Study on Mechanism and Model Influence of Loop Seal Clearing in PWR SBLOCA Accident
-
摘要: 环路水封清除(LSC)是压水堆冷管段小破口失水事故(SBLOCA)的典型事故特征之一。为确定LSC现象的物理模型影响,探究准确复现LSC现象的物理模型设置,从LSC现象物理机理的角度,对影响LSC的主要物理模型进行梳理和分析。结合LOBI台架SBLCOA系列实验,对LSC现象物理机理、物理模型影响进行模拟和验证。结果表明,在对影响LSC现象的物理模型进行合理设置后,RELAP5程序模型能较好地复现LOBI台架实验工况中的LSC现象,验证了LSC现象物理模型影响及模型设置的合理性。Abstract: Loop seal clearing (LSC) is one of the typical accident characteristics of cold leg small break loss of coolant accident (SBLOCA) in PWR. In order to determine the influence of the physical model of LSC phenomenon and explore the setting of the physical model for accurately reproducing the LSC phenomenon, this study combs and analyzes the main physical models affecting LSC from the perspective of the physical mechanism of LSC phenomenon. The physical mechanism of LSC phenomenon and the influence of physical model are simulated and verified by SBLOCA series experiments of LOBI bench. The results show that after reasonable setting of the physical model affecting the LSC phenomenon, the RELAP5 program model can better reproduce the LSC phenomenon in the LOBI bench experiment, which verifies the rationality of the physical model influence and model setting of the LSC phenomenon.
-
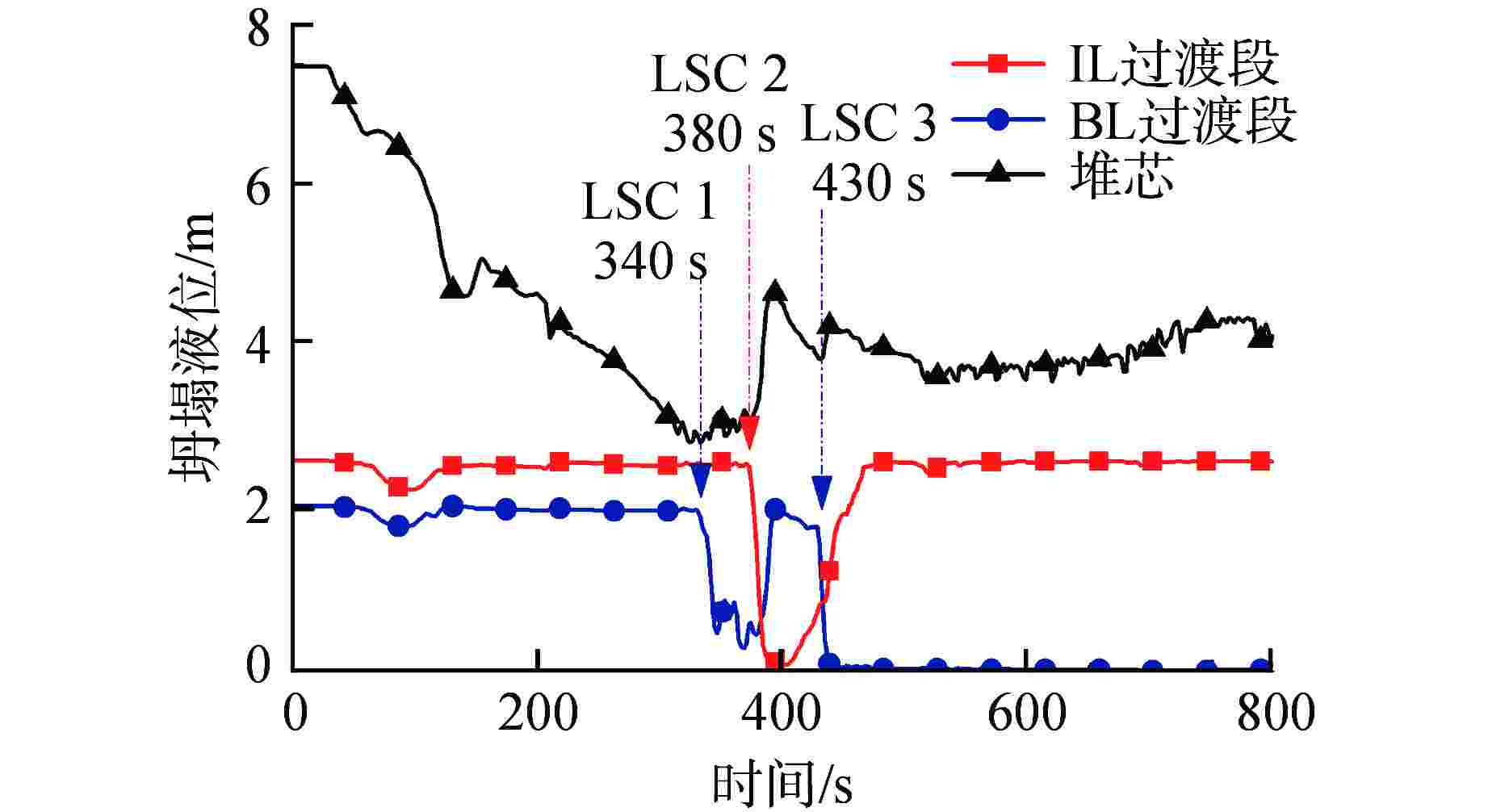
表 1 LOBI BL-02工况稳态参数实验值与计算值
Table 1. Experimental and Calculated Values of Steady-state Parameters of LOBI BL-02 Condition
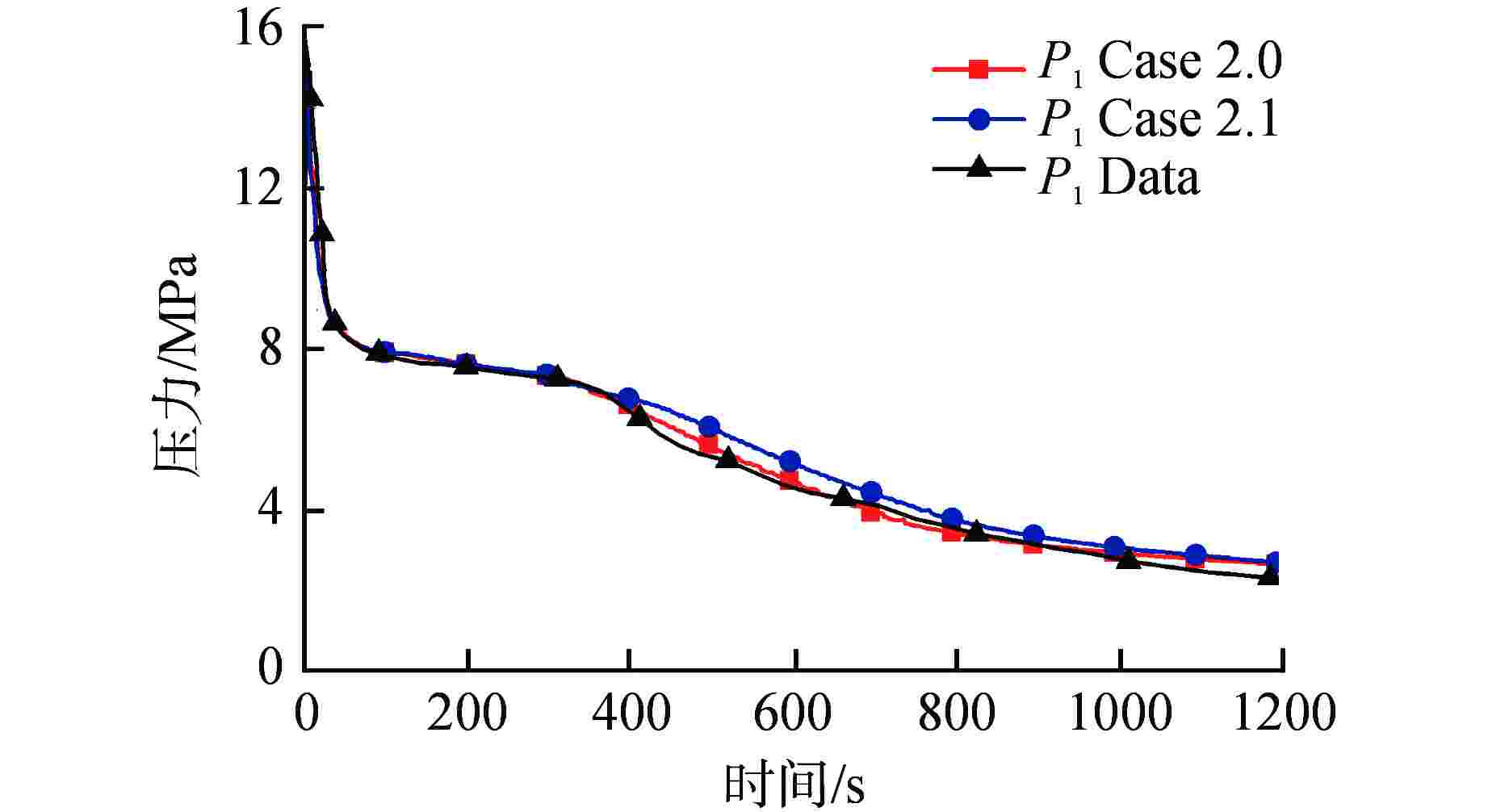
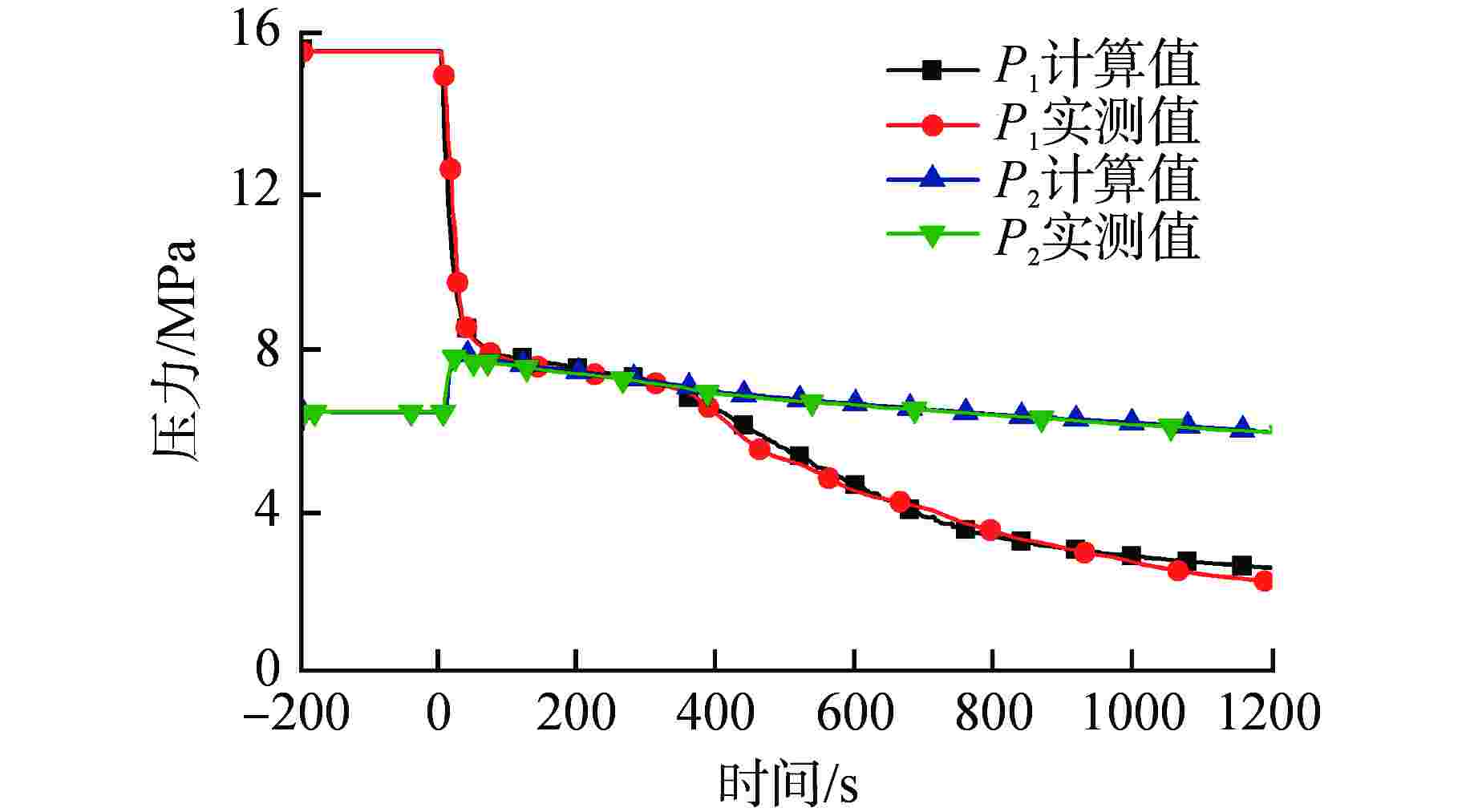
主要参数 实测值 计算值 一回路 冷却剂流量/(kg·s−1) 完整环路 21.0 21.0 破口环路 7.0 7.0 上腔室压力(P1)/MPa 15.6 15.6 冷却剂温度/℃ 完整环路入口 290.5 290.6 破口环路入口 290.5 290.3 稳压器液位/m 4.8 4.8 二回路 给水流量/(kg·s−1) 完整环路 2.00 2.02 破口环路 0.68 0.67 蒸汽联箱压力(P2)/MPa 6.25 6.25 主给水温度/℃ 完整环路 210 210 破口环路 210 210 表 2 LOBI BL-02工况LSC现象模拟与实验对比
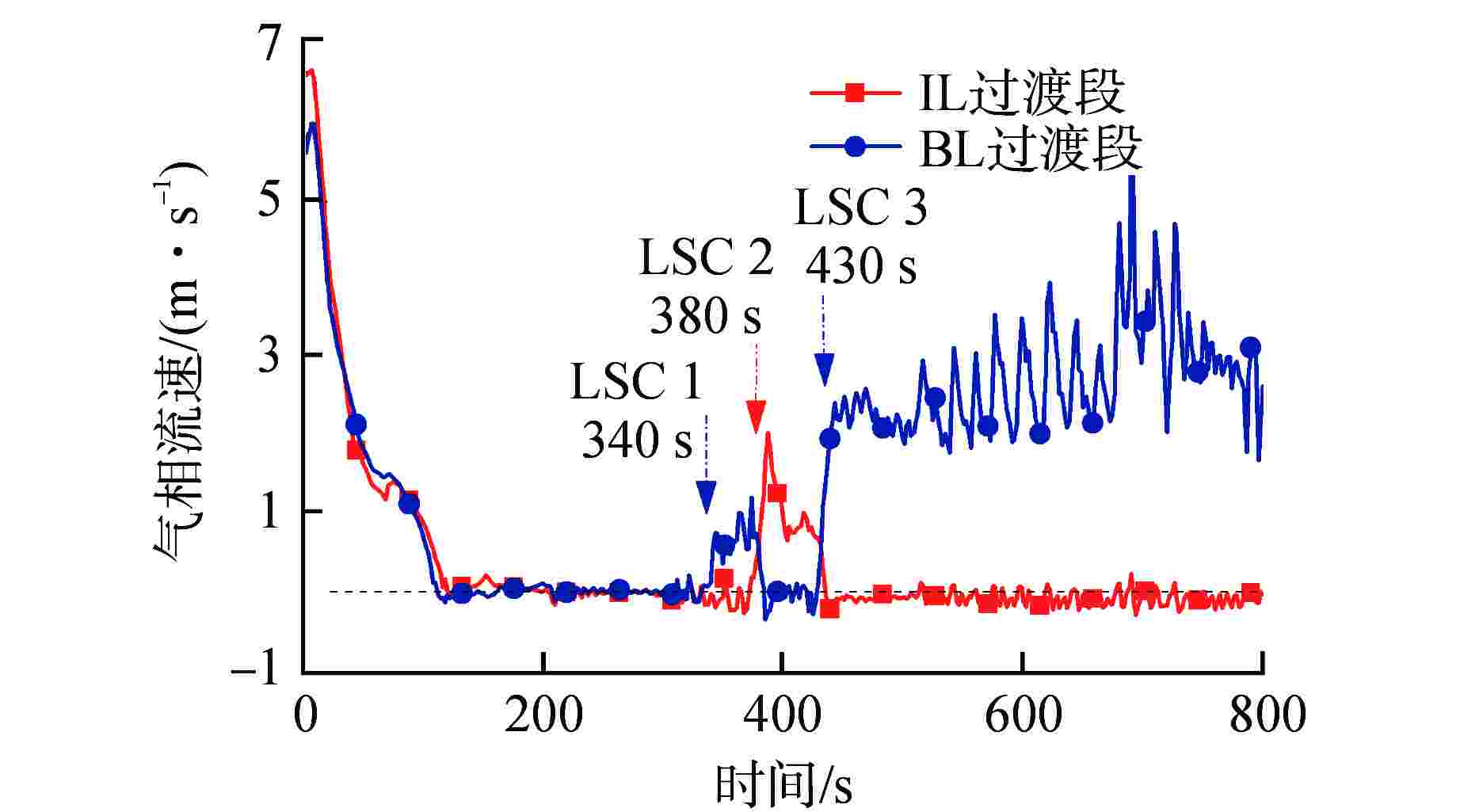
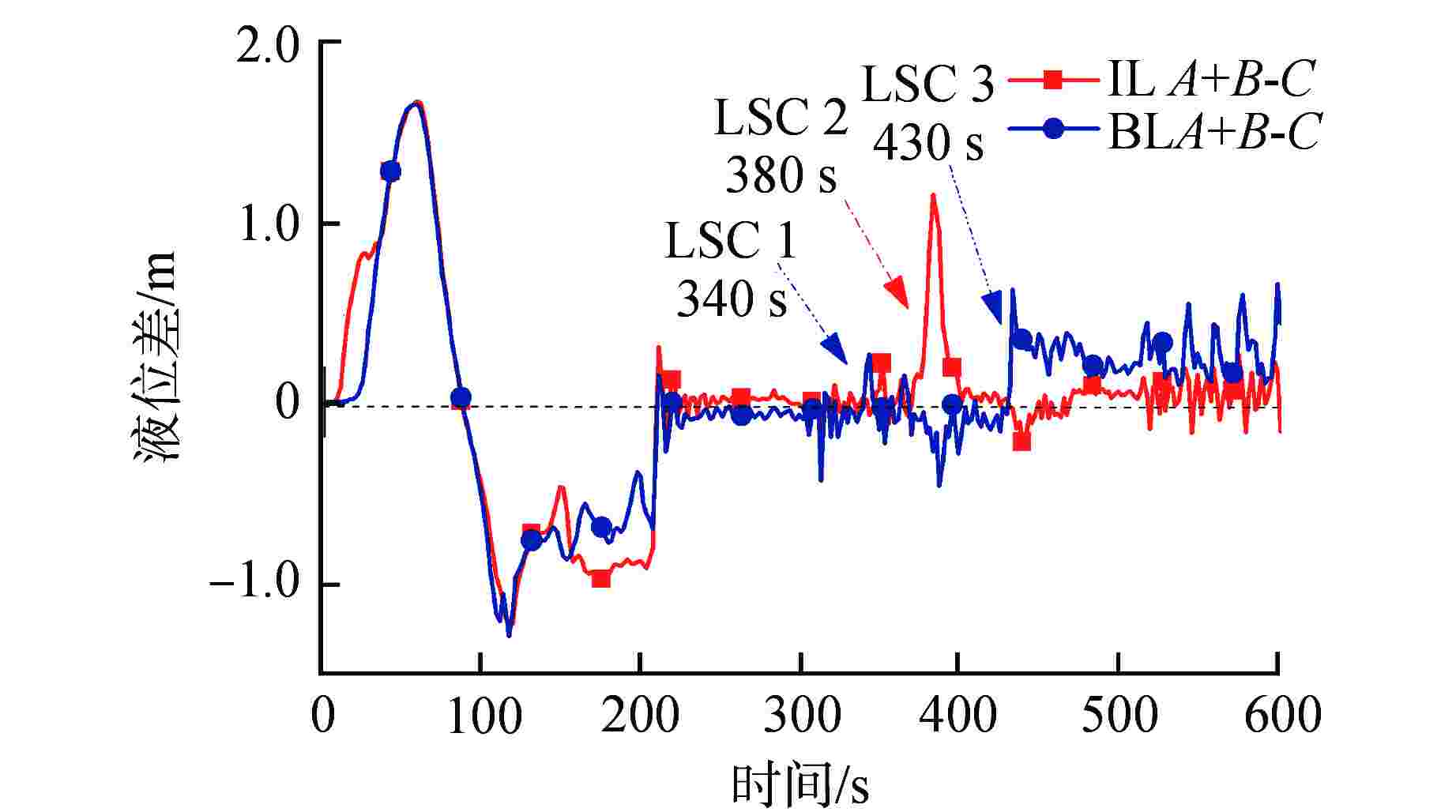
Table 2. Comparison between Simulation and Experiment of LSC Phenomenon for LOBI BL-02 Condition
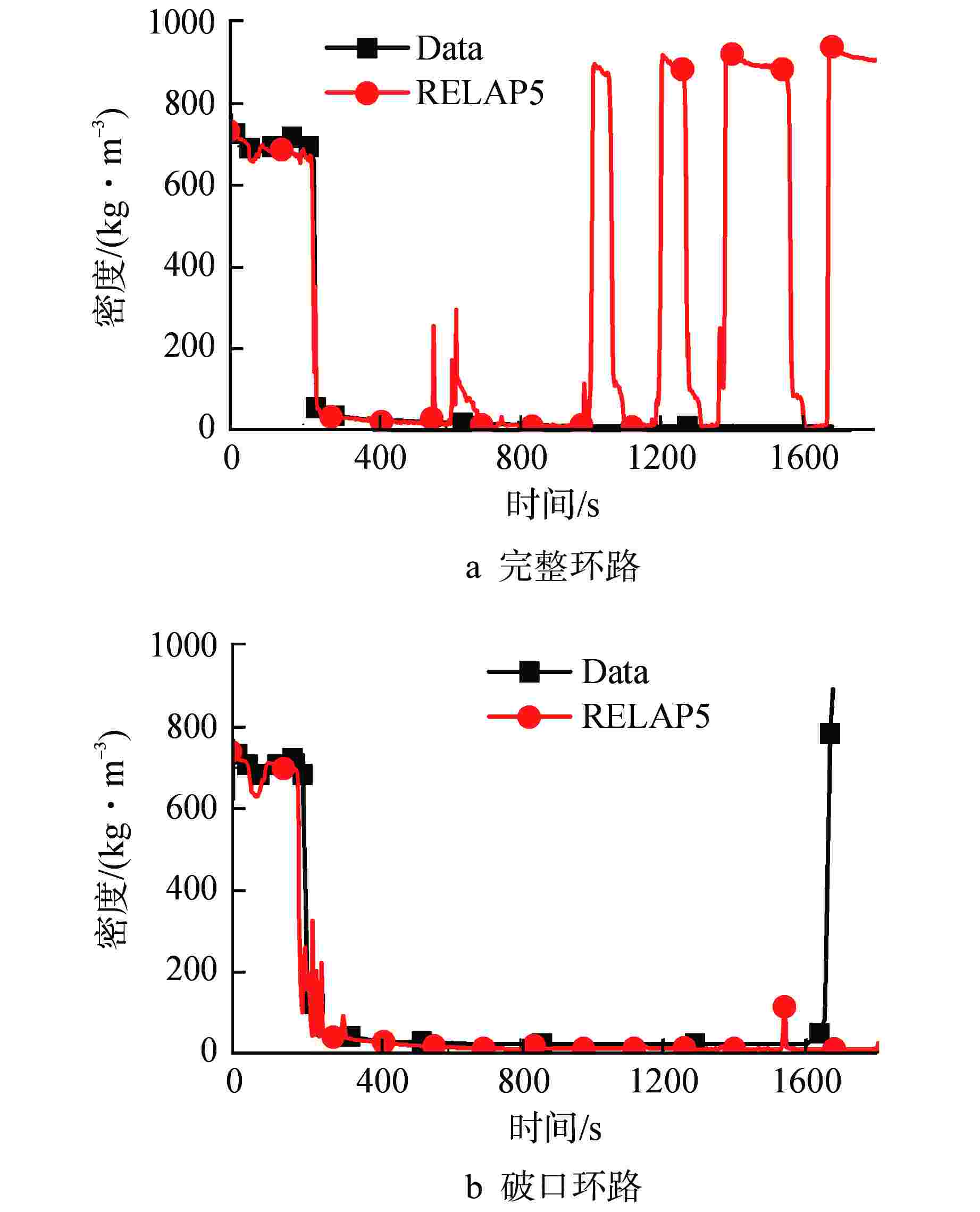
环路及现象 程序初步模拟值 实验观测值 完整环路 水封清除时间/s 380 350 再填充时间/s 430 380 破口环路 水封清除时间/s 340/430 380 再填充时间/s 380 未发生 表 3 影响LSC现象的主要物理模型
Table 3. Main Physical Models Affecting LSC Phenomenon
物理模型 影响分析 影响对象 衰变热 影响堆芯内蒸汽的产生速率 A项:LCUP 壁面换热 影响堆芯内换热及SG内换热及冷凝回流 A项:LCUP
B项:LSGD
C项:LSGU临界流 影响一回路压降速率,进而影响一回路冷却剂汽化程度 A项:LCUP
B项:LSGD
C项:LSGU面积突变与形阻 影响压力容器进出口形阻及堆芯旁路流量 A项:LCUP CCFL 影响堆芯、热管段及SG U型管上升段的液体回流 A项:LCUP
B项:LSGD
C项:LSGU表 4 影响LSC现象的主要物理模型工况设置
Table 4. Setting of Main Physical Model Conditions Affecting LSC Phenomenon
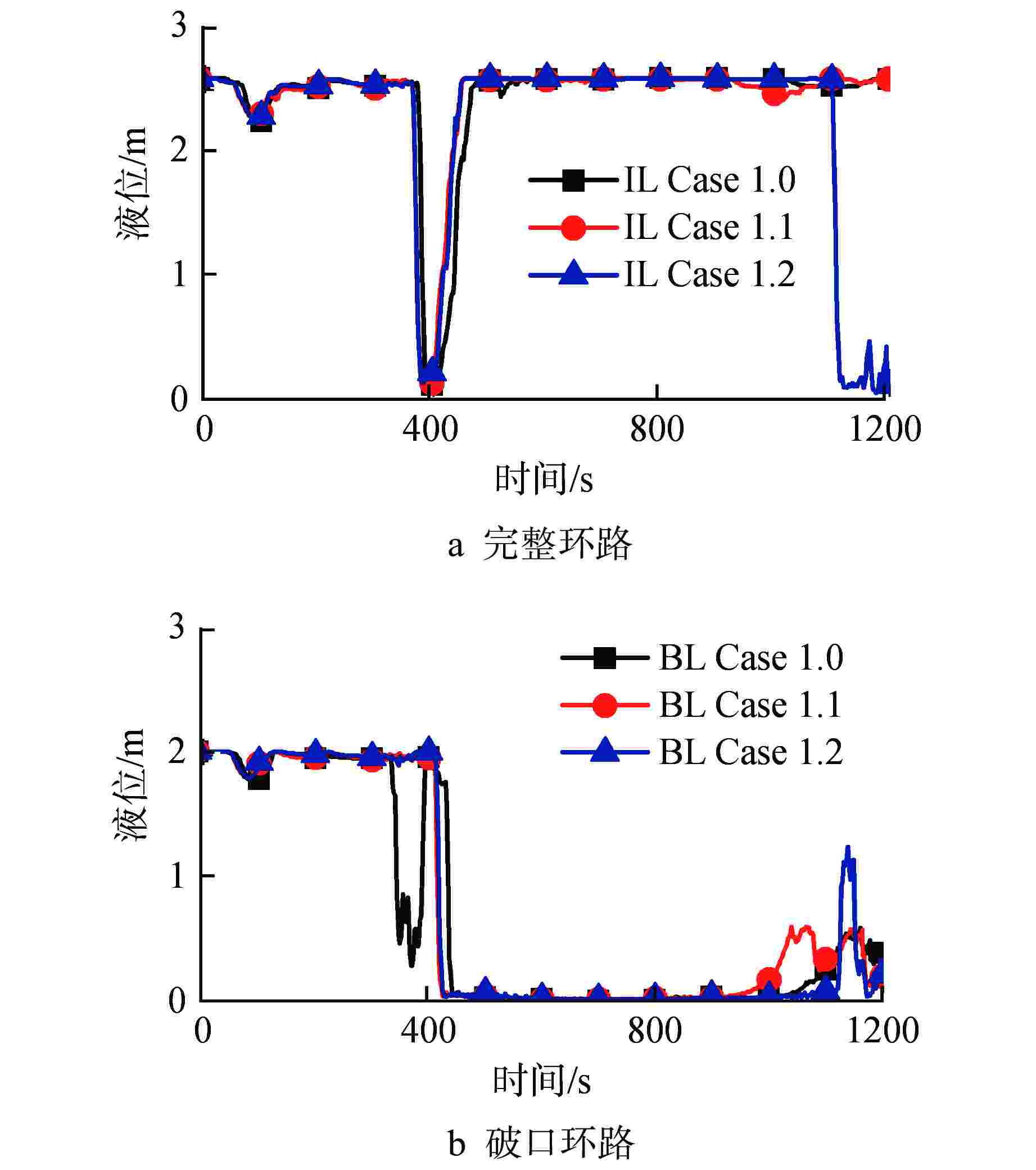
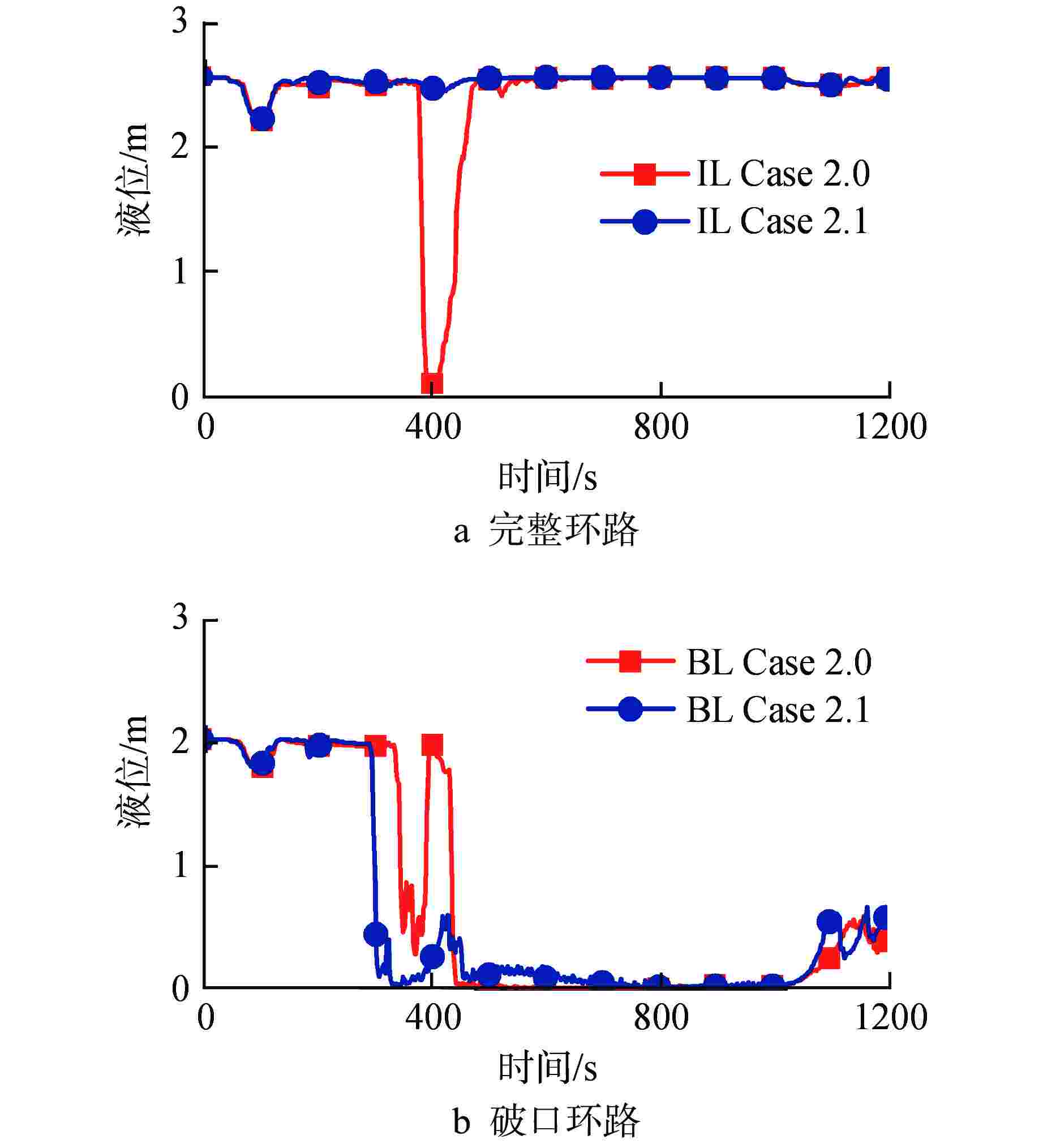
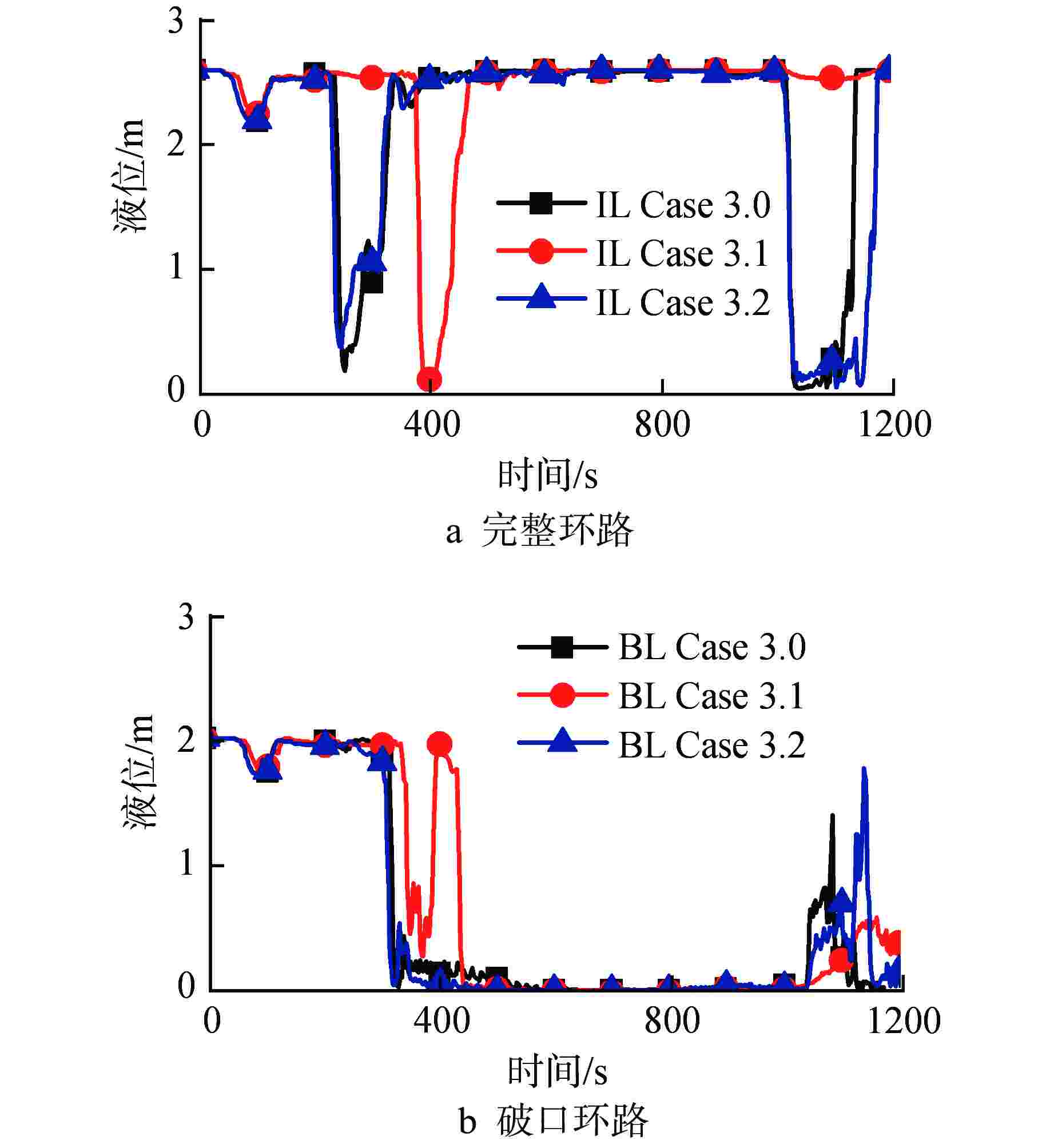
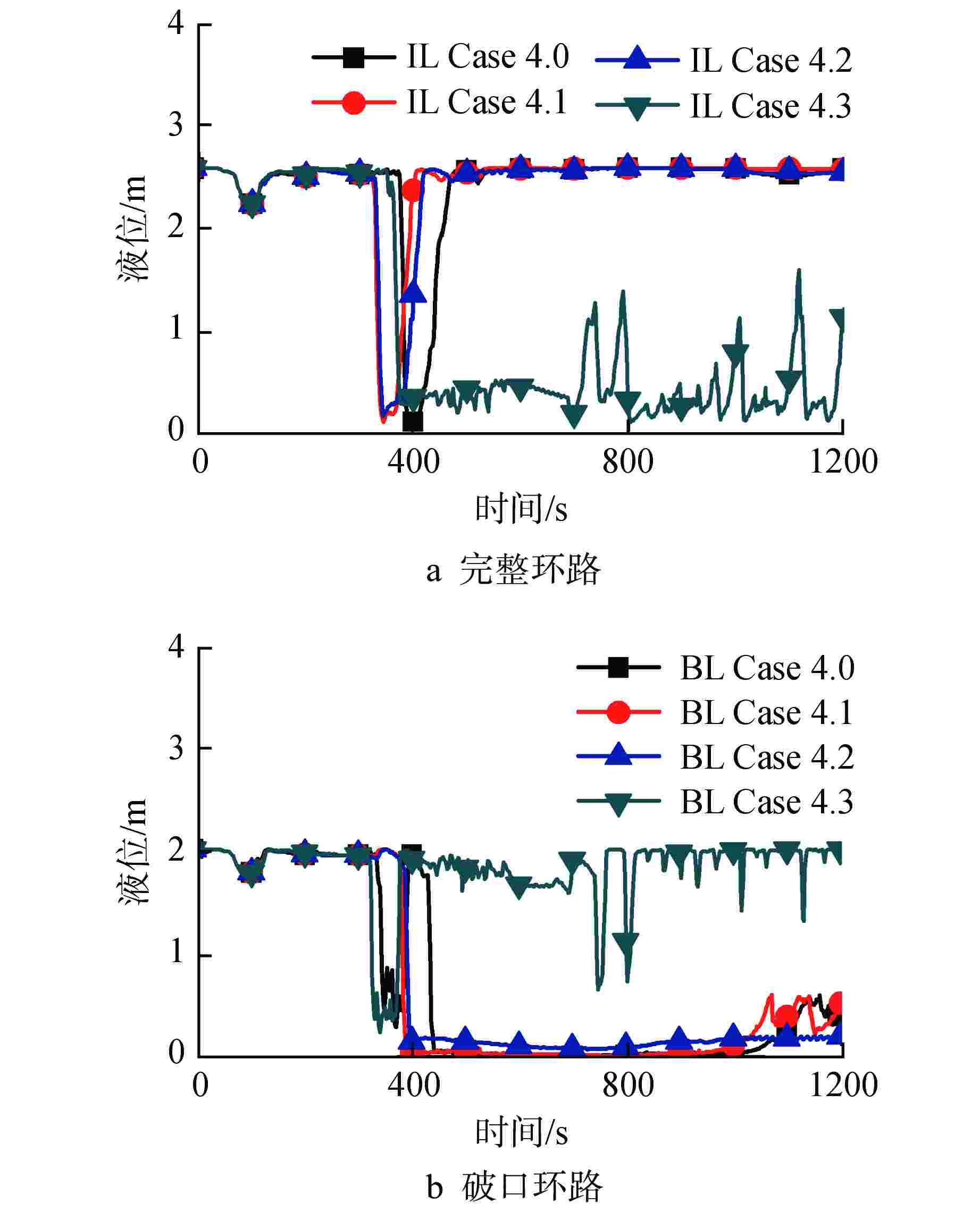
物理模型 部件 工况设置 衰变热 堆芯热构件 Case 1.0:使用通用表格组件General Table手动设置,模拟台架电加热器加热工况 Case 1.1:选用点堆中子ANS 79-1,模拟反应堆寿期初工况 Case 1.2:选用点堆中子ANS 79-3,模拟反应堆寿期末工况 临界流 破口 Case 2.0:选用Henry-Fauske模型,目前RELAP5程序默认的临界流模型 Case 2.1:选用Trapp-Ransom模型,较早版本RELAP5程序中的临界流模型 面积突变和形阻 压力容器进出口及其旁路 Case 3.0:面积平滑变化(a=0),认为压力容器进出口之间接口平滑 Case 3.1:面积突变(a=1),认为压力容器进出口部件形阻较大 Case 3.2:部分面积突变(a=2),认为压力容器进出口部件损耗较小 CCFL 压力容器、
SG及其
一回路管道Case 4.0:不选用CCFL模型 Case 4.1:选用CCFL模型,使用Walls关系式 (C=1, m=1) Case 4.2:选用CCFL模型,其中反应堆压力容器(PRV)和SG选用Walls关系式 (C=1, m=1);一回路管道选用Kutateladze关系式(C=1.36, m=1) Case 4.3:选用CCFL模型,使用Kutateladze关系式 (C=1.36, m=1) 注:C、m说明见文献[10] 表 5 LOBI台架压力容器进出口压差
Table 5. Pressure Difference of LOBI Bench Pressure Vessel Inlet and Outlet
部位 环路 实验测量
值/kPa计算模拟
值/kPa模拟误
差/%压力容器
进口压差完整环路 45.0 46.6 3.56 破口环路 26.9 27.0 0.37 压力容器
出口压力完整环路 35.7 35.5 0.56 破口环路 34.1 34.8 2.05 表 6 LOBI模型各部件的CCFL模型配置
Table 6. CCFL Model Configuration of LOBI Model Parts
模型组合 压力容器 热管段、SG进出口、
过渡段及冷管段SG U型管 最佳工况 Walls关系式
C=1, m=1Kutateladze关系式
C=1.36, m=1Walls关系式
C=0.88, m=1表 7 BL-02工况LSC现象调试后模拟对比
Table 7. Simulation Comparison of LSC Phenomenon under BL-02 Condition after Debugging
环路及现象 实验观测值 调试后程序模拟值 完整环路 水封清除时间/s 350 343 再填充时间/s 380 380 破口环路 水封清除时间/s 380 388 再填充时间/s 未发生 未发生 -
[1] Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, LTD. Scaling analysis for US-APWR small break LOCAs: UAP-HF-09472-NP[R]. 2009 [2] KIM Y S, CHOI K Y. An analytical investigation of loop seal clearings for the SBLOCA tests[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2014, 68: 30-42. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2014.01.003 [3] KIM Y S, CHO S. An experimental investigation of loop seal clearings in SBLOCA tests[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2014, 63: 721-730. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2013.09.014 [4] KAUPPINEN O P, KOUHIA V, RIIKONEN V, et al. Computer analyses on loop seal clearing experiment at PWR PACTEL[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2015, 85: 47-57. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2015.04.036 [5] ADDABBO C, ANNUNZIATO A. The LOBI integral system test facility experimental programme[J]. Science and Technology of Nuclear Installations, 2012, 2012: 238019. [6] JACOBS G, MANSOOR S H. Double blind post-test prediction for LOBI-MOD 2 small break experiment A 2-81 using RELAP 5/ MOD 1/19 computer code as contribution to international CSNI-standardproblem no. 18: KfK 4087[R]. Karlsruhe: Kernforschungszentrum Karlsruhe, 1986. [7] SCRIVEN A H. Analysis of LOBI test BLO2 (three percent cold leg break) with RELAP5 code: NUREG/IA-0036[R]. Washington: Office of Nuclear Regulatory Research, U. S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission, 1992. [8] LIAO J. System scaling analysis for modeling small break LOCA using the FULL SPECTRUM LOCA evaluation model[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2016, 87: 443-453. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2015.09.014 [9] LABORATORIES I S. RELAP5/MOD3.3 code manual volume IV: models and correlations[Z]. Rockville, Maryland, 2006. [10] HOSSEN M M, KANG J Y, BAE B U, et al. Analysis of lsc phenomena of atlas cold leg sbloca tests using mars-ks code[J]. Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 2018, 55(11): 1336-1354. doi: 10.1080/00223131.2018.1505568 [11] REVENTÓS F, PLA P, MATTEOLI C, et al. Consistent posttest calculations for LOCA scenarios in LOBI integral facility[J]. Science and Technology of Nuclear Installations, 2012, 2012: 474162. -





 下载:
下载: