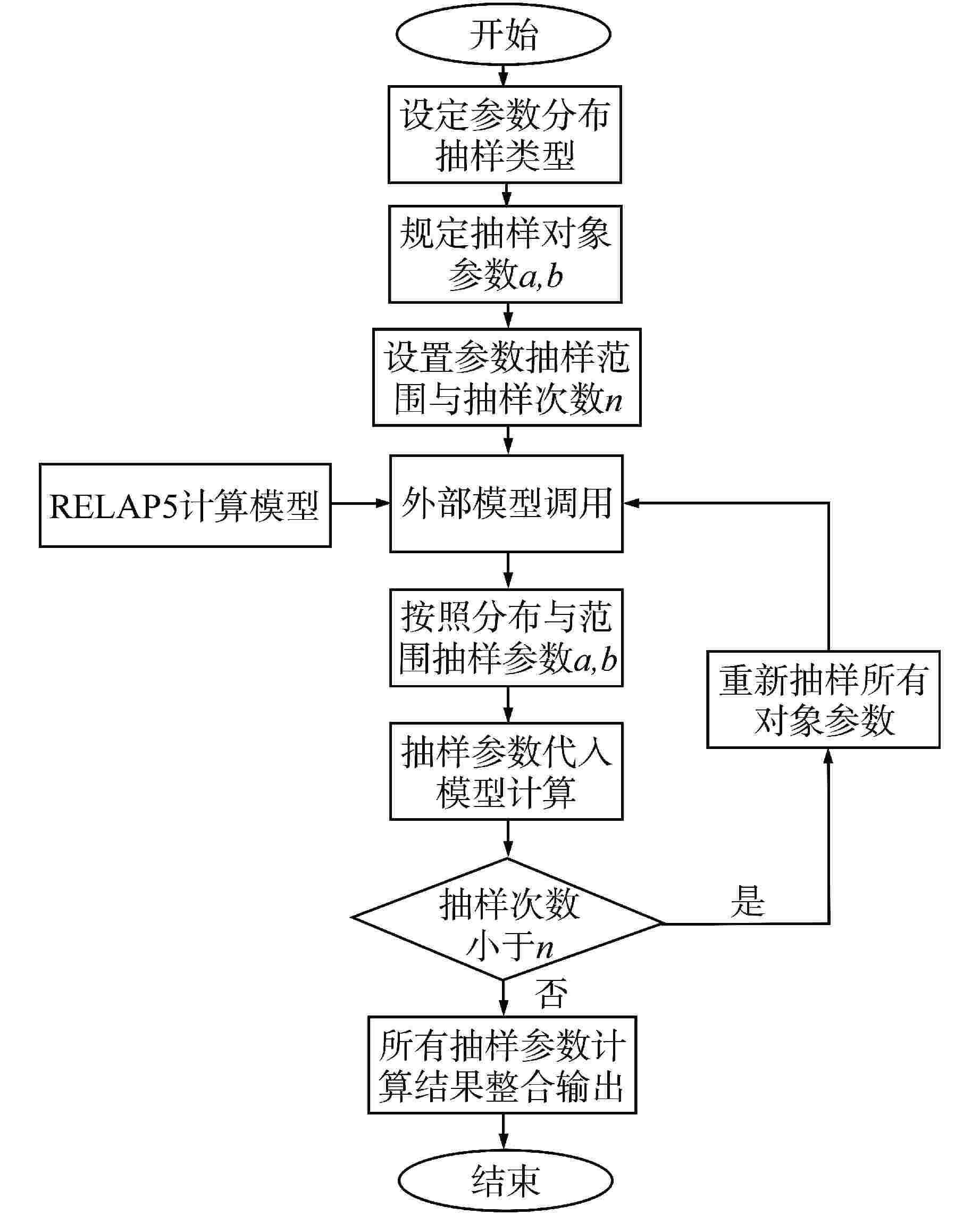
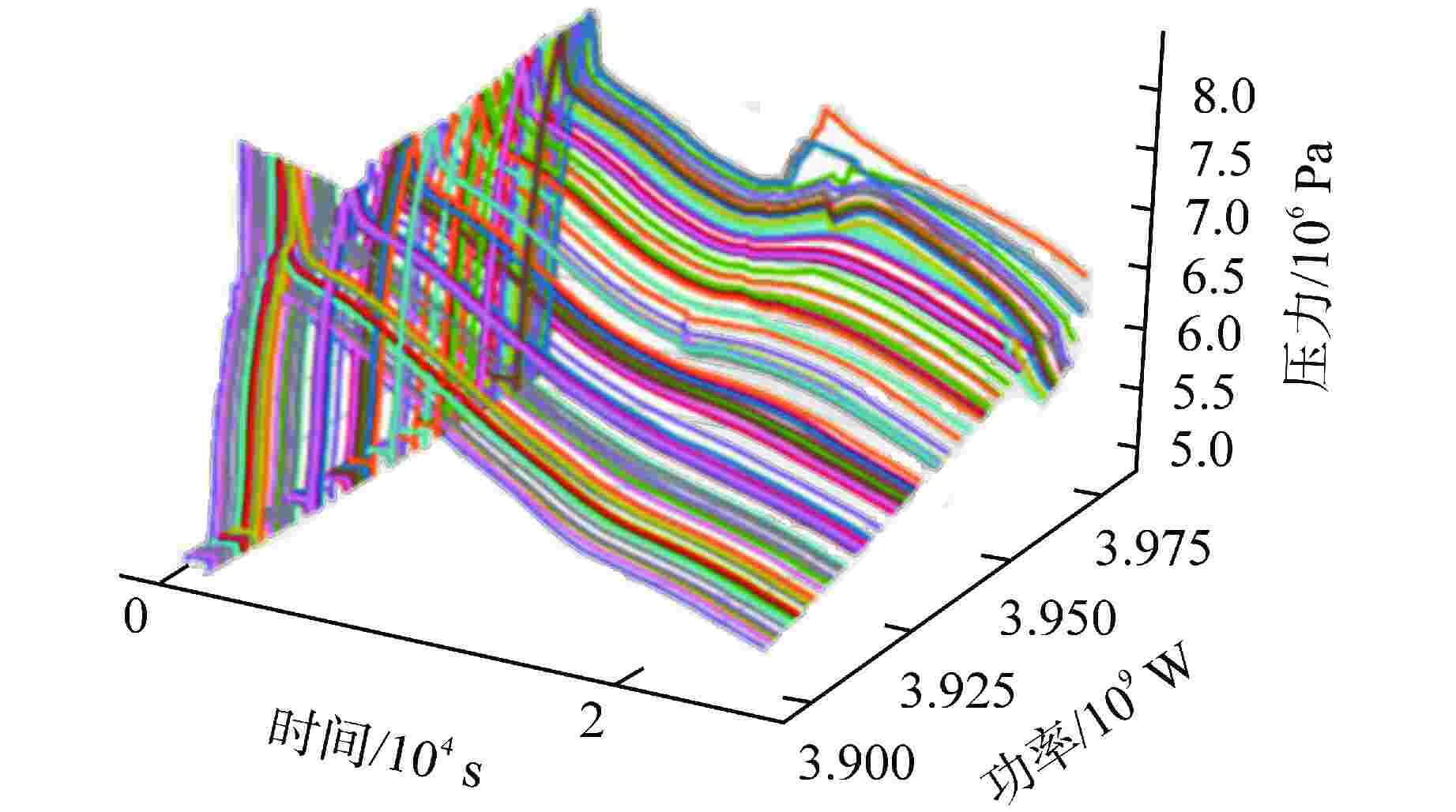
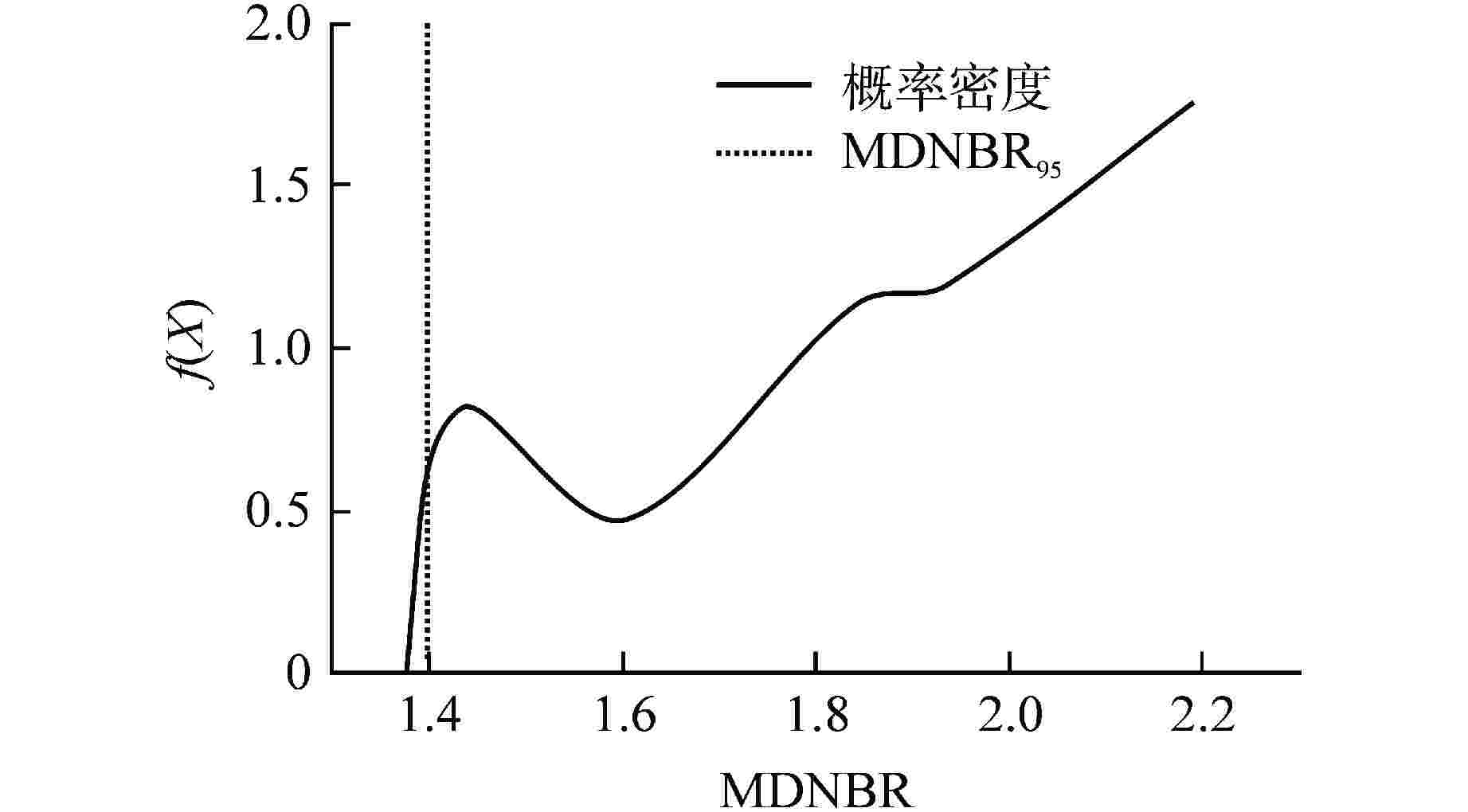
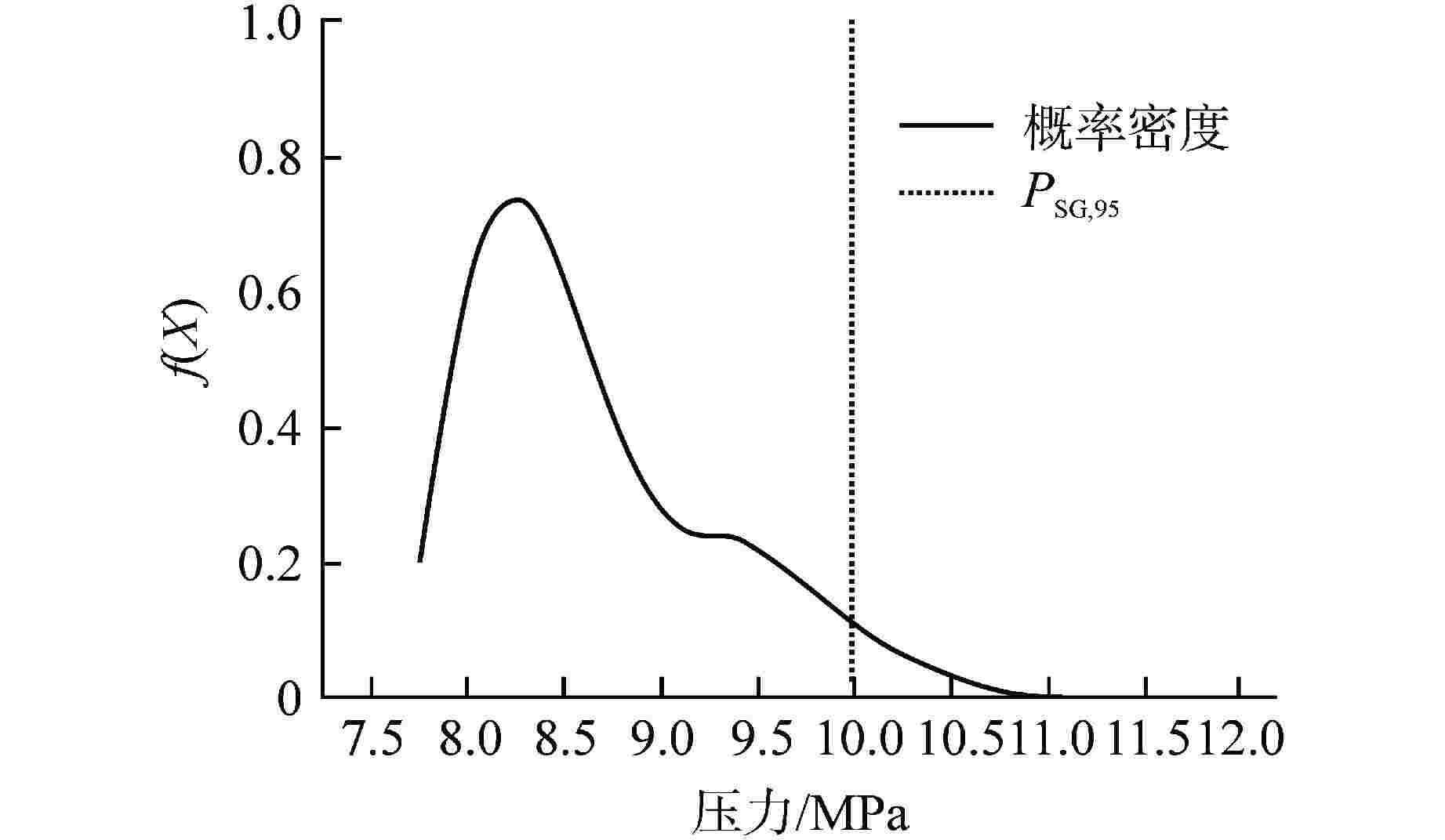
Research on Probabilistic Safety Margin Analysis Method of SGTR Based on Raven
-
摘要: 介绍了一种基于RAVEN软件通过蒙特卡洛(MC)抽样的风险指引的安全裕度特性分析(RISMC)方法,综合分析热工参数、人员动作时刻不确定性对蒸汽发生器传热管破裂(SGTR)事故安全裕度的影响,并将计算结果与传统安全评价方法进行比证。针对事故关键影响参数,基于MC抽样量化影响安全裕度的关键参数样本,利用RELAP5程序建立SGTR事故的系统仿真模型,通过RAVEN软件进行耦合计算并加以分析,最终获得该电厂模型在辅助给水系统失效情况下SGTR事故的概率安全裕度及其对各影响参数的敏感度。
-
关键词:
- 风险指引的安全裕度特性分析(RISMC) /
- 蒙特卡洛(MC)抽样 /
- RAVEN /
- 蒸汽发生器传热管破裂事故(SGTR)
Abstract: A Risk-informed Safety Margin Characterization (RISMC) analysis method based on RAVEN software and Monte Carlo (MC) sampling is introduced in the paper. The influence of thermal parameters and personnel action time uncertainty on the safety margin of steam generator tube rupture (SGTR) accident is comprehensively analyzed. The calculation results are compared with the traditional safety assessment methods. Aiming at the key influence parameters of the accident, based on MC sampling to quantify the key parameter samples affecting the safety margin, the system simulation model of SGTR accident is established by RELAP5 program, coupled calculation and analysis are carried out by RAVEN software. And finally the probabilistic safety margin of SGTR accident and its sensitivity to various influencing parameters are obtained under the condition of auxiliary water supply system failure. -
表 1 耦合文件说明
Table 1. Description of Coupling Documents
模块名称 作用说明 实现功能 <Simulation> 包含整个输入的根节点,下列所有模块都包含在Simulation模块内 程序开始与结束的标志 <RunInfo> 指定计算的设置,如并行模拟的数量等 运行信息说明 <Files> 指定要在计算中使用的文件 RELAP5模型的调用 <Models> 系统仿真模型以及后处理分析等 <Distributions> 定义描述参数等所需的分布 MC抽样的实现 <Samplers> 建立用于模拟不确定性参数的策略 <DataObjects> 指定RAVEN使用的内部数据对象 参数输入及结果输出 <Databases> 列出作为RAVEN运行的输入/输出的HDF5数据库 <OutStreams> 可视化和打印系统模块 <Steps> 结合其他模块说明RAVEN工作流的一个步骤,包括要执行的输入/输出(I/O)和计算 统合各模块成工作流程 表 2 系统主要参数
Table 2. Main Parameters of System
参数名 模型设定值 反应堆热功率/MW 3900 运行压力/MPa 15.50~15.70 堆芯冷却剂流量/(kg·s−1) 20.60 堆芯进口温度/K 560.1 堆芯出口温度/K 589.5 蒸汽发生器(SG)二次侧压力/MPa 4.85~5.10 表 3 SGTR事故序列
Table 3. SGTR Accident Sequence
序号 事故序列 时间/s 1 SG传热管断裂 500 2 稳压器低压停堆信号 990 3 汽轮机跳闸 991 4 关闭主蒸汽管道阀门 991 5 蒸汽释放阀开启 992 6 高压安注信号 995 7 切除主给水 998 8 辅助给水投入信号(投入失败) 998 9 操纵员隔离破损SG 1295 10 停止主泵运行 1295 11 隔离破损SG 1295 12 操纵员执行feed-bleed措施 3295 13 SGTR侧高压安注停止运行 3295 14 打开稳压器安全阀 3295 13 一、二回路压力共同下降 3310 表 4 确定论分析SGTR事故安全裕度
Table 4. Safety Margin for Deterministic Analysis of SGTR
参数名称 计算极限值 失效值 安全裕量 安全裕度百分比/% SG压力/MPa 9.08 10.1 1.02 10.10 一回路压力/MPa 16.6 19.62 3.02 15.39 SG水位/m 17.1 19 1.9 10.00 包壳温度/℃ 589.3 1204 614.7 51.05 包壳DNBR 1.48 1.3 0.18 13.85 安全裕度百分比 = (安全裕量/失效值)×100% 表 5 SGTR事故重要影响参数及其不确定性
Table 5. Important Influence Parameters and Uncertainties of SGTR Accidents
序号 影响参数 分布形式[11] 不确定性范围 备注 1 堆芯功率 均匀分布 1.00~1.02[12] 乘数因子 2 稳压器压力/MPa 均匀分布 −0.34~+0.36[11] 附加值 3 安注箱压力 正态分布 0.9~1.1[12] 乘数因子α=0.025 4 安注箱温度/K 均匀分布 −11.11~+16.67[12] 附加值 5 主给水流量 正态分布 0.9646~1.0354[15] 乘数因子α=0.0177 6 主蒸汽流量 正态分布 0.9646~1.0354[15] 乘数因子α=0.0177 7 主给水温度/K 均匀分布 −1.67~+1.67[12] 附加值 8 环境温度/K 均匀分布 298~310 经验值 9 操纵员介入时间/s 均匀分布 300~500[13] 此外时间是安注信号发出后的时间而非模拟时间 10 进行feed-bleed操作的时间/s 均匀分布 30~2200[13] 此外时间是在操纵员介入后的计时而非模拟时间 表 6 各影响参数对事故后果的影响对比
Table 6. Comparison of Influence Parameters on Accident Consequence
影响参数名称 MDNBR1范围/% Ps范围/% PCT1范围/% Psg范围/% 堆芯功率 58.35~93.22 87.37~87.48 39.89~39.95 74.95~83.24 稳压器最低压力 59.06~94.20 87.42~87.48 39.87~39.89 83.26~84.16 稳压器最高压力 58.24~59.27 87.43~87.48 39.88~39.89 83.23~83.36 安注箱压力 59.27 86.09 39.89 83.27 安注箱温度 59.27 86.09 39.89 83.27 完好SG主给水/蒸汽流量 58.25~69.71 87.41~87.48 39.88~39.89 81.38~85.55 破损SG主给水/蒸汽流量 58.25~61.48 87.41~87.48 39.88~39.89 75.56~84.86 主给水温度 58.28~60.14 87.41~87.48 39.88~39.89 76.77~84.25 环境温度 59.27~59.36 87.40~87.48 39.88~39.89 81.93~83.24 操纵员介入时间 59.27~59.28 87.40~87.48 39.88~39.89 83.25~90.00 feed-bleed启动时间 59.27~59.28 87.47~87.48 39.88~39.89 61.70~95.15 MDNBR1=1.3/MDNBR;Ps=稳压器最高压力/19.62;PCT1=PCT/1477.1;Psg=SG最高压力/10.10 表 7 参数不确定性下SGTR事故MDNBR分布
Table 7. MDNBR Distribution of SGTR Accident under Parameter Uncertainty
MDNBR分布区间 均值 频次 1.35~1.45 1.40 151 1.45~1.55 1.49 43 1.55~1.65 1.60 46 1.65~1.75 1.71 56 1.75~1.85 1.81 130 1.85~1.95 1.90 114 1.95~2.05 2.00 123 2.05~2.15 2.10 163 2.15~2.25 2.19 174 表 8 参数不确定性下SGTR事故SG最高压力分布
Table 8. Maximum SG Pressure Distribution of SGTR Accident under Parameter Uncertainty
SG最高压力分布区间/MPa 均值/MPa 频次 6.10~6.60 6.38 295 6.60~7.10 6.88 193 7.10~7.60 7.35 231 7.60~8.10 7.85 151 8.10~8.60 8.31 70 8.60~9.10 8.81 30 9.10~9.60 9.31 17 9.60~10.10 9.81 10 10.10~10.60 10.17 3 -
[1] 汤搏,种毅敏,张和林,等. 关于PRA技术在国内核安全管理中应用的若干问题[J]. 核安全,2007(3): 10-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5360.2007.03.003 [2] SMITH C, SCHWIEDER D, PHELAN C, et al. Light water reactor sustainability program: risk informed safety margin characterization (RISMC) advanced test reactor demonstration case study: INL/EXT-12-27015[R]. Idaho: Idaho National Laboratory, 2012. [3] EPINEY A S, ALFONSI A, PARISI C, et al. RISMC industry application #1 (ECCS/LOCA): Core characterization automation: Lattice codes interface for PHISICS/RELAP5-3D[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2019(345): 15-27. doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2019.02.005 [4] SMITH C, RABITI C, SZILARD R. Risk-Informed safety margins characterization (RISMC) pathway technical program plan: INL/EXT-17-43243-Rev000[R]. Idaho: Idaho National Laboratory, 2017. [5] MANDELLI D, RABITI C, COGLIATI J J, et al. RAVEN user manual: INL/EXT-15-34123[R]. Idaho: Idaho National Laboratory, 2015. [6] ALFONSI A, RABITI C, MANDELLI D, et al. RAVEN user guide: INL/EXT-18-44465[R]. Idaho: Idaho National Laboratory, 2018. [7] 林原胜,王加庆,张德奎,等. 船用核动力SGTR事故安全分析[J]. 核安全,2005(4): 39-43. [8] MACDONALD P E, SHAH V N, WARD L W, et al. Steam generator tube failures: NUREG/CR-6365[R]. Washington: Nuclear Regulatory Commission, 1996. [9] NEMATOLLAHI M R, ZARE A. A simulation of a steam generator tube rupture in a VVER-1000 plant[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2008, 49(7): 1972-1980. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2007.12.018 [10] 张顺香. AP1000电厂状态参数不确定性对LBLOCA影响的量化分析[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2013. [11] 郑玉涛. 风险告知的PCT安全裕度量化中认知不确定性处理方法研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2018. [12] ZHANG H B, SZILARD R, EPINEY A, et al. Industry application ECCS/LOCA integrated cladding/emergency core cooling system performance: demonstration of LOTUS-baseline coupled analysis of the South Texas plant model: INL/EXT-17-42461[R]. Idaho: Idaho National Laboratory, 2017. [13] 大亚湾核电培训中心. 大亚湾核电站事故规程解读[M]. 北京: 原子能出版社, 2007: 130-141. [14] 郭城. 核电厂蒸汽发生器传热管断裂事故运行管理[J]. 核动力工程,2013, 34(2): 107-110. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0926.2013.02.025 [15] 冉旭,吴丹,陈炳德,等. 最佳估算加不确定性分析方法及其应用研究[J]. 核动力工程,2013, 34(3): 120-123. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0926.2013.03.027 [16] GUBA A, MAKAI M, PÁL L. Statistical aspects of best estimate method-I[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2003, 80(3): 217-232. [17] WILKS S S. Determination of sample sizes for setting tolerance limits[J]. The Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 1941, 12(1): 91-96. doi: 10.1214/aoms/1177731788 -





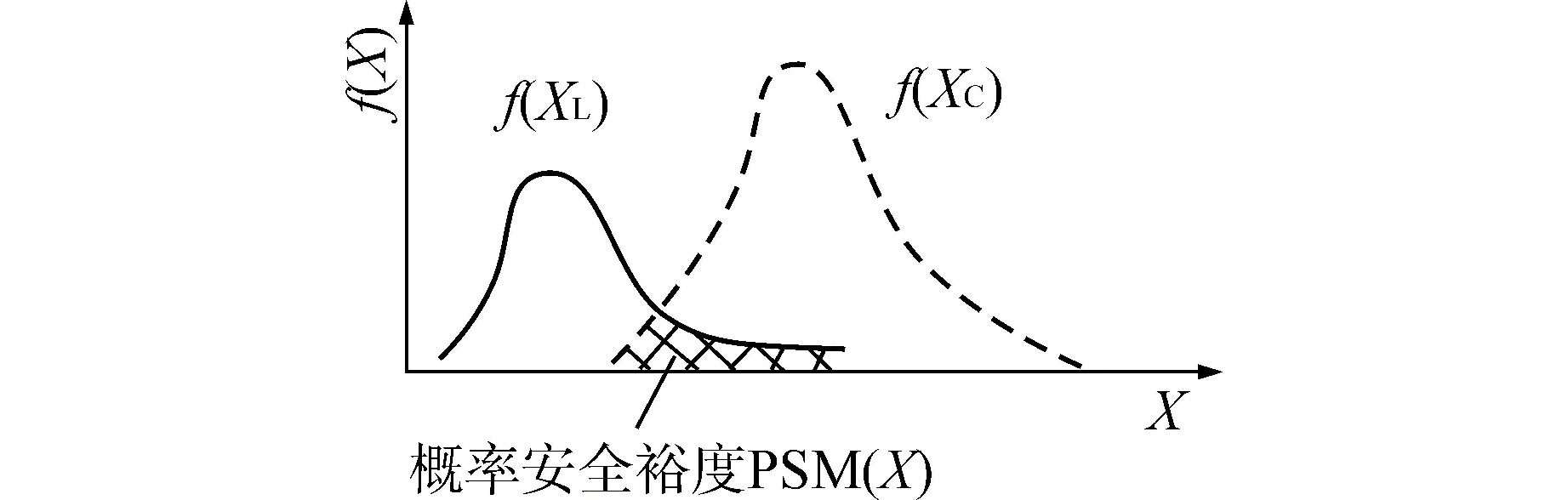
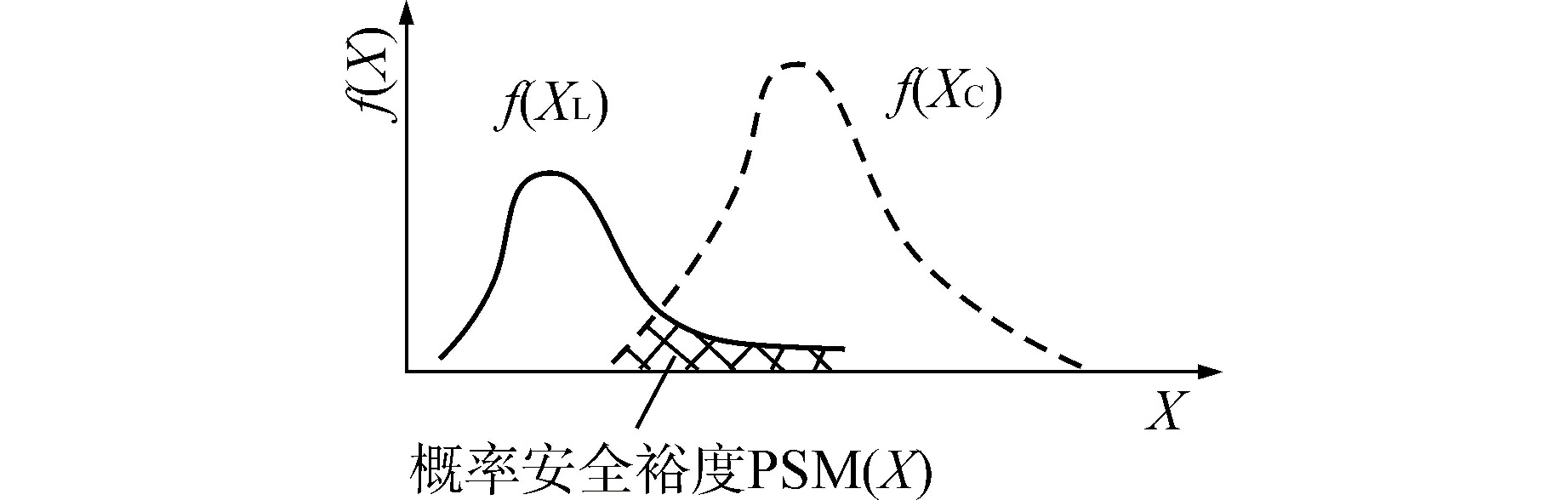
 下载:
下载: