Theoretical Calculation of High Temperature Potential-pH Based on Fe-H2O, Cr-H2O and Zr-H2O Systems
-
摘要: 本文从热力学角度出发,利用能斯特方程进行计算,研究了423、573 K温度条件下Fe-H2O体系、Cr-H2O体系及Zr-H2O体系的电位-pH图(E-pH图),从理论上说明了铁、铬、锆3种反应堆结构材料的主要组成元素在高温高压水中,受电位、pH影响的腐蚀行为倾向,为后续在堆内水化学环境中进行材料电化学腐蚀试验研究以预防材料的腐蚀、延长材料的使用寿命提供了数据参考。Abstract: From the perspective of thermodynamics, this paper uses the Nernst equation to calculate the potential-pH diagrams (E-pH diagrams) of the Fe-H2O system, Cr-H2O system and Zr-H2O system at temperatures of 423 K and 573 K. This paper theoretically explain the corrosion behavior tendency of the main constituent elements of reactor structural materials of iron, chromium and zirconium in high temperature and high pressure water, which are affected by potential and pH. This provides data reference for the materials electrochemical corrosion tests in the water chemical environment in reactor, preventing the corrosion of the material, and extending the service life of the material.
-
表 1 298 K常见物质的热力学数据[9]
Table 1. Thermodynamic Data of Common Substances at 298 K
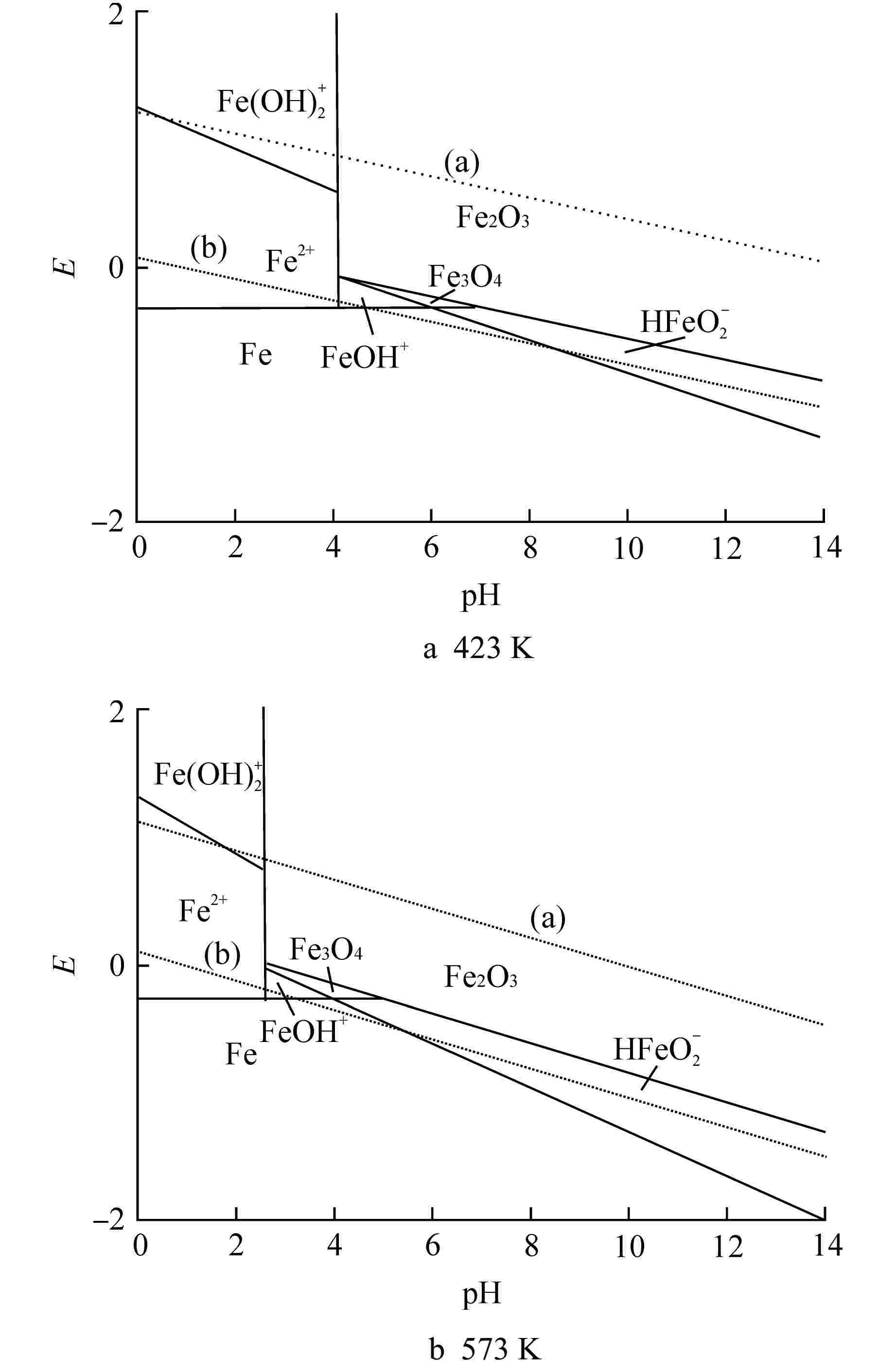
物质 ${ {\Delta } }G_{298}^{ {\text{θ} } }$/(KJ·mol−1) $S_{ {\text{298} } }^{ {\text{θ} }}$/(J·K−1·mol−1) CP/(J·K−1·mol−1) H2 0 130.68 28.836 O2 0 205.152 29.378 H2O −237.14 69.95 75.351 H+ 0 0 0 e− 0 65.285 0 表 2 Fe-H2O体系的主要E-pH反应式
Table 2. Main E-pH Equations of Fe-H2O System
序号 反应式 (a) O2+4H++4e−=2H2O (b) 2H++2e−=H2 1 Fe2++H2O=FeOH++H+ 2 Fe2++2H2O=Fe(OH)2++2H++e− 3 3Fe2O3+2H++2e−=2Fe3O4+H2O 4 2Fe(OH)2+=Fe2O3+H2O+2H+ 5 Fe2++2e−=Fe 6 HFeO2−+3H++2e−=Fe+2H2O 表 3 不同温度下Fe-H2O体系主要反应式的E-pH计算式
Table 3. E-pH Calculation Formula of Main Equations of Fe-H2O System at Different Temperatures
序号 计算式 423 K 573 K (a) E=1.209−0.084pH+0.0211lgaO2 E=1.116−0.114pH+0.0281lgaO2 (b) E=0.082−0.084pH−0.042lgaH2 E=0.103−0.114pH−0.057lgaH2 1 pH=4.11+lg(FeOH+/Fe2+) pH=2.55+lg(FeOH+/Fe2+) 2 E=1.274−0.1679pH+0.839lg[Fe(OH)2+/Fe2+] E=1.32−0.2274pH+0.1137lg[Fe(OH)2+/Fe2+] 3 E=0.28−0.084pH E=0.29−0.114pH 4 2pH=−16.74−lg{[Fe(OH)2+]2} 2pH=−15.67−lg{[Fe(OH)2+]2} 5 E=−0.307+lg(Fe2+) E=−0.272+lg(Fe2+) 6 E=0.497−0.13pH+0.042lg(HFeO2−) E=0.398−0.17pH+0.057lg(HFeO2−) 表中离子符号表示该离子的浓度 表 4 Zr-H2O体系的E-pH反应式
Table 4. E-pH Equations of Zr -H2O System
序号 反应式 (a) 2H++2e=H2 (b) 2H2O=O2+4H++4e− 1 Zr4++H2O=ZrO2++2H+ 2 ZrO2++2H2O=HZrO3−+3H+ 3 Zr+2H2O=ZrO2+4H++4e− 4 Zr4++2H2O=ZrO2+4H+ 5 ZrO2++H2O=ZrO2+2H+ 6 ZrO2+H2O=HZrO3−+H+ 7 Zr=Zr4++4e− 8 Zr+H2O=ZrO2++2H++4e− 9 Zr+3H2O=HZrO3−+5H++4e− 表 5 Zr-H2O体系的E-pH计算式
Table 5. E-pH Calculation Formula of Zr-H2O System
序号 反应式 423 K 573 K 1 2pH=3.955+lg(Zr4+/ZrO2+) 2pH=1.027+lg(Zr4+/ZrO2+) 2 3pH=−19.857+lg(ZrO2+/HZrO3−) 3pH=−5.659+lg(ZrO2+/HZrO3−) 3 E=1.336−0.084pH-0.021lg(Zr/ZrO2) E=1.445−0.114pH−0.028lg(Zr/ZrO2) 4 4pH=−3.361+lg(Zr4+/ZrO2) 4pH=8.08+lg(Zr4+/ZrO2) 5 2pH=−7.316+lg(ZrO2+/ZrO2) 2pH=6.96+lg(ZrO2+/ZrO2) 6 pH=−12.542+lg(ZrO2/HZrO3−) pH=−12.62+lg(ZrO2/HZrO3−) 7 E=1.41−0.021lg(Zr/Zr4+) E =1.22−0.028lg(Zr/Zr4+) 8 E=1.489−0.042pH−0.021lg(Zr/ZrO2+) E=1.25−0.057pH−0.028lg(Zr/ZrO2+) 9 E=1.073−0.105pH−0.021lg(Zr/HZrO3−) E=1.086−0.142pH−0.028lg(Zr/HZrO3−) (a) E=−0.084pH E=0.114pH (b) E=−1.282−0.084pH E=−1.367−0.1144pH 表中离子符号表示该离子的浓度 表 6 Cr-H2O体系的E-pH反应式
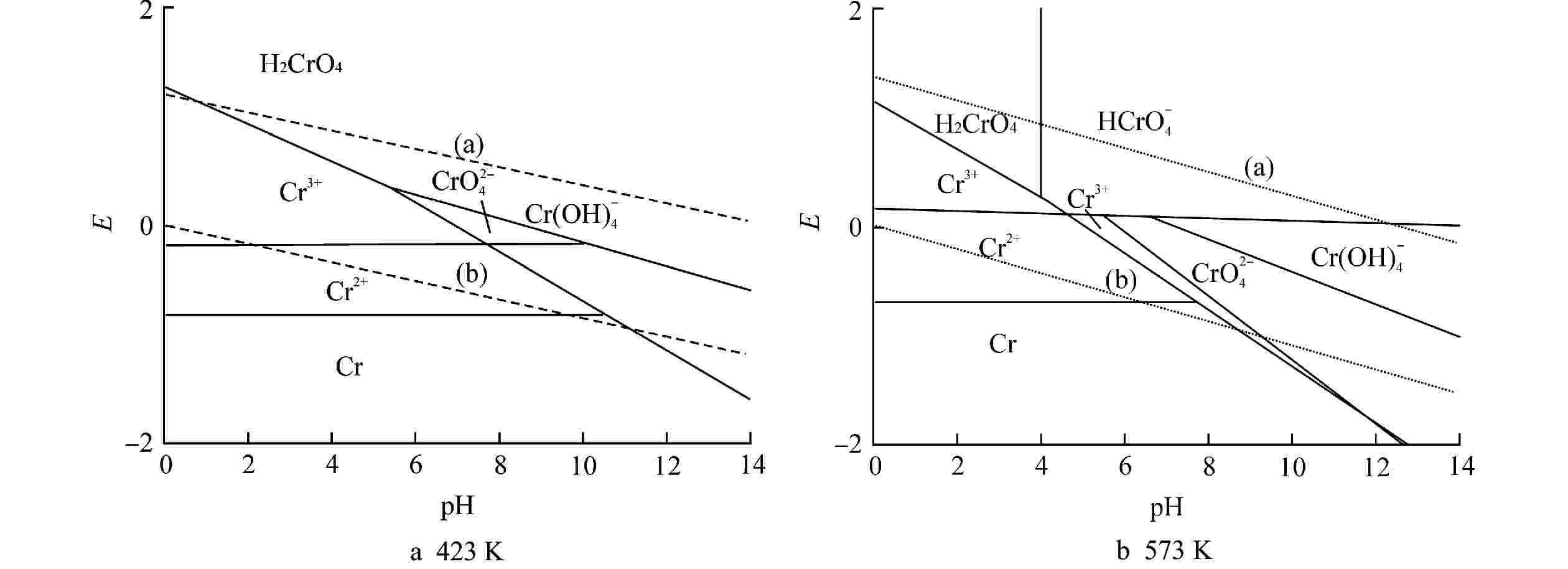
Table 6. E-pH Equations of Cr-H2O System
序号 反应式 (a) O2+4H++4e−→2H2O (b) 2H++2e−→H2 1 Cr2++2e−→Cr(s) 2 Cr3++e−→Cr2+ 3 H2CrO4+6H++3e−→Cr3++4H2O 4 HCrO4−+7H++3e−→Cr3++4H2O 5 CrO42-+4H++3e−→Cr(OH)4− 6 H2CrO4→HCrO4−+H+ 7 HCrO4−→CrO4++H+ 8 CrO42-+8H++3e−→Cr3++4H2O 表 7 Cr-H2O体系的E-pH计算式
Table 7. E-pH Calculation Formula of Cr-H2O System
序号 计算式 423 K 573 K (a) E=1.21−0.084pH+0.02lgPO2 E=1.37−0.11pH+0.03lgPO2 (b) E=−0.084pH−0.042lgPH2 E=−0.11pH−0.06lgPH2 1 E=−0.817+0.042lgCr2+ E=−0.71+0.06lgCr2+ 2 E=−0.17−0.084lg(Cr3+/Cr2+) E=0.14+0.11lg(Cr3+/Cr2+) 3 E=1.26−0.168pH+0.028lg(H2CrO4/Cr3+) E=1.14−0.22pH+0.04lg(H2CrO4/Cr3+) 4 E=1.31−0.196pH+0.028lg(HCrO4−/Cr3+) E=1.29−0.26pH+0.33lg(HCrO4−/Cr3+) 5 E=0.96−0.112pH+0.028lg[CrO42−/Cr(OH)4−] E=1.06−0.15pH+0.04lg[CrO42−/Cr(OH)4−] 6 pH=−2.03+lg(H2CrO4/HCrO4−) pH=4.02+lg(H2CrO4/HCrO4−) 7 E=1.52−0.224 pH+0.028 lg(CrO42−/Cr3+) E=1.62−0.29pH+0.04lg(CrO42−/Cr3+) 表中离子符号表示该离子的浓度 -
[1] ALLEN T R, KONINGS R J M, MOTTA A T. Corrosion of zirconium alloys[J]. Comprehensive Nuclear Materials, 2012(5): 49-68. [2] COUET A, MOTTA A T, COMSTOCK R J. Effect of alloying elements on hydrogen pickup in zirconium alloys[C]//Proceedings of the 17th International Symposium on Zirconium in the Nuclear Industry. Andhra Pradesh, India: ASTM International, 2015. [3] MOTTA A T, COUET A, COMSTOCK R J. Corrosion of zirconium alloys used for nuclear fuel cladding[J]. Annual Review of Materials Research, 2015, 45: 311-343. doi: 10.1146/annurev-matsci-070214-020951 [4] FONTANA M G. Corrosion engineering[M]. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1986: 67. [5] NATISHAN P. Corrosion and corrosion control[M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. , 2002: 123-124. [6] ANDERKO A, SANDERS S J, YOUNG R D. Real-solution stability diagrams: a thermodynamic tool for modeling corrosion in wide temperature and concentration ranges[J]. Corrosion, 1997, 53(1): 43-53. doi: 10.5006/1.3280432 [7] POURBAIX M. Atlas of electrochemical equilibria in aqueous solutions[M]. Houston, Texas: National Association of Corrosion Engineers, 1974: 5-6. [8] 陈小文,白新德,邓平晔,等. 升温条件下Zr-H2O系电位-pH平衡图[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程,2004, 33(7): 710-713. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-185X.2004.07.009 [9] YOU H X, XU H B, ZHANG Y, et al. Potential-pH diagrams of Cr-H2O system at elevated temperatures[J]. Transaction of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010, 20(S1): s26-s31. [10] BIERNAT R J, ROBINS R G. High-temperature potential/pH diagrams for the iron-water and iron-water-sulphur systems[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1972, 17(7): 1261-1283. doi: 10.1016/0013-4686(72)80013-6 [11] BEVERSKOG B, PUIGDOMENECH I. Revised pourbaix diagrams for iron at 25-300℃[J]. Corrosion Science, 1996, 38(12): 2121-2135. doi: 10.1016/S0010-938X(96)00067-4 [12] KAYE M H, THOMPSON W T. Computation of pourbaix diagrams at elevated temperature[M]//REVIE R W. Uhlig's Corrosion Handbook. 3rd ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2011. [13] BEVERSKOG B, PUIGDOMENECH I. Revised pourbaix diagrams for chromium at 25-300℃[J]. Corrosion Science, 1997, 39(1): 43-57. doi: 10.1016/S0010-938X(97)89244-X [14] 那璇,邹德宁,杨欢,等. 基于Fe-Cr-Cl-H2O体系E-pH图的时效Cr22Ni5Mo3不锈钢的电化学性能研究[J]. 材料保护,2018, 51(9): 18-23,79. -





 下载:
下载: