Research on Fundamental Characteristics of Nuclear Grade 316H Stainless Steel at Ultra High Temperature
-
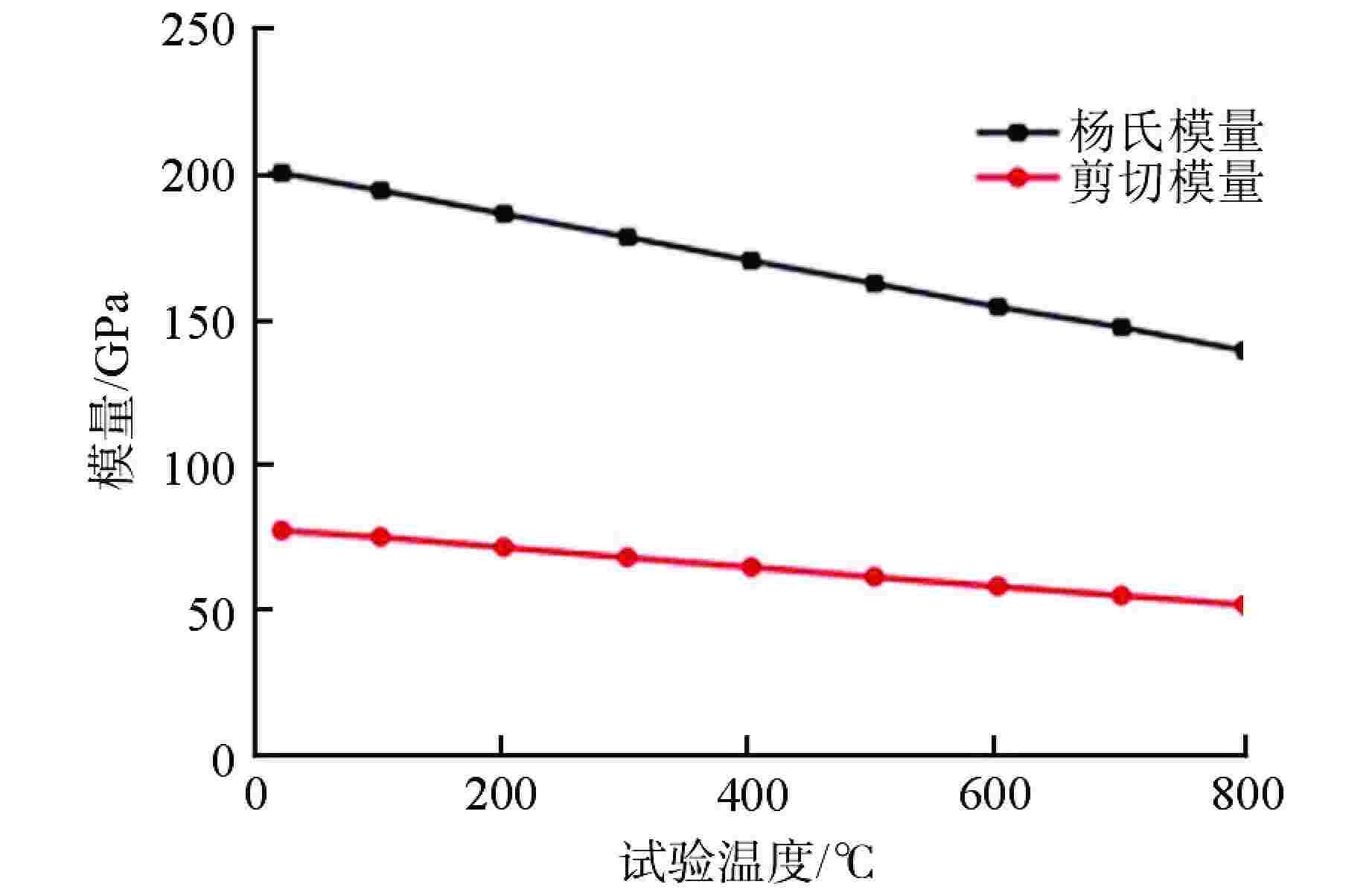
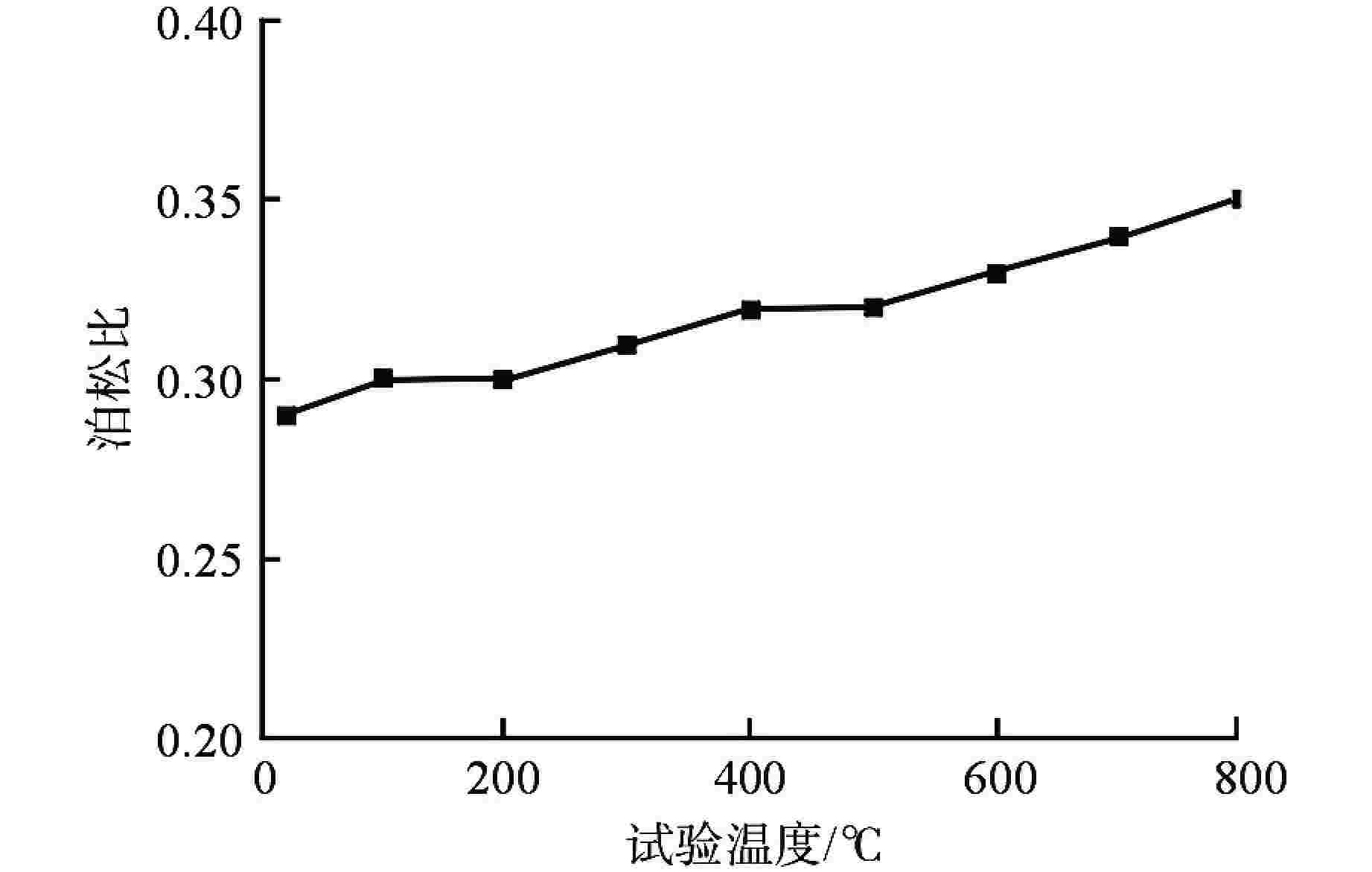
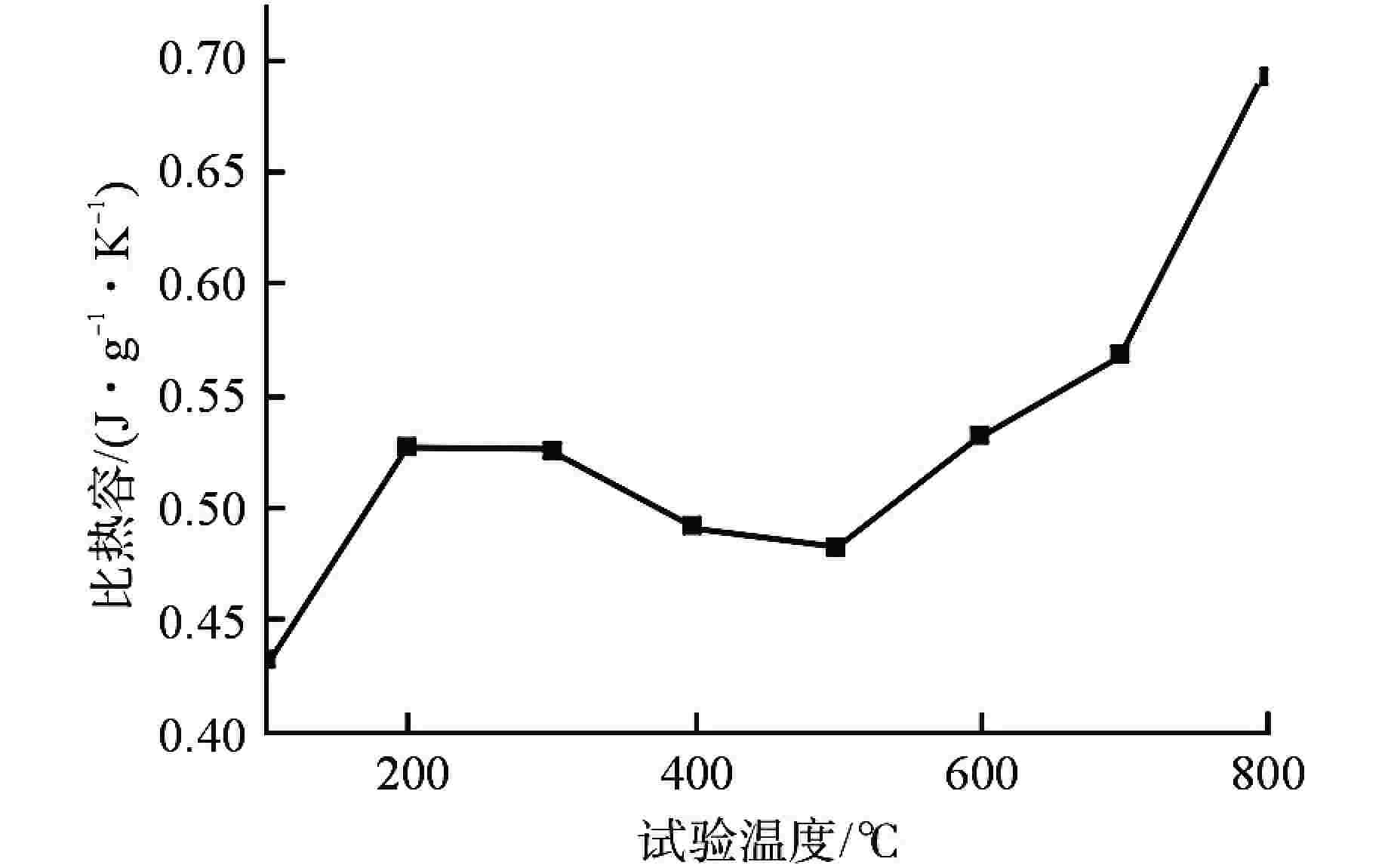
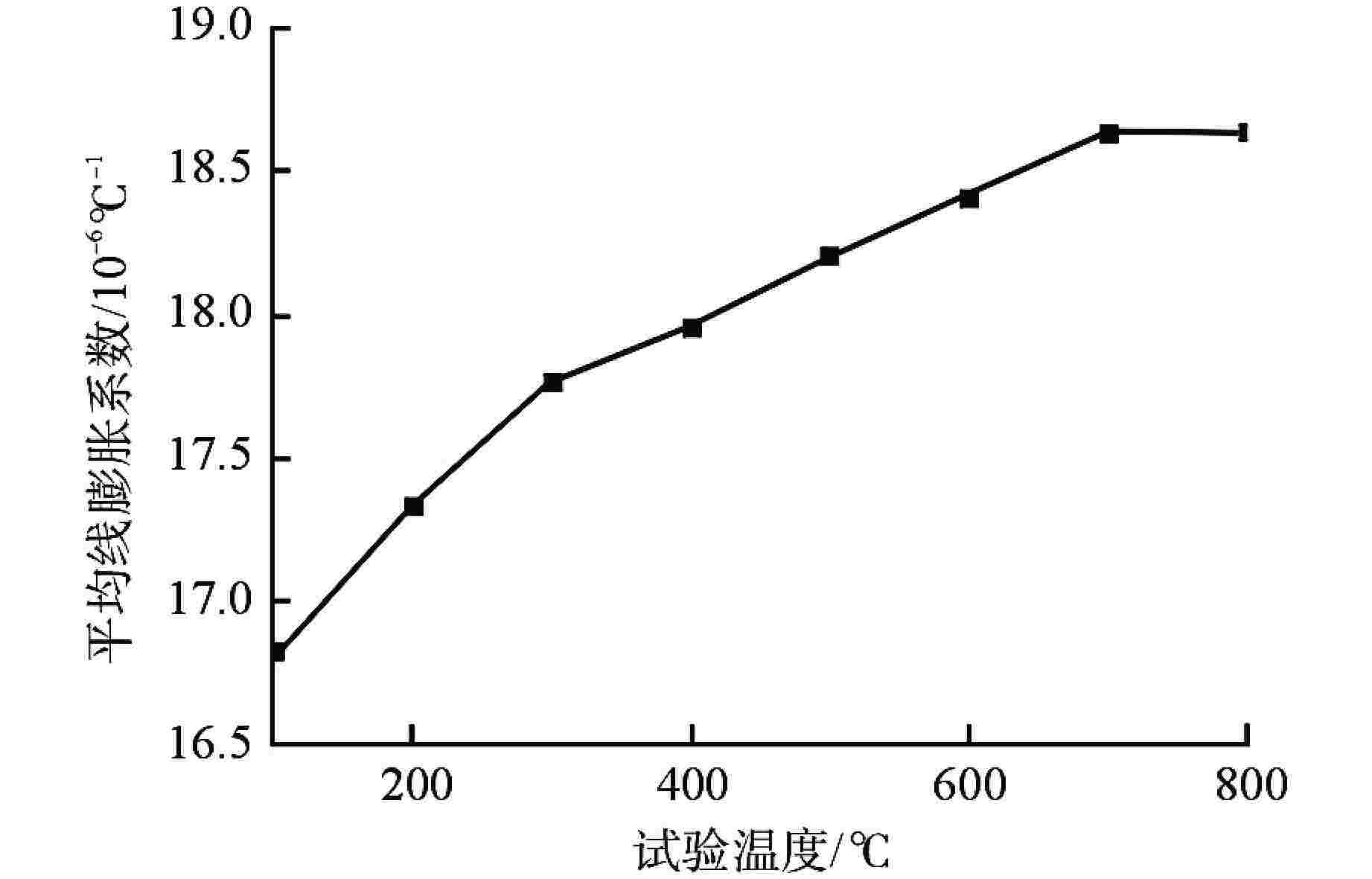
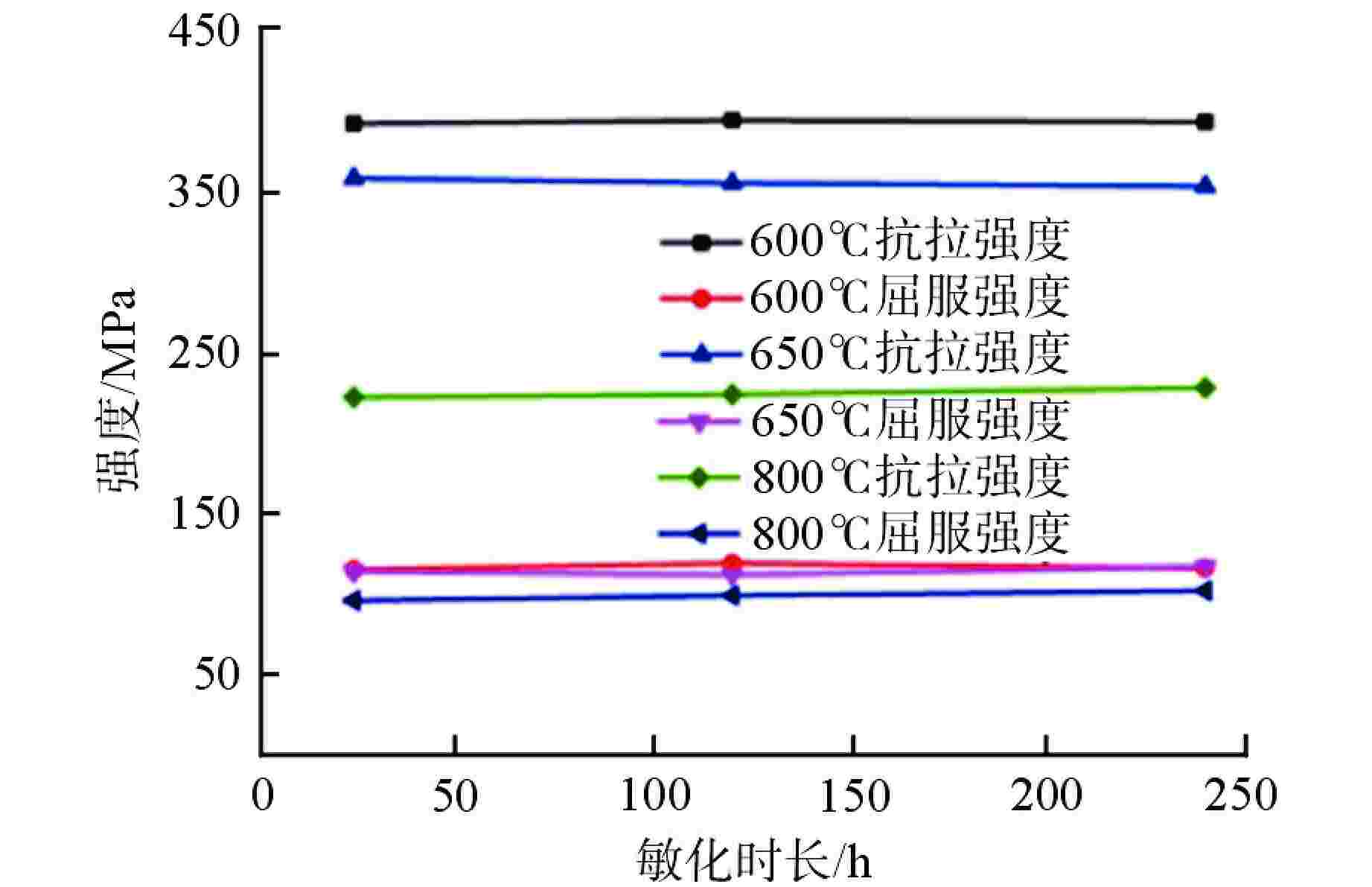
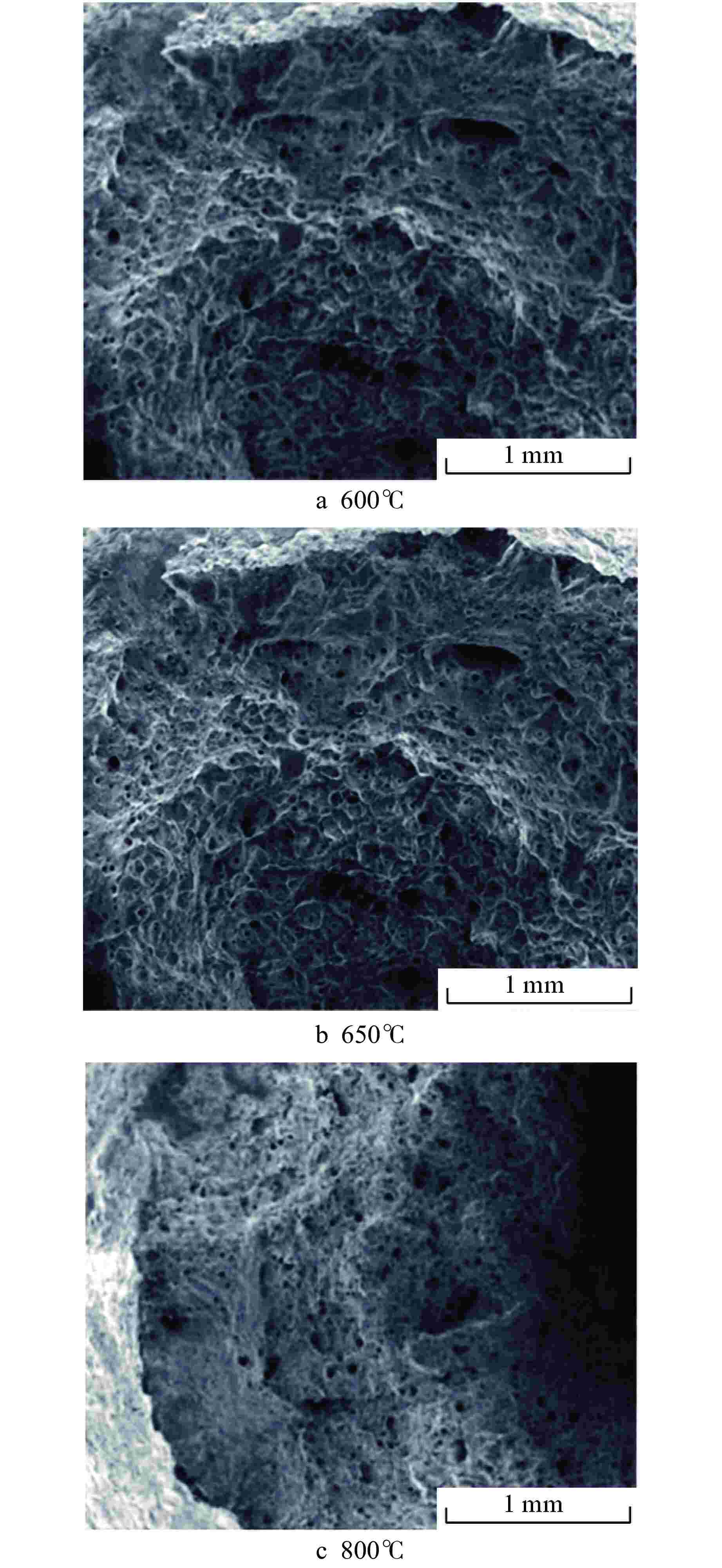
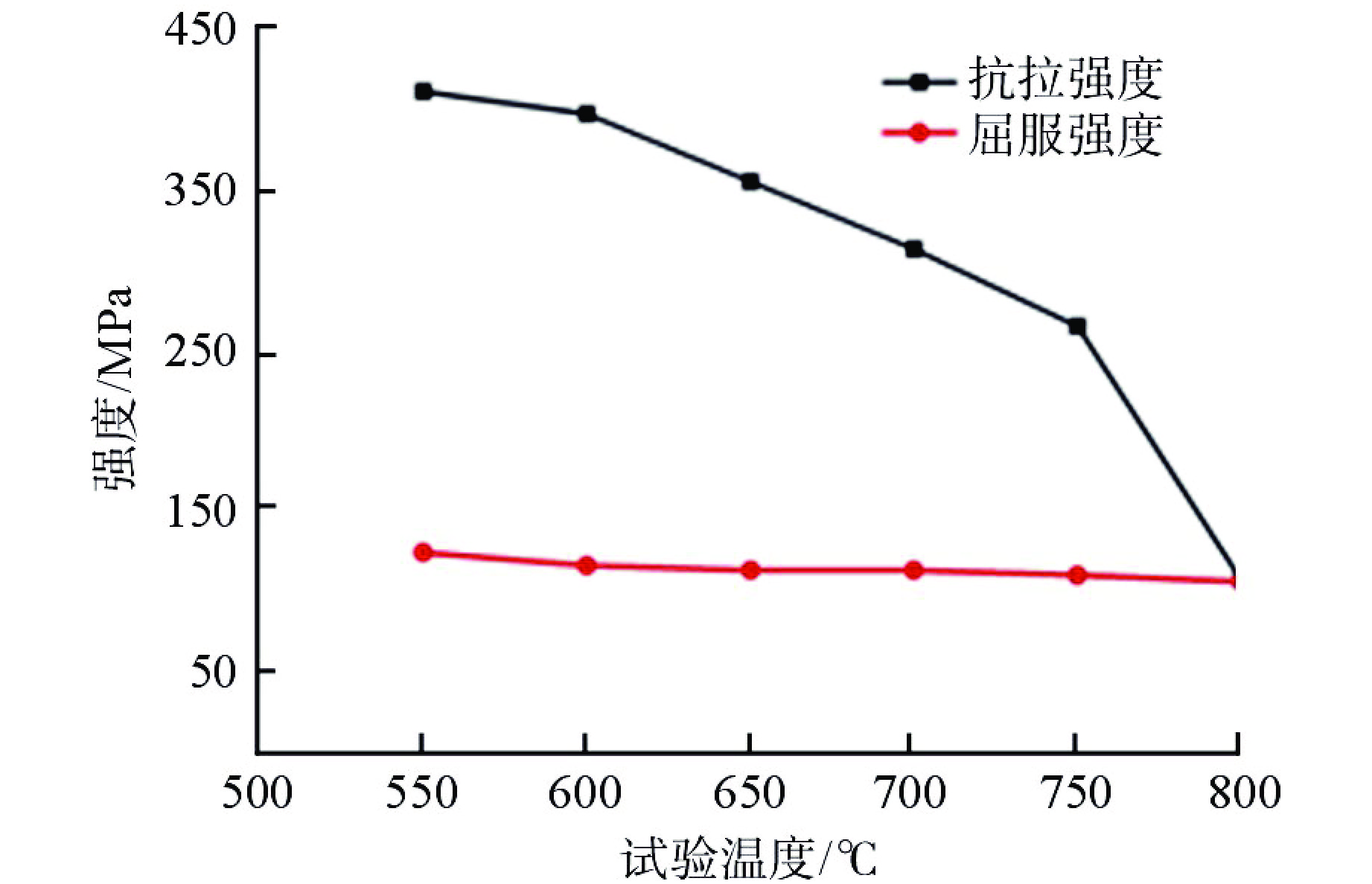
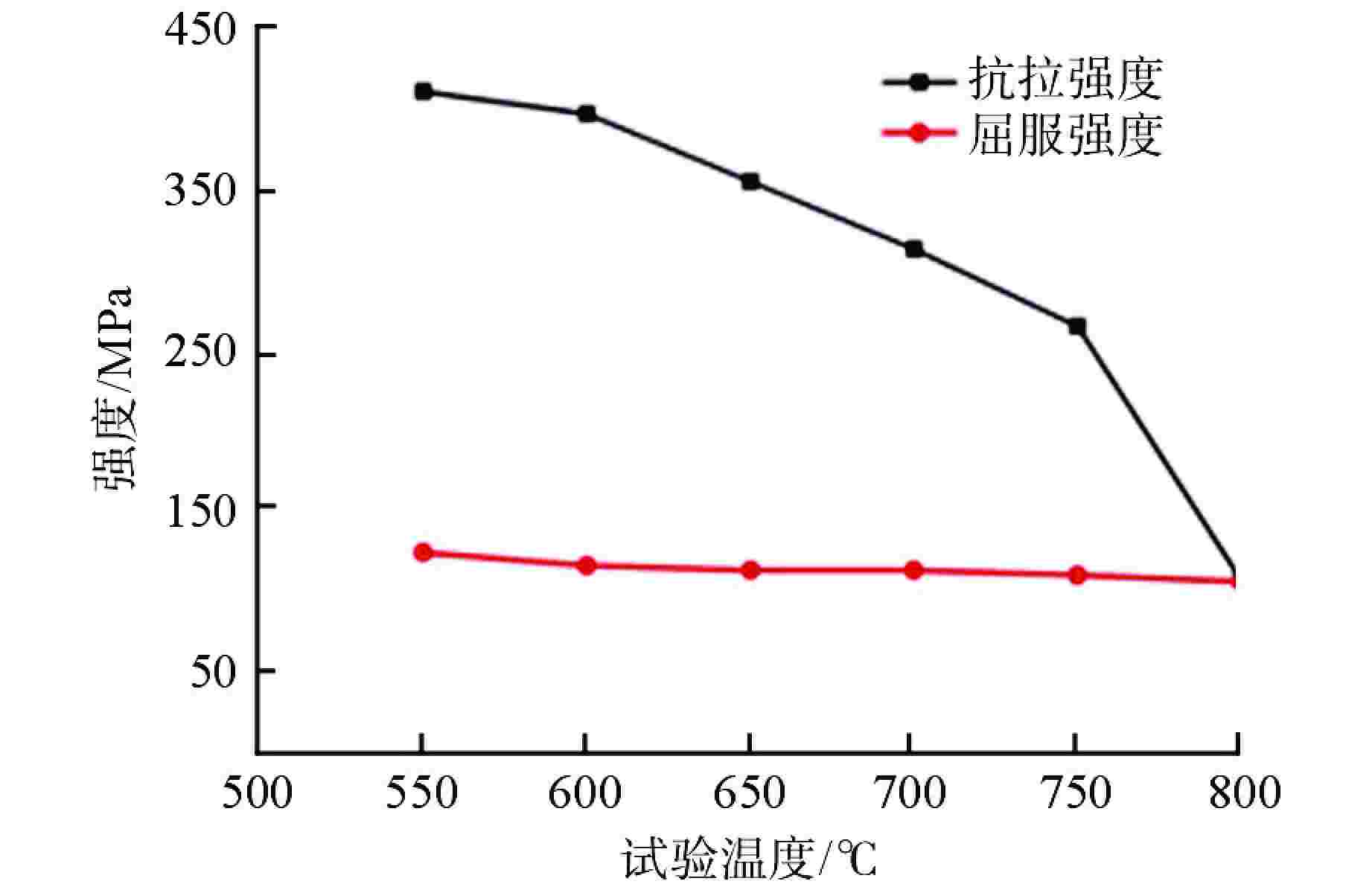
摘要: 第四代反应堆的一个基础特征是设计运行温度大多数在500~800℃,而传统压水堆材料体系和数据均在350℃以下得到,无法满足需求。本文通过广泛论证分析,筛选出了适用于大多数反应堆、最接近工程应用的316H不锈钢材料作为研究对象。开展800℃超高温下力学性能、比热容、平均线膨胀系数、晶间腐蚀特性、低周疲劳等试验研究,结果表明,316H不锈钢实测数据结果大幅高于规范标准值,长期应用温度限值建议不超过700℃,短时瞬态运行温度限值建议不超过800℃。该研究为第四代反应堆结构材料筛选和评价提供了依据。Abstract: A fundamental feature of the fourth-generation-reactor is that most of the designed operating temperature are between 500℃ to 800℃, while the traditional material system and data of the PWR are below 350℃, which cannot meet the requirements. In this paper, 316H is selected as the research object through demonstration and analysis, which is suitable for most reactors and closest to engineering application. The experimental study on mechanical properties, specific heat capacity, average linear expansion coefficient, intergranular corrosion characteristics and low cycle fatigue at 800℃ was carried out. the result shows that the measured data are significantly higher than the standard values. It is recommented that the temperature limit for the long-term operation shall not exceed 700℃, and the temperature limit for the short-term operation shall not exceed 800℃. This study provides a basis for the selection and evaluation of the structural materials of the fourth-generation-reactor.
-
Key words:
- 316H stainless steel /
- Ultra high temperature /
- Mechanical properties /
- Low cycle fatigue
-
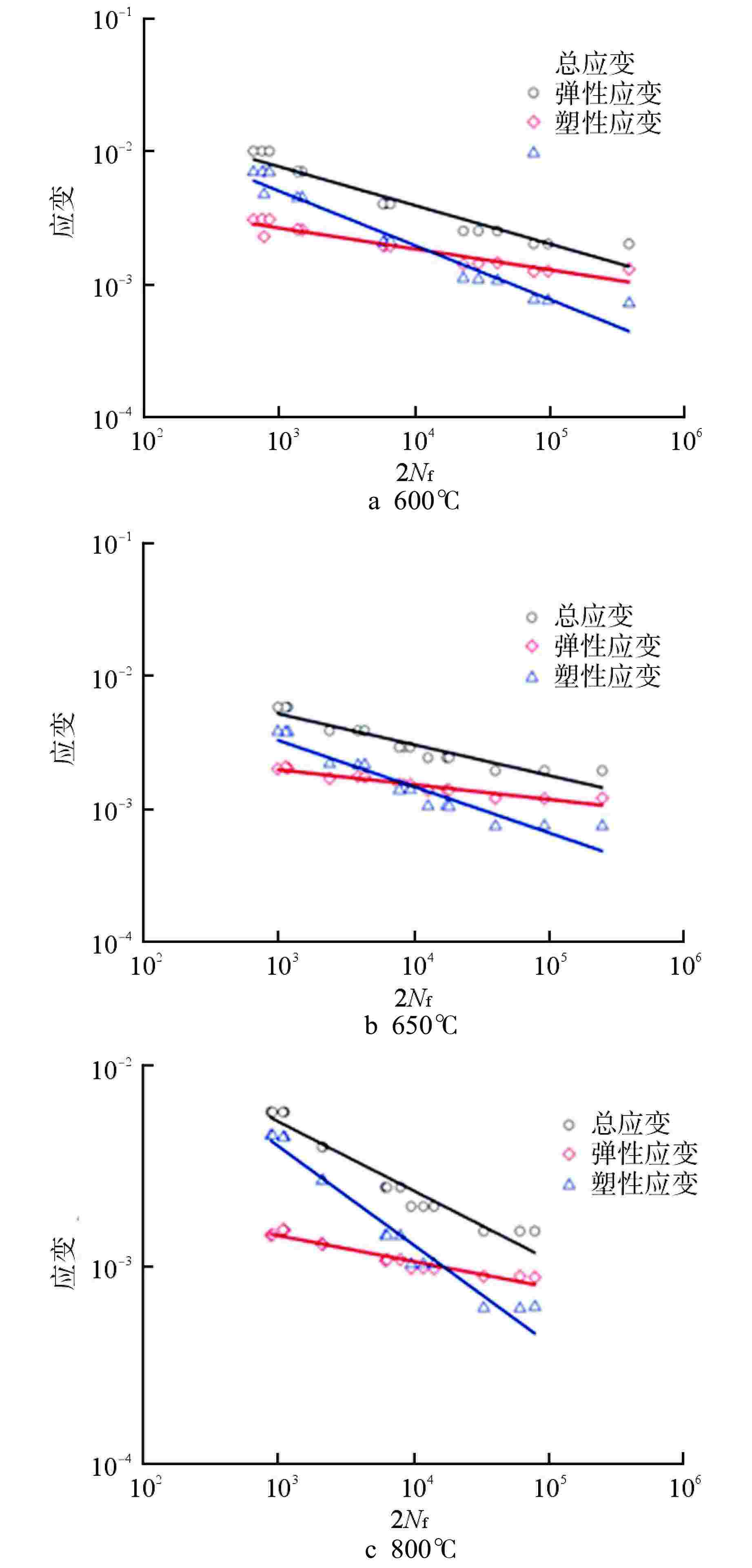
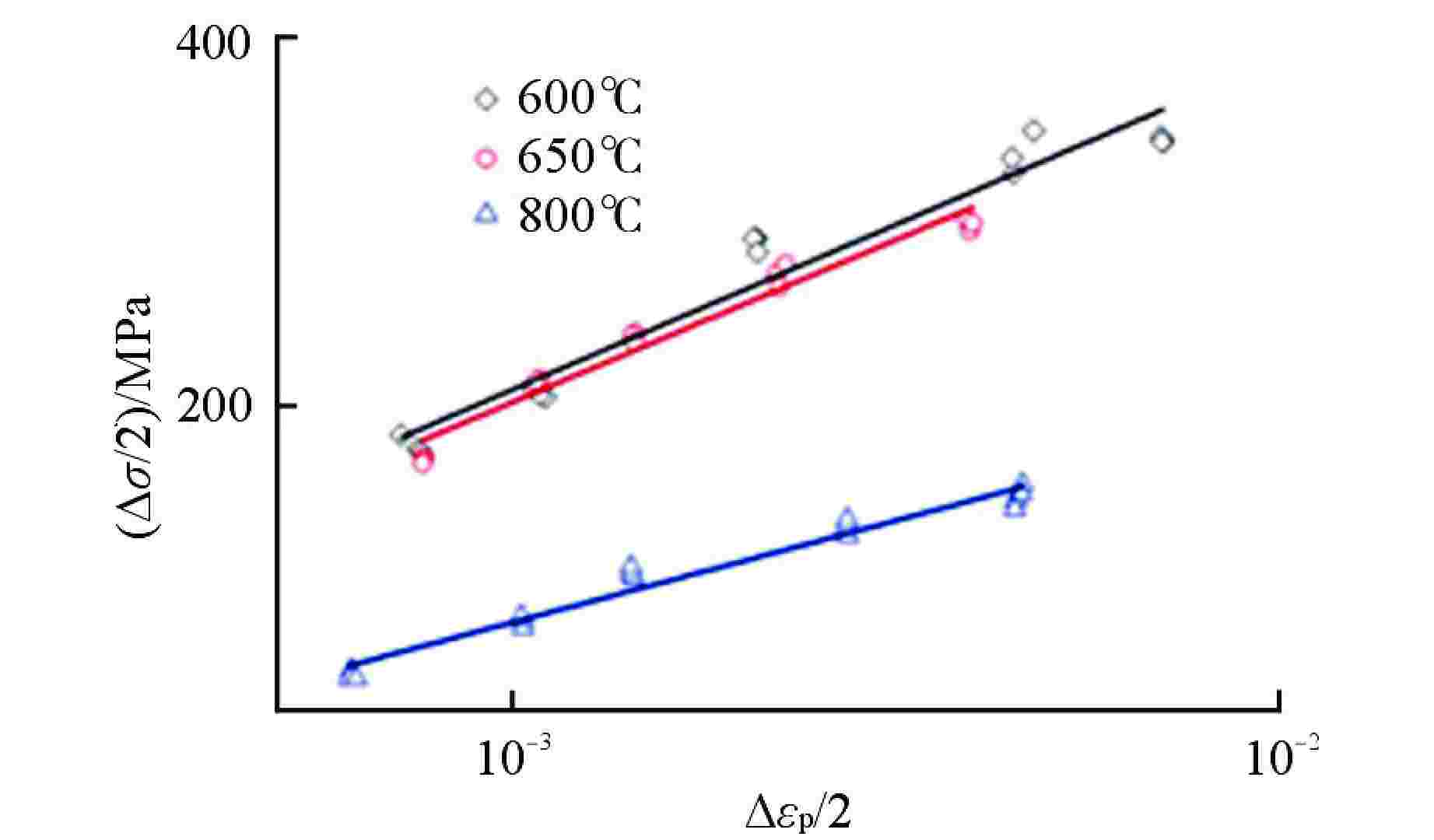
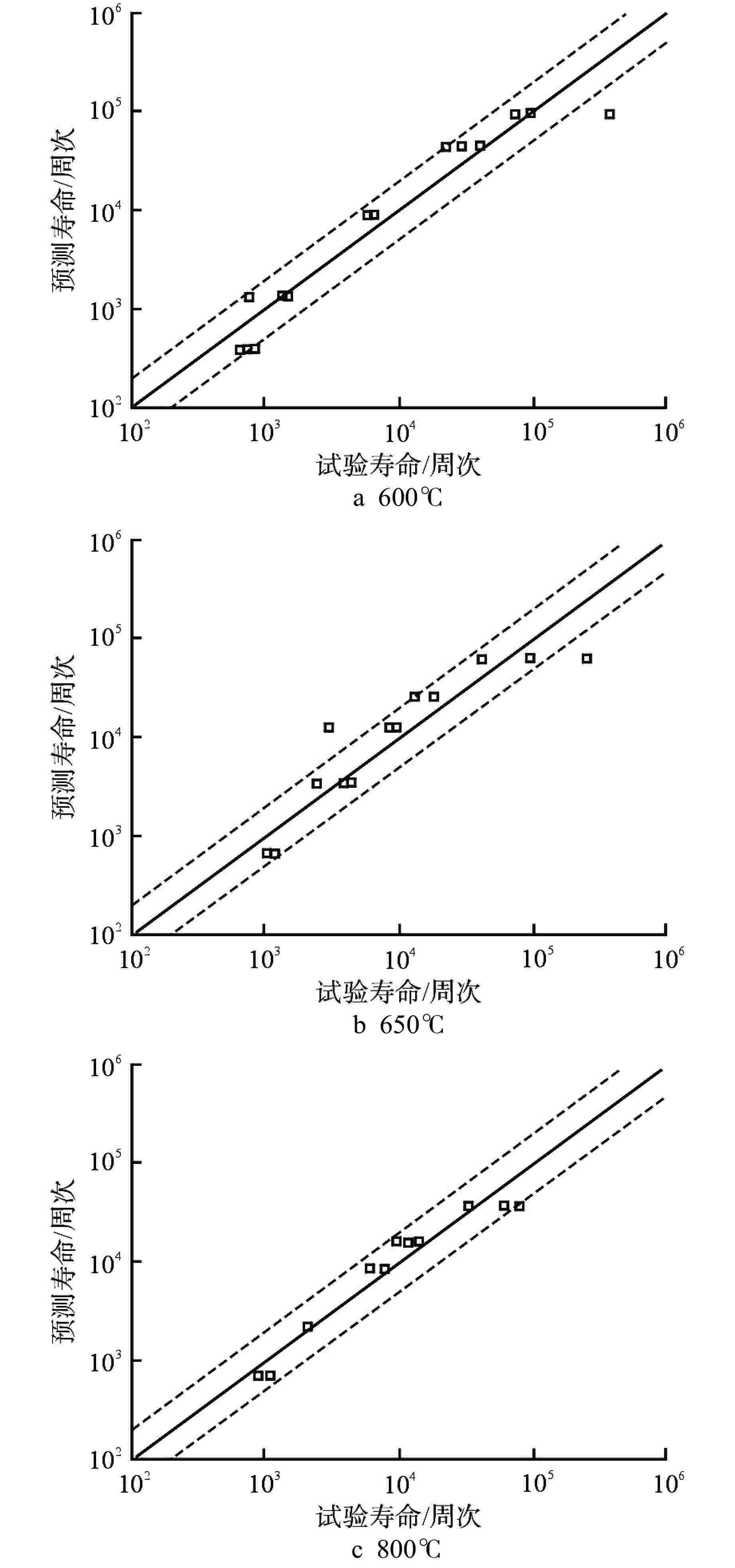
表 1 拟合得到的高温疲劳参数
Table 1. Fitting for High Temperature Fatigue Parameters
温度/℃ $\sigma {'_{\rm{f}}} $/MPa b ε′f c 600 1053 −0.1577 0.0847 −0.4097 650 632 −0.1118 0.0378 −0.3485 800 452 −0.131 0.1246 −0.4983 表 2 不同温度下316H的
$k'$ 和$n'$ Table 2.
$k'$ and$n'$ of 316H at Different Temperature温度/℃ $k'$ $n'$ 600 1345 0.2708 650 1273 0.2663 800 427 0.1683 -
[1] 李长香,莫锦涛,段春辉. 316不锈钢长时总体一次薄膜应力强度许用值预测方法研究[J]. 核动力工程,2020, 41(5): 49-52. [2] 谭晓惠,马建中,刘宇杰,等. 316不锈钢蠕变-疲劳交互作用试验研究[J]. 核动力工程,2013, 34(1): 140-145. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0926.2013.01.029 [3] ZHAO L L, WEI S T, WU D, et al. δ-ferrite transformation mechanism and its effect on mechanical properties of 316H weld metal[J]. Journal of Materials Science and Technology, 2020(57): 33-42. [4] 武宜梁,缪宏,滕增,等. 316H奥氏体不锈钢焊接接头裂纹失效分析[J]. 化工装备技术,2016, 37(2): 40-42+46. [5] MEHMANPARAST A, DAVIES C M, DEAN D W, et al. Material pre-conditioning effects on the creep behaviour of 316H stainless steel[J]. International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 2013(108-109): 88-93. [6] MEHMANPARAST A. Prediction of creep crack growth behaviour in 316H stainless steel for a range of specimen geometries[J]. International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 2014(120-121): 55-65. [7] MEHMANPARAST A, DAVIES C M, DEAN D W. Effects of plastic pre-straining level on the creep deformation, crack initiation and growth behaviour of 316H stainless steel[J]. International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 2016(141): 1-10. [8] DEAN D W, ALLPORT L. Difficulties in interpreting data from creep crack growth tests on type 316H weldments[J]. Materials Research Innovations, 2013, 17(5): 344-349. doi: 10.1179/1432891713Z.000000000254 [9] HARES E A, MOSTAFAVI M, BRADFORD R. The effect of creep strain rate on damage accumulation in Type 316H austenitic stainless steel[J]. International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 2018(168): 132-141. [10] 姜恒,江慧丰,范志超,等. 保载应力和加载速率对316H不锈钢蠕变行为的影响[J]. 压力容器,2011, 28(8): 6-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4837.2011.08.002 [11] 张博俊,余华金,荆洪阳,等. 核级316H 管道熔敷金属蠕变性能表征[J]. 焊接学报,2019, 40(12): 97-102. [12] AFCEN. Design and construction rules for mechanical components of PWR nuclear islands: RCC-M 2007[S]. France: AFCEN, 2007. [13] ASME. ASME boiler and pressure vessel code[S]. USA: ASME, 2007. [14] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 金属材料 拉伸试验 第2部分: 高温试验方法: GB/T 228.2—2015[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2015. [15] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 金属材料 弹性模量和泊松比试验方法: GB/T 22315—2008[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008. [16] 国家技术监督局. 贵金属及其合金熔化温度范围的测定 热分析试验方法: GB/T 1425—1996[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 1997. [17] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 金属材料热膨胀特征参数的测定: GB/T 4339—2008[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2009. [18] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 金属和合金的腐蚀 不锈钢晶间腐蚀试验方法: GB/T 4334—2008[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2009. [19] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 金属材料轴向等幅低循环疲劳试验方法: GB/T 15248—2008[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008. -





 下载:
下载: