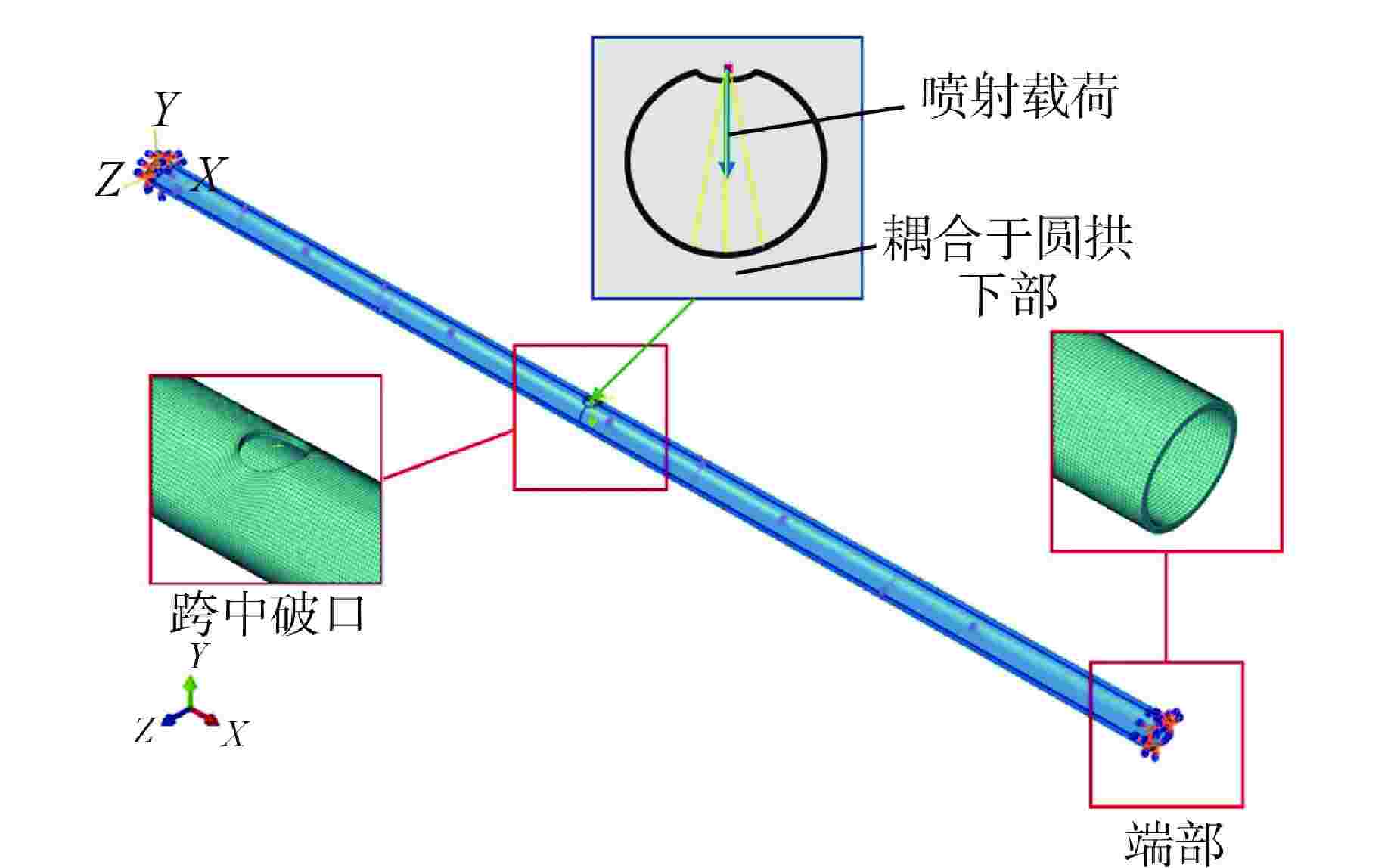
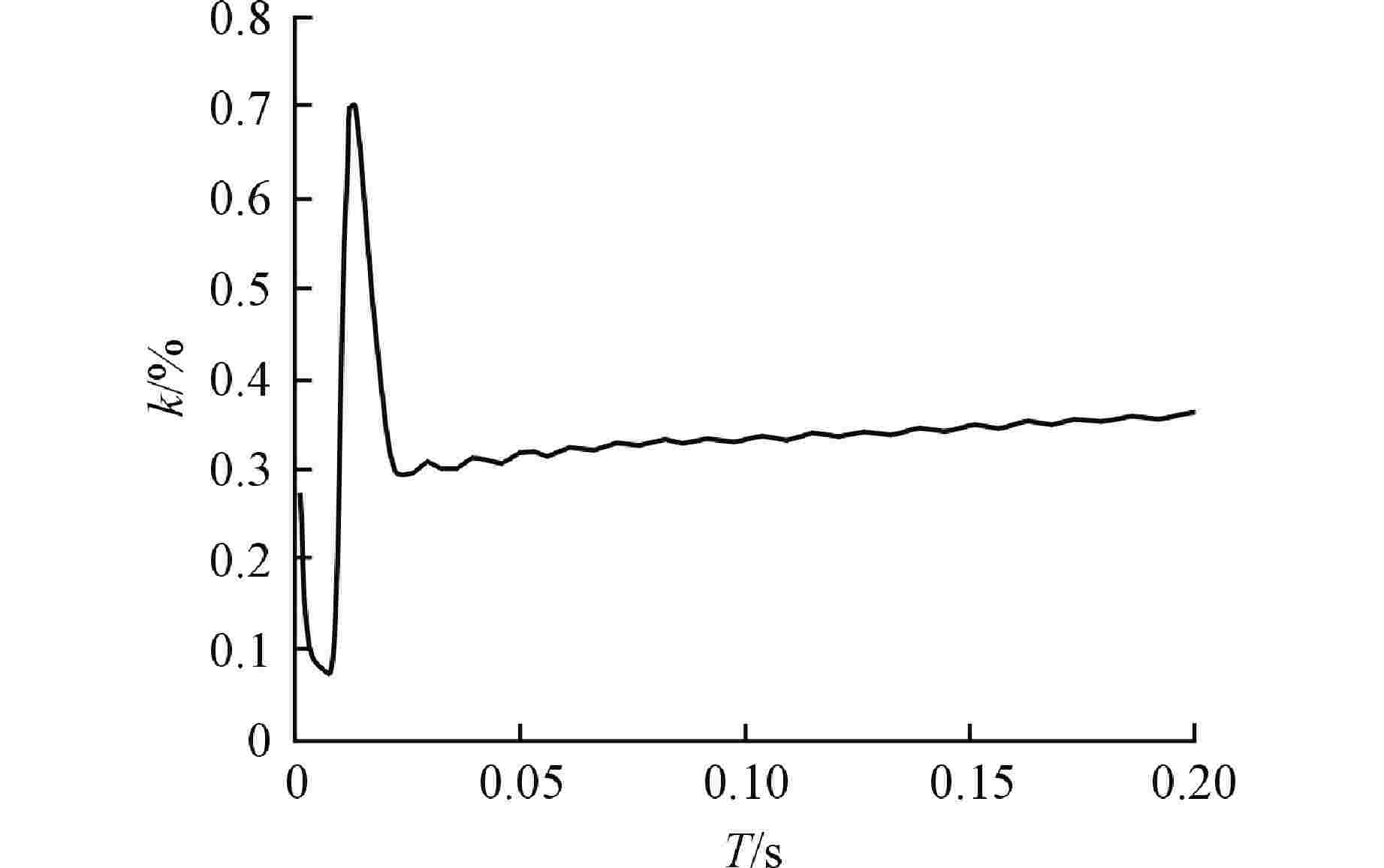
Maximum Deflection Prediction Method for Plastic Large Deformation of High-energy Pipelines under Impact Load
-
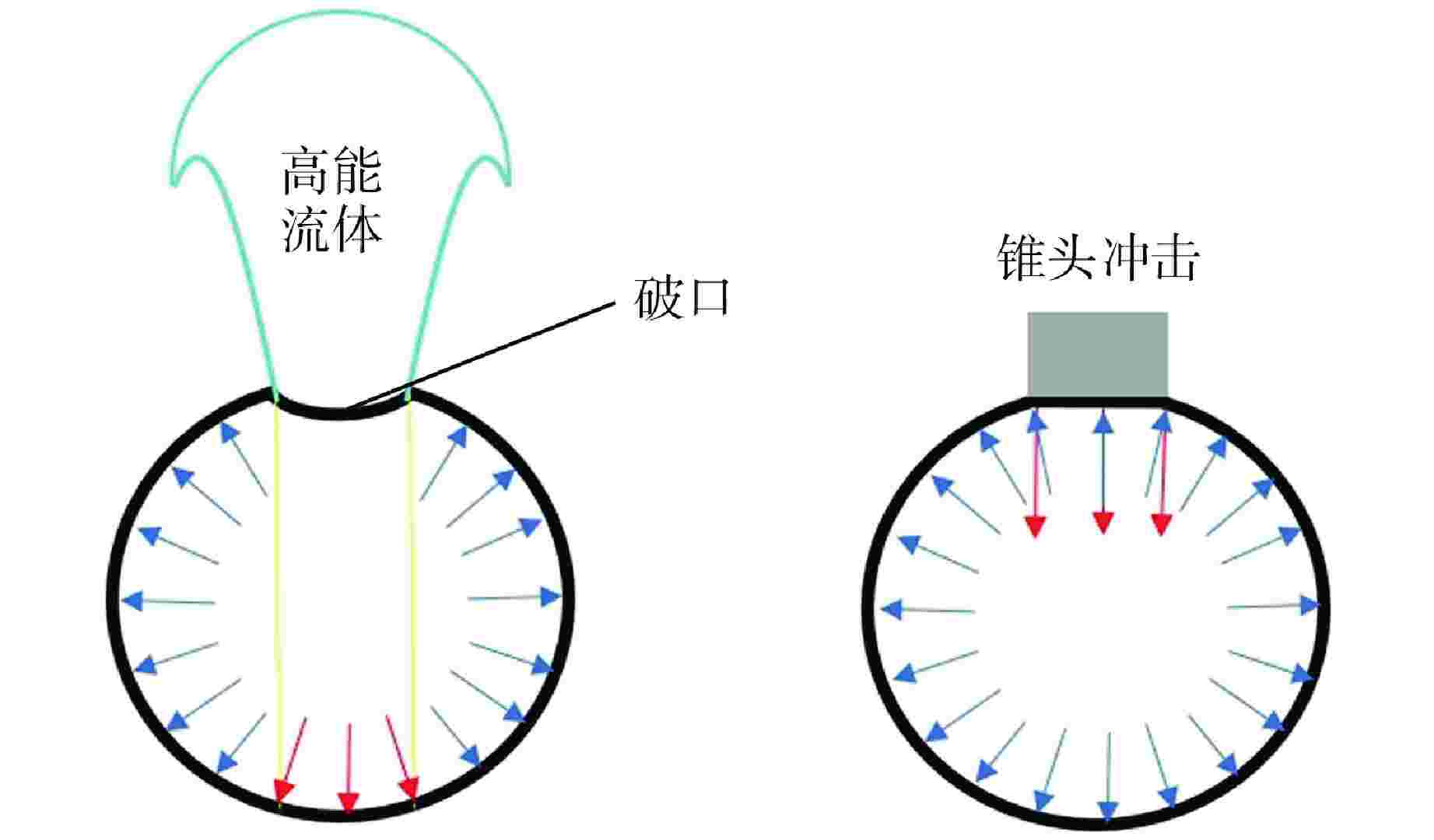
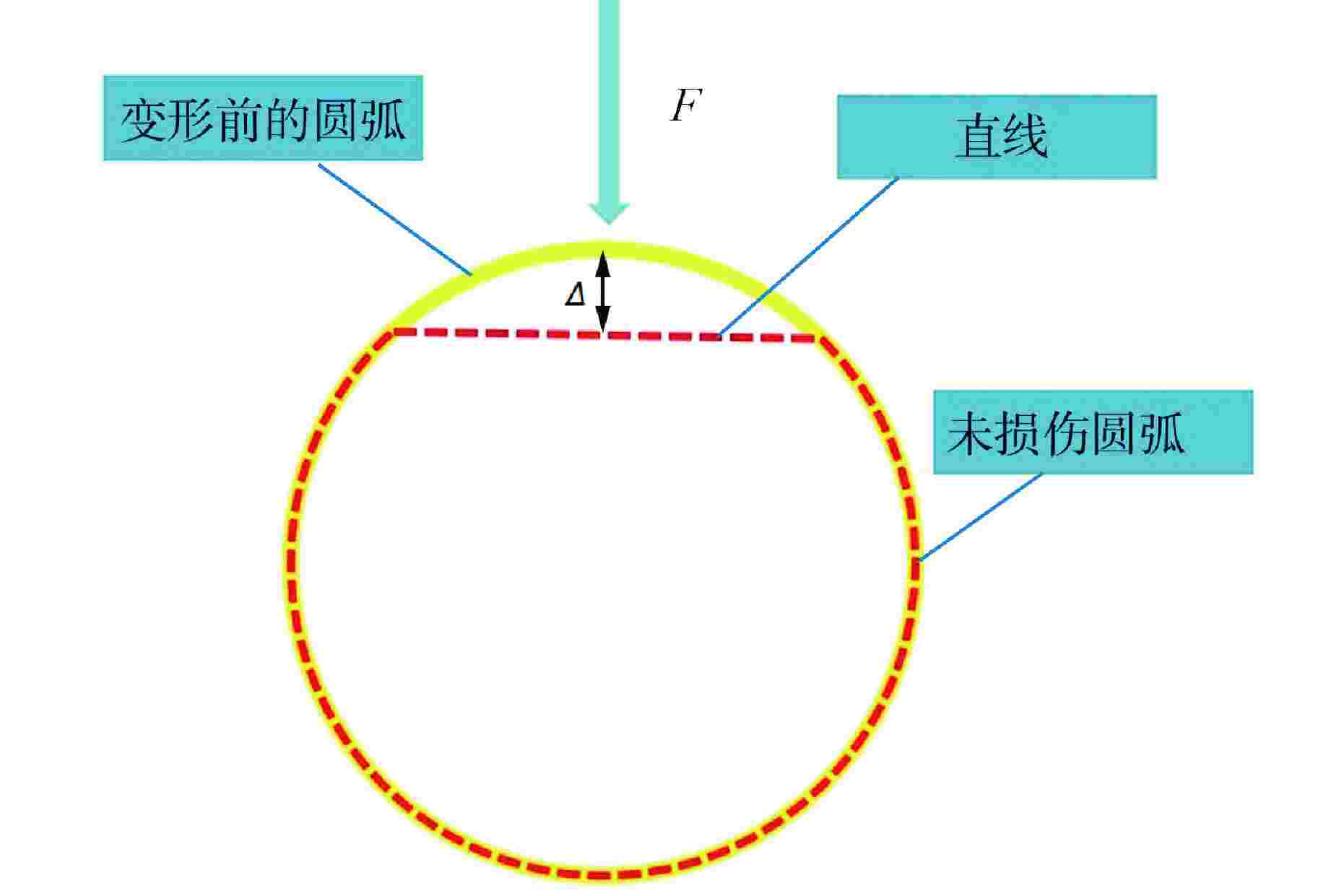
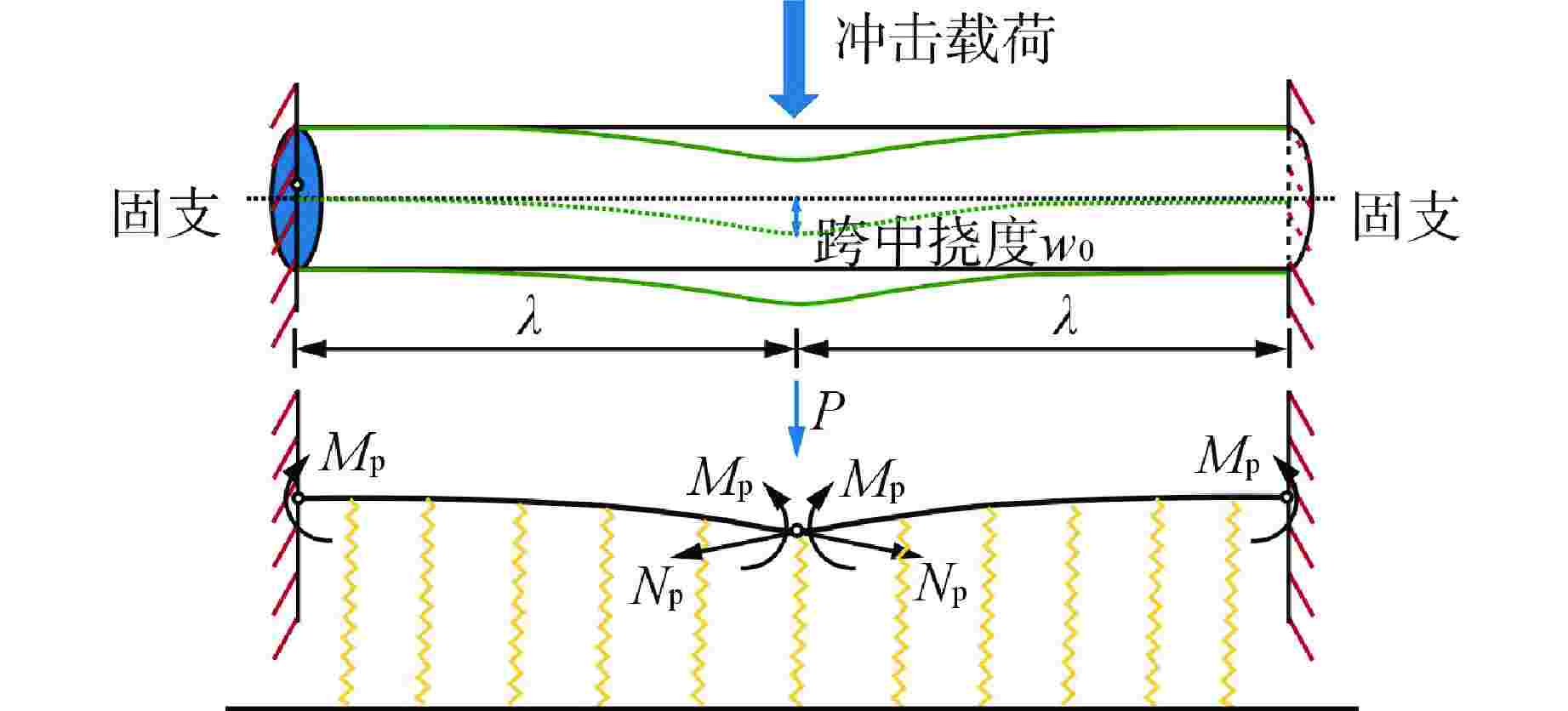
摘要: 高能管道在冲击载荷的作用下,结构会发生大挠度变形。为了预测高能管道的最大变形挠度,本文基于膜力因子法(MFM)推导了适用于该结构的膜力因子,建立了相较于传统方法更便捷的跨中挠度计算方法,并与数值模拟结果和试验结果进行了对比,验证了其准确性。研究结果表明:MFM对管道结构挠度预测有较高的准确度;跨中挠度的大小由变量因子控制,跨中挠度随着冲击荷载与管道长度的增加而增加,随着塑性极限弯矩的增加而减小。由于MFM未考虑截面塌陷所耗散的能量,所以对于椭圆化程度较高的管道,挠度预测结果与实际情况相比偏大,但是由于管道内部高能流体的支承,管道的塌陷效应不明显,因此该方法可用于对高能管道大挠度变形进行预测。针对塌陷程度较高的管道,结合塌陷模型对MFM预测结果进行了修正,大大提高了预测方法的准确性。
-
关键词:
- 膜力因子法(MFM) /
- 跨中挠度 /
- 塌陷模型 /
- 高能管道;塑性大变形
Abstract: When high-energy pipelines under the action of impact loads, the structure will subject to large deflection deformation. In order to predict the maximum deformation deflection of high-energy pipelines, a membrane force factor applicable to the structure was derived based on the membrane force factor method (MFM). A more convenient calculation method than traditional methods for mid-span deflection was established, and its accuracy was verified by comparing it with numerical simulation results and experiment results. The research results indicate that MFM has a high accuracy in predicting the deflection of pipeline structures; The magnitude of mid-span deflection is controlled by variable factors. The mid-span deflection increases with the increase of impact load and pipeline length, and decreases with the increase of plastic ultimate bending moment. The predicted deflection of pipelines with high degree of ellipticity is larger than the actual situation beacuse of MFM not taking into account the energy dissipated by section collapse. However, due to the support of high-energy fluid inside the pipeline, the collapse effect of the high-energy pipeline is not obvious. Therefore, this method can be used to predict the large deflection deformation of high-energy pipelines. For pipelines with high degree of collapse, the MFM prediction results are modified by combining the collapse model, which greatly improves the accuracy of the prediction method. -
表 1 管道甩击试验工况参数
Table 1. Conditions of Pipe Whip Test
管道
长度/mm管道
半径/mm管道
厚度/mm压力/
MPa等效冲击
荷载/ kN温度/K 屈服
应力/MPa3000 25.4 2.6 5 11 553.1 295 表 2 不同冲击载荷工况下的结果
Table 2. Results under Different Impact Load Conditions
冲击载荷/kN MFM预测跨中
挠度/mm数值模拟跨中
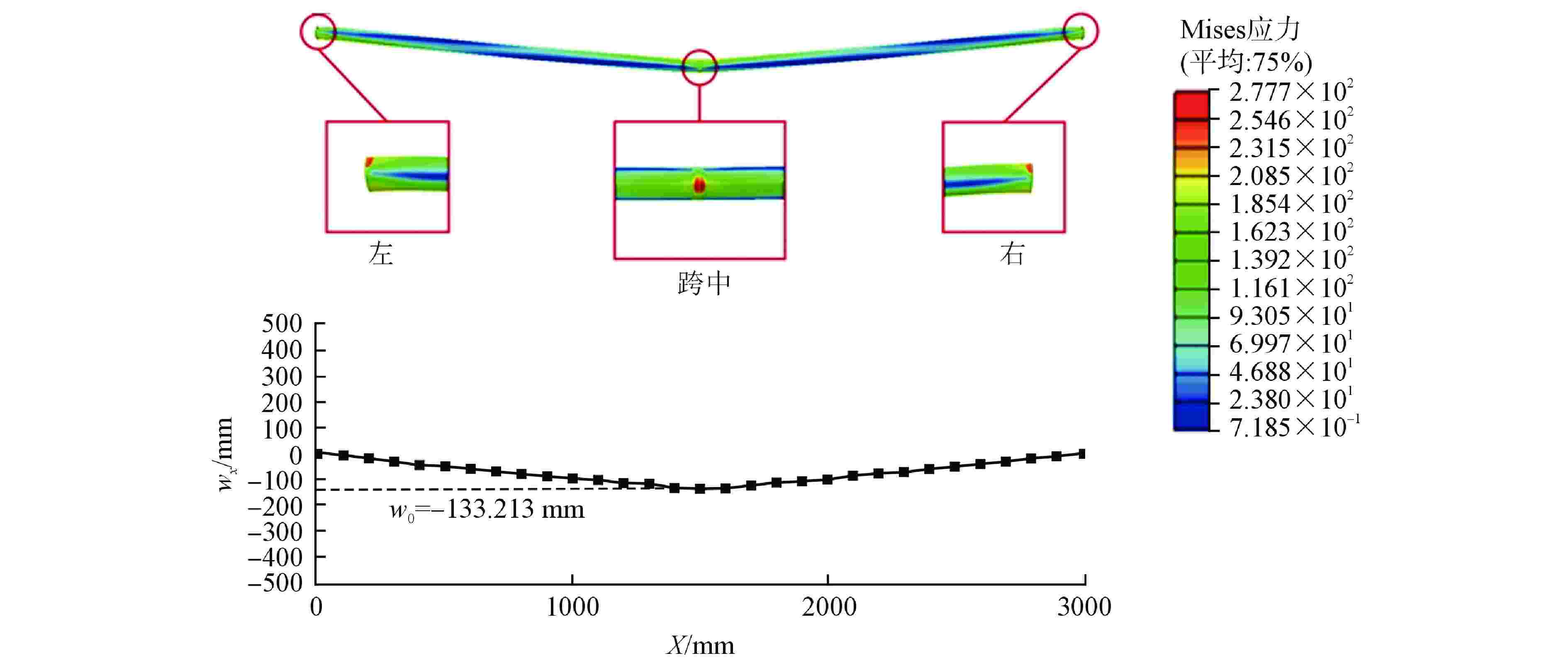
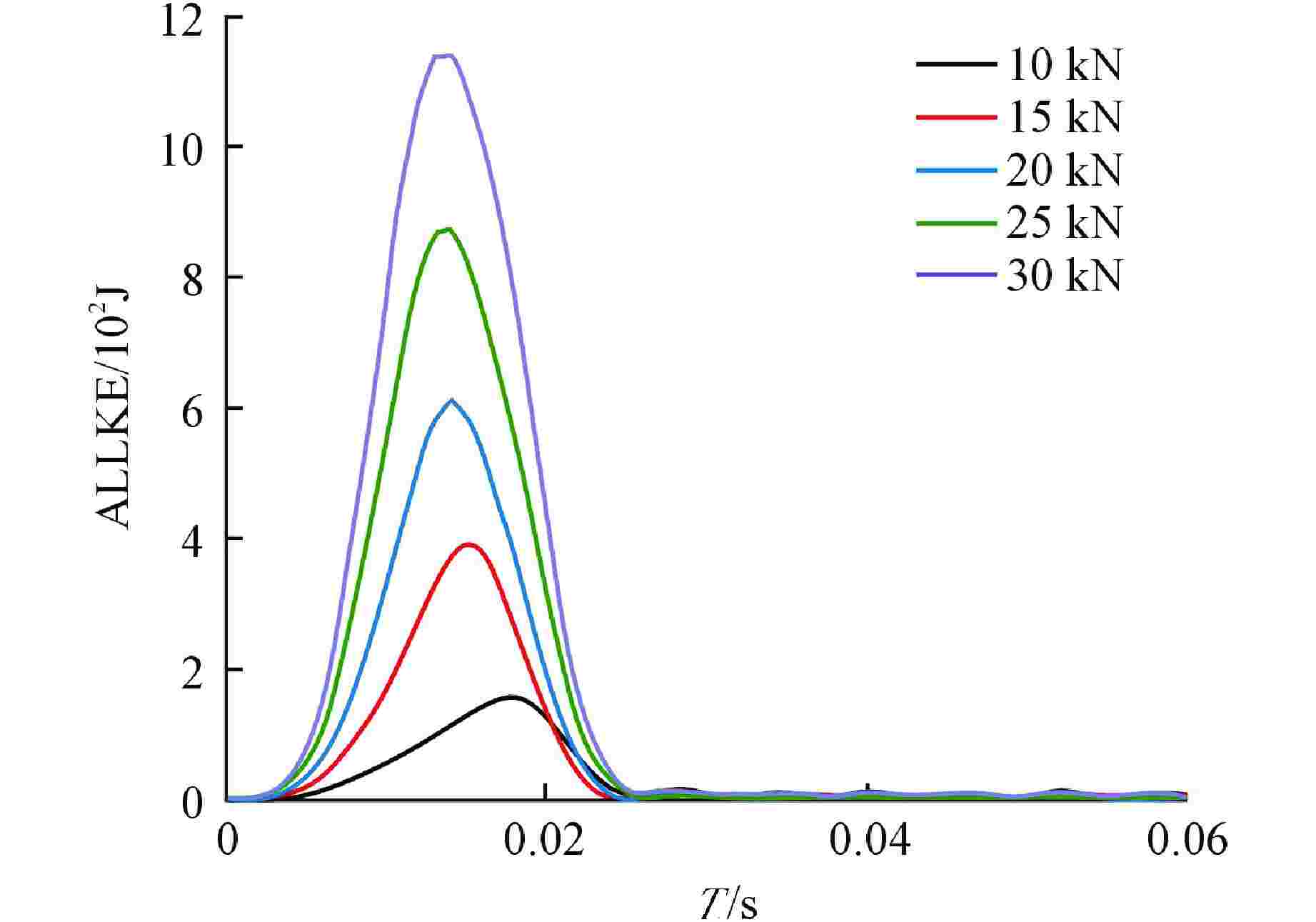
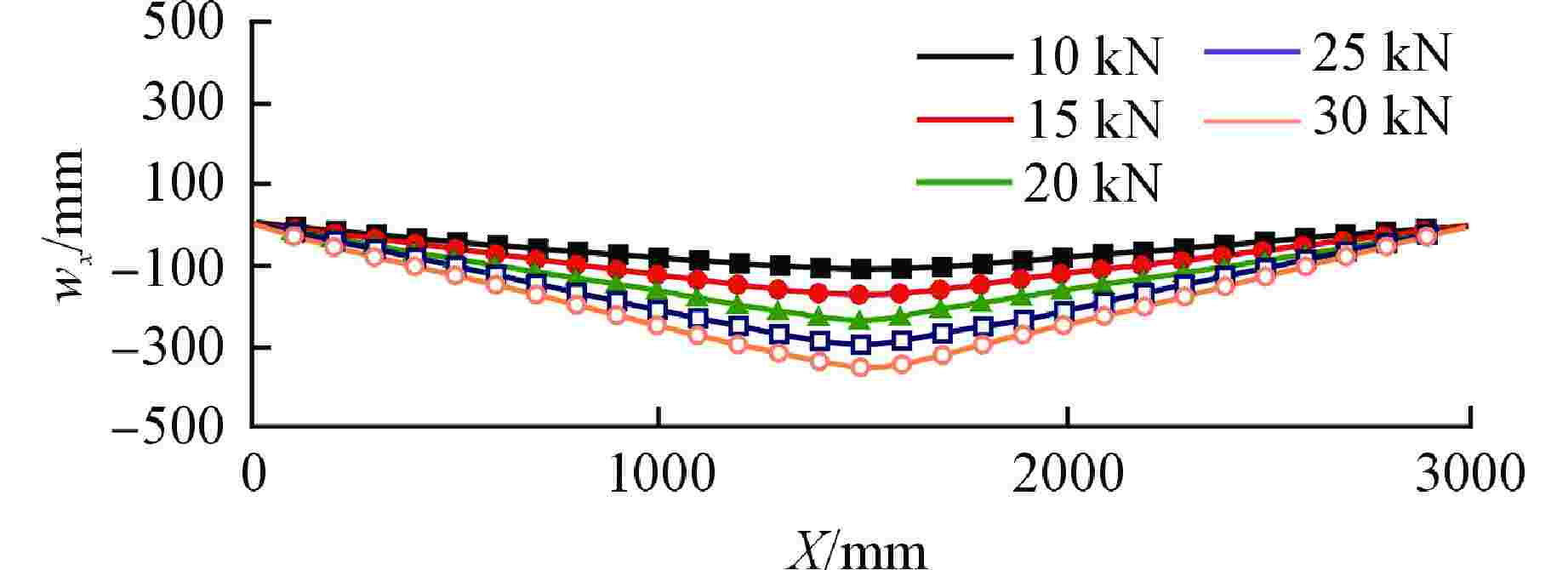
挠度/mm误差/% 10 −109.850 −107.823 1.845 15 −175.879 −171.221 2.648 20 −239.253 −229.872 3.921 25 −301.731 −296.891 1.604 30 −363.792 −351.575 3.358 表 3 落锤冲击试验的工况参数
Table 3. Condition Parameters of Drop Hammer Impact Test
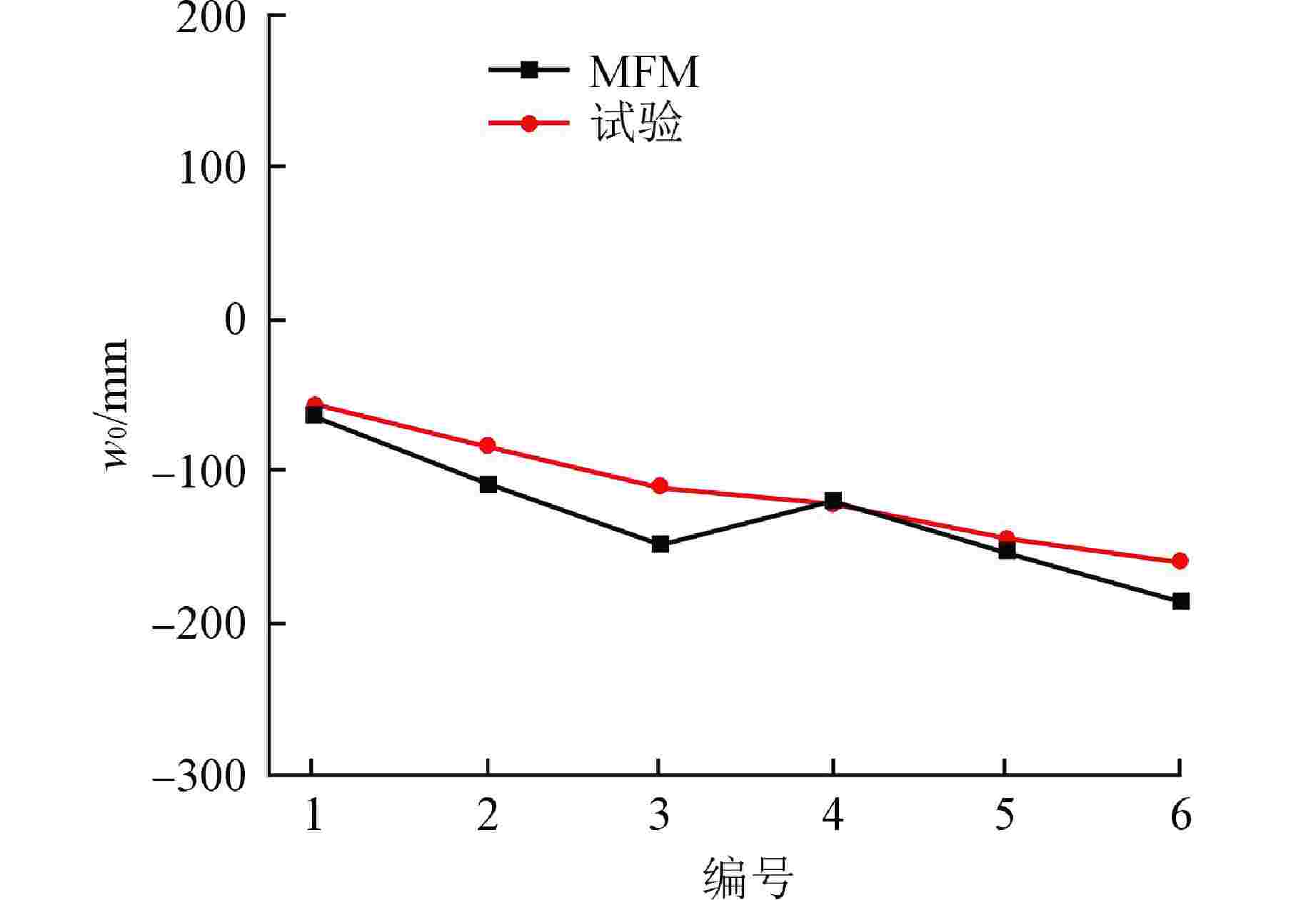
编号 试件代号 质量/kg 高度/mm 直径/mm 壁厚/mm 长度/mm 屈服应力/MPa 挠度/mm 1 B1-WM-1 427 509.8 60 3.5 900 250 −56.42 2 B1-WM-2 427 1012.5 60 3.5 900 250 −83. 11 3 B1-WM-3 427 1703.7 60 3.5 900 250 −110.00 4 D2-WM-1 427 3011.8 114 4.0 1200 275 −120.90 5 D2-WM-2 427 4001.5 114 4.0 1200 275 −144.00 6 D2-WM-3 427 5006.7 114 4.0 1200 275 −159.90 表 4 FEA工况参数及结果
Table 4. Condition Parameters and Results by FEA
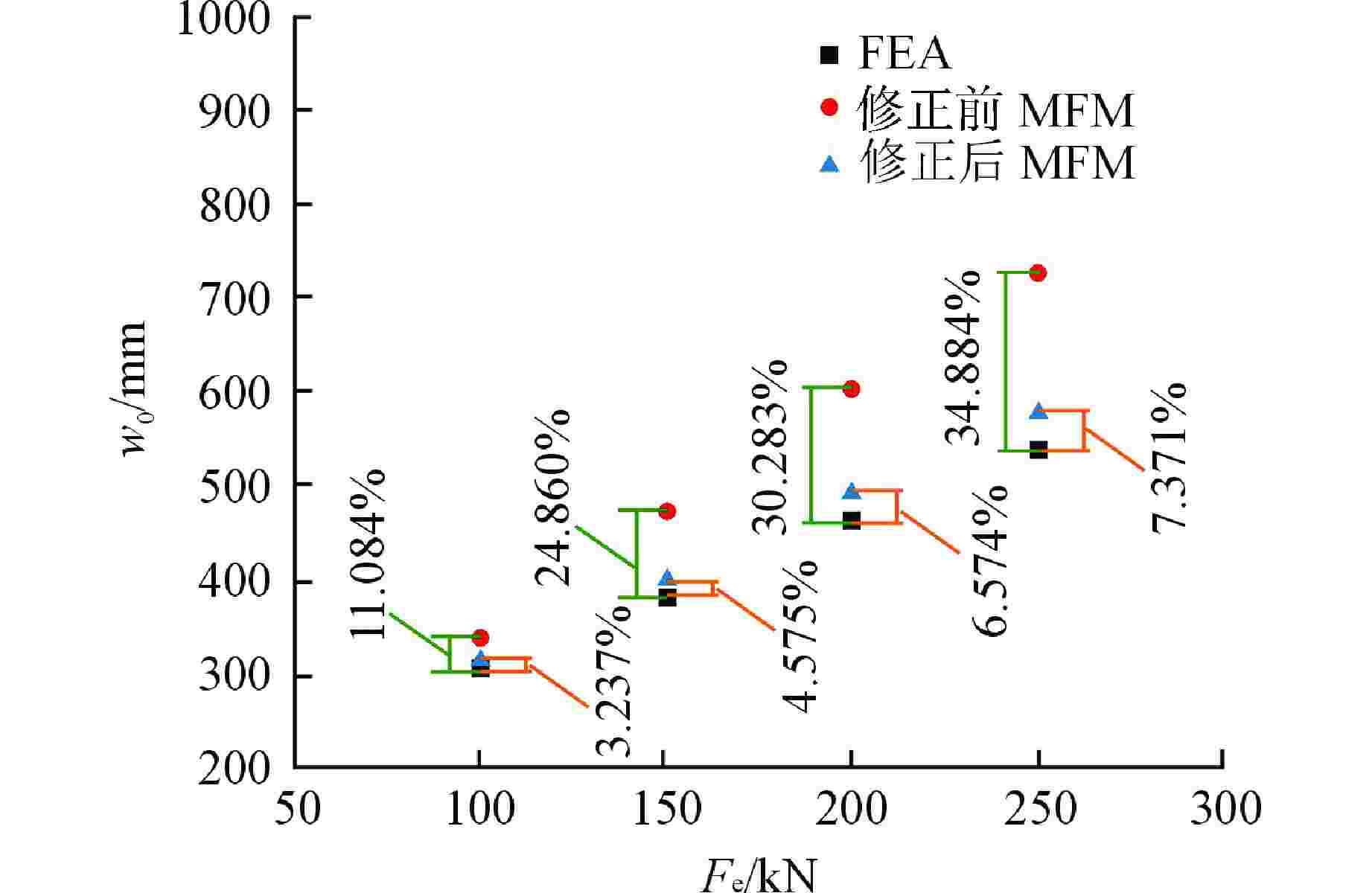
等效喷射载荷/kN 直径/mm 壁厚/mm 长度/mm 温度/K 压强/MPa FEA结果/mm MFM结果/mm 误差/% 100 168.3 9.9 6626 613 10 305.472 339.330 11.084 150 168.3 9.9 6626 613 10 381.980 476.940 24. 860 200 168.3 9.9 6626 613 10 463.662 604.073 30.283 250 168.3 9.9 6626 613 10 540.138 728.558 34.884 表 5 软件计算结果
Table 5. Calculation Results by Software
编号 Fe/ kN 管道
长度/mm管道
半径/mm管道
厚度/mm跨中
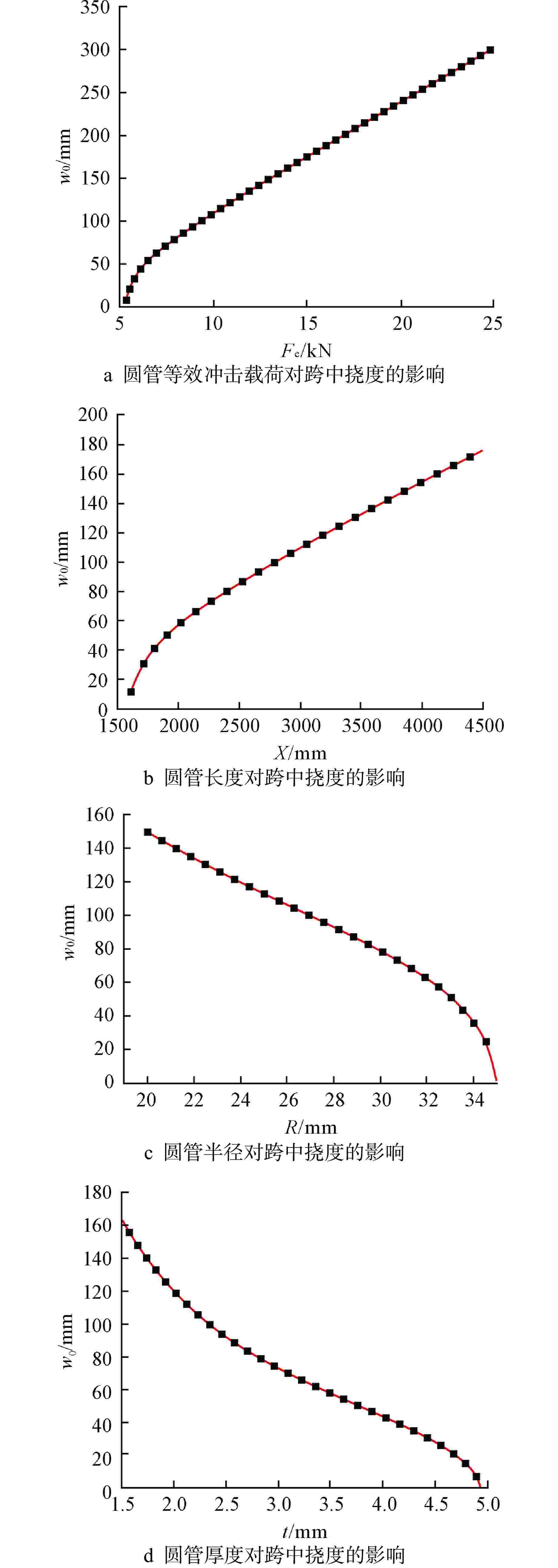
挠度/mm1 10 3000 25.4 2.6 −109.850 2 20 3000 25.4 2.6 −239.253 3 30 3000 25.4 2.6 −363.792 4 10 2000 25.4 2.6 −57.459 5 10 2500 25.4 2.6 −85.880 6 10 4000 12.7 2.6 −154.353 7 10 3000 38.1 2.6 −243.651 8 10 3000 50.8 2.6 0 9 10 3000 25.4 2.6 0 10 10 3000 25.4 1.0 −314.168 11 10 3000 25.4 2.0 −150.007 12 10 3000 25.4 3.5 −71.537 -
[1] CHEN K S, SHEN W Q. Further experimental study on the failure of fully clamped steel pipes[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1998, 21(3): 177-202 . doi: 10.1016/S0734-743X(97)00083-3 [2] BROOKER D C. Denting of pressurised pipelines under localised radial loading[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2004, 46(12): 1783-1805. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2004.11.004 [3] KARAMANOS S A, ANDREADAKIS K P. Denting of internally pressurized tubes under lateral loads[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2006, 48(10): 1080-1094. [4] 李晨, 闫秋实, 李亮, 等. 侧向冲击荷载作用下不锈钢管混凝土柱的力学性能研究[J]. 防护工程, 2019, 41(6): 7-14. [5] 姜珊, 路国运, 杨会伟. 侧向冲击载荷下钢管混凝土结构的动力响应及参数分析[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2023, 43(11): 112203. doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2023-0039 [6] 余同希, 田岚仁, 朱凌. 强脉冲载荷作用下结构塑性大变形的最大挠度直接预测[J]. 力学学报, 2023, 55(5): 1113-1123. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-22-607 [7] 郭君, 张文启, 郭建军, 等. 水下爆炸冲击波作用下单向加筋板的大挠度塑性变形[J]. 兵工学报, 2015, 36(S1): 163-168. [8] 张新春, 王俊瑜, 汪玉林, 等. 基于膜力因子法的方形锂离子电池冲击动力响应研究[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2022, 43(11): 1203-1213. [9] YU T X, STRONGE W J. Large deflections of a rigid-plastic beam-on-foundation from impact[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1990, 9(1): 115-126. doi: 10.1016/0734-743X(90)90025-Q [10] 杨桂通. 弹塑性力学引论[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2004: 55-58. [11] YOUNGDAHL C K. Correlation parameters for eliminating the effect of pulse shape on dynamic plastic deformation[J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 1970, 37(3): 744-752. [12] ZHU L, TIAN L R, CHEN F L, et al. A new equivalent method for complex-shaped pulse loading based on saturation analysis and membrane factor method[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2021, 158: 104018. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2021.104018 [13] REID S R, YU T X, YANG J L, et al. Dynamic elastic-plastic behaviour of whipping pipes: experiments and theoretical model[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1996, 18(7-8): 703-733. doi: 10.1016/S0734-743X(96)00034-6 [14] 张荣. 建筑用圆钢管构件侧向冲击响应及失效机理[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2018. [15] FURNES O, AMDAHL J. Ship collisions with offshore platforms[C]. In: Proceedings of Intermaritec, Hamburg, Germany; 1980; 310–318. [16] 余同希, 邱信明. 冲击动力学[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2011: 199. -





 下载:
下载: