Preliminary Study on 950℃ Coolant Outlet Temperature in HTR-PM under the OTTO Scheme
-
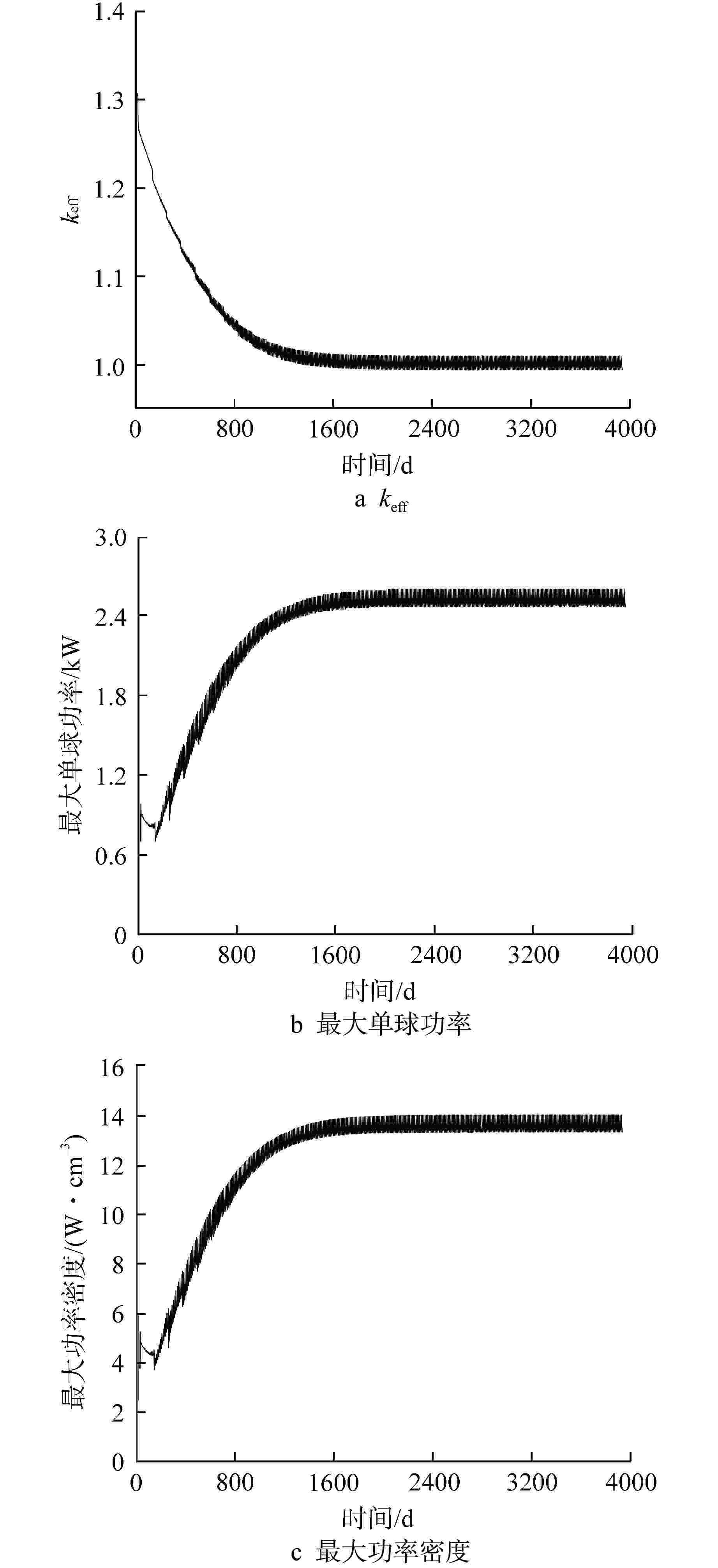
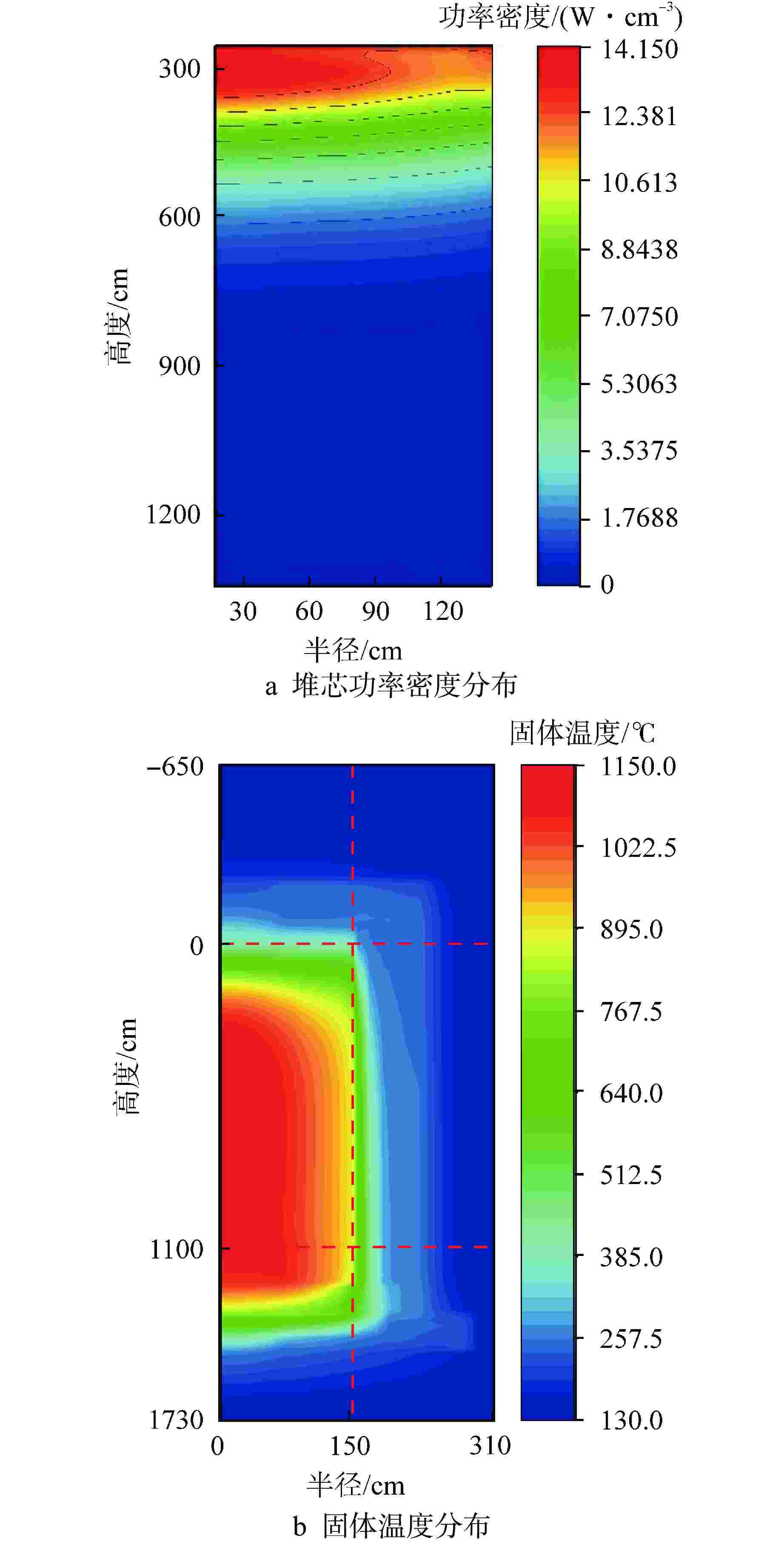
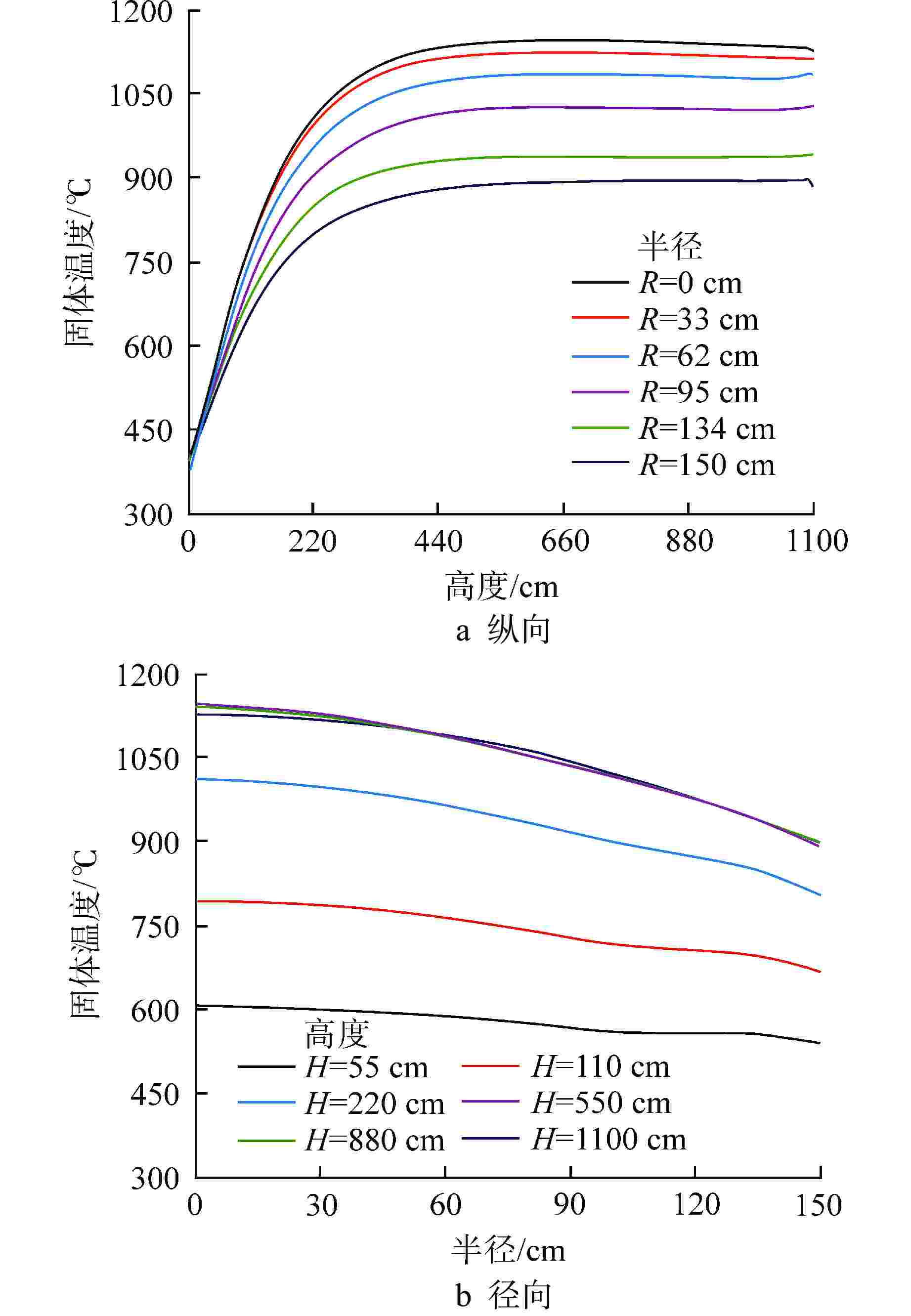
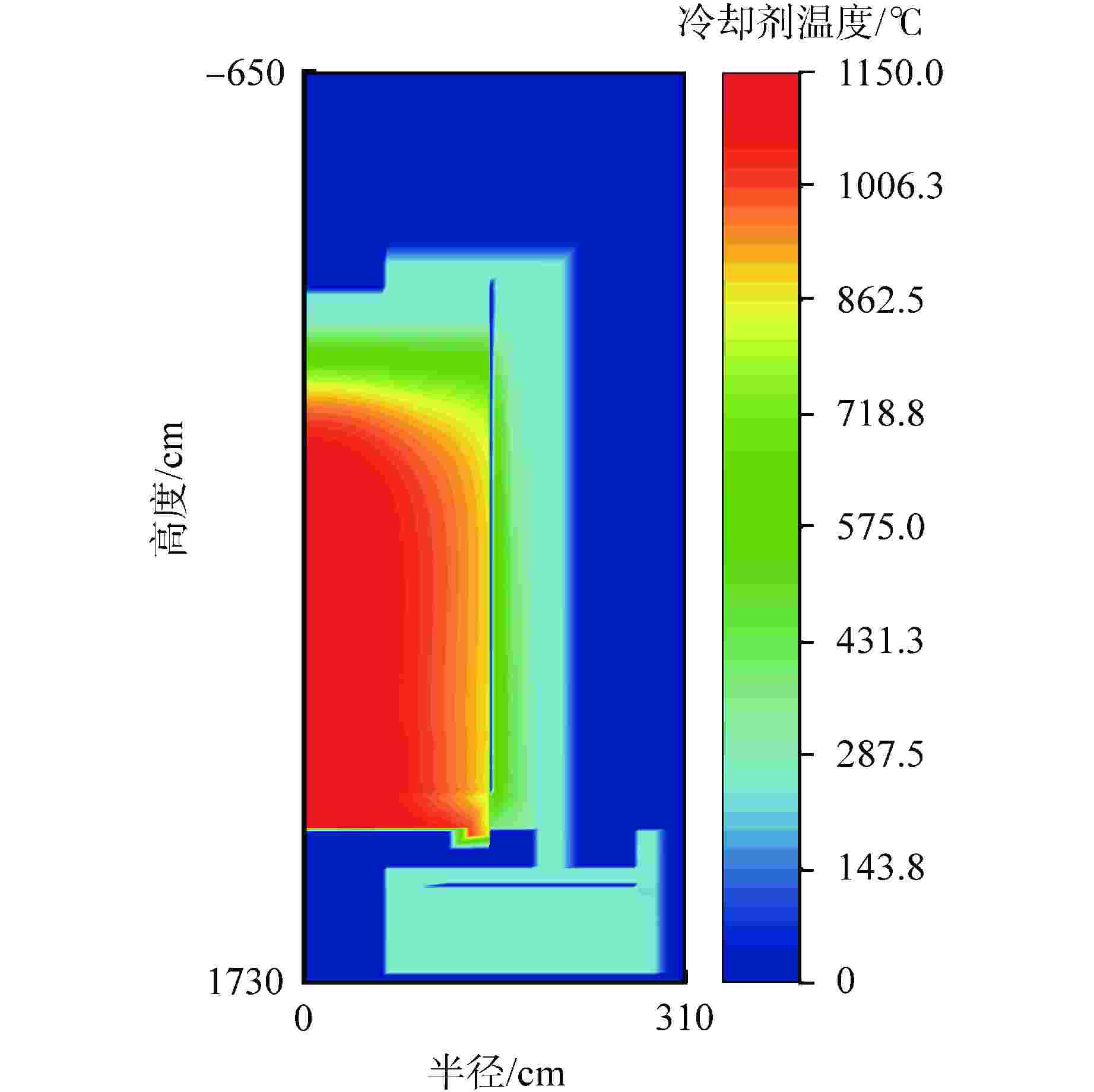
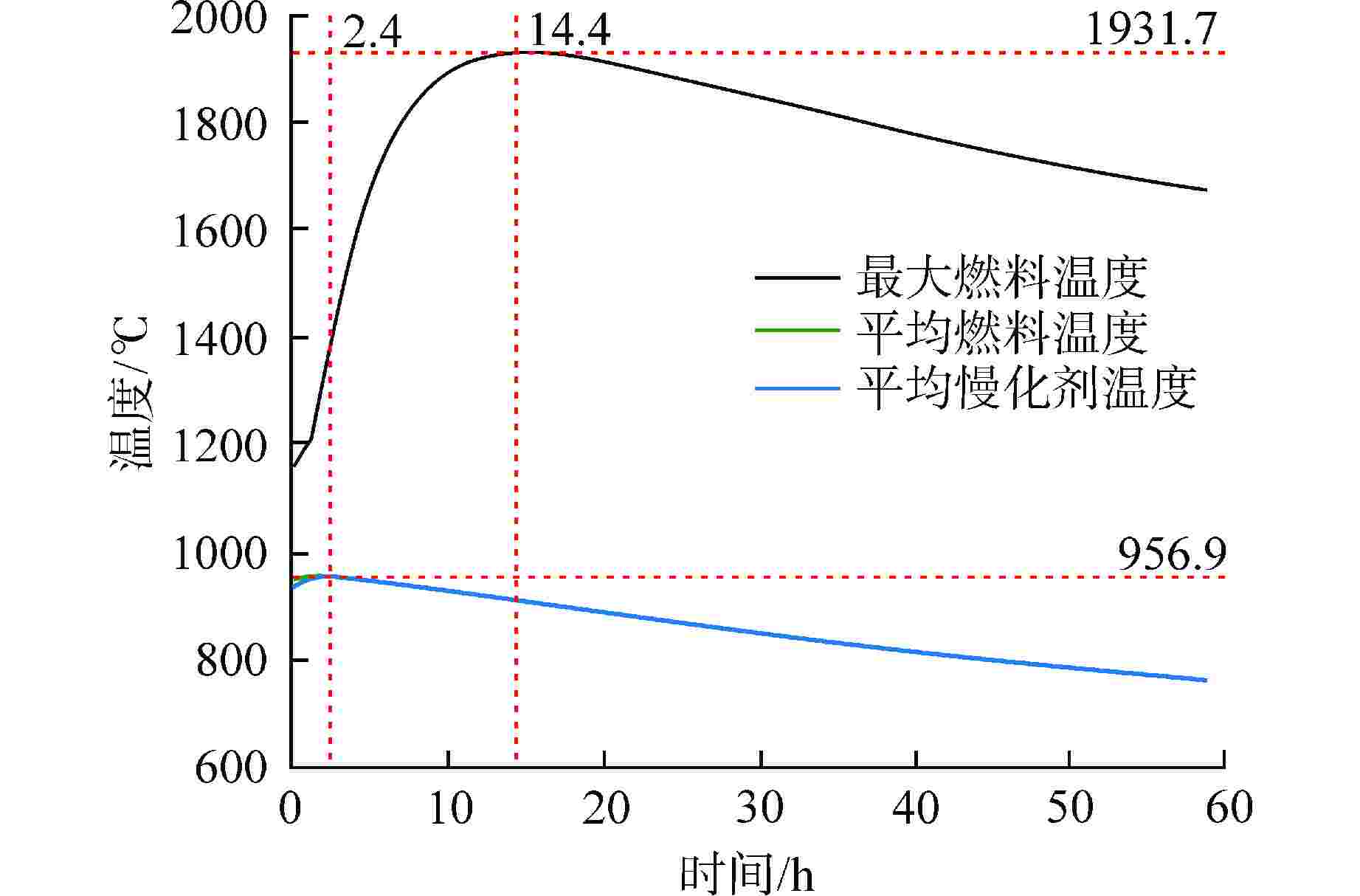
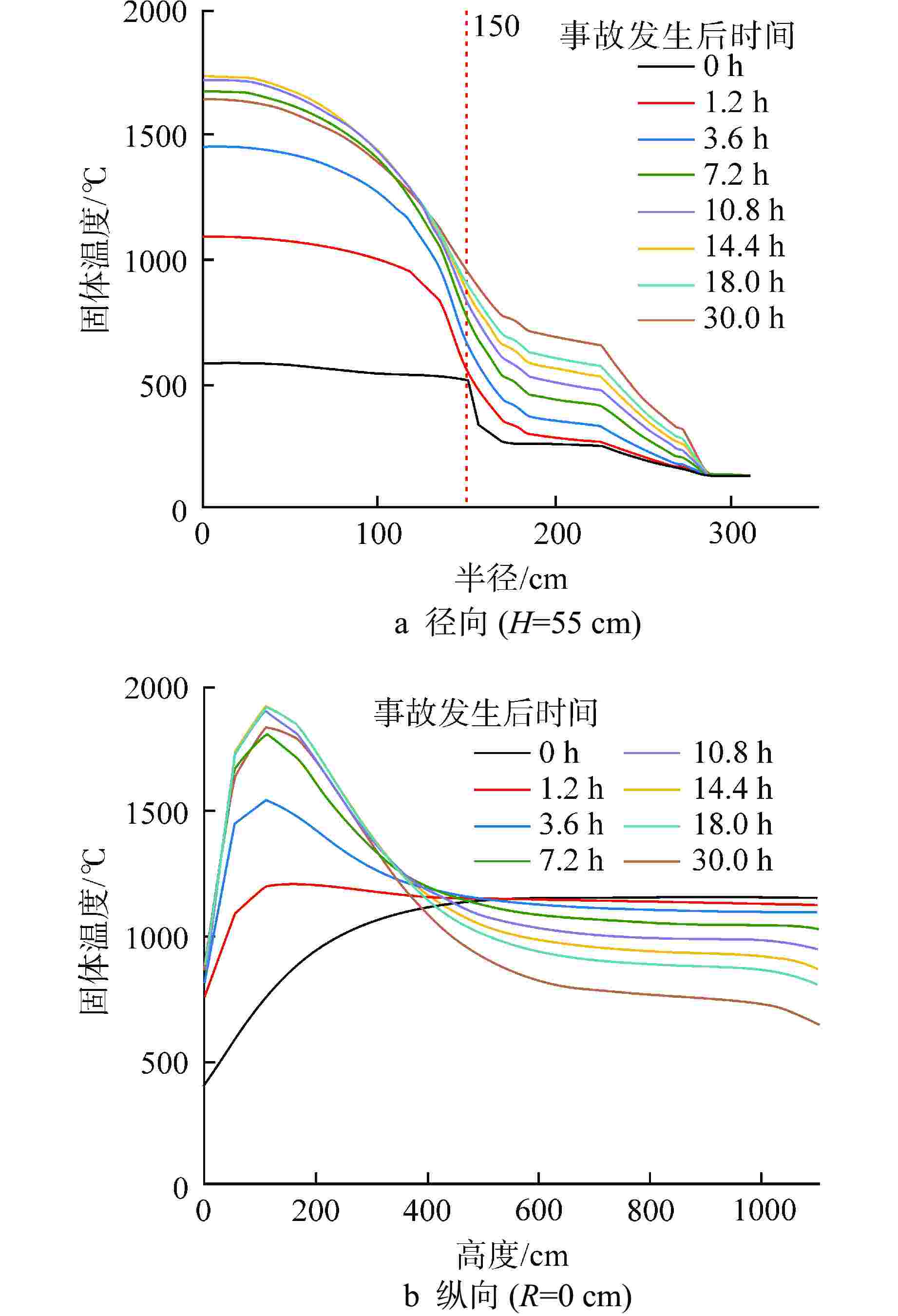
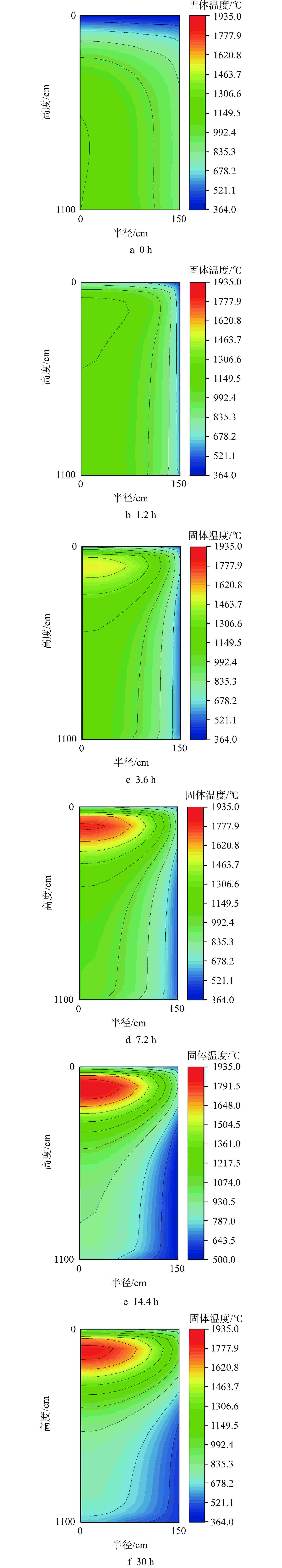
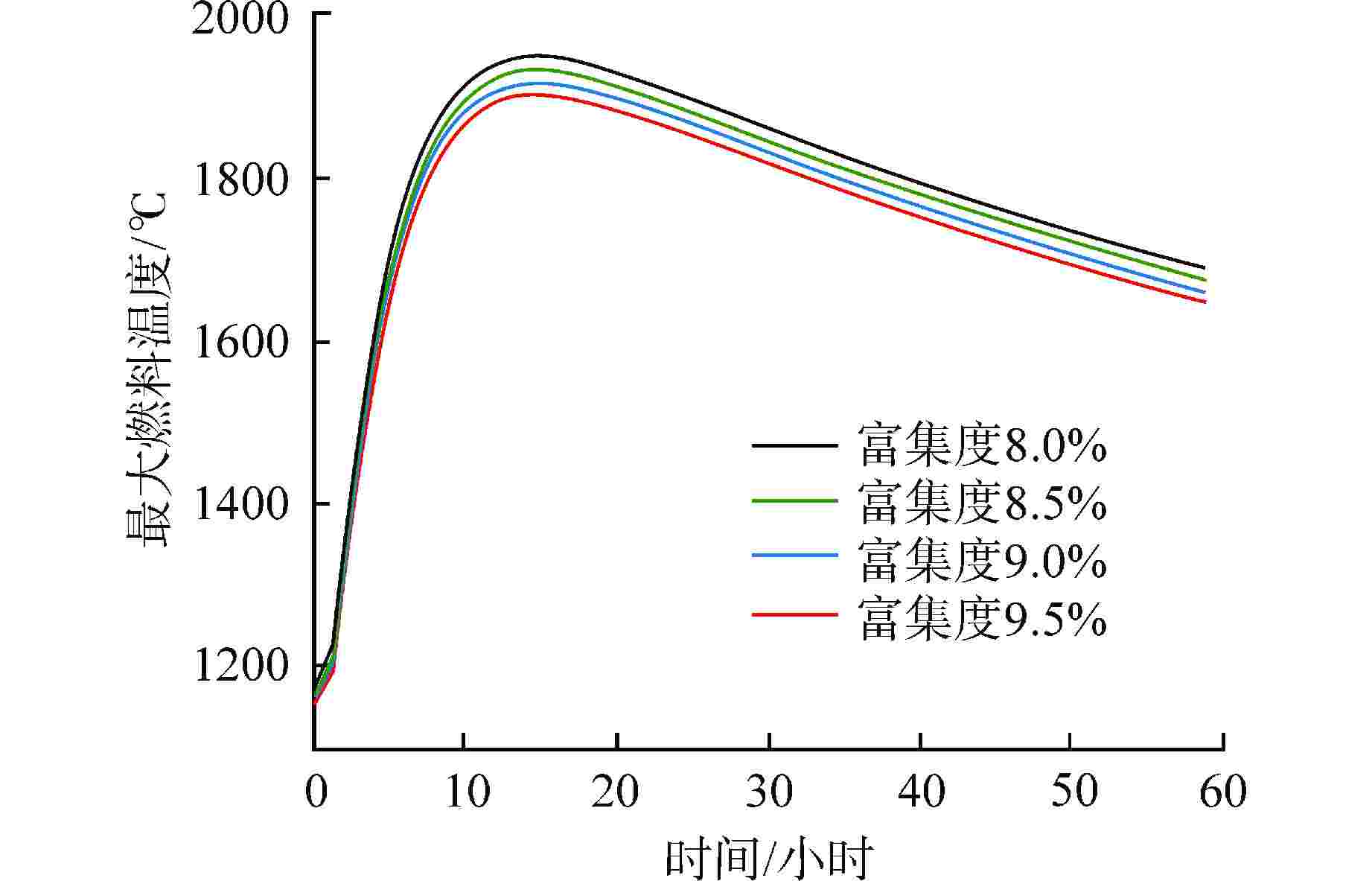
摘要: 模块化高温气冷堆(HTR-PM)采用氦气作为冷却剂,入口温度为250℃,出口温度为750℃,本文基于现有HTR-PM公开设计参数,采用单批次通过堆芯(OTTO)换料模式,冷却剂出口温度设定为950℃,通过VSOP-THERMIX程序分析HTR-PM在平衡堆芯阶段下的各重要参数分布。核热耦合计算结果显示稳态工况下堆芯最高燃料温度为1157℃,低于1200℃安全限值,满足稳态运行工况下燃料元件对放射性裂变产物包容的温度限值。为进一步研究950℃出口温度设计在事故工况下的安全性,本文选取失冷失压(DLOFC)事故分析其最大燃料温度变化情况。结果显示事故发生后14.4 h,最高燃料温度达到最大值1931.7℃,超过1620℃事故温度限值,但低于石墨和碳化硅熔点,堆芯不会发生熔毁事故。该时间节点后,燃料最高温度逐步降低。同时结果显示,DLOFC下最大热点从堆芯底部逐渐上移至堆芯上部。为分析燃料元件富集度对事故温度的影响,本文采用相同换料方案和运行工况,选取8.0%~9.5%共4组富集度装载方案进行对比,结果显示OTTO换料模式下平衡堆芯稳态功率峰随着燃料元件富集度增加而上移,同时在DLOFC事故下,最大燃料温度分别为1949.2、1931.7、1916.2、1900.8℃,依次降低。
-
关键词:
- VSOP-THERMIX /
- 模块化高温气冷堆(HTR-PM) /
- 单批次通过堆芯(OTTO)
Abstract: The High-Temperature Reactor Pebble-bed Module (HTR-PM) adopts helium as the coolant, with 250/750 ℃ for core inlet/outlet temperature. Based on the public HTR-PM design parameters, this study adopts the once-through-then-out (OTTO) refueling scheme with a coolant outlet temperature of 950℃. The VSOP-THERMIX code is employed to analyze the distribution of key parameters in the HTR-PM during the equilibrium core phase. The coupled results of the neutronic–thermal hydraulics show that the maximum fuel temperature under steady-state conditions reaches 1157℃, which is below the safety limit of 1200℃, meeting the temperature criterion for retaining radioactive fission products under steady-state operating conditions. To further investigate the safety of HTR-PM with a 950℃ outlet temperature under accident conditions, a depressurized loss-of-forced-cooling (DLOFC) accident is selected to analyze the changing of maximum fuel temperature. The results indicate that 14.4 hours after the accident, the maximum fuel temperature reaches 1931.7℃, exceeding the accident temperature limit of 1620℃, but remains below the melting points of graphite and silicon carbide. Therefore, the core meltdown will not occur in the DLOFC accident. After this time point, the maximum fuel temperature gradually decreases. Moreover, the results reveal that the location of the maximum fuel temperature moved from the bottom to the upper part of the core during the DLOFC accident. To further analyze the influence of fuel enrichment in the DLOFC accident, four different fuel enrichments ranging from 8.0% to 9.5% are compared under the same refueling and operating conditions. The results show that the steady-state power peak of the equilibrium core shifts upward with increasing fuel enrichment under the OTTO scheme. Under DLOFC conditions, the maximum fuel temperatures are 1949.2, 1931.7, 1916.2℃, and 1900.8℃, respectively, showing a decreasing trend with higher enrichment levels. -
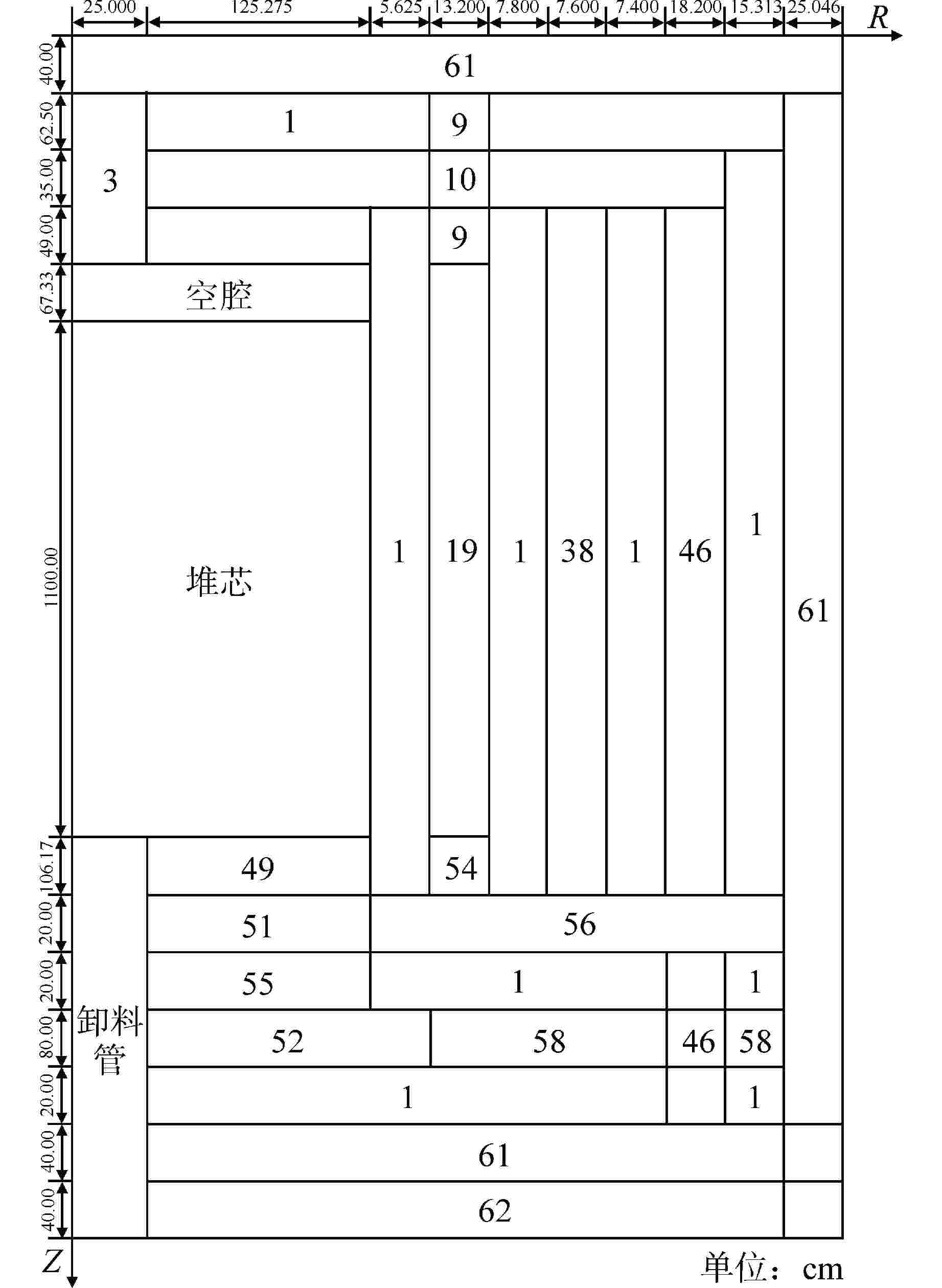
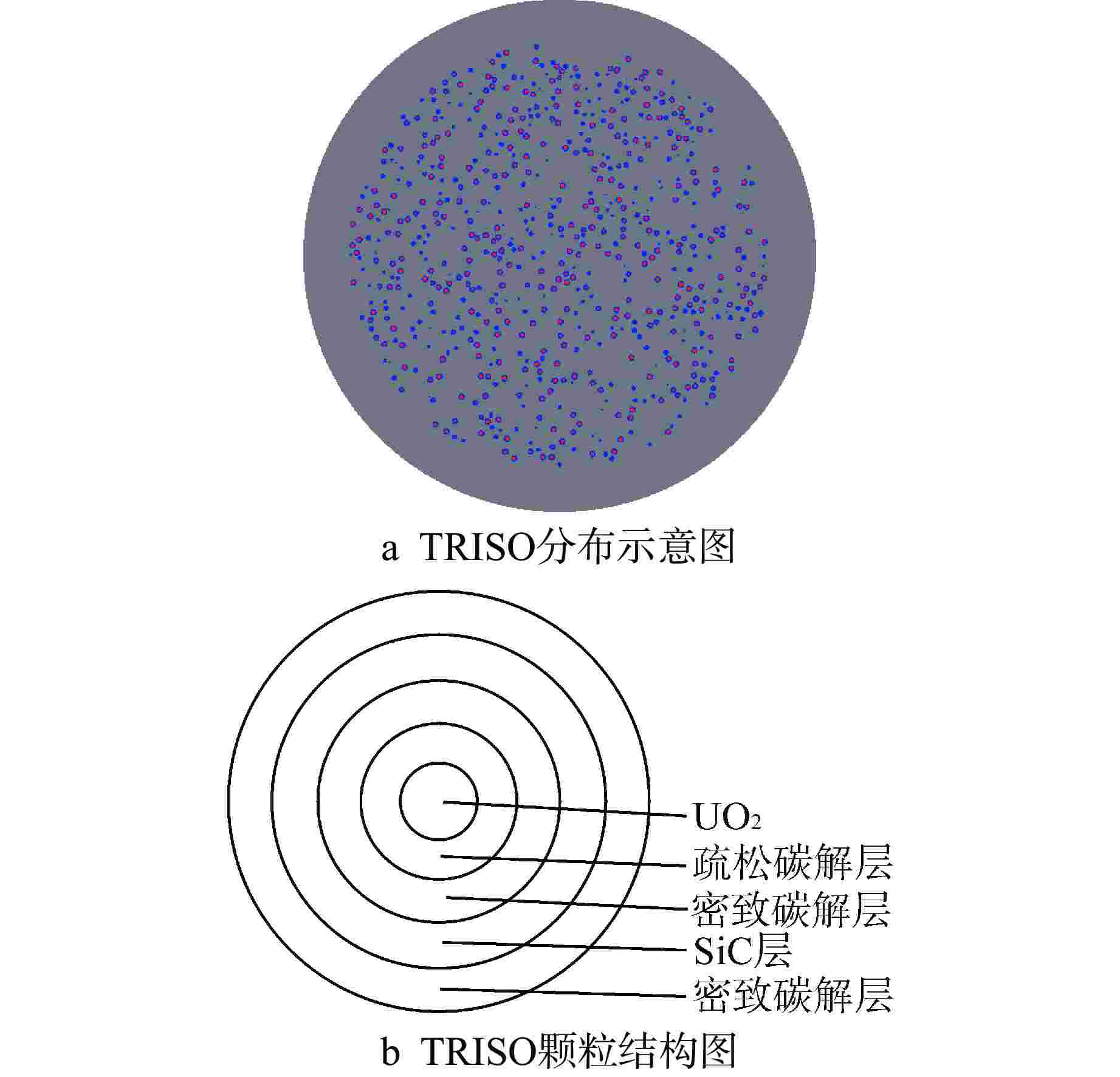
表 1 燃料元件和石墨元件物理参数[2]
Table 1. Physical Parameters of Fuel Elements and Graphite Elements
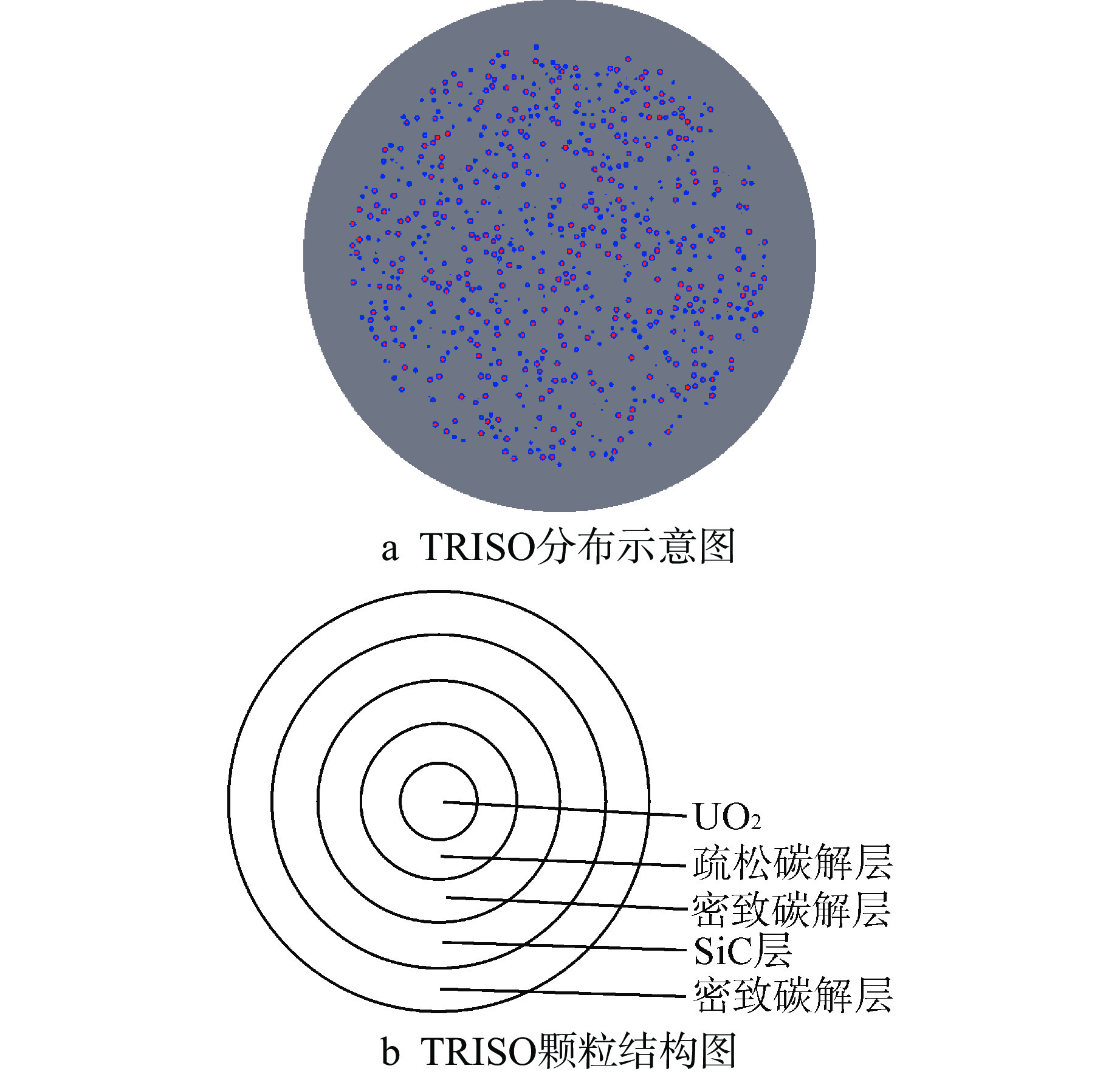
参数 数值 参数 数值 燃料元件 燃料元件铀装料/g 7.0 TRISO颗粒 核心半径/μm 250 235U富集度/% 4.2/8.5 疏松碳解层厚度/μm 95 直径/cm 6.0 密致内碳解层厚度/μm 40 燃料区直径/cm 5.0 SiC包覆层厚度/μm 35 石墨密度(基体和外壳区间)/(g·cm−3) 1.74 密致外碳解层厚度/μm 40 铀杂质等效硼浓度/ppm 4.0 UO2密度/(g·cm−3) 10.4 石墨杂质等效硼浓度/ppm 0.795 疏松碳解层密度/(g·cm−3) 1.05 石墨元件 直径/cm 6.0 密致内碳解层密度/(g·cm−3) 1.9 石墨密度/(g·cm−3) 1.74 SiC包覆层密度/(g·cm−3) 3.18 等效硼浓度/10−6 1.0 表 2 区间材料组成成分[2]
Table 2. Material Composition by Model Zones
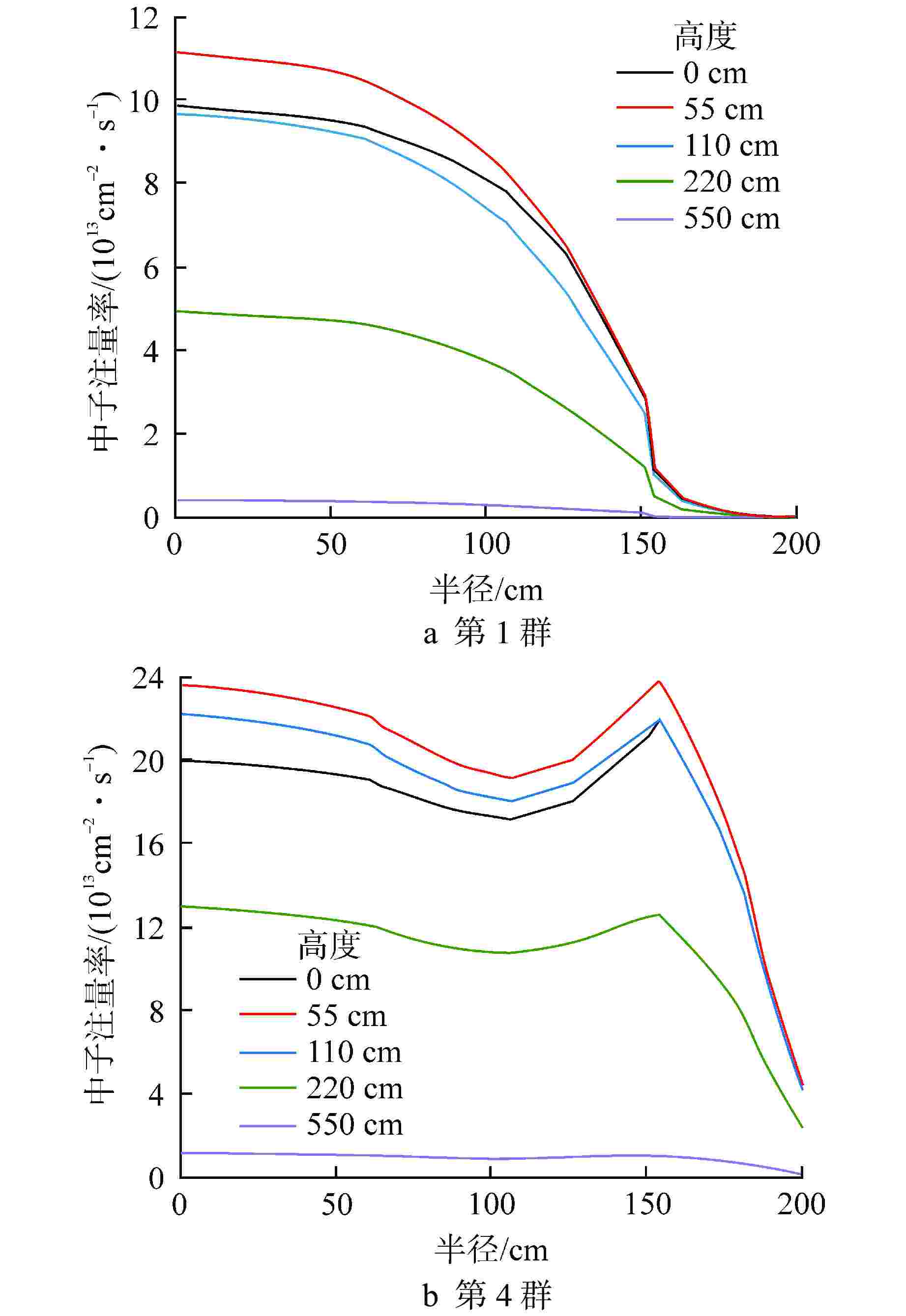
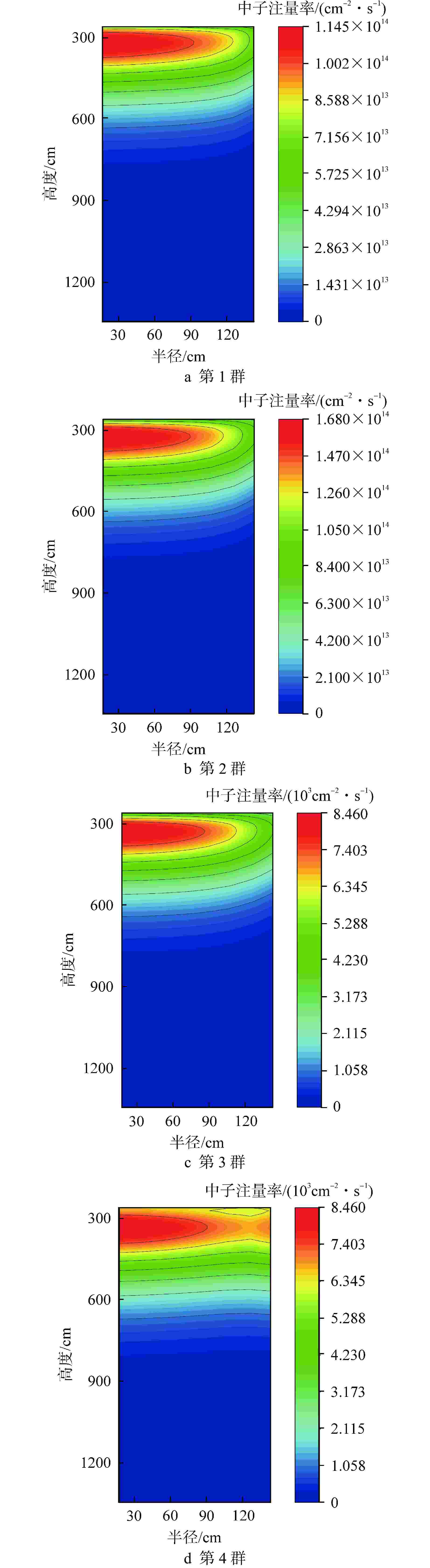
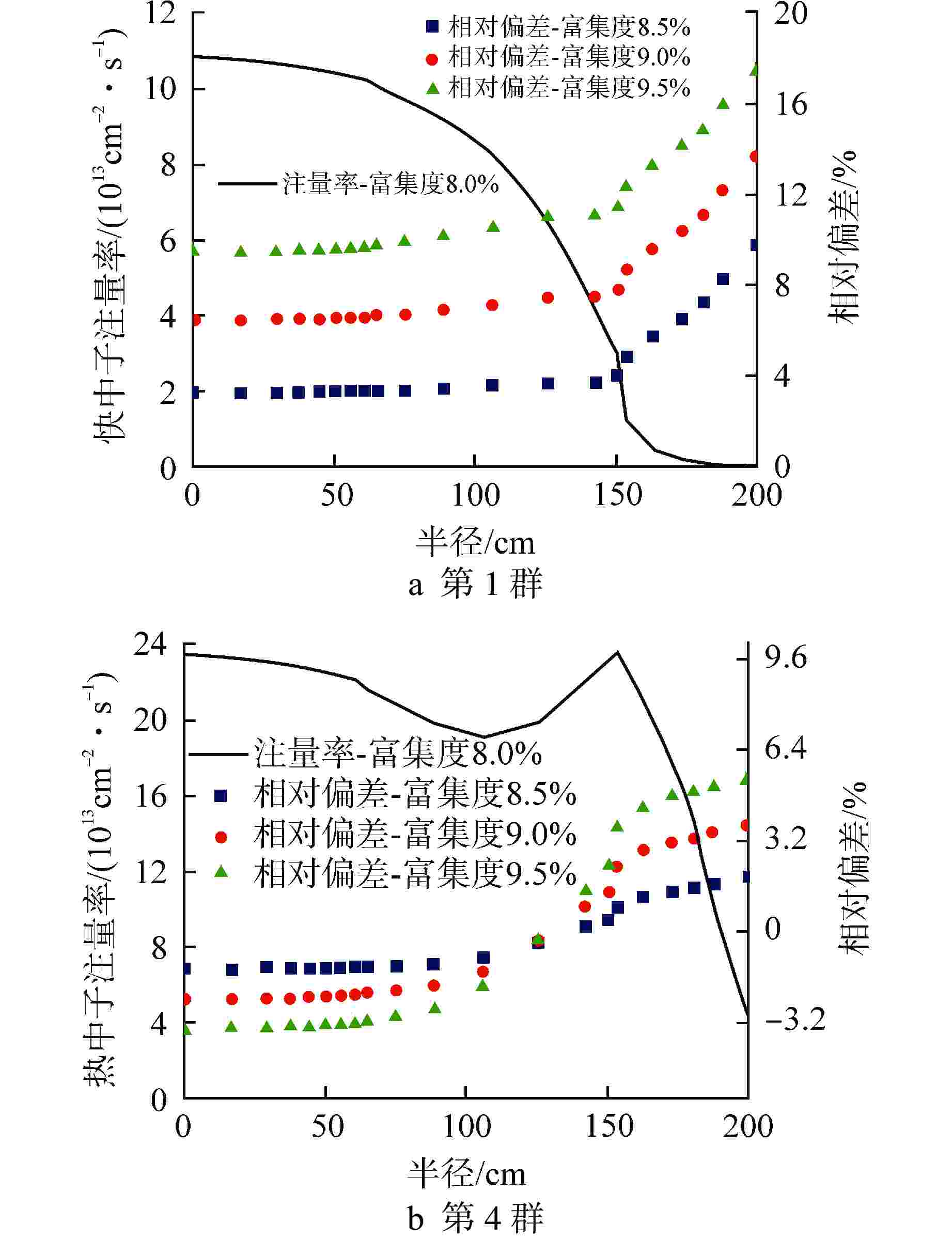
编号(ID) 材料成分/(barn−1·cm−1) 12C 硼(天然) 1 8.92947×10–2 4.41429×10–8 3 0.91×ID1① 5 0.84×ID1 6 0.6286×ID1 19 0.719×ID1 38 0.99×ID1 46 0.6679×ID1 49 0.7135×ID1 52 0.5079×ID1 54 0.8315×ID1 55 0.8741×ID1 58 0.9317×ID1 9 5.62021×10–2 3.69779×10–6 10 2.30380×10–2 3.68139×10–6 51 7.49075×10–2 1.26898×10–4 56 8.14783×10–2 1.22899×10–4 61 8.39217×10–2 3.79675×10–3 62 8.53015×10–2 3.79190×10–5 注:①N×ID1表示该编号(ID)的填充材料是体积占比为N的ID1材料;1 barn=10−28 m2。 表 3 中子能群划分方案
Table 3. Energy Group Boundary of Neutron
中子能群 能量边界/eV 第1群 1×105~2×108 第2群 130~1×105 第3群 1.86~130 第4群 0~1.86 表 4 OTTO方案下HTR-PM平衡堆芯稳态工况重要参数
Table 4. Key Parameters of HTR-PM Equilibrium Core under Steady State and OTTO Scheme
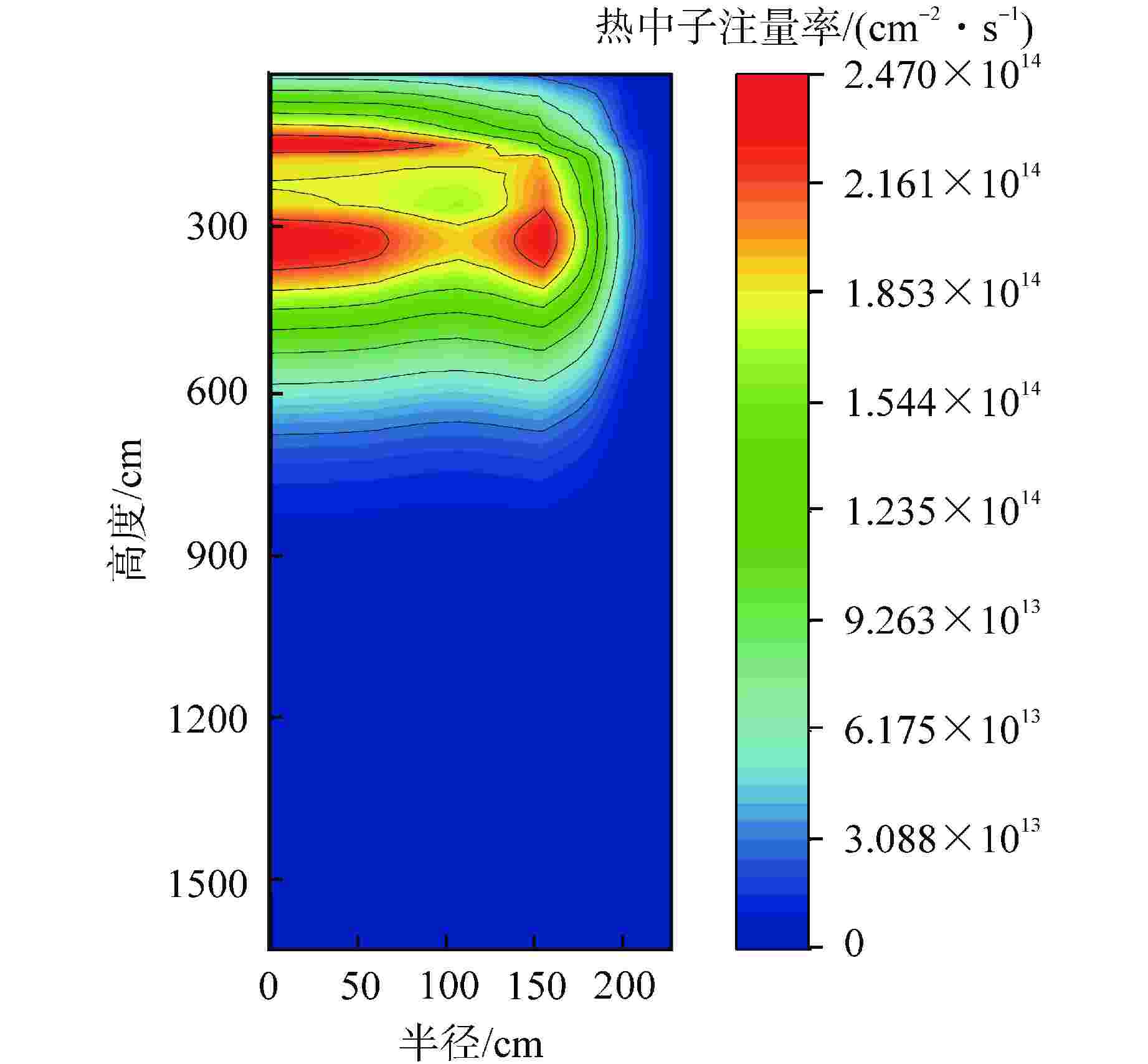
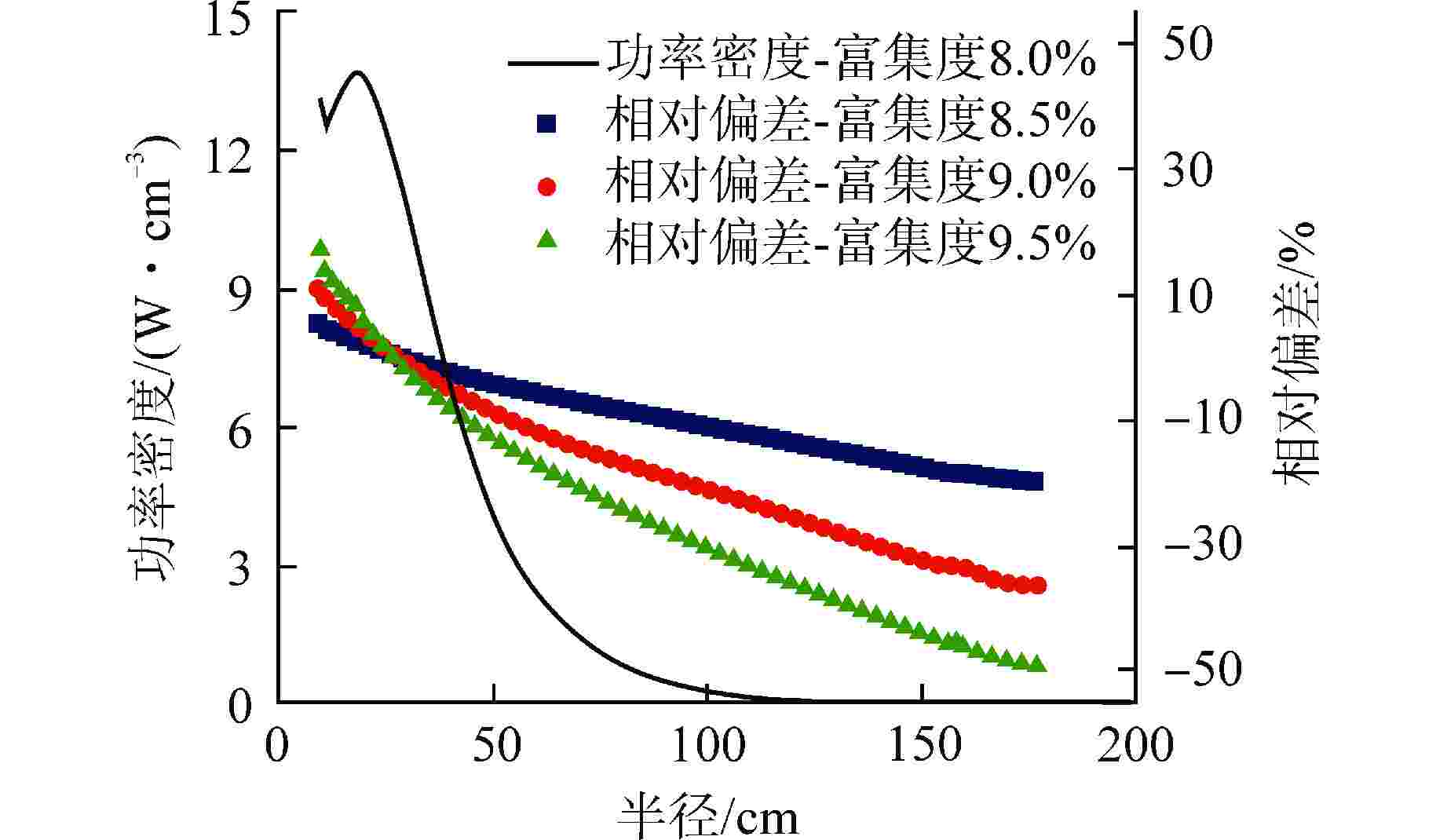
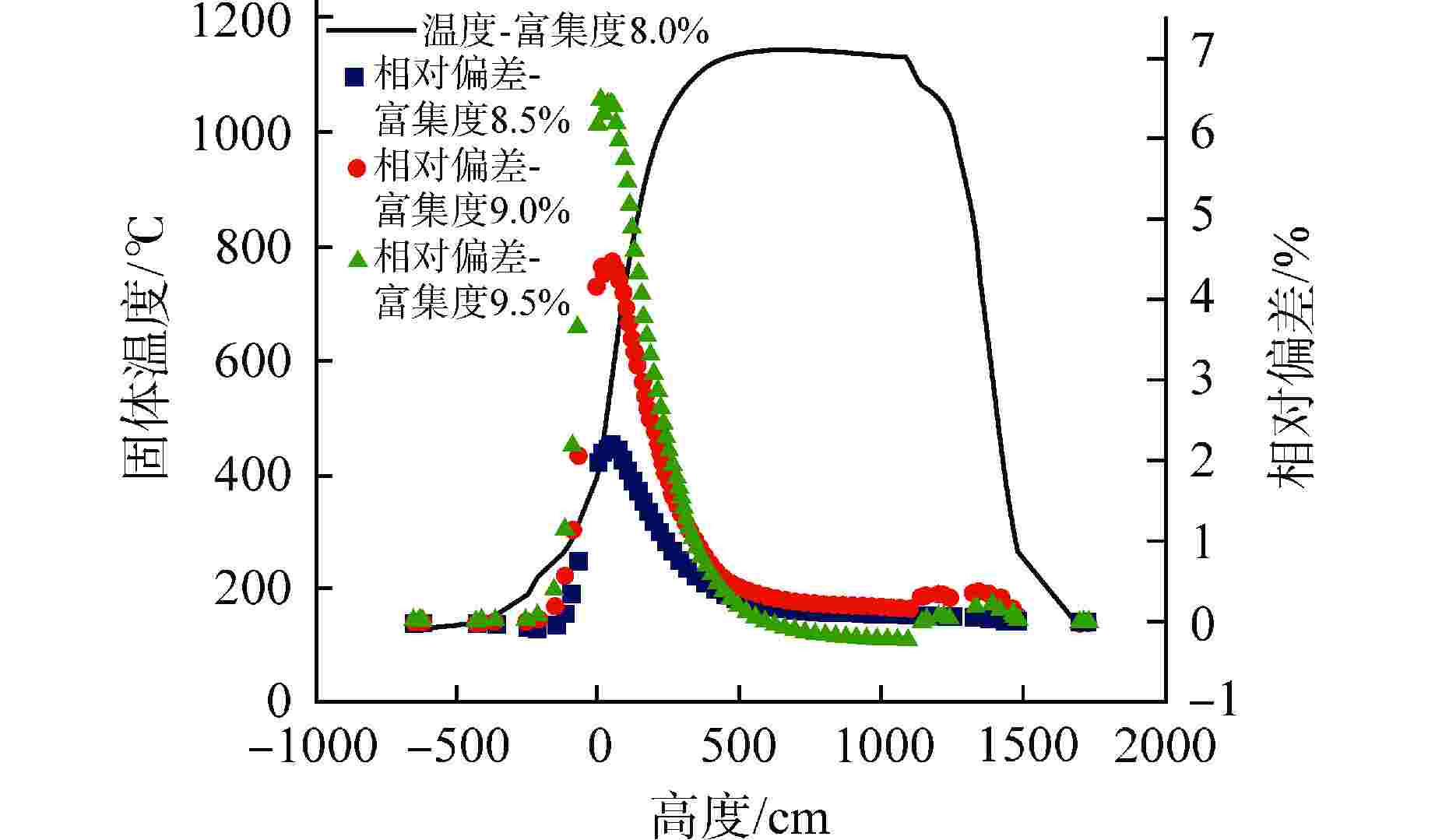
参数 数值 参数 数值 换料步首keff 1.01496 换料步尾keff 0.99917 每天投入新燃料元件个数 382 最大单球功率/kW 2.43 最大功率密度/(W·cm−3) 13.11 最高燃料温度/℃ 1157 卸料燃耗/[MW·d·t−1(U)] 69801 冷却剂出口温度/℃ 947 表 5 不同富集度下稳态与DLOFC事故的燃料最高温度等参数变化情况
Table 5. The Changes of Parameters with Different Fuel Enrichments Under Steady States and DLOFC Accident Conditions
富集度/% 最大功率密度/(W·cm−3) 最大单球功率/kW 最大燃料温度/℃ DLOFC事故下燃料温度/℃ 最大值 平均值 8.0 12.77 2.37 1154 1949.2(14.4 h)① 959.5 (2.4 h) 8.5 13.11 2.43 1157 1931.7(14.4 h) 956.9 (2.4 h) 9.0 13.44 2.49 1159 1916.2(14.4 h) 954.9 (2.4 h) 9.5 14.19 2.63 1158 1900.8(14.4 h) 952.9 (2.4 h) 注:①括号内数据为事故发生后时间。 -
[1] KUGELER K, ZHANG Z Y. Modular high-temperature gas-cooled reactor power plant[M]. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer, 2019: 85-86. [2] SHE D, GUO J, LIU Z H, et al. PANGU code for pebble-bed HTGR reactor physics and fuel cycle simulations[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2019, 126: 48-58. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2018.11.005 [3] RÜTTEN H J, HAAS K A, POHL C. Computer code system V. S. O. P. (99/11) update 2011 of V. S. O. P(99)-version 2009 code manual: Jul-4348[R]. Jül-4348, Bundesrepublik Deutschland: Forschungszentrum Jülich, 2012. [4] CHEN F B, HAN Z H. Steady-state thermal fluids analysis for the HTR-PM equilibrium core[J]. International Journal of Advanced Nuclear Reactor Design and Technology, 2021, 3: 11-17. doi: 10.1016/j.jandt.2021.04.001 [5] ZHENG Y H, SHI Y, DONG Y J. Thermohydraulic transient studies of the Chinese 200 MWe HTR-PM for loss of forced cooling accidents[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2009, 36(6): 742-751. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2009.02.007 -





 下载:
下载: