Investigation of Pivotal Models for Subcooled Boiling Based on the Eulerian-Eulerian Framework
-
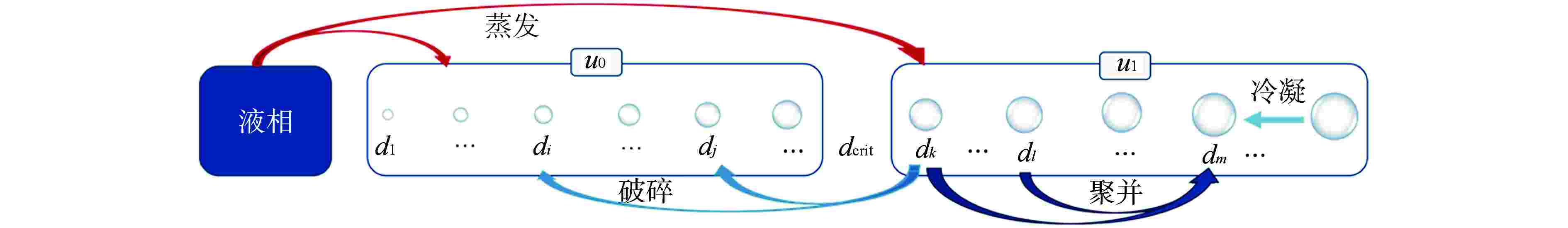
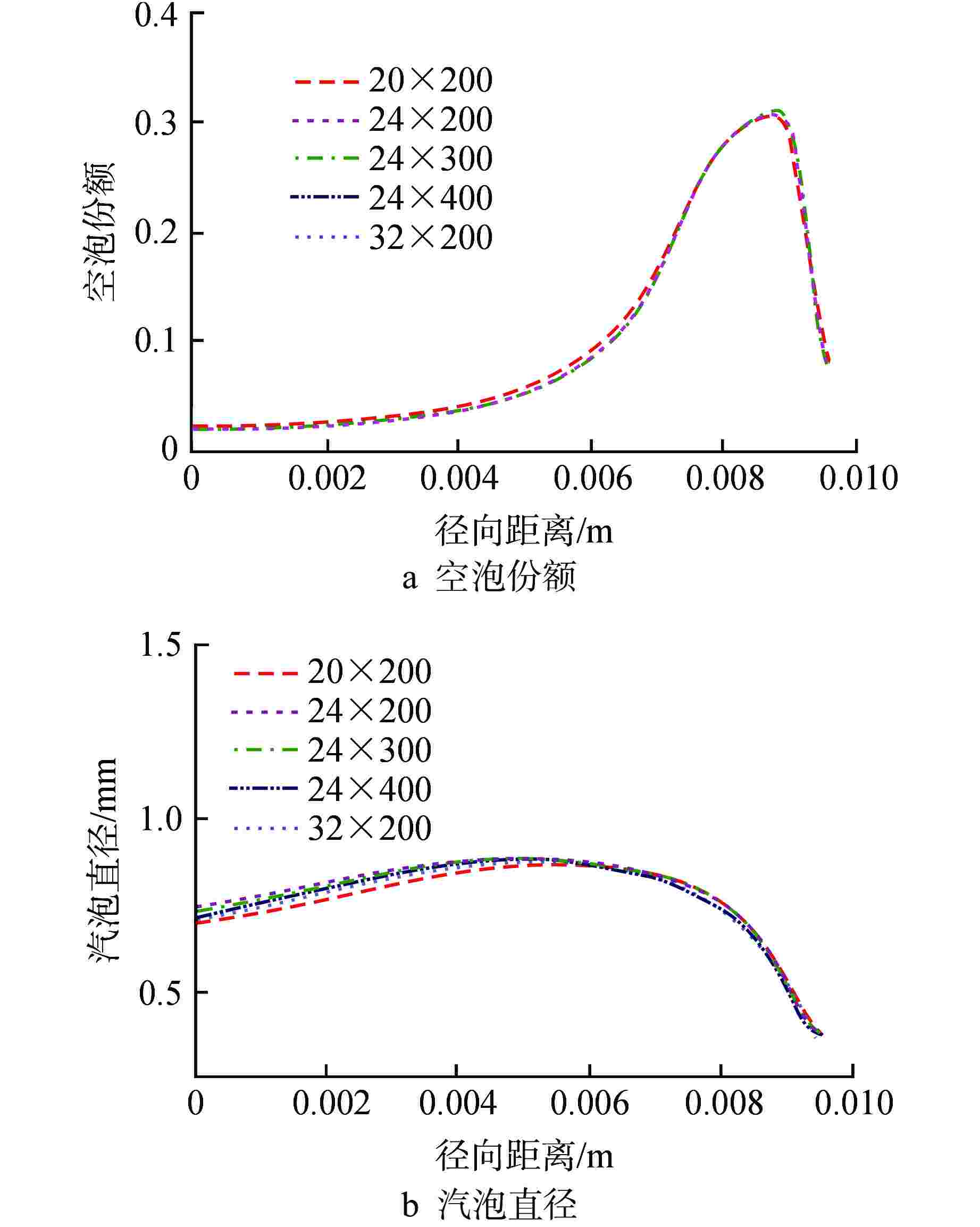
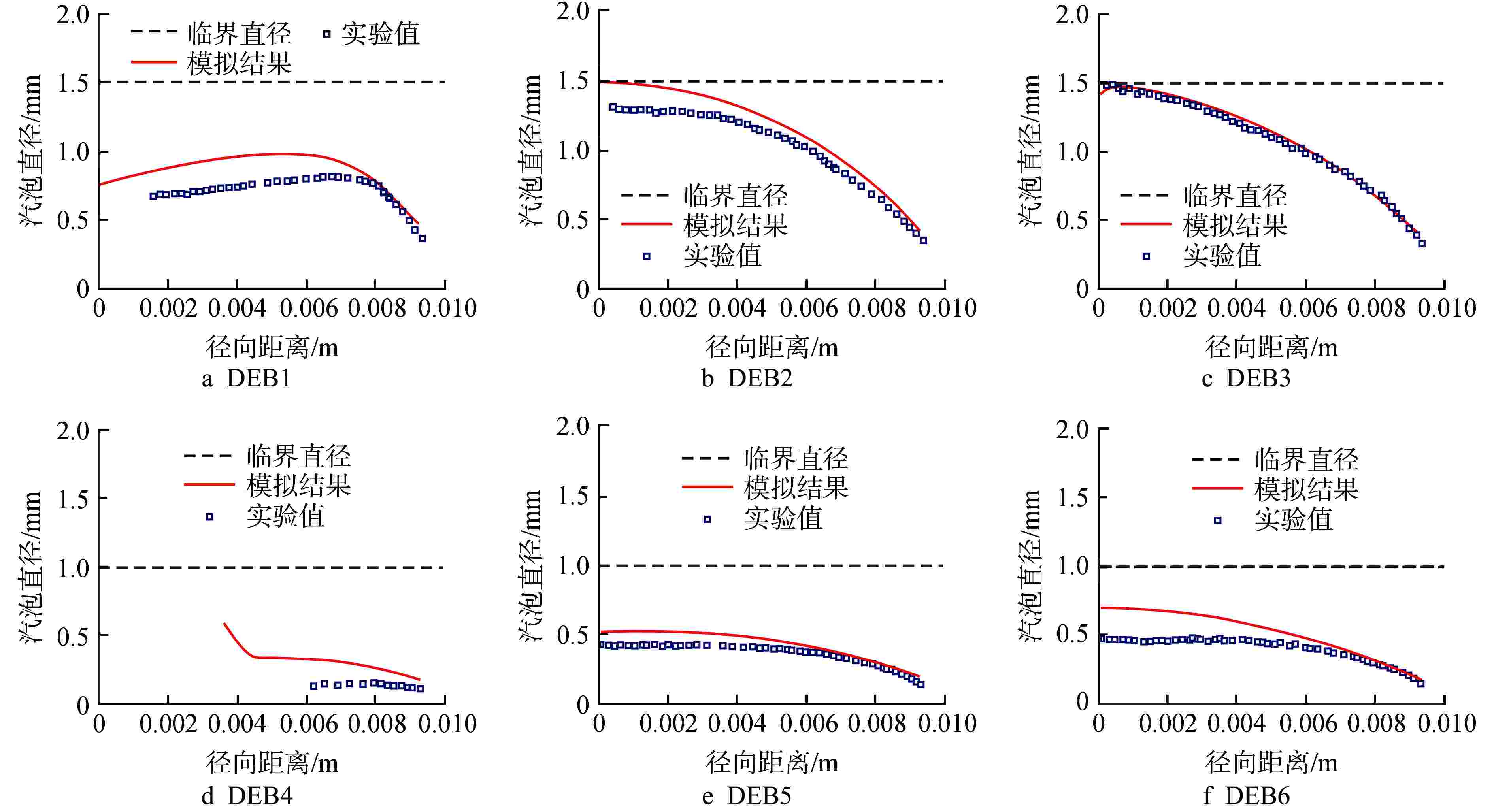
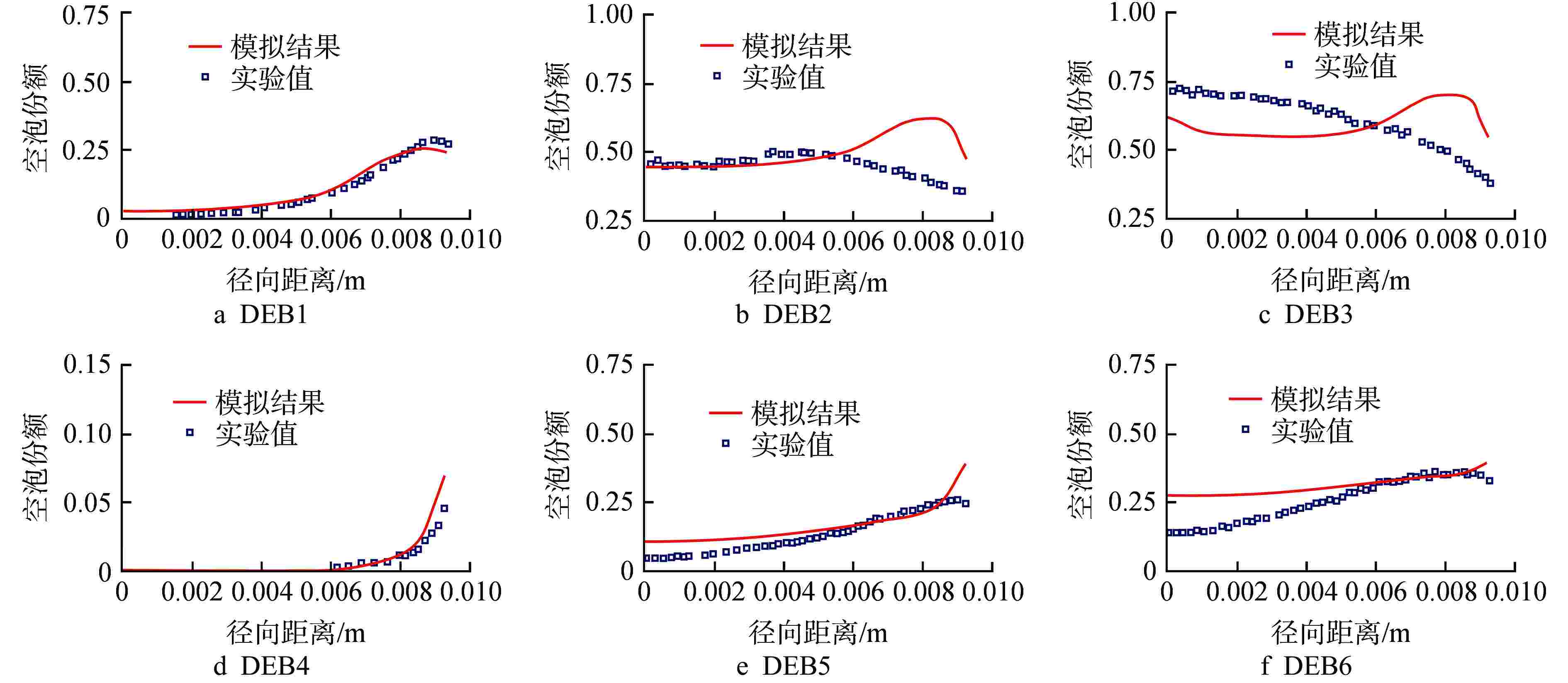
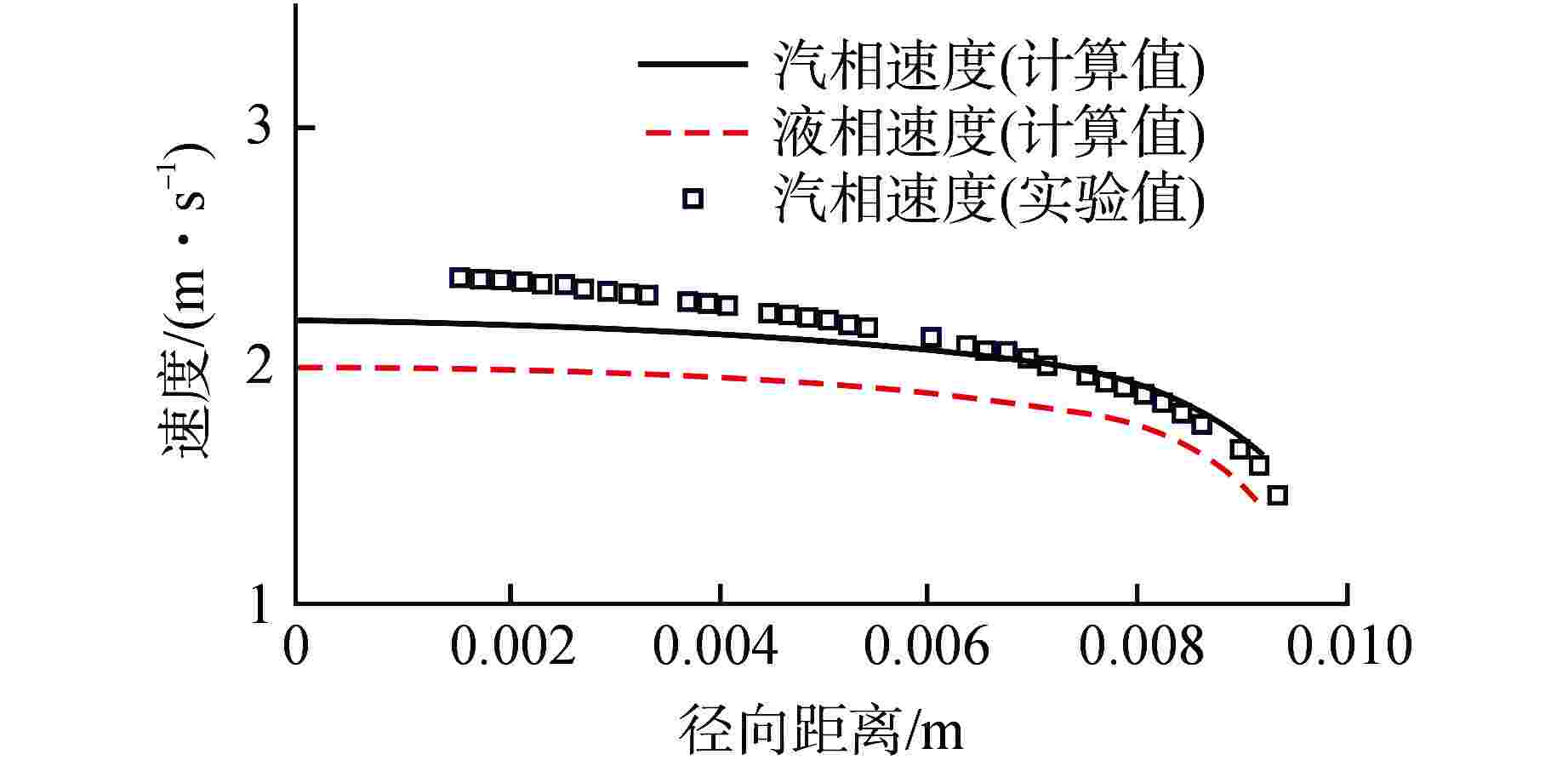
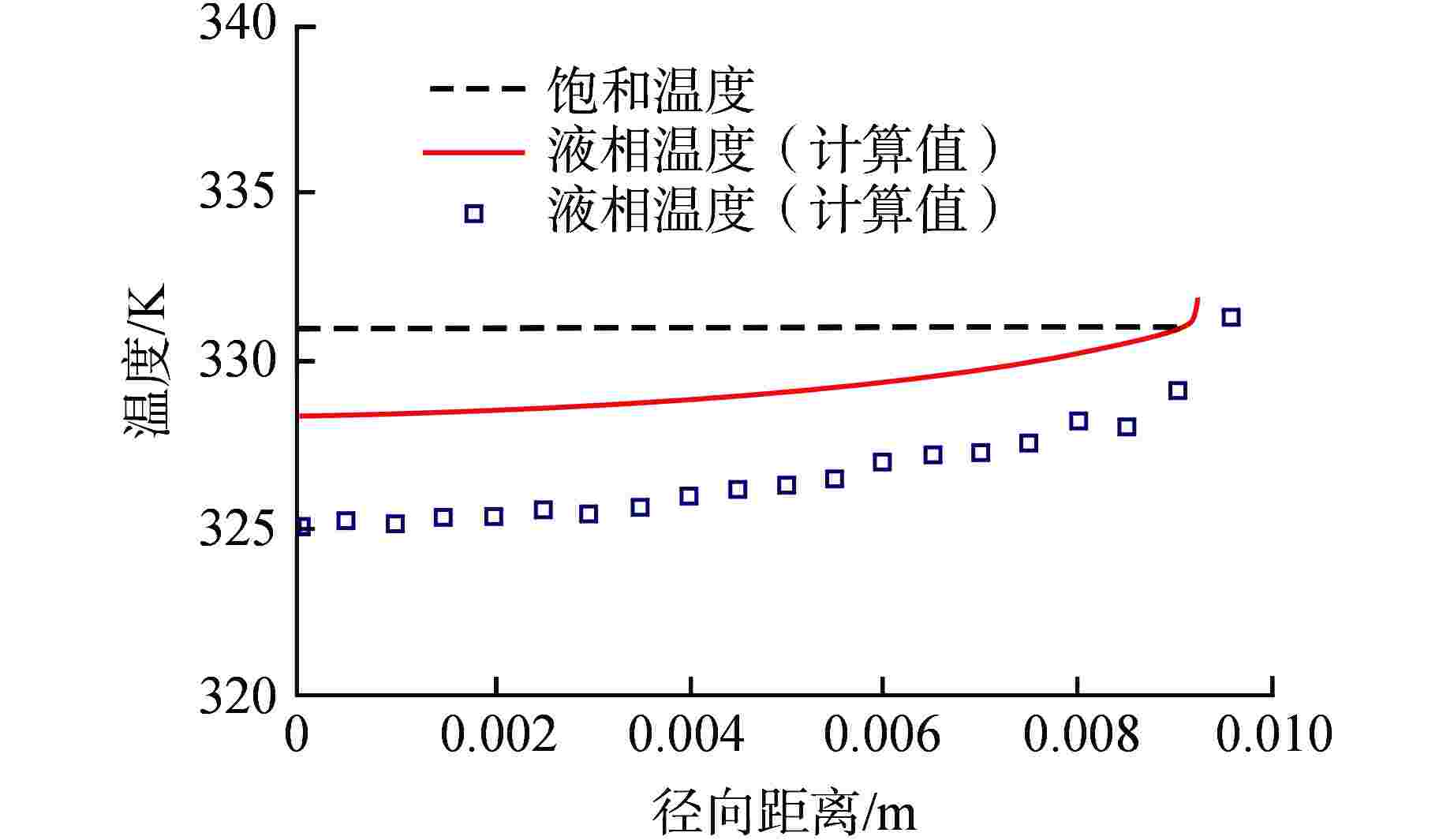
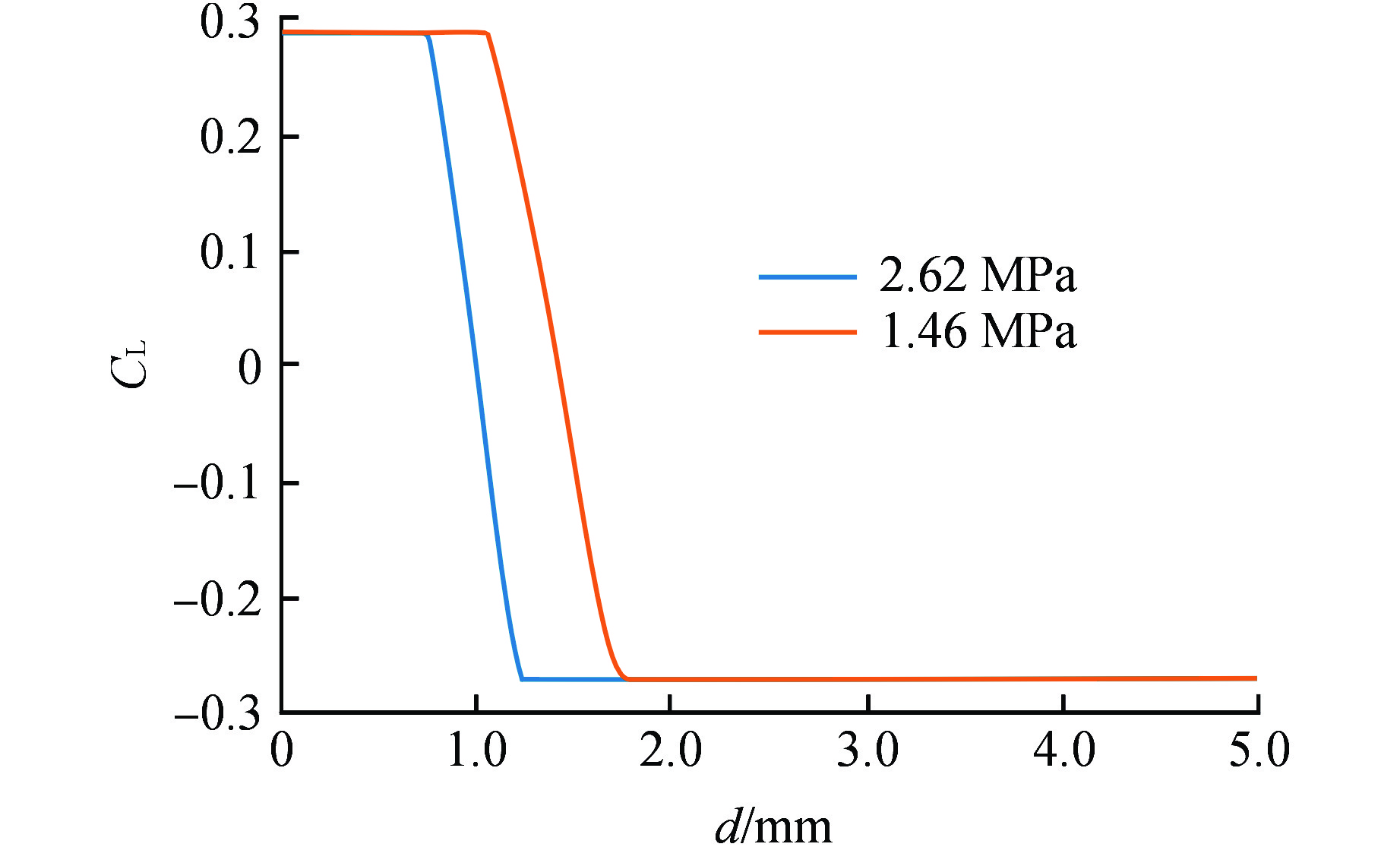
摘要: 针对计算流体动力学(CFD)中欧拉-欧拉两流体模型体系的壁面沸腾、相间作用、汽泡聚并/破碎等关键模型开展研究。基于五分量壁面沸腾模型描述加热表面汽泡成核、生长、脱离、滑移和浮升等行为,基于非均速汽泡分群(iMUSIG)模型考虑汽泡直径分布对相间作用的影响,同时基于Prince-Blanch模型、Luo-Svendsen模型模拟了汽泡聚并/破碎。通过与国际标准算题 DEBORA的实验结果对比表明,该模型能够较准确地预测压水堆正常运行工况下高过冷度条件的空泡份额分布和汽泡直径分布。对低过冷度、高空泡份额工况,模型无法预测空泡份额的中心峰值。同时,比较计算和实验测量的汽泡运动速度和液相温度发现,现有五分量壁面沸腾模型可能低估了蒸发量。Abstract: Wall boiling, interphase interaction and bubble coalescence/breakup models involved in the Eulerian-Eulerian two-fluid model framework within Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) are investigated. In the framework, the five-component wall boiling model is employed to account for the on-wall bubble behavior, including nucleation, growth, detachment, sliding and lift-off. The inhomogeneous multi-size group (iMUSIG) model is utilized to consider the bubble size distribution and its effects on interphase interaction. The Prince-Blanch model and Luo-Svendsen model are used to model the bubble coalescence/breakup. The model performance is assessed based on the DEBORA benchmark, which indicates that the models can accurately predict the distribution of void fraction and bubble size under the condition of high subcooling in normal operation of PWR. However, the void fraction in the pipe center in the case of low subcooling and high void fraction cannot be predicted. It is also found that the five-component model may underestimate the evaporation at the heated wall by comparing the calculated bubble velocity and liquid temperature with the measured ones.
-
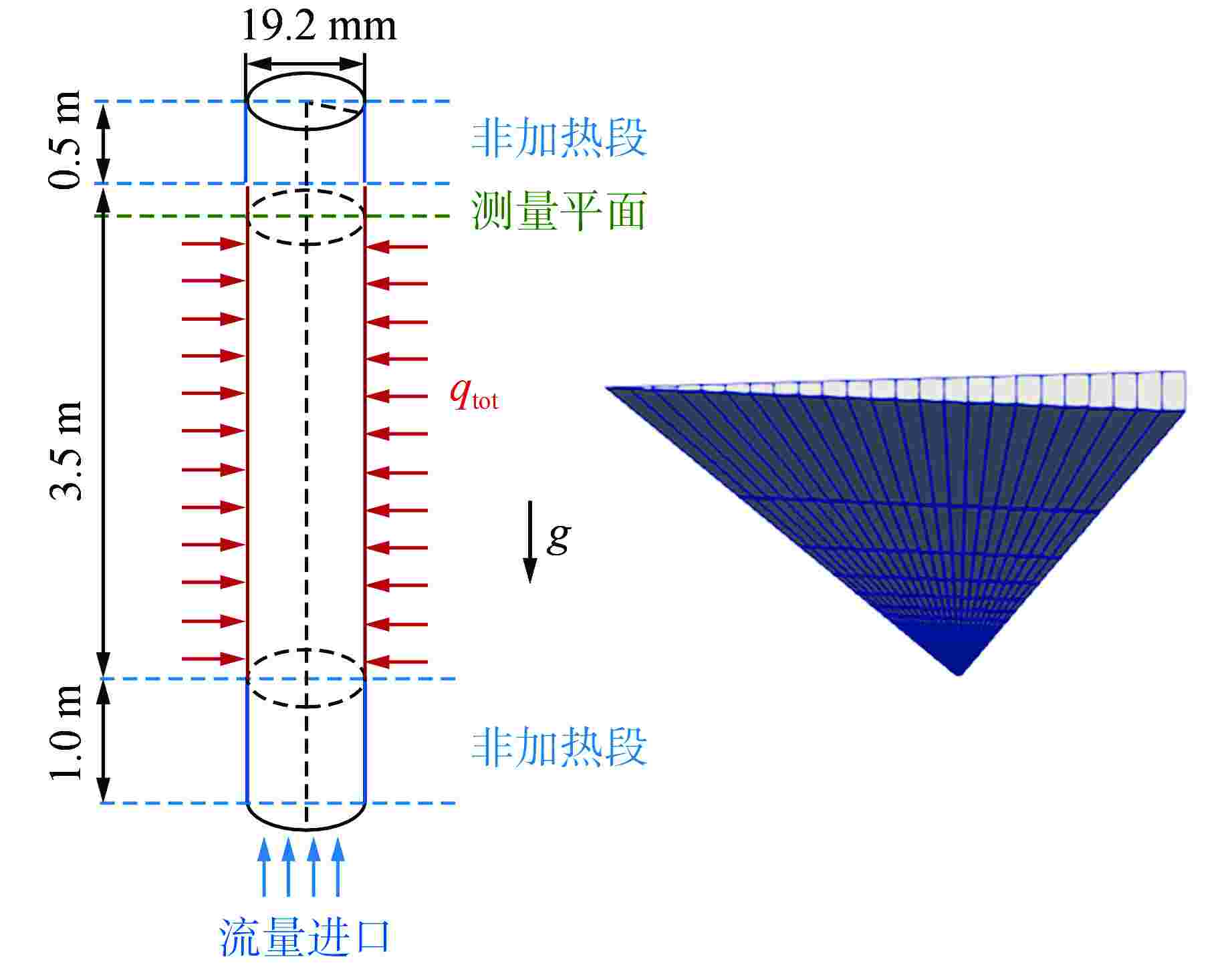
表 1 工况和边界条件
Table 1. Operating Conditions and Boundary Conditions
工况 压力/MPa 质量流速/
(kg·m−2·s−1)热流密度 /
(kW·m−2)入口温度/K DEB1 1.46 2030 76.24 304.31 DEB2 1.46 2023 76.26 312.82 DEB3 1.46 2024 76.26 317.36 DEB4 2.62 2992.6 107.52 334.07 DEB5 2.62 3000 109.3 341.5 DEB6 2.62 2984.3 107.52 345.64 -
[1] JOSHI J B, NAYAK A K. Advances of computational fluid dynamics in nuclear reactor design and safety assessment[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2018: 261-263. [2] YUN B J, SPLAWSKI A, LO S, et al. Prediction of a subcooled boiling flow with advanced two-phase flow models[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2012, 253: 351-359. doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2011.08.067 [3] YANG G, ZHANG W C, BINAMA M, et al. Review on bubble dynamic of subcooled flow boiling-part b: Behavior and models[J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2023, 184: 108026. doi: 10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2022.108026 [4] CHUANG T J, HIBIKI T. Interfacial forces used in two-phase flow numerical simulation[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2017, 113: 741-754. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2017.05.062 [5] KURUL N, PODOWSKI M Z. Multidimensional effects in forced convection subcooled boiling[C]//International Heat Transfer Conference 9. Jerusalem: Begel House Inc. , 1990. [6] WANG H B, XIONG J B, WANG J. Development and assessment of five-component wall boiling heat flux partitioning model[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2023, 158: 104306. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmultiphaseflow.2022.104306 [7] LEMMERT M, CHAWLA J M. Influence of flow velocity on surface boiling heat transfer coefficient[M]//HAHNE E, GRIGULL U. Heat Transfer in Boiling. New York: Academic Press, 1977: 237-247. [8] KREPPER E, RZEHAK R. CFD for subcooled flow boiling: Simulation of DEBORA experiments[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2011, 241(9): 3851-3866. doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2011.07.003 [9] RANZ W E, MARSHALL W R JR. Evaporation from drops, part I[J]. Chemical Engineering Progress, 1952, 48(3): 141-146. [10] ISHII M, ZUBER N. Drag coefficient and relative velocity in bubbly, droplet or particulate flows[J]. AIChE Journal, 1979, 25(5): 843-855. doi: 10.1002/aic.690250513 [11] TOMIYAMA A, TAMAI H, ZUN I, et al. Transverse migration of single bubbles in simple shear flows[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2002, 57(11): 1849-1858. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2509(02)00085-4 [12] BURNS A, FRANK T, HAMILL I, et al. The favre averaged drag model for turbulent dispersion in Eulerian multi-phase flows[C]//5th International Conference on Multiphase Flow. Yokohama: ICMF, 2004. [13] FRANK T, ZWART P J, SHI J M, et al. Inhomogeneous MUSIG model – a population balance approach for polydispersed bubbly flows[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference “Nuclear Energy for New Europe 2005”. Bled: NSS, 2005. [14] LUO H A, SVENDSEN H F. Theoretical model for drop and bubble breakup in turbulent dispersions[J]. AIChE Journal, 1996, 42(5): 1225-1233. doi: 10.1002/aic.690420505 [15] PRINCE M J, BLANCH H W. Bubble coalescence and break-up in air-sparged bubble columns[J]. AIChE Journal, 1990, 36(10): 1485-1499. doi: 10.1002/aic.690361004 -





 下载:
下载: