Numerical Investigation of Aerosol Generation by Laser Decontamination and Aerosol Removal by Spray Based on OpenFOAM
-
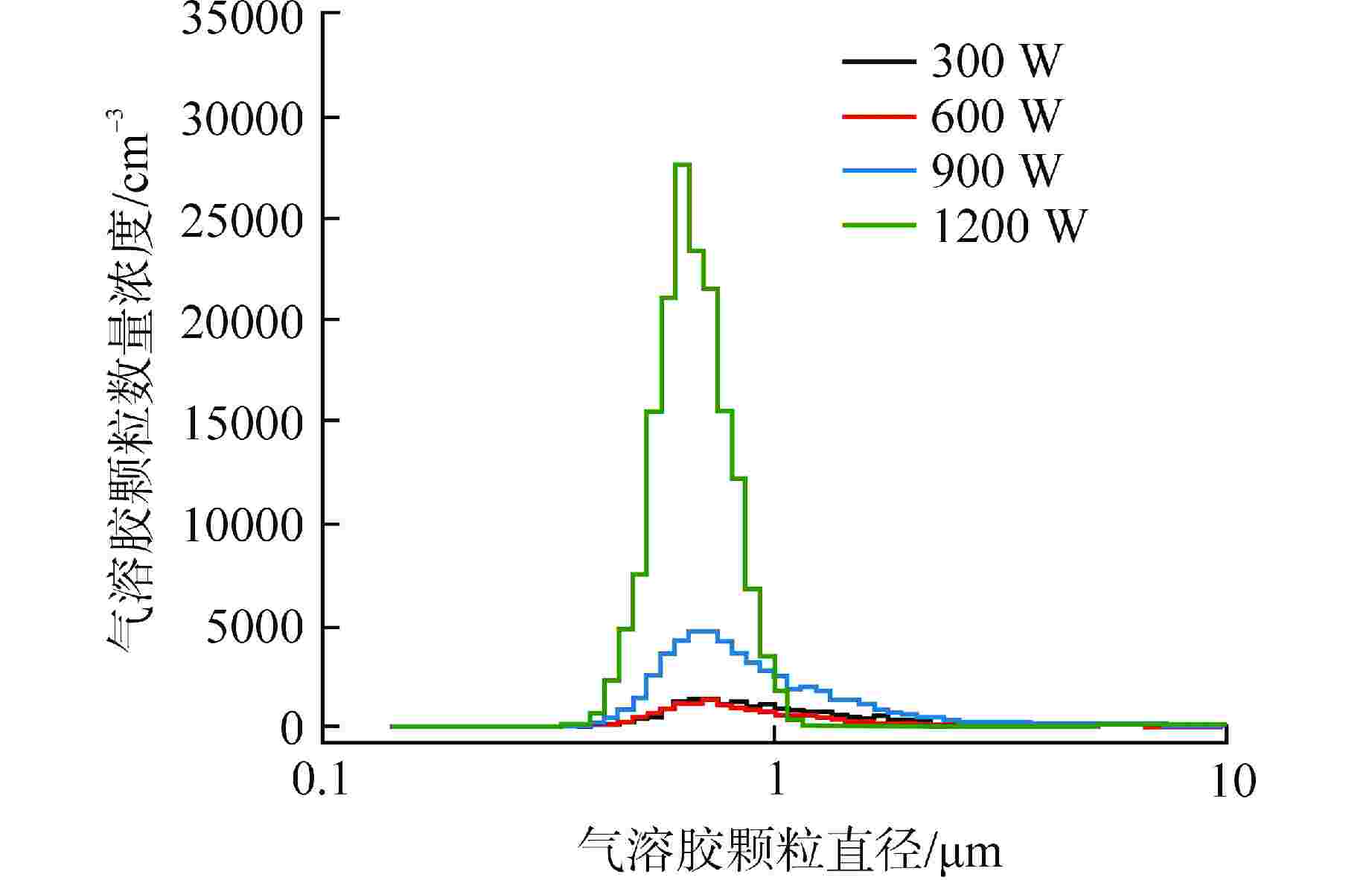
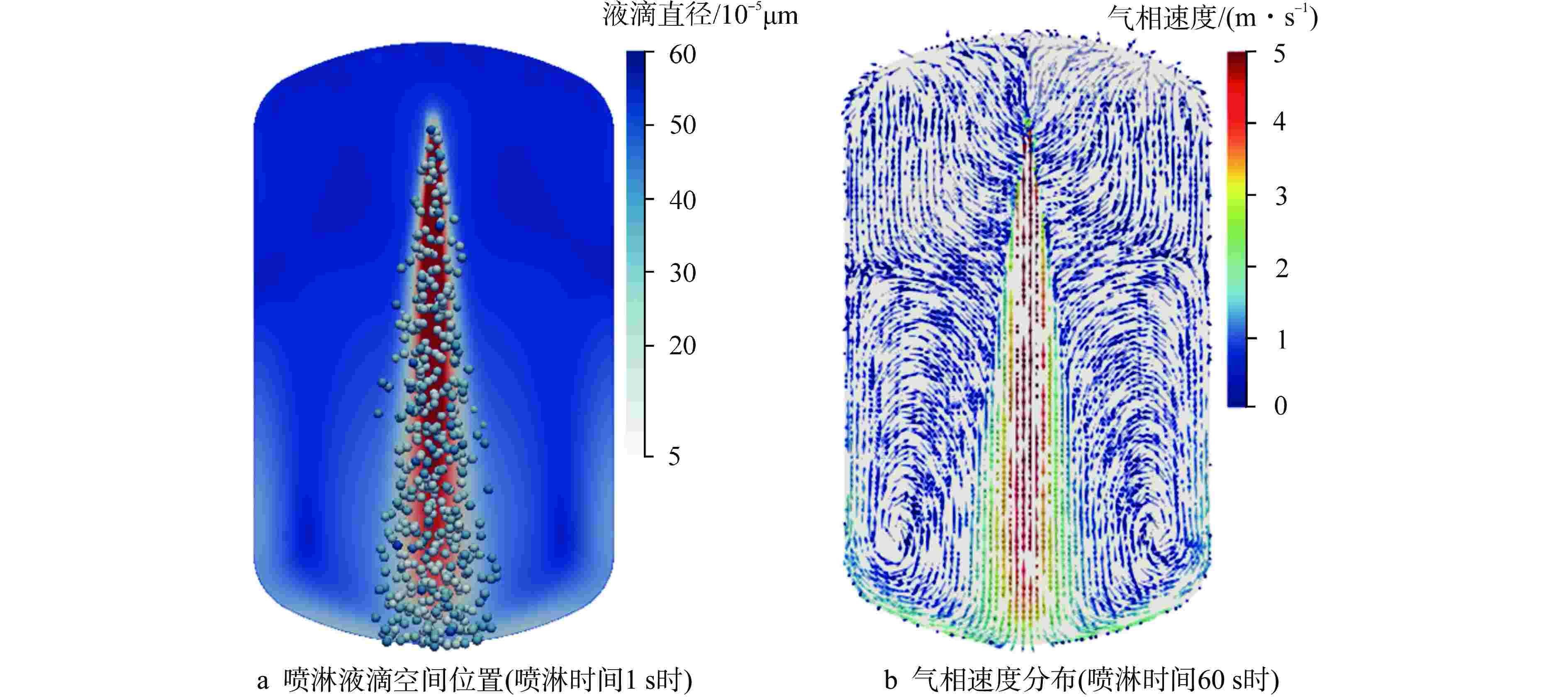
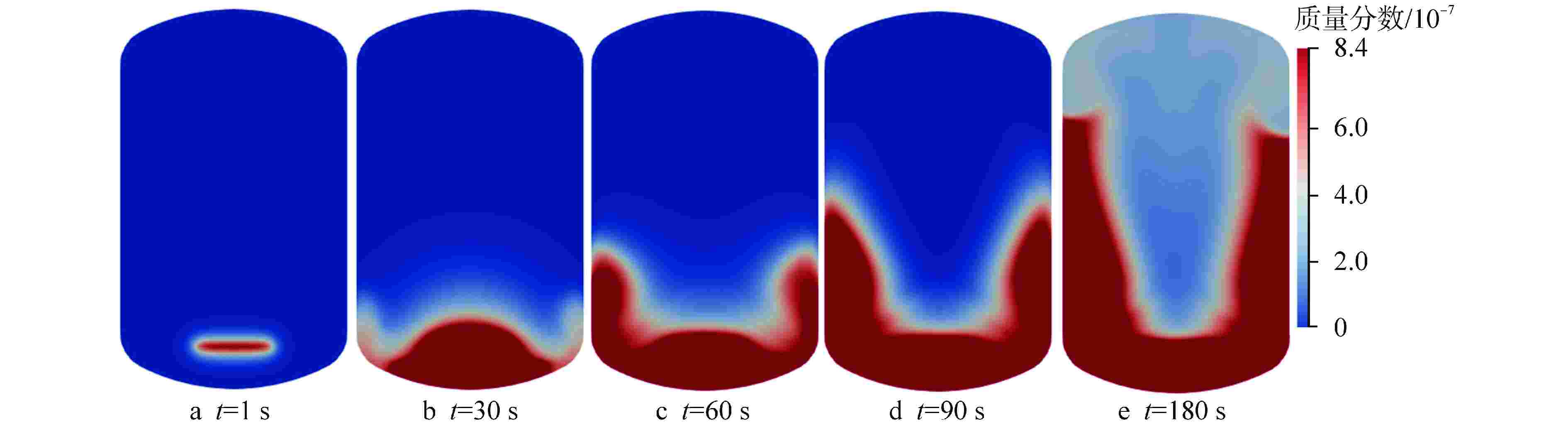
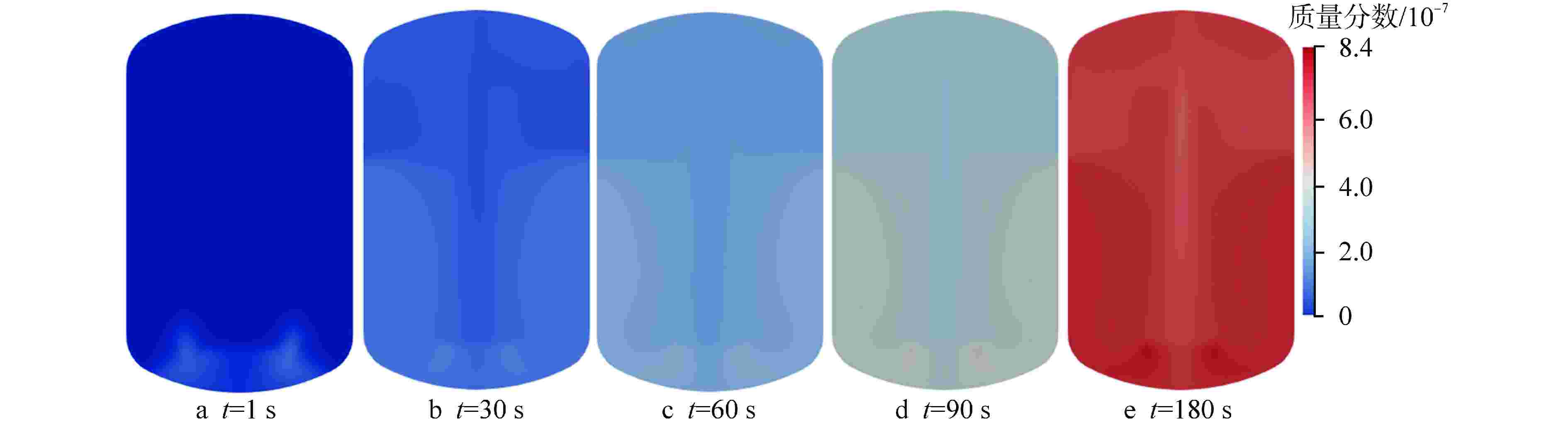
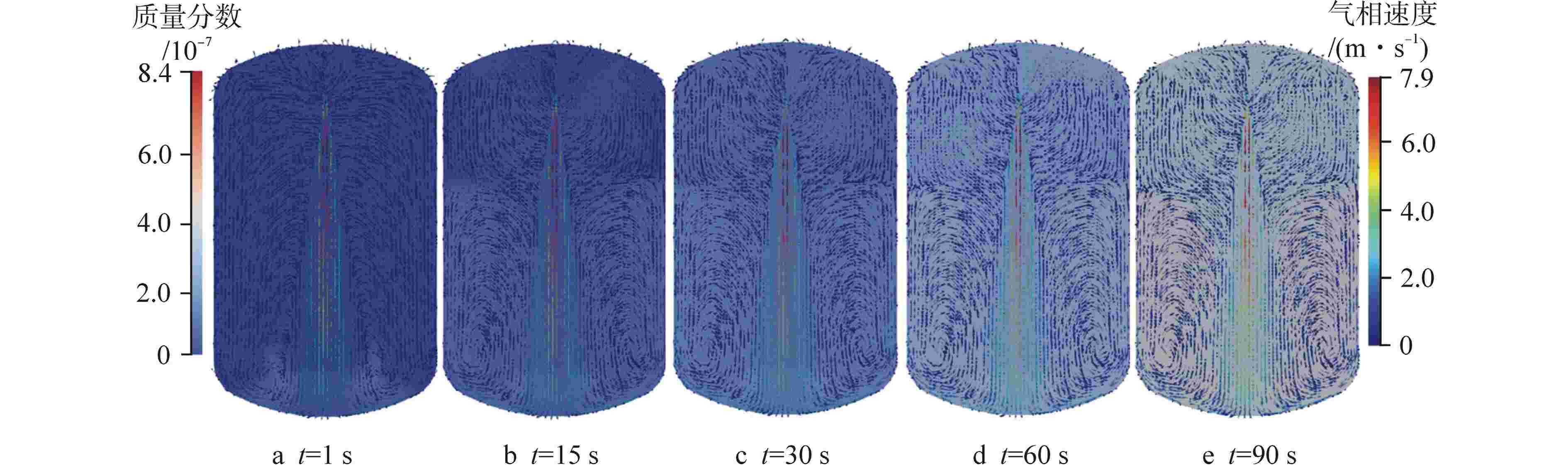
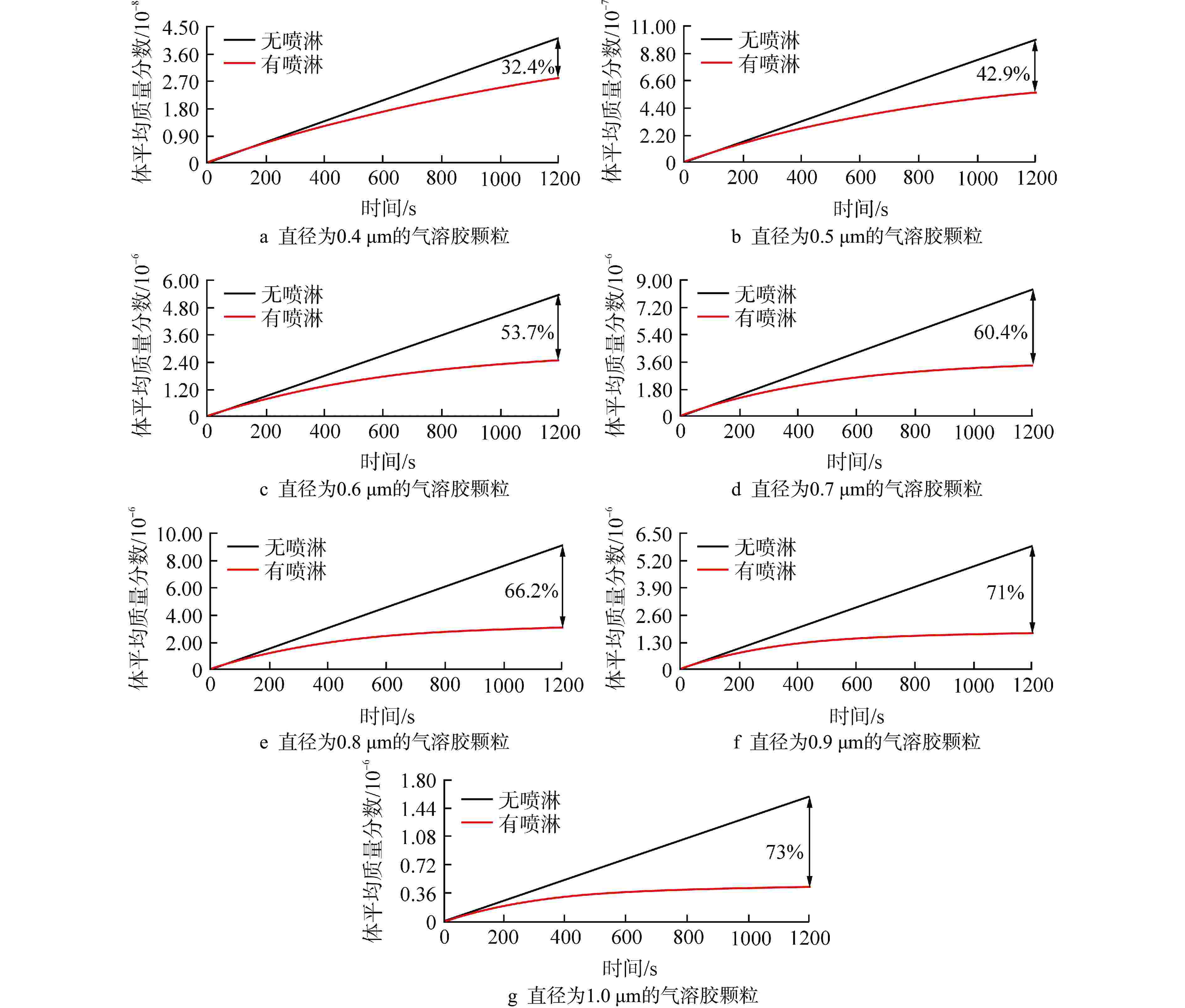
摘要: 在核设施维修及退役过程中,可利用激光去污技术对安全壳内高放射性污染的构件表面进行清洗,但过程中会产生大量亚微米级放射性气溶胶颗粒。为防止放射性物质扩散至环境中,可采用安全壳喷淋系统对其进行去除。为研究激光去污产生气溶胶的物化特性以及气溶胶的喷淋去除效果,本研究进行激光去污实验以获取气溶胶生成速率、数量浓度和颗粒直径分布等数据;基于欧拉-拉格朗日方法,在OpenFOAM中开发了能够同时模拟气溶胶生成和气溶胶喷淋去除的数值模拟模型,对封闭空间内气溶胶的生成、迁移扩散以及喷淋去除特性进行了模拟和分析。模拟结果表明:喷淋区域内的气溶胶可以直接与喷淋液滴相互作用而被去除;非喷淋区域的气溶胶会随气流运动被夹带进入喷淋区域再被去除;气溶胶颗粒直径越大,喷淋去除效率也越高。本研究建立的数值模拟预测方法能够为未来优化封闭空间内激光去污及气溶胶喷淋去除技术提供模型基础和技术参考。Abstract: During the maintenance and decommissioning of nuclear facilities, laser decontamination technology can be utilized to clean the radioactively contaminated surfaces inside the primary containment vessel. However, a significant amount of sub-micron radioactive aerosol particles will be generated during the laser decontamination operations. To prevent these radioactive substances from leaking into the environment, the containment spray system can be employed to remove these submicron aerosol praticles. To investigate the physicochemical properties of the aerosols produced by laser decontamination and the efficiency of aerosol removal by spray droplets, the laser decontamination experiments were firstly conducted to measure the aerosol characteristics such as aerosol generation rates, concentrations, and particle diameter distributions. Subsequently, a CFD model was developed and implemented into OpenFOAM to simulate both the aerosol generation by laser decontamination and aerosol removal by spray droplets using Euler-Lagrange approach, and the characteristics of aerosol generation, migration and diffusion and removal by spray in an enclosed space were simulated and analyzed. The simulation results demonstrate that aerosols within the spray region can be directly removed by interacting with the spray droplets, while those in the non-spraying region need to be entrained into the spray region with the airflow movement and then removed. Furthermore, it was observed that the larger the aerosol particle size, the higher its spray removal efficiency. The numerical simulation model established in this study can be served as a foundation and technical reference for future optimizations of laser decontamination and aerosol removal by spray in enclosed space.
-
Key words:
- OpenFOAM /
- Laser decontamination /
- Aerosol /
- Removal by spray
-
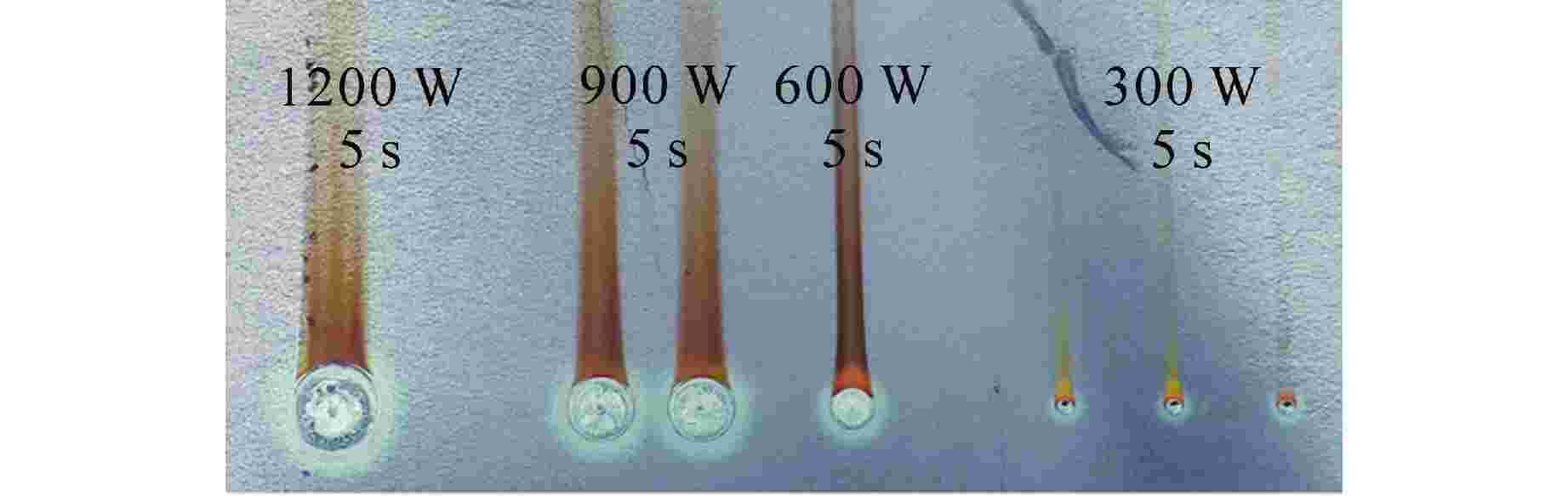
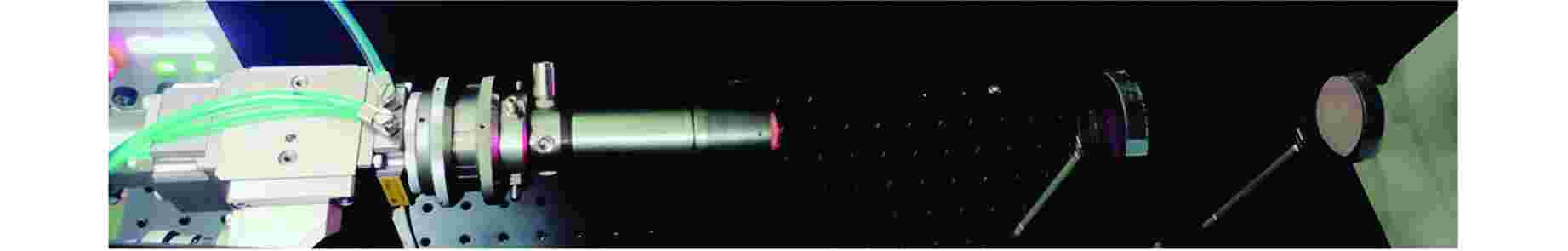
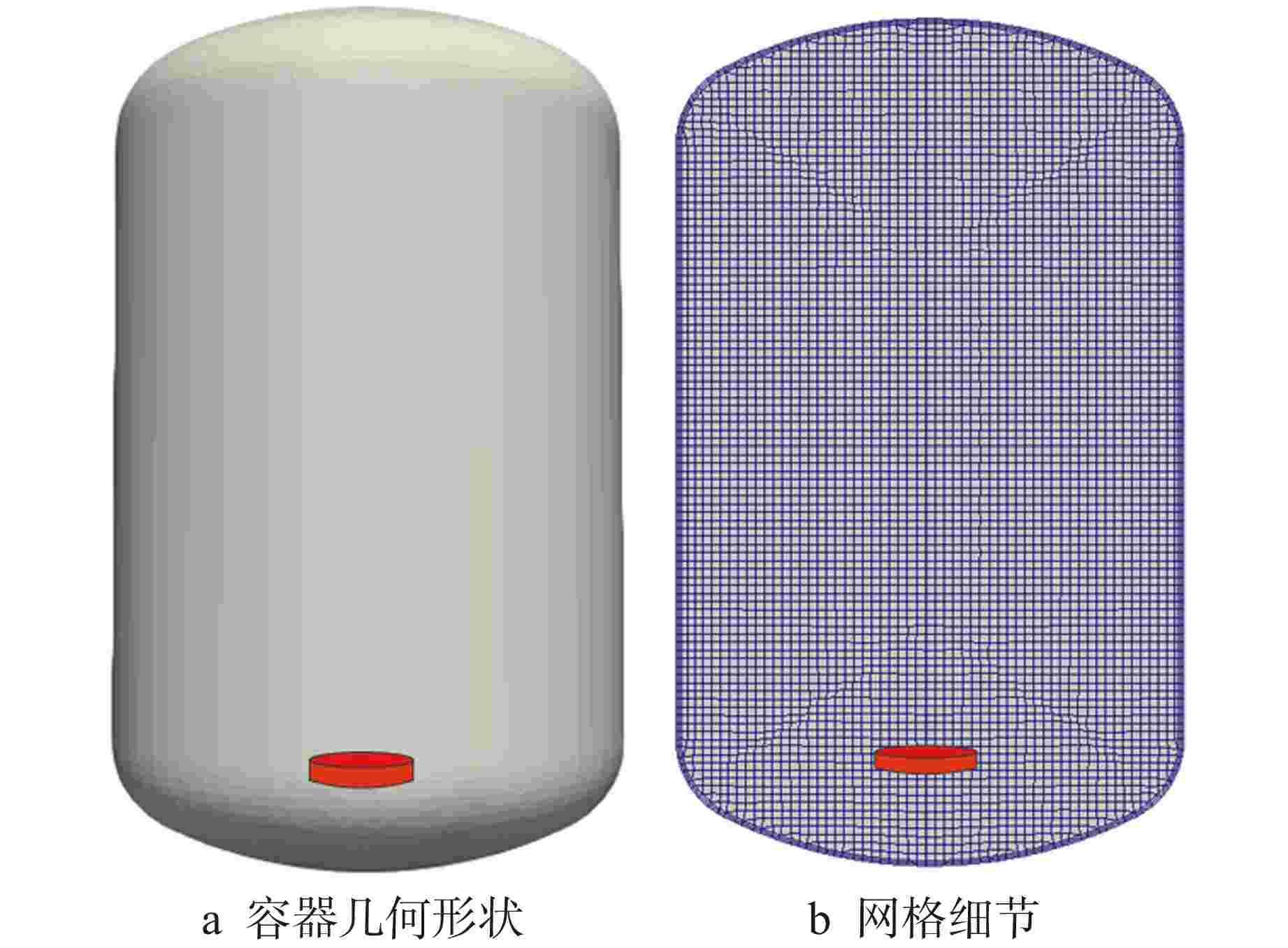
图 1 表面激光去污及气溶胶生成测量实验装置示意图[7]
Figure 1. Schematic Diagram of Experimental Setup for Laser Decontamination and Aerosol Generation Measurement
表 1 3种机械机制对单个液滴的气溶胶去除效率的经验公式[10-11]
Table 1. Empirical Formula for Aerosol Removal Efficiency of a Single Droplet by the Three Mechanical Mechanisms
机械机制种类 经验公式 惯性碰撞 $ \begin{array}{l} {\eta _{_{{\text{imp}}}}} = \left\{ \begin{array}{*{20}{l}}0{\text{ }} & S t < 0.0833 \\ {\left( {\dfrac{S t}{{S t + 0.5}}} \right)^2}{\text{ }} & 0.0833 \leqslant S t \leqslant 0.2 \\ 8.57 \cdot {\left( {\dfrac{S t}{{S t + 0.5}}} \right)^2} \cdot \left( {S t - 0.08336} \right) & S t > 0.2\end{array} \right. \\ S t = \dfrac{{{\rho _{\text{p}}}d_{\text{p}}^2\left| {{U_{\text{G}}} - {U_{\text{D}}}} \right|}}{{9{\mu _{\text{G}}}{d_{\text{D}}}}} \end{array} $ 拦截 $ \begin{array}{l}{\eta }_{\mathrm{int}}=\dfrac{1-{\alpha }_{\text{L}}}{J+\sigma \cdot K}\left[\left(\dfrac{R}{1+R}\right)+\dfrac{1}{2}{\left(\dfrac{R}{1+R}\right)}^{2} \cdot \left(3\sigma +4\right)\right] \\ \sigma =\dfrac{{\mu }_{\text{D}}}{{\mu }_{\text{G}}},R=\dfrac{{d}_{\text{p}}}{{d}_{\text{D}}}\\ J=1-\dfrac{6}{5} \cdot {\alpha }_{\text{L}}^{\tfrac{1}{3}}+\dfrac{1}{5} \cdot {\alpha }_{\text{L}}^{2},K=1-\dfrac{9}{5}{\alpha }_{\text{L}}^{\tfrac{1}{3}}+\alpha +\dfrac{1}{5} \cdot {\alpha }_{\text{L}}^{2}\end{array} $ 布朗扩散 $ \begin{gathered} {\eta _{{\text{diff}}}} = {\left( {2 \cdot Pe \cdot {d_{\text{D}}}} \right)^{ - \tfrac{1}{2}}} \\ Pe = \frac{{{d_{\text{D}}}\left| {{U_{\text{G}}} - {U_{\text{D}}}} \right|}}{{{D_{{\text{diff}}}}}},{D_{{\text{diff}}}} = \frac{{{k_{\text{B}}}TC}}{{3\pi {v_{\text{G}}}{\rho _{\text{G}}}{d_{\text{p}}}}} \\ C = \frac{{2.609\sqrt {2l} }}{{\sqrt {{d_{\text{p}}}} }}\quad 0.05{\text{ μm}} < {d_{\mathrm{p}}} < 1.0{\text{ μm}} \\ \end{gathered} $ $ {\rho _{\text{p}}} $—颗粒密度,kg/m3;$ {d_{\text{p}}} $—颗粒直径,m;$ {\mu _{\text{G}}} $—空气动力粘度,Pa·s;$ {\alpha _{\text{L}}} $—液相体积分数;J和K—经验系数;R—颗粒直径与液滴直径之比;$ \sigma $—液体动力粘度与空气动力粘度之比;Pe—贝克莱数;Ddiff—扩散系数,m2/s;kB—波尔兹曼常数;T—空气温度,K;C—坎宁安校正因子;$ {v_{\text{G}}} $—空气运动粘度,m2/s;${\rho _{\text{G}}} $—空气密度,kg/m3;l—空气平均自由程,m 表 2 容器内气溶胶生成速率
Table 2. Rate of Aerosol Generation in the Container
气溶胶命名 dp/μm 生成速率SG/(mg·s−1) AP2 0.198 0 AP3 0.305 0 AP4 0.407 8.26427×10−8 AP5 0.505 1.96517×10−6 AP6 0.583 1.06248×10−5 AP7 0.724 1.65405×10−5 AP8 0.778 1.82688×10−5 AP9 0.899 1.16819×10−5 AP10 1.038 3.16325×10−6 -
[1] 赵菀,曹俊杰,王帅,等. 放射性表面污染金属废物激光去污工艺研究[J]. 核动力工程,2021, 42(5): 250-255. doi: 10.13832/j.jnpe.2021.05.0250. [2] 范凯,赵菀,张永领,等. 高能激光去污技术在核设施退役中的应用研究[J]. 核动力工程,2015, 36(S1): 207-210. [3] ZHOU Q, SAITO T, SUZUKI S, et al. Microparticles with diverse sizes and morphologies from mechanical and laser cutting of fuel debris simulants and geopolymer as a covering material[J]. Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 2021, 58(4): 461-472. doi: 10.1080/00223131.2020.1869623 [4] PORCHERON E, DAZON C, GELAIN T, et al. Fukushima Daiichi fuel debris retrieval: results of aerosol characterization during laser cutting of non-radioactive corium simulants[J]. Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 2021, 58(1): 87-99. doi: 10.1080/00223131.2020.1806135 [5] PORCHERON E, LEMAITRE P, MARCHAND D, et al. Experimental and numerical approaches of aerosol removal in spray conditions for containment application[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2010, 240(2): 336-343. doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2008.08.023 [6] KALTENBACH C, LAURIEN E. CFD simulation of aerosol particle removal by water spray in the model containment THAI[J]. Journal of Aerosol Science, 2018, 120: 62-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jaerosci.2018.03.005 [7] SHARMA A K, LIANG H, XU R C, et al. Radioactive aerosol control and decontamination in the decommissioning of the fukushima daiichi nuclear power station[J]. Nuclear Technology, 2023, 209(12): 2030-2043. doi: 10.1080/00295450.2023.2186675 [8] LIANG H, ERKAN N, SOLANS V, et al. Numerical simulation and validation of aerosol particle removal by water spray droplets with OpenFOAM during the fukushima daiichi fuel debris retrieval[J]. Frontiers in Energy Research, 2020, 8: 102. doi: 10.3389/fenrg.2020.00102 [9] LIANG H, ERKAN N, WANG K, et al. Numerical simulation of aerosol generation by cutting fuel debris and aerosol removal by spray droplets during Fukushima decommissioning[J]. Progress in Nuclear Energy, 2023, 160: 104667. doi: 10.1016/j.pnucene.2023.104667 [10] PARK S H, JUNG C H, JUNG K R, et al. Wet scrubbing of polydisperse aerosols by freely falling droplets[J]. Journal of Aerosol Science, 2005, 36(12): 1444-1458. doi: 10.1016/j.jaerosci.2005.03.012 [11] POWERS D A, BURSON S B. A simplified model of aerosol removal by containment sprays:NUREG/CR-5966[R]. Washington: Nuclear Regulatory Commission, 1993, doi: 10.2172/6503368. [12] BRUNEL M, SHEN H H. Design of ILIDS configurations for droplet characterization[J]. Particuology, 2013, 11(2): 148-157. doi: 10.1016/j.partic.2012.06.014 [13] RAFFEL M, WILLERT C E, SCARANO F, et al. Particle image velocimetry: a practical guide[M]. 3rd ed. Cham: Springer, 2018: 669. [14] LIANG H, ZHOU Q, ERKAN N, et al. Improvement of aerosol spray scavenging efficiency with water mist[J]. Journal of Aerosol Science, 2021, 153: 105697. doi: 10.1016/j.jaerosci.2020.105697 -





 下载:
下载: