Simulation Study on Switching Operation Law of Feed Water Pumps in Multi-pump Parallel Feed Water System
-
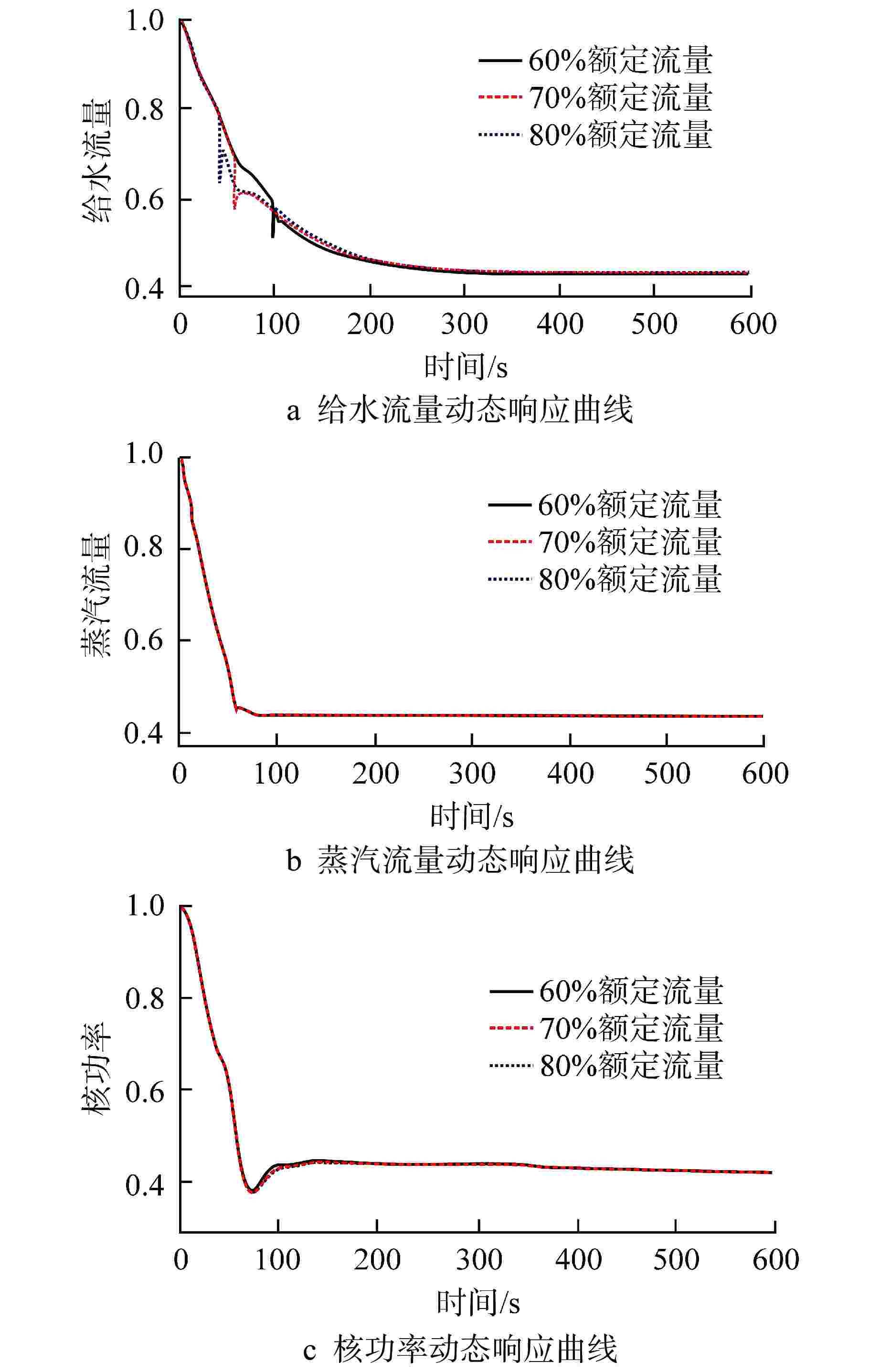
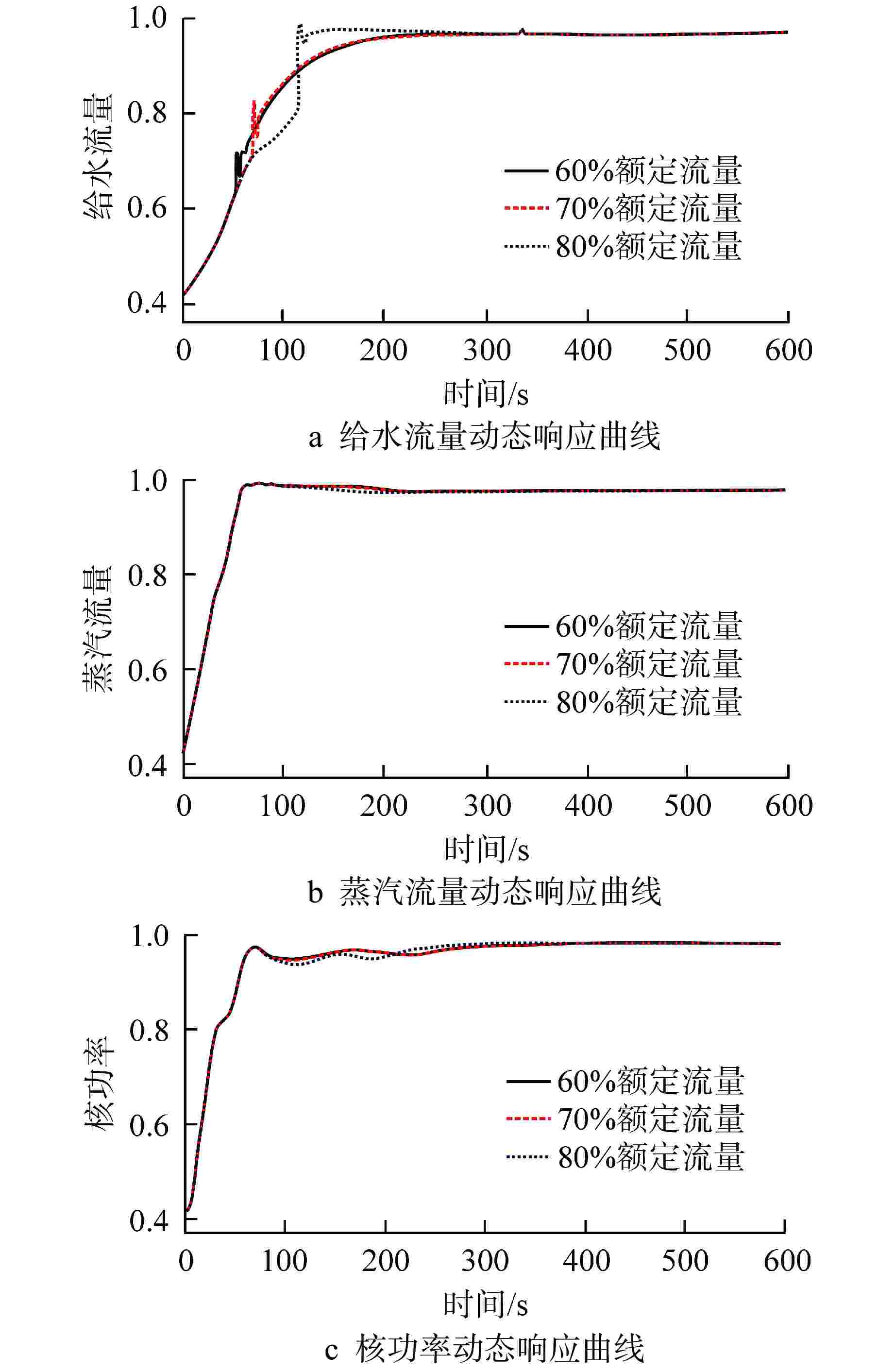
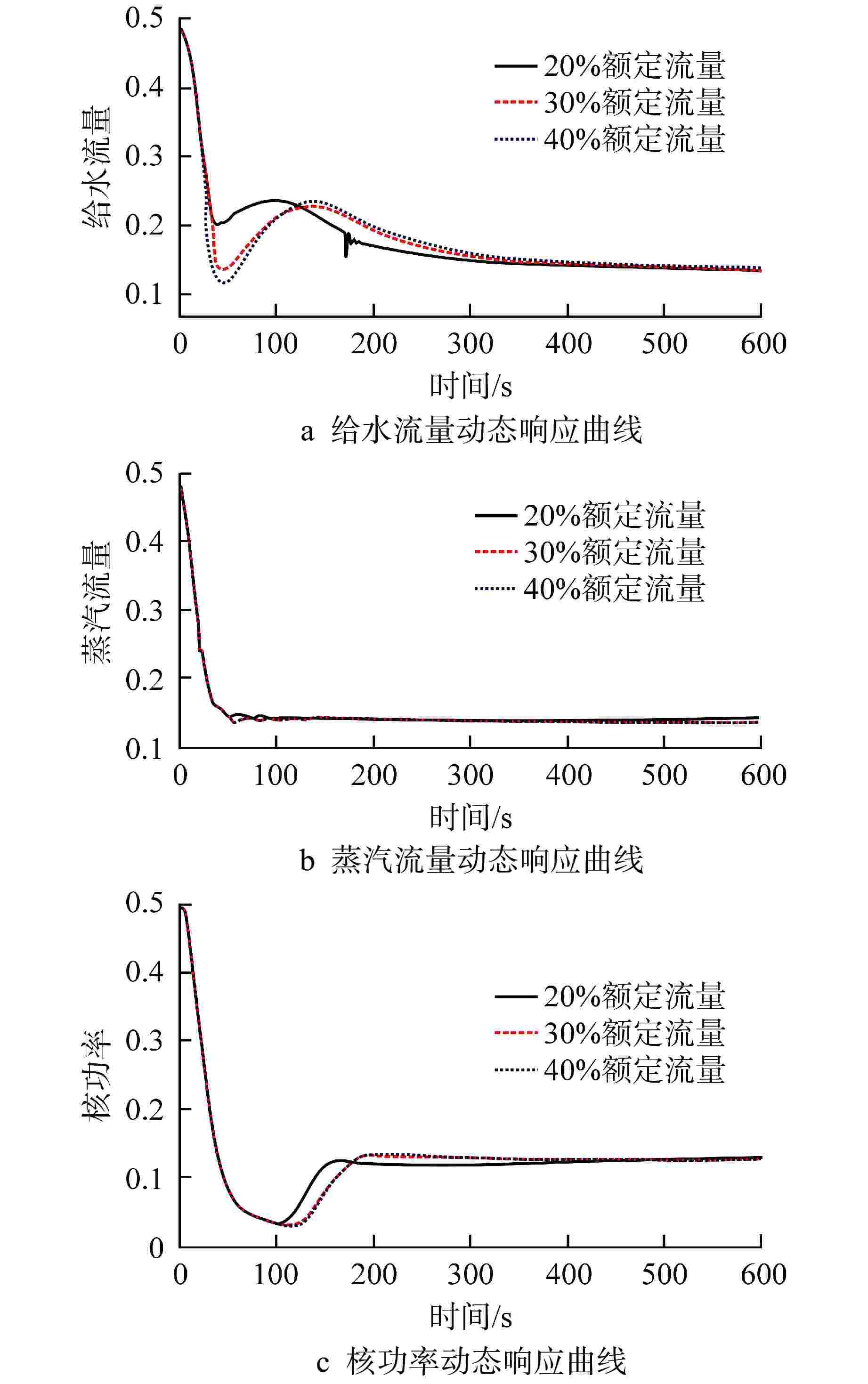
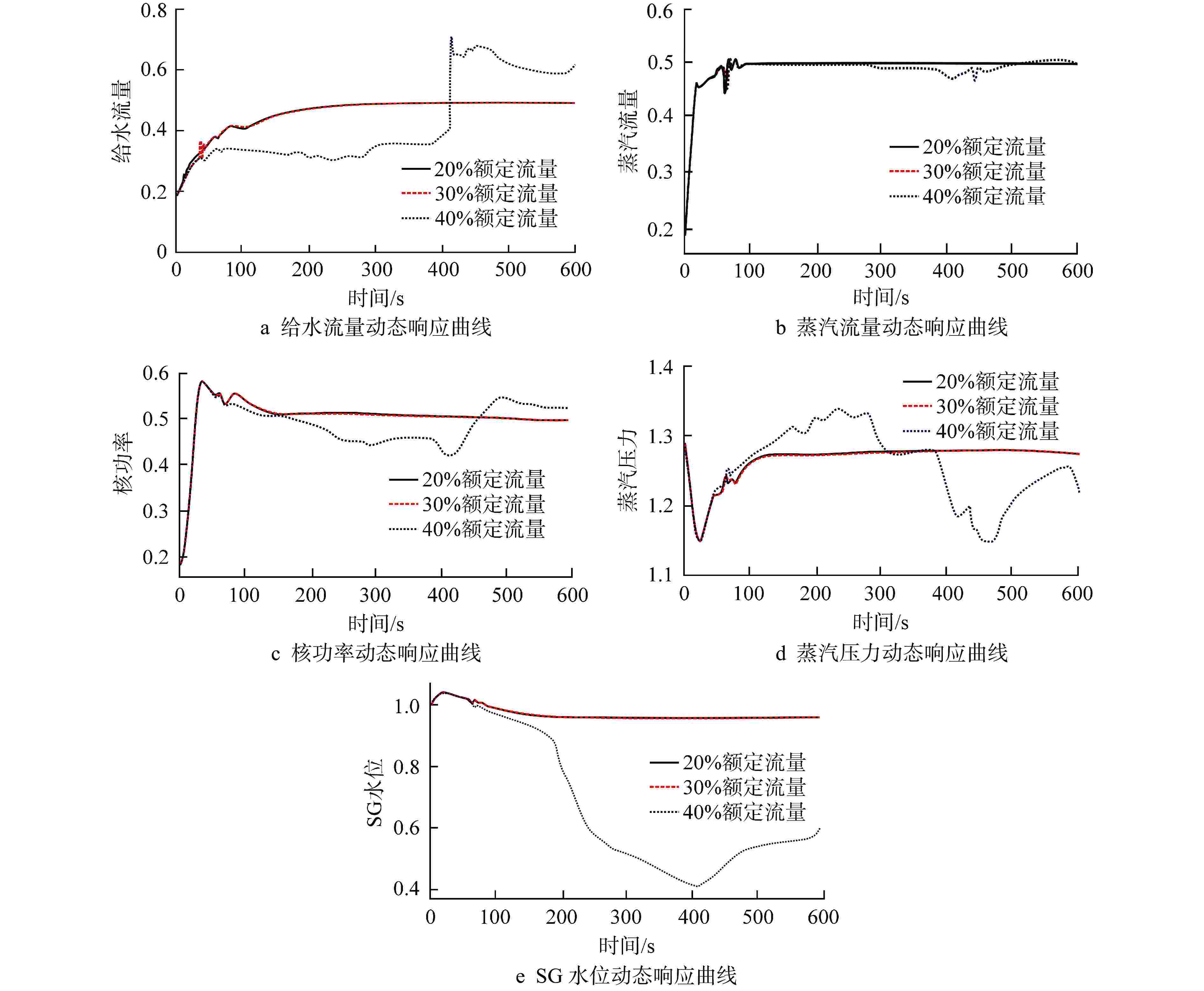
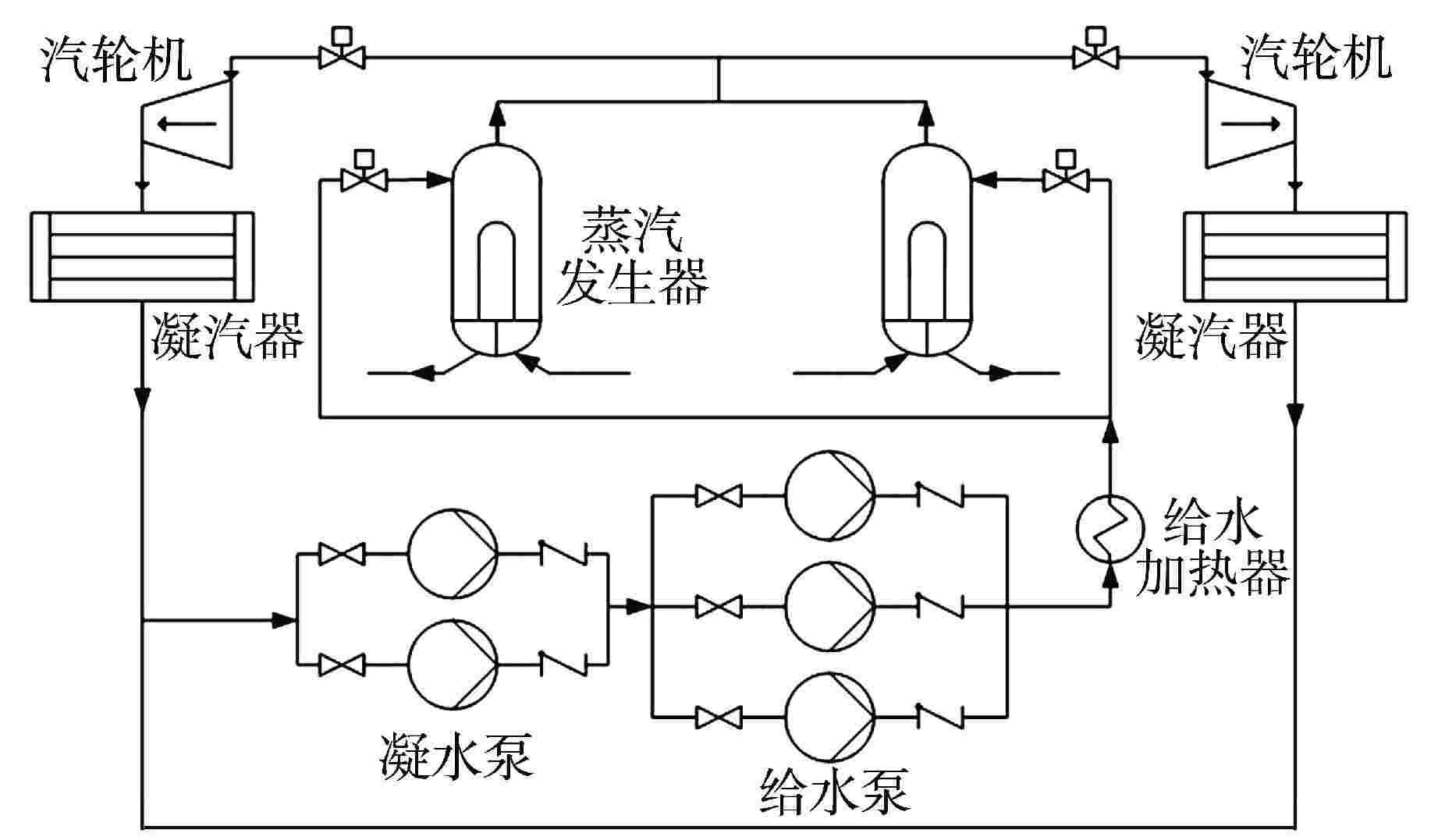
摘要: 多泵并联给水系统作为核动力系统的主要子系统之一,其给水泵的切换运行规律对系统运行经济性以及系统运行特性至关重要。本研究利用系统仿真支撑软件APROS建立了多泵并联给水系统仿真模型,并依据额定设计值验证了模型的准确性。基于此,通过进行不同切换条件下的线性升、降负荷仿真,对给水泵切换运行规律和系统动态特性进行了研究。研究结果表明,针对本研究对象,其高负荷工况切换点选取为70%额定流量,低负荷工况切换点选取为30%额定流量时,既能获得良好的系统动态响应,还能保持给水泵运行经济性较高。此外,低负荷工况对给水泵切换引入的扰动更为敏感。低负荷工况下,若切换条件选取不当,则会导致降负荷过程中系统触发超压排放。Abstract: As one of the main subsystems of the nuclear power system, the switching operation law of the feed water pumps in the multi-pump parallel feed water system is critical to the system operation economy and system operation characteristics. In this study, the simulation model of multi-pump parallel water supply system is established by using the system simulation support software APROS, and the accuracy of the model is verified according to the rated design value. Based on this, the switching operation law and system dynamic characteristics of feed water pump are studied through the simulation of linear rising and falling load under different switching conditions. The research results show that, for this research object, when the switching point under high load condition is selected as 70% of the rated flow, and the switching point under low load condition is selected as 30% of the rated flow, good system dynamic response can be obtained, and high economy of feed water pump operation can be maintained. In addition, the low load condition is more sensitive to the disturbance caused by the switching of feed water pump. Under low load conditions, if the switching conditions are not selected properly, the system will trigger overpressure discharge in the process of load reduction.
-
Key words:
- Multi-pump parallel feed water system /
- APROS /
- Feed water pump /
- Switching operation law /
- Simulation
-
表 1 额定工况下稳态仿真结果对比
Table 1. Comparison of Steady-state Simulation Results under Rated Conditions
参数名 设计值 模拟值 相对误差/% 反应堆热功率 1.00000 0.99827 −0.173 冷却剂流量 1.00000 1.00001 0.001 冷却剂平均温度 1.00000 1.00002 0.002 稳压器压力 1.00000 0.99493 −0.507 给水温度 1.00000 0.99986 −0.014 给水总流量 1.00000 0.99066 −0.934 蒸汽总产量 1.00000 1.00065 0.065 主蒸汽压力 1.00000 0.99987 −0.013 SG水位 1.00000 0.99879 −0.121 汽轮机总功率 1.00000 1.00038 0.038 表 2 不同工况下单台泵的功率和效率
Table 2. Power and Efficiency of Single Pump under Different Conditions
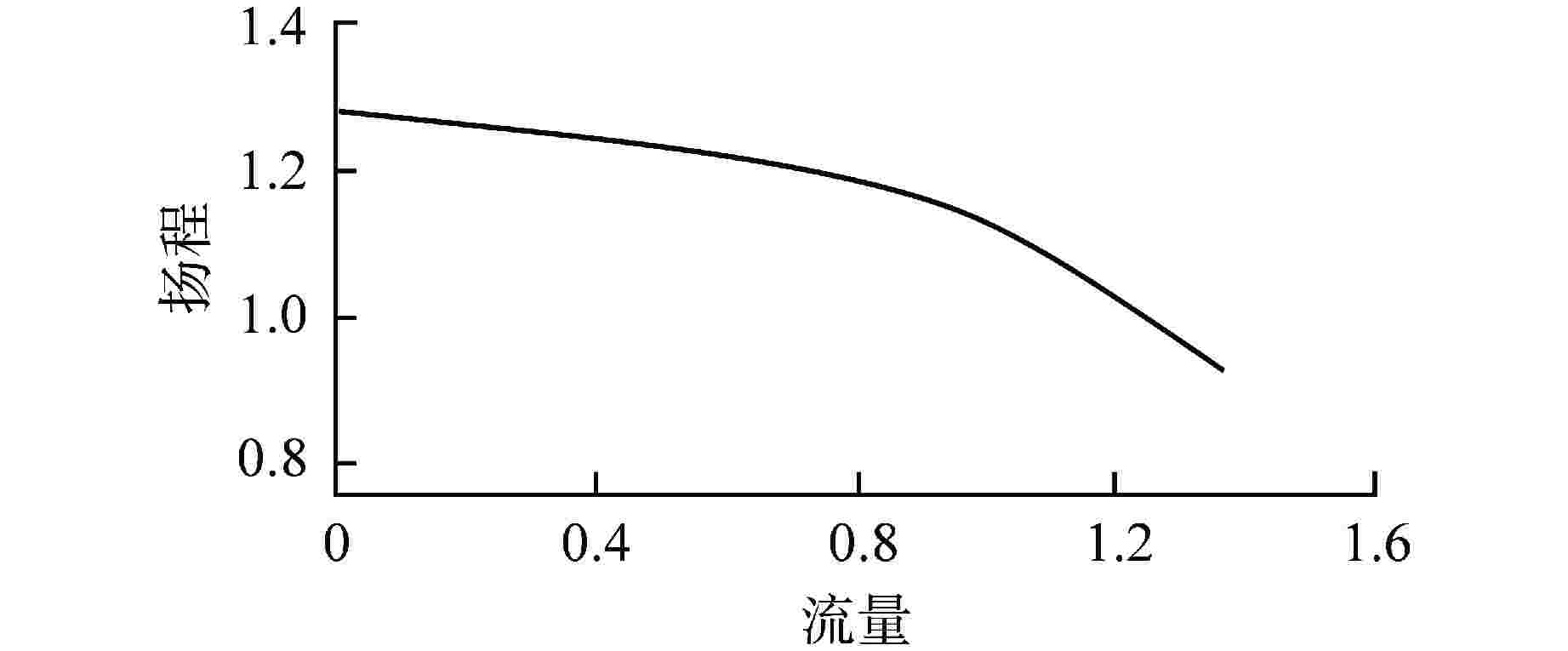
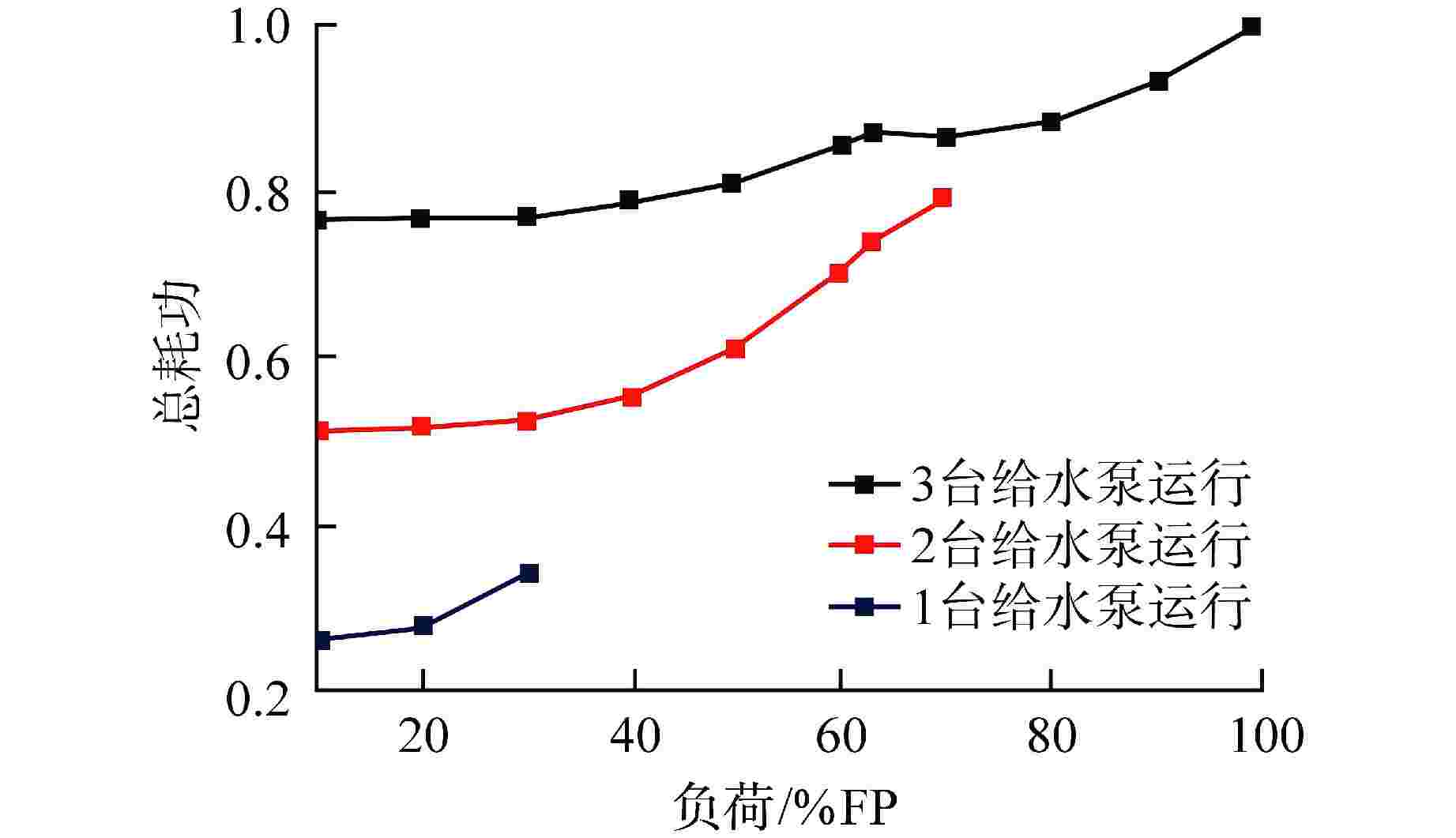
负荷/%FP① 3台给水泵运行 2台给水泵运行 1台给水泵运行 耗功② 效率/% 耗功 效率/% 耗功 效率/% 100 0.697 55.898 —③ — — — 90 0.667 55.454 — — — — 80 0.663 53.767 — — — — 70 0.673 49.858 0.932 54.5 — — 63 0.687 45.891 0.883 53.996 — — 60 0.681 44.401 0.847 53.795 — — 50 0.663 38.67 0.747 51.132 — — 40 0.654 31.545 0.689 44.723 — — 30 0.652 24.094 0.665 35.327 0.863 54.513 20 0.654 16.123 0.661 24.017 0.703 44.824 10 0.655 8.133 0.661 12.165 0.672 23.911 注:①FP—满功率;②耗功均以满转速下单泵提供额定流量所需功率为基准进行了归一化处理;③“—”表示无数据,即单台给水泵转速超过100%,所以不进行计算 -
[1] 王鑫,韩伟实,何艺峰,等. 双泵并联给水系统切换方式模拟研究[J]. 核科学与工程,2012, 32(3): 234-237,253. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0918.2012.03.008 [2] 李民,陈齐清. 优化主给水泵切换条件 避免触发给水流量限制[J]. 中国核工业,2008(5): 32-34. [3] 解涛. 300 MW机组低负荷给水泵运行方式优化[J]. 山西电力,2010(4): 46-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0320.2010.04.016 [4] 杨洪波,吴焕云. 核电厂常规岛电动给水泵切换瞬态分析[J]. 热力发电,2011, 40(1): 82-83,90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3364.2011.01.082 [5] 王鑫,韩伟实. 双泵切换对给水量影响的实验研究[J]. 核动力工程,2012, 33(1): 124-128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0926.2012.01.026 [6] 杨元龙,吴金祥,郑子都,等. 汽轮给水机组切换工况下船舶蒸汽动力系统的响应特性[J]. 中国舰船研究,2019, 14(2): 150-155. doi: 10.19693/j.issn.1673-3185.01248 [7] 袁寿其, 施卫东, 刘厚林, 等. 泵理论与技术[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2014: 1-23. -





 下载:
下载: