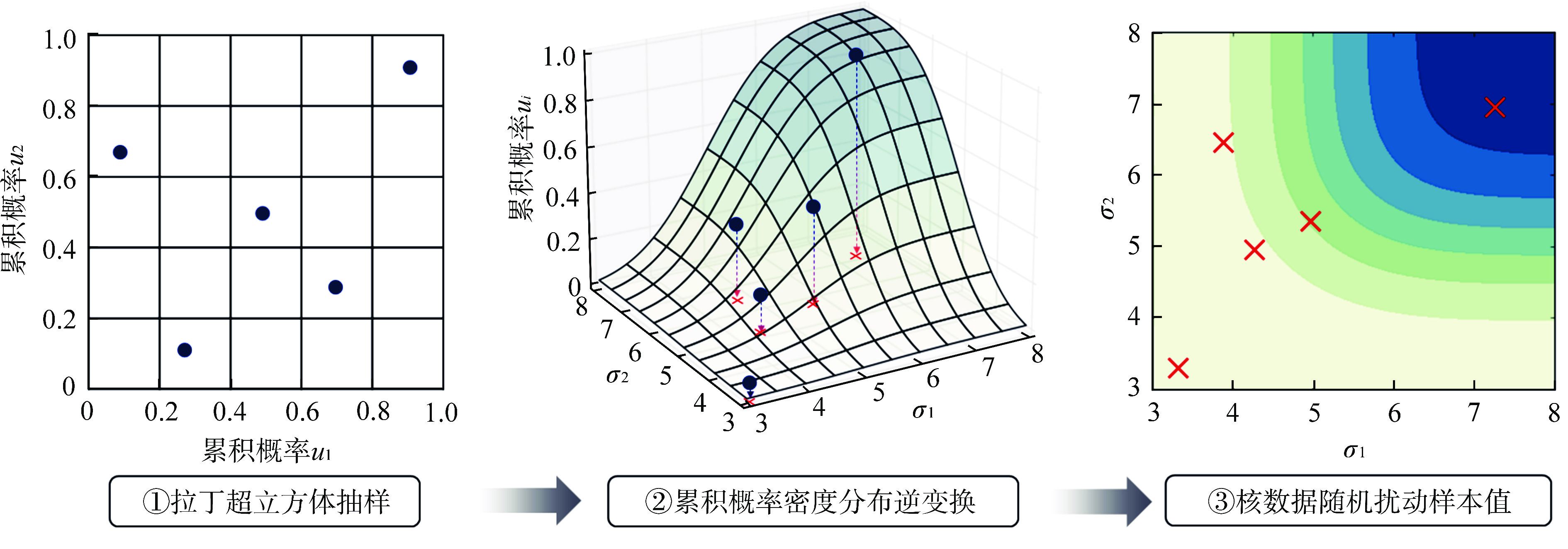
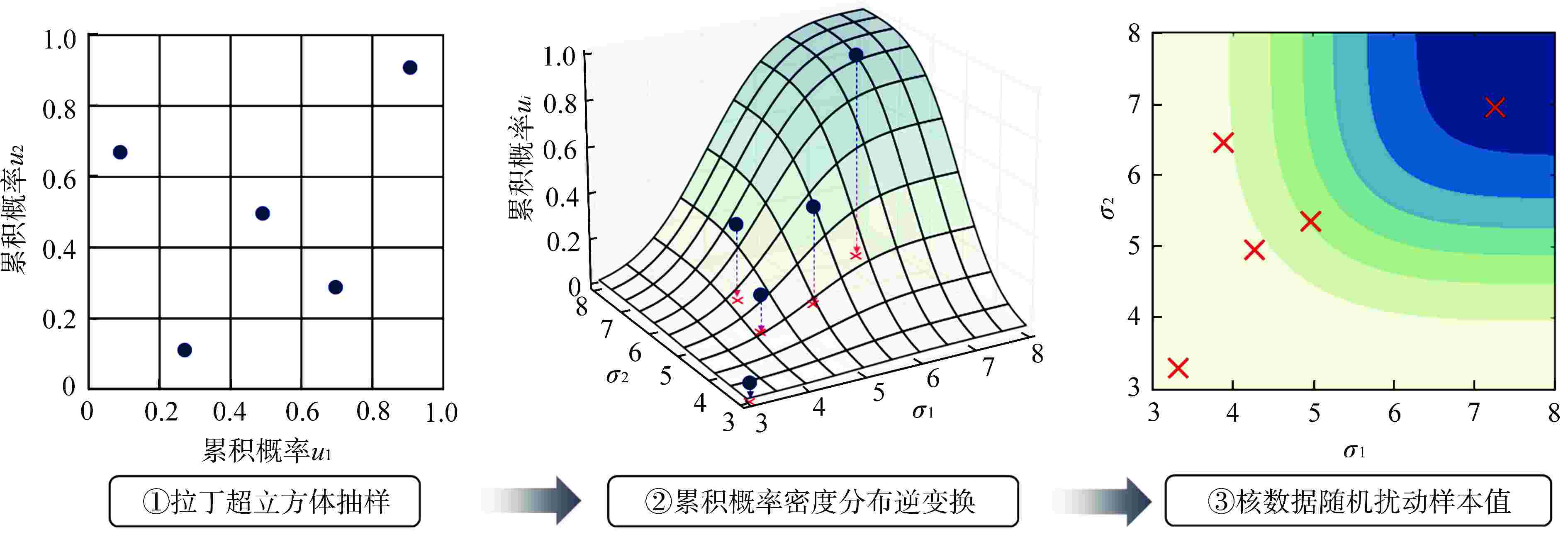
摘要: 提供符合核数据已知统计矩信息和物理约束的随机扰动样本,是核数据作为分析输入的各类堆芯物理计算相关的统计学习算法的基础。合理扰动的核数据样本是保证堆芯物理响应量特征提取、降阶建模等数据驱动人工智能模型预测准确性的重要因素之一。选取能够满足核数据自身物理约束特征的概率密度分布是保证上述核数据随机抽样合理性的关键。本文针对核数据库中常见的两类物理约束特征,即非负性取值约束(例如裂变产额数据、核反应截面数据等)以及归一化约束(例如衰变分支比等),研究其对应的概率密度分布选取方法并提供相应的抽样算法。结合评价核数据库中提供的核数据不确定度信息,本文对不同概率密度分布下的核数据随机抽样效果进行对比,并给出概率密度分布的选取建议。
-
关键词:
- 对数正态分布 /
- 广义Dirichlet分布 /
- 随机抽样 /
- 核数据不确定性分析
Abstract: For statistical learning algorithms that are related to various core physical calculations with nuclear data as the analysis input, providing stochastic disturbance samples that are consistent with the known statistical moment information and physical constraints of nuclear data is fundamental. Reasonably perturbed nuclear data samples are one of the important factors to ensure the prediction accuracy of data-driven artificial intelligence models such as core physical response feature extraction and reduced-order modeling. Selecting the probability density distribution that can meet the physical constraints of nuclear data itself is the key to ensure the rationality of the above stochastic sampling of nuclear data. This work focuses on two types of physical constraints that are commonly seen in the evaluated nuclear data library, namely, non-negativity constraints (e.g. fission product yield, nuclear reaction cross section) and normalization constraints (e.g. decay branch ratio), studies the corresponding probability density distribution selection methods and provides the corresponding sampling algorithms. Combined with the uncertainty information of nuclear data provided in the evaluated nuclear data library, this work compares the stochastic sampling effects of nuclear data with different probability density distributions, and gives some suggestions on the selection of probability density distributions. -
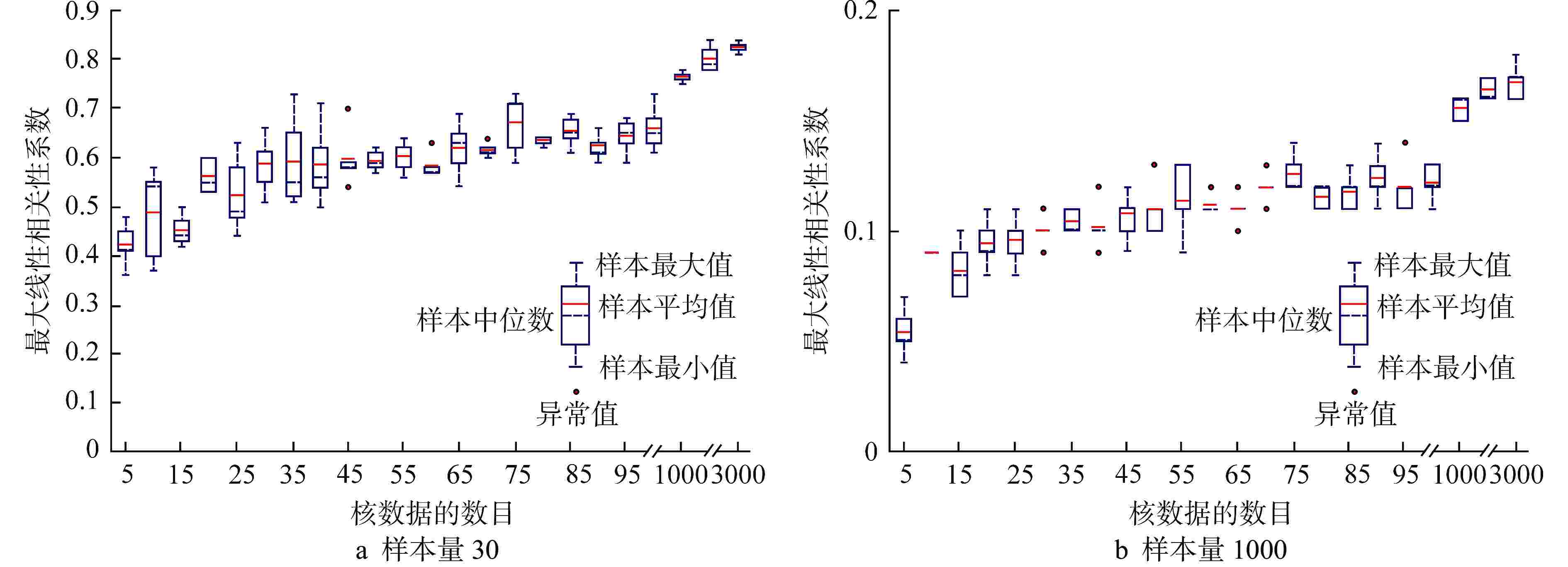
表 1 基于对数正态分布的独立裂变产额随机抽样样本检验结果
Table 1. Test Results of Independent Fission Yield Stochastic Sampling Samples Based on Lognormal Distribution
样本检验 基于不同概率分布的抽样方法 检验类型 检验量 参考值 截断正态分布 对数正态分布 统计矩的复现精度 均值的相对误差*/% 0.64 0.12 方差的相对误差*/% 0.50 1.15 裂变系统的守恒量检验 总产额 2.00000 2.00066 (7.54×10−4)** 2.00030 (4.19×10−3)** 0.00066↑ 0.00030↑ 总质量数 233.57915 233.66592 (7.4×10−2)** 233.63804 (4.2×10−1)** 0.08677↑ 0.05889↑ 总电荷数 92.05318 92.07948 (2.9×10−2)** 92.06808 (1.9×10−1)** 0.02630↑ 0.01490↑ 注:* 为最大相对误差的绝对值;** 为统计标准差;“↑”为正向绝对误差 表 2 基于广义Dirichlet分布的衰变分支比随机抽样流程
Table 2. Decay Branch Ratio Stochastic Sampling Procedures Based on Generalized Dirichlet Distribution
编号 步骤 1 输入:样本量$ M $,衰变分支比均值$ {\mu }_{i} $和标准差$ {\sigma }_{i} $ 2 遍历各衰变分支比:$ i\leftarrow 1 $ 3 计算 $ ({A}_{i-1},{B}_{i-1}) $ 4 计算 $ ({\alpha }_{i},{\beta }_{i}) $ 5 遍历各样本点:$ M\leftarrow 1 $ 6 随机区间样本值$ {u}_{i}^{\left(m\right)}\leftarrow \mathrm{B}\mathrm{e}\mathrm{t}\mathrm{a}\left({\alpha }_{i},{\beta }_{i}\right) $ 7 剩余区间计算值$ {r}_{i}^{\left(m\right)}\leftarrow \displaystyle\prod_{s=1}^{i-1}\left[1-{u}_{s}^{\left(m\right)}\right] $ 若$ i=1 $,则$ {r}_{1}^{\left(m\right)} \leftarrow 1 $ 8 分支比随机扰动样本值$ {b}_{i}^{\left(m\right)}\leftarrow {u}_{i}^{\left(m\right)}{r}_{i}^{\left(m\right)} $ 9 $ m\leftarrow m+1 $ 依次遍历所有样本点 10 令$ i\leftarrow i+1 $ 依次遍历所有衰变分支比 11 遍历各样本点:$ M\leftarrow 1 $ 12 $ {b}_{i}^{\left(m\right)}\leftarrow 1-\displaystyle\sum_{k=1}^{i-1}{b}_{k}^{\left(m\right)} $ 13 结束 表 3 基于广义Dirichlet分布的衰变分支抽样样本检验
Table 3. Decay Branch Ratio Sampling Sample Inspection Based on Generalized Dirichlet Distribution
核素 类别 衰变分支比/% 评价库参考值
均值(标准差)均值检验
(参考值/样本统计值)标准差检验
(参考值/样本统计值)79Ga 分支1 0.0890 (0.0190) 0.0890/0.0890 0.0190/0.0189 分支2 4.9663 (0.1671) 4.9663/4.9668 0.1671/0.1671 分支3 94.9447 (0.1671) 94.9447/94.9442 0.1671/0.1681 81Ga 分支1 11.900 (0.7000) 11.900/11.901 0.7000/0.6973 分支2 41.4771 (3.8260) 41.4771/41.4884 3.8260/3.8250 分支3 46.6229 (3.8260) 46.6229/46.6103 3.8260/3.8297 81Rbm 分支1 0.0203 (0.0075) 0.0203/0.0203 0.0075/0.0075 分支2 2.3797 (0.8372) 2.3797/2.3823 0.8372/0.8373 分支3 97.6000 (0.6000) 97.6000/97.5974 0.6000/0.8373 98Rb 分支1 0.0510 (0.0070) 0.0510/0.0510 0.0070/0.0070 分支2 13.8000 (0.6000) 13.8000/13.8019 0.6000/0.6000 分支3 86.1490 (0.6000) 86.1490/86.1471 0.6000/0.6000 97Sr 分支1 0.0200 (0.0100) 0.0200/0.0200 0.0100/0.0100 分支2 14.8690 (1.9979) 14.8690/14.8752 1.9979/1.9979 分支3 85.1110 (1.9979) 85.1110/85.1048 1.9979/1.9979 111Pdm 分支1 7.8912 (0.9316) 7.8912/7.8927 0.9316/0.9281 分支2 19.1088 (2.6269) 19.1088/19.1166 2.6269/2.6263 分支3 73.0000 (3.0000) 73.0000/72.9906 3.0000/2.7220 -
[1] 郝琛,李富. 核反应堆物理计算不确定性分析[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社,2022: 4. [2] SIEFMAN D J. Development and application of data assimilation methods in reactor physics[D]. Andreas Pautz: EPFL, 2019. [3] CACUCI D G. Sensitivity theory for nonlinear systems. I. Nonlinear functional analysis approach[J]. Journal of Mathematical Physics, 1981, 22(12): 2794-2802. doi: 10.1063/1.525186 [4] CACUCI D G. Second-order adjoint sensitivity analysis methodology (2nd-ASAM) for computing exactly and efficiently first- and second-order sensitivities in large-scale linear systems: I. Computational methodology[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2015, 284: 687-699. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2014.12.042 [5] SMITH R C. Uncertainty quantification: theory, implementation, and applications[M]. Philadelphia: Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, 2013. [6] HELTON J C, DAVIS F J. Latin hypercube sampling and the propagation of uncertainty in analyses of complex systems[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2003, 81(1): 23-69. [7] 王毅箴. 球床高温堆燃料多次通过对燃耗不确定性影响及机理研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学,2021. [8] WANG Y Z, CUI M L, GUO J, et al. Lognormal-based sampling for fission product yields uncertainty propagation in pebble-bed HTGR[J]. Science and Technology of Nuclear Installations, 2020, 8014521. [9] CONNOR R J, MOSIMANN J E. Concepts of independence for proportions with a generalization of the Dirichlet distribution[J]. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 1969, 64(325): 194-206. doi: 10.1080/01621459.1969.10500963 [10] WONG T T. Parameter estimation for generalized Dirichlet distributions from the sample estimates of the first and the second moments of random variables[J]. Computational Statistics & Data Analysis, 2010, 54(7): 1756-1765. [11] WANG Y Z, CUI M L, GUO J, et al. Decay Branch ratio sampling method with Dirichlet distribution[J]. Energies, 2023, 16(4): 1962. doi: 10.3390/en16041962 -





 下载:
下载: