Research on CANDU Channel Power Prediction Based on Stacking Ensemble Learning
-
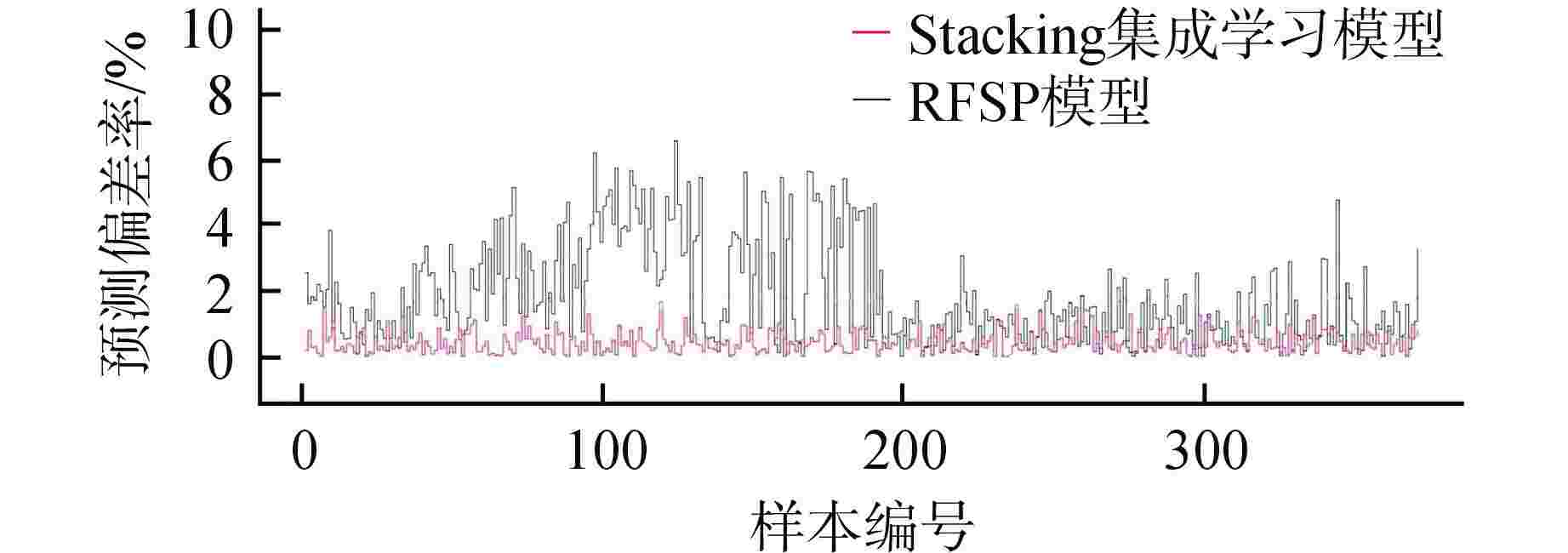
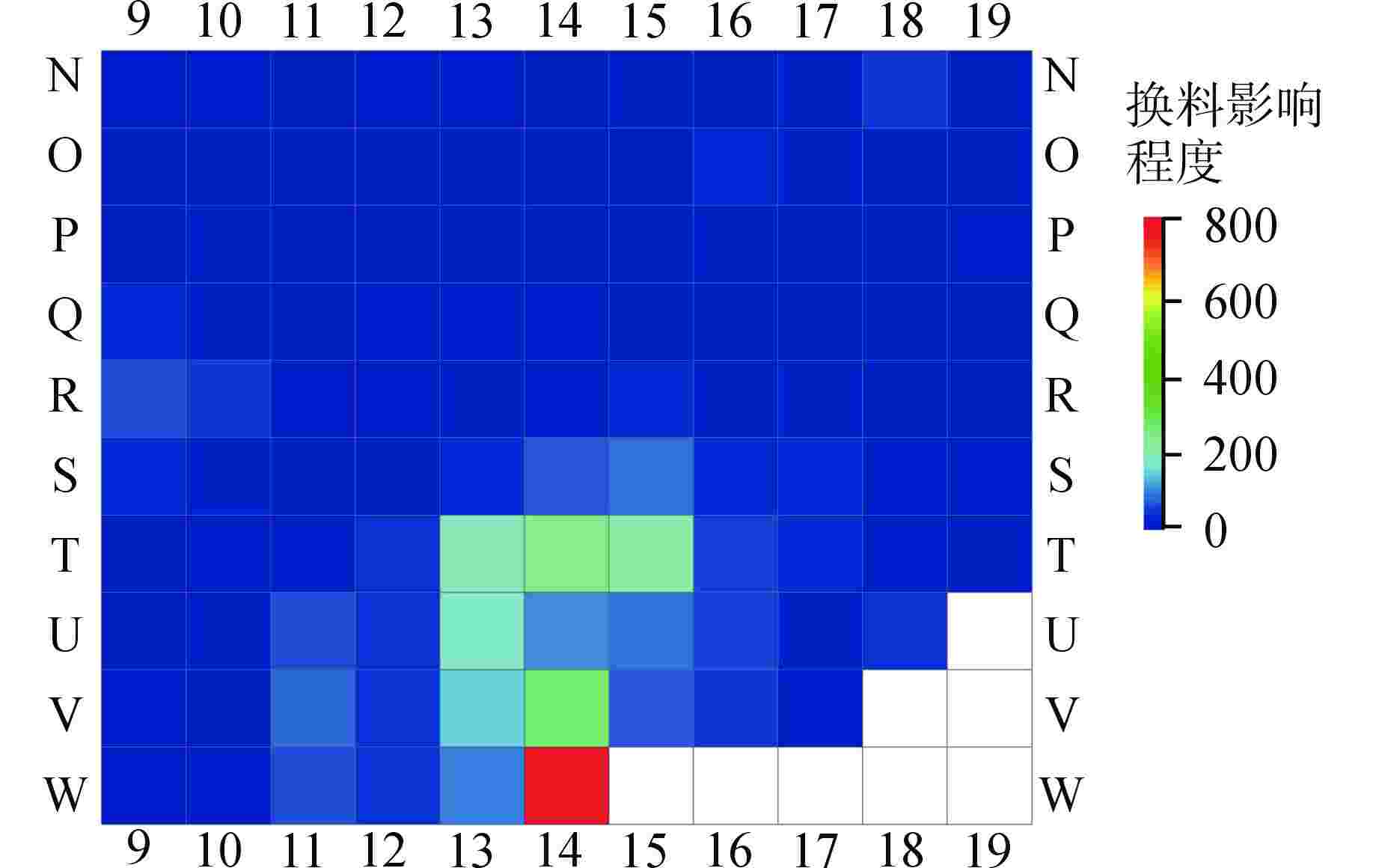
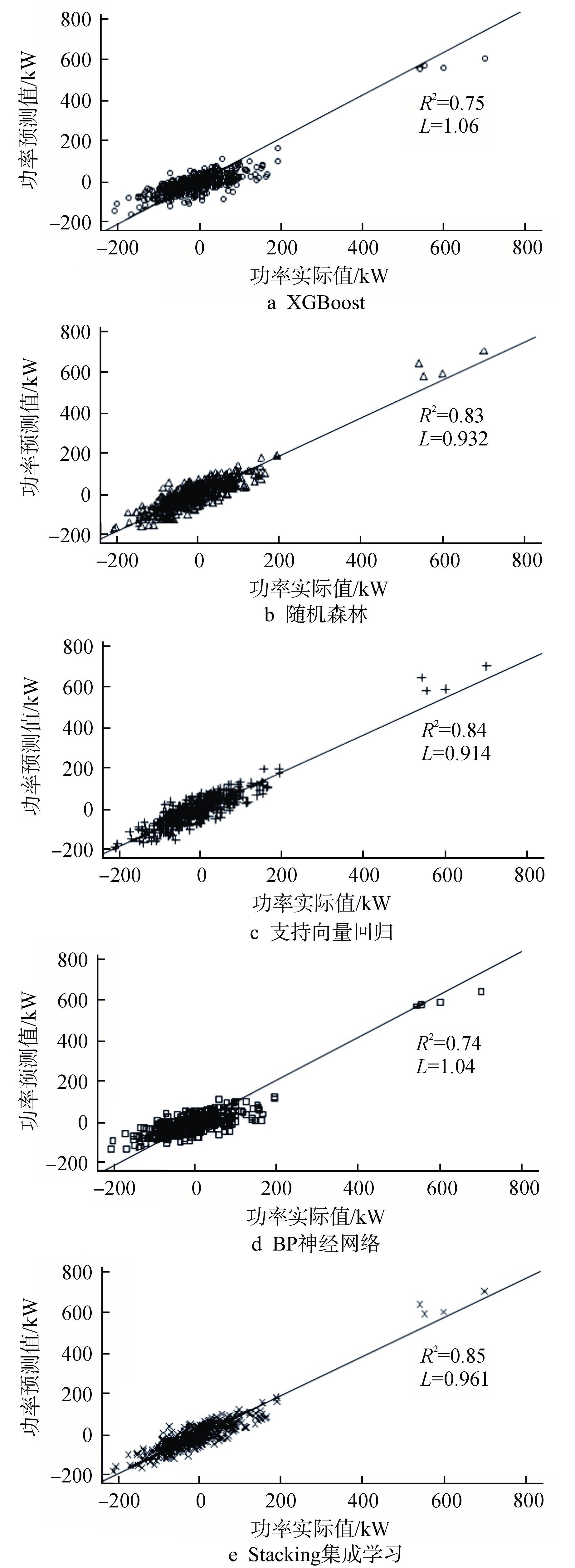
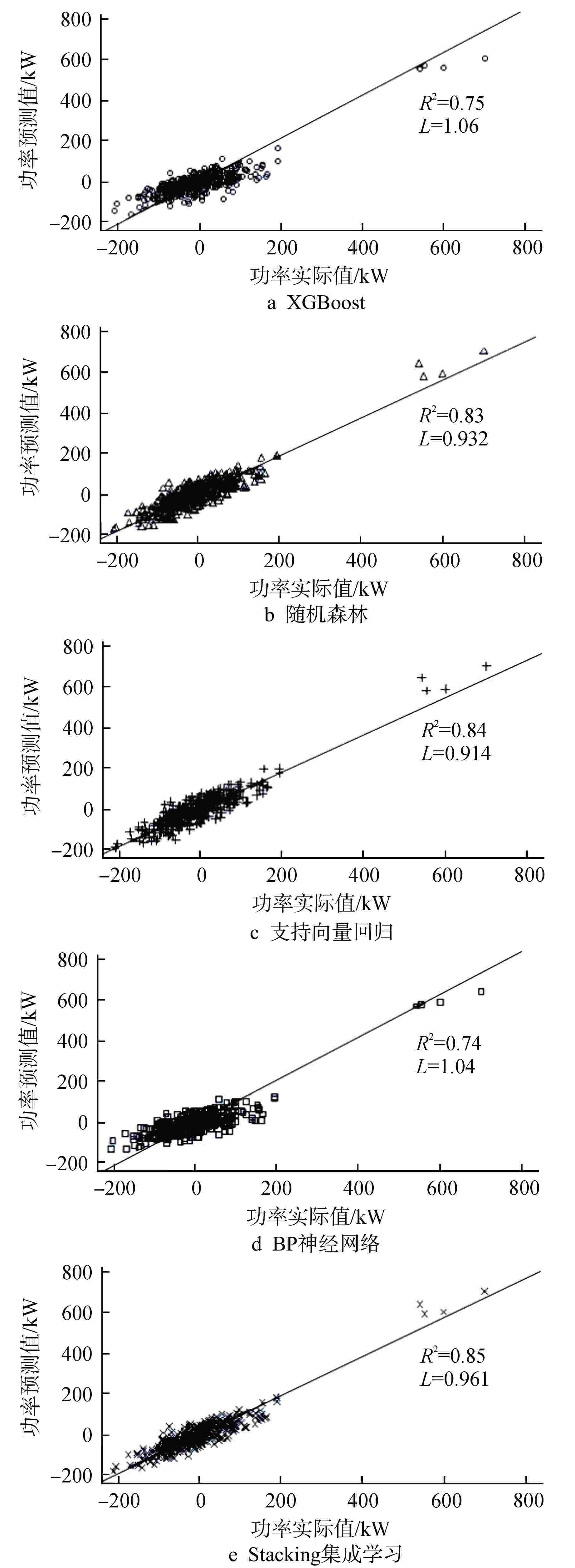
摘要: CANDU堆通道功率预测的准确性直接影响换料方案的优劣,进而影响反应堆运行的经济性和安全性。为提升预测效果,主张引入人工智能算法从历史运行数据中挖掘潜在变量关系。经数据清洗、特征选择后,设计“换料影响指数”特征,以XGBoost、随机森林、支持向量回归和反向传播(BP)神经网络为初级学习器,支持向量回归为次级学习器,构建基于Stacking的集成学习模型。经对比分析,Stacking集成学习模型在单一学习模型的基础上实现了预测效果的“二次提升”,且在平均预测偏差率、最大预测偏差率和预测偏差率方差上,Stacking集成学习模型的效果均显著优于传统RFSP模型,这使得物理工程师在换料计划制定过程中能够得到更为准确的功率反馈,以科学地选取换料通道,进而在保证反应堆安全性的基础上提升经济效益。
-
关键词:
- CANDU堆 /
- 人工智能 /
- 通道功率预测 /
- Stacking集成学习
Abstract: The accuracy of CANDU reactor channel power prediction directly affects the quality of the refueling plan, which in turn affects the economy and safety of reactor operation. To improve the prediction effect, it is advocated to introduce artificial intelligence algorithms to mine the potential variable relationship from historical operation data. After data cleaning and feature selection, a feature termed "Refueling Impact Index" is designed. With XGBoost, random forest, support vector regression, and BP neural network as primary learners and support vector regression as secondary learners, an ensemble learning model based on Stacking is constructed. Through comparative analysis, the Stacking ensemble learning model has achieved a "secondary improvement" in prediction effect on the basis of a single learning model. Moreover, the Stacking ensemble learning model has significantly better effect than the traditional RFSP methods in terms of average prediction deviation rate, maximum prediction deviation rate, and prediction deviation rate variance. This enables physical engineers to obtain more accurate power feedback in the process of formulating refueling plans, scientifically select refueling channels, and thereby improve economic benefits while ensuring reactor safety. -
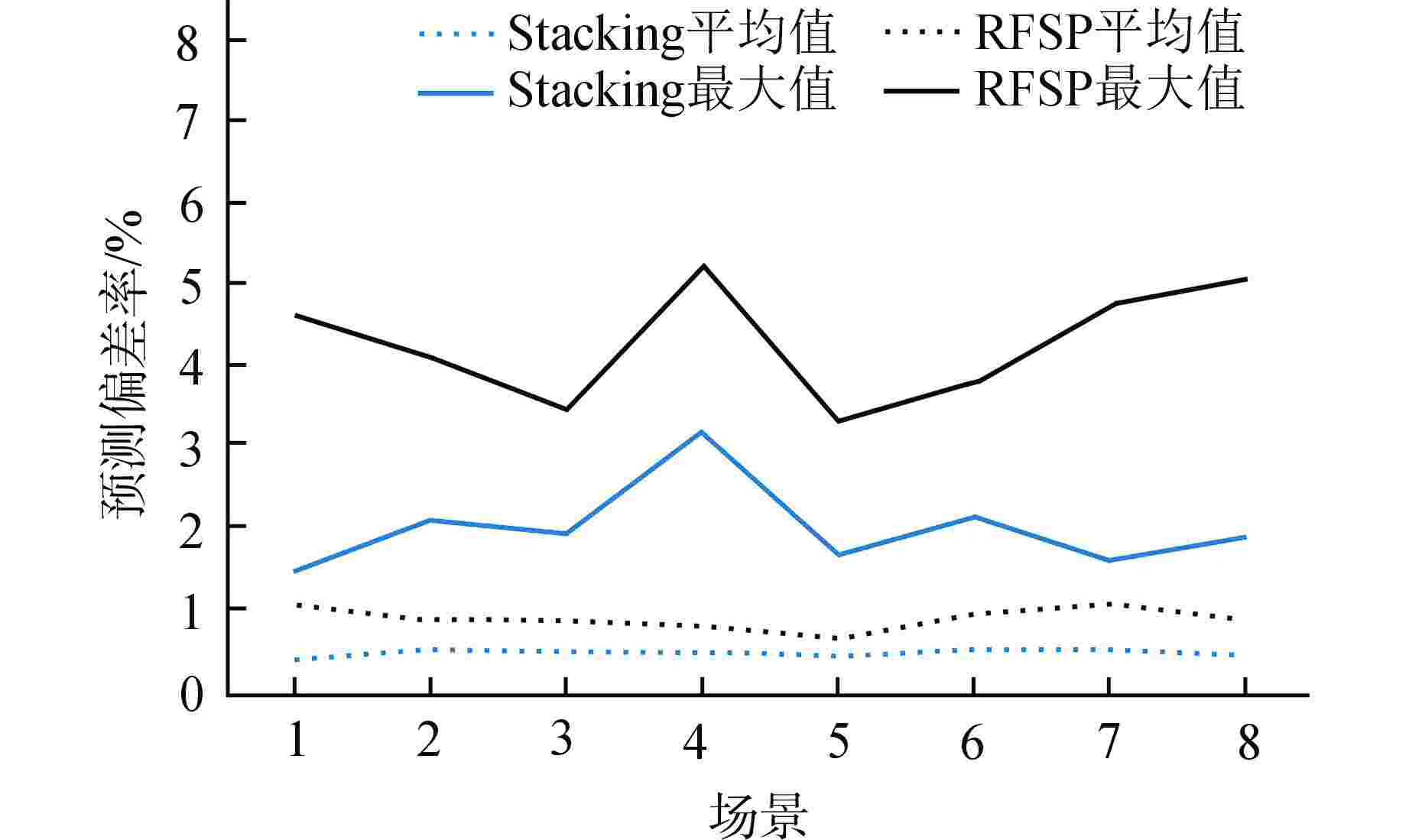
图 4 Stacking集成学习模型与RFSP模型在新数据下预测效果对比图
场景1—1#5473.4→5474.4;场景2—1#5474.4→5477.3;场景3—1#5477.3→5481.4;场景4—1#5465.1→5458.1;场景5—1#5464.1→5465.1;场景6—2#5357→5361;场景7—2#5354→5357;场景8—2#5347.5→5350.5
Figure 4. Comparison of Prediction Effects between Stacking Ensemble Learning Model and RFSP Model under New Data
-
[1] JEONG C J, CHO N Z. Power mapping in a Canada deuterium uranium reactor using Kalman filtering technique[J]. Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 2000, 37(9): 758-768. doi: 10.1080/18811248.2000.9714954 [2] MENESES A, DE LIMA A, SCHIRRU R. Artificial intelligence methods applied to the in-core nuclear fuel management optimization[M]//Nuclear Power. InTech, 2010,123-145. [3] ORTIZ J J, REQUENA I. Using a multi-state recurrent neural network to optimize loading patterns in BWRs[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2004, 31(7): 789-803. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2003.11.001 [4] DO B, ROH G, CHOI H. Optimal refueling pattern search for a CANDU reactor using a genetic algorithm[C]//International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants ICAPP-2006. Reno: ICAPP, 2006: 2422-2431. [5] 夏虹,李彬,刘建新. 基于RBF神经网络的压水堆堆芯三维功率分布方法研究[J]. 原子能科学技术,2014, 48(4): 698-702. doi: 10.7538/yzk.2014.48.04.0698 [6] 霍小东,谢仲生. 遗传算法在CANDU堆燃料管理中应用的研究[J]. 核动力工程,2005, 26(6): 539-543. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0926.2005.06.003 [7] 高雪东. CANDU核反应堆换料算法研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学,2007. [8] 刘志宾. 基于中子等效均匀扩散理论的CANDU堆堆芯功率分布计算研究[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学(北京),2017. [9] CHEN T Q, GUESTRIN C. XGBoost: a scalable tree boosting system[C]//Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. San Francisco: ACM, 2016: 785-794. [10] BREIMAN L. Random forests[J]. Machine Learning, 2001, 45(1): 5-32. doi: 10.1023/A:1010933404324 [11] CORTES C, VAPNIK V. Support-vector networks[J]. Machine Learning, 1995, 20(3): 273-297. [12] 邓乃扬,田英杰. 支持向量机: 理论、算法与拓展[M]. 北京: 科学出版社,2009: 5-32. [13] WERBOS P J. Beyond regression: new tools for prediction and analysis in the behavioral sciences[D]. Cambridge: Harvard University, 1974. [14] RUMELHART D E, HINTON G E, WILLIAMS R J. Learning internal representations by error propagation[J]. Biometrika, 1986, 71: 599-607. [15] RUMELHART D E, HINTON G E, WILLIAMS R J. Learning representations by back-propagating errors[J]. Nature, 1986, 323(6088): 533-536. doi: 10.1038/323533a0 [16] 周志华. 机器学习[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社,2016:126-131. -





 下载:
下载: