Research on the Impact Vector Evaluation Methods of Common Cause Failure in PSA of Nuclear Power Plants
-
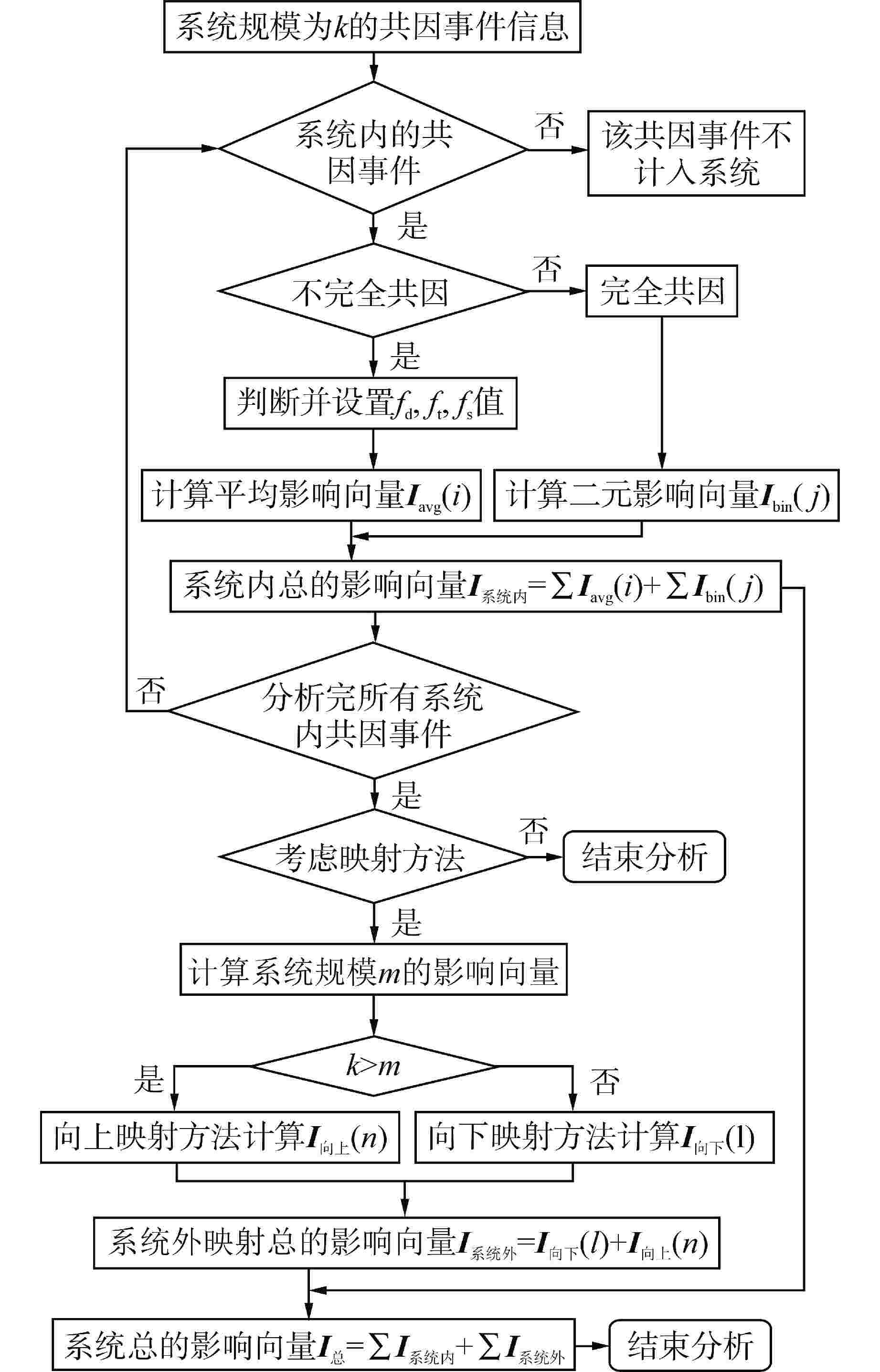
摘要: 共因失效分析是核电厂概率安全分析(PSA)的重要组成部分,共因失效事件的影响向量评估是共因失效分析的基础。由于目前尚未清晰建立适用于任意系统规模的共因失效事件影响向量的定量计算数学方法,因此,本文对影响向量的定义及分类开展研究,系统地给出不完全共因失效事件影响向量评估的数学表达式,以及不同规模间共因失效影响向量映射计算方法,进一步提出任意规模系统总的共因失效影响向量评估流程,以具有4个冗余部件的系统为实例,计算该系统共因失效总的影响向量。考虑了目标系统内影响向量和外部系统映射到目标系统的影响向量,实例中目标系统共因失效下总的影响向量为(3.03,23.26,11.40,3.72,3.07)。该方法能够实现任意系统规模下共因失效的影响向量的计算,可为共因参数估计模型提供输入数据。
-
关键词:
- 概率安全分析(PSA) /
- 共因失效 /
- 影响向量评估 /
- 向上映射 /
- 向下映射
Abstract: Common cause failure analysis is an important component of probabilistic safety analysis (PSA) for nuclear power plants. The evaluation of the impact vector of common cause failure events is the foundation of common cause failure analysis. At present, the quantitative mathematical method for calculating the impact vector of common cause failure events applicable to any system sizes has not been clearly established. Therefore, the definition and classification of impact vectors are studied in this paper, the mathematical expressions for evaluating impact vectors under incomplete common cause failure events are systematically demonstrated, as well as the mapping calculation method of impact vectors of common cause failure between different system sizes. Furthermore, the evaluation process of the total common cause failure impact vectors of any system sizes is proposed, and the total common cause failure impact vectors of the system is calculated by taking the system with four redundant components as an example. Considering the impact vectors in the target system and the impact vectors mapped from the external system to the target system, the total impact vectors in the case of common cause failure of the target system are (3.03, 23.26, 11.40, 3.72, 3.07). This method can calculate the impact vector of common cause failures with any system sizes, and could provide input data for common cause parameter estimation model. -
表 1 共因事件状态因子表
Table 1. State Factors of Common Cause Events
共因失效事件 部件状态因子 时间因子 原因因子 $ f_{\mathrm{d}1} $ $ f_{\mathrm{d}2} $ $ f_{\mathrm{d}3} $ $ f_{\mathrm{d}4} $ $ f_{\rm{t}} $ $ f_{\rm{s}} $ 事件1 0.1 0.5 0.0 0.0 0.1 1.0 事件2 1.0 1.0 0.5 0.0 0.5 1.0 事件3 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.0 1.0 1.0 事件4 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 事件5 0.5 0.5 0.5 1.0 1.0 0.5 表 2 系统内共因失效事件的平均影响向量
Table 2. The Average Impact Vector of Common Cause Failure Events within the System
CCF事件 平均影响向量 $ {F_0} $ $ {F_1} $ $ {F_2} $ $ {F_3} $ $ {F_4} $ 事件1 1.300 0.590 0.005 事件2 0.25 1.250 0.25 0.25 事件3 0.73 0.24 0.027 0.001 事件4 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 事件5 0.75 1.31 0.188 0.188 0.063 系统内总的影响向量 3.03 3.39 0.470 0.439 1.063 表 3 不同规模系统的总的影响向量
Table 3. The Total Impact Vector of Different Size Systems
系统规模 总的影响向量(不含$ {N_{{0 \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {0 m}} \right. } m}}} $) 2 (2, 1) 4 (10, 9, 3, 2) 16 (12, 3, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0) 表 4 不同规模系统映射到目标系统的影响向量
Table 4. Impact Vectors Mapped from Systems with Different Size to Target Systems
系统规模 映射到目标系统的影响向量(不含$ {N_{{0 \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {0 k}} \right. } k}}} $) 2 (4.80, 1.28, 0.16, 0.006) 4 (10, 9, 3, 2) 16 (5.067, 0.649, 0.117, 0.0082) 系统外映射到目标系
统的总的影响向量(19.87, 10.93, 3.28, 2.01) -
[1] U. S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission. Common-cause failure parameter estimations: NUREG/CR-5497[R]. Washington: Nuclear Regulatory Commission, 2015 [2] 李翠玲,谢里阳. 共因失效数据分析方法[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版),2004, 25(12): 1183-1186. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-3026.2004.12.017 [3] 马超. 概率安全分析中共因失效数据处理方法研究[J]. 中国高新技术企业,2013(31): 11-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2374.2013.21.009 [4] MA Z G, KVARFORDT K J. CCF parameter estimations, 2020 update: INL/EXT-21-62940-Revision1[R]. Idaho Falls: Idaho National Laboratory, 2022. [5] U. S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission. Guidelines on modeling common-cause failures in probabilistic risk assessment: NUREG/CR-5485[R]. Maryland: Idaho National Engineering and Environmental Laboratory, 1998. [6] U. S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission. Procedures for treating common cause failures in safety and reliability studies: analytical background and techniques: NUREG/CR-4780[R]. Washington: Nuclear Regulatory Commission, 1989. [7] KVAM P H. Estimation techniques for common cause failure data with different system sizes[J]. Technometrics, 1996, 38(4): 382-388. doi: 10.1080/00401706.1996.10484550 [8] TU D L D, VASSEUR D. A new approach for estimation of the CCF parameters in case of incomplete data[C].Sun Valley:International Topical Meeting on Probabilistic Safety Assessment and Analysis PSA 2015,2015. [9] Mahesh Pandey. Statistical analysis of common cause failure data to support safety and reliability analysis of nuclear plant systems: RSP-0296[R]. Waterloo: University of Waterloo, 2014. -





 下载:
下载:


