Diagnostic of Loose Parts Event in Water Chamber of Steam Generator
-
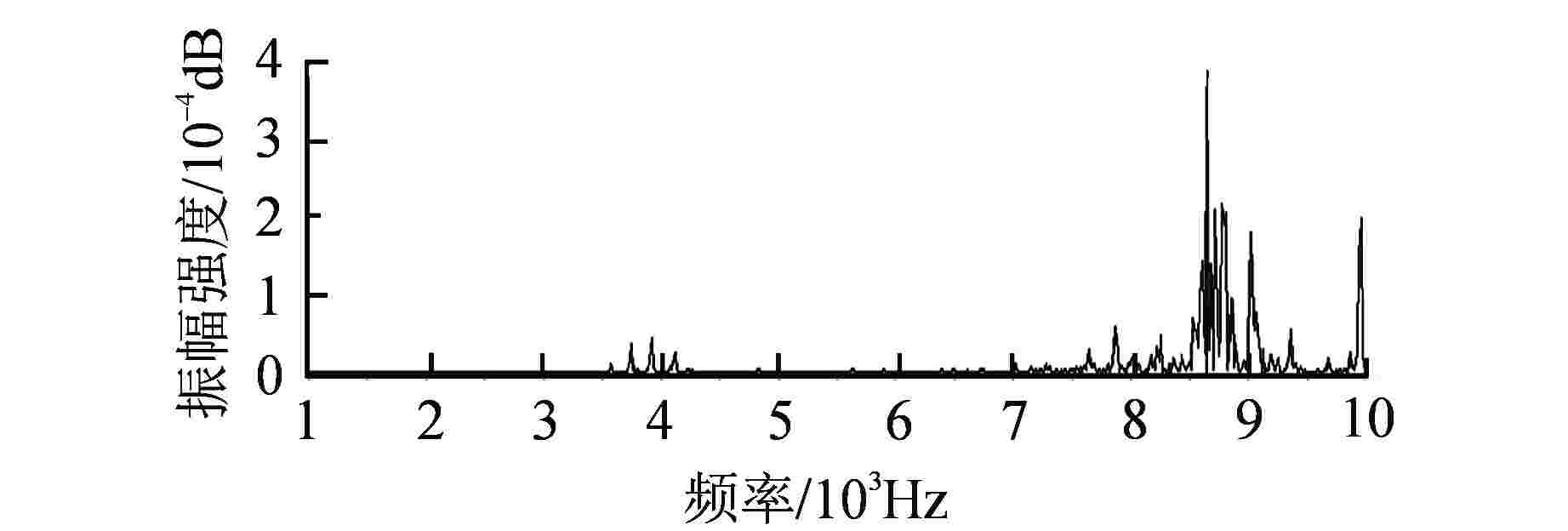
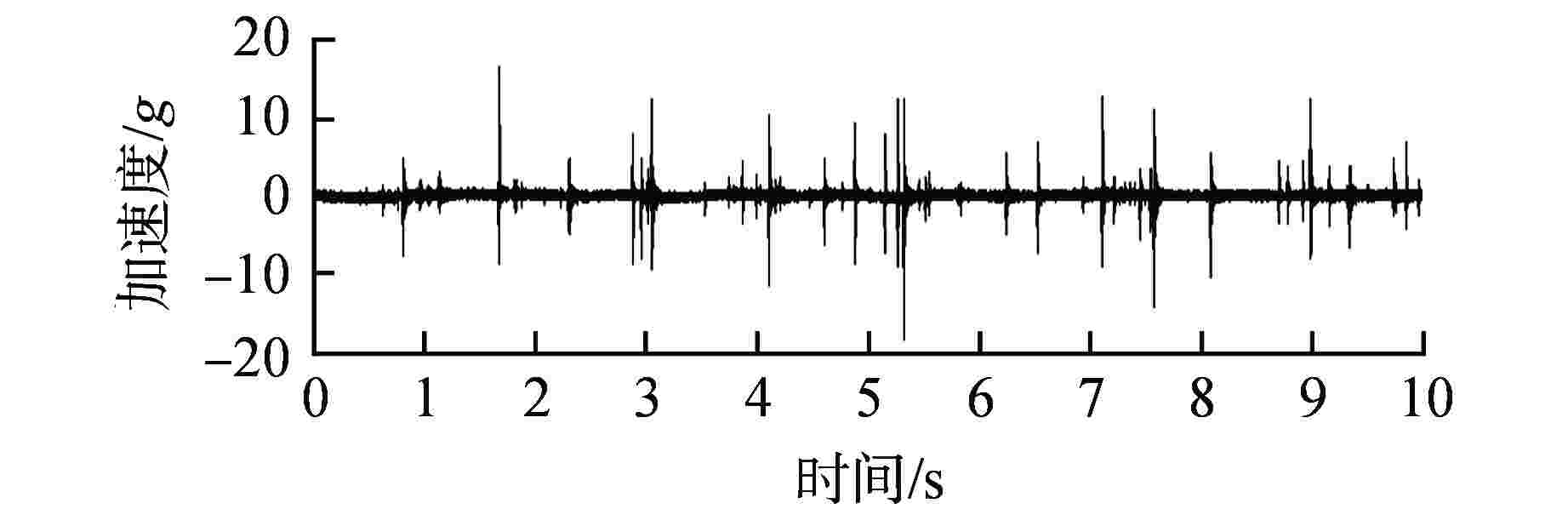
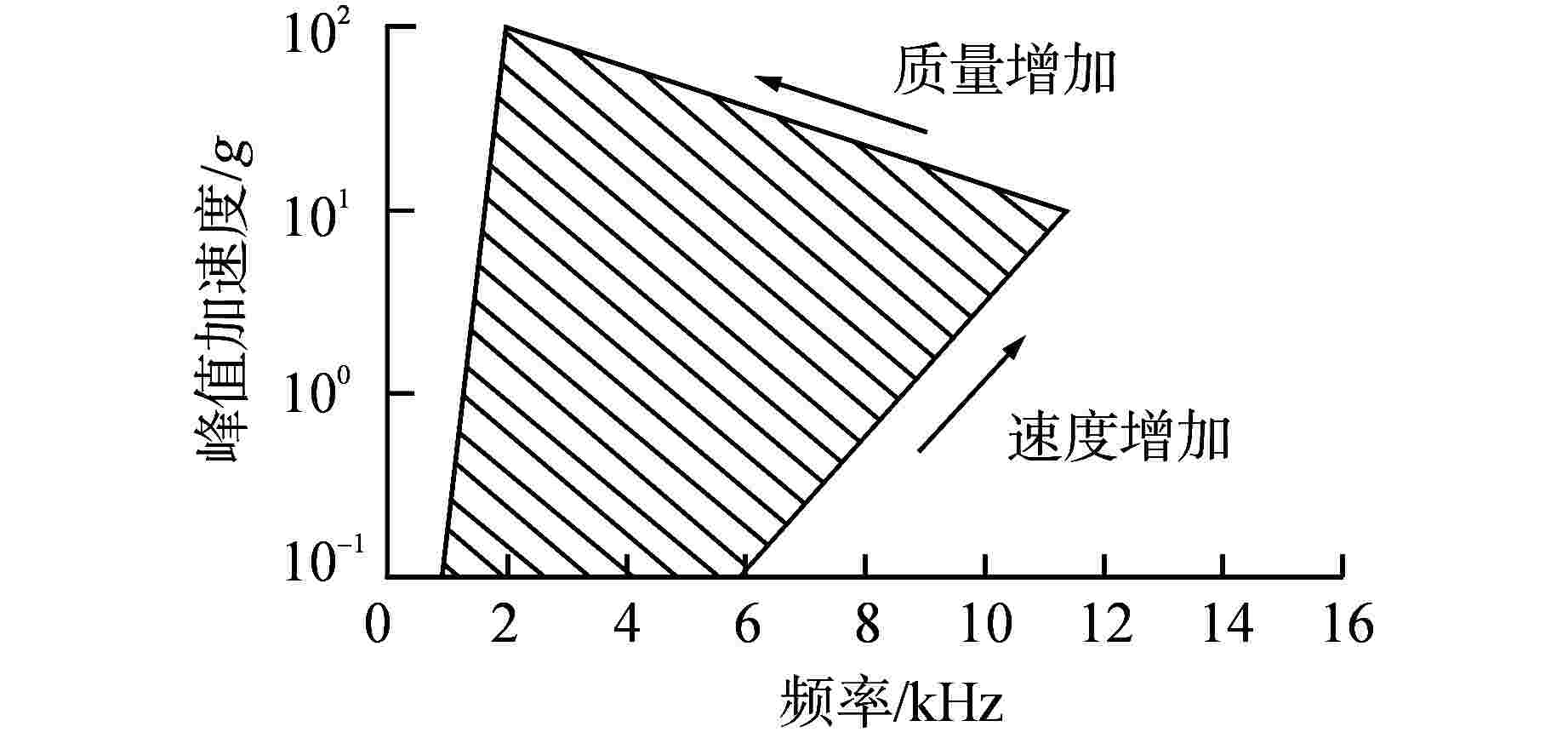
摘要: 某核电厂在热态性能试验(简称热试)期间出现蒸汽发生器松脱部件报警事件,为探究松脱部件报警原因以及评估设备损害程度,需对松脱部件进行及时确认。通过建立松脱部件诊断分析模型,对松脱事件发生时的原始数据进行详细分析,估计了松脱信号的传播速度、松脱部件质量和能量,最后评估了此次松脱报警事件的危害性。结果表明,蒸汽发生器内存在的松脱部件为游动的金属部件,该部件是反应堆内部结构脱落部件,其撞击频率为8700~9300 Hz,碰撞加速度峰值范围为3g~90g,松脱信号传播群速度为3200~3300 m/s,估计松脱部件质量约0.1 kg,撞击能量为0.45~0.89 J;质量和能量诊断结果与实际符合较好,表明本文提出的质量和能量估计方法是有效的。Abstract: During the hot performance test in a nuclear power plant, the alarm event of the loose parts of the steam generator occurred. In order to explore the alarm cause for the loose parts and evaluate the damage of the equipment, it is necessary to confirm the loose parts in time. By establishing the diagnosis and analysis model of the loose parts, the original data of the loose event is analyzed in detail, and the propagation speed of the loose signal, the quality and energy of the loose parts are estimated. Finally, the harmfulness of the loose alarm event is evaluated. The results show that the loose part in the steam generator is a moving metal part, which is a loose part of the internal structure of the reactor. The impact frequency of the loose part is 8700~9300 Hz, the peak range of impact acceleration is 3g~90g, the propagation group velocity of the loose signal is 3200~3300 m/s, and the mass of the loose part is estimated to be about 0.1 kg. The impact energy is 0.45~0.89 J. The diagnostic results of mass and energy are in good agreement with the actual situation, which shows that the proposed method is effective.
-
Key words:
- Steam generator /
- Loose parts event /
- Diagnosis /
- Loose parts location /
- Mass estimation
-
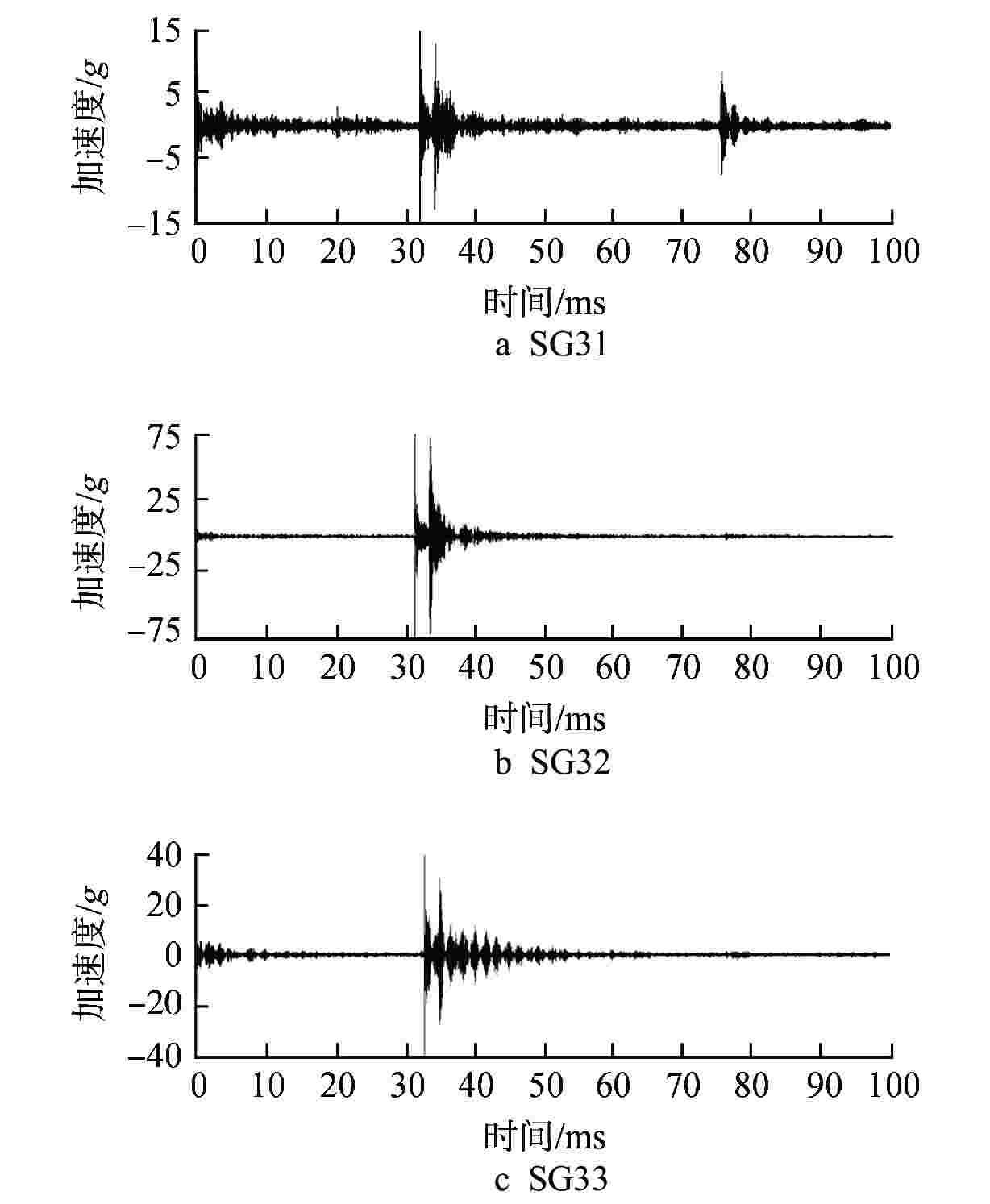
表 1 松脱部件触发通道、次小通道及通道加速度
Table 1. Loose Part Trigger Channel, Sub Small Channel and Channel Acceleration
触发通道 次小通道 通道号 通道加速度/g 通道号 通道加速度/g SG32 13.5 SG31 22.5 SG31 18.3 SG32 26.5 SG33 29.4 SG32 14.9 SG31 18.9 SG32 20.2 SG32 29.1 SG31 28.4 SG31 55.5 SG32 81.7 SG31 9.7 SG32 11.7 SG32 35.6 SG31 58.3 SG31 9.8 SG32 10.0 SG32 81.7 SG31 75.8 表 2 蒸汽发生器材料及参数
Table 2. Material and Parameter of Steam Generator
部件名称 材料 密度/
(kg·m−3)E/1011Pa 泊松比 厚度/
mm近似半径/
mm管板 16MND5 7800 2.1 0.30 557 1743 隔板1 NC30Fe 7800 2.1 0.30 62 1670 下封头 16MND5 7800 2.1 0.30 225 1670 松脱物 金属 7800 2.06 0.27 — — “—”—无此项 表 3 松脱部件质量和能量估计
Table 3. Mass and Energy Estimation of Loose Parts
数据
编号Ap/g f/Hz Cg/(m·s−1) 估计质量/g v0/(m·s−1) 能量/J 1 32 9066 3298.85 125.24 3.77 0.89 2 9.9 9030 3298.76 103.78 1.87 0.45 3 23.7 8567 3225.47 121.28 2.15 0.59 4 11.1 9039 3232.81 97.00 1.22 0.48 5 36.4 8762 3228.61 119.00 2.56 0.58 6 72.9 8649 3226.80 140.59 4.02 0.68 7 72.9 9027 3232.64 123.79 3.54 0.60 表 4 松脱部件质量估计及误差
Table 4. Mass Estimation and Error of Loose Parts
数据编号 估计质量/g 实际质量/g 误差/% 1 125.24 118 6.14 2 103.78 118 −12.05 3 121.28 118 2.78 4 97.00 118 −17.80 5 119.00 118 0.85 6 140.59 118 19.14 7 123.79 118 4.91 -
[1] 赵志德,何宏龙. 反应堆下部堆内构件的损坏分析和修复方案[J]. 核电工程与技术,2007(2): 8-11. [2] 李如源,杨璋,周亚平. 田湾核电厂1号机组主泵松脱部件报警事件诊断分析[J]. 核动力工程,2011, 32(3): 127-129. [3] PARK G Y, CHEON S W, LEE C K, et al. An estimation method of for impact location of loose parts[J]. Progress in Nuclear Energy, 2006, 48(4): 360-370. doi: 10.1016/j.pnucene.2005.09.012 [4] YOON D B, PARK J H, CHOI Y C, et al. Enhancement of impact mass estimation algorithm for a plate type structure[J]. Materials Transactions, 2007, 48(6): 1249-1253. doi: 10.2320/matertrans.I-MRA2007854 [5] 方力先,楼永坚,倪益华,等. 基于神经网络的松动部件监测系统小波质量估计方法研究[J]. 原子能科学技术,2004, 38(4): 321-323. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6931.2004.04.008 [6] MAYO C W. Loose-part mass and energy estimation[J]. Progress in Nuclear Energy, 1999, 34(3): 263-282. doi: 10.1016/S0149-1970(98)00010-9 [7] 刘才学,汪成元,郑武元,等. 核电站LPMS研制[J]. 核动力工程,2010, 31(1): 97-101. [8] 胡建荣,罗婷,简捷,等. 防城港核电站堆内中子通量测量系统指套管碰磨分析[J]. 核科学与工程,2017, 37(5): 750-755. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0918.2017.05.007 [9] The American Society of Mechanical Engineers. Standards and Guides for Operation and Maintenance of Nuclear Power Plants: ASME OM-S/G—2007[S]. New York: The American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2007: 43-59. -





 下载:
下载: