Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Heat-affected Zone of Repeated Welding on 304 Stainless Steel
-
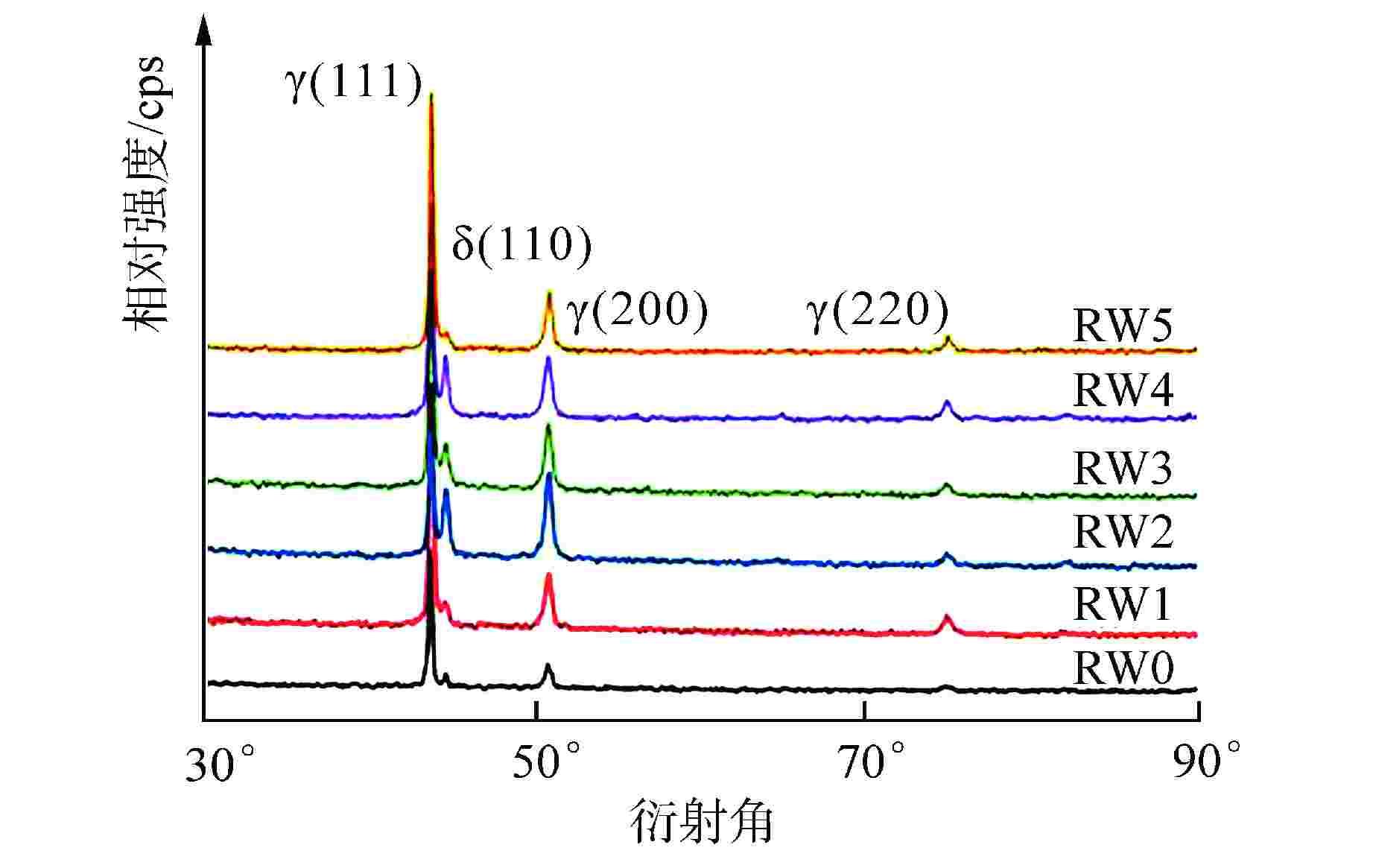
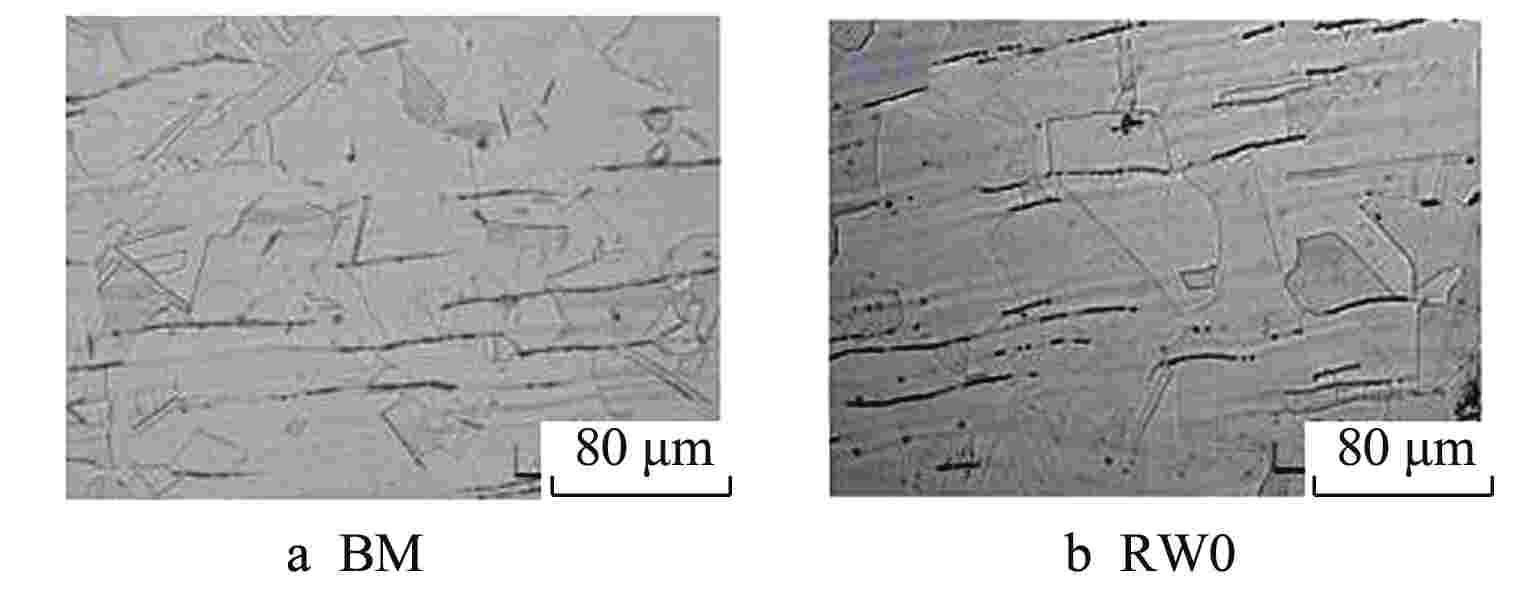
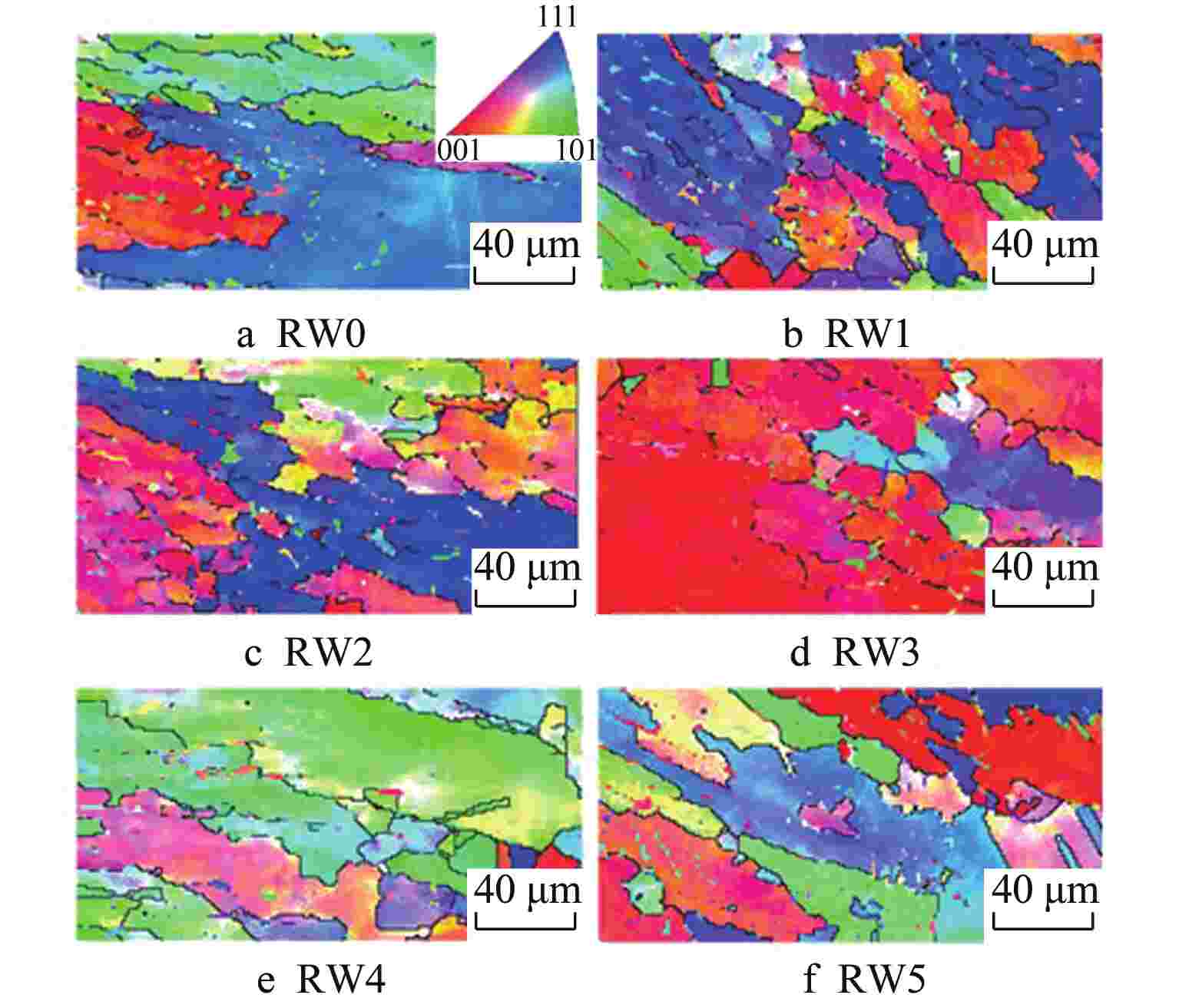
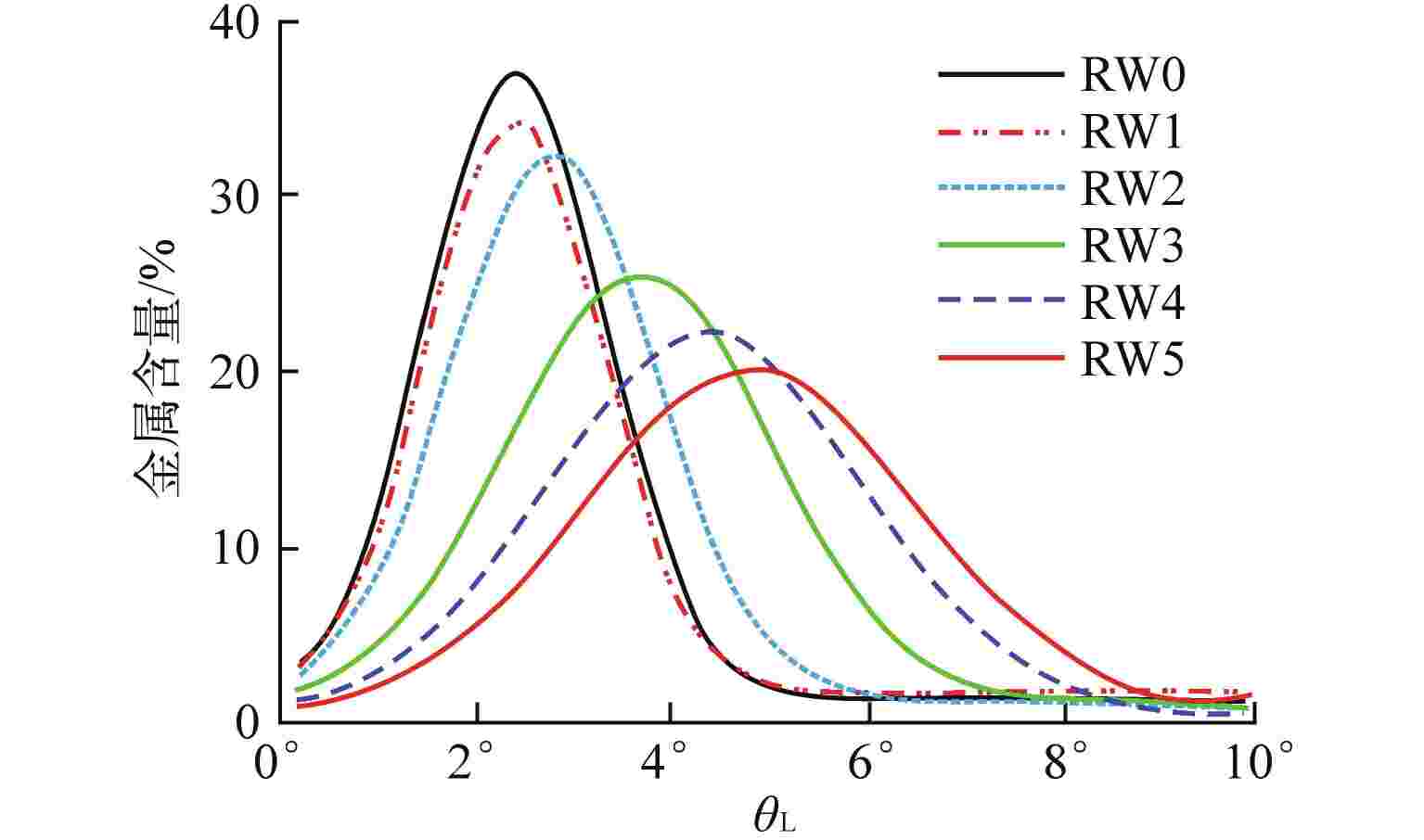
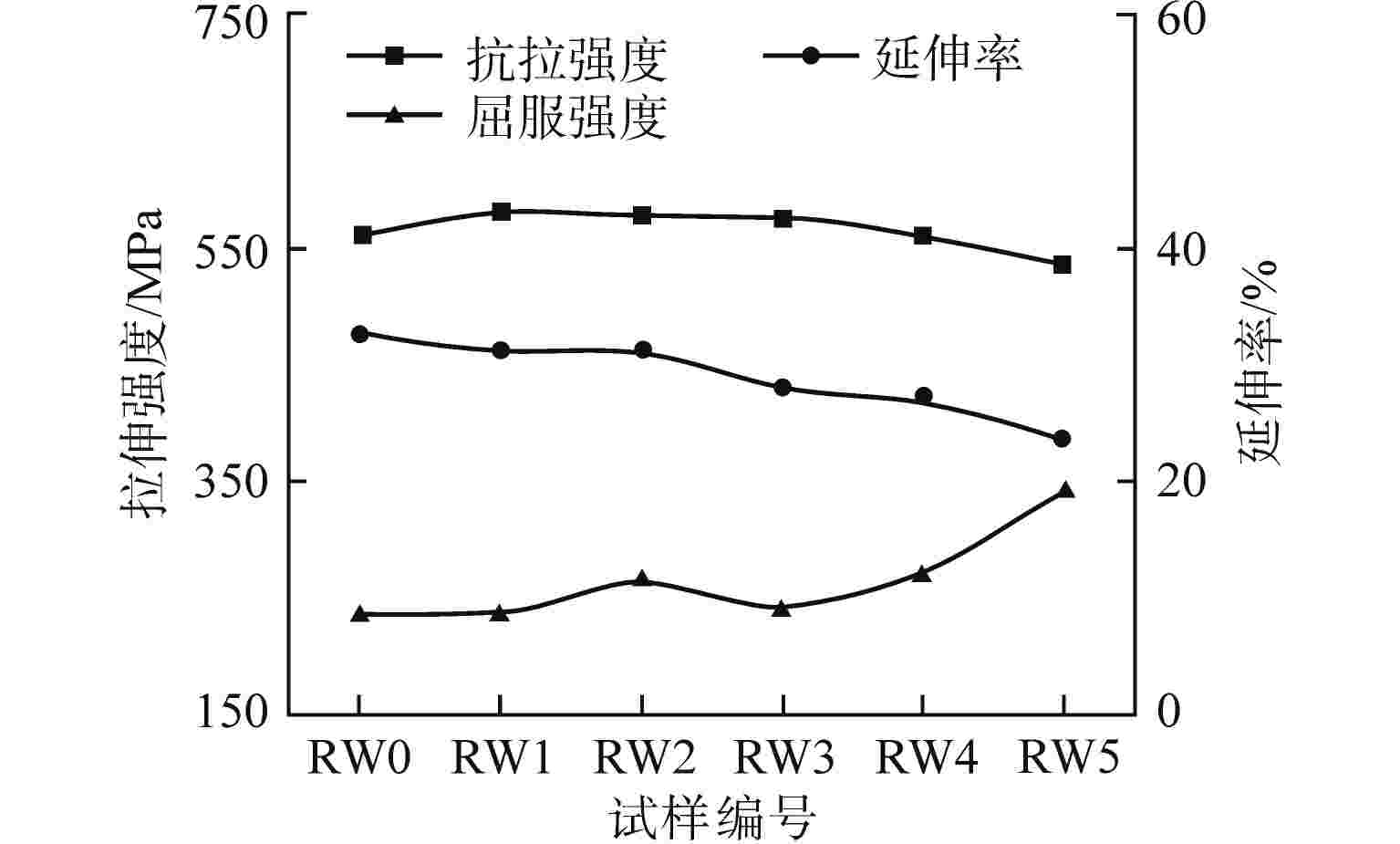
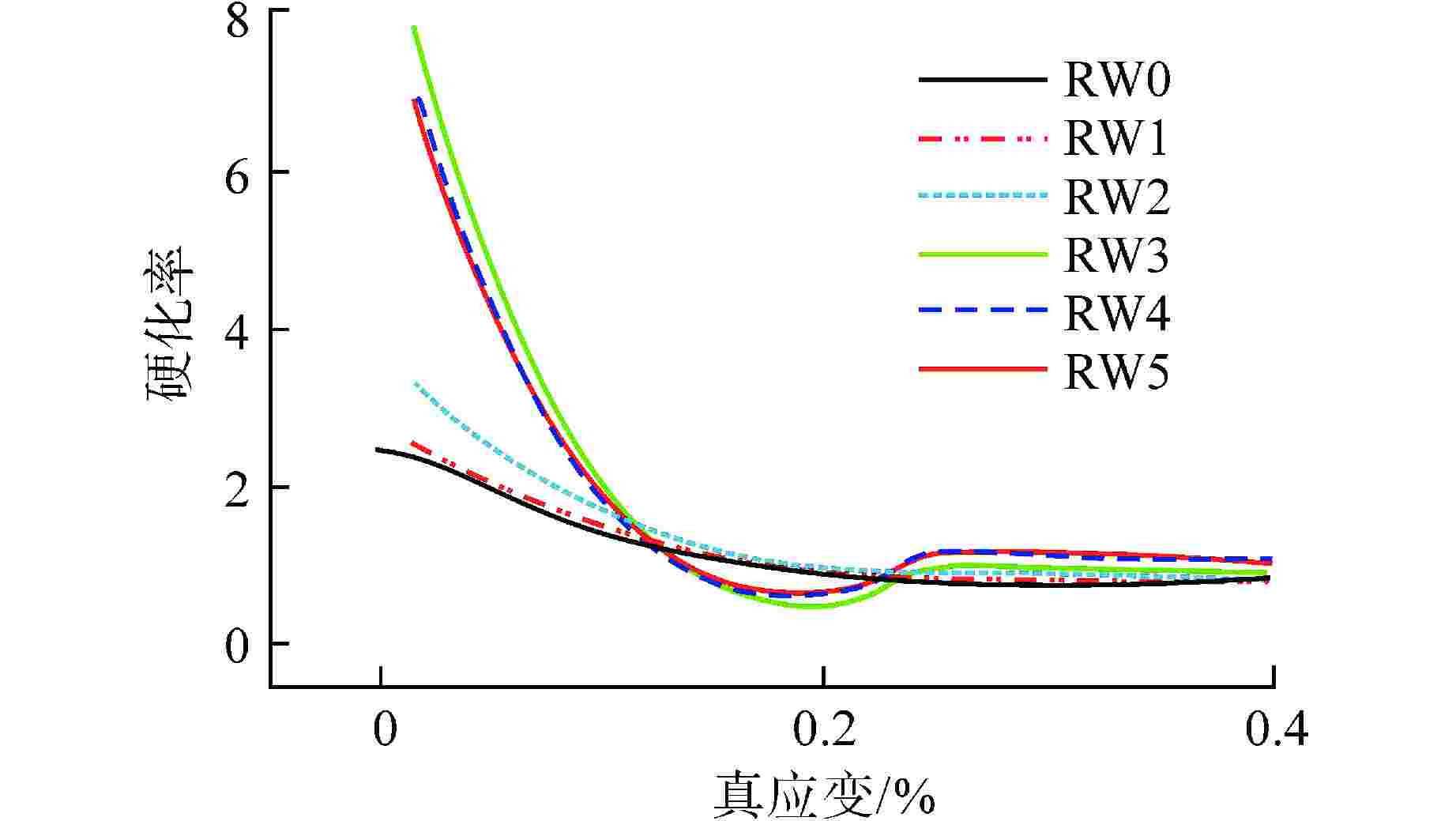
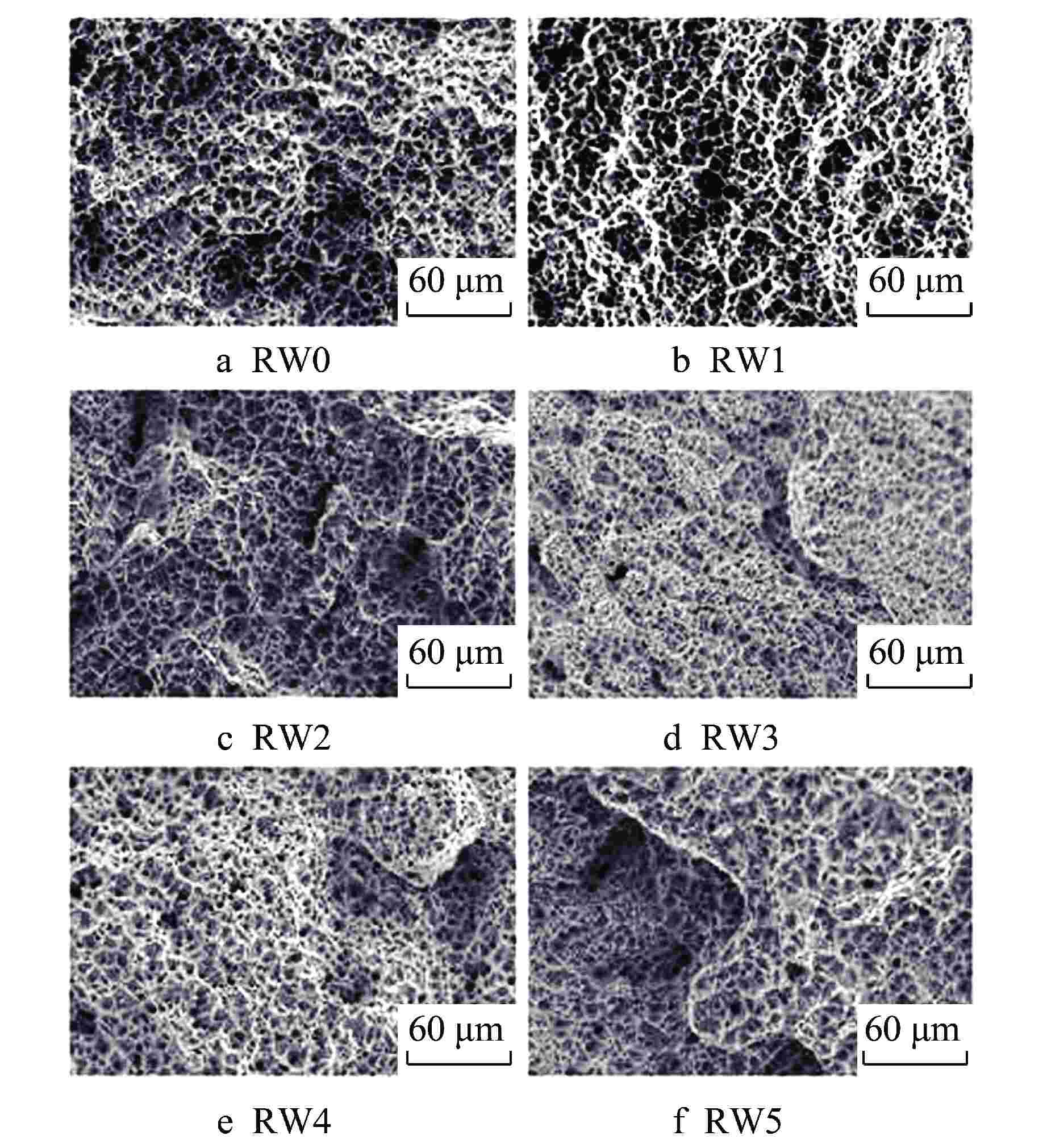
摘要: 采用自动钨极氩弧焊接(GTAW)工艺设计刚性约束坡口,制备了304不锈钢1次焊接和1~5次试样。采用光学显微镜、X射线衍射(XRD)、扫描电子显微镜(SEM)与电子背散射衍射(EBSD)技术对重复焊接试样的热影响区(HAZ)显微组织进行观察分析,并开展室温拉伸性能测试,研究重复焊接对显微组织与力学性能的影响。结果表明,重复焊接试样的HAZ显微组织主要由奥氏体和条状δ铁素体组成,随着重复焊接次数增加,HAZ奥氏体晶粒尺寸呈长大趋势,δ铁素体含量先减少后增加,组织择优取向由<101>转变为<111>,局域取向差逐渐增大;晶粒尺寸是影响抗拉强度和延伸率变化的主要原因,加工硬化致使试样屈服强度逐渐增加。Abstract: The effect of the repeated welding on the microstructure and mechanical properties of the heat-affected zone (HAZ) for 304 stainless steel were investigated under repeated welding up to five times by automatic gas tungsten arc welding using an optical microscope, a x-ray diffraction, a scanning electron microscope and an electron back-scattered diffraction. The repeated welding specimens were consisted with the microstructures of austenitic matrices with lath δ-ferrite. With the increasing of the repeated welding times, the average values of the austenitic grain size increased, and the δ-ferrite content decreased then increased. The preferred orientation of the HAZ changed from <101> to <111>. The values of location misorientation increased monotonically with the increasing number of repeated welding. The variation of the ultimate tensile strength and elongation was affected by the grain size mainly. Due to the hardening rate increasing, the yield tensile strength was increasing.
-
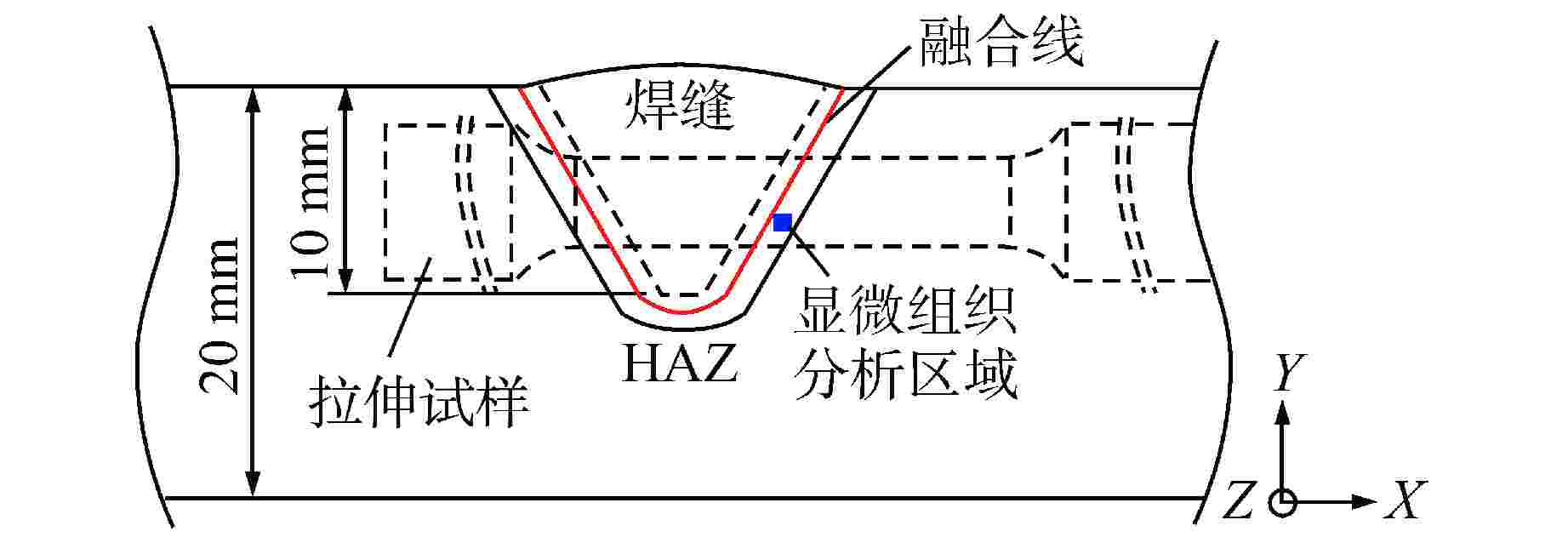
表 1 钢板化学成分与力学性能
Table 1. Chemical Composition and Mechanical Properties of AISI 304 Stainless Steel
位置 化学成分/wt%① 拉伸强度/MPa C Cr Ni Mn Si P S N 平均抗
拉强度屈服
强度母材 0.05 18.545 8.211 1.6 0.5 0.034 0.001 0.12 550 240 焊材 0.023 19.111 9.303 1.56 0.543 0.026 0.006 —② — — 注:①wt%—质量百分数;②“—”—无数据 表 2 自动GTAW焊接参数
Table 2. Welding Parameters of Auto-GTAW
焊道
编号电流/
A电压/
V焊接速度/
(mm·s−1)送丝速度/
(mm·min−1)热输入/
(kJ·mm−1)1 260 9.50 1.52 89 1.62 2 260 9.20 1.52 89 1.57 3~7 260 9.50 1.52 89 1.62 -
[1] MILLS W J. Fracture toughness of type 304 and 316 stainless steels and their welds[J]. International Materials Reviews, 1997, 42(2): 45-82. doi: 10.1179/imr.1997.42.2.45 [2] LANT T, ROBINSON D L, SPAFFORD B, et al. Review of weld repair procedures for low alloy steels designed to minimise the risk of future cracking[J]. International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 2001, 78(11-12): 813-818. doi: 10.1016/S0308-0161(01)00094-1 [3] YI H J, LEE Y J, LEE K O. Influences of the welding heat input and the repeated repair welding on Ti-3Al-2.5V titanium alloy[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica (English Letters), 2015, 28(6): 684-691. doi: 10.1007/s40195-015-0248-2 [4] NASCIMENTO M P, VOORWALD H J C, FILHO J D C P. Effects of several TIG weld repairs on the axial fatigue strength of AISI 4130 aeronautical steel-welded joints[J]. Fatigue & Fracture of Engineering Materials & Structures, 2012, 35(3): 191-204. [5] AGHAALI I, FARZAM M, GOLOZAR M A, et al. The effect of repeated repair welding on mechanical and corrosion properties of stainless steel 316L[J]. Materials & Design (1980-2015), 2014(54): 331-341. [6] LIN C M, TSAI H L, CHENG C D, et al. Effect of repeated weld-repairs on microstructure, texture, impact properties and corrosion properties of AISI 304L stainless steel[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2012(21): 9-20. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2011.11.014 [7] ASME. ASME Boiler & Pressure Vessel Code - Section 3:Rules for construction of nuclear facility components–Division 1:Subsection NB-2013[S]. New York: ASME International, 2013. [8] AFCEN. Design and construction rules for mechanical components of PWR Island:RCC-M-2002[S]. France: FRAMATOME, 2002. [9] FENG W, YANG S, YAN Y B. Dependence of grain boundary character distribution on the initial grain size of 304 austenitic stainless steel[J]. Philosophical Magazine, 2017, 97(13): 1057-1070. doi: 10.1080/14786435.2017.1288943 [10] LIPPOLD J C, SAVAGE W F. Solidification of austenitic stainless steel weldments: Part I-A proposed mechanism[C]. U.S.: AWS 60th Annual Meeting ,Detroit, Michigan, 1979 [11] TSENG C C, SHEN Y, THOMPSON S W, et al. Fracture and the formation of sigma phase, M23C6 and austenite from delta-ferrite in an AlSl 304L stainless steel[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1994, 25(6): 1147-1158. doi: 10.1007/BF02652290 [12] FUKUOKA C, MORISHIMA K, YOSHIZAWA H, et al. Misorientation development in grains of tensile strained and crept 2.25%Cr-1%Mo steel[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2002, 46(1): 61-66. doi: 10.1016/S1359-6462(01)01197-6 [13] JANG C, CHO P Y, KIM M, et al. Effects of microstructure and residual stress on fatigue crack growth of stainless steel narrow gap welds[J]. Materials & Design, 2010(31): 1862-1870. -





 下载:
下载: