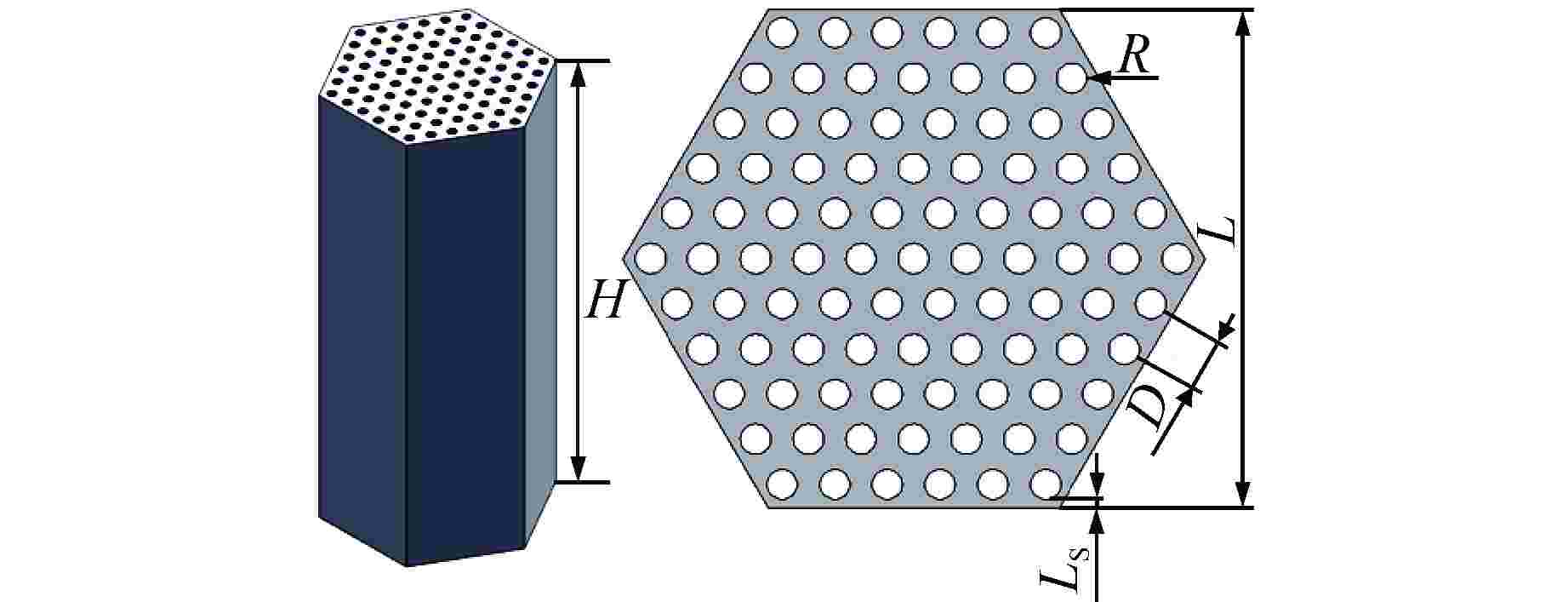
Research on Analysis for Performance and Optimization of Prismatic Dispersed Microencapsulated Fuel in Gas-Cooled Reactor
-
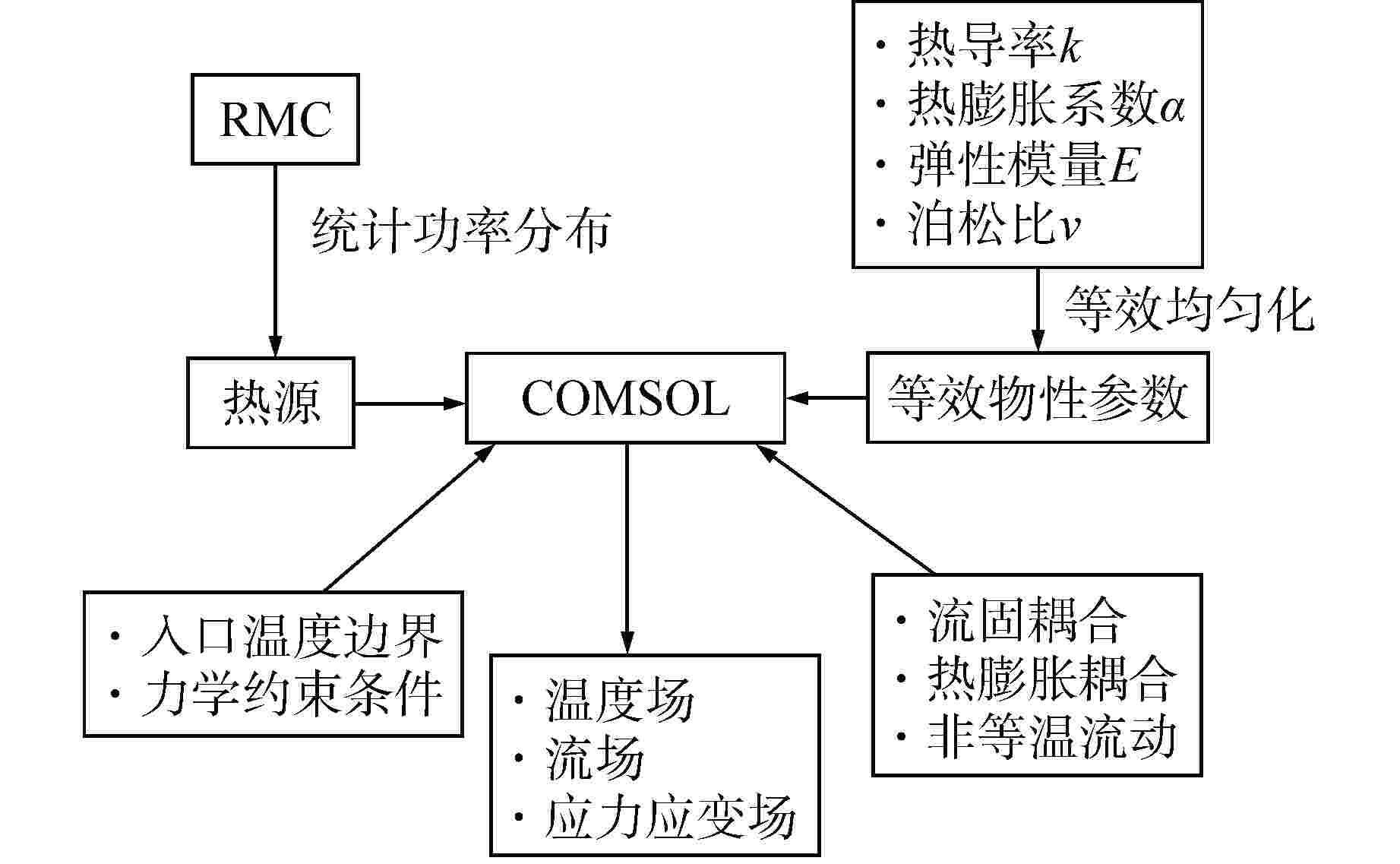
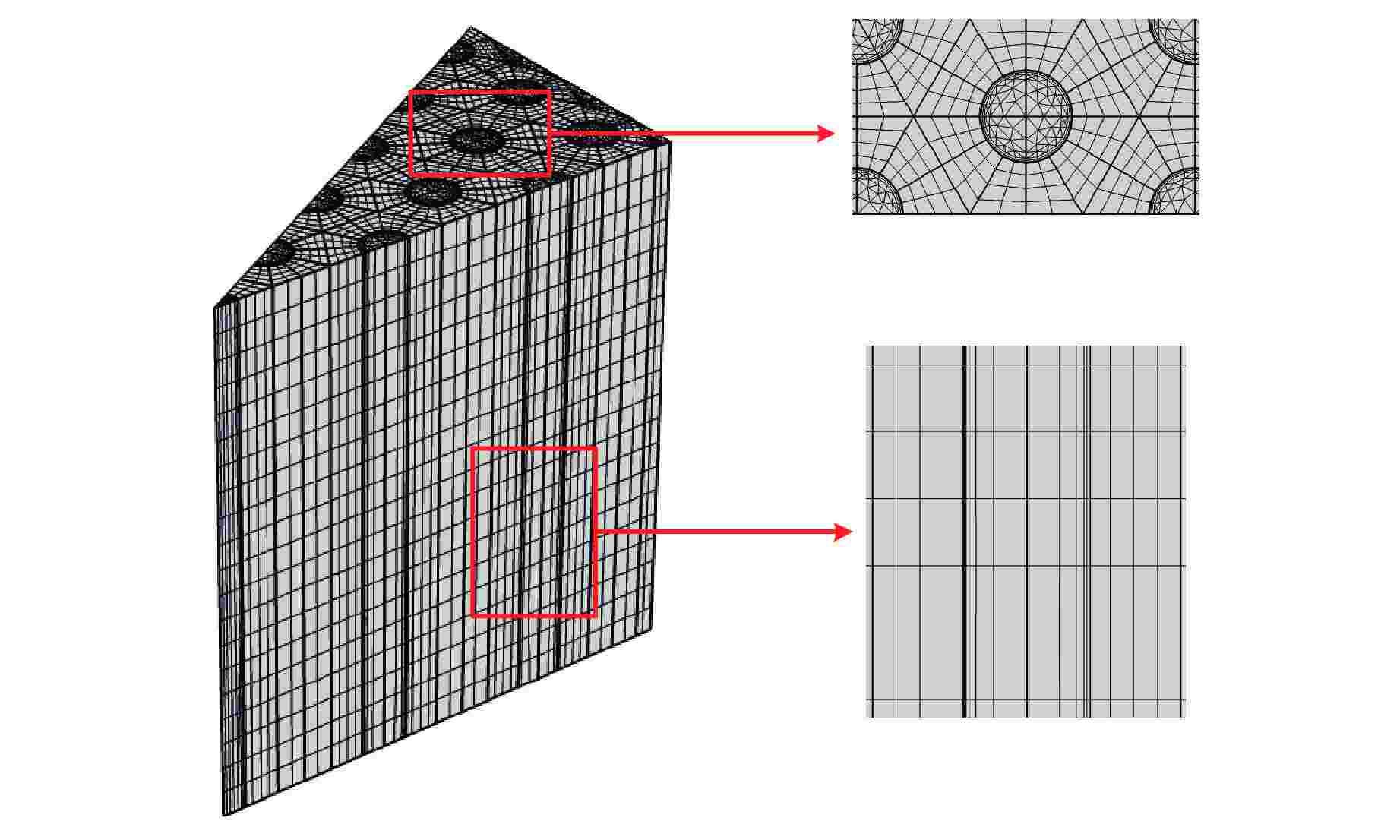
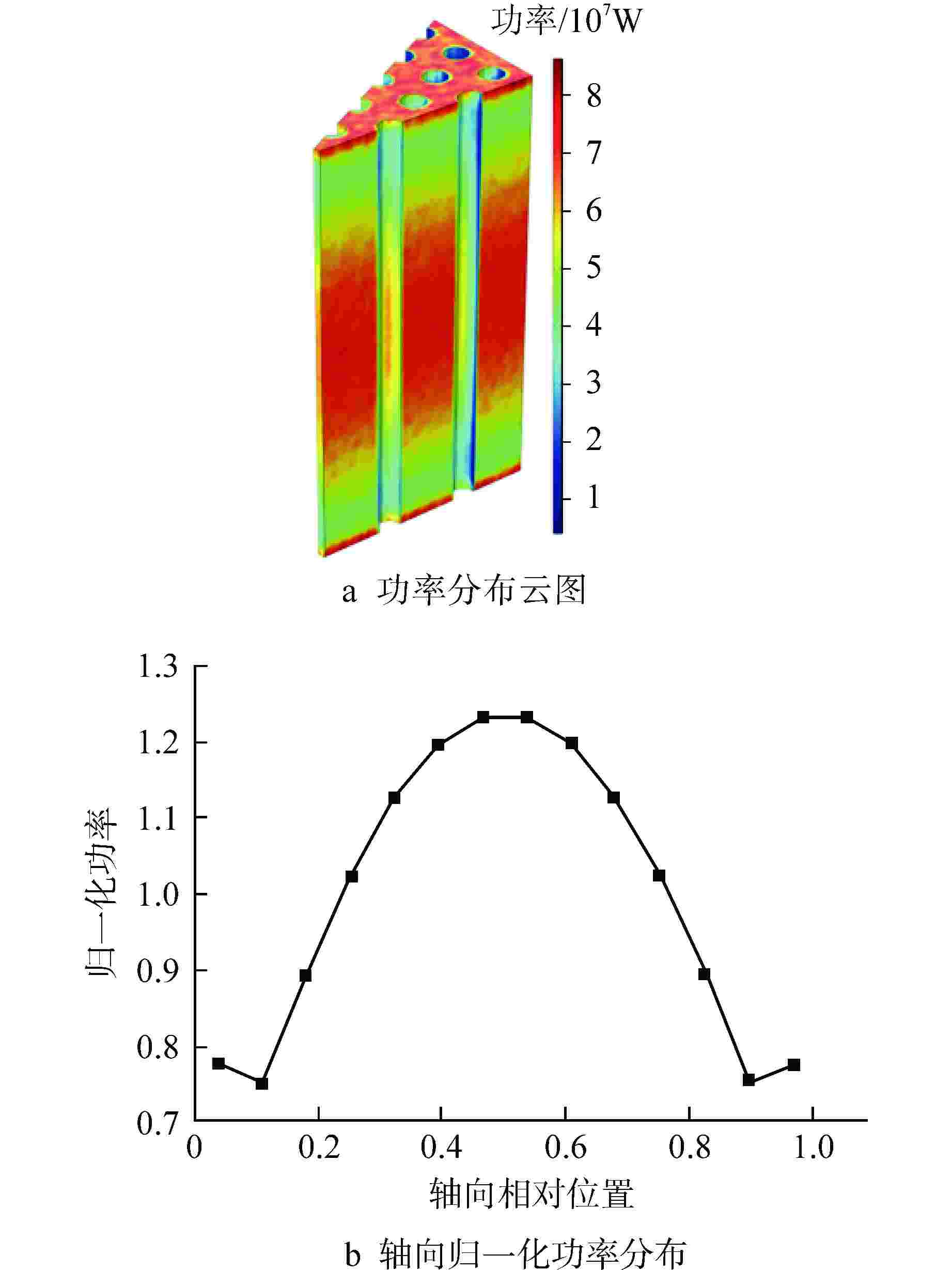
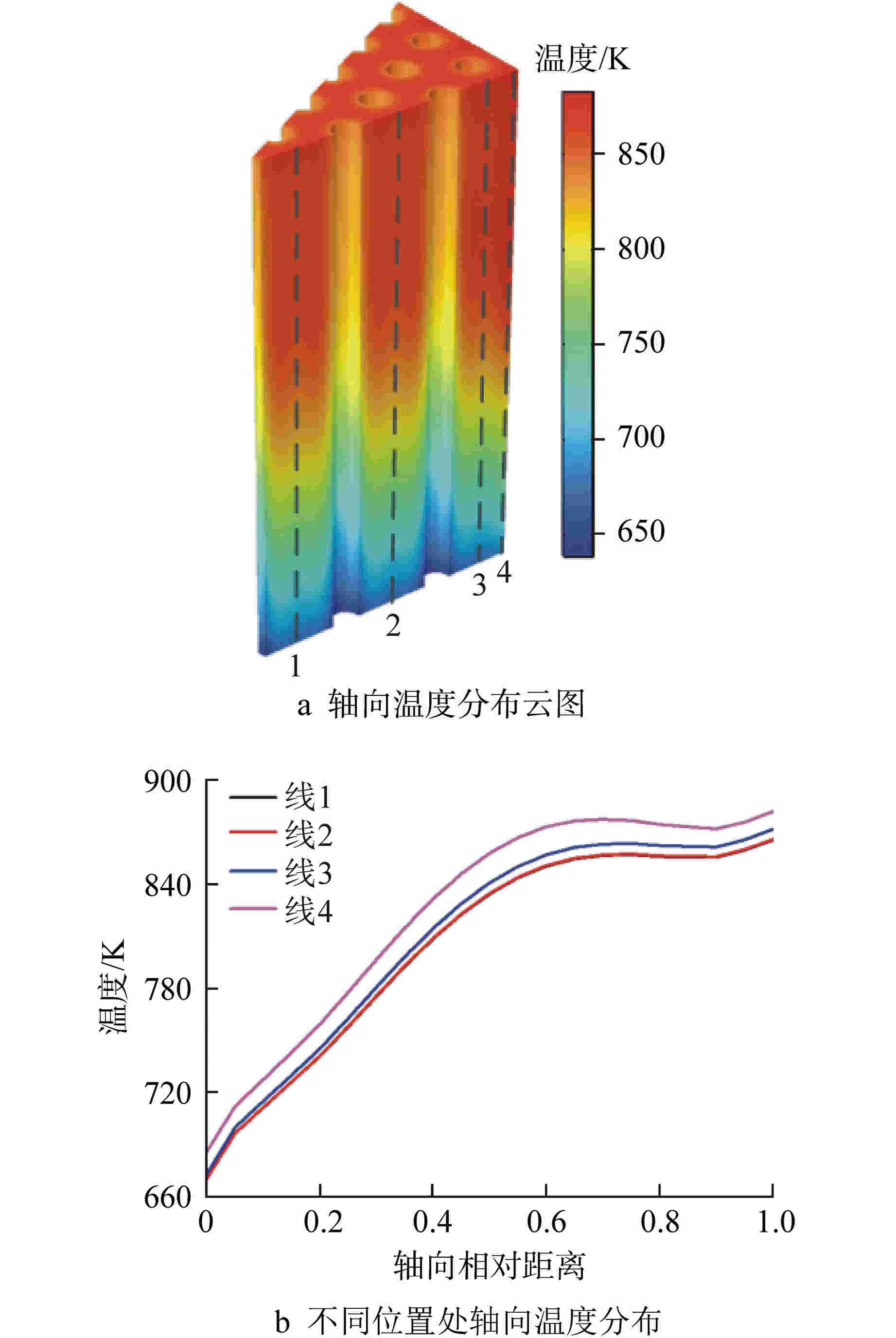
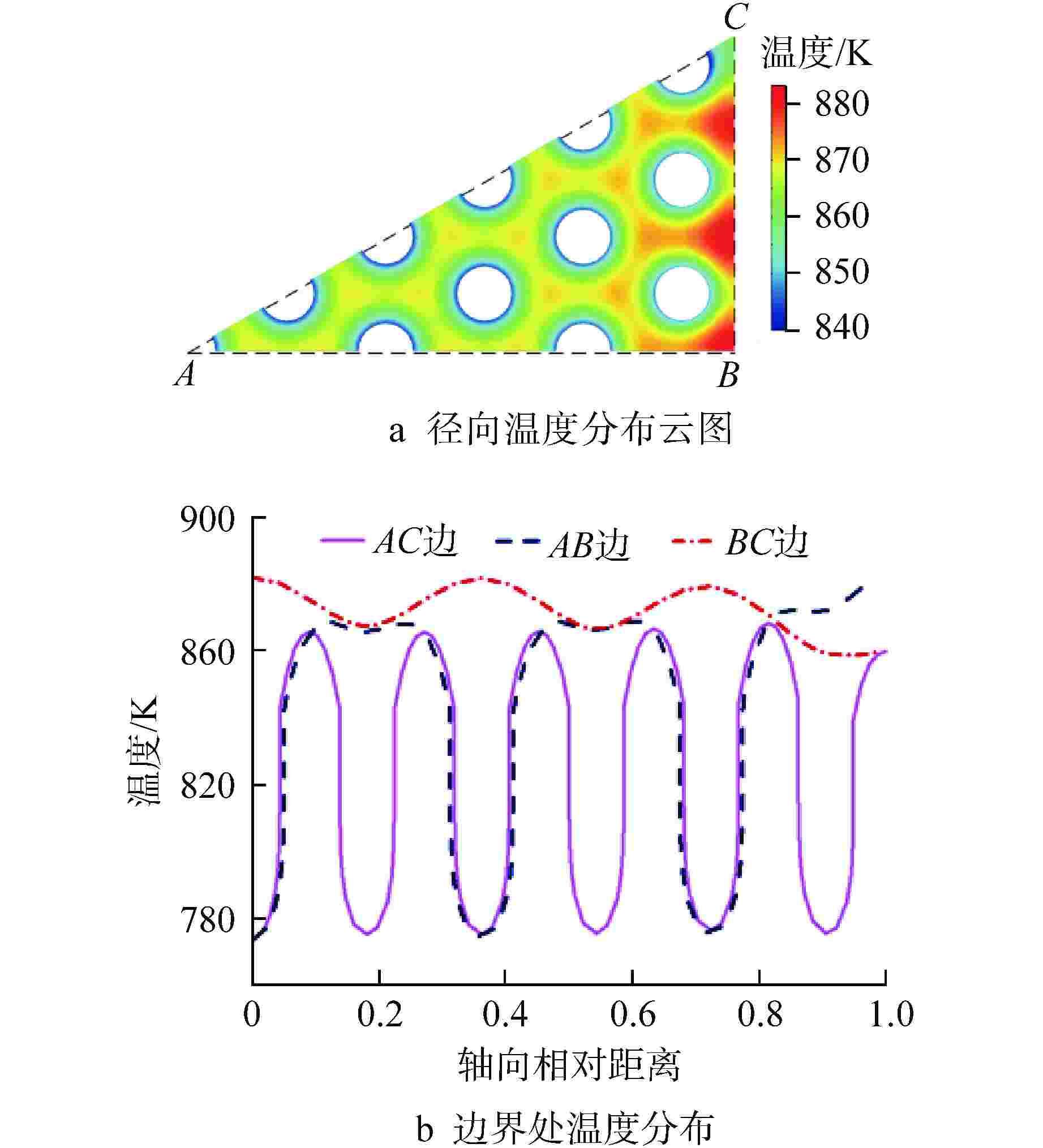
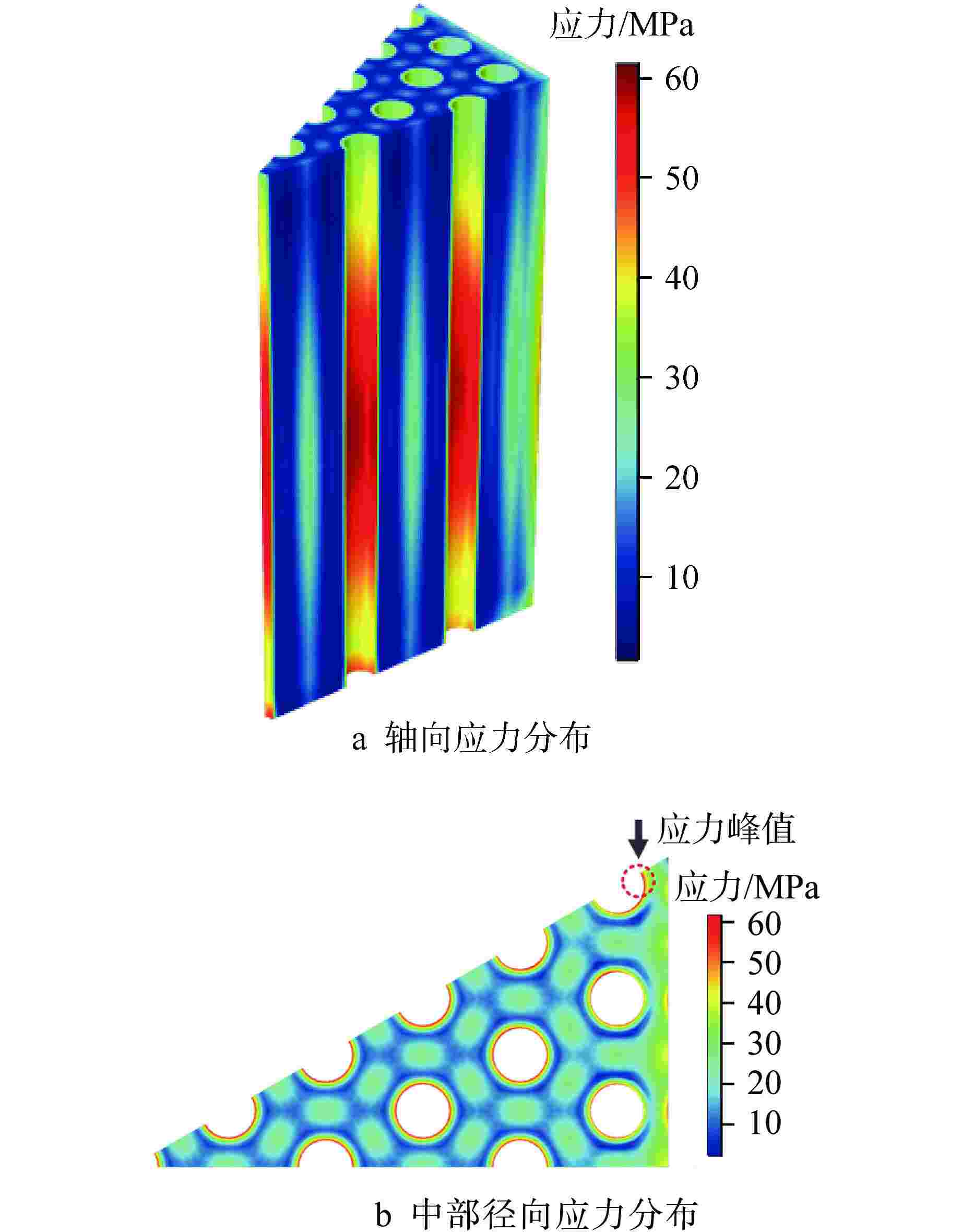
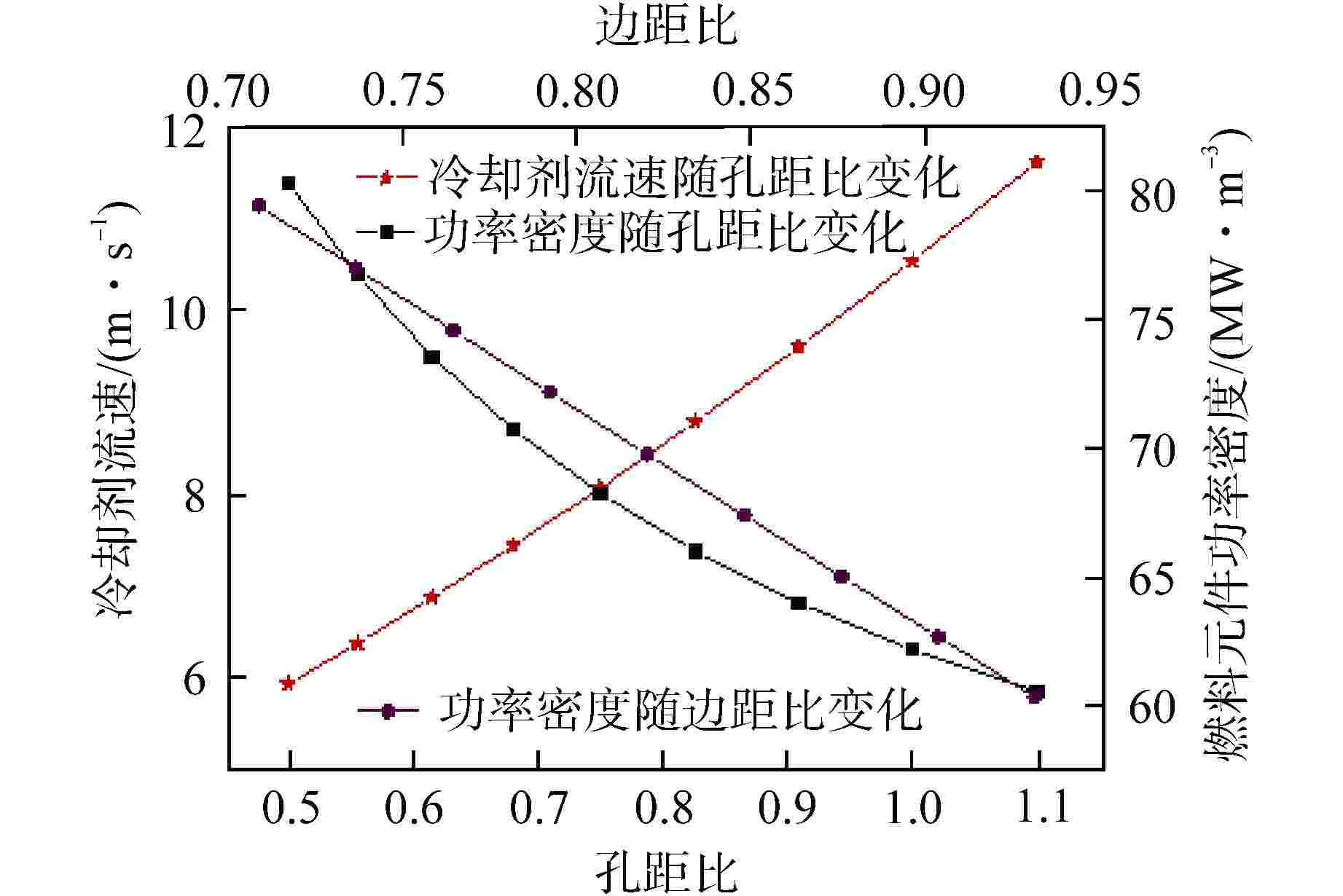
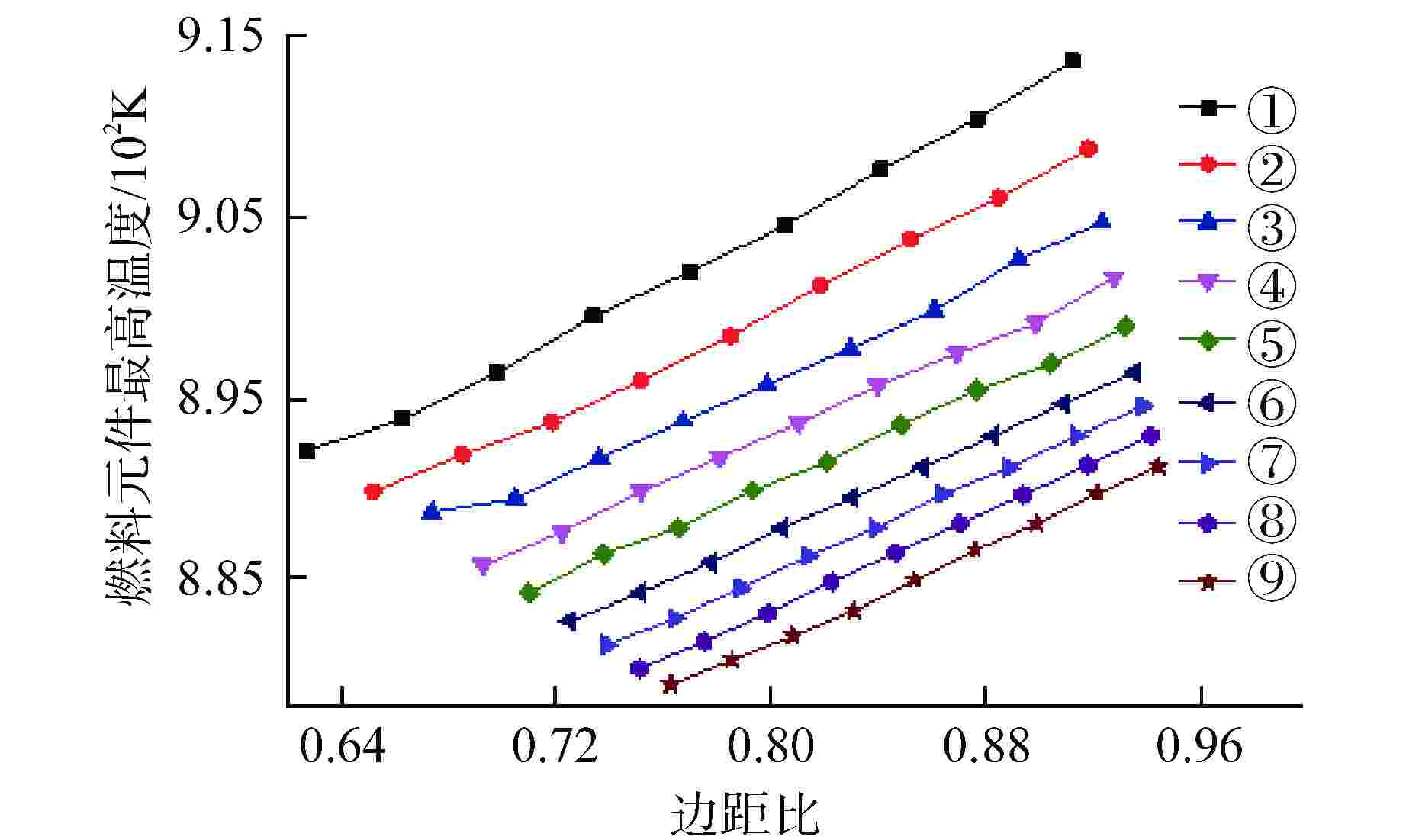
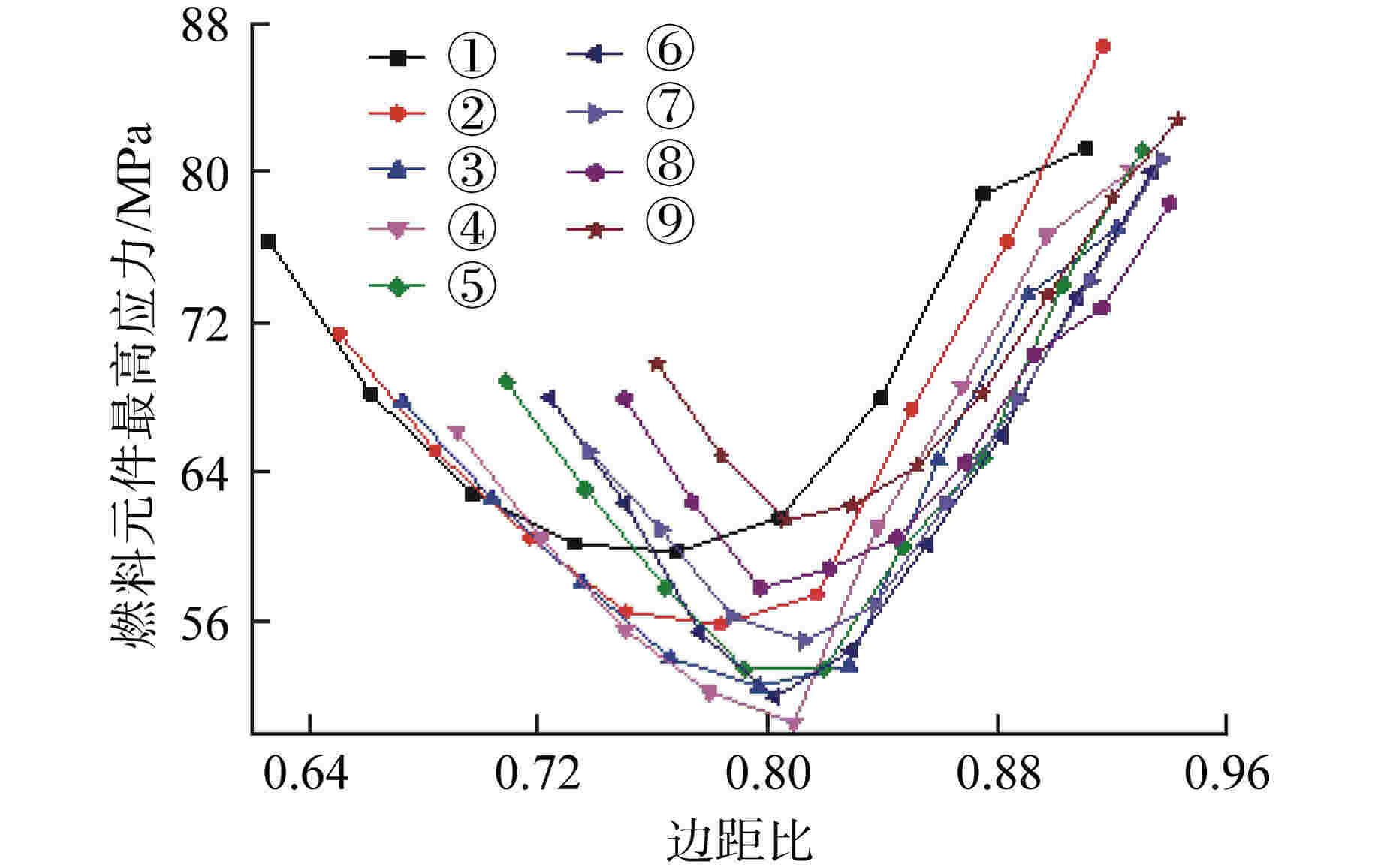
摘要: 棱柱型弥散微封装燃料是将三重各向同性包覆(TRISO)燃料颗粒弥散于金属或陶瓷基体形成的颗粒增强复合燃料,具有良好的结构稳定性、裂变产物包容能力和辐照稳定性,是高温气冷堆中较具发展前景的燃料形式之一。本文提出将TRISO燃料颗粒弥散于SiC基体的棱柱型弥散微封装燃料设计方案,并基于有限元分析软件COMSOL建立了该燃料元件三维热流固耦合分析模型,初步实现了该燃料元件性能分析和优化设计。结果表明,棱柱型弥散微封装燃料元件的温度最大值位于燃料元件外侧,应力峰值位于冷却剂通道壁面,边距比为0.76~0.84、孔距比为0.68~0.75时燃料元件热应力最小。本文建立的棱柱型弥散微封装燃料性能分析方法和研究结论,可为后续该型气冷堆燃料元件设计提供指导和参考。Abstract: Prismatic dispersed microencapsulated fuel is a particle-reinforced composite fuel which is formed by TRISO fuel particles dispersed in metal or ceramic matrix. It has good structural stability, fission product inclusion capacity and irradiation stability, and it is one of the promising fuels in high temperature gas-cooled reactor. A prismatic dispersed microencapsulated fuel with TRISO particles dispersed in SiC matric was proposed in this paper. Based on the finite element analysis software COMSOL, the 3D thermal-fluid-solid coupling analysis model of the fuel element is established, and the performance analysis and optimization design of the fuel element are preliminarily realized. The results show that the maximum temperature of the prismatic dispersed microencapsulated fuel element is located on the outside of the fuel element, the peak stress is on the wall of the coolant channel, and the thermal stress of the fuel element is the lowest when the edge-distance ratio is 0.76 to 0.84 and the hole-distance ratio is 0.68 to 0.75. The performance analysis method and research conclusions of the prismatic dispersed microencapsulated fuel established in this paper can provide guidance and reference for the subsequent design of this type of gas-cooled reactor fuel element.
-
Key words:
- Prismatic /
- Dispersed microencapsulated fuel /
- COMSOL /
- Thermal-fluid-solid coupling /
- Optimization
-
表 1 材料性能参数
Table 1. Material Performance Parameters
材料 热导率/(W·m−1·K−1) 热膨胀系数/K−1 弹性模量/GPa 泊松比 UO2核芯 Lucuta修正模型[12] 式(1) 式(2) 0.316 Buffer层 0.5 3.5×10−6 式(3) 0.23 IPyC层 4 5.5×10−6 式(4) 0.23 SiC层 式(5) 式(6) 式(7) 0.13 OPyC层 4 5.5×10−6 式(4) 0.23 SiC基体 式(5) 式(6) 式(7) 0.13 -
[1] KING J C, EL-GENK M S. Submersion-subcritical safe space (S4) reactor[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2006, 236(17): 1759-1777. doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2005.12.010 [2] BENDER M, CARLSMITH R S, DELENE J G, et al. Gas-cooled fast reactor concepts: ORNL-3642[R]. Oak Ridge, Tennessee: Oak Ridge National Laboratory, 1964. [3] NISHIHARA T, YAN X, TACHIBANA Y, et al. Excellent feature of Japanese HTGR technologies: JAEA-Technology 2018-004[R]. Japan Atomic Energy Agency, 2018. [4] SHAMANIN I V, GRACHEV V M, CHERTKOV Y B, et al. Neutronic properties of high-temperature gas-cooled reactors with thorium fuel[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2018(113): 286-293. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2017.11.045 [5] HANDWERK C S, DRISCOLL M J, HEJZLAR P. Optimized core design of a supercritical carbon dioxide-cooled fast reactor[J]. Nuclear Technology, 2008, 164(3): 320-336. doi: 10.13182/NT08-A4030 [6] ATTOM A M, WANG J C, HUANG J, et al. Neutronic analysis of thorium S& B fuel blocks with different driver fuels in advanced Block-type HTRs[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2020(136): 107041. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2019.107041 [7] 辛勇,李垣明,唐昌兵,等. 金属基弥散微封装燃料中TRISO燃料颗粒的尺寸优化设计[J]. 核动力工程,2019, 40(2): 176-179. [8] 李垣明,唐昌兵,余红星,等. 锆基弥散微封装燃料在稳态运行条件下的失效机理研究[J]. 核动力工程,2019, 40(1): 156-161. [9] Idaho National Engineering and Environmental Laboratory. A handbook of materials properties for use in the analysis of light water reactor fuel rod behavior[Z]. Idaho: Idaho National Engineering and Environmental Laboratory, 2003. [10] POWERS J J, WIRTH B D. A review of TRISO fuel performance models[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2010, 405(1): 74-82. doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2010.07.030 [11] SNEAD L L, NOZAWA T, KATOH Y, et al. Handbook of SiC properties for fuel performance modeling[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2007, 371(1-3): 329-377. doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2007.05.016 [12] LUCUTA P G, MATZKE H J, HASTINGS I J. A pragmatic approach to modelling thermal conductivity of irradiated UO2 fuel: review and recommendations[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 1996, 232(2-3): 166-180. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3115(96)00404-7 [13] MAXWELL J C. A Treatise on electricity and magnetism[M]. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1873. [14] KERNER E H. The elastic and thermo-elastic properties of composite media[J]. Proceedings of the Physical Society, 1956, 69(8): 808-813. doi: 10.1088/0370-1301/69/8/305 [15] 黄克智, 黄永刚. 固体本构关系[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 1999. -





 下载:
下载: