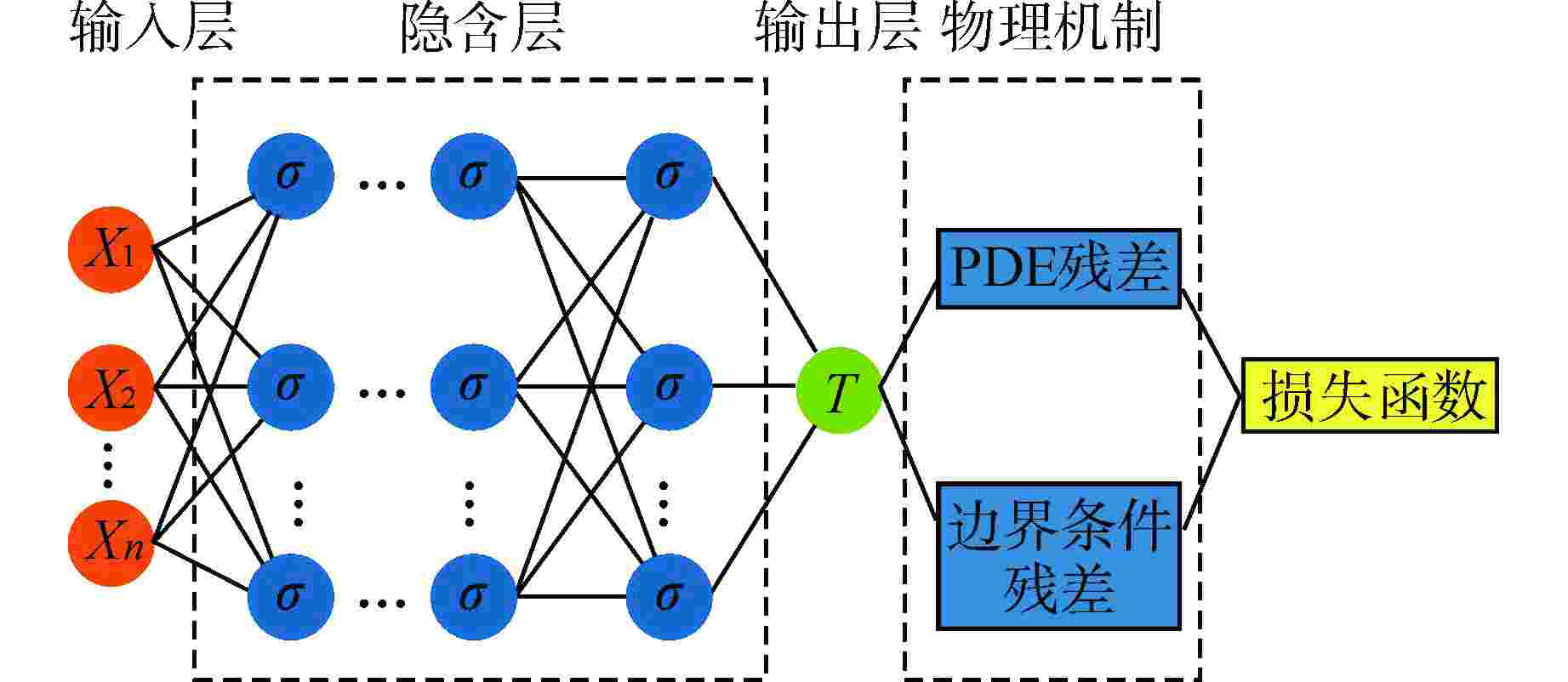
Research on Fast Prediction Method of Fuel Rod Steady-state Temperature Distribution Based on PINN
-
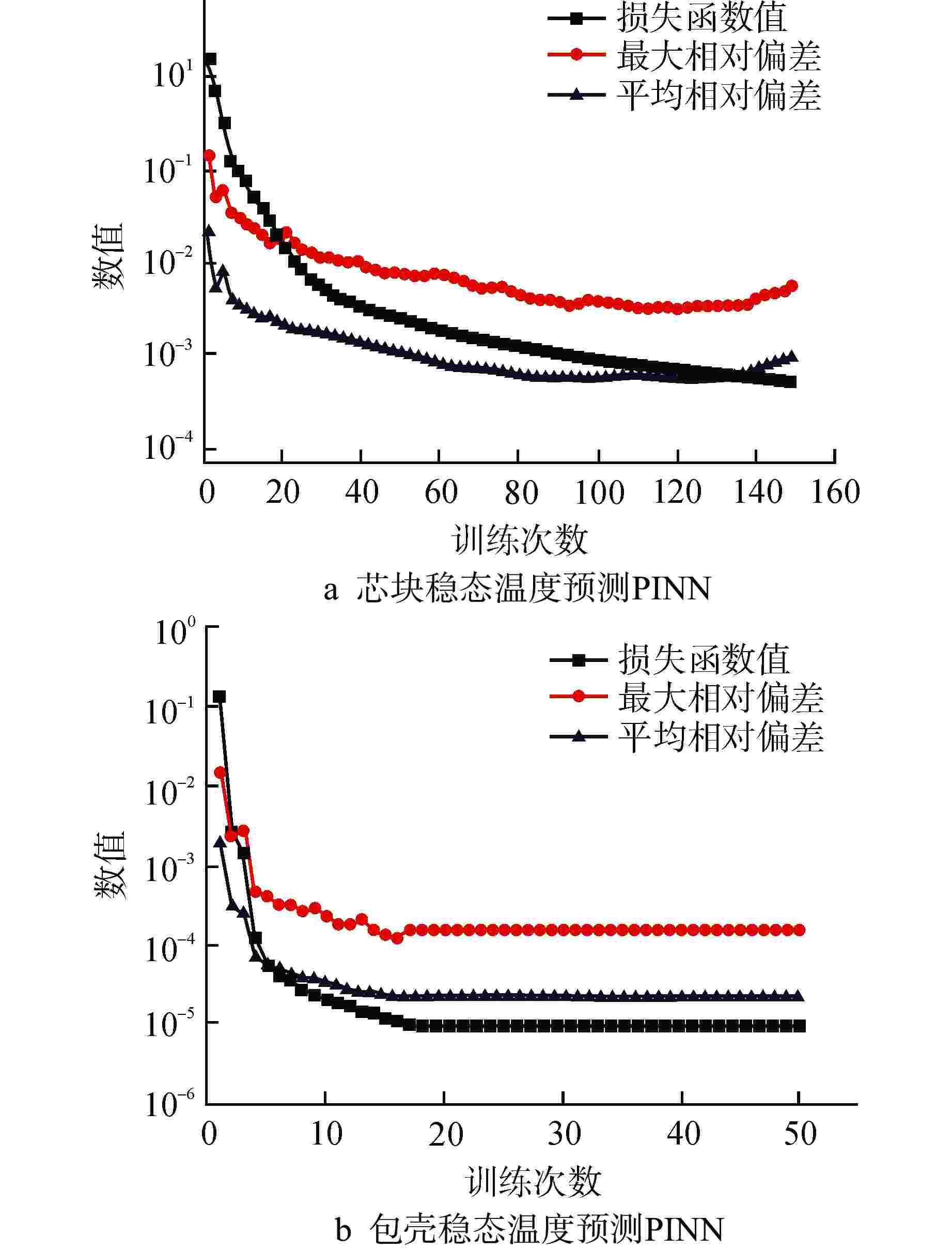
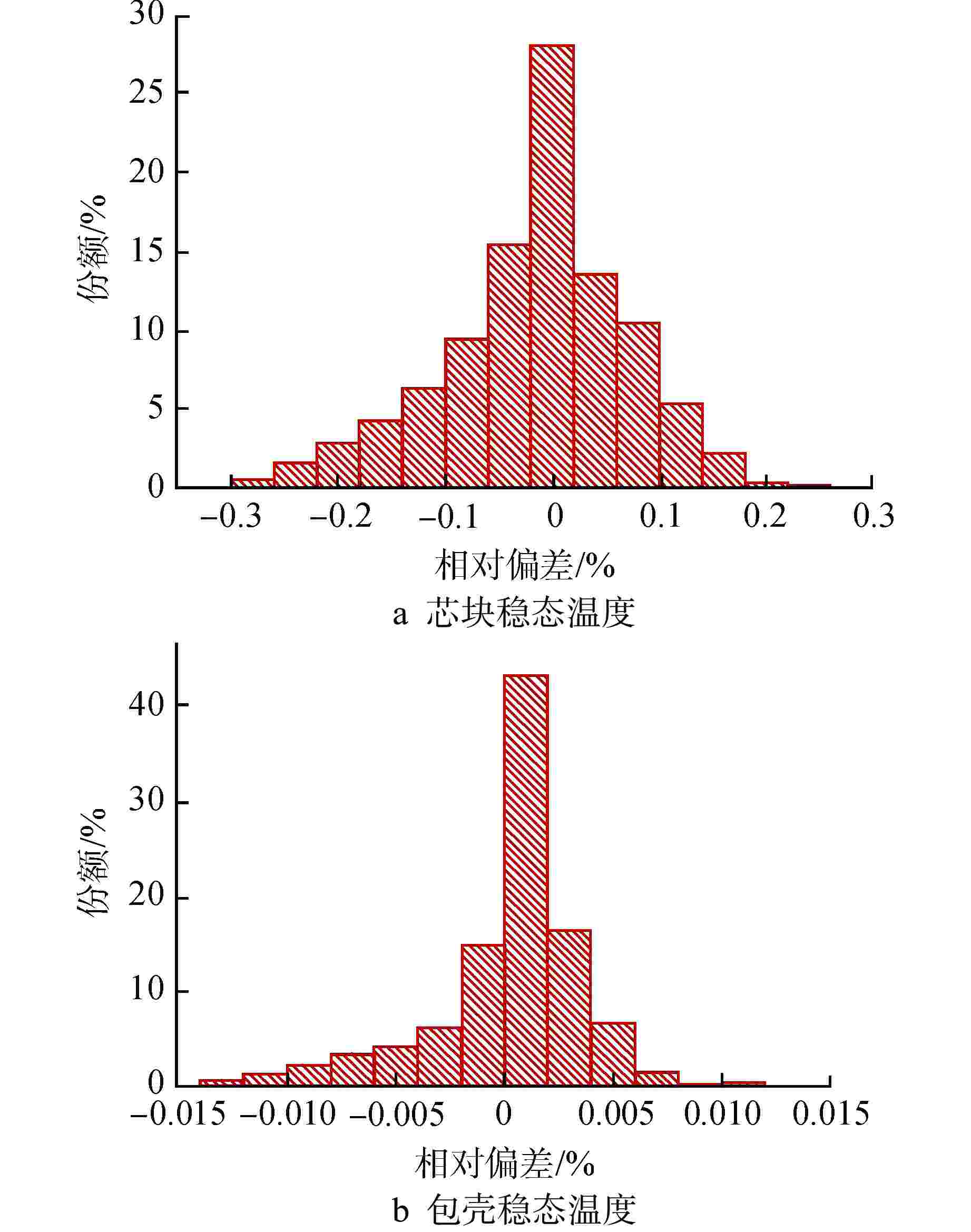
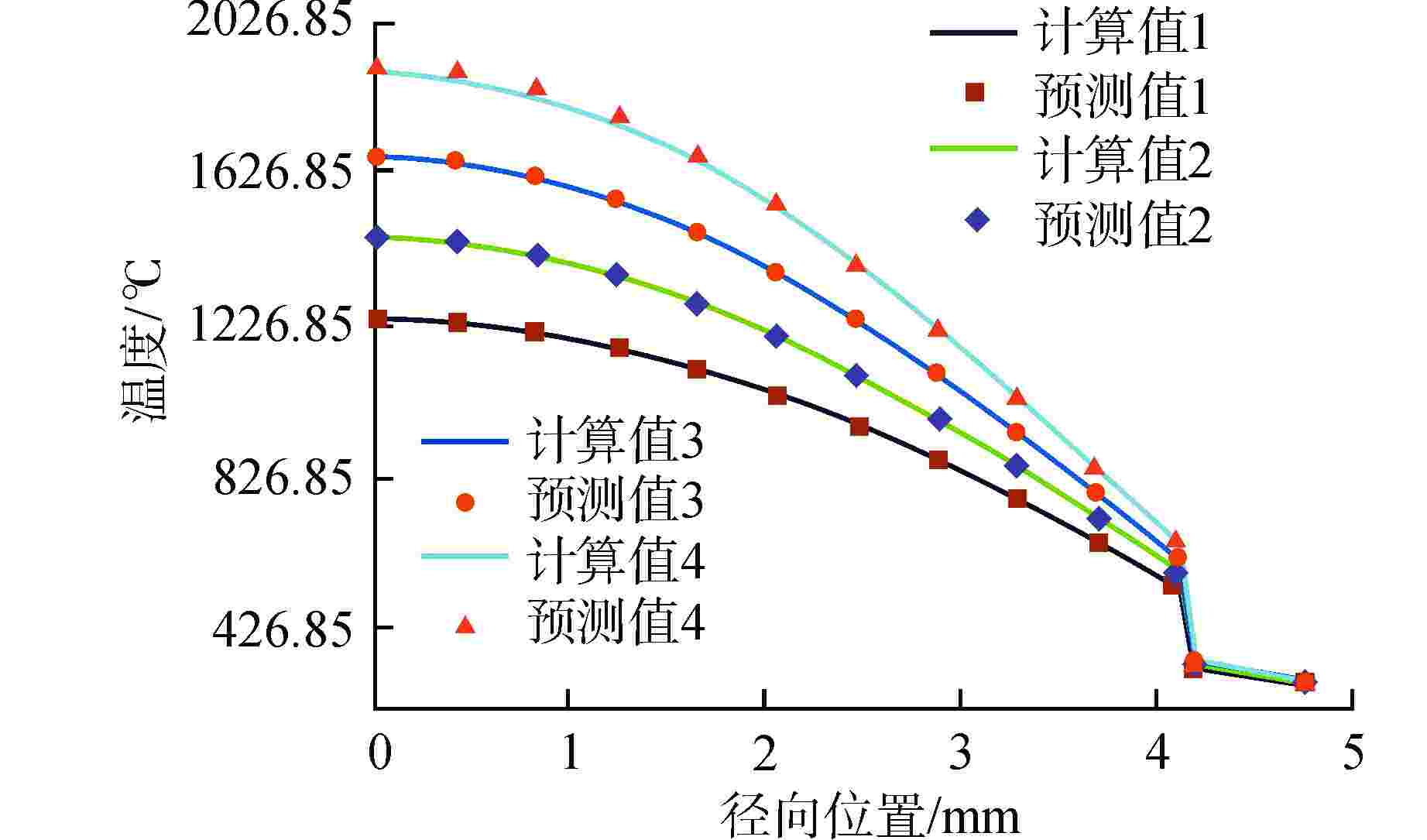
摘要: 本研究建立了一种基于物理信息神经网络(PINN)的燃料棒稳态温度分布快速预测方法。将燃耗、线功率、温度边界、空间位置等作为特征参数,利用PINN求解参数化的固体导热方程。基于该方法分别建立了燃料芯块和包壳稳态温度分布快速预测模型,计算结果表明:快速预测模型的计算速度相比商业有限元软件而言快1000倍,同时具有较高精度,芯块和包壳稳态温度与验证集相比预测最大相对偏差分别约0.318%、0.013%,可以快速且准确地预测燃料棒稳态温度分布。
-
关键词:
- 物理信息神经网络(PINN) /
- 燃料棒稳态温度 /
- 快速预测 /
- 燃料行为
Abstract: A fast prediction method of fuel rod steady-state temperature distribution base on Physical Informed Neural Network (PINN) is established in this research. The burnup, linear power, boundary temperature and space position are taken as characteristic parameters to solve the parametric solid heat conduction equations using PINN. Based on this method, rapid prediction models for the steady-state temperature distribution of fuel pellet and cladding were constructed. The calculation results show that the calculation speed of fast prediction models are about 1000 times faster than that of commercial finite element method software, and they also have high accuracy. The maximum relative deviation of the steady-state temperature prediction of fuel pellets and cladding is about 0.318% and 0.013% respectively compared with the validation set. The established PINN model can quickly and accurately predict the steady-state temperature distribution of fuel rods. -
表 1 PINN参数表
Table 1. Parameters of PINN
参数 芯块稳态温度预测PINN 包壳稳态温度预测PINN 输入参数维度 4 3 隐含层数目 2 1 隐含层神经元数 20 10 其他层激活函数 tanh函数 输出参数维度 1 表 2 燃料芯块稳态温度预测PINN采样方案
Table 2. Sampling Scheme of PINN for Predicting Fuel Pellet Temperature
参数 训练采样点数目 验证采样点数目 平均燃耗
[0~60000 MW·d·t−1(U)]5 10 平均线功率
(0~35 W·mm−1)5 10 外表面温度
(573~873 K)5 10 无量纲化径向位置
(0~1)20 40 括号中数据为取值范围,下同 表 3 燃料包壳稳态温度预测PINN采样方案
Table 3. Sampling Scheme of PINN for Predicting Fuel Cladding Temperature
参数 训练采样点数目 验证采样点数目 平均线功率
(0~35 W·mm−1)5 10 外表面温度
(293~673 K)5 10 无量纲化径向位置
(0.88~1)5 10 表 4 PINN预测值与FEM计算值的对比
Table 4. Comparison between PINN Predictions and FEM Calculations
参数 芯块稳态温度预测PINN 包壳稳态温度预测PINN 绝对偏差①/℃ [−3.97, 4.96] [−0.036, 0.045] 绝对偏差平均值②/℃ 0.68 0.011 相对偏差③/% [−0.262, 0.318] [−0.011, 0.013] 相对偏差平均值④/% 0.064 0.002 注:①绝对偏差=PINN预测值–FEM计算值;②绝对偏差平均值基于绝对值计算;③相对偏差=(PINN预测值–FEM计算值)/FEM计算值;④相对偏差平均值基于绝对值计算 表 5 PINN预测速度与FEM求解速度的对比
Table 5. Comparison between PINN Prediction Speed and FEM Solution Speed
对比项 PINN训练耗时/s PINN预测耗时/s FEM计算耗时/s 加速比 芯块 113.2 7.20×10−3 7.38 1025 包壳 19.4 1.50×10−4 0.44 2933 总计 132.6 7.35×10−3 7.82 1064 -
[1] 洪亮,金鑫,刘虓瀚,等. 机器学习算法在燃料棒温度性能预测中的应用[J]. 深圳大学学报: 理工版,2022, 39(5): 515-520. [2] CHE Y F, YURKO J, SEURIN P, et al. Machine learning-assisted surrogate construction for full-core fuel performance analysis[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2022, 168: 108905. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2021.108905 [3] RAISSI M, PERDIKARIS P, KARNIADAKIS G E. Physics-informed neural networks: a deep learning framework for solving forward and inverse problems involving nonlinear partial differential equations[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2019, 378: 686-707. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2018.10.045 [4] BERNARD L C, JACOUD J L, VESCO P. An efficient model for the analysis of fission gas release[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2002, 302(2-3): 125-134. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3115(02)00793-6 [5] LUSCHER W G, GEELHOOD K J, PORTER I E. Material property correlations: comparisons between FRAPCON-4.0, FRAPTRAN-2.0, and MATPRO: PNNL-19417 Rev. 2[R]. Richland, Washington: Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, 2015. [6] 阎昌琪. 核反应堆工程[M]. 黑龙江: 哈尔滨工程大学出版社,2004: 160. -





 下载:
下载: