Study on Oxidation Corrosion Characteristics of Horizontal Lead-Bismuth Reactor Core
-
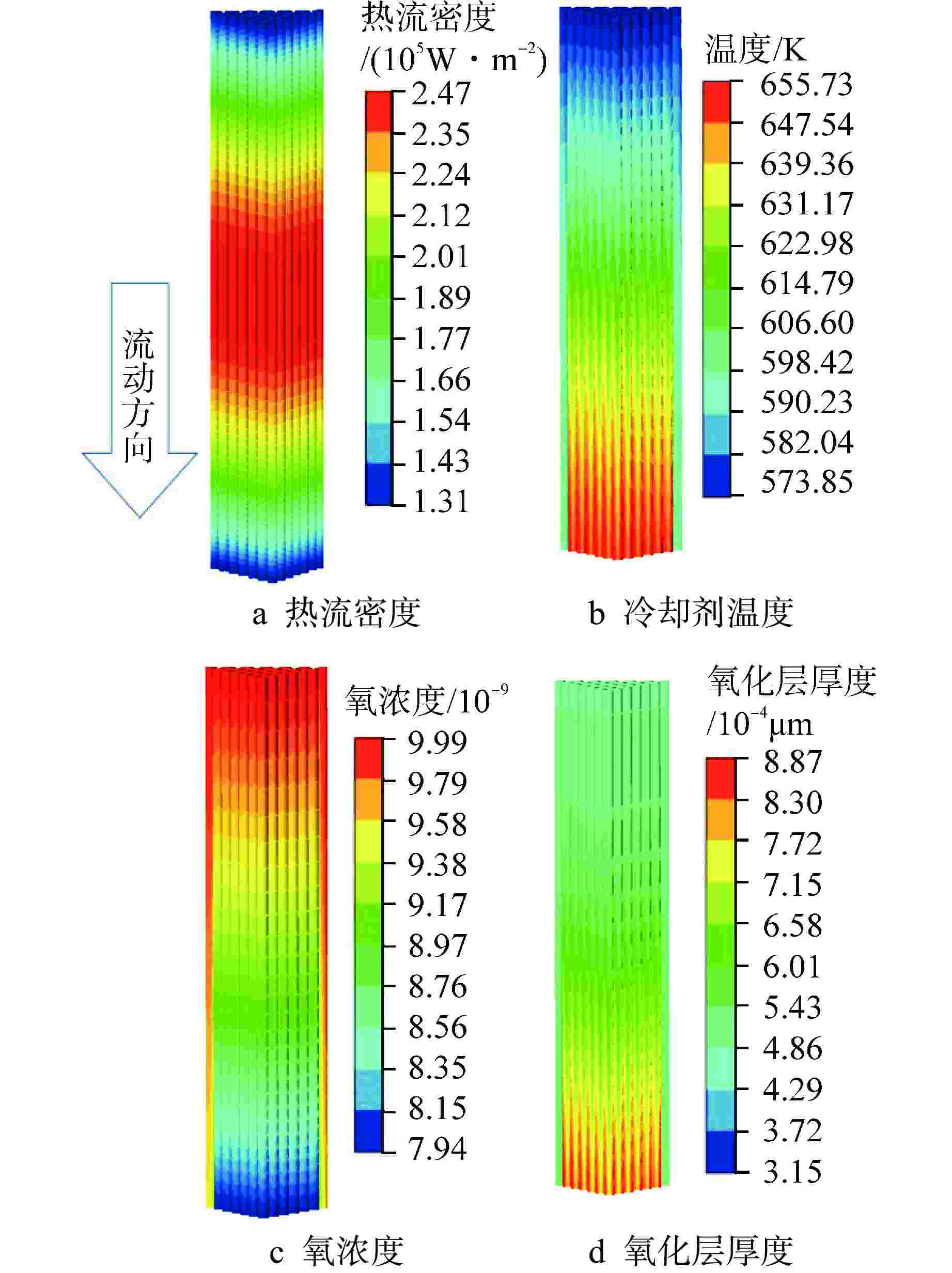
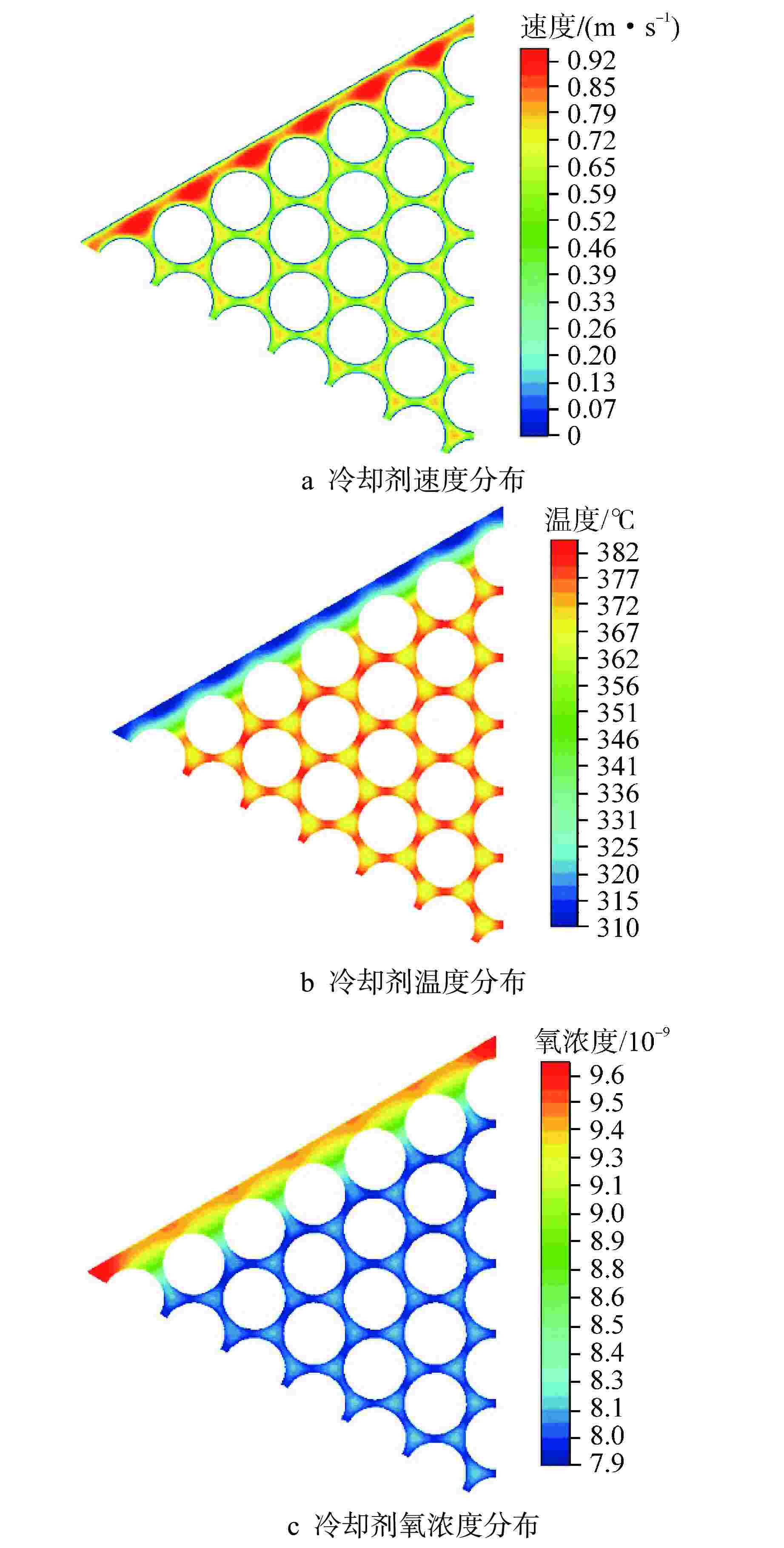
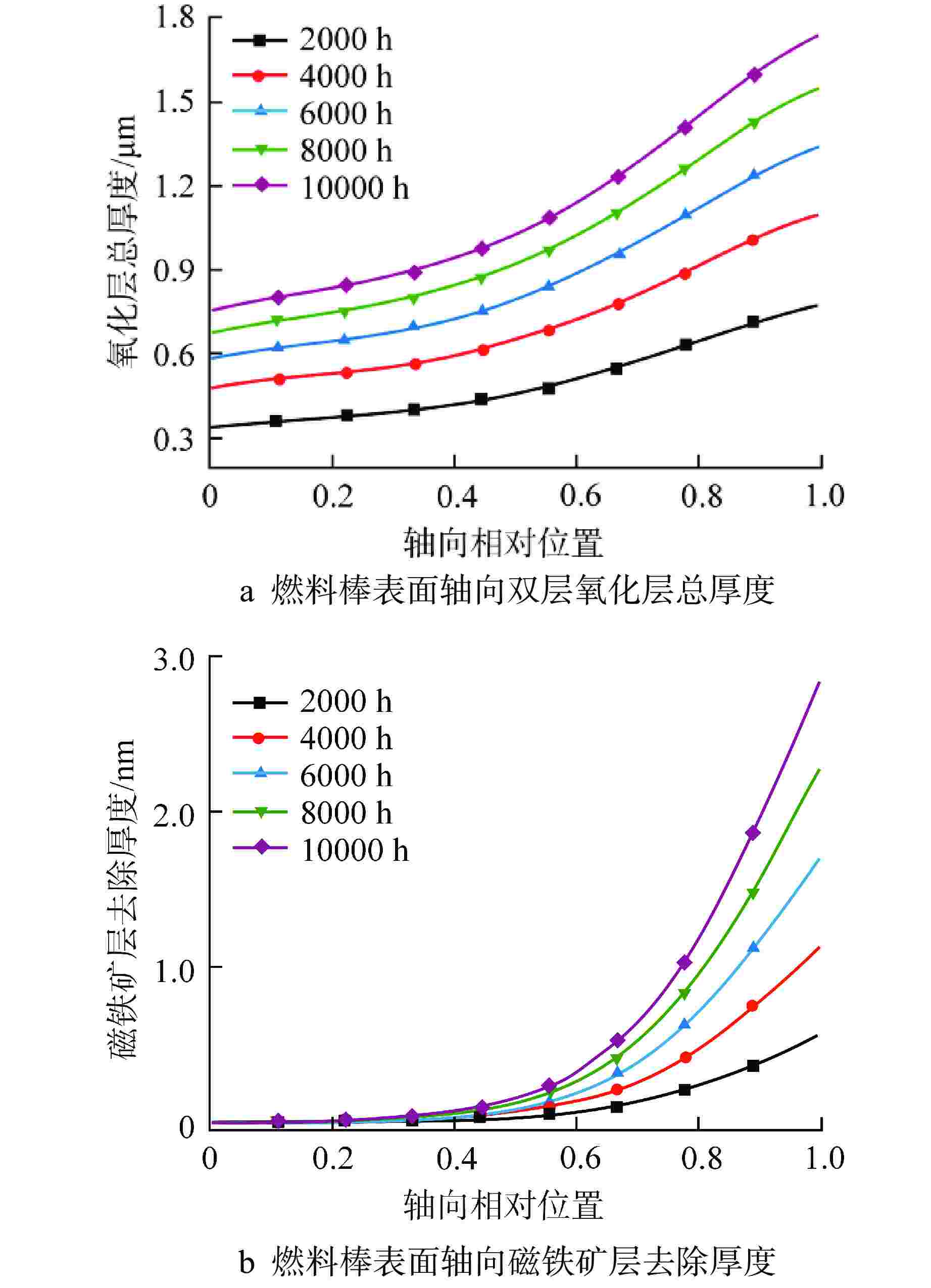
摘要: 为开展卧式铅铋堆芯氧化腐蚀特性研究,本研究建立液态铅铋氧化腐蚀模型,并基于计算流体动力学方法,运用输运方程源项自定义方法实现耦合计算。研究表明,基准工况下堆芯燃料棒表面氧化层最厚位于出口位置处,中心位置燃料棒表面氧化层厚度显著高于靠近燃料组件盒燃料棒表面氧化层。10000 h后中心位置燃料棒表面仍保持双层氧化层结构,双层氧化层平均总厚度为1.32 μm。本研究提出了铅铋堆芯氧化腐蚀特性数值模拟研究方法,能够用于铅铋堆芯氧化腐蚀的预测。
-
关键词:
- 铅铋快堆 /
- 氧化腐蚀 /
- 计算流体动力学(CFD)
Abstract: In order to study the oxidation corrosion characteristics of horizontal lead-bismuth reactor core, a liquid lead-bismuth oxidation corrosion model was established in this study. Based on computational fluid dynamics method, the self-defined source term method of transport equation was used to realize coupling calculation. The results show that the thickest oxidation layer on the fuel rod surface of the reactor core is located at the outlet position under the reference condition, and the oxidation layer on the fuel rod surface at the center is significantly higher than that near the fuel assembly box. After 10,000 hours, the surface of the fuel rod at the center still maintained a double oxide layer structure, and the average total thickness of the double oxide layer was 1.32 μm. This study provides a numerical simulation method for the oxidation corrosion characteristics of lead-bismuth reactor cores, which can be used for the prediction of oxidation corrosion of lead-bismuth reactor cores. -
表 1 磁铁矿层中铁扩散系数及氧活性浓度计算式[15-17]
Table 1. Formula for Calculating Iron Diffusion Coefficient and Oxygen Active Concentration in Magnetite Layer
扩散系数 计算式/值 ${D_{\text{v}}}$ $\begin{gathered} 0.177\exp \left( {\dfrac{{ - 14600}}{T}} \right) + 1.16 \times {10^{ - 3}} \times (1 - \eta )\exp \left( { - \dfrac{{8670}}{T}} \right) \\ \eta = \dfrac{1}{{\left[ {1 + 3 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}\exp \left( {\dfrac{{11900}}{T}} \right)} \right]}} \\ \end{gathered} $ ${D_{\text{I}}}$ $\dfrac{{1.22 \times {{10}^4}\exp \left( { - \dfrac{{27700}}{T}} \right)}}{{1 + 1.56 \times {{10}^6}\exp \left( { - \dfrac{{20100}}{T}} \right)}}$ ${K_{\text{v}}}$ $2.04 \times {10^{ - 7}}\exp \left( {\dfrac{{27170}}{T}} \right)$ ${K_{\text{I}}}$ $1.93 \times {10^3}\exp \left( { - \dfrac{{43140}}{T}} \right) + 3.01 \times {10^9}\exp \left( { - \dfrac{{63270}}{T}} \right)$ $ \dfrac{{D_{{\text{sp}}}^{{\text{Topfer}}}({\text{I}})}}{{D_{{\text{mag}}}^{{\text{Topfer}}}({\text{I}})}} $ $3.3 \times {10^{ - 6}} \times {\left( {a_{{{\text{O}}_2}}^{{\text{sp}}/{\text{mag}}}} \right)^{ - 0.18}}$ $ \dfrac{{D_{{\text{sp}}}^{{\text{Topfer}}}({\text{V}})}}{{D_{{\text{mag}}}^{{\text{Torfer}}}({\text{V}})}} $ 0.7 $a_{{{\text{O}}_2}}^{{\text{T}}91/{\text{sp}}}$ $\begin{gathered} a_{ {\text{Fe} } }^{ - \frac{3}{2} }\exp \left( {\dfrac{ {\Delta {G^0} } }{ {RT} } } \right) \\ {a_{ {\text{Fe} } } } = 0.9 \\ \Delta {G^0} = - 549.05 + 0.1531T \\ \end{gathered}$ $a_{{{\text{O}}_2}}^{{\text{mag}}/{\text{LM}}}$ $\begin{gathered} \exp \left( {2\dfrac{ {\Delta G_{^{\text{O} } }^0} }{ {RT} } + 2\ln \dfrac{ { {M_{_{^ {\text{LM} } } } } } }{ { {M_{_{^{\text{O} }}} } } } + 2\ln {C_{_{^{\text{O} }}} } } \right) \\ \Delta G_{^{\text{O} } }^0 = - 127 + 0.0279T \\ \end{gathered}$ T—局部温度,K;CO—氧浓度,%;$\Delta {G^0}$和$\Delta G_{^{\text{O}}}^0$—分别为氧化反应四氧化三铁和氧化铅的吉布斯自由能,kJ/mol;MLM、MO—分别为铅铋与氧的相对分子(原子)质量 表 2 堆芯主要几何及基准运行工况参数
Table 2. Main Core Geometric Parameters and Standard Operating Conditions
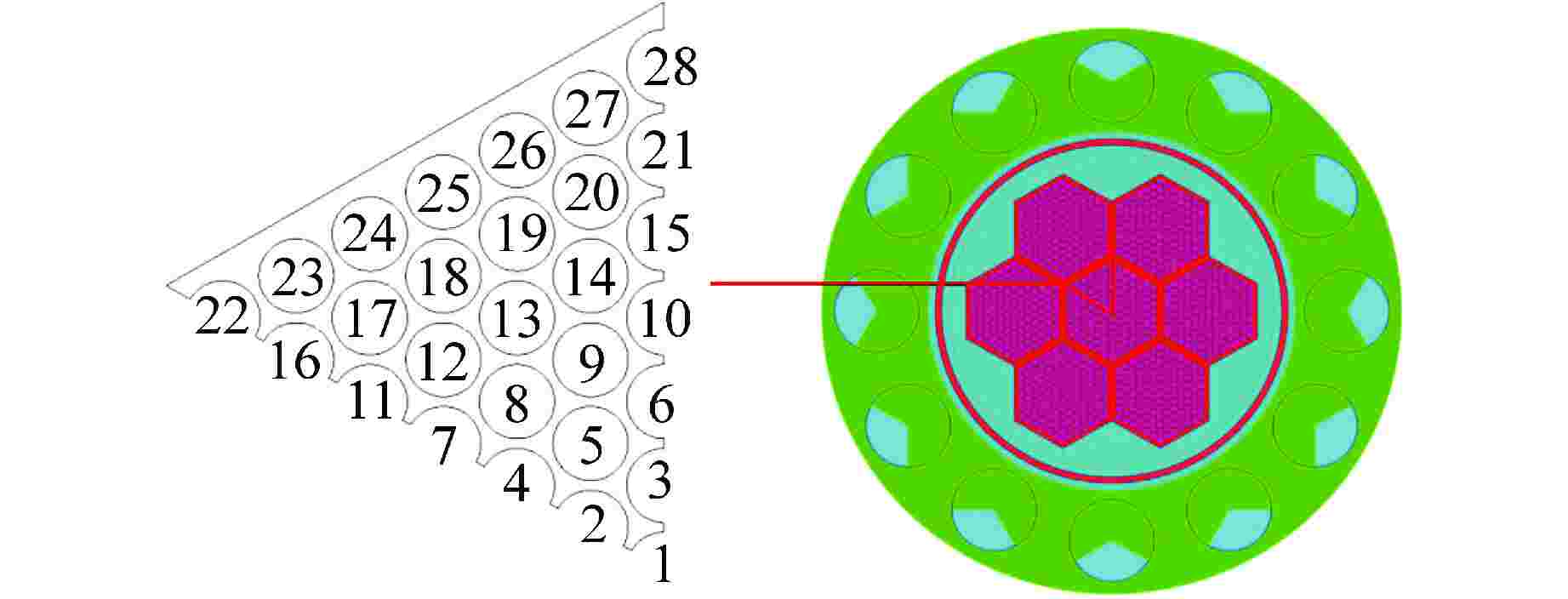
参数 参数值 反应堆热功率/MW 1.5 燃料棒直径/mm 9.0 燃料棒中心距/mm 10.17 燃料组件内边间距/mm 123.3 堆芯活性区高度/mm 290 燃料棒总数量/根 889 冷却剂入口温度/℃ 300 冷却剂总流量/(kg·s−1) 201.28 冷却剂运行压力/MPa 0.1 表 3 主要模拟计算条件参数
Table 3. Main Simulated Calculation Condition Parameters
边界 条件设置 数值 入口 速度边界/(m·s−1) 0.657 温度/℃ 300 氧浓度 1×10−8 出口 压力边界/Pa 0 燃料棒表面 热流密度/(W·m−2) 如式(15)所示 绝热壁面 无滑移壁面 表 4 网格划分情况表
Table 4. Meshing Table
划分方案 网格1 网格2 网格3 网格4 网格总数量 573万 746万 934万 1064万 轴向氧浓度相对误差/% 8 2 1 径向壁面切应力相对误差/% 1.1 0.6 0.3 -
[1] MIHARA T, TANAKA Y, ENUMA Y, et al. Feasibility studies on commercialized fast breeder reactor system (3) - HLMC Fast Reactor[C]. Washington: IASMiRT, 2001. [2] ZHANG J S, LI N. Review of the studies on fundamental issues in LBE corrosion[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2008, 373(1-3): 351-377. doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2007.06.019 [3] ZHANG J S. A review of steel corrosion by liquid lead and lead–bismuth[J]. Corrosion Science, 2009, 51(6): 1207-1227. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2009.03.013 [4] FAZIO C, BALBAUD F. Corrosion phenomena induced by liquid metals in Generation IV reactors[M]//YVON P. Structural Materials for Generation IV Nuclear Reactors. Cambridge: Woodhead Publishing, 2017: 23-74. [5] ZHANG Y, WANG C L, LAN Z K, et al. Review of thermal-hydraulic issues and studies of lead-based fast reactors[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2020, 120: 109625. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2019.109625 [6] ZHANG Y, ZHANG D L, WANG C L, et al. Oxygen transport analysis in lead-bismuth eutectic coolant for solid-phase oxygen control[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2021, 154: 108128. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2021.108128 [7] TEDMON C S. The effect of oxide volatilization on the oxidation kinetics of Cr and Fe‐Cr alloys[J]. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 1966, 113(8): 766-768. doi: 10.1149/1.2424115 [8] MARINO A, LIM J, KEIJERS S, et al. Numerical modeling of oxygen mass transfer in a wire wrapped fuel assembly under flowing lead bismuth eutectic[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2018, 506: 53-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2017.12.017 [9] WANG C L, ZHANG Y, ZHANG D L, et al. Numerical study of oxygen transport characteristics in lead-bismuth eutectic for gas-phase oxygen control[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 2021, 53(7): 2221-2228. doi: 10.1016/j.net.2021.01.031 [10] 苏光辉, 秋穗正, 田文喜. 核动力系统热工水力计算方法[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2013: 221-226. [11] MARTINELLI L, BALBAUD-CÉLÉRIER F, TERLAIN A, et al. Oxidation mechanism of a Fe–9Cr–1Mo steel by liquid Pb–Bi eutectic alloy (Part I)[J]. Corrosion Science, 2008, 50(9): 2523-2536. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2008.06.050 [12] MARTINELLI L, BALBAUD-CÉLÉRIER F, TERLAIN A, et al. Oxidation mechanism of an Fe–9Cr–1Mo steel by liquid Pb–Bi eutectic alloy at 470°C (Part II)[J]. Corrosion Science, 2008, 50(9): 2537-2548. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2008.06.051 [13] MARTINELLI L, BALBAUD-CÉLÉRIER F, PICARD G, et al. Oxidation mechanism of a Fe-9Cr-1Mo steel by liquid Pb–Bi eutectic alloy (Part III)[J]. Corrosion Science, 2008, 50(9): 2549-2559. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2008.06.049 [14] MARTINELLI L, BALBAUD-CÉLÉRIER F. Modelling of the oxide scale formation on Fe-Cr steel during exposure in liquid lead-bismuth eutectic in the 450–600°C temperature range[J]. Materials and Corrosion, 2011, 62(6): 531-542. doi: 10.1002/maco.201005871 [15] BACKHAUS‐RICOULT M, DIECKMANN R. Defects and cation diffusion in magnetite (VII): Diffusion controlled formation of magnetite during reactions in the iron‐oxygen system[J]. Berichte der Bunsengesellschaft für Physikalische Chemie, 1986, 90(8): 690-698. [16] DIECKMANN R. Defects and cation diffusion in magnetite (IV): Nonstoichiometry and point defect structure of magnetite (Fe3‐δO4) [J]. Berichte der Bunsengesellschaft für Physikalische Chemie, 1982, 86(2): 112-118. [17] Fazio C, Sobolev V P, Aerts A, et al. Handbook on lead-bismuth eutectic alloy and lead properties, materials compatibility, thermal-hydraulics and technologies – 2015 edition[R]. Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development, 2015. [18] HE B X, NING L, MINEEV M. A kinetic model for corrosion and precipitation in non-isothermal LBE flow loop[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2001, 297(2): 214-219. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3115(01)00603-1 [19] CHEN T Y, MOCCARI A, MACDONALD D D. Development of controlled hydrodynamic techniques for corrosion testing[J]. Corrosion, 1992, 48(3): 239-255. doi: 10.5006/1.3315930 [20] SILVERMAN D C. Technical note: On estimating conditions for simulating velocity-sensitive corrosion in the rotating cylinder electrode[J]. Corrosion, 1999, 55(12): 1115-1118. doi: 10.5006/1.3283948 [21] SCHROER C, WEDEMEYER O, SKRYPNIK A, et al. Corrosion kinetics of Steel T91 in flowing oxygen-containing lead–bismuth eutectic at 450°C[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2012, 431(1-3): 105-112. doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2011.11.014 [22] TSISAR V, SCHROER C, WEDEMEYER O, et al. Characterization of corrosion phenomena and kinetics on T91 ferritic/martensitic steel exposed at 450 and 550 °C to flowing Pb-Bi eutectic with 10−7 mass% dissolved oxygen[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2017, 494: 422-438. doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2017.07.031 -





 下载:
下载: