Comparative Analysis of Genetic Algorithms Based on Different Selection Strategies for Refueling Optimization in the Ratio Method
-
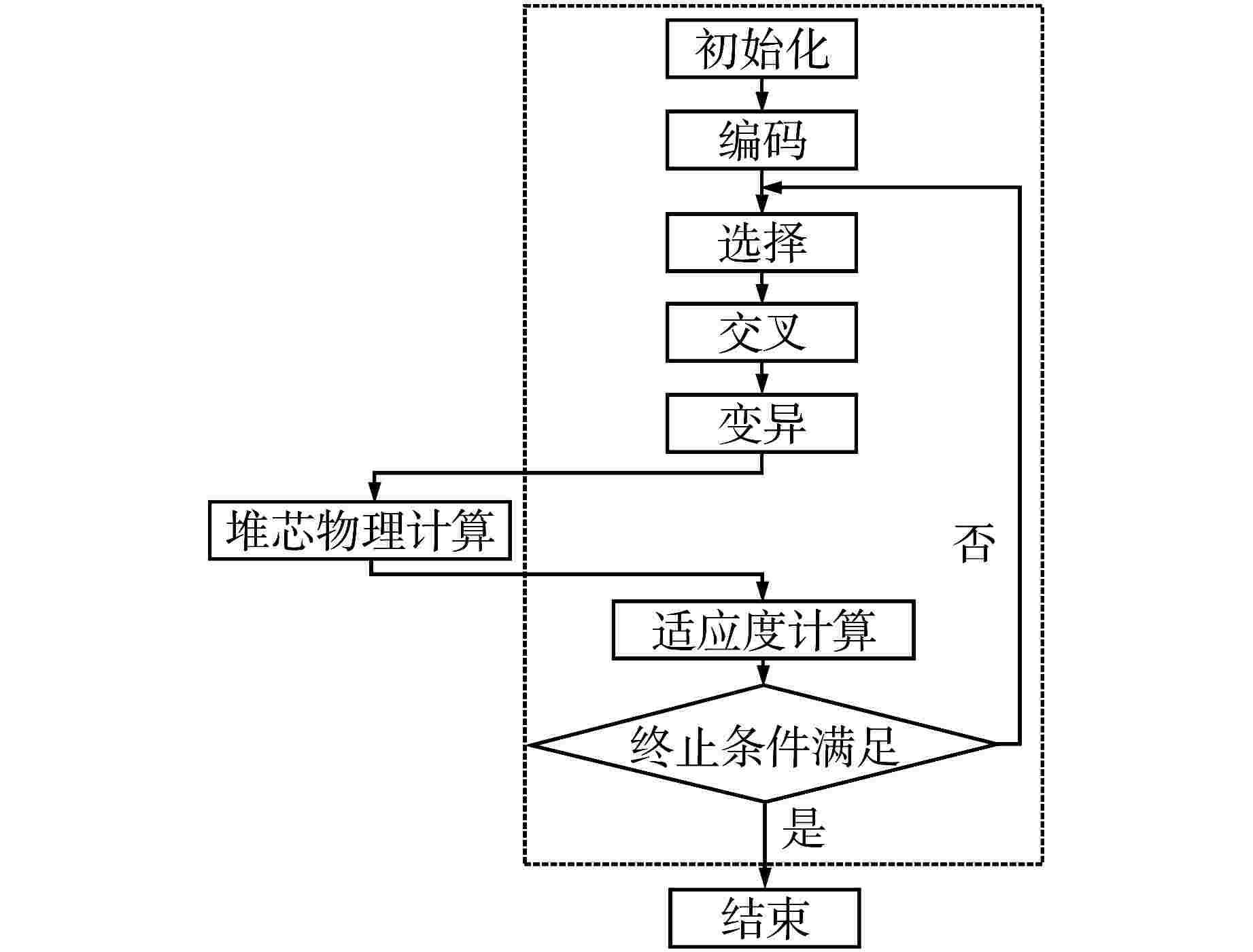
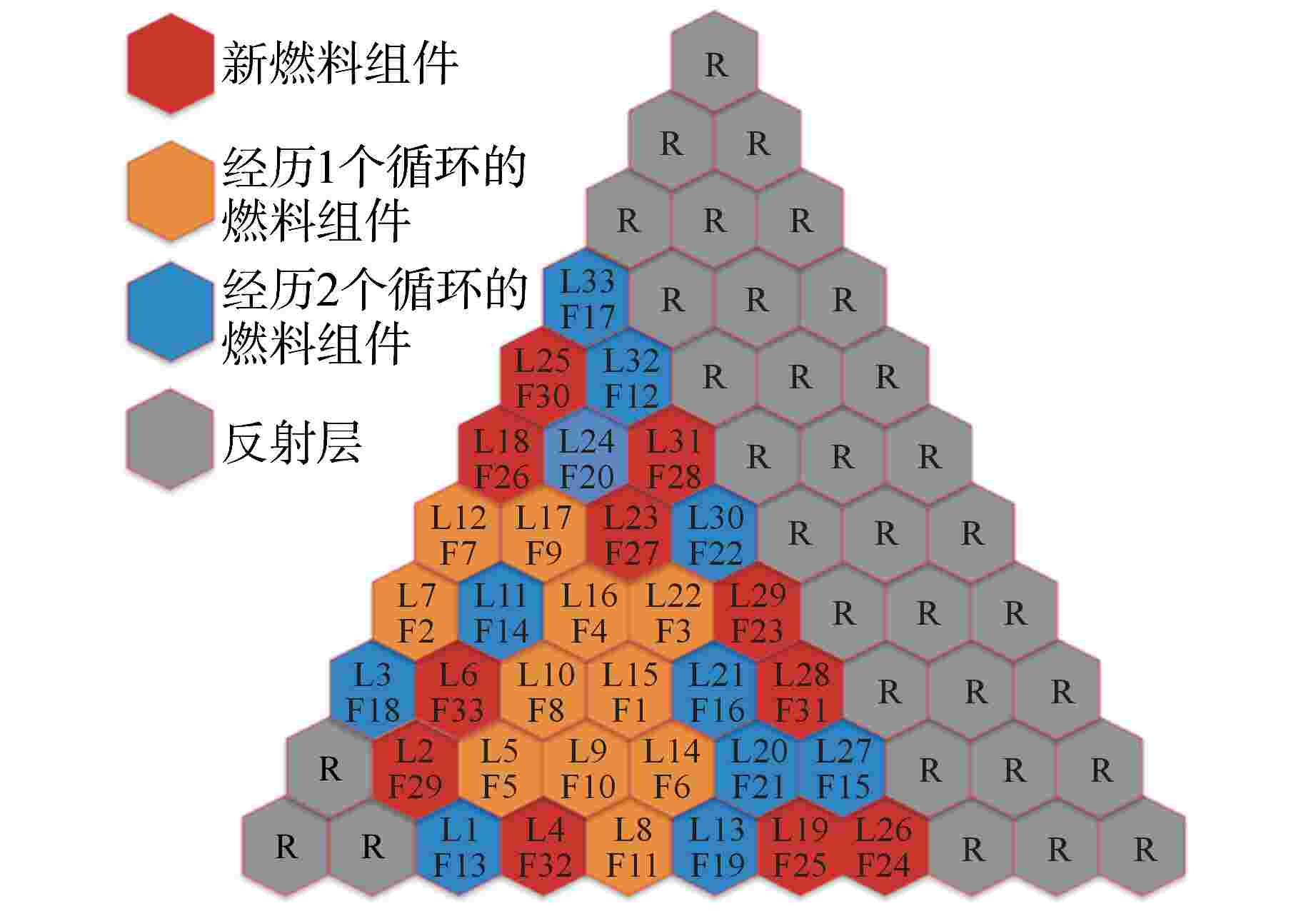
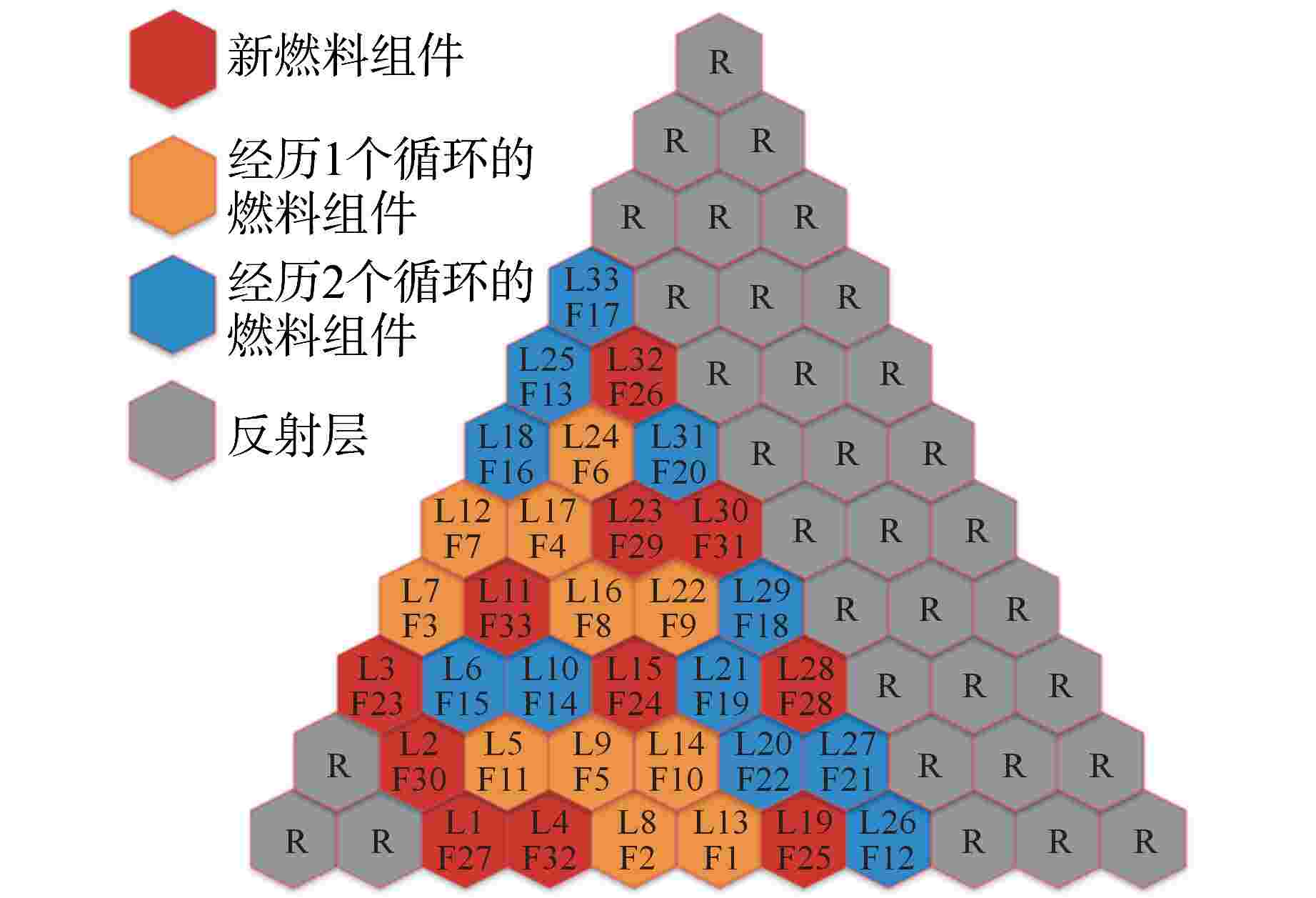
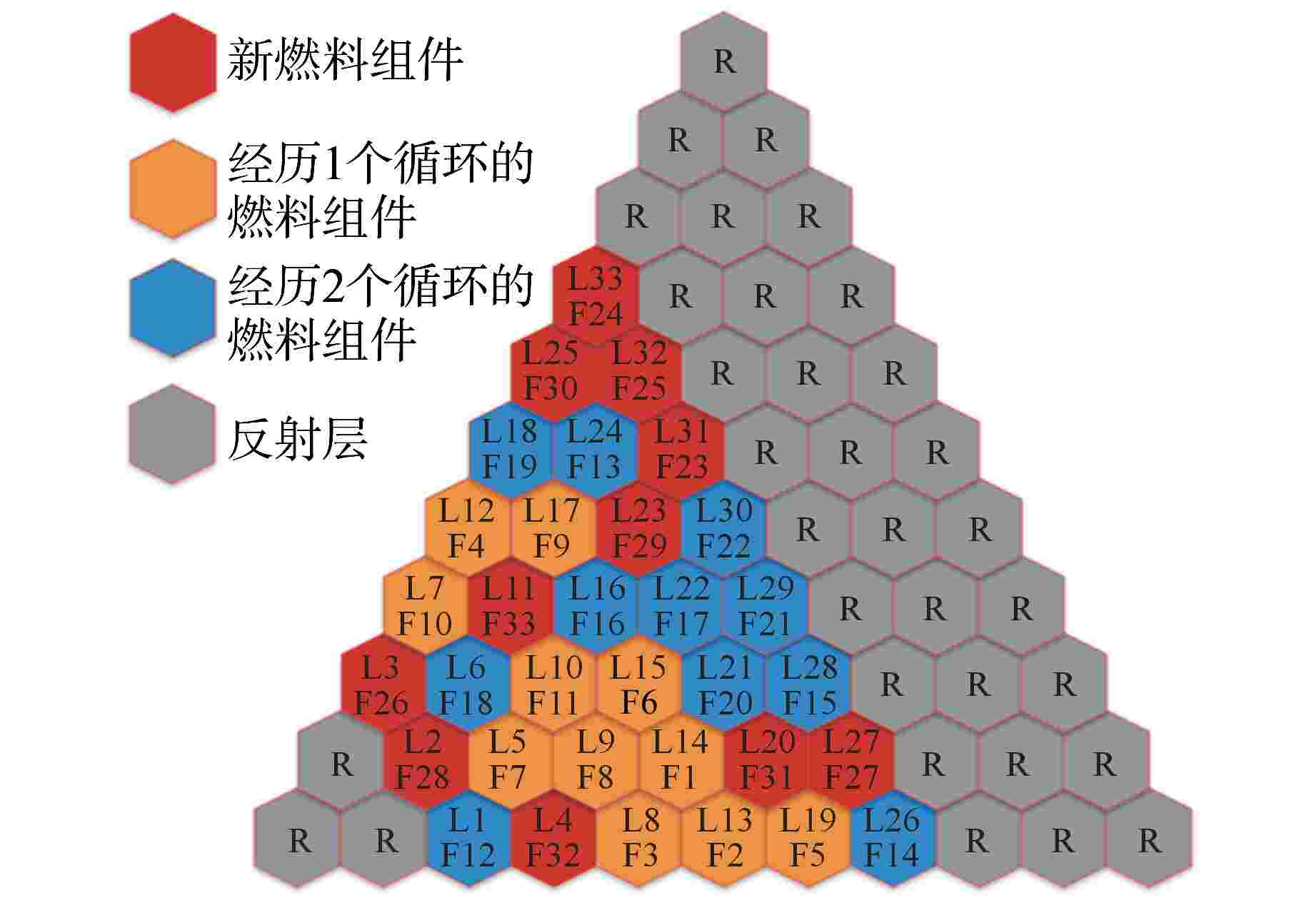
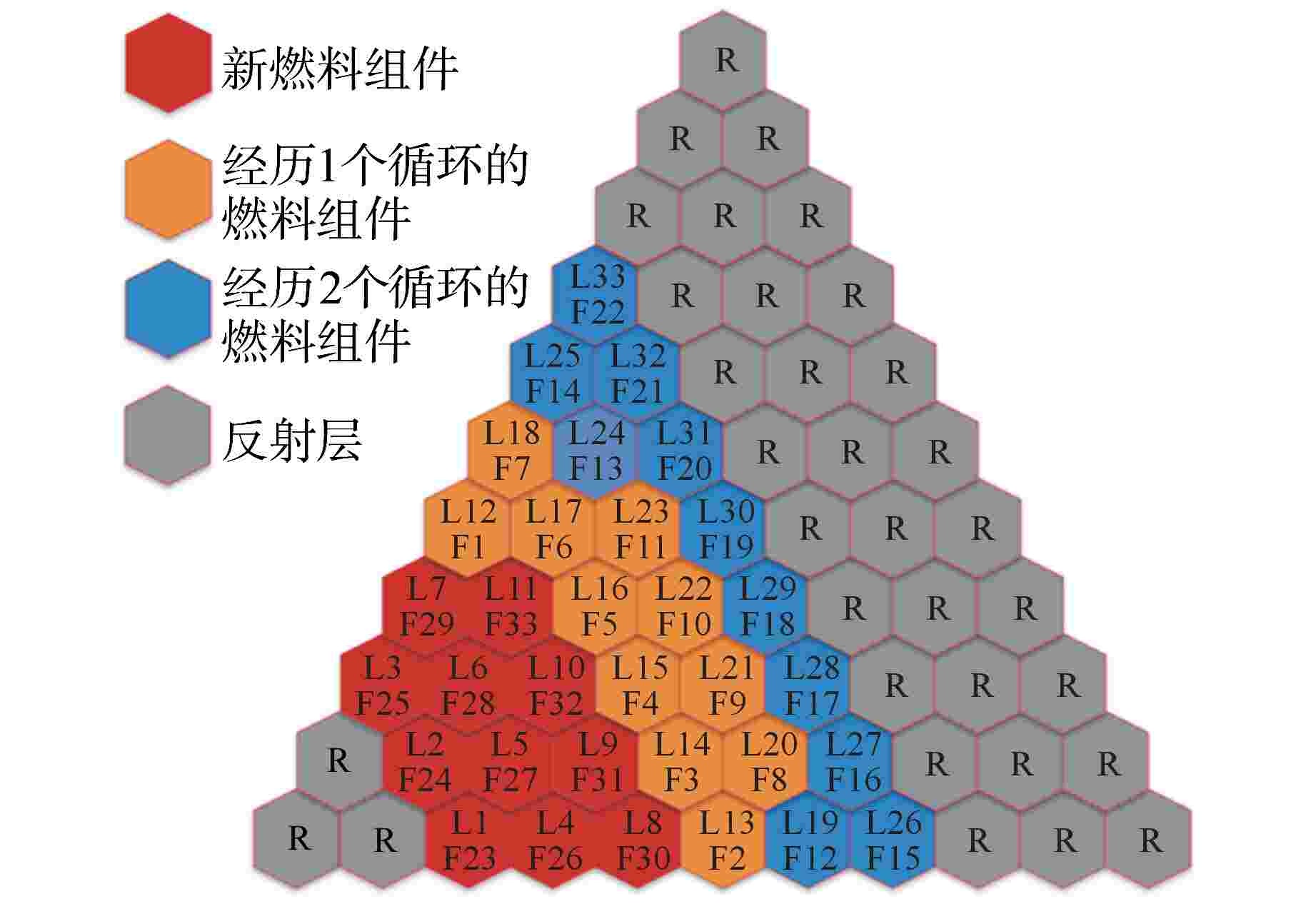
摘要: 遗传算法是一种应用于反应堆换料优化问题的经典算法,该算法的一个重要组成部分为选择策略。在目前的文献中,选择策略常直接选轮盘赌选择法或随机竞争选择法,缺乏对不同选择策略的比较与分析。为得到寻优能力最强的选择策略,本研究以钍基柱状高温气冷堆1/6堆芯为例,以比值法构造适应度函数,利用DRAGON程序进行堆芯物理计算,结合精英保留策略,对轮盘赌选择法、随机竞争选择法、均匀排序法、指数排序法和确定式选择法5种选择策略的寻优能力进行了比较分析。分析结果表明,在这5种选择策略中,指数排序法的寻优能力最强,是最适合求解换料优化问题的选择策略。Abstract: The genetic algorithm is one of the classic algorithms applied to the refueling optimization. An important part of this algorithm is the selection strategies. The existing studies often directly adopt the roulette wheel selection and stochastic tournament selection, and are lacking in comparison and analysis of different selection strategies. To obtain the selection strategy with the strongest optimization capability, this study, with the 1/6 core of a thorium-based prismatic high-temperature gas-cooled reactor (HTGR) taken as an example, constructs the fitness function in the ratio method, performs core physics calculation using the DRAGON code, and in conjunction with the elitism strategy, compares the optimization capabilities of the five selection strategies, including the roulette wheel selection, stochastic tournament selection, uniform ranking method, exponential ranking selection and deterministic selection. The study results show that the optimization capability of the exponential ranking selection is superior to the other four strategies, so the exponential ranking selection is most suitable for solving the refueling optimization problems.
-
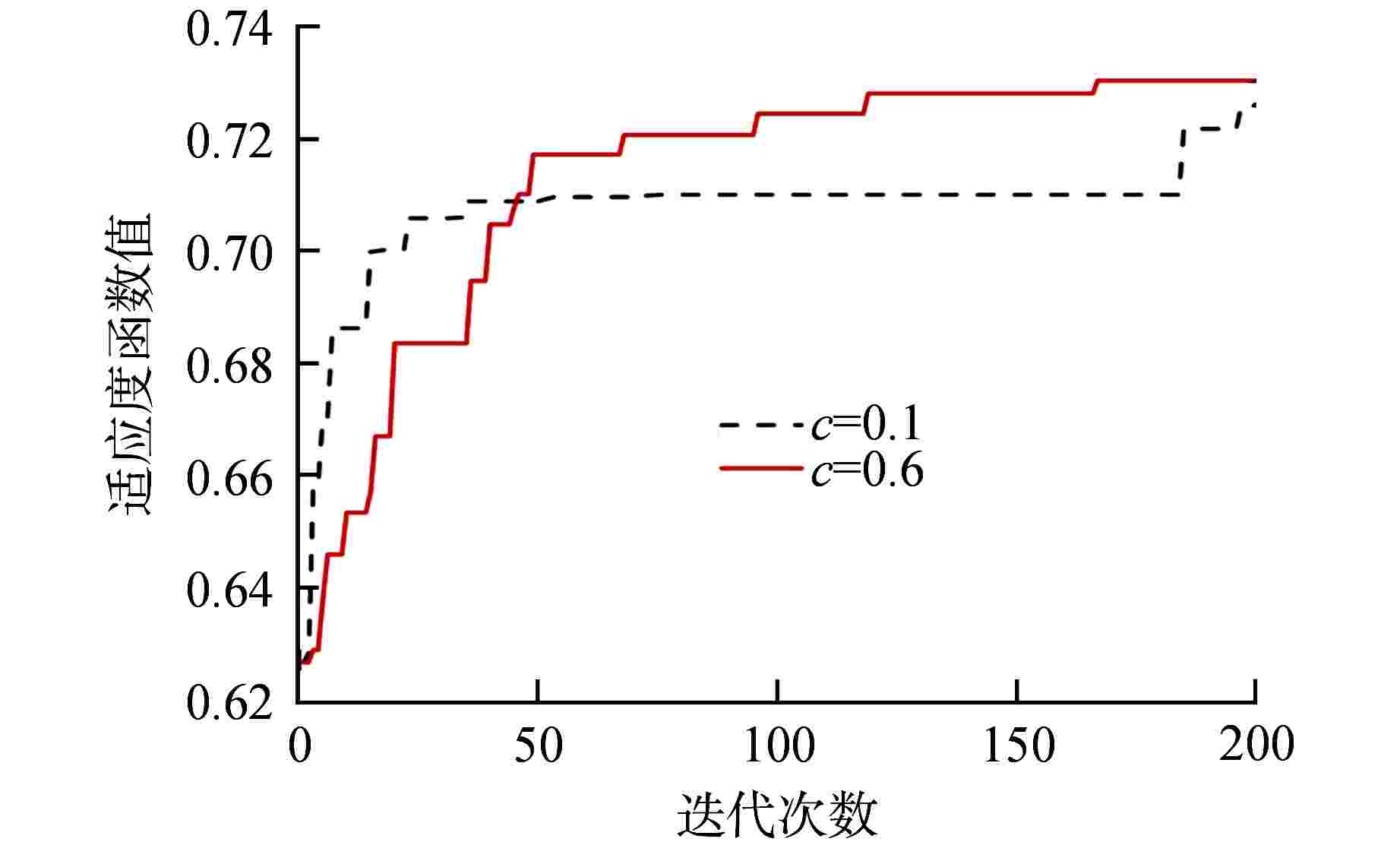
表 1 不同c值指数排序适应度函数值
Table 1. Fitness Function Values for Exponential Ranking Selection Corresponding to Different c Values
c 适应度函数值 c 适应度函数值 0.1 0.726011 0.6 0.730443 0.2 0.721447 0.7 0.721562 0.3 0.721939 0.8 0.721453 0.4 0.720984 0.9 0.723934 0.5 0.722818 表 2 不同选择策略的适应度函数值
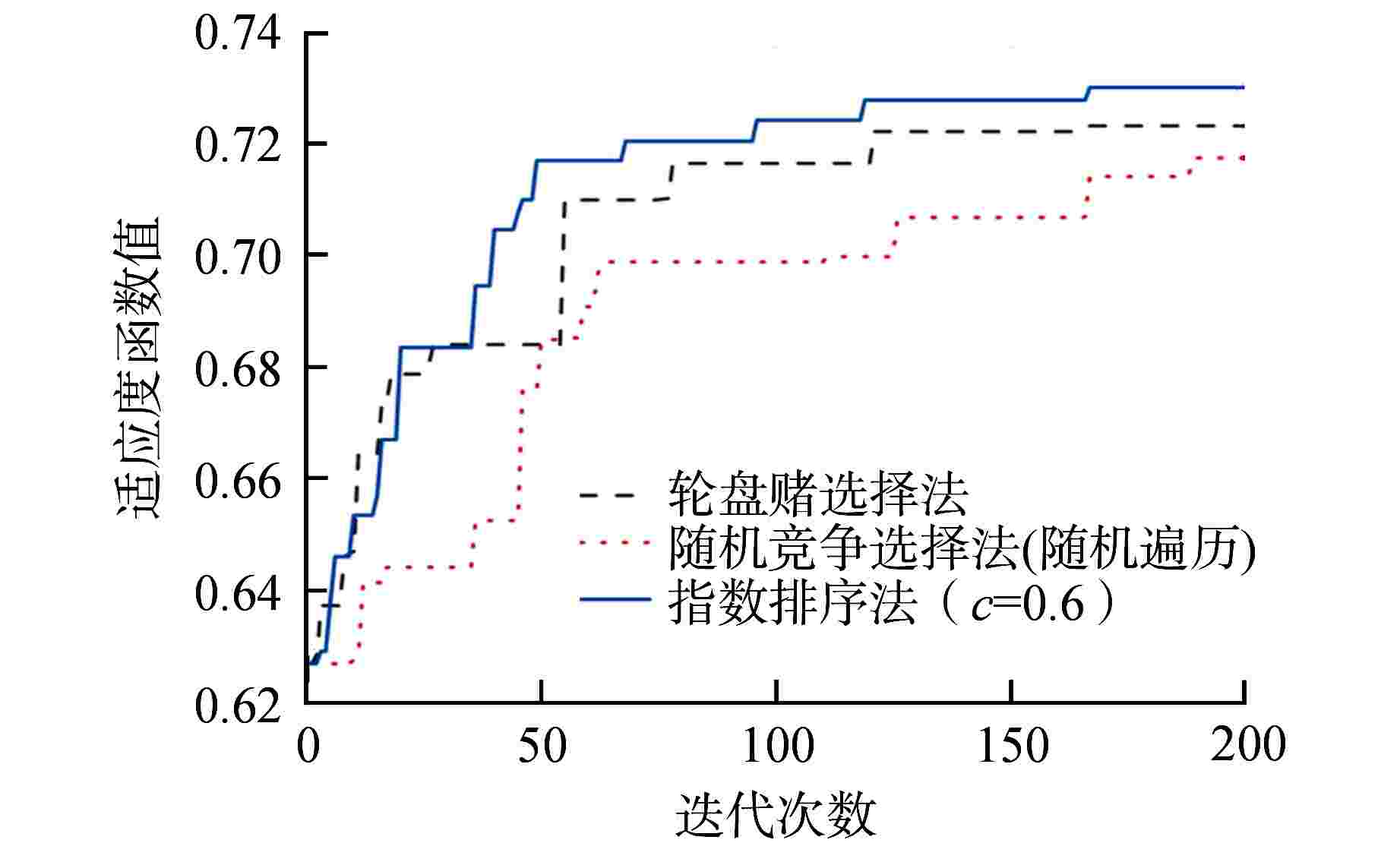
Table 2. Fitness Function Values for Different Selection Strategies
选择策略 适应度函数值 轮盘赌选择法 0.723576 随机竞争选择法(随机遍历) 0.717843 随机竞争选择法(全遍历) 0.716831 确定式选择 0.716290 均匀排序 0.722588 指数排序(c=0.6) 0.730443 -
[1] 黄杰,李文强,丁铭. 遗传算法在柱状高温气冷堆换料优化问题中的应用[J]. 强激光与粒子束,2017, 29(1): 11-17. [2] 夏冰,吕应中,经荥清,等. 熔盐球床堆堆芯燃料管理优化初步分析[J]. 原子能科学技术,2013, 47(增刊): 150-155. [3] 刘仕倡,蔡杰进. 基于粒子群优化算法的压水堆换料优化初步研究[J]. 核动力工程,2013, 34(5): 1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0926.2013.05.001 [4] TAYEFI S, PAZIRANDEH A. Using hopfield neural network to optimize fuel rod loading patterns in VVER/1000 reactor by applying axial variation of enrichment distribution[J]. Applied Soft Computing Journal, 2014(21): 501-508. [5] 周明, 孙树栋. 遗传算法原理及应用[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2000: 45-57. [6] 咸春宇,左劼,于中华. 遗传算法在压水堆核电厂低泄漏换料堆芯装载方案优化中的应用[J]. 核动力工程,2002, 23(S1): 12-16. [7] JALUVKA D, EYNDE G V, VANDEWALLE S. Development of a core management tool for MYRRHA[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2013(74): 562-568. [8] ALIM F, IVANOV K N, YILMAZ S, et al. New genetic algorithms (GA) to optimize PWR reactors[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2007, 35(1): 113-120. [9] 石秀安,胡永明. 我国钍燃料循环发展研究[J]. 核科学与工程,2011, 31(3): 281-288. [10] 高立本,沈健. 高温气冷堆的发展与前景[J]. 中国核工业,2016(10): 24-26+55. [11] CHAPOT J L C, SILVA F C D, SCHIRRU R. A new approach to the use of genetic algorithms to solve the pressurized water reactor's fuel management optimization problem[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 1999, 26(7): 641-655. doi: 10.1016/S0306-4549(98)00078-4 [12] KUMAR A, TSVETKOV P V. A new approach to nuclear reactor design optimization using genetic algorithms and regression analysis[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2015(85): 27-35. [13] DESCOTES V M. Reactor physics of a deep-burner prismatic core for VHTR[D]. Montréal: Université de Montréal, 2011. [14] NOROUZI A, ZOLFAGHARI A, MINUCHEHR A H, et al. An enhanced integer coded genetic algorithm to optimize PWRs[J]. Progress in Nuclear Energy, 2011, 53(5): 449-456. doi: 10.1016/j.pnucene.2011.03.005 [15] CHAKRABORTY M, CHAKRABORTY U K. An analysis of linear ranking and binary tournament selection in genetic algorithms[C]. Proceedings of ICICS, 1997 International Conference on Information, Communications and Signal Processing. Theme: Trends in Information Systems Engineering and Wireless Multimedia Communications, 1997, 1: 407-411. [16] TSAI M C, CAI Y X, WANG C D, et al. Tinnitus abnormal brain region detection based on dynamic causal modeling and exponential ranking[J]. BioMed Research International, 2018(2018): 1-10. -





 下载:
下载: