Reduced Order Modeling for Neutron Transport Equation Based on Operator Inference
-
摘要: 为建立瞬态中子输运方程的快速预测模型,本文采用仿射参数化算子推断构建中子输运方程的降阶模型。算子推断通过奇异值分解与构造最优化问题,非侵入式地拟合降阶空间中的动力学方程,同时能够保留原控制方程所描述的物理规律。而仿射参数化结构有效地处理瞬态中子输运方程中常见的时变参数问题,在无需参数空间插值的情况下,实现时变堆芯参数到物理量的快速求解。研究结果表明,基于高保真数据与仿射参数化算子推断构建的降阶模型具有较好的泛化能力,能够对不同时变参数下的瞬态问题进行准确求解。因此,本文构建的降阶模型能够用于高保真中子输运方程的快速预测。Abstract: To establish a real-time prediction model for the time-dependent neutron transport equation, the affine-parametric operator inference is employed to train a reduced-order model of the neutron transport equation. Operator inference, through singular value decomposition and solving optimization problem, non-intrusively fits the operators of the reduced dynamic equations in the subspace while preserving the physical structure described by the original governing equations. The affine-parametric structure effectively addresses the issue of time-varying parameters commonly encountered in time-dependent neutron transport equations, enabling rapid computation from time-varying core parameters to physical quantities without the need for parameter space interpolation. The numerical results show that the reduced-order model based on high-fidelity data and affine-parametric operator inference has good generalization ability, accurately solving transient problems under different time-varying parameters. Therefore, the reduced-order model proposed in this study can be used for real-time prediction of high-fidelity neutron transport equations.
-
表 1 模型训练与在线预测的计算耗时
Table 1. Computational Cost for Model Training and Online Predictions
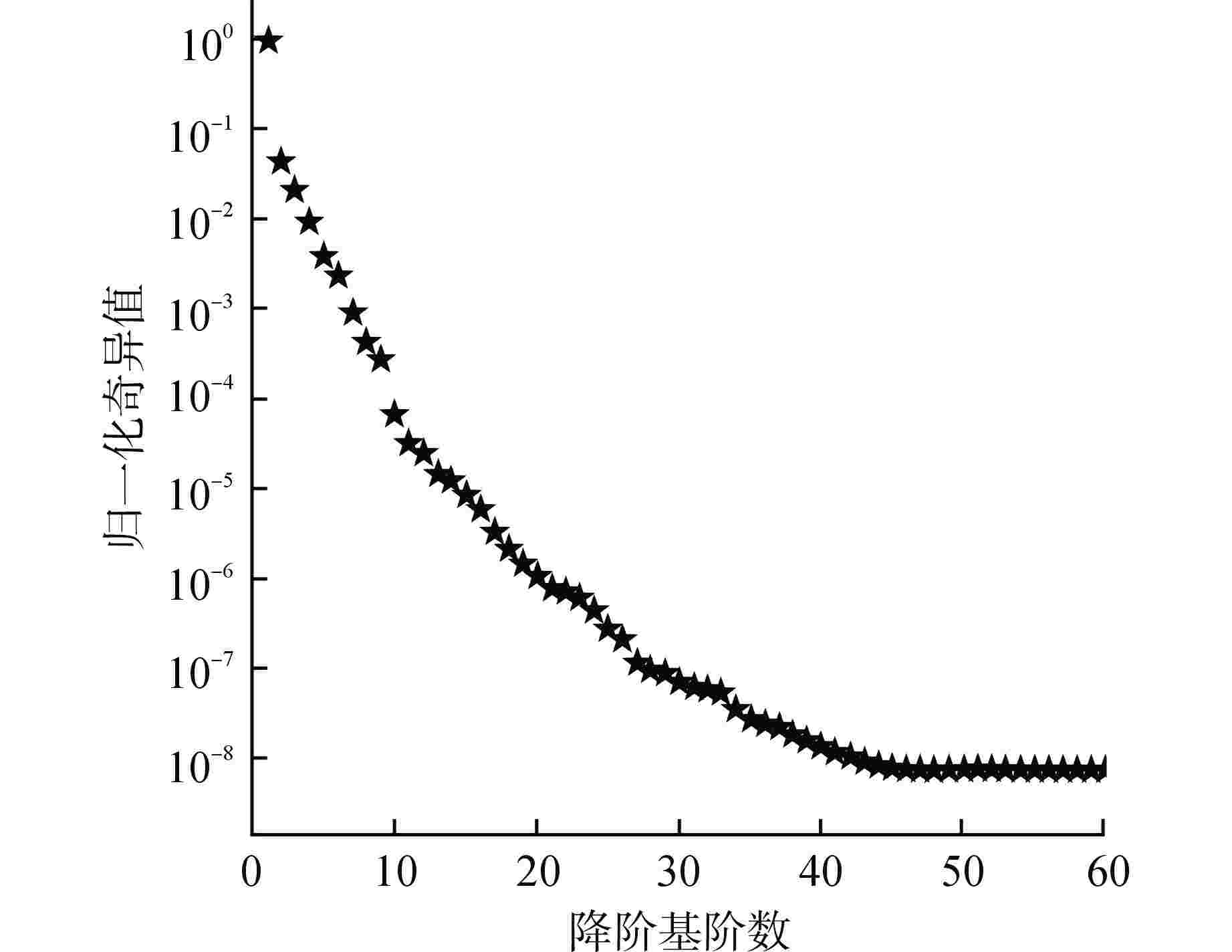
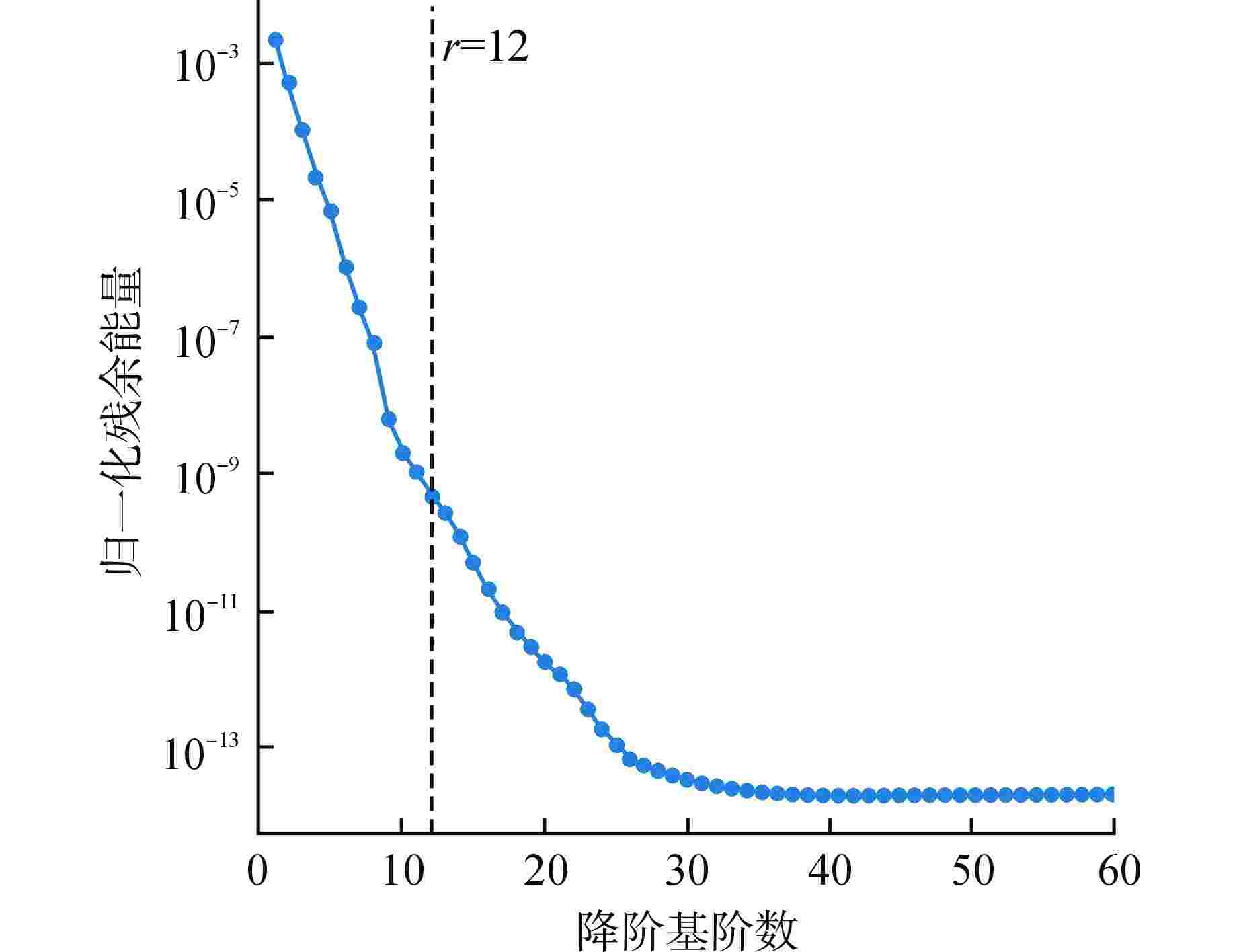
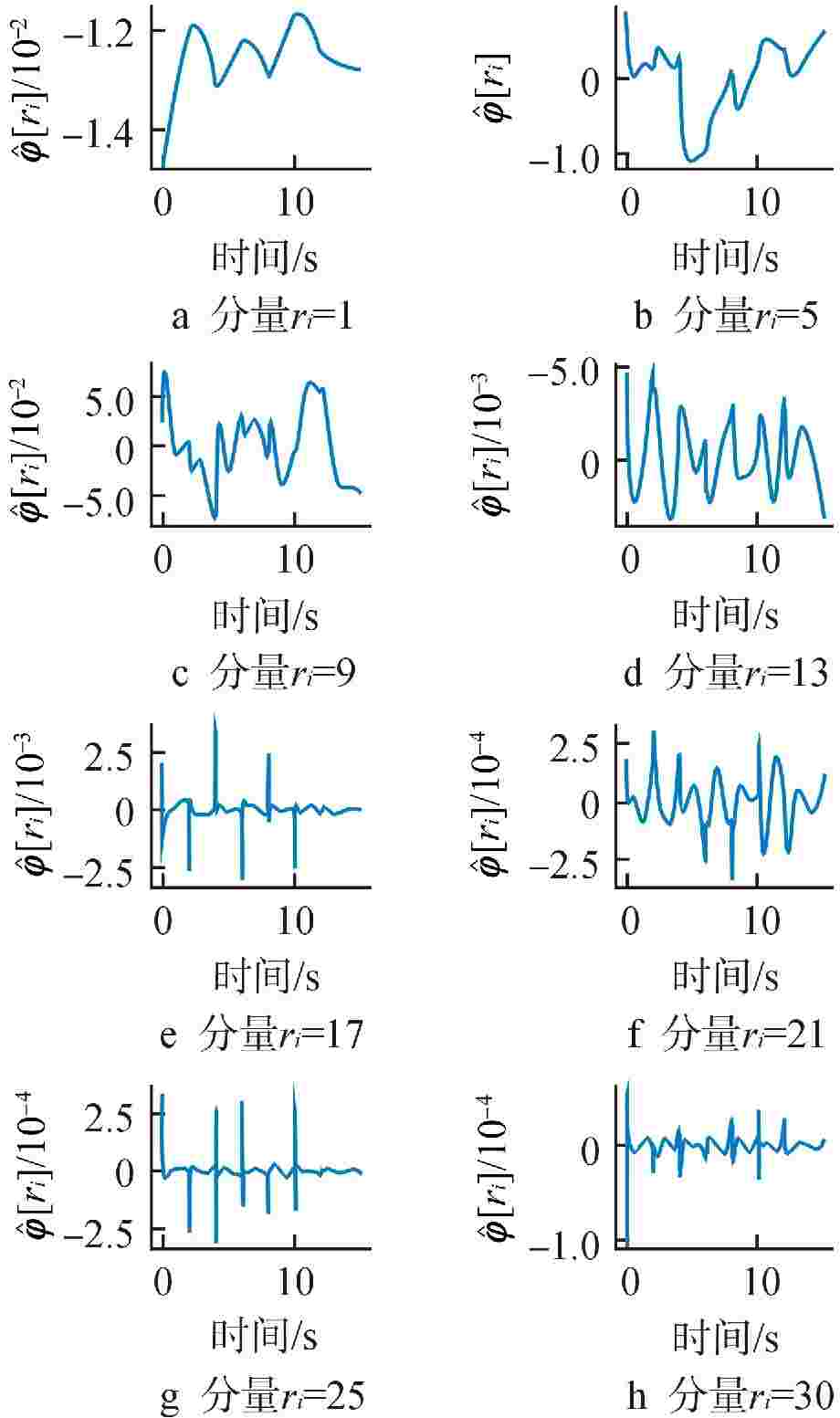
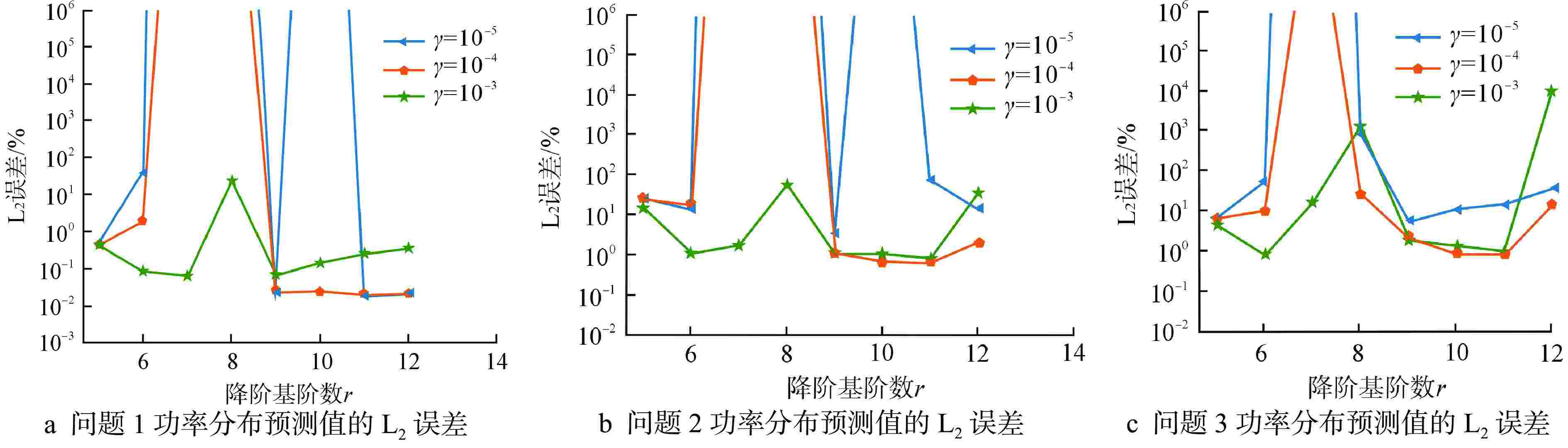
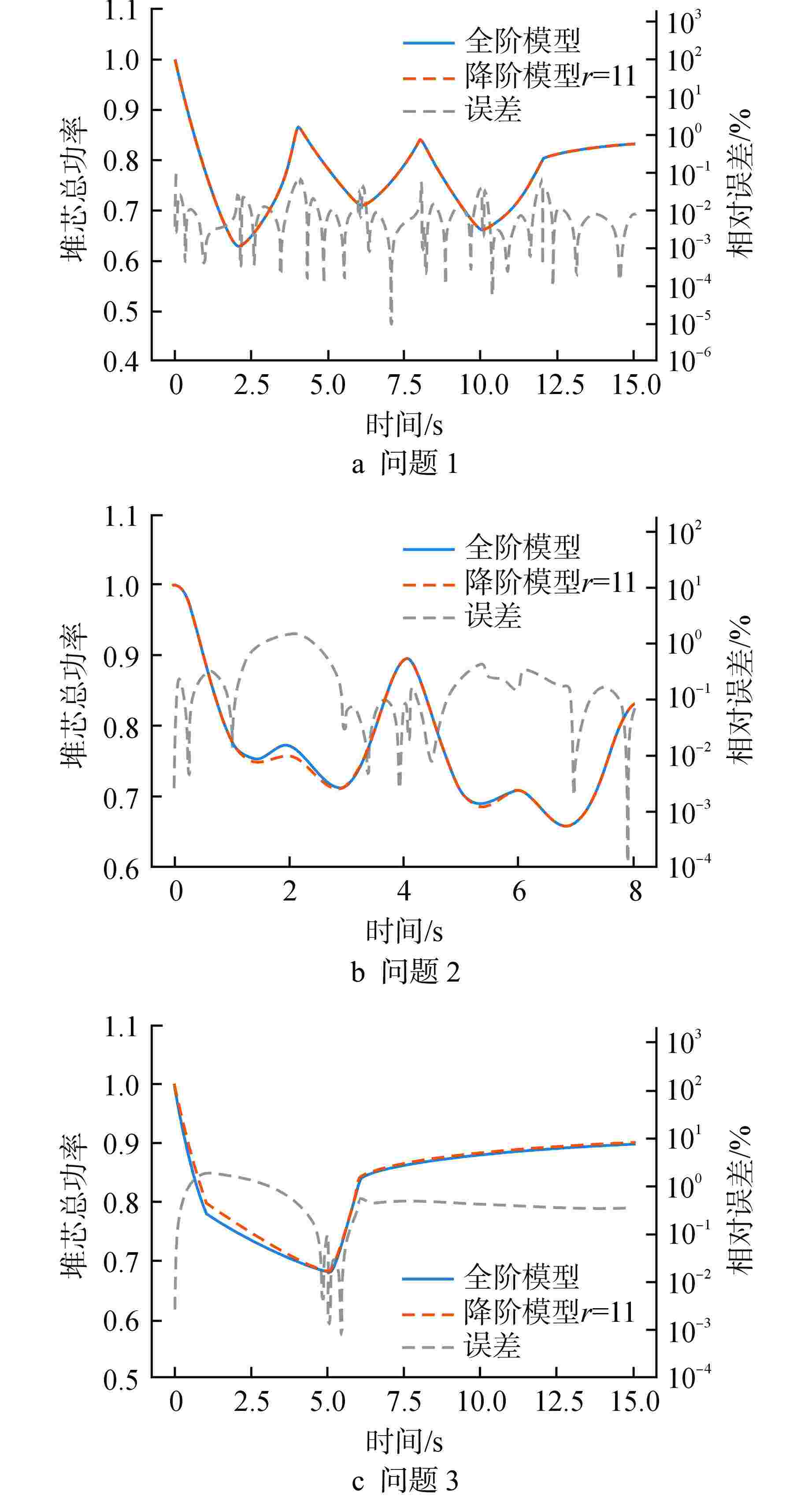
计算时间 降阶模型r=11 全阶模型 在线阶段:每步平均求解时间/s 3.3×10−5 0.17 core-hours 在线阶段:每步平均重构时间/s 6.4×10−3 离线阶段:训练时间/s 13.3 core-hours—使用一个核心执行计算工作1个小时 表 2 预测功率分布误差
Table 2. Error of Power Distributions
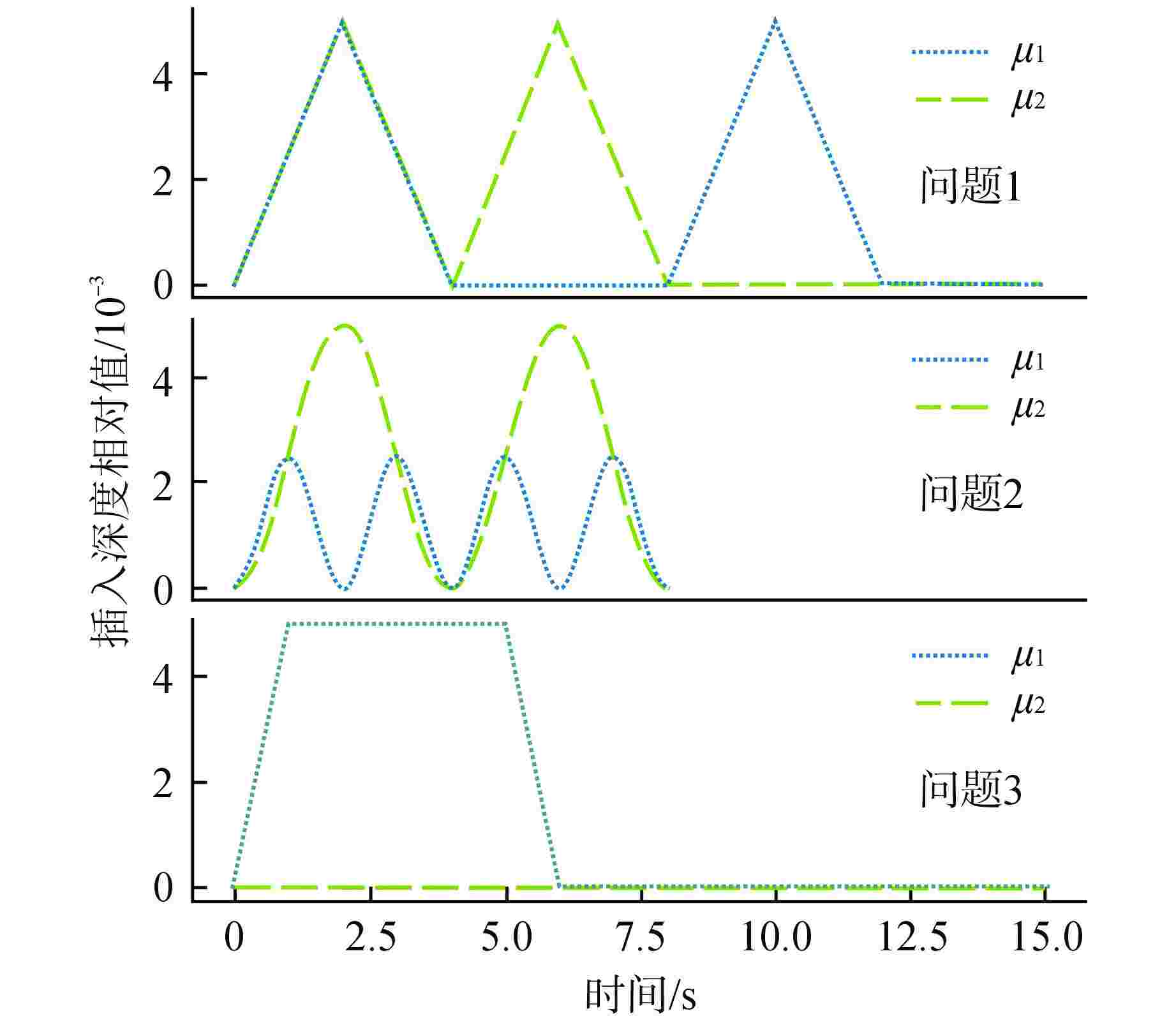
问题 功率分布L2误差/% 功率分布最大误差/% 1 0.02 0.14 2 0.65 3.05 3 0.84 3.19 -
[1] GONG H L, CHENG S B, CHEN Z, et al. Data-enabled physics-informed machine learning for reduced-order modeling digital twin: application to nuclear reactor physics[J]. Nuclear Science and Engineering, 2022, 196(6): 668-693. doi: 10.1080/00295639.2021.2014752 [2] ZHANG T F, XIAO W, YIN H, et al. VITAS: A multi-purpose simulation code for the solution of neutron transport problems based on variational nodal methods[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2022, 178: 109335. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2022.109335 [3] XIAO W, YIN H, LIU X J, et al. On the transient models of the VITAS code: applications to the C5G7-TD pin-resolved benchmark problem[J]. Nuclear Science and Techniques, 2023, 34(2): 20. doi: 10.1007/s41365-023-01170-x [4] BENNER P, GUGERCIN S, WILLCOX K. A survey of projection-based model reduction methods for parametric dynamical systems[J]. SIAM Review, 2015, 57(4): 483-531. doi: 10.1137/130932715 [5] HUHN Q A, TANO M E, RAGUSA J C, et al. Parametric dynamic mode decomposition for reduced order modeling[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 475: 111852. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2022.111852 [6] DUAN J M, HESTHAVEN J S. Non-intrusive data-driven reduced-order modeling for time-dependent parametrized problems[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2024, 497: 112621. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2023.112621 [7] SARTORI A, BAROLI D, CAMMI A, et al. Comparison of a modal method and a proper orthogonal decomposition approach for multi-group time-dependent reactor spatial kinetics[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2014, 71: 217-229. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2014.03.043 [8] DI RONCO A, INTROINI C, CERVI E, et al. Dynamic mode decomposition for the stability analysis of the molten salt fast reactor core[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2020, 362: 110529. doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2020.110529 [9] HARDY Z K, MOREL J E. Proper orthogonal decomposition mode coefficient interpolation: a non-intrusive reduced-order model for parametric reactor kinetics[J]. Nuclear Science and Engineering, 2024, 198(4): 832-852. doi: 10.1080/00295639.2023.2218581 [10] LI W H, PENG S T, LI J G, et al. Prediction of state transitions in 3D core dynamics and xenon transients based on dynamic mode decomposition[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2024, 197: 110258. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2023.110258 [11] PEHERSTORFER B, WILLCOX K. Data-driven operator inference for nonintrusive projection-based model reduction[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2016, 306: 196-215. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2016.03.025 [12] BENNER P, GOYAL P, KRAMER B, et al. Operator inference for non-intrusive model reduction of systems with non-polynomial nonlinear terms[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 372: 113433. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2020.113433 [13] MCQUARRIE S A, KHODABAKHSHI P, WILLCOX K E. Nonintrusive reduced-order models for parametric partial differential equations via data-driven operator inference[J]. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 2023, 45(4): A1917-A1946. doi: 10.1137/21M1452810 [14] 张滕飞,殷晗,孙启政,等. 通用型中子输运程序VITAS应用研究[J]. 核动力工程,2023, 44(2): 15-23. [15] 孙启政,刘晓晶,张滕飞. 非结构网格变分节块法在氦氙冷却小型反应堆中的应用[J]. 核动力工程,2024, 45(5): 26-31. [16] YIN H, LIU X J, ZHANG T F. An efficient parallel algorithm of variational nodal method for heterogeneous neutron transport problems[J]. Nuclear Science and Techniques, 2024, 35(4): 69. doi: 10.1007/s41365-024-01430-4 [17] HSIEH A, ZHANG G C, YANG W S. Consistent transport transient solvers of the high-fidelity transport code PROTEUS-MOC[J]. Nuclear Science and Engineering, 2020, 194(7): 508-540. doi: 10.1080/00295639.2020.1746619 [18] CHO N Z. KAIST benchmark problems in reactor and particle transport physics[EB/OL]. (2022-05-29)[2024-01-01]. https://github.com/nzcho/Nurapt-Archives/tree/master/KAIST-Benchmark-Problems. [19] HOU J, IVANOV K N, BOYARINOV V F, et al. OECD/NEA benchmark for time-dependent neutron transport calculations without spatial homogenization[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2017, 317: 177-189. doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2017.02.008 [20] UY W I T, HARTMANN D, PEHERSTORFER B. Operator inference with roll outs for learning reduced models from scarce and low-quality data[J]. Computers & Mathematics with Applications, 2023, 145: 224-239. [21] PEHERSTORFER B. Sampling low-dimensional markovian dynamics for preasymptotically recovering reduced models from data with operator inference[J]. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 2020, 42(5): A3489-A3515. doi: 10.1137/19M1292448 -





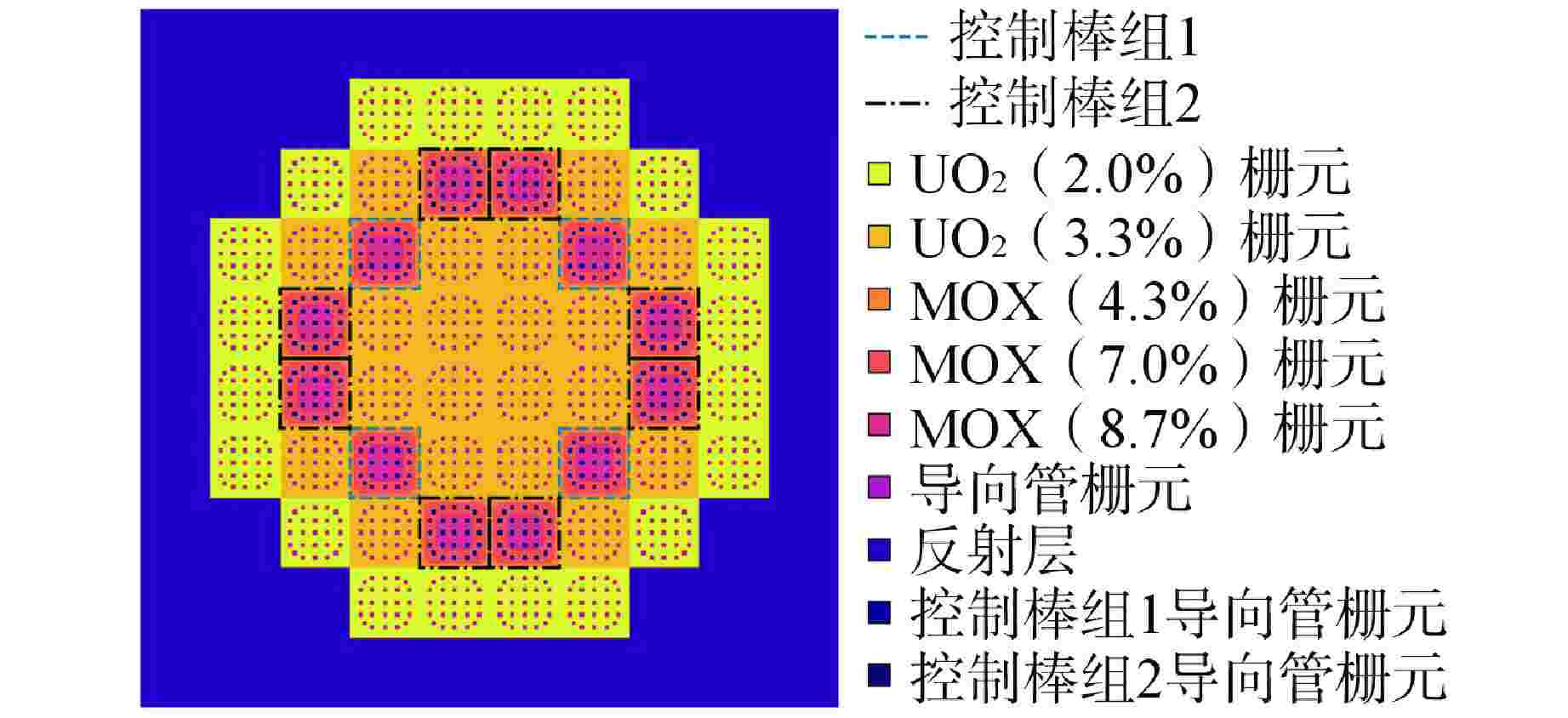
 下载:
下载: