Study on the Thermal Aged Microstructure of Candidate Austenitic Heat-resistant Stainless Steel for Supercritical Water-cooled Reactor
-
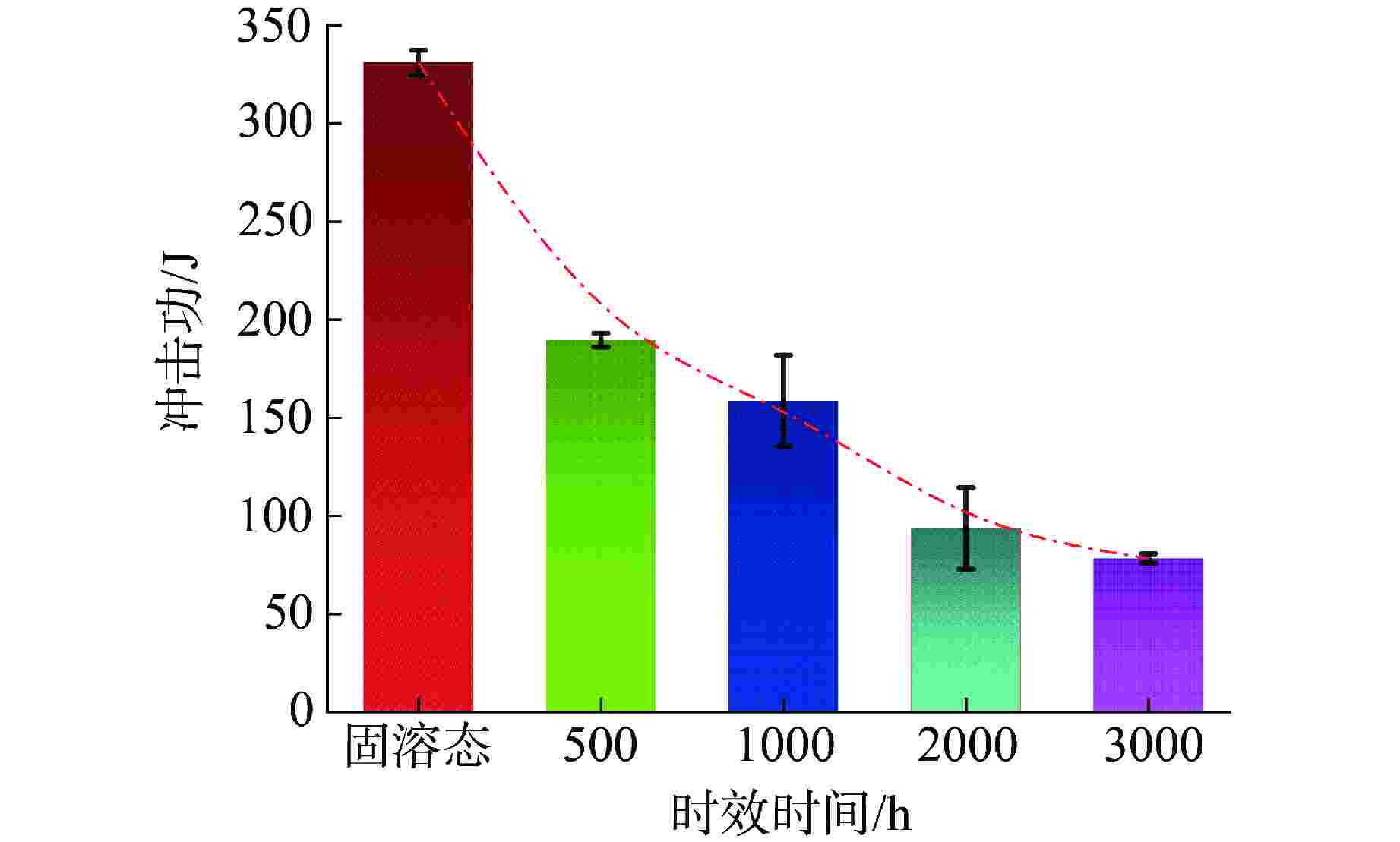
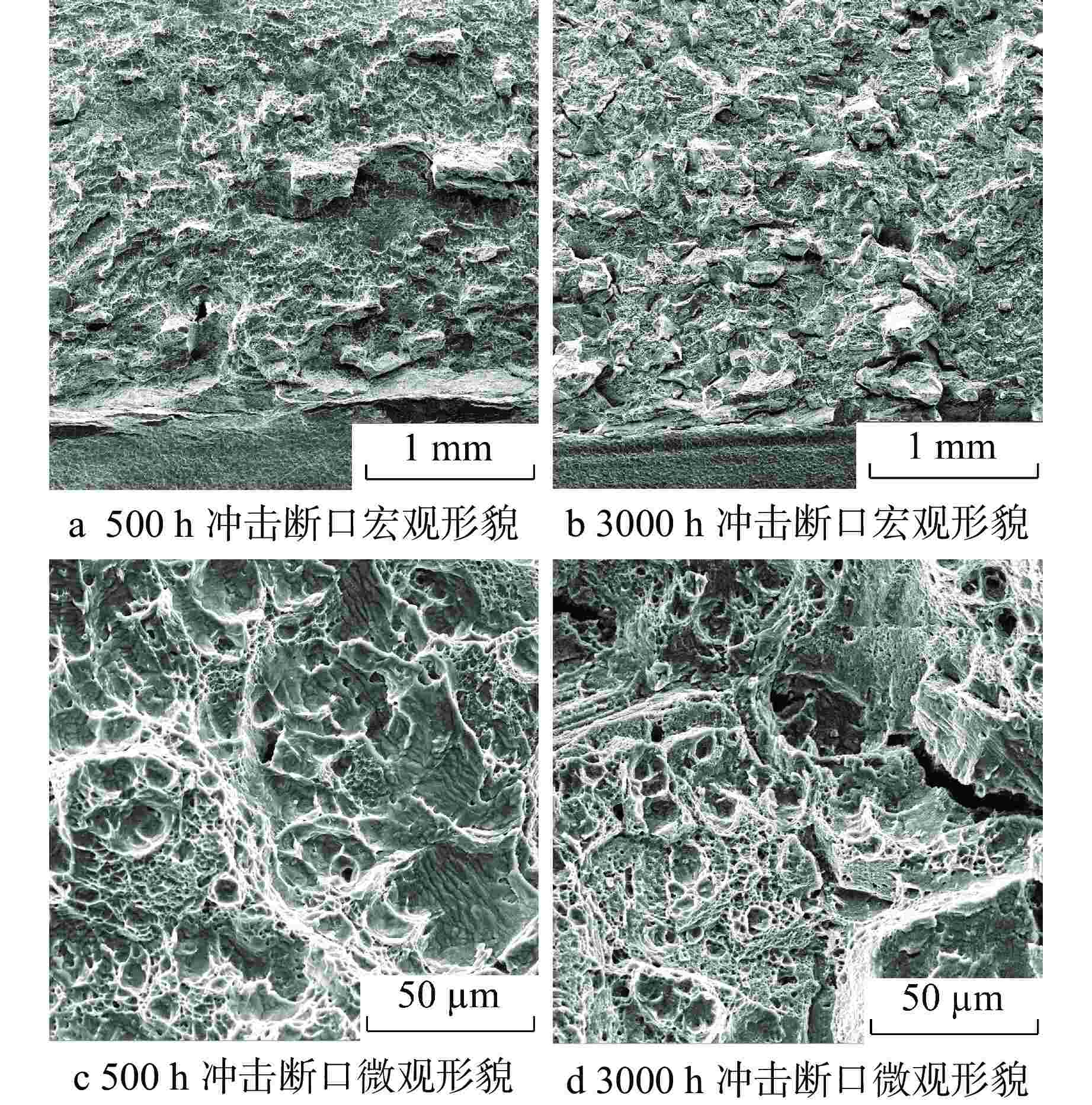
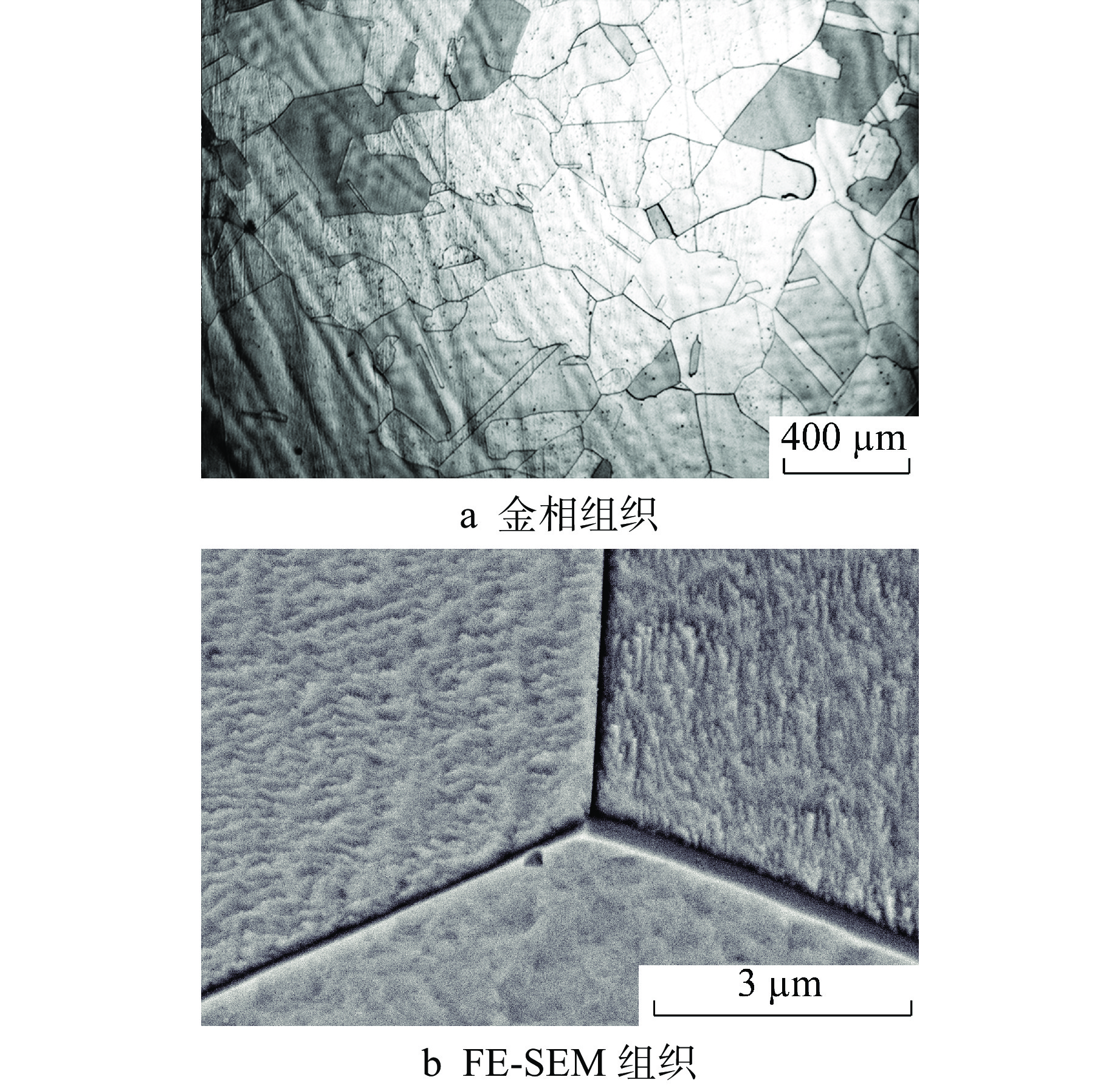
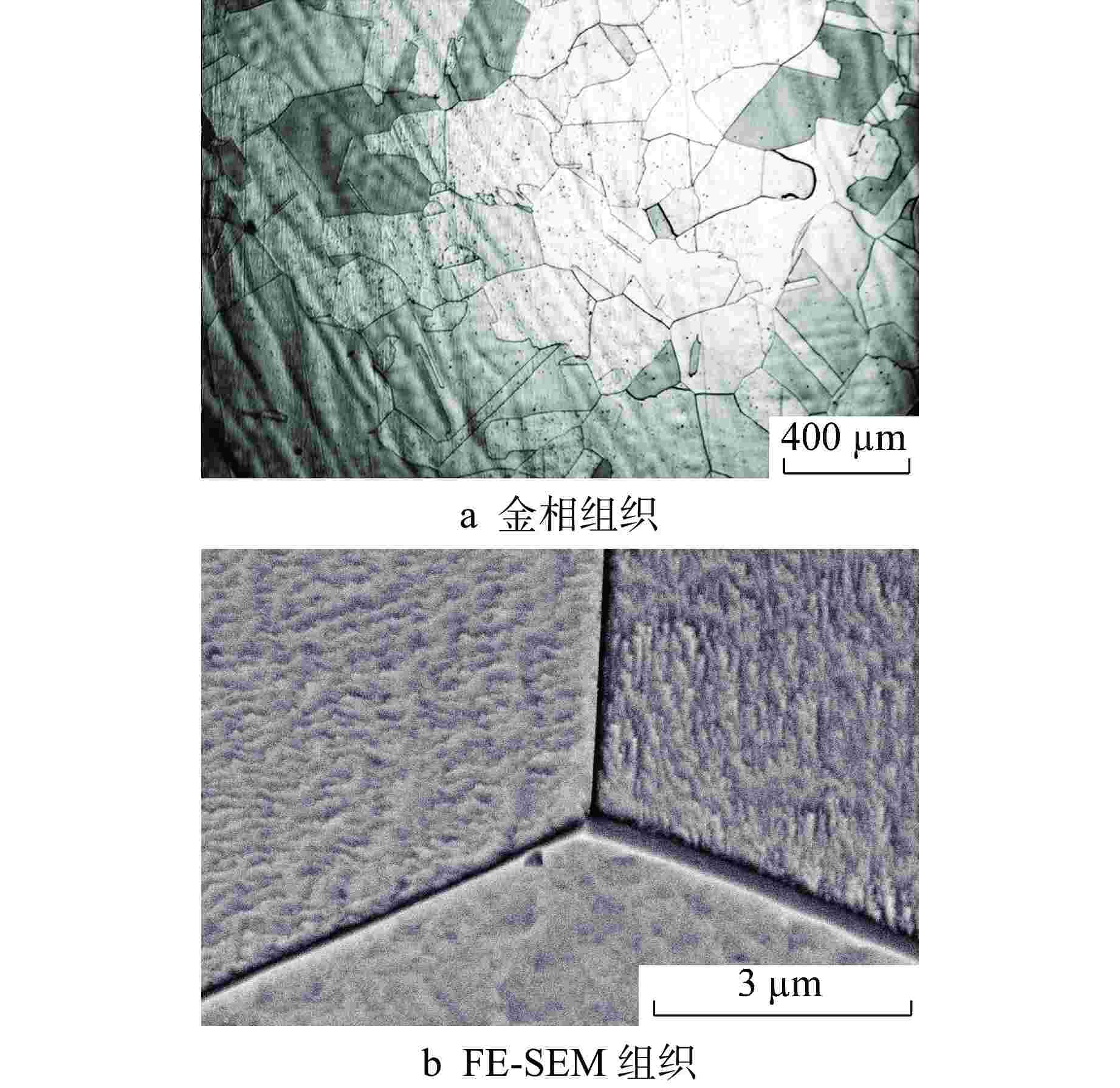
摘要: 为了研究热时效过程中超临界水冷堆(SCWR)用候选包壳材料含铝奥氏体耐热钢(AFA)热时效组织和冲击性能的变化,对铝含量为2.5%的AFA钢在650℃进行了500~3000 h热时效处理。利用场发射扫描电镜对析出相及冲击断口进行观察,利用透射电镜对热时效试验钢中析出相的类型和结构进行研究。结果表明:试验钢的冲击韧性随时效时间延长而逐渐降低,试验钢断裂由韧窝断裂逐渐向韧窝断裂和解理断裂的混合断裂方式过渡。热时效过程中Laves相在晶界上析出以及γ'-Ni3Al相大量析出并粗化是AFA钢冲击韧性随时效时间延长而降低的主要原因。
-
关键词:
- 超临界水冷堆(SCWR) /
- 燃料包壳 /
- AFA钢 /
- 冲击性能
Abstract: In order to study the change of thermal aged microstructure and impact properties of alumina-forming austenitic stainless (AFA) steel, a candidate cladding material for Supercritical water-cooled reactor(SCWR), the AFA steel with 2.5% aluminum content was subjected to thermal aging treatment at 650℃ for 500~3000 h. The precipitated phases and the impact fracture were observed by field emission scanning electron microscopy. The types and crystal structures of the precipitated phases were studied by transmission electron microscopy. The results show that the impact toughness of the test steel decreases gradually with the extension of aging time, and the fracture of the test steel gradually transits from dimple fracture to mixed fracture mode of dimple fracture and cleavage fracture. The precipitation of Laves phase at grain boundaries and the precipitation and coarsening of γ'-Ni3Al phase during thermal aging are the main reasons for the decrease of impact toughness of AFA steel with the extension of aging time.-
Key words:
- SCWR /
- Fuel cladding /
- AFA steel /
- Impact properties
-
表 1 AFA钢化学成分
Table 1. Chemical Composition of AFA Steel
元素 C Si Mn P S Ni Cr Cu Mo V Ti Al Nb B Fe 质量分数/% 0.024 0.081 0.051 0.0085 0.0066 23.46 13.980 0.007 1.981 0.014 0.013 2.507 0.470 0.005 57.40 -
[1] RAHMAN M M, JI D X, JAHAN N, et al. Design concepts of supercritical water-cooled reactor (SCWR) and nuclear marine vessel: A review[J]. Progress in Nuclear Energy, 2020, 124: 103320. doi: 10.1016/j.pnucene.2020.103320 [2] RODRIGUEZ D, CHIDAMBARAM D. Oxidation of stainless steel 316 and Nitronic 50 in supercritical and ultrasupercritical water[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2015, 347: 10-16. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.03.127 [3] CHOUDHRY K I, MAHBOUBI S, BOTTON G A, et al. Corrosion of engineering materials in a supercritical water cooled reactor: Characterization of oxide scales on Alloy 800H and stainless steel 316[J]. Corrosion Science, 2015, 100: 222-230. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2015.07.035 [4] SHEN Z, ZHANG L F, TANG R, et al. SCC susceptibility of type 316Ti stainless steel in supercritical water[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2015, 458: 206-215. doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2014.12.014 [5] YAMAMOTO Y, BRADY M P, LU Z P, et al. Creep-resistant, Al2O3-forming austenitic stainless steels[J]. Science, 2007, 316(5823): 433-436. doi: 10.1126/science.1137711 [6] YAMAMOTO Y, BRADY M P, LU Z P, et al. Alumina-forming austenitic stainless steels strengthened by laves phase and MC carbide precipitates[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2007, 38(11): 2737-2746. doi: 10.1007/s11661-007-9319-y [7] YAMAMOTO Y, BRADY M P, SANTELLA M L, et al. Overview of strategies for high-temperature creep and oxidation resistance of alumina-forming austenitic stainless steels[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2011, 42(4): 922-931. doi: 10.1007/s11661-010-0295-2 [8] 孙达云,高阳,张乐福,等. 新型含铝奥氏体不锈钢在超临界水环境下的腐蚀行为[J]. 核动力工程,2023,44(5):91-97. [9] 马赵丹丹,丛硕,陈勇,等. 含铝奥氏体耐热钢在超临界二氧化碳中的腐蚀行为[J]. 核动力工程,2022,43(6):101-107. doi: 10.13832/j.jnpe.2022.06.0101 [10] NIE S H, CHEN Y, REN X, et al. Corrosion of alumina-forming austenitic steel Fe-20Ni-14Cr-3Al-0.6Nb-0.1Ti in supercritical water[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2010, 399(2-3): 231-235. doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2010.01.025 [11] BEI H, YAMAMOTO Y, BRADY M P, et al. Aging effects on the mechanical properties of alumina-forming austenitic stainless steels[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2010, 527(7-8): 2079-2086. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2009.11.052 [12] TROTTER G, BAKER I. The effect of aging on the microstructure and mechanical behavior of the alumina-forming austenitic stainless steel Fe–20Cr–30Ni–2Nb–5Al[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2015, 627: 270-276. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2014.12.072 [13] SHEN L, WU B J, ZHAO K, et al. Reason for negative effect of Nb addition on oxidation resistance of alumina-forming austenitic stainless steel at 1323 K[J]. Corrosion Science, 2021, 191: 109754. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2021.109754 [14] 王雪俊,程晓农,罗锐,等. 新型含铝奥氏体耐热钢高温氧化行为[J]. 金属热处理,2019,44(9):5-10. doi: 10.13251/j.issn.0254-6051.2019.09.002 [15] WEN H Y, ZHAO B B, DONG X P, et al. How big is the difference between precipitation at twin boundary and normal grain boundary in an alumina-forming austenitic steel during creep at 700℃[J]. Materials Letters, 2020, 274: 128019. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2020.128019 [16] WEISS B, STICKLER R. Phase instabilities during high temperature exposure of 316 austenitic stainless steel[J]. Metallurgical Transactions, 1972, 3(4): 851-866. doi: 10.1007/BF02647659 [17] SHI C B, ZHU X, ZHENG X, et al. Precipitation and growth of Laves phase and NbC during aging and its effect on tensile properties of a novel 15Cr–22Ni–1Nb austenitic heat-resistant steel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2022, 854: 143822. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2022.143822 [18] GAO Q Z, LU B Y, MA Q S, et al. Effect of Cu addition on microstructure and properties of Fe-20Ni-14Cr alumina-forming austenitic steel[J]. Intermetallics, 2021, 138: 107312. doi: 10.1016/j.intermet.2021.107312 [19] YAMAMOTO Y, TAKEYAMA M, LU Z P, et al. Alloying effects on creep and oxidation resistance of austenitic stainless steel alloys employing intermetallic precipitates[J]. Intermetallics, 2008, 16(3): 453-462. doi: 10.1016/j.intermet.2007.12.005 [20] WANG L M, XUE C C, YANG G, et al. Laves phase in 22Cr-27Ni-2Ti-Al austenitic valve steel[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research International, 2016, 23(12): 1303-1308. doi: 10.1016/S1006-706X(16)30192-3 [21] MOON J, LEE T H, HEO Y U, et al. Precipitation sequence and its effect on age hardening of alumina-forming austenitic stainless steel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2015, 645: 72-81. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2015.08.005 [22] YAMAMOTO Y, MURALIDHARAN G, BRADY M P. Development of L12-ordered Ni3(Al, Ti)-strengthened alumina-forming austenitic stainless steel alloys[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2013, 69(11-12): 816-819. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2013.09.005 [23] JANG M H, MOON J, KANG J Y, et al. Effect of tungsten addition on high-temperature properties and microstructure of alumina-forming austenitic heat-resistant steels[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2015, 647: 163-169. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2015.09.018 [24] YAMAMOTO Y, SANTELLA M L, LIU C T, et al. Evaluation of Mn substitution for Ni in alumina-forming austenitic stainless steels[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2009, 524(1-2): 176-185. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2009.06.043 -





 下载:
下载: